Trichinella Outbreaks on Pig Farms in Poland in 2012–2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
- −
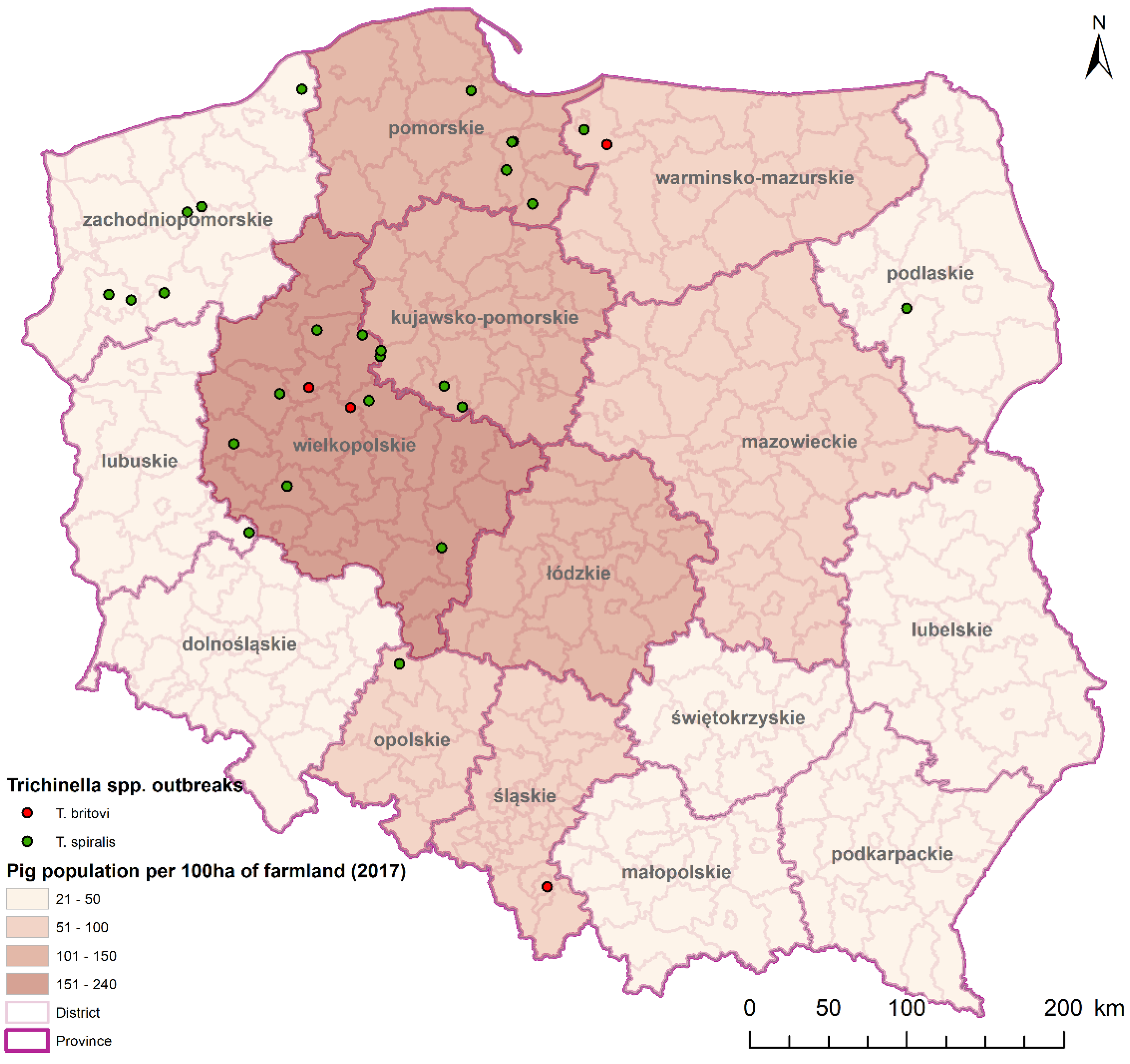
- Moderate positive correlation between the number of tested pigs and the number of farms in which Trichinella spp. were detected (r = 0.45, p < 0.005);
- −
- Strong positive correlation between the number of pigs in general in each province and the number of farms with infected pigs (r = 0.78, p < 0.005);
- −
- Strong positive correlation between the number of pigs per 100 ha of agricultural land in each province and the number of farms with infected pigs (r = 0.86, p < 0.005) [16].
