Reuse of Retired Wind Turbine Blades in Civil Engineering
Abstract
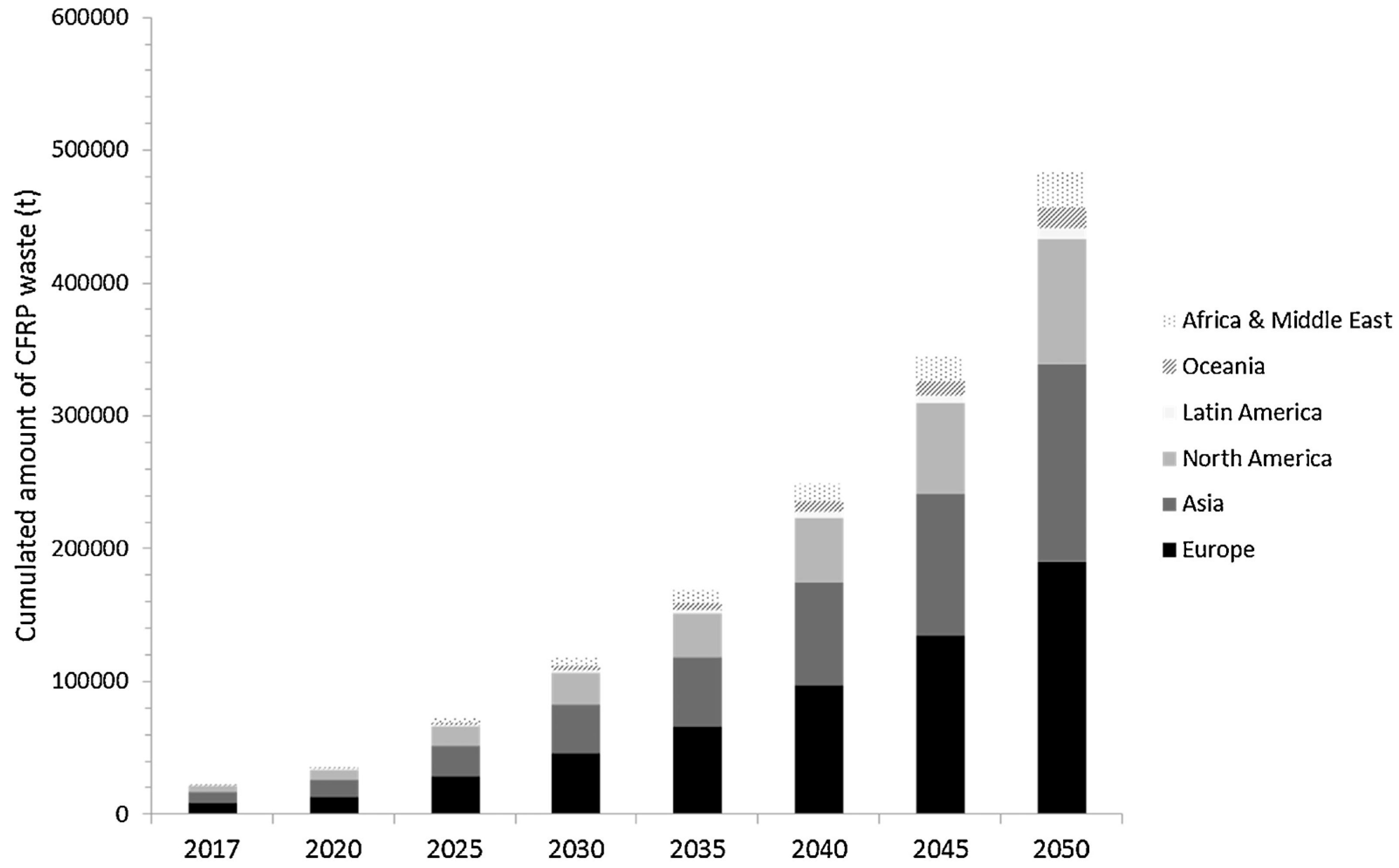
1. Introduction
2. Current Treatment Strategies for Retired Wind Turbine FRP Materials
2.1. Mechanical Recycling
2.1.1. Shredding and Grinding
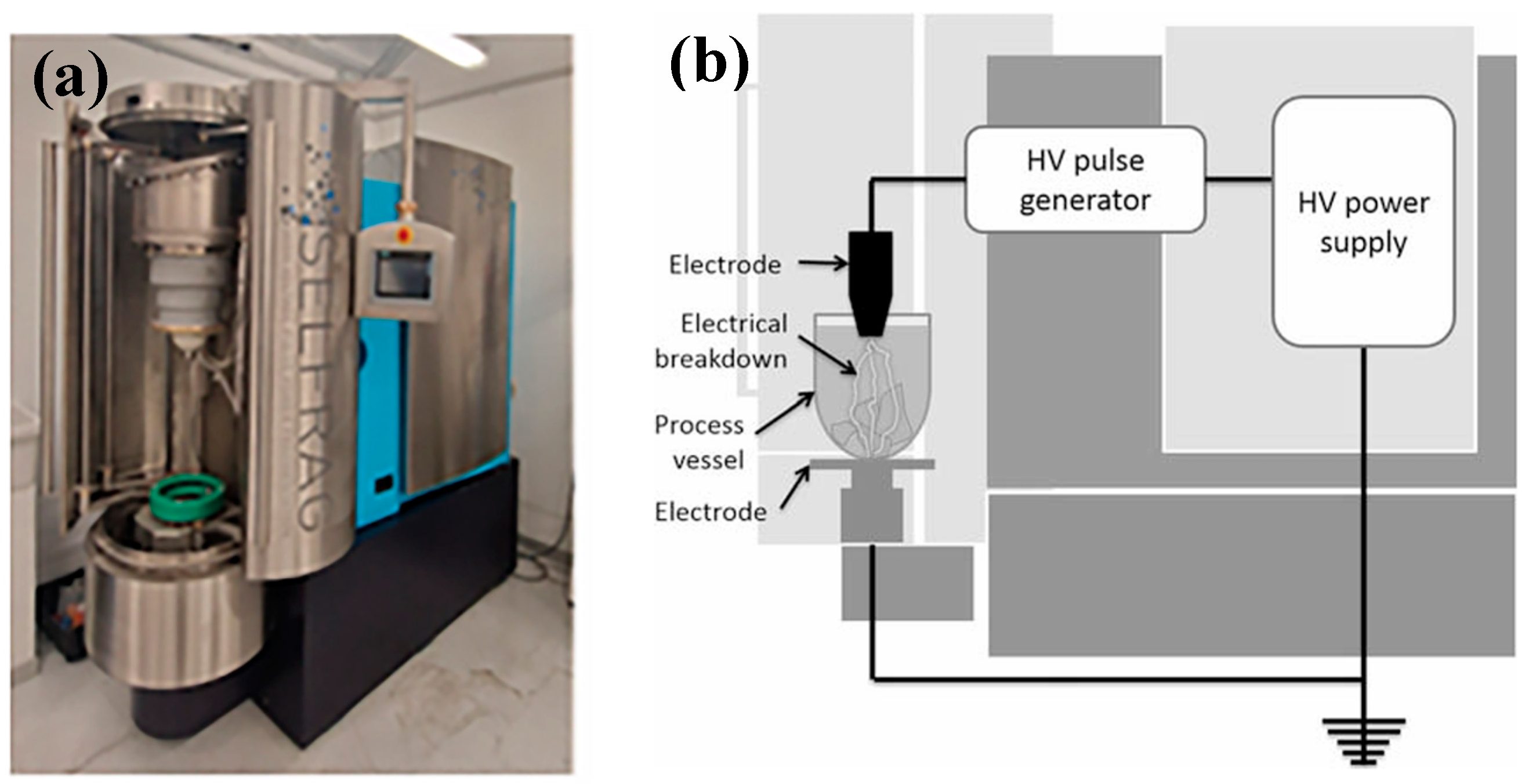
2.1.2. High-Voltage Fragmentation
2.2. Chemical Recycling
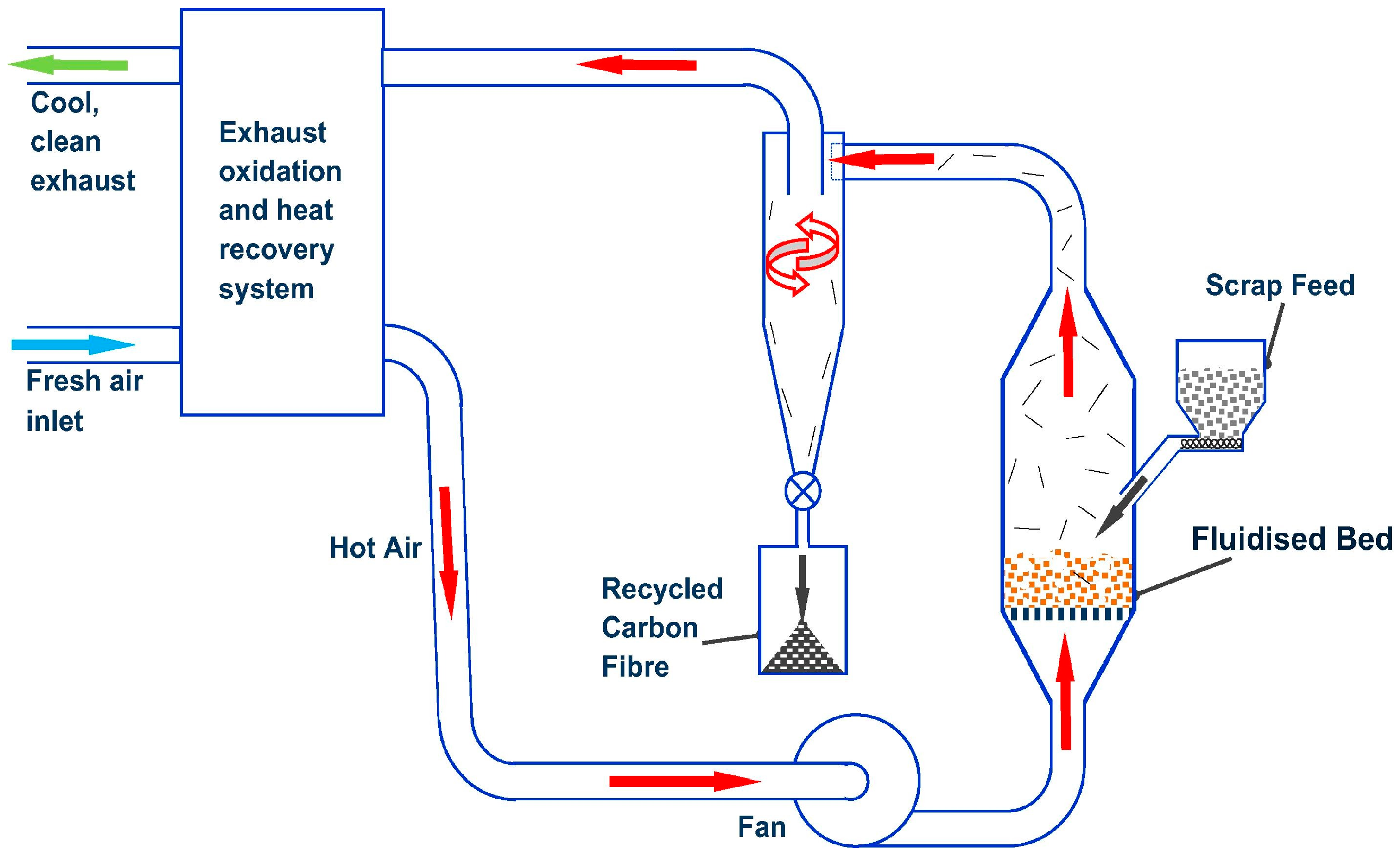
2.3. Thermal Recycling
2.4. Landfills
2.5. Negative Effects of Current Treatment Strategies
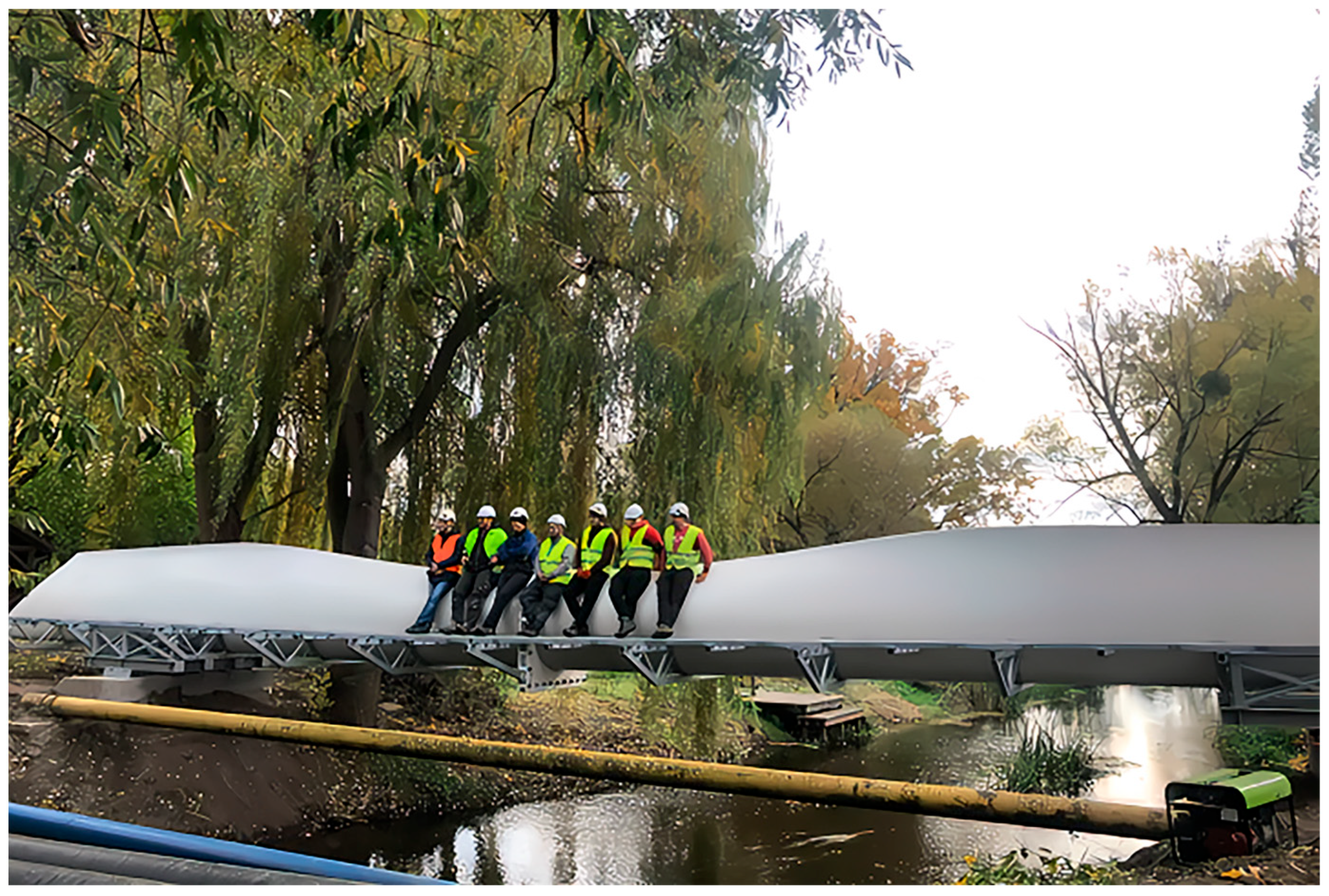
3. Direct Reuse in Construction
3.1. Infrastructures
3.2. Architecture
3.3. Coastal Protection
4. Application of Retired Wind Turbine Blades in the Production of Cementitious Materials
4.1. Micro- and Macro-Fibers, Flakes, and Powder
4.2. Reinforcement Mechanism
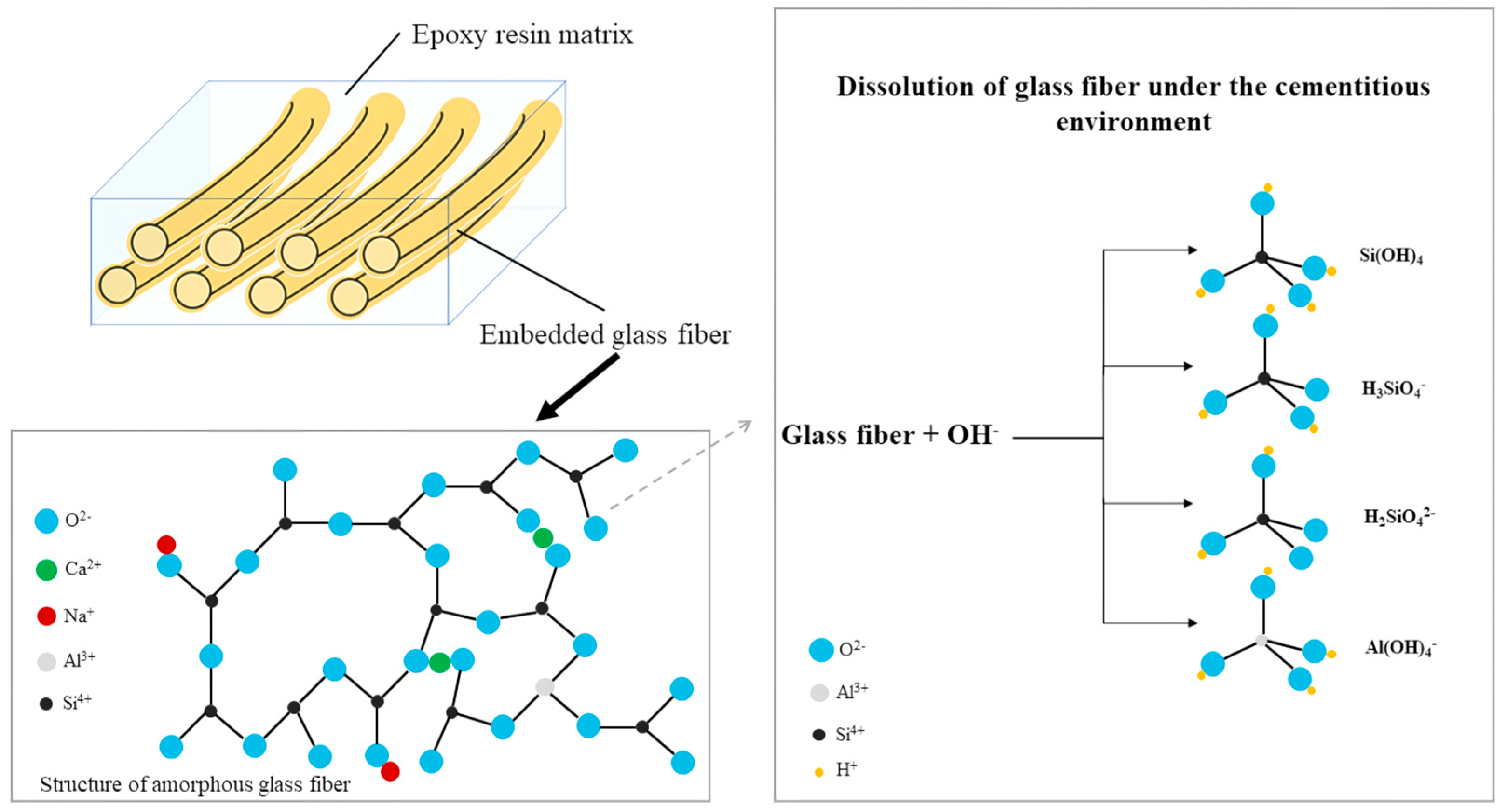
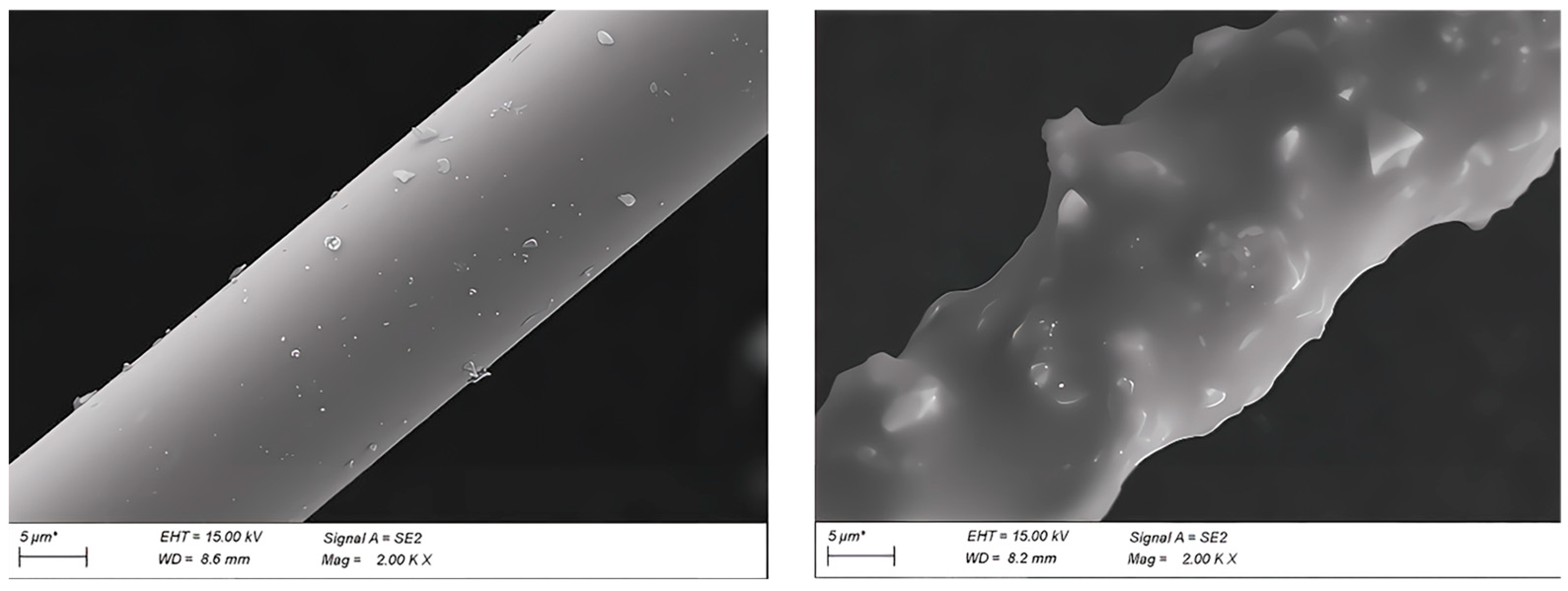
4.3. Chemical Reactions at the Interfacial Zone
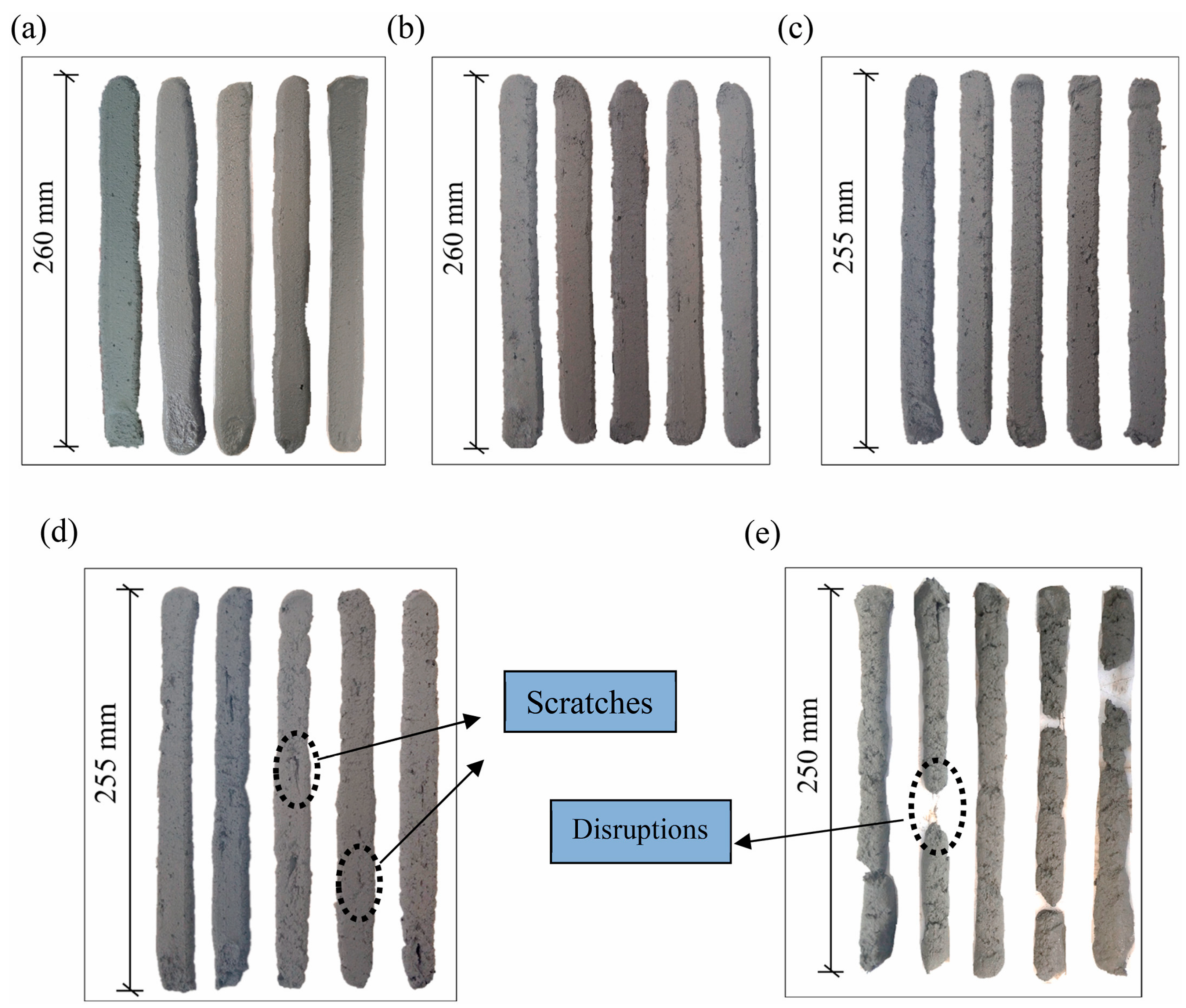
4.4. Mechanical Properties and Durability
5. Application of Retired Wind Turbine Blades in the Production of Asphalt Materials
5.1. Dispersion in Asphalt
5.2. Effect of Mixing Temperature
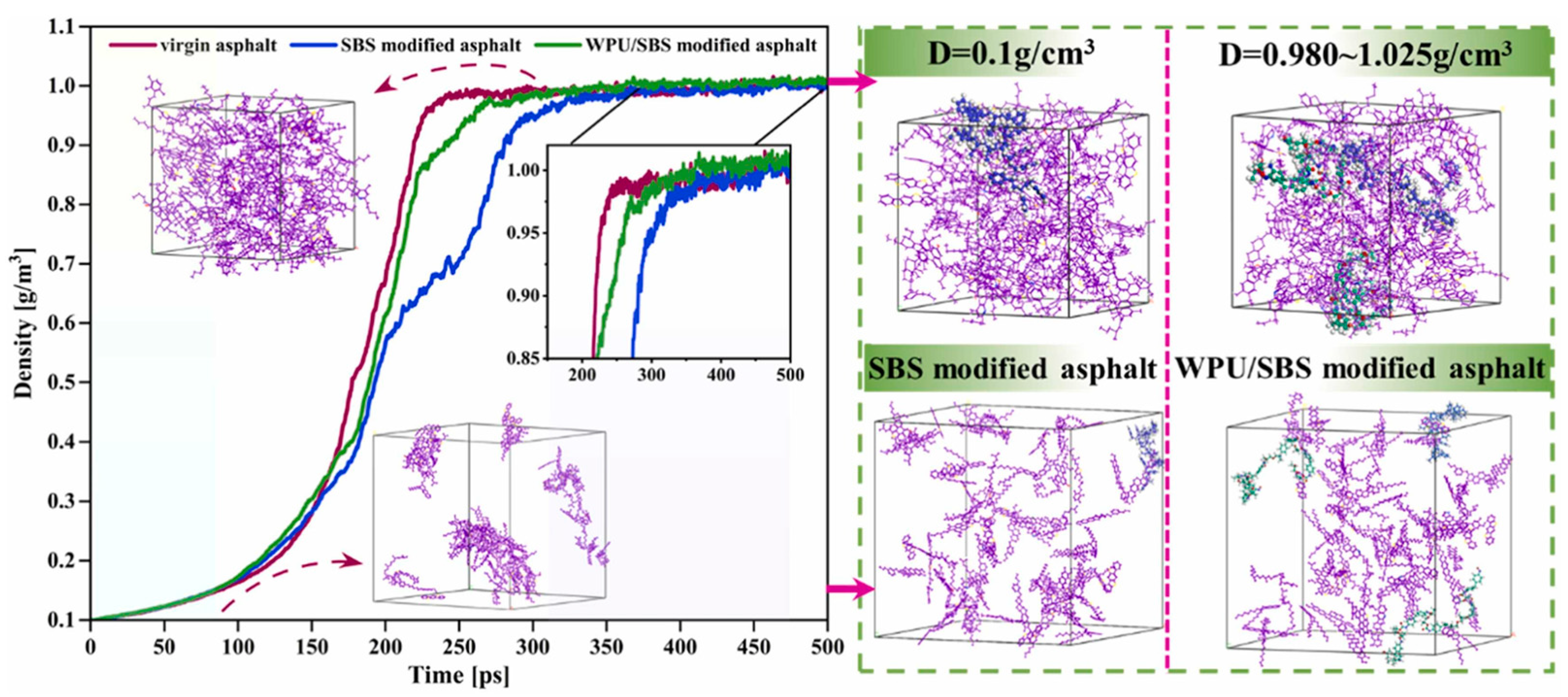
5.3. Chemical Interactions Between the Asphalt and the Remaining Polymer
5.4. Aging and Degradation
6. Conclusions, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
- (1)
- Current treatment strategies for recycled FRP materials
- (2)
- Direct reuse in construction
- (3)
- Application of RTWBs in the production of cementitious materials
- (4)
- Application of RTWBs in the production of asphalt matrix
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Lin, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, B.; Li, X. Exploring recycling strategies for retired wind turbine blades: The impact of policy subsidies and technological investments using a game-theoretic approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 490, 144628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Marquez, D.; Florin, N.; Hall, W.; Majewski, P.; Wang, H.; Stewart, R.A. State-of-the-art review of product stewardship strategies for large composite wind turbine blades. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2022, 15, 200109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, A.; Bonde, A.; Sun, H.; Wittig, N.K.; Hammershøj, H.C.D.; Batista, G.M.F.; Sommerfeldt, A.; Frølich, S.; Birkedal, H.; Skrydstrup, T. Catalytic disconnection of C–O bonds in epoxy resins and composites. Nature 2023, 617, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, A.; Liew, K.M. Assessing recycling potential of carbon fiber reinforced plastic waste in production of eco-efficient cement-based materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Jinping, Q.; Bi, S.; Ning, C.; Min, N.; Shuangqiao, Y. Prevention