Abstract
The construction industry is undergoing a transformative shift through automation, with advancements in Generative AI (GenAI) and prompt engineering enhancing safety and efficiency, particularly in high-risk fields like underground construction, geotechnics, and mining. In underground construction, GenAI-powered prompts are revolutionizing practices by enabling a shift from reactive to predictive approaches, leading to advancements in design, project planning, and site management. This study explores the use of Google Gemini, a recent advancement in GenAI, for the prediction of rockburst intensity levels in underground construction. The Python programming language and the Google Gemini tool are combined with prompt engineering to generate prompts that incorporate essential variables related to rockburst. A comprehensive database of 93 documented rockburst cases is compiled. Subsequently, a systematic method is established that involves the categorization of intensity levels through data visualization and factor analysis in order to identify a reduced number of unobservable underlying factors. Furthermore, K-means clustering is utilized to identify data patterns. The gradient boosting classifier is then employed to predict the intensity levels of rockburst. The results demonstrate that GenAI and prompt engineering offers an effective approach for accurately predicting rockburst events, achieving an accuracy rate of 89 percent. Through predictive modeling with GenAI, construction engineering experts can proactively evaluate the likelihood of rockburst, allowing for improved risk management, optimized excavation strategies, and enhanced safety protocols. This approach enables the automation of complex analyses and provides a powerful tool for real-time decision-making and predictive insights, offering significant benefits to industries reliant on underground construction. However, despite the considerable potential of GenAI and prompt engineering in the construction sector, challenges related to output accuracy, the dynamic nature of projects, and the need for human oversight must be carefully addressed to ensure effective implementation.
1. Introduction
1.1. Generative AI (GenAI)
Tom Freston once stated, “Innovation is taking two things that exist and putting them together in a new way”. This perspective is consistent with the transformative role of artificial intelligence (AI) in construction engineering as AI technologies are now performing functions previously exclusive to humans, including designing, planning, and optimizing construction processes. These accomplishments contest conventional beliefs on human creativity and craftsmanship, illustrating that AI can now be integrated with human efforts to aid in the development and supervision of complex construction methods.
Generative AI (GenAI) is a type of AI that uses computational methods to create novel, significant content—such as construction layouts, design blueprints, or architectural sketches—derived from acquired data. Technologies such as Google Gemini, DALL-E 2, GPT-4, and Copilot are pioneering advancements in the construction sector by automating processes ranging from design drafting to project management. In addition to design uses, GenAI can serve as an intelligent decision support system for construction activities, including forecasting project schedules, producing cost estimates, and automating inter-team communication. Industry assessments forecast that the emergence of GenAI may elevate global GDP by 7% and potentially transform millions of occupations, including construction management and skilled trades [1]. This potential presents both promising prospects and significant obstacles, particularly in a domain where safety and accuracy are essential.
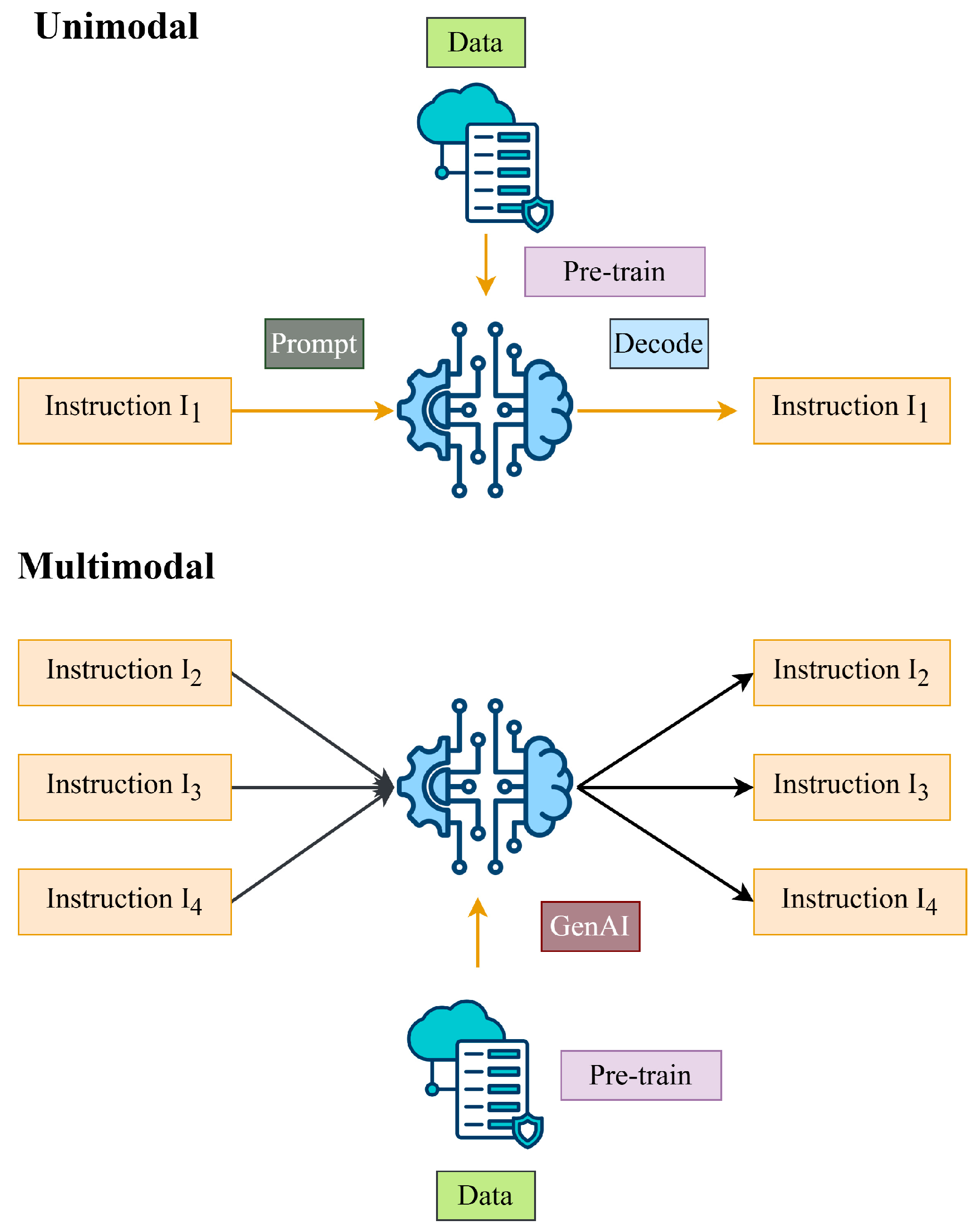
Unimodal and multimodal generative models represent different approaches in GenAI [2], principally differentiated by the type and variety of content they produce or analyze. Unimodal generative models, such as GPT for text and StyleGAN for images, focus on the production and understanding of data within a singular modality. In contrast, multimodal generative models like DALL-E and CLIP can process and integrate various data types, such as text and images, facilitating cross-modal functionalities, such as generating images from textual descriptions or comprehending relationships between visual and textual content. Figure 1 presents a comprehensive examination of the distinct methodologies employed in GenAI.
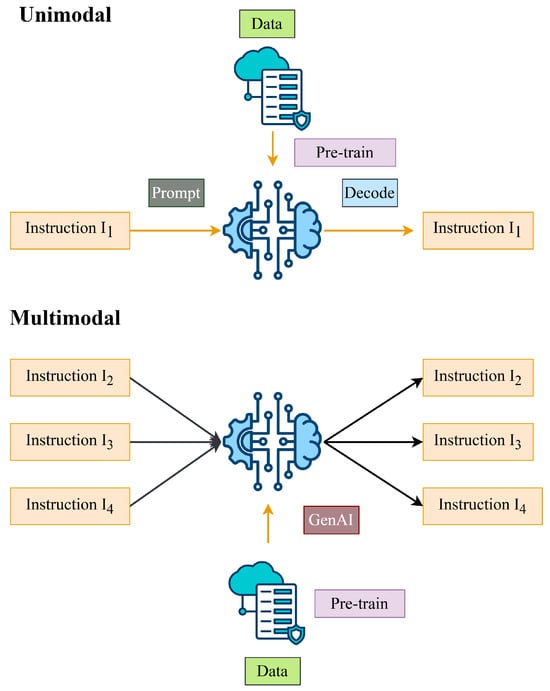
Figure 1.
An extensive overview of various approaches utilized in GenAI.
A prime example of a multimodal GenAI model is Google Gemini. Google Gemini is designed to understand and respond to a wide range of prompts, including text, code, audio, image, and video [3]. This versatility enables it to perform tasks like translating languages, writing different kinds of creative content, and even assisting in complex problem-solving. The multimodal characteristics of Google Gemini make it a potent instrument for several applications, ranging from productivity enhancement to the advancement of scientific research.
The swift advancement of tools such as Google Gemini and ChatGPT [4] exemplifies the transformative characteristics of GenAI, which not only produces superior content but also provides insight into the future of GenAI [5,6]. The dispute regarding AI’s sentience persists; nonetheless, the incorporation of machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) has enhanced AI’s functionalities in construction automation, yielding increased efficiencies in areas such as predictive maintenance and supply chain management. As GenAI becomes more integrated into construction workflows, it facilitates intelligent collaboration between human engineers and GenAI systems, optimizing project outcomes and improving decision-making [7,8]. For example, GenAI can aid construction managers by proposing effective solutions to problems, automating safety inspections, and facilitating real-time data analysis [9].
The adoption of GenAI in construction automation stands at a pivotal juncture, offering transformative potential across design, project planning, and site management. Although corporations such as Microsoft persist in advancing more efficient and proficient GenAI models [10], the scholarly discussion regarding its foundational concepts and socio-economic implications remains insufficiently explored [11,12]. The integration of GenAI in construction heralds substantial innovation, encompassing automated design, layout planning, and construction site oversight. However, difficulties such as assuring transparency, mitigating biases in prediction algorithms, and preventing misuse must be meticulously addressed to guarantee successful implementation [13,14]. Consequently, a comprehensive ethical framework is essential to direct the incorporation of GenAI into construction, guaranteeing its responsible and sustainable application in the development of underground structures. This study utilizes the capabilities of Google Gemini to transform rockburst prediction in underground construction. By capitalizing on Google Gemini’s ability to analyze and integrate diverse data sources, the research aims to develop a reliable prediction model.
GenAI has transformed the landscape in a variety of construction domains, bridging the gap between past lessons, present challenges, and future possibilities. Historically, risk assessments relied on manual data analysis and reactive approaches [15,16,17]. Today, GenAI enables predictive modeling, automates complex analyses, and supports real-time decision-making, ensuring safer and more sustainable operations. Looking forward, this technology holds the potential to transform industries by forecasting risks with unparalleled precision, enhancing resilience against unforeseen events, and driving innovative solutions for environmental sustainability in increasingly complex systems.
1.2. Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is an emerging field that entails the formulation and refinement of input inquiries, or “prompts”, to elicit specific responses from Large Language Models (LLMs). This technique is vital as it directs LLMs to produce relevant and useful outputs, allowing both developers and users to enhance model performance and discover new applications efficiently [18]. Well-structured prompts guide LLMs to generate more precise and valuable results, helping users maximize the capabilities of these models. Effective prompt engineering serves as a valuable tool, enabling the customization of outputs, exploring innovative applications, and optimizing resources [19]. It offers consistent solutions to recurring issues encountered in generating accurate responses with LLMs, supporting progress in AI research, especially within conversational AI.
In addition, prompt engineering delineates systematic methodologies for constructing prompts applicable to diverse contexts, rendering it versatile across multiple disciplines. This adaptability enables the integration of various prompt patterns to enhance outputs, promoting knowledge exchange between LLM users and developers [20]. It enables developers to comprehend model behavior more effectively, directs LLMs towards accurate and informative responses, and improves few-shot learning by integrating optimized prompts with conventional in-context learning prompts. These methodologies facilitate the development of effective chatbots, virtual assistants, and specialized tools, enhancing performance in NLP tasks [21].
