Computer Vision-Based Monitoring of Bridge Structural Vibration During Incremental Launching Construction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
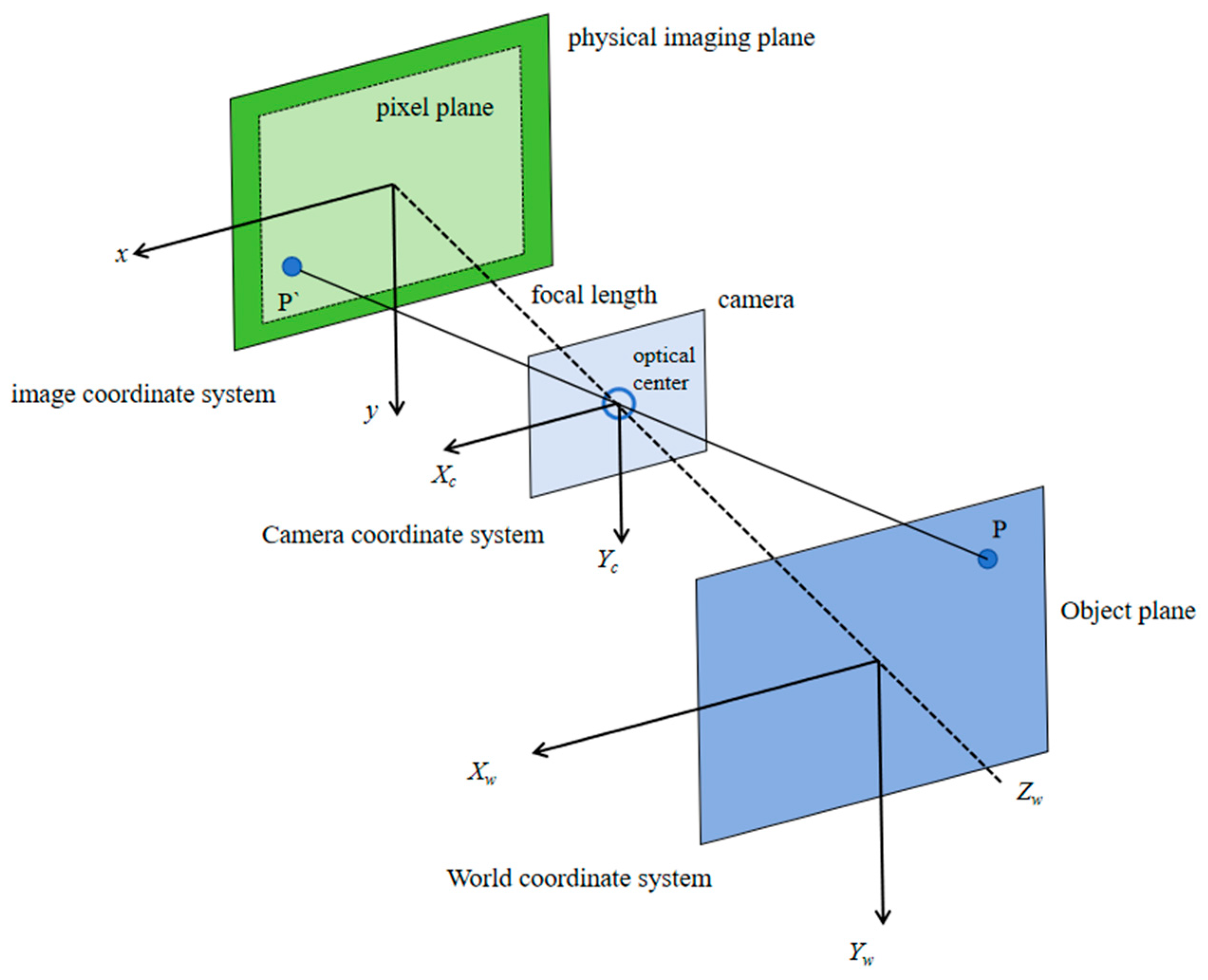
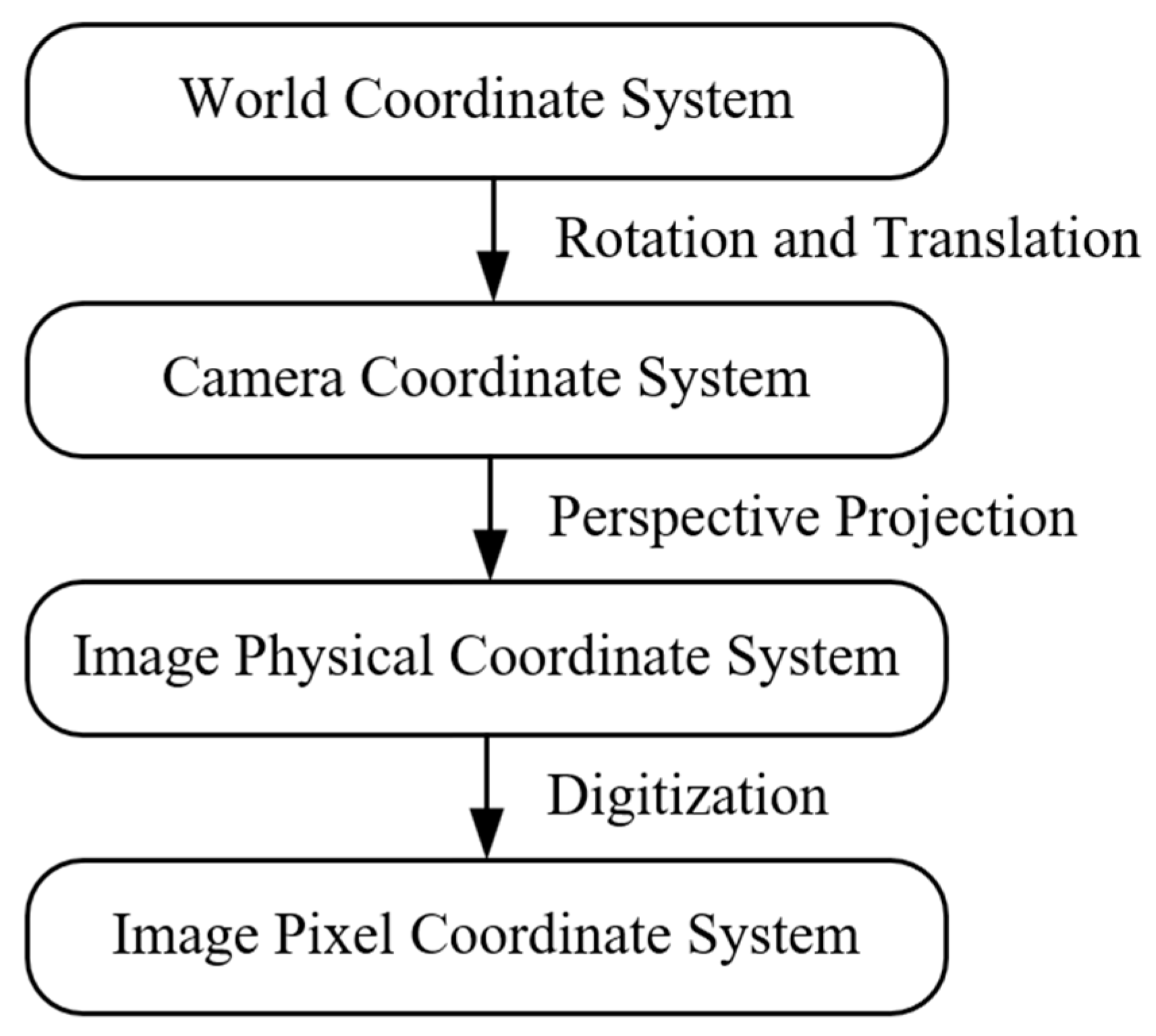
2. Bridge Structure Vibration Monitoring Method Based on Computer Vision
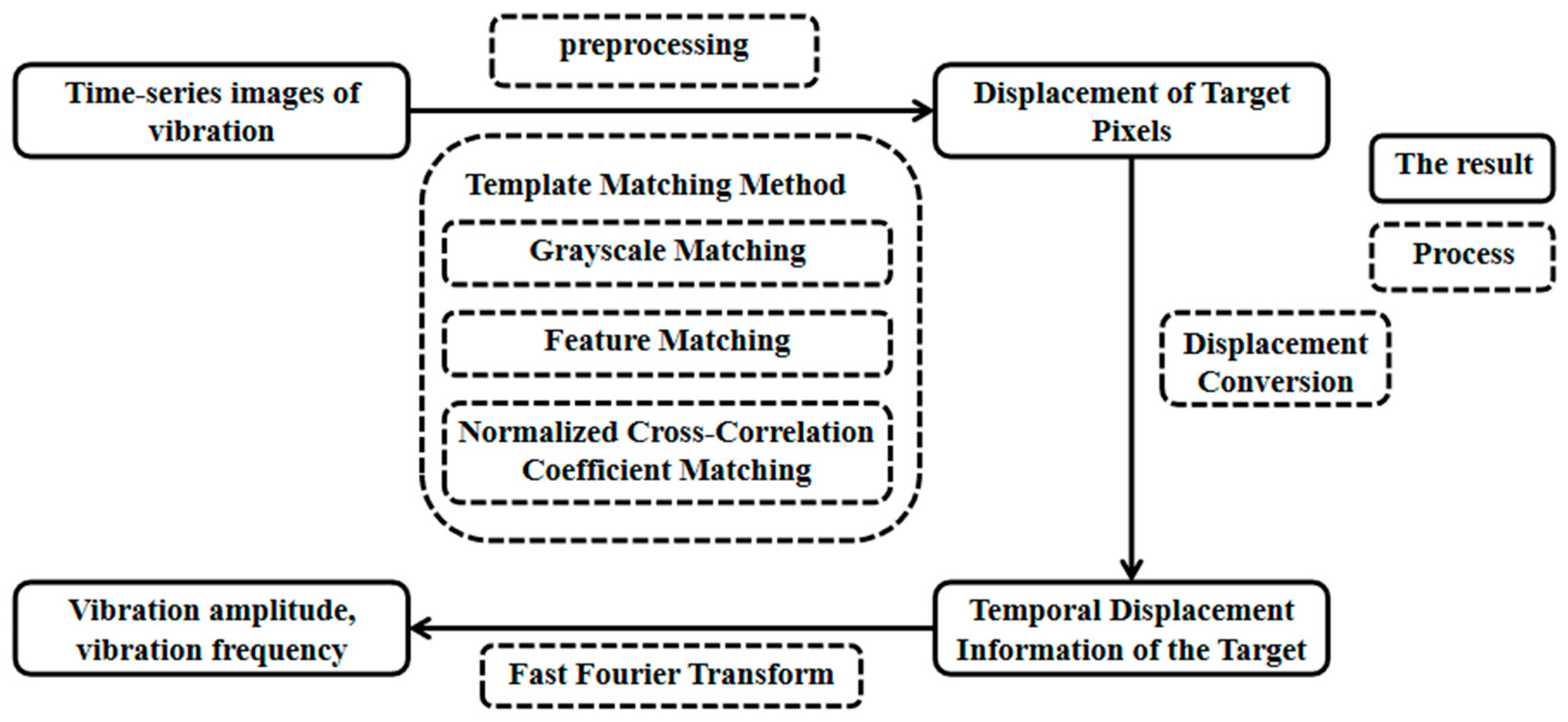
2.1. Basic Process
2.2. Template Matching Method
3. Indoor Experimental Verification
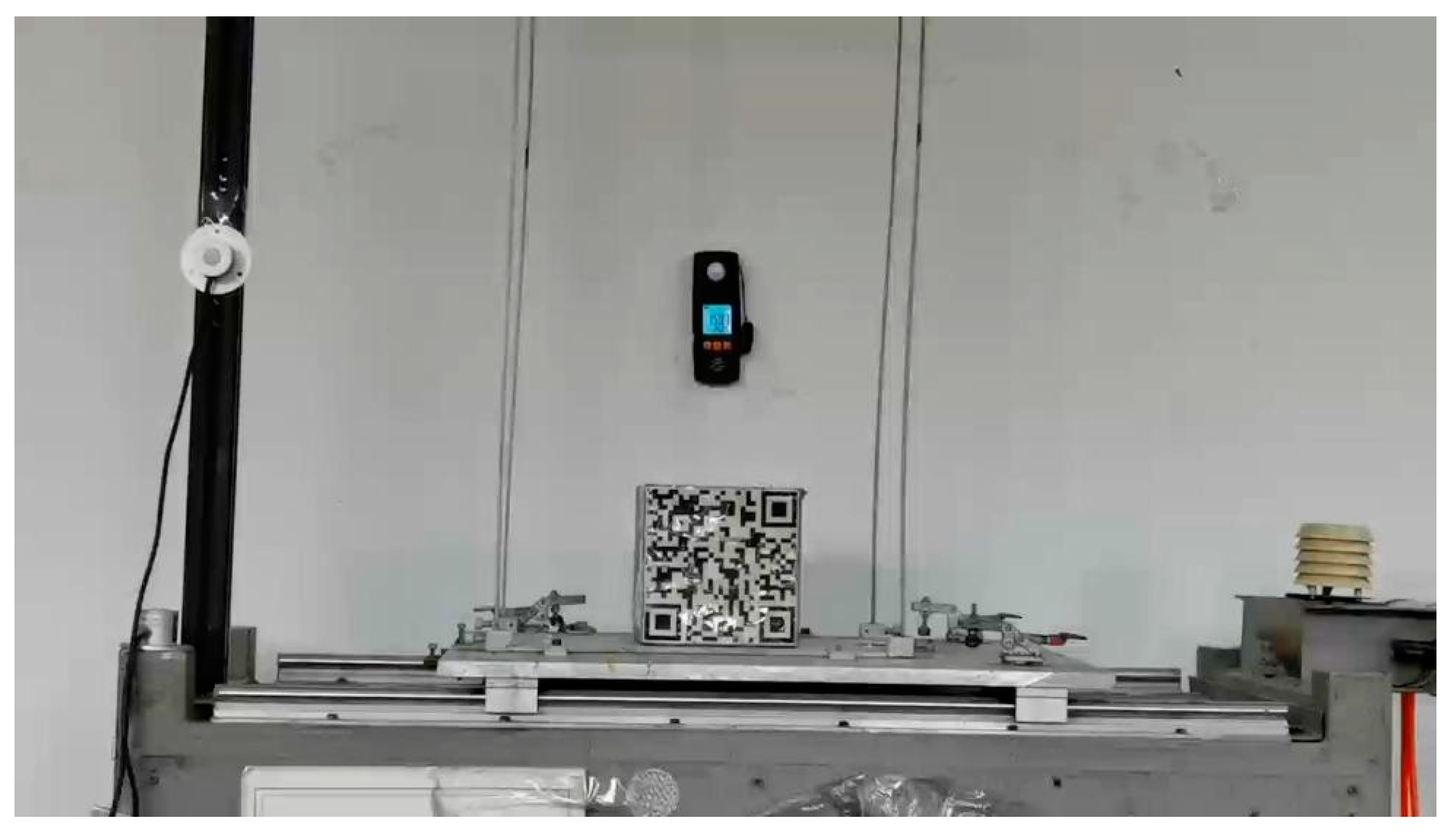
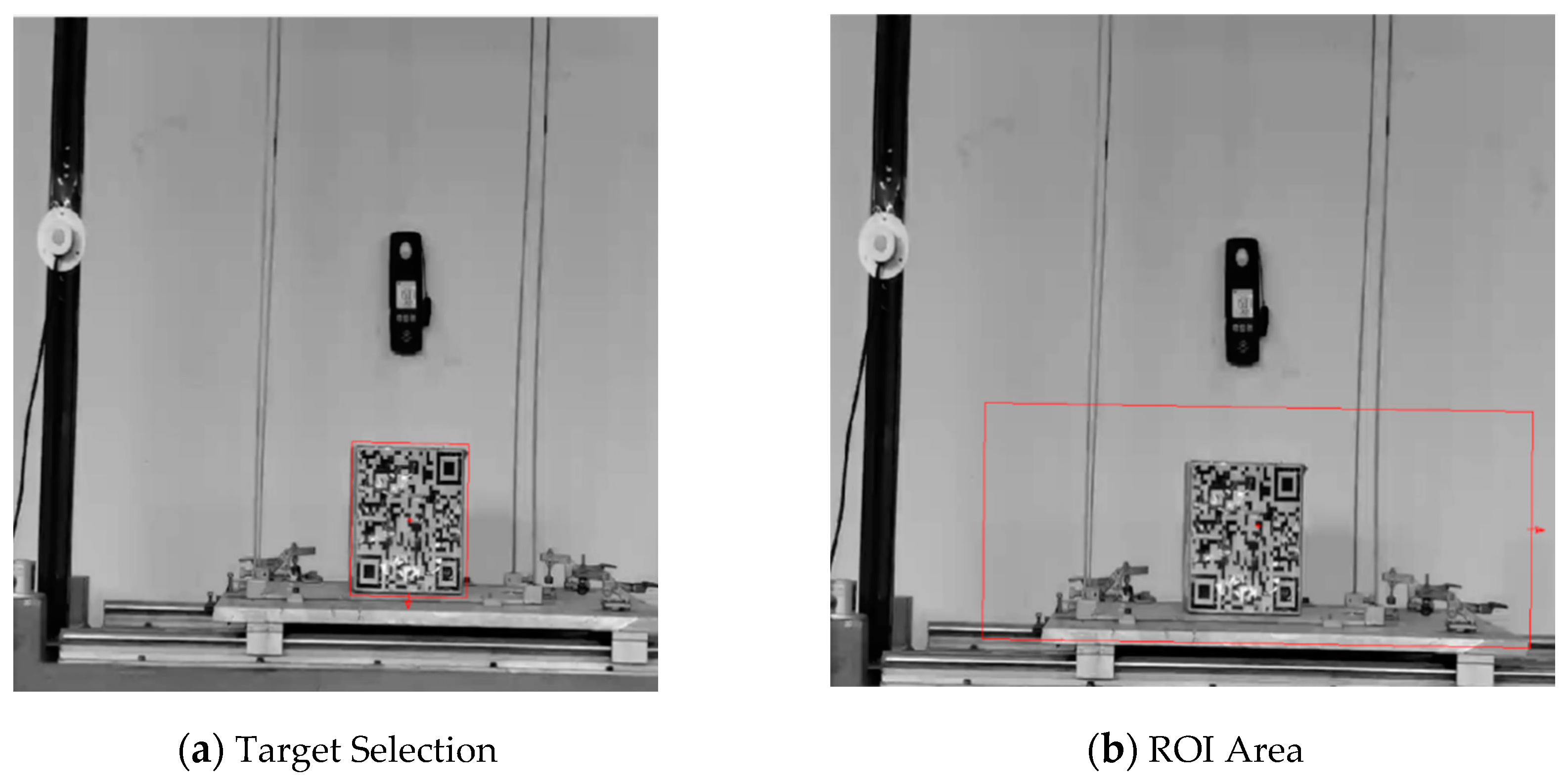
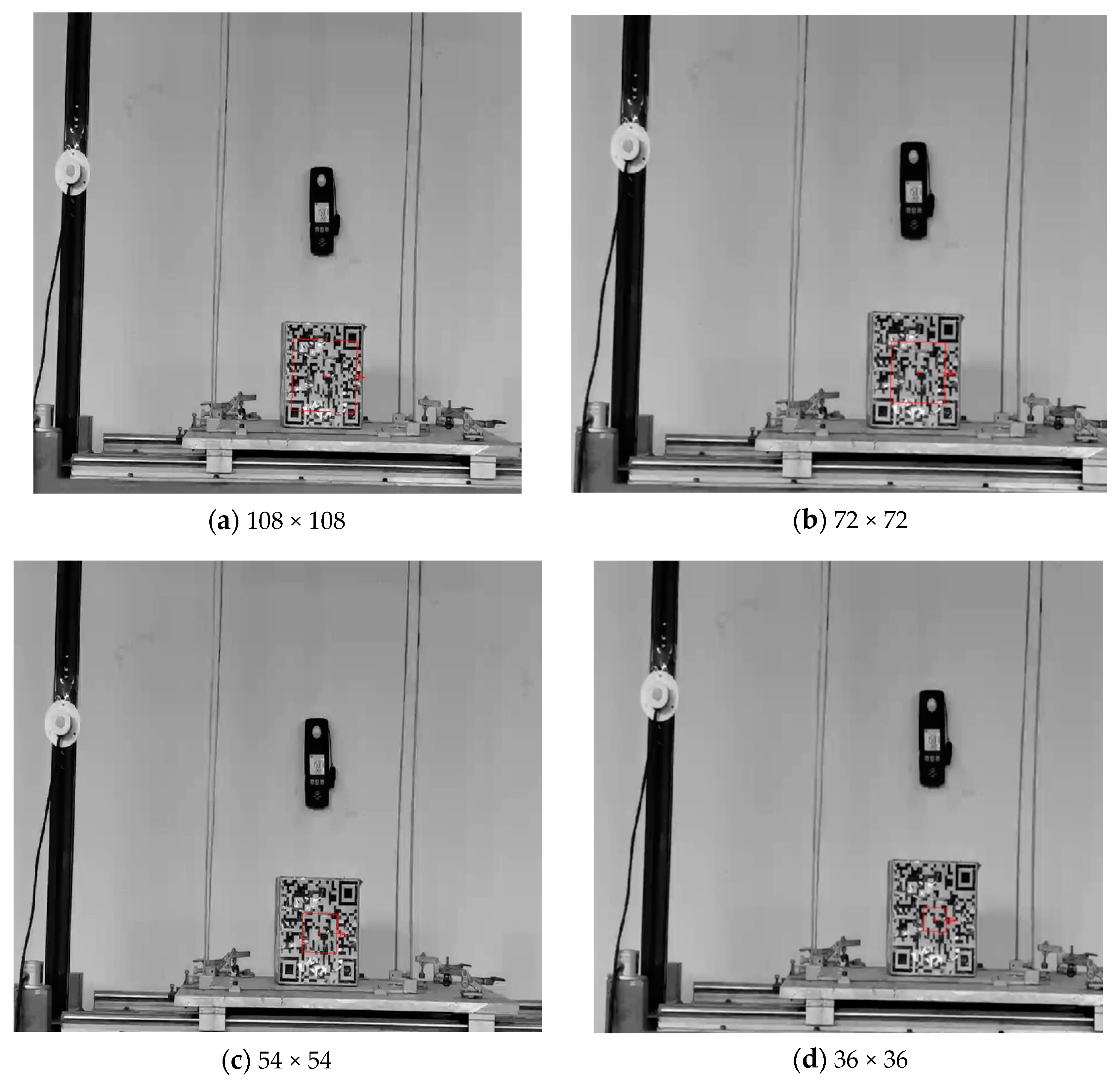
3.1. Hardware System and Test Conditions
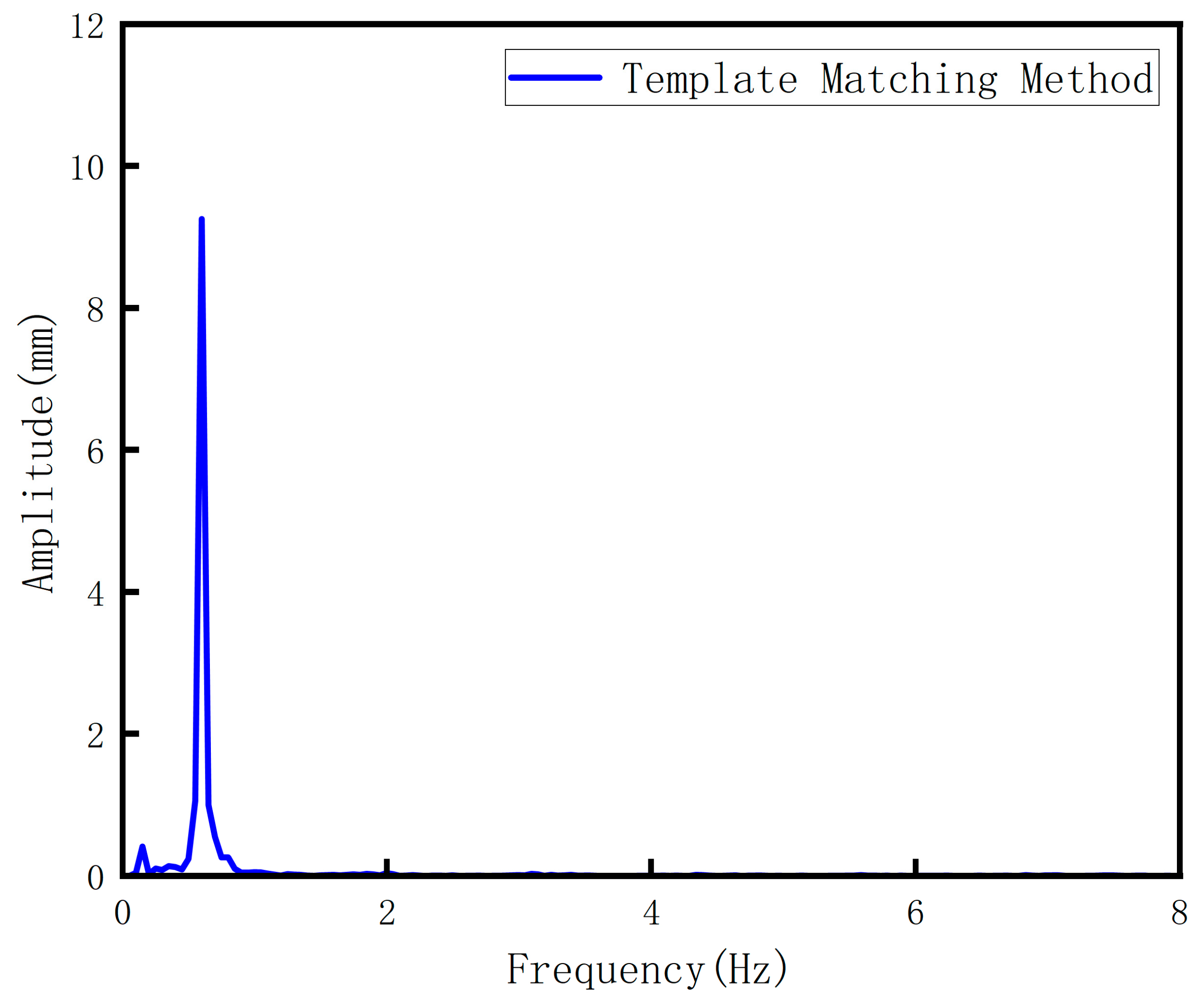
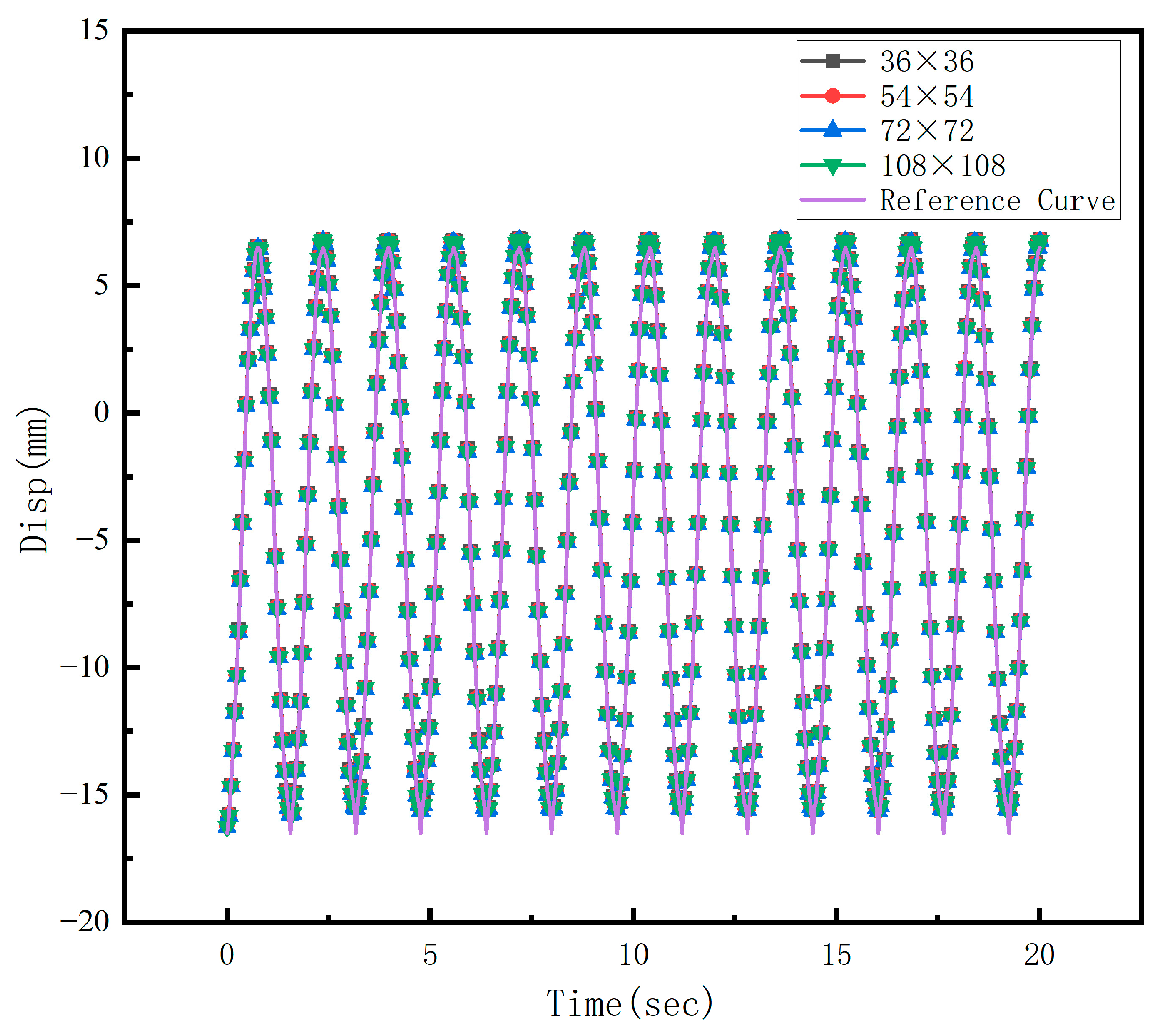
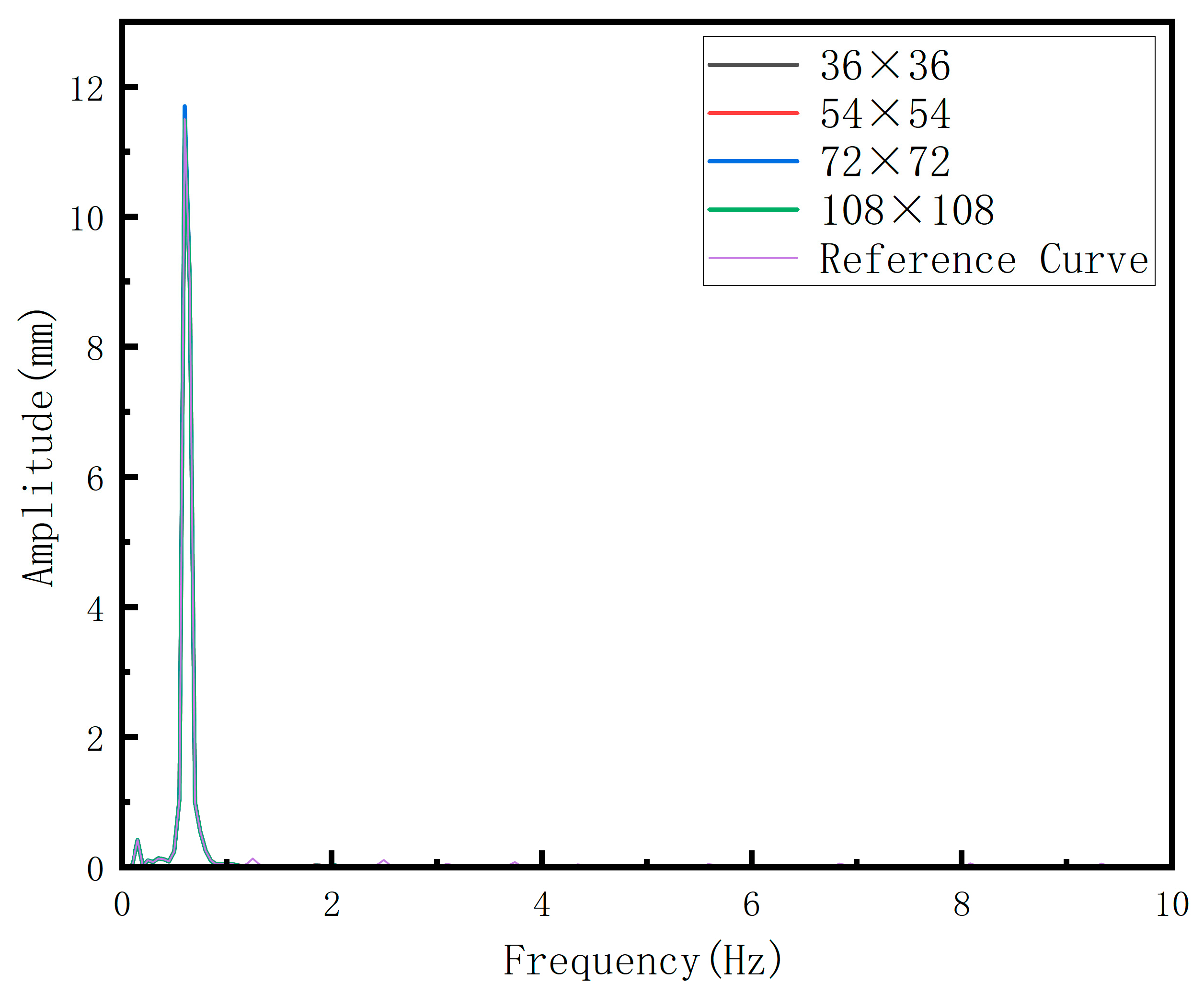
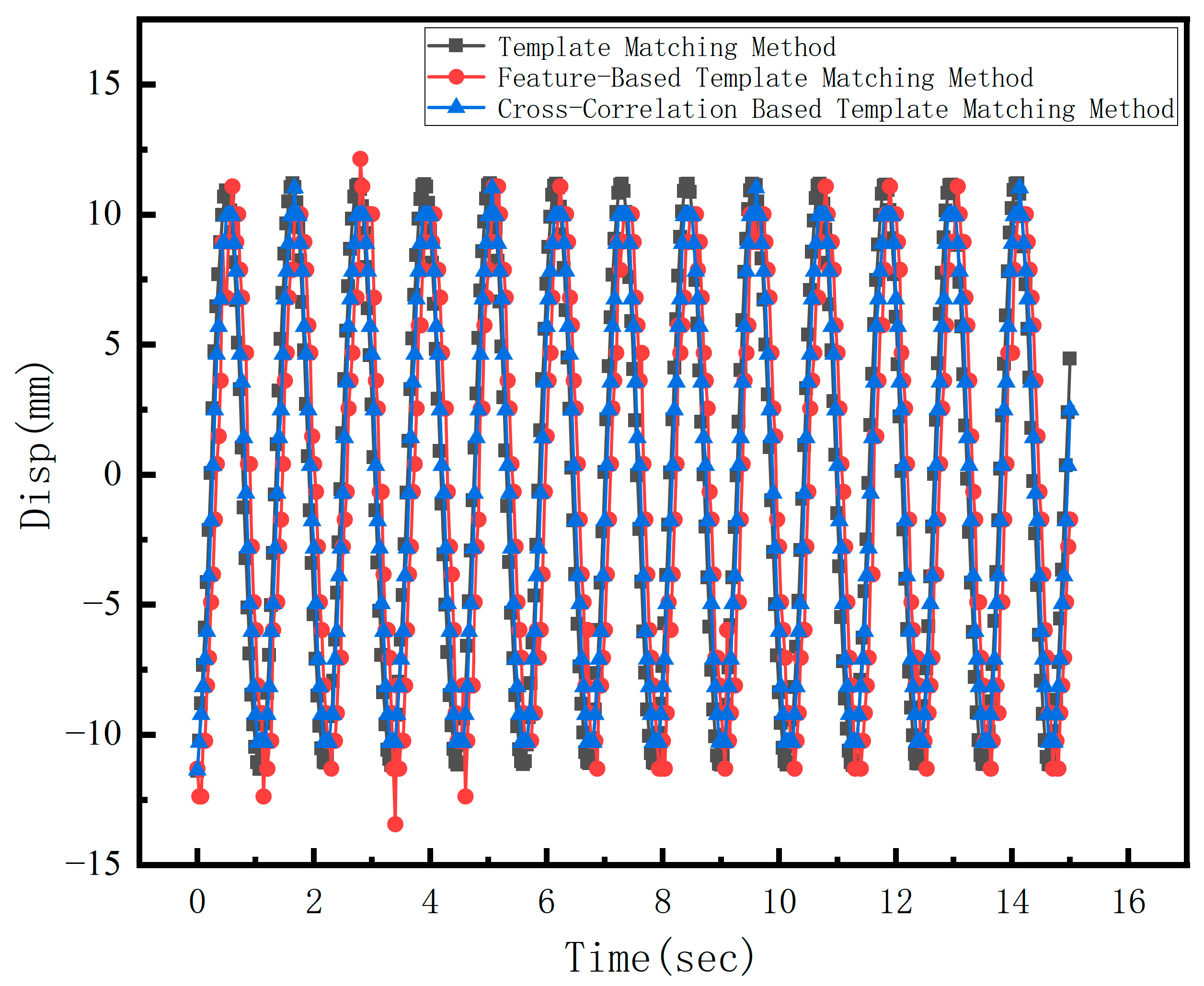
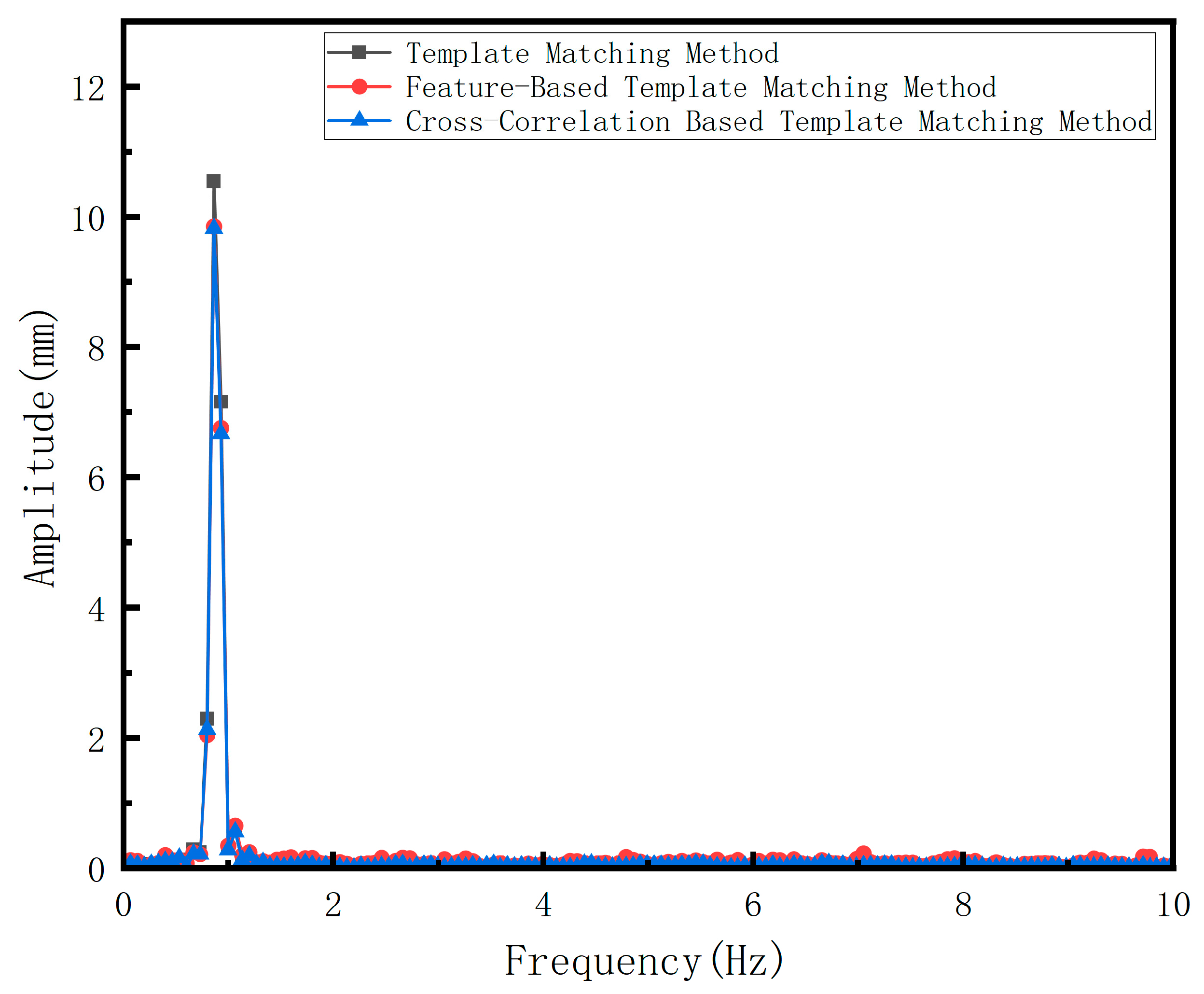
3.2. Experimental Research on Vibration Monitoring
4. Field Bridge Vibration Monitoring
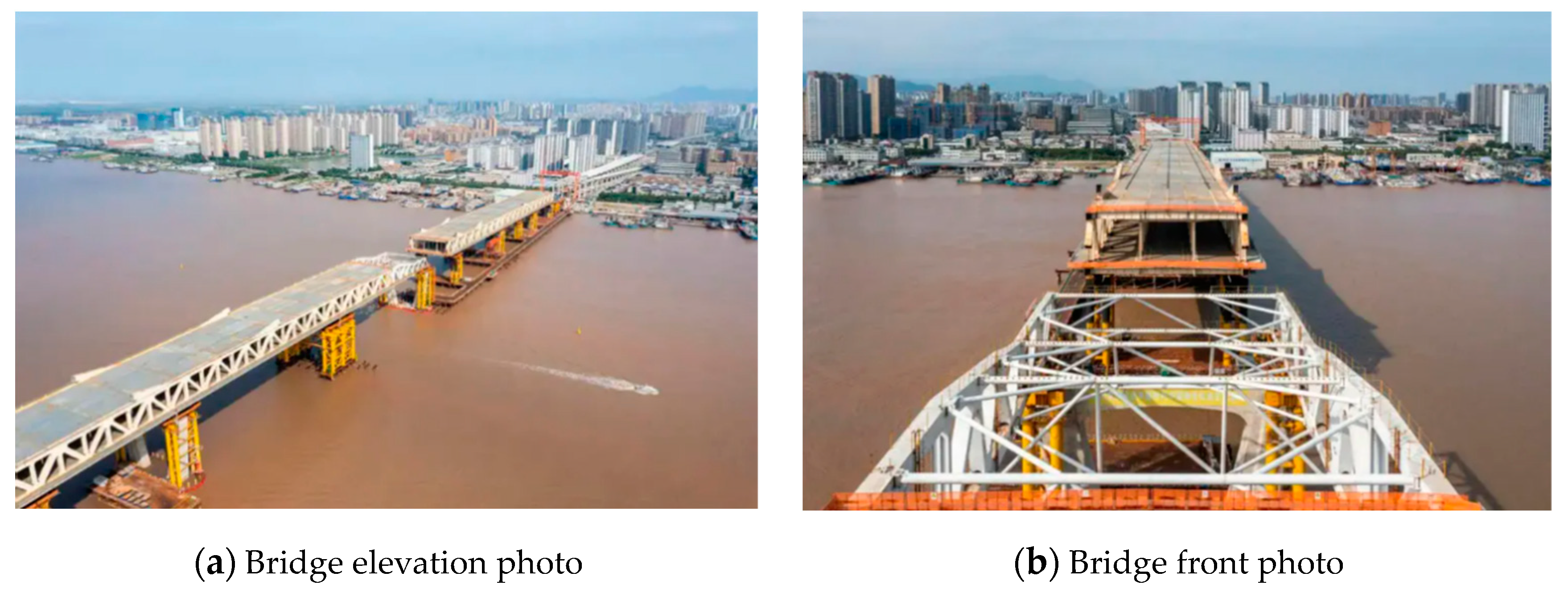
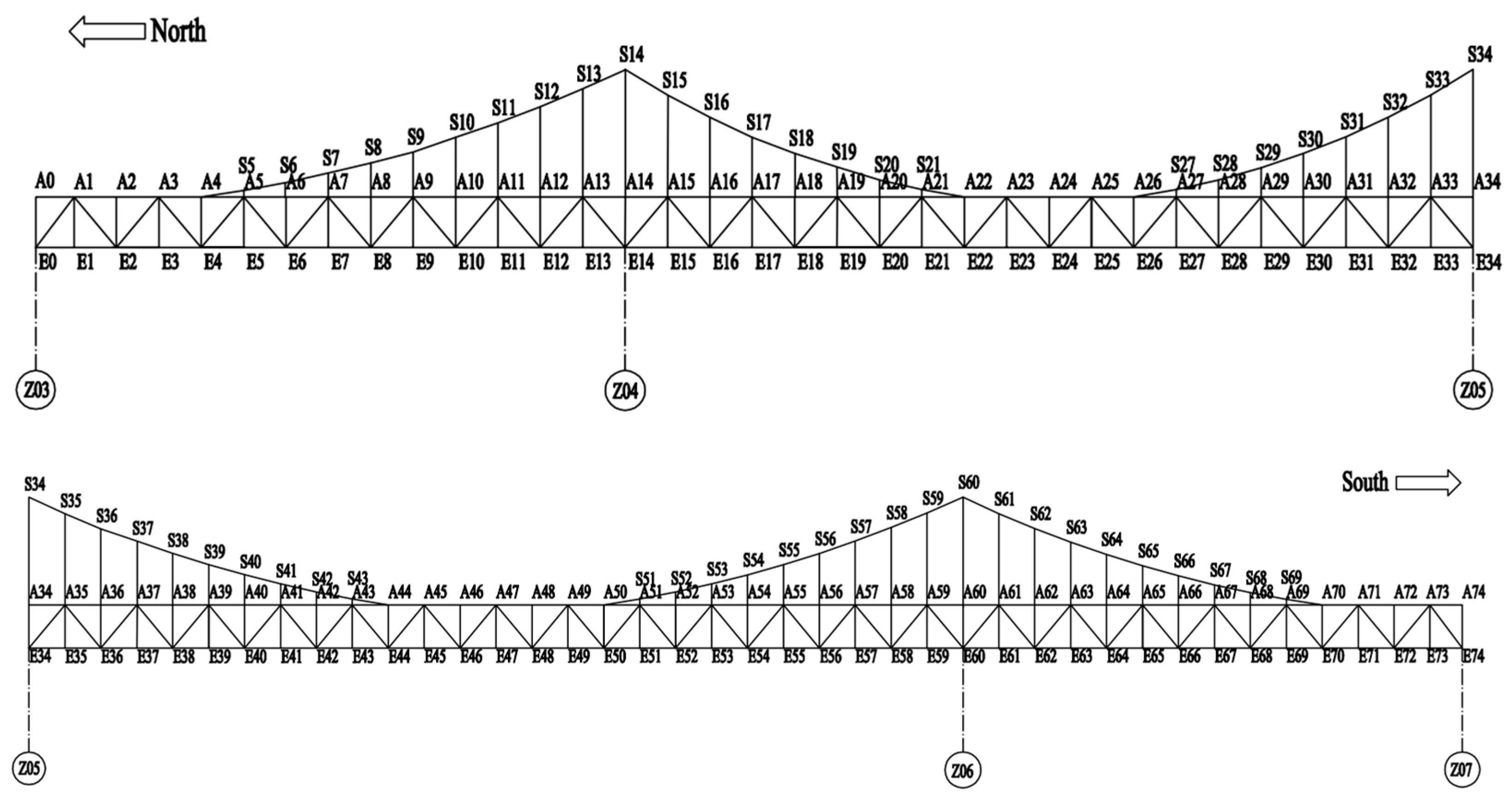
4.1. Introduction to Yongning Bridge Background
4.2. Vibration Monitoring of the Incremental Launching Construction of Yongning Bridge
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niyirora, R.; Ji, W.; Masengesho, E.; Munyaneza, J.; Niyonyungu, F.; Nyirandayisabye, R. Intelligent damage diagnosis in bridges using vibration-based monitoring approaches and machine learning: A systematic review. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100761. [Google Scholar]