and Control of Waste Plastics Pollution in China. Chin. J. Eng. Sci. 2021, 23, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.; Skelton, K. Wind turbine blade recycling: Experiences, challenges and possibilities in a circular economy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 97, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, J.R.; Almeida, N.M.; Figueira, J.R. Recycling of FRP composites: Reusing fine GFRP waste in concrete mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofinejad, D.; Sanginabadi, K.; Eftekhar, M.R. Effects of coarse aggregate volume on CFRP-concrete bond strength and behavior. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 198, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, P.; Osmani, M.; Price, A. Improvement of the mechanical properties of glass fibre reinforced plastic waste powder filled concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, P.; Osmani, M.; Price, A. Assessing the recycling potential of glass fibre reinforced plastic waste in concrete and cement composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, T.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.; Si, W.; Ling, T. The Effect of GFRP Powder on the High and Low-Temperature Properties of Asphalt Mastic. Materials 2023, 16, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joustra, J.; Flipsen, B.; Balkenende, R. Structural reuse of high end composite products: A design case study on wind turbine blades. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spini, F.; Bettini, P. End-of-Life wind turbine blades: Review on recycling strategies. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 275, 111290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefeuvre, A.; Garnier, S.; Jacquemin, L.; Pillain, B.; Sonnemann, G. Anticipating in-use stocks of carbon fibre reinforced polymers and related waste generated by the wind power sector until 2025. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Cui, Y.; Pickering, S.; McKechnie, J. From aviation to aviation: Environmental and financial viability of closed-loop recycling of carbon fibre composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 200, 108362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, X. Wind turbine blade recycling: A review of the recovery and high-value utilization of decommissioned wind turbine blades. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 210, 107813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Meng, F.; Barlow, C.Y. Wind turbine blade end-of-life options: An eco-audit comparison. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atoyebi, O.; Gana, A.; Longe, J. Strength assessment of concrete with waste glass and bankoro (Morinda Citrifolia) as partial replacement for fine and coarse aggregate. Results Eng. 2020, 6, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.; Choudhary, P.; Krishnan, V.; Zafar, S. A review on recycling and reuse methods for carbon fiber/glass fiber composites waste from wind turbine blades. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 215, 108768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.; Prabhakara, H.M.; Bramer, E.; Dierkes, W.; Akkerman, R.; Brem, G. A critical review on recycling of end-of-life carbon fibre/glass fibre reinforced composites waste using pyrolysis towards a circular economy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.; Ghita, O.; Savage, L.; Evans, K. Successful closed-loop recycling of thermoset composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauson, J.; Lilholt, H.; Brøndsted, P. Recycling solid residues recovered from glass fibre-reinforced composites—A review applied to wind turbine blade materials. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.; Loppinet-Serani, A.; Cansell, F.; Aymonier, C. Near- and supercritical solvolysis of carbon fibre reinforced polymers (CFRPs) for recycling carbon fibers as a valuable resource: State of the art. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 66, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mativenga, P.T.; Shuaib, N.A.; Howarth, J.; Pestalozzi, F.; Woidasky, J. High voltage fragmentation and mechanical recycling of glass fibre thermoset composite. CIRP Ann. 2016, 65, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bru, K.; Touzé, S.; Auger, P.; Dobrusky, S.; Tierrie, J.; Parvaz, D.B. Investigation of lab and pilot scale electric-pulse fragmentation systems for the recycling of ultra-high performance fibre-reinforced concrete. Miner. Eng. 2018, 128, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diani, M.; Torvi, S.; Colledani, M. Exploiting High Voltage Fragmentation to Enable Demand-Driven Recycling of End-of-Life Wind Blades. Procedia CIRP 2024, 122, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fazio, D.; Boccarusso, L.; Formisano, A.; Viscusi, A.; Durante, M. A Review on the Recycling Technologies of Fibre-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Materials Used in Industrial Fields. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestalozzi, F.; Eisert, S.; Woidasky, J. Benchmark Comparison of High Voltage Discharge Separation of Photovoltaic Modules by Electrohydraulic and Electrodynamic Fragmentation. Recycling 2018, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyama, K.; Kubota, M.; Shirai, M.; Yoshida, H. Effect of alcohols on the degradation of crosslinked unsaturated polyester in sub-critical water. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, W.; Kubouchi, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Sembokuya, H.; Tsuda, K. An approach to chemical recycling of epoxy resin cured with amine using nitric acid. Polymer 2002, 43, 2953–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Boom, R.; Irion, B.; Van Heerden, D.J.; Kuiper, P.; De Wit, H. Recycling of composite materials. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2012, 51, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero-Hernanz, R.; Dodds, C.; Hyde, J.; García-Serna, J.; Poliakoff, M.; Lester, E.; Cocero, M.J.; Kingman, S.; Pickering, S.; Wong, K.H. Chemical recycling of carbon fibre reinforced composites in nearcritical and supercritical water. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero-Hernanz, R.; García-Serna, J.; Dodds, C.; Hyde, J.; Poliakoff, M.; Cocero, M.J.; Kingman, S.; Pickering, S.; Lester, E. Chemical recycling of carbon fibre composites using alcohols under subcritical and supercritical conditions. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2008, 46, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, N.; Liu, T. Microstructure and performance of recycled wind turbine blade based 3D printed concrete. Clean. Waste Syst. 2025, 10, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y. Glycolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) catalyzed by ionic liquids. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, D.K.; Pagar, D.D.; Menezes, P.L.; Linul, E. Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: Manufacturing, Properties, and Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunliffe, A.M.; Jones, N.; Williams, P.T. Recycling of fibre-reinforced polymeric waste by pyrolysis: Thermo-gravimetric and bench-scale investigations. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2003, 70, 315–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.; Schulte, K.; Grove-Nielsen, E. CFRP-Recycling Following a Pyrolysis Route: Process Optimization and Potentials. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahil, M.A.; Williams, P.T. Recycling of carbon fibre reinforced polymeric waste for the production of activated carbon fibres. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2011, 91, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butenegro, J.A.; Bahrami, M.; Abenojar, J.; Martínez, M.Á. Recent Progress in Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers Recycling: A Review of Recycling Methods and Reuse of Carbon Fibers. Materials 2021, 14, 6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, R.; Xydis, G. Wind turbine blade recycling: An evaluation of the European market potential for recycled composite materials. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, S.J.; Kelly, R.M.; Kennerley, J.R.; Rudd, C.D.; Fenwick, N.J. A fluidised-bed process for the recovery of glass fibres from scrap thermoset composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2000, 60, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; McKechnie, J.; Turner, T.A.; Pickering, S.J. Energy and environmental assessment and reuse of fluidised bed recycled carbon fibres. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 100, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle, A.J.; Delaney, E.L.; Bank, L.C.; Leahy, P.G. A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment between landfilling and Co-Processing of waste from decommissioned Irish wind turbine blades. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Barlow, C.Y. Wind turbine blade waste in 2050. Waste Manag. 2017, 62, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manso-Morato, J.; Hurtado-Alonso, N.; Revilla-Cuesta, V.; Ortega-López, V. Management of wind-turbine blade waste as high-content concrete addition: Mechanical performance evaluation and life cycle assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baturkin, D.; Hisseine, O.A.; Masmoudi, R.; Tagnit-Hamou, A.; Massicotte, L. Valorization of recycled FRP materials from wind turbine blades in concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Ji, Y.; Qie, R.; Wang, D.; Liu, G. Mechanical Properties and Microscopic Study of Recycled Fibre Concrete Based on Wind Turbine Blades. Materials 2024, 17, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, F.P.; Bosco, E.; Salet, T.A.M. Ductility of 3D printed concrete reinforced with short straight steel fibers. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2018, 14, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiao, B.; Fang, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Chu, S.; Kwan, A. Feasibility of glass/basalt fiber reinforced seawater coral sand mortar for 3D printing. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 37, 101684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
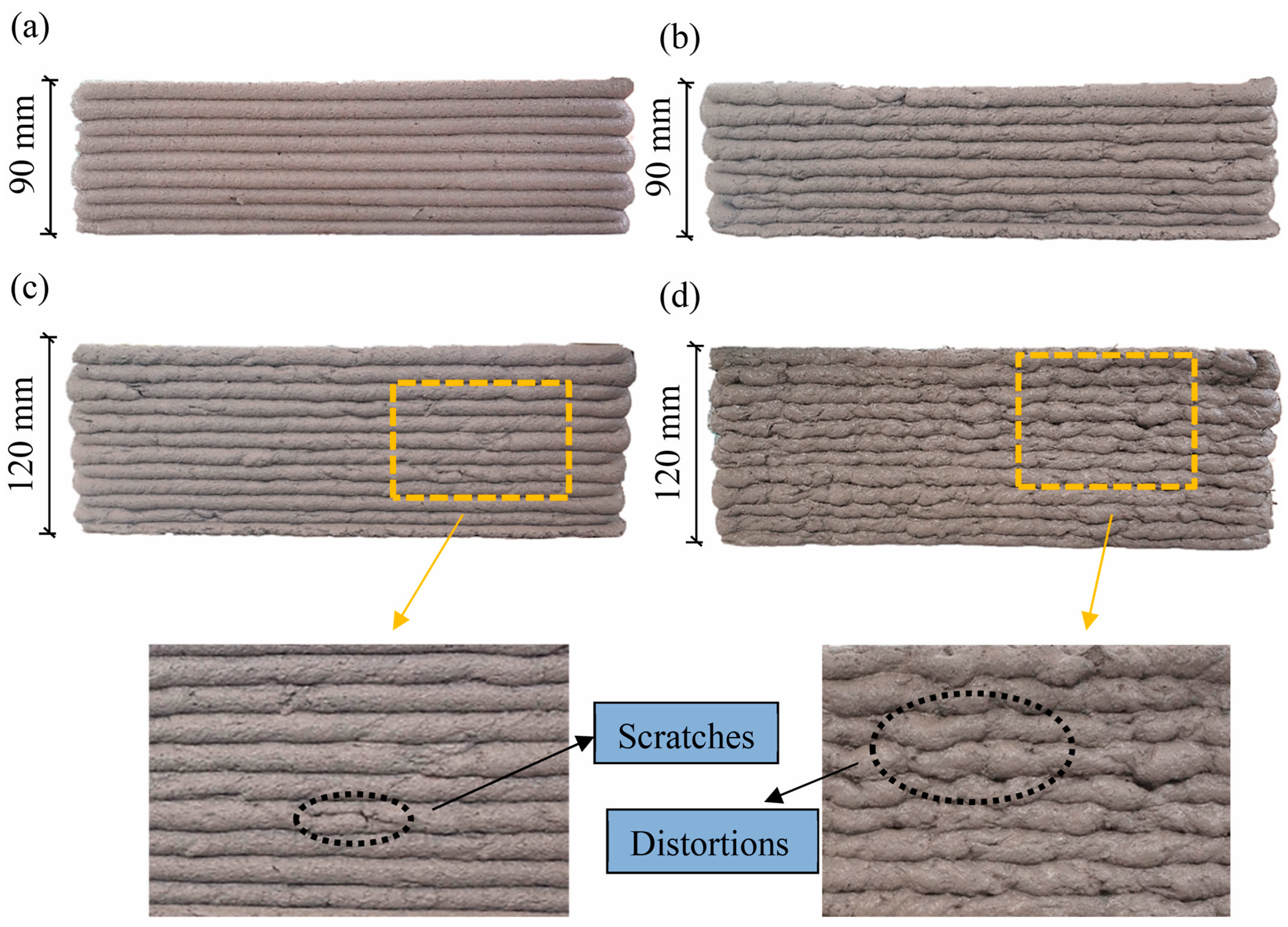
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, M.; Ma, G. An experimental study on 3D printed concrete reinforced with fibers recycled from wind turbine blades. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 91, 109578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, P.; Dobbelsteen, A.v.D.; Peck, D. Safety and Health Concerns for the Users of a Playground, Built with Reused Rotor Blades from a Dismantled Wind Turbine. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, H. Anmet Installs First Recycled Wind Turbine Blade-Based Pedestrian Bridge. 