With the expansion of the area, rapid engineering is expected to have an increasingly vital role in realizing the complete capabilities of LLMs. By empowering developers and users to produce precise language outputs rapidly, it is poised to become an increasingly significant resource for enhancing efficiency and advancing corporate operations across all sectors. This nascent area may potentially create new employment opportunities for individuals proficient in prompt engineering. Ongoing experimentation with enhanced prompts may facilitate the creation of user-friendly interfaces for precise control over LLM outputs, enabling the fine-tuning of generated content and broadening the scope of LLM applications in previously unattainable ways [22,23]. Prompt engineering plays a vital role in automating processes in construction, particularly in addressing challenges like rockburst. By designing targeted prompts and leveraging automation tools, engineers can streamline data analysis, predict rockburst occurrences, and implement safety measures effectively. Automation enhances efficiency by reducing manual intervention, allowing for more accurate assessments of construction sites prone to rockburst.
1.3. Google Gemini
Google Gemini, introduced on 6 December 2023, by Google DeepMind, is a fifth-generation multimodal AI tool designed to compete with leading models in the field [3,24]. The Google Gemini lineup includes three versions—Gemini Nano, Gemini Pro, and Gemini Ultra—each tailored to meet diverse user requirements and application needs.
Google Gemini’s primary advantage lies in its ability to handle and generate content across multiple formats, including text, images, audio, PDFs, and video, making it highly applicable for educational technology, where comprehensive responses are valuable [25,26]. It is particularly proficient in tasks such as text manipulation, programming computations, question interpretation, and code generation, which distinguishes it from other AI models and enhances its effectiveness in solving complex issues and producing a variety of content.
Google Gemini’s multimodal functionality, enabling it to work seamlessly with text, images, audio files, PDFs, and videos, is crucial to our research as it supports the integration of data from multiple formats for comprehensive analysis [27]. The model’s capabilities in text analysis, programming assistance, logical reasoning, and code generation further enhance its suitability for organizing queries by complexity and hierarchy. By evaluating its performance across simple to complex environments, a broad understanding of its strengths and limitations were gained, making Google Gemini an essential model [28].
The integration of GenAI and prompt engineering presents transformative possibilities in construction engineering, where precision and adaptability are paramount. These technologies offer powerful tools to analyze structural behavior, assess risks, and enhance predictive capabilities, enabling more effective responses to complex geotechnical challenges. The combination of GenAI with prompt engineering offers significant potential for improving rockburst assessment using advanced predictive models. This method is proficient at handling large datasets and intricate geotechnical situations, thereby providing more reliable insights.
This study aims to enhance the comprehension of rockburst prediction in underground structures by investigating the contributions of GenAI and prompt engineering techniques. It utilizes Python programming, integrated within the Google Gemini platform, to create prompts that incorporate significant variables affecting rockburst. This methodology seeks to enhance the application of GenAI in construction engineering, offering more accurate and efficient solutions for managing rockburst in underground engineering structures.
2. Recent Developments in Rockburst Assessment: Contemporary Methods and Related Challenges
Contemporary societies rely significantly on intricate civil infrastructures that are susceptible to numerous natural disasters, environmental influences, and excessive operational pressures [29,30,31]. Tunneling operations have historically faced technical challenges, which become increasingly significant as tunnels are constructed at greater depths [32]. The instability of rock formations and the potential for rockburst present significant risks to personnel and equipment [33]. Advanced solutions and best practices are essential for mitigating these risks and reducing the severity of rockburst. Deep tunnels exhibit a high vulnerability to rockburst, potentially leading to prolonged operational disruptions [34,35,36]. It is imperative to enhance the methods of risk assessment and to further comprehend the factors that contribute to the occurrence of rockburst. This research examines the applicability of GenAI and prompt engineering methods in tackling these issues.
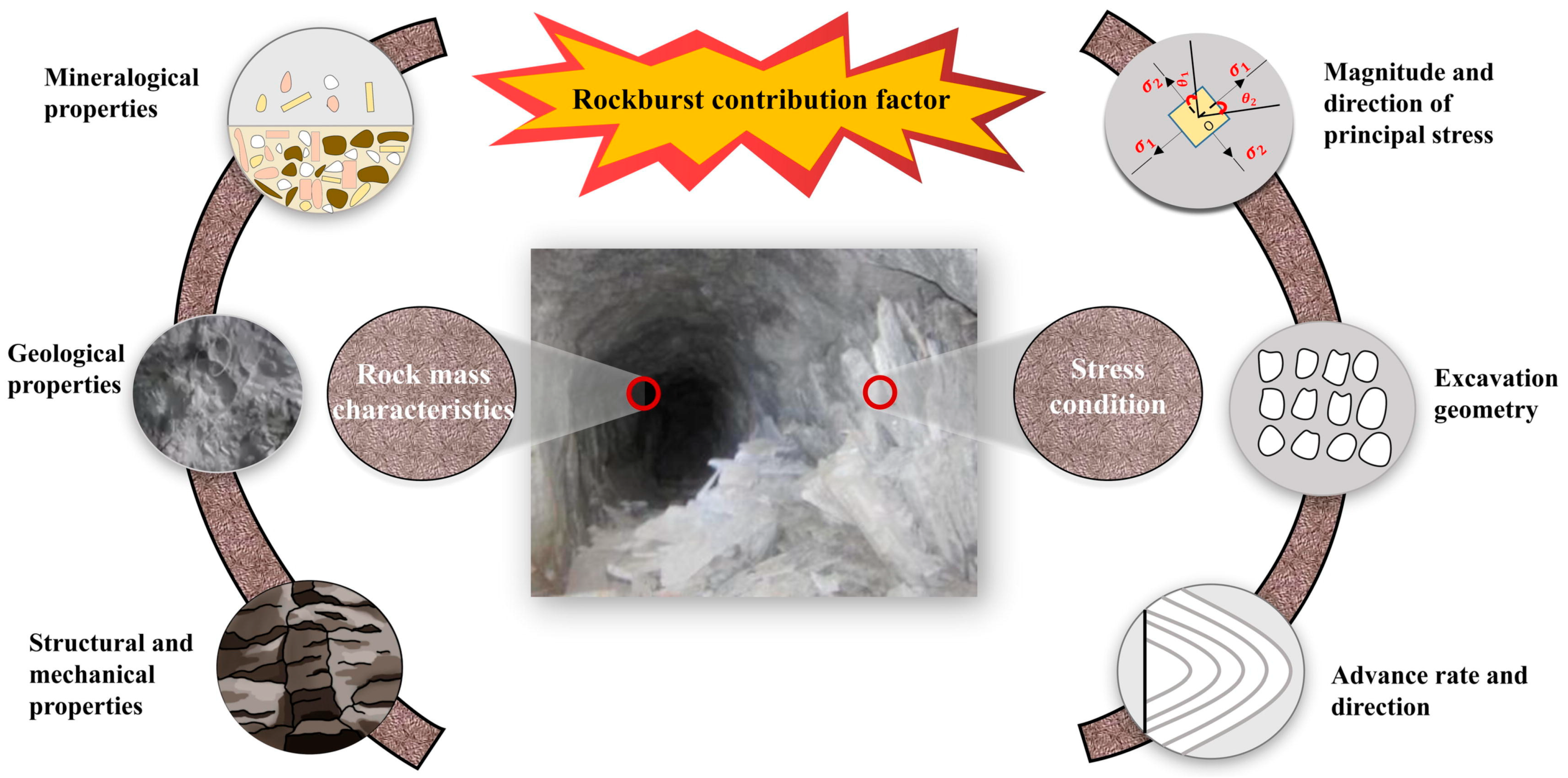
Predicting rockburst is difficult due to the intricacy of their occurrence. In order to produce a dependable tool that can accurately predict this event and consider all of the factors that are influencing it, a significant amount of effort must be devoted [37]. For the development of a predictive tool that is effective, it is essential to have a thorough comprehension of the components that contribute to rockburst. The incidence of rockburst is affected by various factors, some of which are extensively documented by several researchers. In [31,38,39] four principal categories has delineated that contain the most significant factors: mining activities, geology, seismic events, and geotechnical characteristics. Multiple researchers [40,41,42,43] have investigated the influence of these factors on the rockburst phenomenon. Figure 2 presents a schematic representation of factors contributing to rockburst events, organized into two primary categories: rock mass characteristics and stress conditions.

Figure 2.
Key factors influencing rockburst occurrence (Zhou et al., 2024) [44].
The effects of dynamic disturbances, such as earthquakes, vibrations, explosions, and stress impacts from nearby rockburst, may exacerbate the damage caused by rockburst [45]. In addition, the excavation of underground structures can lead to rockburst situations because it changes the stress field and the stiffness of the surrounding material [46]. The geotechnical properties of rocks, including their strength and brittleness, cause strain energy to build up and then be released; rocks that are harder and more brittle are more likely to split or fail. Along with discontinuities and in situ stresses, other crucial geotechnical elements are involved in the occurrence of rockburst [47]. Because they change the stress distribution in the area and impact the loading system’s stiffness, faults and shears can make rockburst severe [48].
Rockburst is a common occurrence in underground excavations near geological features like dikes, faults, and wide fractures [49]. Rockburst is more likely to occur if there are weak planes close to these structures. Jiang et al. [50] examined natural rockburst and highlighted the significant role of weak planes. This phenomenon was studied in deep tunnels by Zhou et al. [51] with the use of laboratory shear testing. This parameter affects the probability of rockburst, according to Manouchehrian and Cai. [37], who used numerical simulations to investigate structural plane features. Applying micro-seismic monitoring, Feng et al [52] investigated how geological characteristics impact rockburst events, finding that discontinuities can change micro-seismic patterns. The existence of structural planes significantly increases the likelihood and severity of rockburst [53]. However, it has been observed that the frequency and intensity level of subsequent occurrences frequently decrease after an initial rockburst. Su et al. [54] conducted rockburst testing using real triaxial equipment and video monitoring, revealing that the spatial location of structural plane dips has a substantial influence on the rockburst phenomenon and should be carefully considered.
Physical, numerical, or empirical models are frequently used to predict rockburst in deep tunnels, but this process is time-consuming and costly. Consequently, novel approaches and resources are highly sought after in order to overcome these limitations. There has been a rise in the use of ML and DL techniques in several fields, such as rock mechanics, soil mechanics, geotechnical engineering, and tunneling [55,56,57,58]. ML is useful for making accurate predictions about key project features throughout the planning, development, and completion stages. The ability of ML techniques to represent nonlinear data interactions is a major strength that allows for the uncovering of intricate patterns and correlations that would otherwise go unnoticed by more straightforward analytical or empirical approaches. While ML does require a lot of processing power during training, it makes rapid and accurate predictions in real-time applications once trained. In complex scenarios, traditional approaches may not be as accurate or reliable as ML models, despite the fact that they are more rapid and require less computing capacity for initial predictions. Rockburst in underground constructions, including tunnels and mines, have been predicted through the use of ML in numerous studies [39,59,60]. GenAI is a particular subfield of AI that concentrates on the development of new content or simulations from existing data. AI encompasses a broad spectrum of techniques for data analysis and decision-making. Traditional AI methods employ historical data and pattern recognition to predict events in the context of rockburst prediction, utilizing established models. In contrast, GenAI has the ability to create innovative predictive scenarios, thereby providing a more dynamic and adaptive approach to assessing and mitigating the risks associated with rockburst. This distinction emphasizes the potential of GenAI to improve predictive accuracy and offer more profound insights in comparison to traditional AI methodologies. This study is entirely devoted to the prediction of rockburst through the application of GenAI and prompt engineering in underground construction. The authors’ previous publication [61] is recommended for a comparative analysis of the most recent results from AI models with existing rockburst prediction methods.