- Koganezawa, S.; Terai, S.; Tani, H.; Lu, R.; Kawada, S. Vibration based Scour-Detection for Bridge-Piers Using a Self-Powered Magnetostrictive Vibration Sensor. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2024, 8, 6011604. [Google Scholar]
- Gonen, S.; Erduran, E. A Hybrid Method for Vibration-Based Bridge Damage Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalizhanova, A.; Kunelbayev, M.; Kozbakova, A. Bridge Vibration Analysis Using Fiber-Optic Bragg Sensors with an Inclined Grid. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2024, 27, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Shen, Y.F.; Weng, B.W.; Zhong, C.J. Characteristic parameter analysis for identification of vortex-induced vibrations of a long-span bridge. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2024, 15, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidin, S.S.; Jamadin, A.; Kudus, S.A.; Amin, N.M.; Anuar, M.A. An Overview: The Application of Vibration-Based Techniques in Bridge Structural Health Monitoring. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2022, 16, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, R.R.; Xia, Y. Review on the new development of vibration-based damage identification for civil engineering structures: 2010–2019. J. Sound Vibr. 2021, 491, 115741. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L.M. Roles of artificial intelligence in construction engineering and management: A critical review and future trends. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103517. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.L.; Zhou, W.; Chen, C.F.; Ma, P.F. Extended D-TomoSAR Displacement Monitoring for Nanjing (China) City Built Structure Using High-Resolution TerraSAR/TanDEM-X and Cosmo SkyMed SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.Q.; Sun, L.M.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, W. Vibration-based damage detection for bridges by deep convolutional denoising autoencoder. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 20, 1880–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.Y.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Cai, H.Y.; Cui, K.R.; Chen, X.D. Automatic Bridge Crack Detection Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.; Jang, K.; An, J.Y. Deep super resolution crack network (SrcNet) for improving computer vision–based automated crack detectability in in situ bridges. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 20, 1428–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.F.; Weng, T.; Xing, J.; Pan, Z.H.; Yuan, Z.H.; Xing, X.M.; Zhang, P. A New Deep Learning Network for Automatic Bridge Detection from SAR Images Based on Balanced and Attention Mechanism. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Q.; Tang, Z.Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.F. Computer vision and deep learning-based data anomaly detection method for structural health monitoring. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 18, 401–421. [Google Scholar]
