Mycoplasma genitalium Protein of Adhesion Promotes the Early Proliferation of Human Urothelial Cells by Interacting with RPL35
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
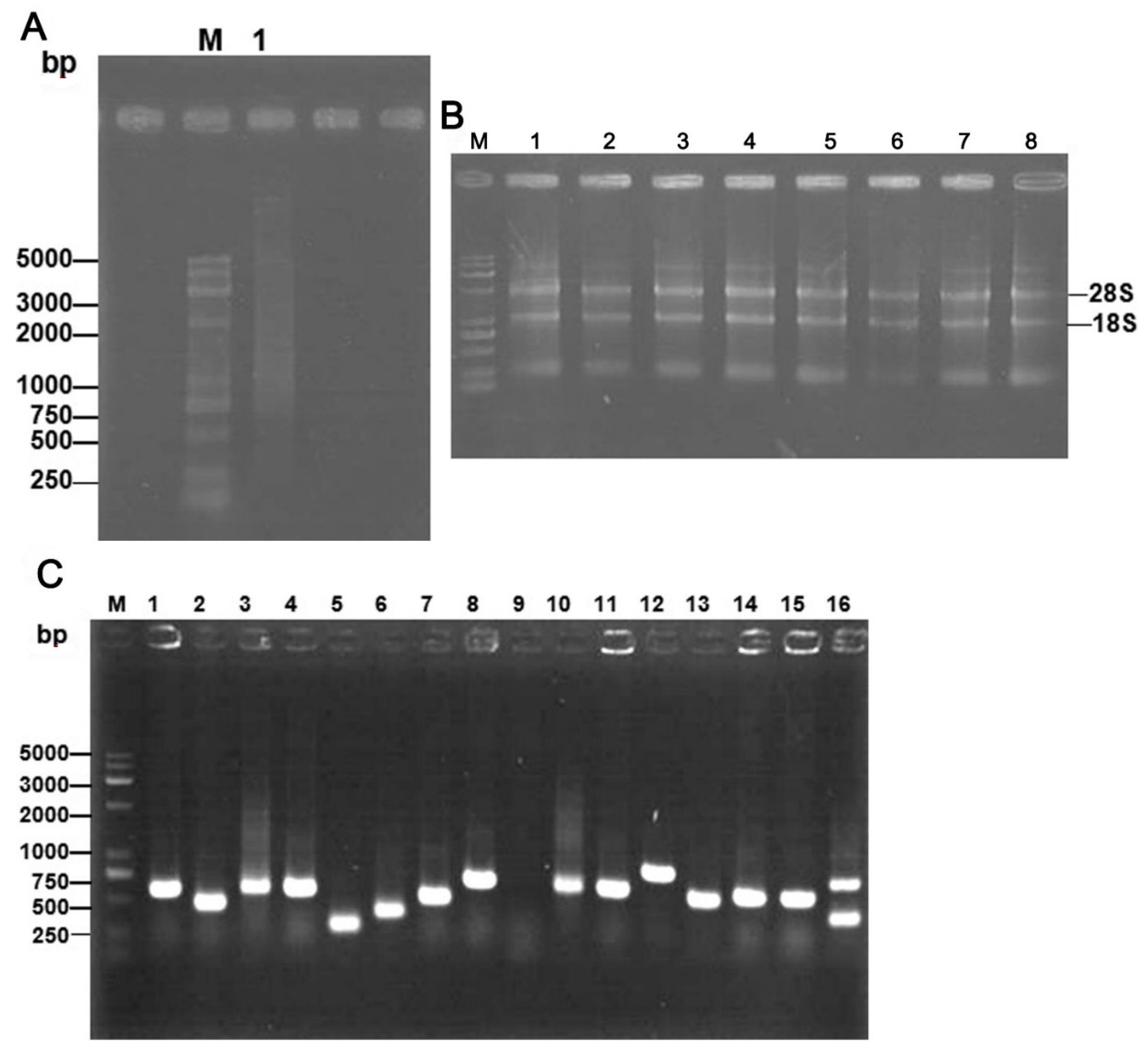
2.1. The T7 Phage-Displayed cDNA Library of SV-HUC-1 Cells Was Successfully Constructed
2.2. rMgPa-Specific T7 Phages Were Enriched Successfully
2.3. The Representative Phages Could Combine Specially with rMgPa
2.4. rMgPa Interacts with RPL35
2.5. rMgPa and RPL35 Could Interact in SV-HUC-1 Cells
2.6. Differential Proteins Were Identified Successfully by TMT Analysis
2.7. The mRNA Expressions of Representative Factors Were Increased
2.8. The Interaction between rMgPa and RPL35 Can Promote Cell Proliferation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Preparation of the T7 Phage-Displayed cDNA Library of SV-HUC-1 Cells
4.3. Biopanning and Analysis
4.4. Phage ELISA and Dot Immunobinding Assay
4.5. Interaction Assays between rMgPa and RPL35 Using Far-Western Blotting
4.6. Co-localization Analysis of rMgPa and RPL35 in the SV-HUC-1 Cells
4.7. Analysis of the Transcriptome of SV-HUC-1 Cells by TMT Analysis
4.8. RT-qPCR Analyses of the mRNA Expression of Differential Protein
4.9. The Detection of Cell Proliferation Using the MTT Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowlinson, E.; Hughes, J.P.; Chambers, L.C.; Lowens, M.S.; Morgan, J.L.; Robinson, T.S.; Romano, S.S.; Leipertz, G.L.; Soge, O.O.; Golden, M.R.; et al. Incidence of Nongonococcal Urethritis in Men Who Have Sex with Women and Associated Risk Factors. Sex Transm. Dis. 2021, 48, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Li, K.T.; Gao, Y.Y.; Xu, J.J.; Huang, D.S. Mycoplasma genitalium and Mycoplasma hominis are prevalent and correlated with HIV risk in MSM: A cross-sectional study in Shenyang, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wen, Y.; Peng, S.; Liao, J.; Liu, Y. Association of Mycoplasma fermentans and the risk of HIV-1 infection: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e18499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smullin, C.P.; Green, H.; Peters, R.; Nyemba, D.; Qayiya, Y.; Myer, L.; Klausner, J.; Joseph Davey, D. Prevalence and incidence of Mycoplasma genitalium in a cohort of HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected pregnant women in Cape Town, South Africa. Sex Transm. Infect. 2020, 96, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Paik, D.J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.S.; Seo, J.T.; Jeong, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Park, D.W.; Han, S.; Lee, Y.K.; et al. Effects of infections with five sexually transmitted pathogens on sperm quality. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2017, 44, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.P.; Rasmussen, W.G.; Baseman, J.B. Isolation and characterization of transposon Tn4001-generated, cytadherence-deficient transformants of Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma genitalium. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1996, 15, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, D.C.; Leith, D.K.; Wilson, R.M.; Baseman, J.B. Identification of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteins associated with hemadsorption and virulence. Infect. Immun. 1982, 35, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, D.; Scheffer, M.P.; Marcos-Silva, M.; Vizarraga, D.; Sprankel, L.; Ratera, M.; Weber, M.S.; Seybert, A.; Torres-Puig, S.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, L.; et al. Structure and mechanism of the Nap adhesion complex from the human pathogen Mycoplasma genitalium. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Morales, L.; González-González, L.; Querol, E.; Piñol, J. A minimized motile machinery for Mycoplasma genitalium. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 100, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, D.; Torres-Puig, S.; Ratera, M.; Querol, E.; Piñol, J.; Pich, O.Q.; Fita, I. Mycoplasma genitalium adhesin P110 binds sialic-acid human receptors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowin, C.L.; Popov, V.L.; Pylesm, R.B. Intracellular Mycoplasma genitalium infection of human vaginal and cervical epithelial cells elicits distinct patterns of inflammatory cytokine secretion and provides a possible survival niche against macrophage-mediated killing. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, K.E.; Warda, A.S.; Sharma, S.; Entian, K.D.; Lafontaine, D.; Bohnsack, M.T. Tuning the ribosome: The influence of rRNA modification on eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis and function. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1138–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, S.; Sakai, Y.; Ishiguro, K.; Suzuki, T. Biogenesis and iron-dependency of ribosomal RNA hydroxylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 12974–12986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Abbas, M.N.; Kausar, S.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Tan, L.; Cui, H. Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms of Antibiotic Tigecycline in the Treatment of Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylina, A.O.; Kostareva, O.S.; Sarskikh, A.V.; Fedorov, R.V.; Piendl, W.; Garber, M.B.; Tishchenko, S.V. Investigation of the regulatory function of archaeal ribosomal protein L4. Biochemistry 2014, 79, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Dai, P.; Yu, M.; Chen, L.; Zhu, C.; You, X.; Li, L.; Zeng, Y. Cyclophilin A is the potential receptor of the Mycoplasma genitalium adhesion protein. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhu, H.L.; Xu, K.R.; Wang, S.Y.; Fan, L.Q.; Zhu, W.B. Mycoplasma and ureaplasma infection and male infertility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Andrology 2015, 3, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, P.M.; Timenetsky, J.; Centonze, V.E.; Wewer, J.J.; Cagle, M.; Stein, M.A.; Krishnan, M.; Baseman, J.B. Interaction of Mycoplasma genitalium with host cells: Evidence for nuclear localization. Microbiology 2008, 154, 3033–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowin, C.L.; Radtke, A.L.; Abraham, K.; Martin, D.H.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M. Mycoplasma genitalium infection activates cellular host defense and inflammation pathways in a 3-dimensional human endocervical epithelial cell model. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1857–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baseman, J.B.; Lange, M.; Criscimagna, N.L.; Giron, J.A.; Thomas, C.A. Interplay between mycoplasmas and host target cells. Microb. Pathog. 1995, 19, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallo, S.F.; Baseman, J.B. Intracellular DNA replication and long-term survival of pathogenic mycoplasmas. Microb. Pathog. 2000, 29, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addepalli, B.; Rao, S.; Hunt, A.G. Phage display library screening for identification of interacting protein partners. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1255, 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- Piggott, A.M.; Karuso, P. Identifying the cellular targets of natural products using T7 phage display. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Kamada, Y.; Sameshima, T.; Yaguchi, M.; Niida, A.; Sasaki, S.; Miwa, M.; Ohkubo, S.; Sakamoto, J.I.; Kamaura, M.; et al. K-Ras(G12D)-selective inhibitory peptides generated by random peptide T7 phage display technology. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 484, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, H.; Hanoudi, S.N.; Draghici, S.; Samavati, L. Novel T7 Phage Display Library Detects Classifiers for Active Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection. Viruses 2018, 10, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Luo, D.; Peng, K.; Zeng, Y. Cyclophilin A: A key player for etiological agent infection. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, D.; Liao, Y.; Peng, K.; Zeng, Y. Mycoplasma genitalium Protein of Adhesion Induces Inflammatory Cytokines via Cyclophilin A-CD147 Activating the ERK-NF-κB Pathway in Human Urothelial Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plow, E.F.; Doeuvre, L.; Das, R. So many plasminogen receptors: Why. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 141806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Zhang, M.; Li, T.; Qin, X. Serum Proteomic Analysis by Tandem Mass Tags (TMT) Based Quantitative Proteomics in Gastric Cancer Patients. Clin. Lab. 2018, 64, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, A.; Branca, R.M.; Lehtiö, J.; Forshed, J. Quantitative accuracy in mass spectrometry based proteomics of complex samples: The impact of labeling and precursor interference. J. Proteomics. 2014, 96, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crozier, T.; Tinti, M.; Wheeler, R.J.; Ly, T.; Ferguson, M.; Lamond, A.I. Proteomic Analysis of the Cell Cycle of Procylic Form Trypanosoma brucei. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2018, 17, 1184–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisly, I.; Remme, J.; Tamm, T. Ribosomal protein eL24, involved in two intersubunit bridges, stimulates translation initiation and elongation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, M.N.; Schreiber, K.H.; Zhang, Y.; Duc, A.C.; Rao, S.; Hale, J.S.; Academia, E.C.; Shah, S.R.; Morton, J.F.; Holstein, C.A.; et al. The ribosomal protein Rpl22 controls ribosome composition by directly repressing expression of its own paralog, Rpl22l1. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oršolić, I.; Bursać, S.; Jurada, D.; Drmić Hofman, I.; Dembić, Z.; Bartek, J.; Mihalek, I.; Volarević, S. Cancer-associated mutations in the ribosomal protein L5 gene dysregulate the HDM2/p53-mediated ribosome biogenesis checkpoint. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3443–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.R.; McIntosh, K.B. How common are extraribosomal functions of ribosomal proteins. Mol. Cell 2009, 34, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, L.; Narla, A.; Mohandas, N. An update on the pathogenesis and diagnosis of Diamond-Blackfan anemia. F1000Research 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S.; Furuki, K.; Oshima, K.; Sawayanagi, T.; Nishigawa, H.; Kakizawa, S.; Jung, H.Y.; Ugaki, M.; Namba, S. Complete nucleotide sequence of the S10-spc operon of phytoplasma: Gene organization and genetic code resemble those of Bacillus subtilis. DNA Cell Biol. 2002, 21, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Chang, S.J.; Lin, P.H.; Averina, O.V.; Kaberdin, V.R.; Lin-Chao, S. Regulation of ribonuclease E activity by the L4 ribosomal protein of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, M.; Ohnishi, K.; Hori, S.; Nakano, A.; Nakano, R.; Yano, H.; Ohnishi, S.; Owari, T.; Morizawa, Y.; Itami, Y.; et al. Mycoplasma genitalium Infection and Chronic Inflammation in Human Prostate Cancer: Detection Using Prostatectomy and Needle Biopsy Specimens. Cells 2019, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erturhan, S.M.; Bayrak, O.; Pehlivan, S.; Ozgul, H.; Seckiner, I.; Sever, T.; Karakök, M. Can mycoplasma contribute to formation of prostate cancer? Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2013, 45, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idahl, A.; Lundin, E.; Jurstrand, M.; Kumlin, U.; Elgh, F.; Ohlson, N.; Ottander, U. Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma genitalium plasma antibodies in relation to epithelial ovarian tumors. Infect. Dis. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 2011, 824627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Liu, L.