3. Methodology
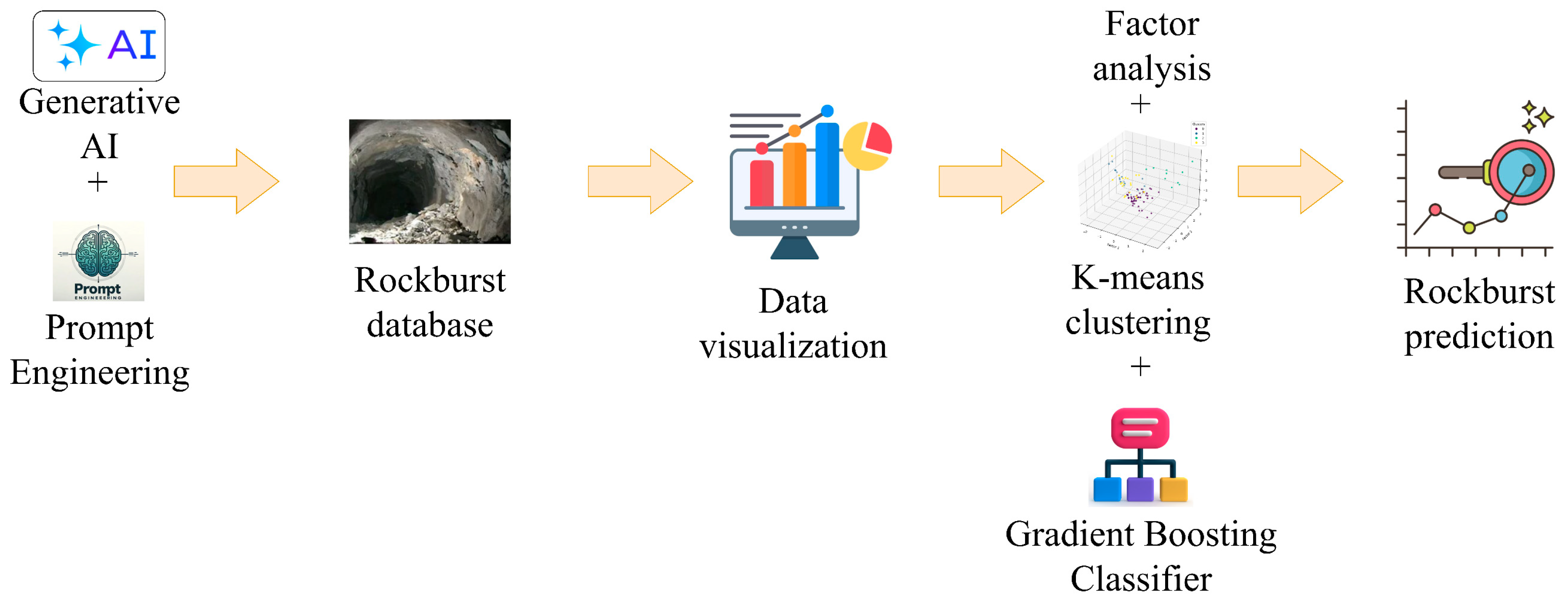
This research focuses on utilizing GenAI and prompt engineering to predict rockburst intensity level within a Python programming language, leveraging Google Gemini platform. The study compiled a comprehensive database consisting of 93 documented rockburst cases. The main steps of the research process are outlined as follows:
- Rockburst intensity levels were categorized into four distinct classes;
- Data visualization methods were employed to analyze the impact of input variables on rockburst intensity levels;
- Factor analysis (FA) was conducted to identify the most critical variables influencing rockburst;
- K-means clustering was utilized to segment the dataset into four clusters, enabling the identification of patterns within the data;
- The gradient boosting classifier was applied to predict rockburst intensity levels;
- Several performance criteria—including the confusion matrix, precision, recall, F1-score, and accuracy—were used to assess the gradient boosting classifier’s performance. Figure 3 provides a detailed flowchart, outlining the sequential steps and methodology employed throughout the study.
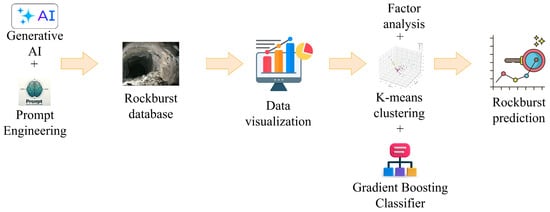 Figure 3. A detailed flowchart illustrating the methodology employed in this study.
Figure 3. A detailed flowchart illustrating the methodology employed in this study.
3.1. Data Acquisition
To construct the database for this study, a total of 93 short-term rockburst events, each characterized by six key variables, were gathered from the microseismic monitoring data of the Jinping-II hydropower project in China [62]. These variables include: Cumulative Number of Events (Z1) per unit, Event Rate (Z2) in events per day, the logarithm of the Cumulative Release Energy (Z3) in joules (J), the logarithm of the Energy Rate (Z4) in joules per day (J/day), the logarithm of the Cumulative Apparent Volume (Z5) in cubic meters (m3), and the logarithm of the Apparent Volume Rate (Z6) in cubic meters per day (m3/day). The dataset used in this analysis is sourced from [63], which is based on data provided by [62]. The comprehensive description of the Jinping-2 Hydropower Project and the preprocessing methods can be found in the authors’ previous publication [61].
The rockburst intensity levels were categorized into four categories: Level 0, representing no rockburst, where the rock specimen exhibits no significant fracture on the free face; Level 1, indicating a slight rockburst, characterized by minor displacement of fragments and limited kinetic energy release; Level 2, describing a moderate rockburst, where block spalling occurs in the rock mass along the tunnel and roadway walls; and Level 3, corresponding to a violent rockburst, marked by massive spalling of the rock mass and significant deformation of the surrounding rock.
3.2. Factor Analysis
Factor analysis (FA) is a widely used statistical method in data preprocessing aimed at reducing dimensionality. It is a complex technique that reduces a large volume of data into a smaller set of factors by grouping related parameters into meaningful constructs [64]. In FA, factors represent a range of variables whose cross-correlation helps minimize the overall variance. The rotation process in FA assumes that each factor could explain the relationship between different sets of variables [65].
Principal Component Analysis (PCA), often employed in FA, transforms a set of correlated input variables into a set of uncorrelated random variables. PCA reconfigures the data by identifying the principal component as the direction of maximum variance, with variables being represented along the new axes. This transformation may lead to some loss of detailed information regarding the relationships between the original variables [66]. The rotation procedure in FA helps to clarify the underlying meaning of the principal components, capturing most of the total variance in the dataset. During this process, the data are rotated counterclockwise, with the first axis representing the largest variance, and subsequent axes reflecting the remaining variance. The rotation can sometimes result in a reduction in data closest to the origin, depending on the configuration of the dataset.
3.3. K-Means Clustering
Cluster analysis is a quantitative method used to categorize data into groups with similar characteristics. It organizes observations into homogeneous subsets or divides large datasets into smaller, meaningful groups. Among the various techniques available, K-means clustering is a popular approach, offering flexibility to select a specific number of clusters to best represent the data [67]. This method evaluates and separates data into distinct groups by assessing the diversity in observed variables, which define the characteristics of each cluster [68]. K-means clustering is widely used by researchers to identify patterns and detect anomalies across datasets.
Determining the optimal number of clusters, k, is a critical step in the clustering process [69], as the final clusters rely on the initial selection of cluster centers. This non-hierarchical technique groups data based on distance, creating specialized clusters by considering quantitative variables. However, it does not account for qualitative data elements. The performance of the K-means algorithm depends significantly on the quality and distribution of the data, making it essential for researchers to ensure well-prepared datasets for accurate clustering outcomes. The detailed description of the K-means clustering algorithm can be found in the authors’ previous publications [29,70].
3.4. Gradient Boosting Classifier
The gradient boosting classifieris a ML technique designed to enhance predictive performance by sequentially combining weak classifiers—models that perform slightly better than random chance—into a single, robust framework [71]. Unlike bagging methods, where base models are trained independently, boosting methods like gradient boosting classifierconstruct models in a sequential manner, focusing on correcting the errors made by earlier models. This iterative process prioritizes hard-to-classify instances, improving the overall accuracy and robustness of the classifier.
The boosting mechanism adapts by refining the predictions of weaker models and iteratively creating stronger learners. The concept was introduced through [72], addressing Kearns’ question on whether a combination of weak learners could create a strong learner. Weak learners are algorithms that marginally outperform random guessing, while strong learners offer significantly better predictive power. Schapire’s [72] findings showed that combining several weak learners effectively results in a powerful, cohesive classification model capable of addressing complex problems with higher accuracy. The detailed mathematical description for the gradient boosting classifier can be found in the author’s previous publication [73].
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Problem-Solving Strategy Leveraging GenAI for Automated Code Creation
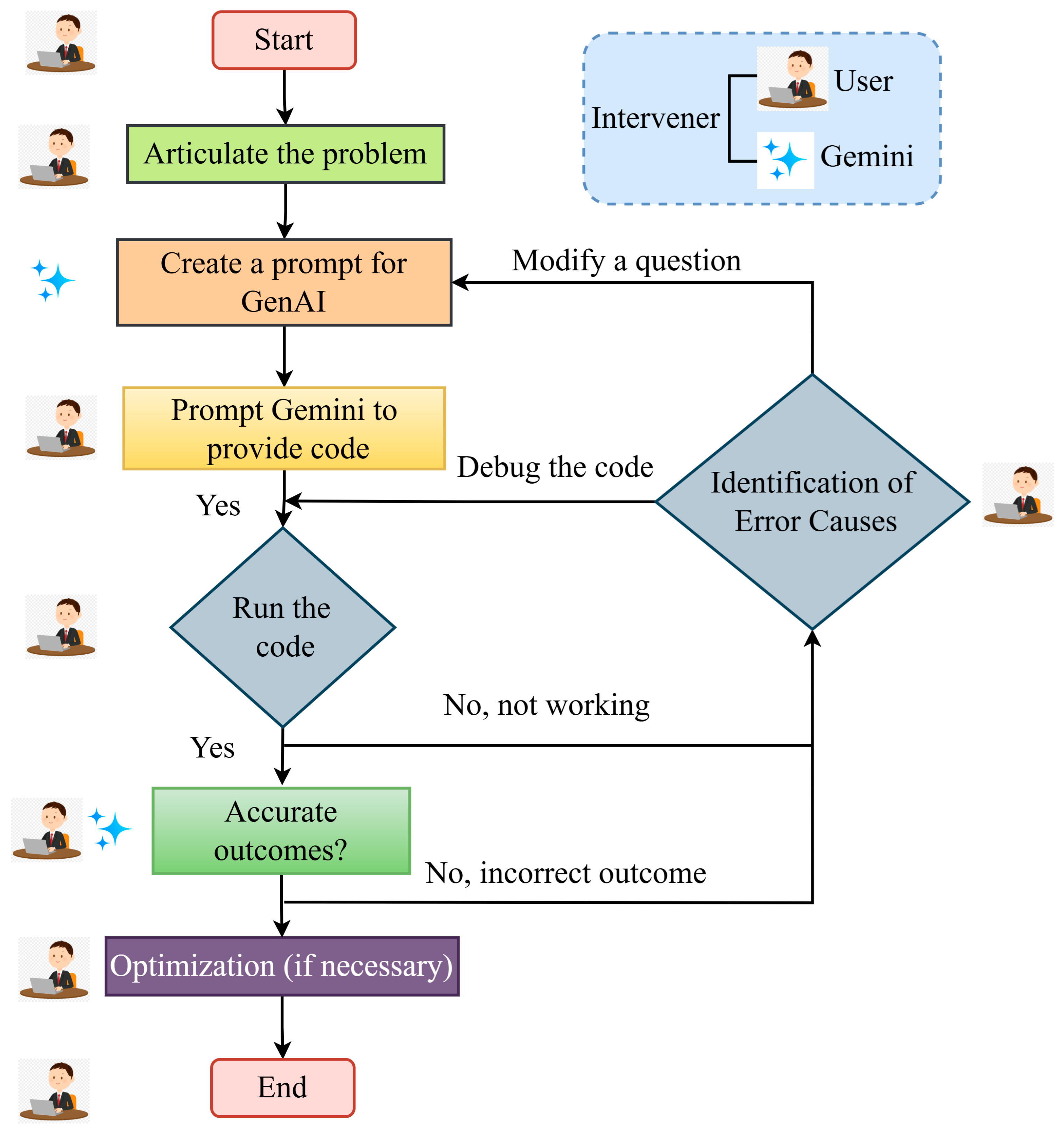
Figure 4 illustrates the systematic workflow adopted to address the problem using GenAI for code generation. The procedure initiates with the formulation of a narrative prompt, intentionally avoiding complex mathematical equations or formulations. This approach allows Google Gemini model to autonomously interpret the problem and generate the corresponding Python code. The code, once generated, is executed, and the resulting outputs are subjected to a rigorous validation process by the users. During this validation phase, any discrepancies or issues identified in the initial output are addressed by the users, who then issue iterative prompts to further refine the code. This process of providing feedback and optimizing the prompts continues, with each iteration aiming to correct any errors and enhance the precision of the generated code.