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Visciano, P.; Schirone, M. Rapid Methods for Assessing Food Safety and Quality. Foods 2020, 9, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sas, A. Pig Meat per Capita Consumption in Poland. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/440754/pig-meat-per-capita-consumption-in-poland/ (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Fosse, J.; Seegers, H.; Magras, C. Foodborne zoonoses due to meat: A quantitative approach for a comparative risk assessment applied to pig slaughtering in Europe. Vet. Res. 2008, 39, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawla, P.; Sharma, S. Trichinella Spiralis. StatPearls [Internet]. 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538511/ (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Golab, E.; Sadkowska-Todys, M. Epidemiology of human trichinellosis in Poland- currently and in the past. Wiad Parazytol. 2006, 52, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Pozio, E. The broad spectrum of Trichinella hosts: From cold- to warm-blooded animals. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 132, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozio, E. Trichinellosis in the European Union: Epidemiology, ecology and economic impact. Parasitol. Today 1998, 14, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozio, E. Searching for Trichinella: Not all pigs are created equal. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Knapen, F. European proposal for alternative Trichinella control in domestic pigs. Fleischwirtschaft 1998, 78, 338–339. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Implementing Regulation. EC No 2075/2005 of 5 December 2005 Laying Down Specific Rules on Official Controls for Trichinella in Meat. 2005. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32005R2075 (accessed on 6 October 2021).
- Commission Implementing Regulation. EC No 2015/1375, Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2015/1375 of 10 August 2015 Laying Down Specific Rules on Official Controls for Trichinella in Meat. 2015. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32015R1375 (accessed on 6 October 2021).
- Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2020/1478 of 14 October 2020 Amending Implementing Regulation (EU) 2015/1375 as Regards Sampling, the Reference Method for Detection and Import Conditions Related to Trichinella control. 2020. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2020/1478/oj (accessed on 6 October 2021).
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union One Health Zoonoses Report 2019. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskwa, B.; Cybulska, A.; Kornacka, A.; Cabaj, W.; Bien, J. Wild boars meat as a potential source of human trichinellosis in Poland: Current data. Acta Parasitol. 2015, 60, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilska-Zajac, E.; Rozycki, M.; Gradziel-Krukowska, K.; Belcik, A.; Mizak, I.; Karamon, J.; Sroka, J.; Zdybel, J.; Cencek, T. Diversity of Trichinella species in relation to the host species and geographical location. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 279, 109052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics Poland. Farm Animals in 2017. Warsaw. 2018. Available online: https://stat.gov.pl/files/gfx/portalinformacyjny/pl/defaultaktualnosci/5508/6/18/1/zwierzeta_gospodarskie_w_2017_roku.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Kozar, Z.; Ogielski, L. Trichinellosis of pigs in Poland in the post-war period with special reference to 1960–1962. Wiad Parazytol. 1965, 11, 245–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kozar, Z.; Ramisz, A.; Kozar, M. Incidence of Trichinella spiralis in some domestic and wild living animals in Poland. Wiad Parazytol. 1965, 11, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cabaj, W. Wild and domestic animals as permanent Trichinella reservoir in Poland. Wiad Parazytol. 2006, 52, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Pozio, E.; Celli, M.; Ludovisi, A.; Interisano, M.; Amati, M.; Gomez-Morales, M.A. Animal welfare and zoonosis risk: Anti-Trichinella antibodies in breeding pigs farmed under controlled housing conditions. Parasit Vect. 2021, 14, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Pannwitz, G.; Mayer-Scholl, A.; Balicka-Ramisz, A.; Nockler, K. Increased Prevalence of Trichinella spp., Northeastern Germany, 2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrescu, C.; Hriscu, H.; Emandi, M.; Zamfir, C.; Nemet, C. Consumption of untested pork contributed to over two-thousand clinical cases of human trichinellosis in Romania. Folia Parasitol. (Praha) 2014, 61, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurdova, R.; Muller, N.; Tsvetkova, N.; Michov, L.; Georgieva, D.; Ivanova, M.; Gottstein, B. Characterisation of Trichinella isolates from Bulgaria by molecular typing and cross-breeding. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 123, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivojinovic, M.; Sofronic-Milosavljevic, L.; Cvetkovic, J.; Pozio, E.; Interisano, M.; Plavsic, B.; Radojicic, S.; Kulisic, Z. Trichinella infections in different host species of an endemic district of Serbia. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 194, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziętara, W. Production of live pigs in Poland—Conditions and prospects. Ann. Parasitol. 2019, XXI, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryszko, K.; Szajner, P. Pork Market in Poland after the EU Accession. In Proceedings of the International Academic Conferences 7010084, International Institute of Social and Economic Sciences, Budapest, Hungary, 5–8 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Woźniakowski, G.; Pejsak, Z.; Jabłoński, A. Emergence of African Swine Fever in Poland (2014–2021). Successes and Failures in Disease Eradication. Agriculture 2021, 11, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation of the Minister of Agriculture and Rural Developement of March 3rd 2020 on the Detailed Conditions and Procedure for Granting Financial Aid in the Frame of an Action Animal Welfare” Covered by the Rural Areas Developement Program for 2014–2020. (Dz.U. z dnia 09.03.2020 r., poz. 38). Available online: http://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20200000382 (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Murrell, K.D.; Stringfellow, F.; Dame, J.B.; Leiby, D.A.; Duffy, C.; Schad, G.A. Trichinella spiralis in an Agricultural Ecosystem. II. Evidence for Natural Transmission of Trichinella spiralis spiralis from Domestic Swine to Wildlife. J. Parasitol. 1987, 73, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilska-Zajac, E.; Rozycki, M.; Antolak, E.; Belcik, A.; Gradziel-Krukowska, K.; Karamon, J.; Sroka, J.; Zdybel, J.; Cencek, T. Occurrence of Trichinella spp. in rats on pig farms. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2018, 25, 698–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiterova, K.; Kincekova, J.; Snabel, V.; Marucci, G.; Pozio, E.; Dubinsky, P. Trichinella spiralis—Outbreak in the Slovak Republic. Infection 2007, 35, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vutova, K.; Velev, V.; Chipeva, R.; Yancheva, N.; Svetlozara, P.; Tomov, T.; Pozio, E.; Robertson, L.J. Clinical and epidemiological descriptions from trichinellosis outbreaks in Bulgaria. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 212, 107874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatsiros, V.G.; Boutsini, S.; Ntousi, D.; Stougiou, D.; Mintza, D.; Bisias, A. Detection and zoonotic potential of Trichinella spp. from free-range pig farming in Greece. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.A. Parasite zoonoses and wildlife: One Health, spillover and human activity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Veterinary Inspectorate. Veterinary Statistical Reporting. Available online: https://www.wetgiw.gov.pl/publikacje/rrw-sprawozdawczosc-statystyczna (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Mohandas, N.; Pozio, E.; La Rosa, G.; Korhonen, P.K.; Young, N.D.; Koehler, A.V.; Hall, R.S.; Sternberg, P.W.; Boag, P.R.; Jex, A.R.; et al. Mitochondrial genomes of Trichinella species and genotypes—A basis for diagnosis, and systematic and epidemiological explorations. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, S.K.; Raman, J.; Duffy, C.W.; Ishengoma, D.S.; Amambua-Ngwa, A.; Greenhouse, B. Applying next-generation sequencing to track falciparum malaria in sub-Saharan Africa. Malar J. 2019, 18, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruschi, F.; Gomez-Morales, M.A.; Hill, D.E. International Commission on Trichinellosis: Recommendations on the use of serological tests for the detection of Trichinella infection in animals and humans. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 14, e00032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarlenga, D.S.; Chute, M.B.; Martin, A.; Kapel, C.M. A multiplex PCR for unequivocal differentiation of all encapsulated and non-encapsulated genotypes of Trichinella. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Year | Farm Location | Province | No of Pig in a Herd | No of Infected Pig | Prevalence | No of Collected Rats | No of Infected Rats | Access to Natural Environment | Species of Trichinella |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 2012 | Oleszno | wielkopolska | 40 | 2 | 5 | None | None | Yes | T. spiralis |