- Busca, G.; Cigada, A.; Mazzoleni, P.; Zappa, E. Vibration monitoring of multiple bridge points by means of a unique vision-based measuring system. Exp. Mech. 2014, 54, 255–271. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Chang, C.C. Nontarget image-based technique for small cable vibration measurement. J. Bridge Eng. 2008, 13, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.C.; Wu, W.H.; Tseng, H.Z.; Chen, C.H.; Lai, G. Application of digital photogrammetry techniques in identifying the mode shape ratios of stay cables with multiple camcorders. Measurement 2015, 75, 134–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.W.; Jeon, B.G.; Cheung, J.H.; Kim, S.D.; Park, J.B. Stay Cable Tension Estimation Using a Vision-based Monitoring System under Various Weather Conditions. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2017, 7, 343–357. [Google Scholar]
- Kohut, P.; Kurowski, P. Application of modal analysis supported by 3D vision-based measurements. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2009, 47, 855–870. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, X.D.; Xia, Y.; Lozano-Galant, J.; Sun, L.M. Traffic Sensing Methodology Combining Influence Line Theory and Computer Vision Techniques for Girder Bridges. J. Sens. 2019, 2019, 3409525. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, Y.; Feng, M.; Narita, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Tanaka, T. Vision-based displacement sensor for monitoring dynamic response using robust object search algorithm. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 4725–4732. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.B.; Graca, M.S.; Bryanston-Cross, P.J.; Whitehouse, D.J. Phase-shifted image matching algorithm for displacement measurement. Opt. Eng. 1996, 35, 2327–2332. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.M.; Feng, M.Q.; Ozer, E.; Fukuda, Y. A Vision-Based Sensor for Noncontact Structural Displacement Measurement. Sensors 2015, 15, 16557–16575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Jeon, H.M.; Myung, H. Pose-graph optimized displacement estimation for structural displacement monitoring. Smart Struct. Syst. 2014, 14, 943–960. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.; Ashebo, D.; Tam, H.Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Chan, T.F.; Lee, P.C.; Gracia, E.P. Vertical displacement measurements for bridges using optical fiber sensors and CCD cameras-a preliminary study. Struct. Health Monit. 2009, 8, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.Z.; Ye, X.W.; Jin, T. Identification of structural dynamic characteristics based on machine vision technology. Measurement 2018, 126, 405–416. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.W.; Ni, Y.Q.; Wai, T.T.; Wong, K.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, F.X. A vision-based system for dynamic displacement measurement of long-span bridges: Algorithm and verification. Smart Struct. Syst. 2013, 12, 363–379. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.J.; Cho, S.; Shinozuka, M.; Yun, C.; Lee, C.G.; Lee, W. Evaluation of bridge load carrying capacity based on dynamic displacement measurement using real-time image processing techniques. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2006, 6, 377–385. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.M.; Feng, M.Q. Experimental validation of cost-effective vision-based structural health monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2017, 88, 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Ji, Y.F. Flexible videogrammetric technique for three-dimensional structural vibration measurement. J. Eng. Mech. 2007, 133, 656–664. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.H.; Chen, L.F.; Long, F.Q.; Li, Z.Q.; Jina, H.X. Automatic Bridge Detection of SAR Images Based on Interpretable Deep Learning Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Industrial Technology Applications, Suzhou, China, 24–26 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mas, D.; Ferrer, B.; Acevedo, P.; Espinosa, J. Method sand algorithms for video based multi-point frequency measuring and mapping. Measurement 2016, 85, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Qian, K.; Xie, H.; Asundi, A. Two-dimensional digital image correlation for in-plane displacement and strain measurement: A review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 062001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debella-Gilo, M.; Kääb, A. Sub-pixel precision image matching for measuring surface displacements on mass movements using normalized cross-correlation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, D.; Perez, J.; Ferrer, B.; Espinosa, J. Realistic limits for subpixel movement detection. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 4974–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ho, H.N.; Shinozuka, M. An advanced vision-based dynamic rotational angle measurement system for large civil structures. Sensors 2012, 12, 7326–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.F.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhu, J.; Gao, X.L.; Yang, B.J.; Tian, Y.S. Coarse-fine point cloud registration based on local point-pair features and the iterative closest point algorithm. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 12569–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydon, D.; Lydo, M.; Kromanis, R.; Dong, C.Z.; Catbas, N.; Taylor, S. Bridge Damage Detection Approach Using a Roving Camera Technique. Sensors 2021, 21, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Jian, X.D.; Yan, B.; Su, D. Infrastructure Safety Oriented Traffic Load Monitoring Using Multi-Sensor and Single Camera for Short and Medium Span Bridges. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.Q.; Liu, C. Accurate Measurement of Bridge Vibration Displacement via Deep Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 5020016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wan, L.; Wan, R.Q.; Yu, J.; Li, R. Automated fatigue crack detection in steel box girder of bridges based on ensemble deep neural network. Measurement 2022, 202, 111805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T. Research on Holographic Dynamic Displacement Monitoring and Damage Identification Methods for Bridges by Integrating Measurement Point Accelerations. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2024. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, H.; Zhang, M.; Jin, T.; Shi, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Guo, X.; Cai, X.; Peng, W. Computer Vision-Based Monitoring of Bridge Structural Vibration During Incremental Launching Construction. Buildings 2025, 15, 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071139
Shi H, Zhang M, Jin T, Shi X, Zhang J, Xu Y, Guo X, Cai X, Peng W. Computer Vision-Based Monitoring of Bridge Structural Vibration During Incremental Launching Construction. Buildings. 2025; 15(7):1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071139
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Hong, Min Zhang, Tao Jin, Xiufeng Shi, Jian Zhang, Yixiang Xu, Xinyi Guo, Xiaoye Cai, and Weibing Peng. 2025. "Computer Vision-Based Monitoring of Bridge Structural Vibration During Incremental Launching Construction" Buildings 15, no. 7: 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071139
APA StyleShi, H., Zhang, M., Jin, T., Shi, X., Zhang, J., Xu, Y., Guo, X., Cai, X., & Peng, W. (2025). Computer Vision-Based Monitoring of Bridge Structural Vibration During Incremental Launching Construction. Buildings, 15(7), 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15071139