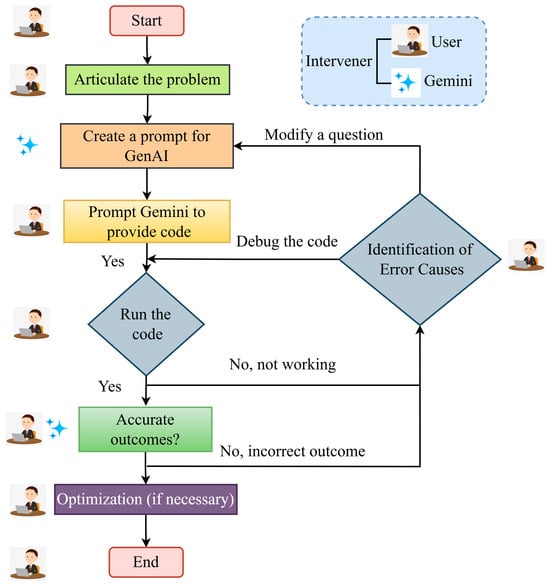
Figure 4.
The structured workflow developed to address the problem, utilizing GenAI for code generation.
Through repeated refinement and adjustment of the prompts, the GenAI model is trained to produce outputs that align more closely with the desired results. This iterative loop of prompt optimization and code validation ensures that the final output is both accurate and robust, meeting the predefined objectives and criteria set by the users. The continuous cycle of refinement facilitates the development of error-free code, with each prompt improving upon the last, ultimately ensuring that the output generated by Google Gemini meets the expected standards of performance and accuracy.
4.2. User Prompts, Responses by Google Gemini, and Generated Results
This section provides a detailed explanation of the process for generating Python code to perform rockburst analysis using GenAI. The procedure begins with loading the relevant dataset into Python, where integration with Google Gemini is used to facilitate the generation of the code. It is important to emphasize that while the user prompt clearly instructs Google Gemini to generate code, it refrains from specifying the exact mathematical formulas or underlying principles behind the chosen method. As a result, Google Gemini autonomously interprets the task, applying its GenAI-driven capabilities to create the necessary code.
The Python code produced by Google Gemini is organized in a structured manner, ensuring readability and coherence. Each section of the code corresponds to specific user prompts, and these sections are presented here in distinct indices to highlight the process of code generation. This ensures a clear understanding of how the prompts align with the AI-generated outputs. The following subsections will elaborate on the individual components of the Python code, providing insights into the AI’s ability to autonomously generate functional code for complex computational tasks, such as rockburst assessment, while maintaining clarity and precision throughout the workflow.
Prompt 1. I have provided the ’Rockburst data.xlsx’ file in the directory. Could you kindly load it and show me the first five rows of the dataset?
Responses by Google Gemini: In response to Prompt 1, Google Gemini first used the panda’s library to import the Excel file into a DataFrame (see Index 1). The df.head() function is then applied, which by default shows the first five rows of the dataset (see Table 1). This method allows for a quick overview of the dataset’s structure and initial content.

Table 1.
The initial five rows from the rockburst database.
Index 1. Load the Excel file into a pandas DataFrame and display the first 5 rows: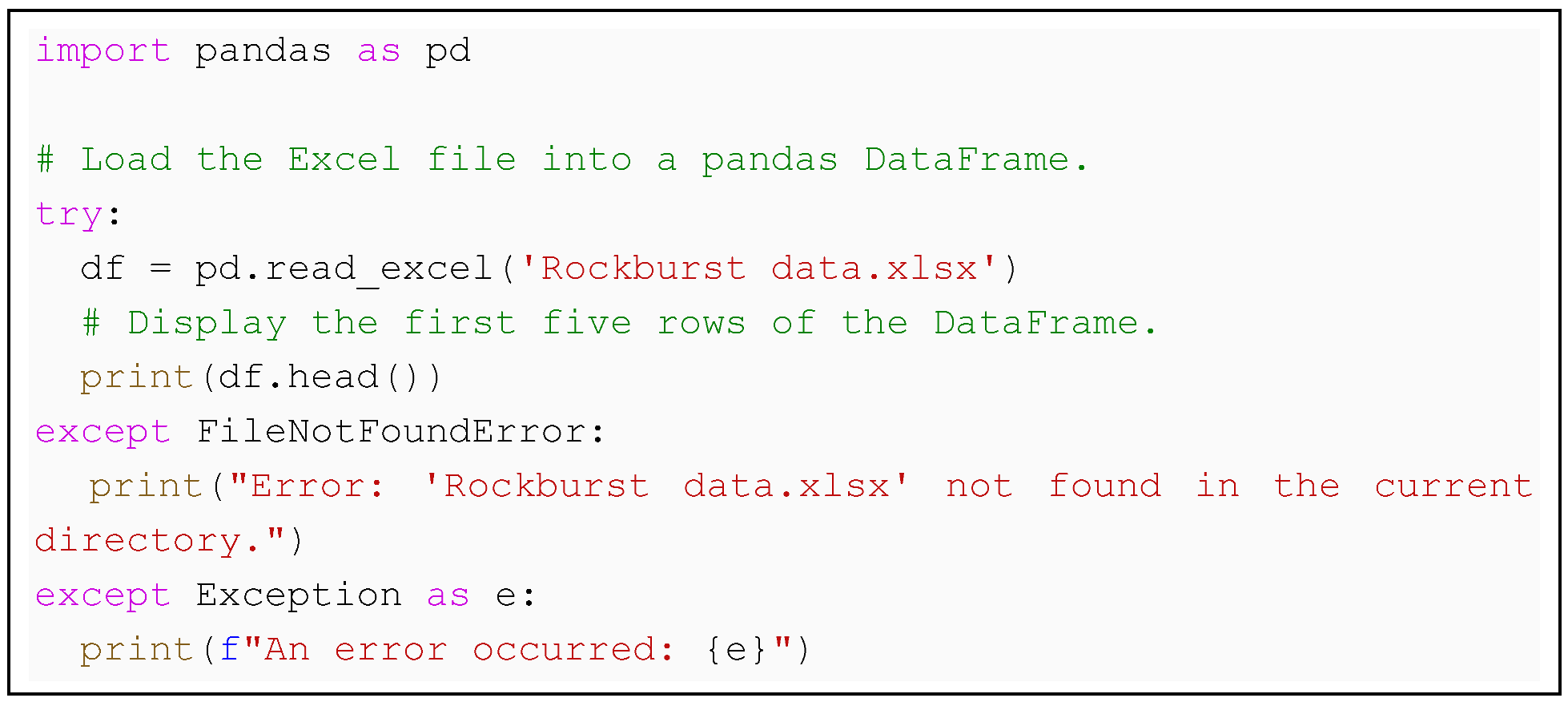

Prompt 2. Please provide the statistical summary of the dataset loaded earlier.
Responses by Google Gemini: To get a statistical summary of the rockburst dataset, the df.describe() function has been used from the pandas library as depicted in Index 2. This function provides key statistical measures for each numerical column in the DataFrame, which are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
The statistical parameter of the rockburst dataset.
Index 2. Compute the statistical summary data for the rockburst database.

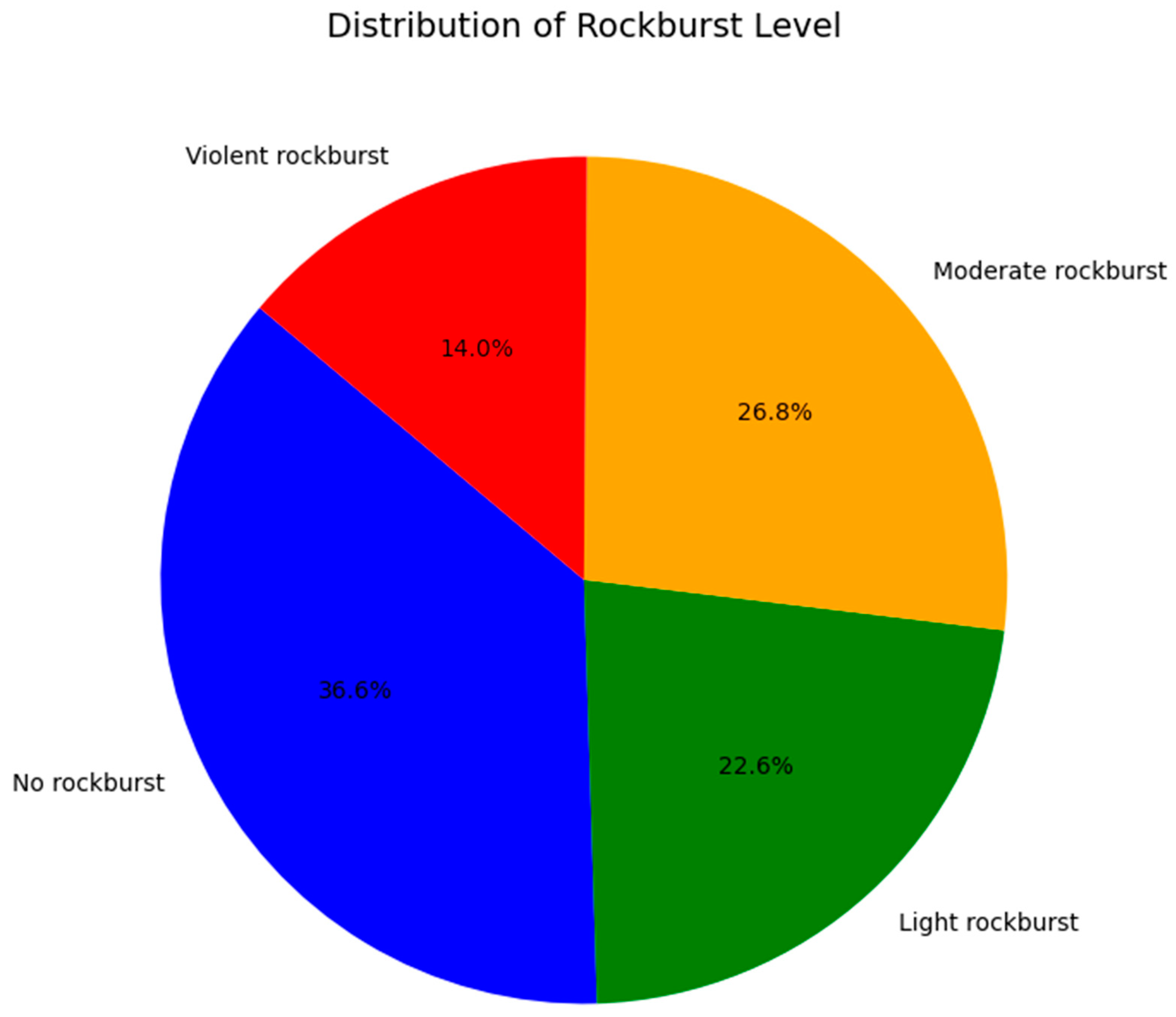
Prompt 3. Please create a pie chart to analyze the distribution of intensity levels in the dataset. Replace the: “0” with “No rockburst”, “1” with “Light rockburst”, “2” with “Moderate rockburst”, and “3” with “Violent rockburst” in the pie chart.
Responses by Google Gemini: To create a pie chart analyzing the distribution of rockburst intensity levels, a data visualization library like Matplotlib has been utilized, as shown in Index 3. This code creates a pie chart where each slice represents a rockburst level, and the size of the slice corresponds to the proportion of instances in that level (see Figure 5). The labels on the slices have been listed as “No Rockburst”, “Light Rockburst”, “Moderate Rockburst”, and “Violent Rockburst”.