| 2. | 2013 | Jeziora Wielkie | kujawsko- pomorskie | 36 | 18 | 50 | 56 | 17 | Yes | T. spiralis |
| 3. | 2013 | Sliwowo- Łopienite | podlaskie | 83 | 24 | 28.9 | 14 | 1 | Yes | T. spiralis |
| 4. | 2013 | Elbląg | warmińsko- mazurskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. britovi |
| 5. | 2013 | Gniezno | wielkopolska | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. britovi |
| 6. | 2013 | Damasławek | wielkopolska | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 7. | 2013 | Kościan | wielkopolska | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 8. | 2013 | Pyrzyce | zachodnio- pomorskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 9. | 2014 | Rzadkwin | kujawsko- pomorskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 10. | 2014 | Kwidzyń | pomorskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 11. | 2014 | Kalisz | wielkopolska | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 12. | 2014 | Rynowo | zachodnio- pomorskie | 20 | 11 | 55 | 21 | 3 | Yes | T. spiralis |
| 13. | 2015 | Tczew | pomorskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 14. | 2015 | Oborniki | wielkopolska | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. britovi |
| 15. | 2015 | Piotrkowice | wielkopolska | 32 | 2 | 6.25 | 10 | None | Yes | T. spiralis |
| 16. | 2015 | Szamotuły | wielkopolska | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 17. | 2016 | Namysłów | opolskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 18. | 2016 | Elbląg | warmińsko- mazurskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 19. | 2016 | Choszczno | zachodnio- pomorskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 20. | 2016 | Łobez | zachodnio- pomorskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 21. | 2017 | Tczew | pomorskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 22. | 2017 | Pelplin | pomorskie | 366 | 11 | 3 | 50 | None | Yes | T. spiralis |
| 23. | 2017 | Bielsko-Biała | śląskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. britovi |
| 24. | 2017 | Sławno | zachodnio- pomorskie | Nd | 1 | Nd | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 25. | 2018 | Małkowo | pomorskie | 101 | 47 | 46.5 | None | None | No | T. spiralis |
| 26. | 2018 | Dziećmiarki | wielkopolska | 800 | 3 | 0.38 | None | None | No | T. spiralis |
| 27. | 2019 | Nowy Tomyśl | wielkopolska | 2 | 2 | 100 | 3 | 3 | Yes | T. spiralis |
| 28. | 2019 | Chodzież | wielkopolska | 343 | 18 | 5.2 | 7 | None | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 29. | 2020 | Wschowa | lubuskie | 52 | 6 | 11.5 | Nd | Nd | Nd | T. spiralis |
| 30. | 2020 | Rosiny | zachodnio- pomorskie | 115 | 10 | 8.9 | Nd | Nd | No | T. spiralis |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bilska-Zając, E.; Różycki, M.; Korpysa-Dzirba, W.; Bełcik, A.; Ziętek-Barszcz, A.; Włodarczyk-Ramus, M.; Gontarczyk, A.; Cencek, T. Trichinella Outbreaks on Pig Farms in Poland in 2012–2020. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111504
Bilska-Zając E, Różycki M, Korpysa-Dzirba W, Bełcik A, Ziętek-Barszcz A, Włodarczyk-Ramus M, Gontarczyk A, Cencek T. Trichinella Outbreaks on Pig Farms in Poland in 2012–2020. Pathogens. 2021; 10(11):1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111504
Chicago/Turabian StyleBilska-Zając, Ewa, Mirosław Różycki, Weronika Korpysa-Dzirba, Aneta Bełcik, Anna Ziętek-Barszcz, Magdalena Włodarczyk-Ramus, Aneta Gontarczyk, and Tomasz Cencek. 2021. "Trichinella Outbreaks on Pig Farms in Poland in 2012–2020" Pathogens 10, no. 11: 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111504
APA StyleBilska-Zając, E., Różycki, M., Korpysa-Dzirba, W., Bełcik, A., Ziętek-Barszcz, A., Włodarczyk-Ramus, M., Gontarczyk, A., & Cencek, T. (2021). Trichinella Outbreaks on Pig Farms in Poland in 2012–2020. Pathogens, 10(11), 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111504