2023. Available online: https://www.compositesworld.com/news/anmet-installs-first-recycled-wind-turbine-blade-based-pedestrian-bridge (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Vizentin, G.; Vukelic, G. Marine environment induced failure of FRP composites used in maritime transport. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 137, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizentin, G.; Vukelic, G. Prediction of the Deterioration of FRP Composite Properties Induced by Marine Environments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Paraskevoulakos, C.; Mughal, U.A.; Tyurkay, A.; Lushnikova, N.; Song, H.; Duyal, C.; Karnick, S.T.; Gauvin, F.; Lima, A.T. Mechanisms and applications of wind turbine blade waste in cementitious composites: A review. Mater. Des. 2025, 251, 113732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.S.; Antunes, M.L.P.; da Cruz, N.C.; Rangel, E.C.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Durrant, S.F. Use of waste collected from wind turbine blade production as an eco-friendly ingredient in mortars for civil construction. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanbakhsh, A.; Bank, L.C.; Tian, Y. Mechanical Processing of GFRP Waste into Large-Sized Pieces for Use in Concrete. Recycling 2018, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, K.; Chen, J.; Teng, J. Concrete reinforced with macro fibres recycled from waste GFRP. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 310, 125063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, V.C. A simplified micromechanical model of compressive strength of fiber-reinforced cementitious composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1992, 14, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, S.M.S.; Munir, M.J.; Wu, Y.-F.; Patnaikuni, I. Effect of macro-synthetic fibers on the fracture energy and mechanical behavior of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 189, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Jing, L.; Peng, S.; Jing, W. A Study on the Mechanical Properties of Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Defective Gypsum Boards. Sustainability 2024, 16, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, L.; Thomas, D. Screening of Aqueous Amine-Based Solvents for Postcombustion CO2 Capture by Chemical Ab-sorption. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2012, 35, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsch, L.; Farmer, S.; Cunningham, K.; Sharrett, Z.; Shea, K.M. Organic Chemistry II; Smith College: Northampton, MA, USA, 2023; Available online: https://scholarworks.smith.edu/textbooks/6 (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Faruk, O.; Sain, M. Biofiber reinforced polymer composites for structural applications. In Developments in Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Composites for Civil Engineering; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 18–53. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, B.; Comini, M.; Salinas, G.; Trujillo, M. Redox Chemistry and Biology of Thiols; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- March, J. Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, F.A.; Sundberg, R.J. Advanced Organic Chemistry: Part A: Structure and Mechanisms; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjbarian, M.; Mechtcherine, V. Influence of loading parameters in cyclic tension-compression regime on crack-bridging behaviour of PVA microfibres embedded in cement-based matrix. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Yoon, H.; Lee, H. Autogenous shrinkage and electrical characteristics of cement pastes and mortars with carbon nanotube and carbon fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 177, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ni, F.; Gu, X.; Yao, L.; Dong, Q. Evaluation of aggregate packing based on thickness distribution of asphalt binder, mastic and mortar within asphalt mixtures using multiscale methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 222, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Romero, P.; Dong, Z.; Li, Y. Investigation on the low temperature property of asphalt fine aggregate matrix and asphalt mixture including the environmental factors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashidhar, N.; Romero, P. Factors Affecting the Stiffening Potential of Mineral Fillers. In Asphalt Mixture Components; National Research Council: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Guo, Z.; Hong, B.; Xu, J.; Fan, Z.; Lu, G.; Wang, D.; Oeser, M. Using recycled waste glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) as filler to improve the performance of asphalt mastics. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 336, 130357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xiang, Z.; Zhong, S.; Huang, X. Performance and Modification Mechanism of Recycled Glass Fiber of Wind Turbine Blades and SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kirumira, N. Techniques of recycling end-of-life wind turbine blades in the pavement industry: A literature review. Clean Technol. Recycl. 2024, 4, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Garg, R. Rheology of waste plastic fibre-modified bitumen. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2011, 12, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, X.; Lv, J.; Zhu, Z.; Ni, F. Mechanism and behavior of fiber-reinforced asphalt mastic at high temperature. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 19, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, A.O. An Evaluation of the Cracking Resistance of Steel- and Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Asphalt Mixtures Produced at Different Temperatures. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, C.; Indacoechea, I.; Wang, D.; Lastra-González, P.; Falchetto, A.C.; Castro-Fresno, D. Low temperature performances of fiber-reinforced asphalt mixtures for surface, binder, and base layers. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2022, 206, 103738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, M.; Hosseini, S.A. Laboratory evaluation of rutting and moisture damage resistance of glass fiber modified warm mix asphalt incorporating high RAP proportion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gillani, S.T.A.; Qiao, Z. Feasibility and environmental assessment of introducing waste polyurethane from wind turbine blades as a modifier for asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 446, 138052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, C.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Huang, Z. Investigation of Surface Modification of Bagasse Fibers: Performance of Asphalt Binders/Mixtures with Bagasse Fibers. Buildings 2024, 14, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hu, Y. Effect of aging on the low-temperature performance of fiber-reinforced asphalt mixtures. AIP Adv. 2023, 13, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnadish, A.M.; Aman, M.Y.; Katman, H.Y.B.; Ibrahim, M.R. Influence of the Long-Term Oven Aging on the Performance of the Reinforced Asphalt Mixtures. Coatings 2020, 10, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Wei, H.; Liu, X. Utilization of waste wind turbine blades in performance improvement of asphalt mixture. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1164693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Bai, X.; Yang, L.; Han, J.; Zhou, G. Reuse of Retired Wind Turbine Blades in Civil Engineering. Buildings 2025, 15, 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142414
Yu X, Zhang C, Li J, Bai X, Yang L, Han J, Zhou G. Reuse of Retired Wind Turbine Blades in Civil Engineering. Buildings. 2025; 15(14):2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142414
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xuemei, Changbao Zhang, Jing Li, Xue Bai, Lilin Yang, Jihao Han, and Guoxiang Zhou. 2025. "Reuse of Retired Wind Turbine Blades in Civil Engineering" Buildings 15, no. 14: 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142414
APA StyleYu, X., Zhang, C., Li, J., Bai, X., Yang, L., Han, J., & Zhou, G. (2025). Reuse of Retired Wind Turbine Blades in Civil Engineering. Buildings, 15(14), 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15142414