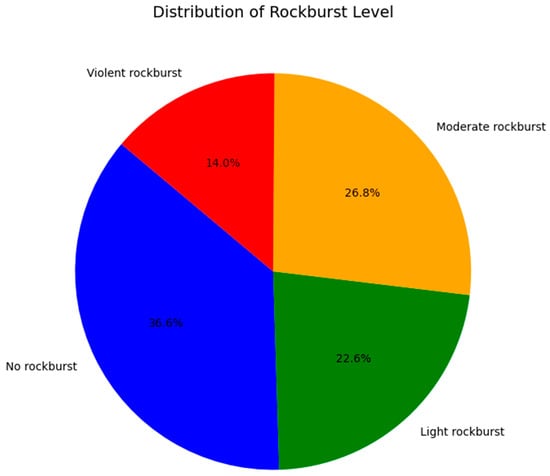
Figure 5.
Correlation matrix of the rockburst database.
Index 3. Distribution of rockburst intensity level.

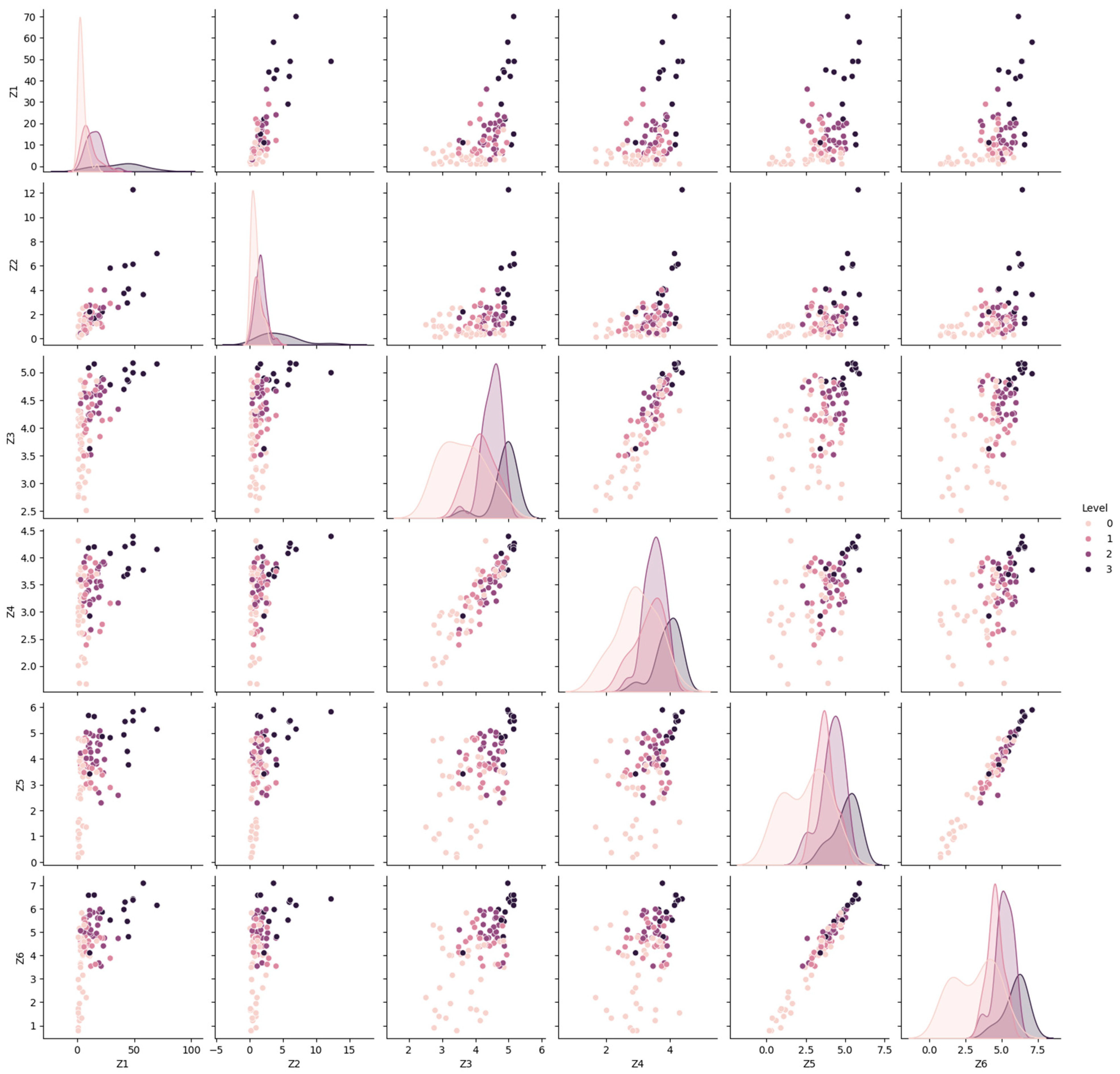
Prompt 4. Please plot the pairwise relationships between the Z1, Z2, Z3, Z4, Z5, and Z6 and “Level”.
Responses by Google Gemini: To visualize the pairwise relationships between the Z1, Z2, Z3, Z4, Z5, Z6, and “Level” columns, the scatter plots have been used (see Index 4). This code creates a matrix of scatter plots, where each plot shows the relationship between two variables. The diagonal line represents the distribution plots for the six parameters, while the non-diagonal line displays the correlation scatter plots between the parameters (see Figure 6). The differences in parameter distributions across the four rockburst intensity levels were minimal, and no significant relationships were identified between the attributes. As a result, it was difficult to classify the rockburst intensity level using a single attribute. To improve accuracy, it would be more effective to consider the combined influence of all parameters.
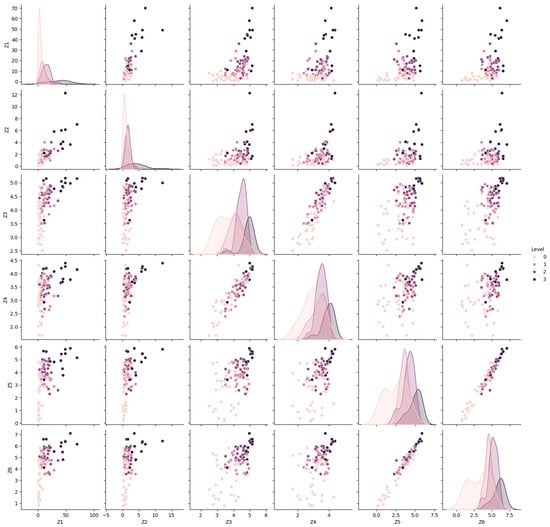
Figure 6.
A pairplot to explore relationships in the rockburst data.
Index 4. Pairwise plot of the rockburst dataset.

Prompt 5. Please divide the dataset into features (X) and target (y), with the target being the last column of the data.
Responses by Google Gemini: The code shown in Index 5 was generated in response to Prompt 5. The features (X) are extracted from all columns except the last one, which is assigned as the target (y).
Index 5. Partitioning the data into independent and dependent variables.

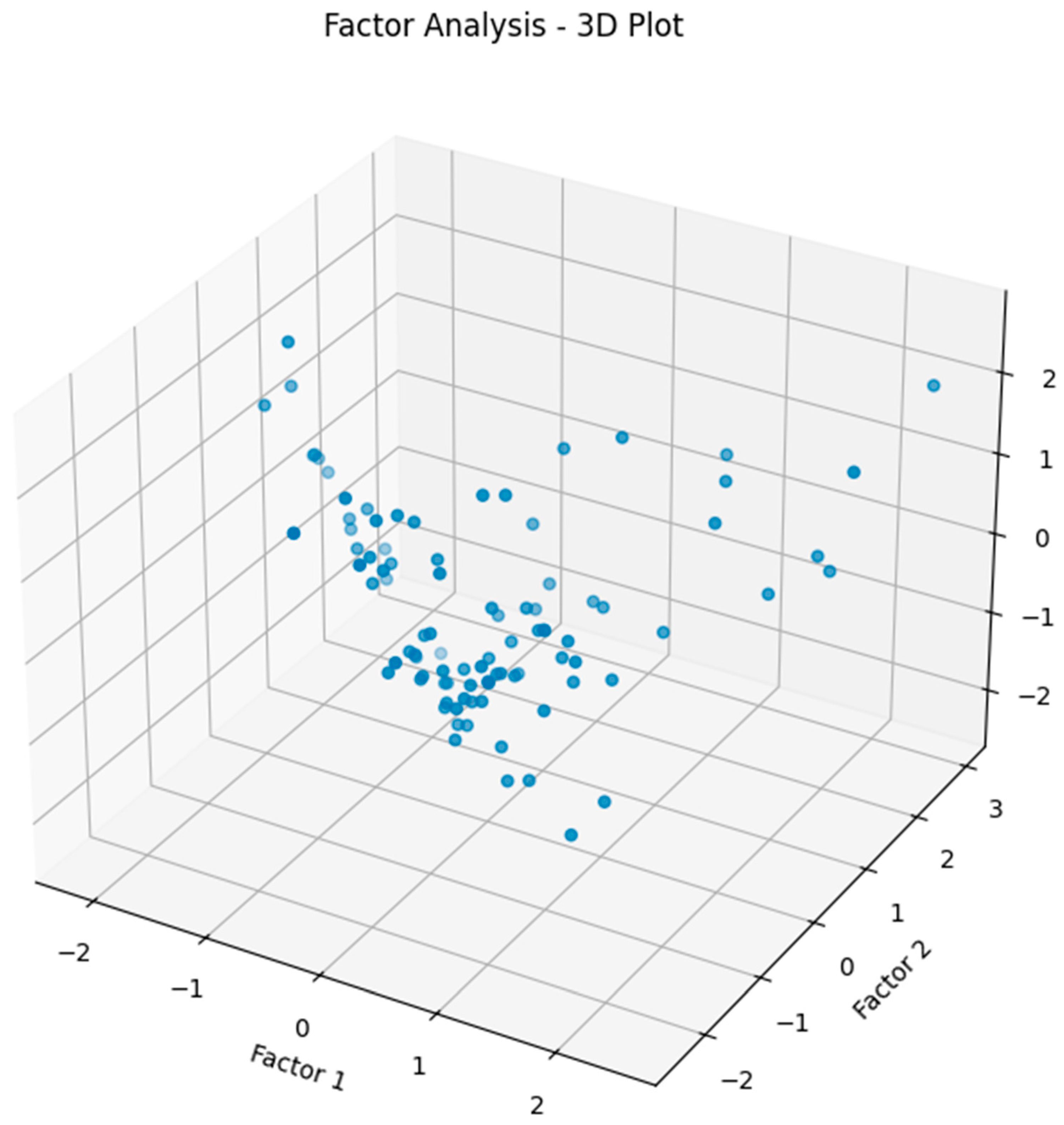
Prompt 6. Please implement the factor analysis algorithm for dimensionality reduction on the X data and plot the results in 3D.
Responses by Google Gemini: FA was implemented on the rockburst dataset to reduce the dimensionality from high to low resolution, as shown in Index 6. The reduced data is then visualized in a 3D plot (see Figure 7).
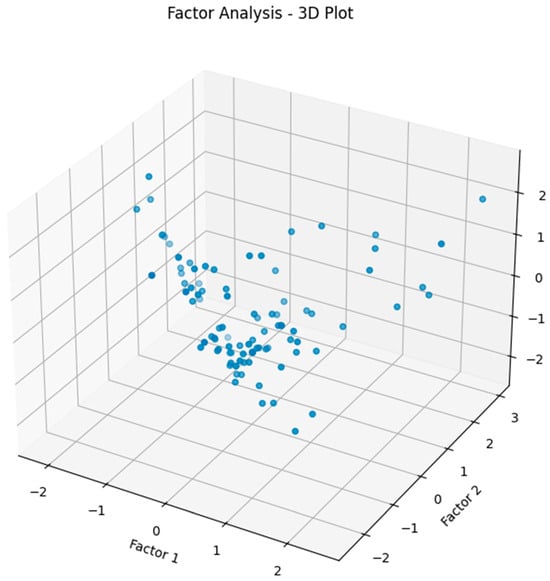
Figure 7.