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; You, X.; Wu, Y. Screening and identification of the mimic epitope of the adhesion protein of Mycoplasma genitalium. Can. J. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Liao, Y.; Yi, X.; Yan, X.; Wan, K.; Zeng, Y. Ribokinase screened from T7 phage displayed Mycobacterium tuberculosis genomic DNA library had good potential for the serodiagnosis of tuberculosis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 5259–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Deng, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, L.; You, X.; Dai, P.; Wan, K.; Zeng, Y. The mimic epitopes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis screened by phage display peptide library have serodiagnostic potential for tuberculosis. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ali, A. Rapid detection of fifteen known soybean viruses by dot-immunobinding assay. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 249, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fecková, B.; Kimáková, P.; Ilkovičová, L.; Szentpéteriová, E.; Debeljak, N.; Solárová, Z.; Sačková, V.; Šemeláková, M.; Bhide, M.; Solár, P. Far-western blotting as a solution to the non-specificity of the anti-erythropoietin receptor antibody. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]






| Rounds | First | Second | Third | Fourth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input (pfu) | 3 × 108 | 3 × 108 | 3 × 108 | 3 × 108 |
| Output (pfu) | 2 × 104 | 4.2 × 104 | 1.9 × 105 | 5 × 105 |
| Ratio | 0.67 × 10−4 | 1.4 × 10−4 | 6.3 × 10−4 | 1.7 × 10−3 |
| Number | Coded Protein | mRNA ID | Matched Sequence Range | Similarity | Repeated Times |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | RPL35 | NM_007209.4 | 102–196 bp | 100% | 20 |
| P2 | Mitochondrial complete genome | NC_012920.1 | 1312–1600 bp | 99% | 3 |
| P3 | RTN4 | NM_020532.5 | 391–490 bp | 100% | 3 |
| P4 | COX6AI | NM_004373.4 | 15–344 bp | 100% | 2 |
| P5 | RPL21 | NM_000982.4 | 50–494 bp | 99% | 2 |
| P6 | RPS23 | NM_001025.5 | 32–453bp | 99% | 1 |
| P7 | RPS26 | NM_001029.5 | 250–597bp | 99% | 1 |
| Total | 32 |
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | F: 5′-GCACCGTCAAGGCTGAGAAC-3′ R:5′-TGGGAAGACGCCAGTGGA-3′ |
| EIF2 | F:5′-CGAGAAGCACAGCAAGAACATCAC-3′ R:5′-TCCTACAGACGCCTTCTCTTCGG-3′ |
| SRP68 | F:5′-CTCTCGCACCTGGTCTCCTACG-3′ R:5′-GCTCCAACACGCTGCCACTG-3′ |
| SERBP1 | F:5′-AAGAGGCTCATGCTGAAGATTCGG-3′ R:5′-AGGAGCAGAAGCACTTGACTTGTC-3′ |
| RPL35A | F:5′-TGGAAGGCTGTGGTCCAAGGC-3′ R:5′-CGCCAGGAGTGACTGTGTTGTTC-3′ |
| EGF | F:5′-ATGGCCAATCTGGATGGTTC-3′ R:5′-CATGCTGCCTTGGAGACGTA-3′ |
| TGF-β | F:5′-GTGAAACACCGAGGACACCT-3′ R:5′-GGTGCGTTGATAAATGTGG-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, P.; Deng, X.; Liu, P.; Li, L.; Luo, D.; Liao, Y.; Zeng, Y. Mycoplasma genitalium Protein of Adhesion Promotes the Early Proliferation of Human Urothelial Cells by Interacting with RPL35. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111449
Dai P, Deng X, Liu P, Li L, Luo D, Liao Y, Zeng Y. Mycoplasma genitalium Protein of Adhesion Promotes the Early Proliferation of Human Urothelial Cells by Interacting with RPL35. Pathogens. 2021; 10(11):1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111449
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Pei, Xiangying Deng, Peng Liu, Lingling Li, Dan Luo, Yating Liao, and Yanhua Zeng. 2021. "Mycoplasma genitalium Protein of Adhesion Promotes the Early Proliferation of Human Urothelial Cells by Interacting with RPL35" Pathogens 10, no. 11: 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111449
APA StyleDai, P., Deng, X., Liu, P., Li, L., Luo, D., Liao, Y., & Zeng, Y. (2021). Mycoplasma genitalium Protein of Adhesion Promotes the Early Proliferation of Human Urothelial Cells by Interacting with RPL35. Pathogens, 10(11), 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111449