A three-dimensional plot using the FA-processed rockburst data.
Index 6. Perform factor analysis on the given rockburst database.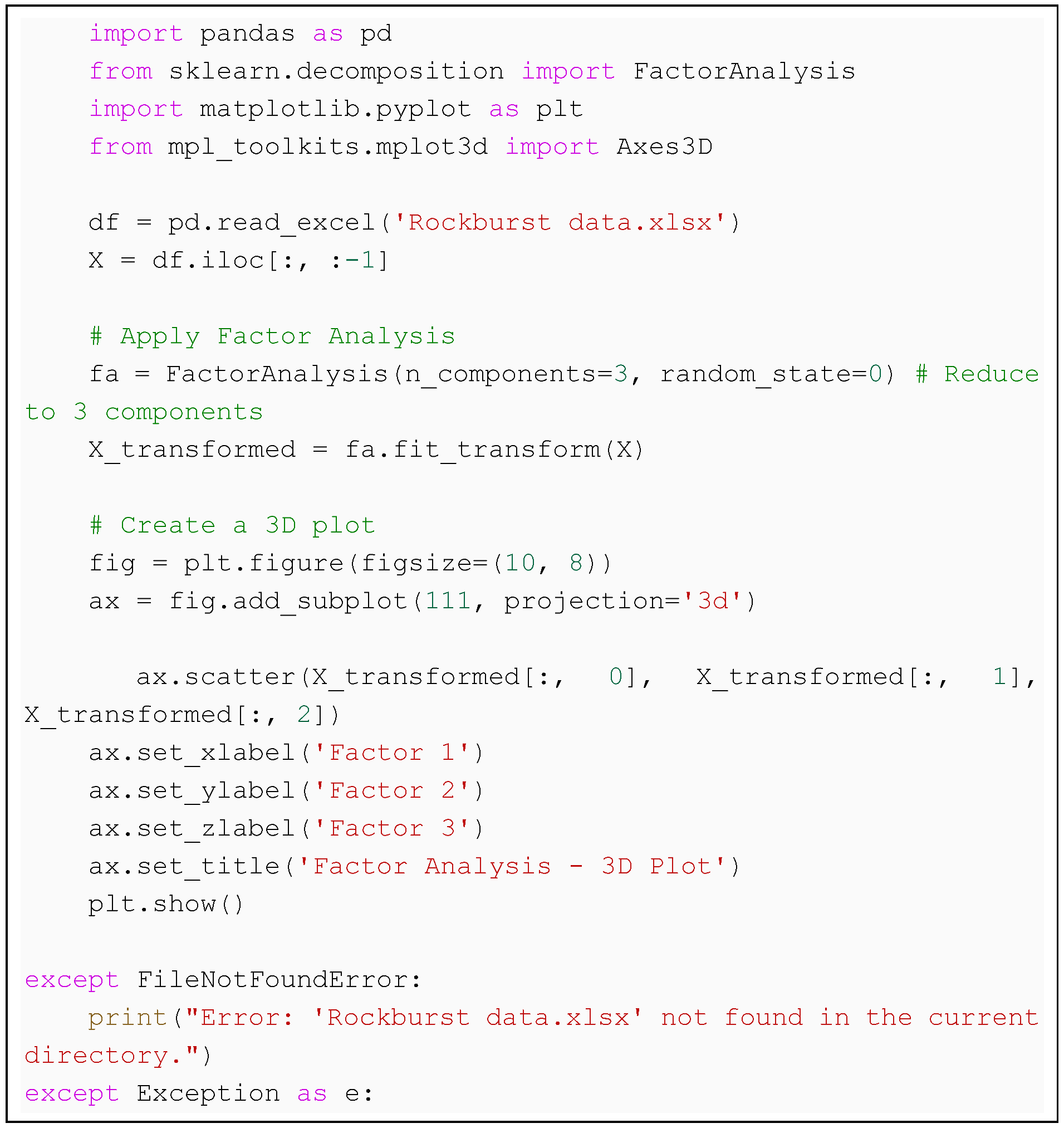

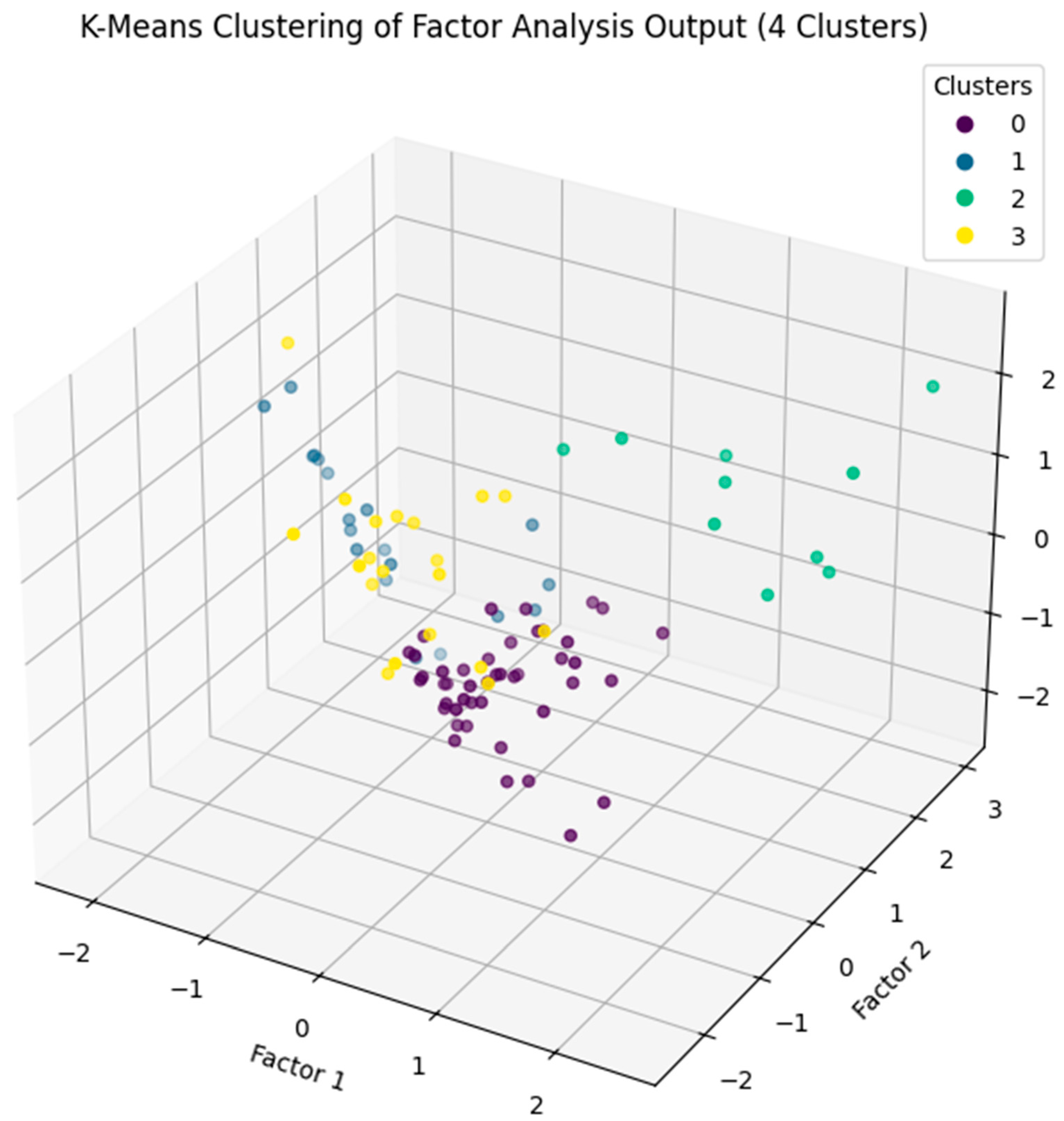
Prompt 7: Please implement the K-means clustering with 4 clusters on the factor analysis output data.
Responses by Google Gemini: In response to Prompt 7, the FA-acquired data is grouped into four clusters using the K-means clustering, based on the four distinct rockburst intensity levels (see Index 7). The resulting clusters are then visualized in a 3D plot, as depicted in Figure 8.
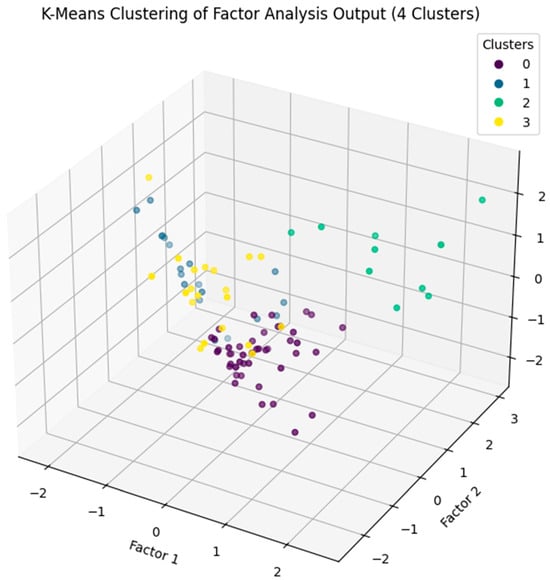
Figure 8.
A visualization of FA results combined with K-Means clustering in rockburst data.
Index 7. Implement K-means clustering on data acquired from FA.

Prompt 8. Please split the X_fa and labels data into training and testing sets using an 80:20 ratio.
Responses by Google Gemini: The FA data, along with the labels obtained from the K-Means clustering, are divided into training and testing datasets to prepare the data for the gradient boosting classifier. Eighty percent of the data is allocated for training, while the remaining twenty percent is designated for testing (see Index 8).
Index 8. Partition the rockburst data into training and testing sets.

Prompt 9. Please apply and fit the gradient boosting classifier algorithm on the X_fa and labels on the training data, and evaluate the results on the X_fa testing and labels data using a classification report.
Responses by Google Gemini: The gradient boosting classifier algorithm is employed to predict the four distinct intensity levels of rockburst in the dataset. To evaluate the performance of the classifier, various performance metrics such as the confusion matrix, precision, recall, F1-score, and accuracy were utilized, as referenced in our previous studies [29,70]. This evaluation method is also applied in this study (see Index 9). Table 3 presents the classification report for the four different rockburst intensity levels: “No Rockburst”, “Light Rockburst”, “Moderate Rockburst”, and “Violent Rockburst”. The results indicate that the integration of GenAI and prompt engineering offers a powerful approach for accurately predicting rockburst events, achieving an impressive accuracy rate of 89%.

Table 3.
Classification report for predicted rockburst intensity levels.
Index 9. Prediction of rockburst intensity level by gradient boosting classifier.

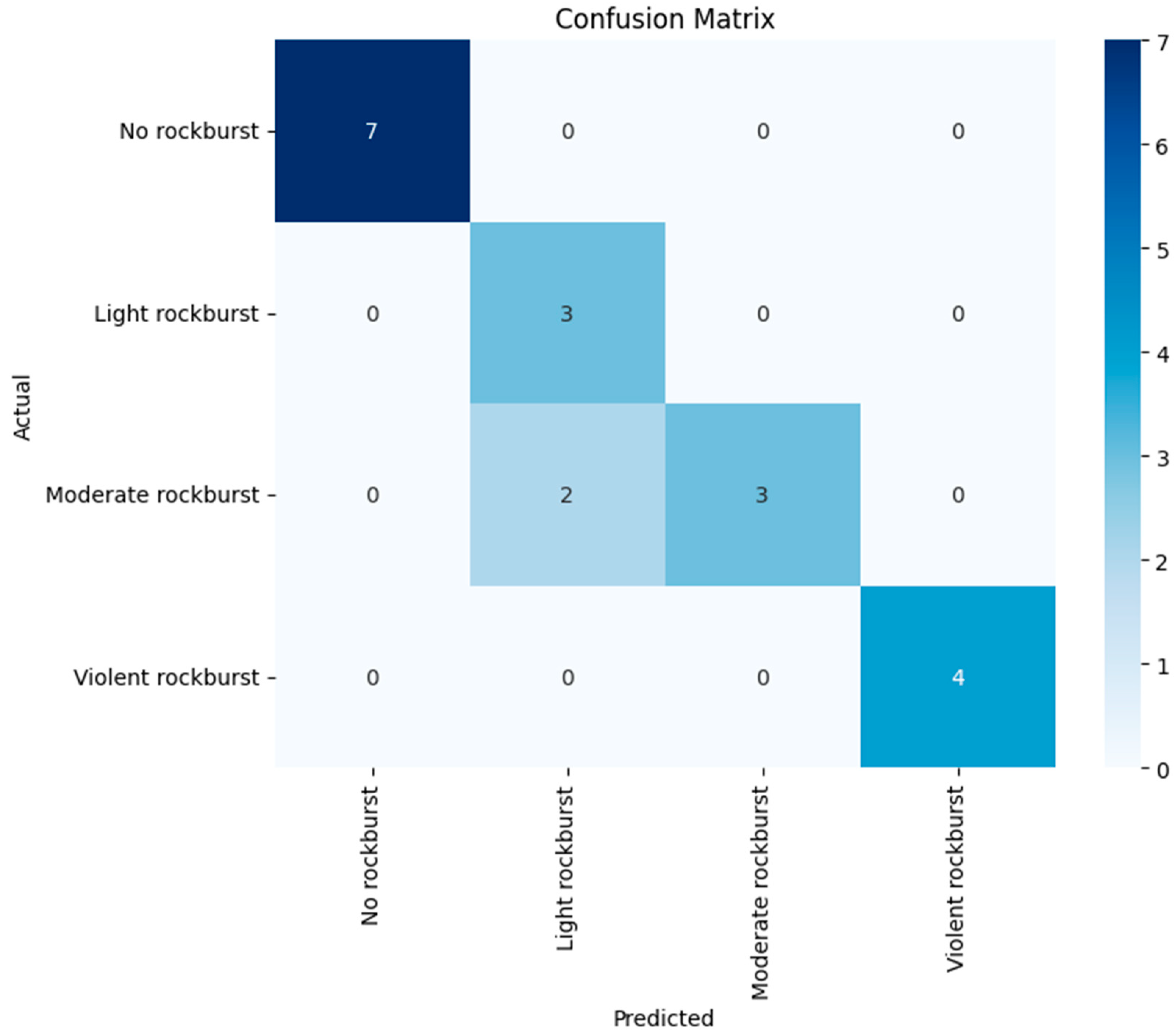
Prompt 10. Please plot a confusion matrix. Replace the “0” with “No rockburst”, “1” with “Light rockburst”, “2” with “Moderate rockburst”, and “3” with “Violent rockburst”.
Responses by Google Gemini: A confusion matrix is generated to assess the performance of the proposed algorithm, as shown in Index 10. Figure 9 displays the confusion matrix for the rockburst dataset, with the labels “0” replaced by “No rockburst”, “1” by “Light rockburst”, “2” by “Moderate rockburst”, and “3” by “Violent rockburst”.
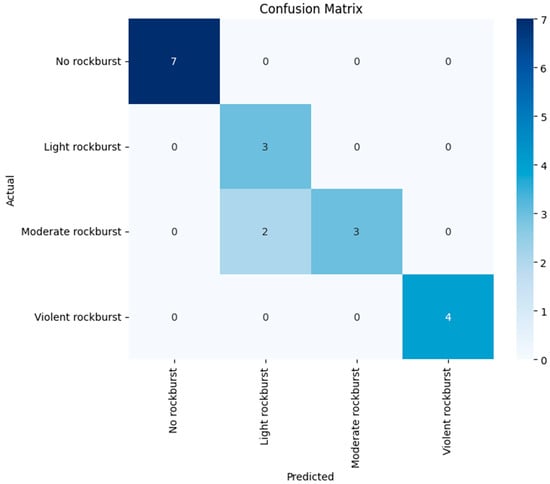
Figure 9.
Confusion matrix to assess predictions in the rockburst dataset.
Index 10. Generate a confusion matrix to interpret the rockburst database.

Hence, it has been demonstrated that GenAI and prompt engineering have the potential to transform the predictive modeling of rockburst in underground construction. With the use of cutting-edge GenAI capabilities, engineers can now produce real-time, more accurate predictive models that offer vital information about probable rockburst incidents. This novel model improves safety and efficiency in underground construction while initiating a new phase of proactive risk management. By utilizing optimal prompts and GenAI insights, the sector may transition from reactive to predictive techniques, thereby enhancing safety and sustainability in construction processes.
4.3. Obstacles in the Strategic Execution of GenAI and Prompt Engineering
GenAI and prompt engineering offer significant potential in construction industry, but they come with notable limitations that must be carefully addressed. One key challenge is the accuracy and reliability of outputs. Construction projects demand precise and context-specific solutions, especially in safety-critical areas like structural design or rockburst risk assessment. However, GenAI models may produce generalized or inaccurate results due to their dependence on input prompts and training data, which often lack the domain-specific depth required for complex construction tasks. This reliance on high-quality data is another limitation, as construction data are frequently incomplete or inconsistent, impacting the effectiveness of GenAI-driven insights.
Another significant limitation lies in the inability of GenAI to fully grasp the dynamic and site-specific nature of construction projects. Factors such as geological variability, local regulations, and project constraints require a nuanced understanding, which AI cannot always provide. Furthermore, while GenAI can generate outputs, it struggles with creating detailed visualizations designs necessary for implementation. Integration with existing construction tools and workflows can also be challenging, requiring substantial customization and expertise.
Moreover, GenAI and prompt engineering in construction still require human oversight. Professionals must validate and interpret GenAI outputs to ensure feasibility, compliance, and safety. Ethical concerns, such as over-reliance on unverified GenAI decisions, further underscore the need for cautious and responsible adoption of these technologies in construction practices.
5. Conclusions
The rapid advancement of automation in construction, particularly through the use of GenAI and prompt engineering, is revolutionizing the way high-risk areas such as underground construction, geotechnical, and mining fields are managed. These technologies play an essential role in enhancing both safety and operational efficiency. The integration of GenAI has enabled a shift from reactive approaches, which primarily focus on responding to issues as they arise, to more proactive and predictive methodologies that anticipate potential challenges and optimize workflows in advance. In particular, the application of Google’ Gemini in underground construction represents a significant leap forward in predictive modeling, enabling the prediction of complex phenomena such as rockburst, which have long been difficult to predict and manage effectively. By automating complex analyses, the integration of rapid engineering and GenAI enhances the theoretical framework, case studies, and experimental research. This method has the potential to offer substantial benefits to industries that depend on underground construction facilities.
This study presents a comprehensive database of 93 documented rockburst cases and outlines a systematic approach to categorize rockburst intensity levels. Through data visualization and factor analysis, a concise set of underlying factors is identified, while K-means clustering uncovers significant data patterns. The gradient boosting classifier algorithm is employed to predict rockburst intensity levels effectively. By integrating multimodal data for robust activity recognition, the methodology facilitates enhanced data exploration and visualization, incorporating both unsupervised and supervised ML techniques. The results indicate that the integration of GenAI with prompt engineering offers a powerful approach for accurately predicting rockburst events, achieving an impressive accuracy rate of 89%. This work highlights the potential of advanced GenAI methodologies in improving predictive modeling within the construction industry.
This research has highlighted the potential of using prompt engineering in conjunction with GenAI tools to generate Python-based solutions tailored to specific challenges in underground construction. By leveraging GenAI’s ability to synthesize data and automate processes, it becomes possible to predict rockburst risk more accurately, incorporating essential variables related to geological, seismic, and geotechnical factors. Through a series of carefully crafted prompts, this study has demonstrated how GenAI can aid in the analysis and prediction of rockburst, which are critical for ensuring the safety of workers and the integrity of infrastructure.
Furthermore, the study has revealed how the combination of prompt engineering, Python programming, and GenAI-driven insights can optimize the design, planning, and site management processes in underground construction. This not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to safer construction practices by enabling real-time risk assessments and improving decision-making at every stage of a project.
As the capabilities of GenAI tools like Google Gemini continue to evolve, their role in construction and engineering will only grow in significance. The findings of this research underscore the importance of embracing these innovations to tackle some of the most challenging issues faced by the construction industry. Moving forward, the continued development and refinement of GenAI applications, along with the integration of more sophisticated prompt engineering techniques, will further enhance the ability to predict and mitigate risks in underground construction, ultimately leading to safer, more efficient, and cost-effective practices.
In addition, robust and large data are essential for the proper training of GenAI in the realm of rockburst prediction in the construction industry. These data allow the model to provide precise simulations and superior assessments tailored to specific geological conditions. Future developments in GenAI will depend on extensive, varied datasets that include different rockburst situations as well as construction, enabling the model to identify subtle patterns and behaviors. This extensive data will augment the model’s capacity to provide realistic and actionable insights, hence enhancing its flexibility for various projects. Moreover, guaranteeing the quality and pertinence of this training data is crucial to alleviate biases and mistakes in predicted results. With the rising need for advanced GenAI applications in rockburst management, it is essential to engage in comprehensive data collecting and curation techniques to promote innovation, sustainability, and improve safety in the construction industry.
In spite of the substantial potential of GenAI and prompt engineering in the construction industry, there are numerous obstacles that must be resolved. These encompass the critical role of the assurance of output accuracy, the dynamic nature of construction projects, and human oversight in the decision-making process. The effective implementation and reliability of GenAI solutions in real-world applications are contingent upon the resolution of these challenges.
In conclusion, this study highlights the potential of GenAI for rockburst prediction in underground construction and sets the stage for future exploration into how GenAI, prompt engineering, and advancements in process safety and environmental protection can further transform the construction and geotechnical industries. The ability to transition from reactive to predictive methodologies offers exciting possibilities for improving the safety, sustainability, and efficiency of construction projects in high-risk environments. As these technologies mature, their widespread adoption will likely shape the future of construction, paving the way for smarter, safer, and more resilient infrastructure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K.; Methodology, M.K. and M.F.; Software, M.K.; Validation, B.H. and W.-Y.W.; Formal analysis, M.F.; Investigation, M.F., B.H. and W.-Y.W.; Resources, B.H.; Data curation, M.K.; Writing—original draft, M.K.; Writing—review & editing, M.K., M.F. and S.W.; Visualization, M.K.; Supervision, S.W.; Project administration, S.W.; Funding acquisition, S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.U1602232), the Liaoning Province Science and Technology Plan Project (2024021200-JH2/1021), P.R. China, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (N2301005 and N2301006). CSC No: 2022GXZ004626.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study is included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors would also like to express their gratitude to the academic editor and the five anonymous reviewers for their valuable feedback, which greatly improved the quality of the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Goldman Sachs. Generative AI Could Raise Global GDP by 7%. 2023. Available online: https://www.goldmansachs.com/insights/pages/generative-ai-could-raise-global-gdp-by-7-percent.html (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Lv, Z. Generative artificial intelligence in the metaverse era. Cogn. Robot. 2023, 3, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Almusharraf, N. Google Gemini as a next generation AI educational tool: A review of emerging educational technology. Smart Learn. Environ. 2024, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K. ChatGPT Sets Record for Fastest-Growing User Base—Analyst Note Reuters. 2023. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/technology/chatgpt-sets-record-fastest-growing-user-base-analyst-note-2023-02-01/ (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Bubeck, S.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Eldan, R.; Gehrke, J.; Horvitz, E.; Kamar, E.; Lee, P.; Lee, Y.T.; Li, Y.; Lundberg, S.; et al. Sparks of artificial general intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.12712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Washington Post. The Google Engineer Who Thinks the Company’s AI has Come to Life. 2022. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2022/06/11/google-ai-lamda-blake-lemoine/ (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Brynjolfsson, E.; McAfee, A. The Second Machine Age: Work, Progress, and Prosperity in a Time of Brilliant Technologies; W.W. Norton Company: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Burström, T.; Parida, V.; Lahti, T.; Wincent, J. AI-enabled business-model innovation and transformation in industrial eco-systems: A framework, model and outline for further research. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 127, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brynjolfsson, E.; Li, D.; Raymond, L.R. Generative AI at Work (No. w31161); National Bureau of Economic Research: Boston, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Microsoft. Microsoft and OpenAI Extend Partnership. 2023. Available online: https://blogs.microsoft.com/blog/2023/01/23/microsoftandopenaiextendpartnership/ (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Strobel, G.; Banh, L.; Möller, F.; Schoormann, T. Exploring generative artificial intelligence: A taxonomy and types. In Proceedings of the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences 2024 (HICSS 2024), Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Susarla, A.; Gopal, R.; Thatcher, J.B.; Sarker, S. The Janus effect of generative AI: Charting the path for responsible conduct of scholarly activities in information systems. Inf. Syst. Res. 2023, 34, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramowski, P.; Turan, C.; Andersen, N.; Rothkopf, C.A.; Kersting, K. Large pre-trained language models contain human-like biases of what is right and wrong to do. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Slyke, C.; Johnson, R.; Sarabadani, J. Generative artificial intelligence in information systems education: Challenges, consequences, and responses. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2023, 53, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakzad, N.; Khan, F.; Amyotte, P. Safety analysis in process facilities: Comparison of fault tree and Bayesian network approaches. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2011, 96, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Rathnayaka, S.; Ahmed, S. Methods and models in process safety and risk management: Past, present and future. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 98, 116–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.I.; Haddara, M.M. Risk-based maintenance (RBM): A quantitative approach for maintenance/inspection scheduling and planning. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2003, 16, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenlaender, J.; Linder, R.; Silvennoinen, J. Prompting AI art: An investigation into the creative skill of prompt engineering. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.13534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Fu, Q.; Hays, S.; Sandborn, M.; Olea, C.; Gilbert, H.; Elnashar, A.; Spencer-Smith, J.; Schmidt, D.C. A prompt pattern catalog to enhance prompt engineering with ChatGPT. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.11382. [Google Scholar]
- Piller, C. Meta-prompt Engineering in ChatGPT-4 for AI-Generated BPM Reference Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Subject-Oriented Business Process Management, Weiden, Germany, 21–22 May 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 315–331. [Google Scholar]
- Strobelt, H.; Webson, A.; Sanh, V.; Hoover, B.; Beyer, J.; Pfister, H.; Rush, A.M. Interactive and visual prompt engineering for ad-hoc task adaptation with large language models. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2023, 29, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abukhalaf, S.; Hamdaqa, M.; Khomh, F. On Codex prompt engineering for OCL generation: An empirical study. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ACM 20th International Conference on Mining Software Repositories (MSR), Melbourne, Australia, 15–16 May 2023; pp. 148–157. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenlaender, J. A taxonomy of prompt modifiers for text-to-image generation. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2023, 43, 3763–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, Z.B. From bard to Gemini: An investigative exploration journey through Google’s evolution in conversational AI and generative AI. Comput. Artif. Intell. 2024, 2, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, T.R.; Susnjak, T.; Liu, T.; Watters, P.; Halgamuge, M.N. From google gemini to openai q*(q-star): A survey of reshaping the generative artificial intelligence (ai) research landscape. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.10868. [Google Scholar]
- Rane, N.; Choudhary, S.; Rane, J. Gemini versus ChatGPT: Applications, performance, architecture, capabilities, and implementation. J. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 5, 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohaib, S.M.; Sajjad, S.M.; Iqbal, Z.; Yousaf, M.; Haseeb, M.; Muhammad, Z. Zero Trust VPN (ZT-VPN): A Systematic Literature Review and Cybersecurity Framework for Hybrid and Remote Work. Information 2024, 15, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Generative AI: A New Challenge for Cybersecurity. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. Stud. 2024, 6, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Shahani, N.M. Decision support system for the prediction of mine fire levels in underground coal mining using machine learning approaches. Min. Metall. Explor. 2022, 39, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidega, R.; Ondiaka, M.N.; Maina, D.; Jonah, K.A.T.; Kamran, M. Decision based uncertainty model to predict rockburst in underground engineering structures using gradient boosting algorithms. Geomech. Eng. 2022, 30, 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Sarmadi, H.; Entezami, A.; De Michele, C. Probabilistic data self-clustering based on semi-parametric extreme value theory for structural health monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 187, 109976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Ghazouani, N.; Mohammed, A.H.; Ibrahim, H.H.; Alghamdi, A.; Albaijan, I.; El Ouni, M.H. Predicting rockbursts in deep tunnels based on ejection velocity and kinetic energy measurements using advanced machine learning. Autom. Constr. 2024, 166, 105671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askaripour, M.; Saeidi, A.; Rouleau, A.; Mercier-Langevin, P. Rockburst in underground excavations: A review of mechanisms, classification, and prediction methods. Undergr. Space 2022, 7, 577–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Wang, S.; Yang, R.; Yang, S. Time-series traction prediction of surrounding rock deformation in tunnel construction based on mechanical parameter inversion. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 152, 105933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Nejati, H.R.; Mohammadi, M. Optimized machine learning modeling for predicting the construction cost and duration of tunneling projects. Autom. Constr. 2022, 139, 104305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Dong, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Hou, Q. Multi-index dominant grouping of rock mass discontinuities based on the combined weighting method: A case study for the Huayang tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 139, 105211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouchehrian, A.; Cai, M. Numerical modeling of rockburst near fault zones in deep tunnels. Tunneling Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 80, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, P.K.; Cai, M. Design of rock support system under rockburst condition. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2012, 4, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, B.; Kamran, M.; Rui, Y. Predictive modeling of short-term rockburst for the stability of subsurface structures using machine learning approaches: T-SNE, K-Means clustering and XGBoost. Mathematics 2022, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armaghani, D.J.; Yang, P.; He, X.; Pradhan, B.; Zhou, J.; Sheng, D. Toward Precise Long-Term Rockburst Forecasting: A Fusion of SVM and Cutting-Edge Meta-heuristic Algorithms. Nat. Resour. Res. 2024, 33, 2037–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Armaghani, D.J.; He, X.; Pradhan, B.; Zhou, J.; Sheng, D. Fuzzy Cognitive Map for Evaluating Critical Factors Causing Rockbursts in Underground Construction: A Fundamental Study. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2024, 57, 9713–9738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, P.; Zhou, J.; Armaghani, D.J. Intelligent rockburst prediction model with sample category balance using feedforward neural network and Bayesian optimization. Undergr. Space 2022, 7, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.Q.; Armaghani, D.J.; Li, X.B.; Mitri, H.S. Rockburst prediction in hard rock mines developing bagging and boosting tree-based ensemble techniques. J. Cent. South Univ. 2021, 28, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; He, H.; Li, X. Rockburst prediction and prevention in underground space excavation. Undergr. Space 2024, 14, 70–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Mikula, P.; Simser, B.; Hebblewhite, B.; Joughin, W.; Feng, X.; Xu, N. Discussions on rockburst and dynamic ground support in deep mines. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M. Rockburst risk control and mitigation in deep mining. Deep Resour. Eng. 2024, 1, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.J.; Cai, M.F.; Guo, Q.F.; Huang, Z.J. Rock burst prediction based on in-situ stress and energy accumulation theory. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2016, 83, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, A.M.; Rehman, H.; Emad, M.Z.; Yoo, H. Impact of shear zone on rockburst in the deep Neelum-Jehlum hydropower tunnel: A numerical modeling approach. Energies 2018, 11, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, H. Rockburst prediction for deep tunneling near fault based on the PD-BEM method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 147, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Feng, X.T.; Xiang, T.B.; Su, G.S. Rockburst characteristics and numerical simulation based on a new energy index: A case study of a tunnel at 2500 m depth. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2010, 69, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Meng, F.; Zhang, C.; Hu, D.; Yang, F.; Lu, J. Analysis of rockburst mechanisms induced by structural planes in deep tunnels. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 74, 1435–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Li, X.; Rostami, J.; Li, D. Modeling hard rock failure induced by structural planes around deep circular tunnels. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2019, 205, 152–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, S.; Cheng, H.; Han, L.; Chang, X.; Fu, X. Experimental Study on the Influence of Structural Planes on Rockbursts in Deep-Buried Hard-Rock Tunnels. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2024, 57, 8057–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Yan, X.; Jiang, J. Influence of Weak Dynamic Disturbances on Rockburst Occurring in the Borehole Containing a Small-Scale Single Structural Plane: An Experimental Study. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2024, 57, 5997–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimunhu, P.; Faradonbeh, R.S.; Topal, E.; Asad, M.W.A.; Ajak, A.D. Development of Novel Hybrid Intelligent Predictive Models for Dilution Prediction in Underground Sub-level Mining. Min. Metall. Explor. 2024, 41, 2079–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissha, Y.; Khatti, J.; Ikeda, H.; Grover, K.S.; Owada, N.; Toriya, H.; Kawamura, Y. Predicting ground vibration during rock blasting using relevance vector machine improved with dual kernels and metaheuristic algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Jiskani, I.M.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, W. Decision intelligence-driven predictive modeling of air quality index in surface mining. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Wattimena, R.K.; Armaghani, D.J.; Asteris, P.G.; Jiskani, I.M.; Mohamad, E.T. Intelligent based decision-making strategy to predict fire intensity in subsurface engineering environments. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 171, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Nejati, H.R.; Mohammadi, M.; Mohammed, A.S.; Ibrahim, H.H.; Rashidi, S. Numerical and Machine learning modeling of hard rock failure induced by structural planes around deep tunnels. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 271, 108648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, F.; Gong, G.; Yang, H.; Han, D. Intelligent technologies for construction machinery using data-driven methods. Autom. Constr. 2023, 147, 104711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Ullah, B.; Ahmad, M.; Sabri, M.M.S. Application of KNN-based isometric mapping and fuzzy c-means algorithm to predict short-term rockburst risk in deep underground projects. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1023890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Chen, B.R.; Zhang, C.Q.; Li, S.J.; Wu, S.Y. Mechanism, Warning and Dynamic Control of Rockburst Development Processes; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Sari, A.; Zhao, G.; McKinnon, S.D.; Wu, H. Short-term rockburst risk prediction using ensemble learning methods. Nat. Hazards 2020, 104, 1923–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, W.; Tang, J. Safety risk factors of metro tunnel construction in China: An integrated study with EFA and SEM. Saf. Sci. 2018, 105, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samigulina, G.A.; Samigulina, Z.I. Modified immune network algorithm based on the Random Forest approach for the complex objects control. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 2457–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.B.; Park, S.H.; Mehdawi, N.; Mokhtari, S.; Chopra, M.; Reddi, L.N.; Park, K.T. Monitoring for close proximity tunneling effects on an existing tunnel using principal component analysis technique with limited sensor data. Tunneling Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 43, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Raman, R. Regional disparities in healthcare services in Uttar Pradesh, India: A principal component analysis. GeoJournal 2022, 87, 5027–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çağlar, M.; Gürler, C. Sustainable Development Goals: A cluster analysis of worldwide countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 8593–8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Chaudhry, W.; Wattimena, R.K.; Rehman, H.; Martyushev, D.A. A multi-criteria decision intelligence framework to predict fire danger ratings in underground engineering structures. Fire 2023, 6, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Shahani, N.M.; Armaghani, D.J. Decision support system for underground coal pillar stability using unsupervised and supervised machine learning approaches. Geomech. Eng. 2022, 30, 107–121. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.; Abe, N. A short introduction to boosting. J. Jpn. Soc. Artif. Intell. 1999, 14, 1612. [Google Scholar]
- Schapire, R.E. The strength of weak learnability. Mach. Learn. 1990, 5, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahani, N.M.; Kamran, M.; Zheng, X.; Liu, C.; Guo, X. Application of gradient boosting machine learning algorithms to predict uniaxial compressive strength of soft sedimentary rocks at Thar Coalfield. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 2565488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).