Trafficking and Association of Plasmodium falciparum MC-2TM with the Maurer’s Clefts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Silico Analysis Predicts PfMC-2TM to Possess 3 Transmembrane Domains
2.2. PfMC-2TM Is Expressed by 4 h Post Merozoite Invasion
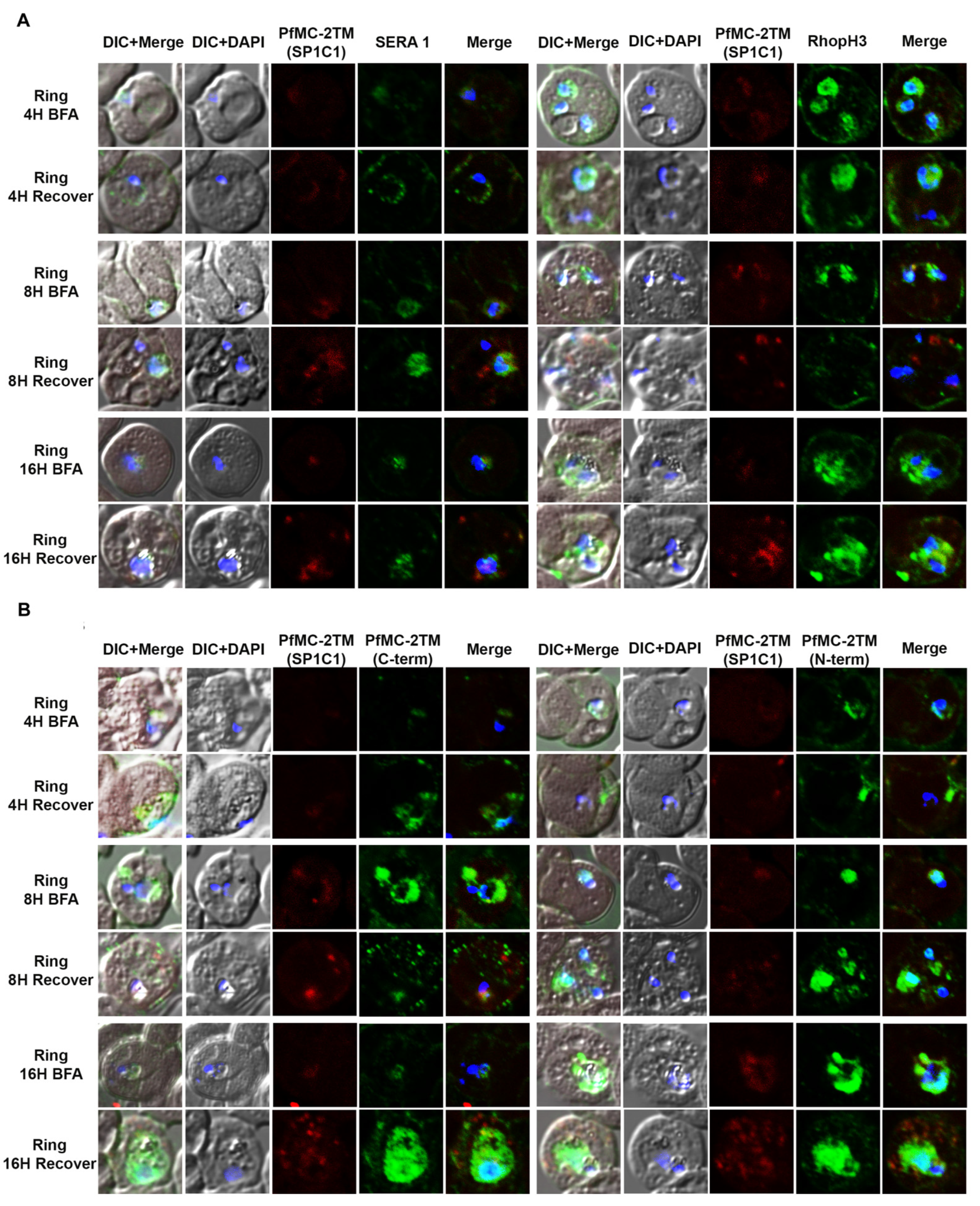
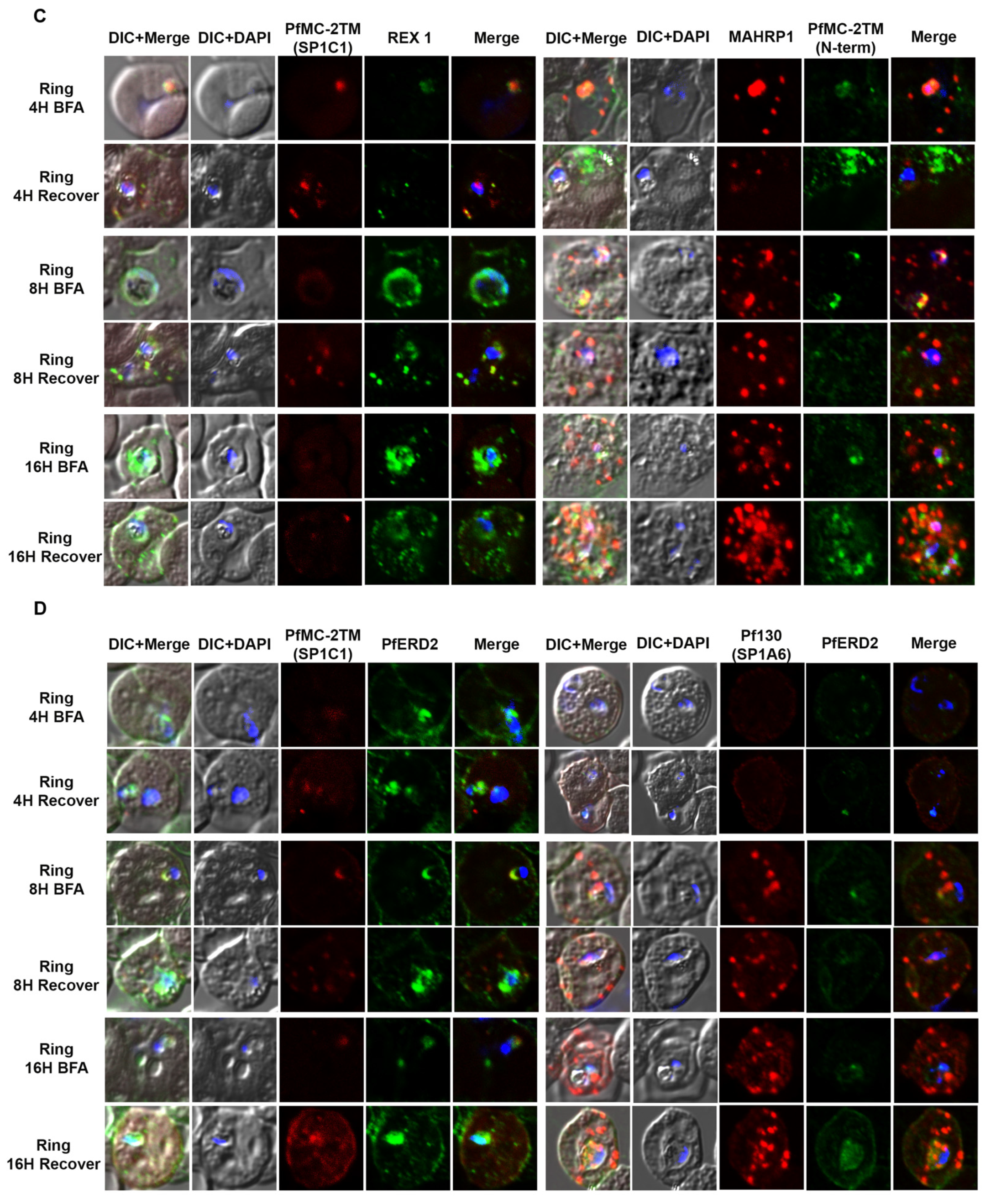
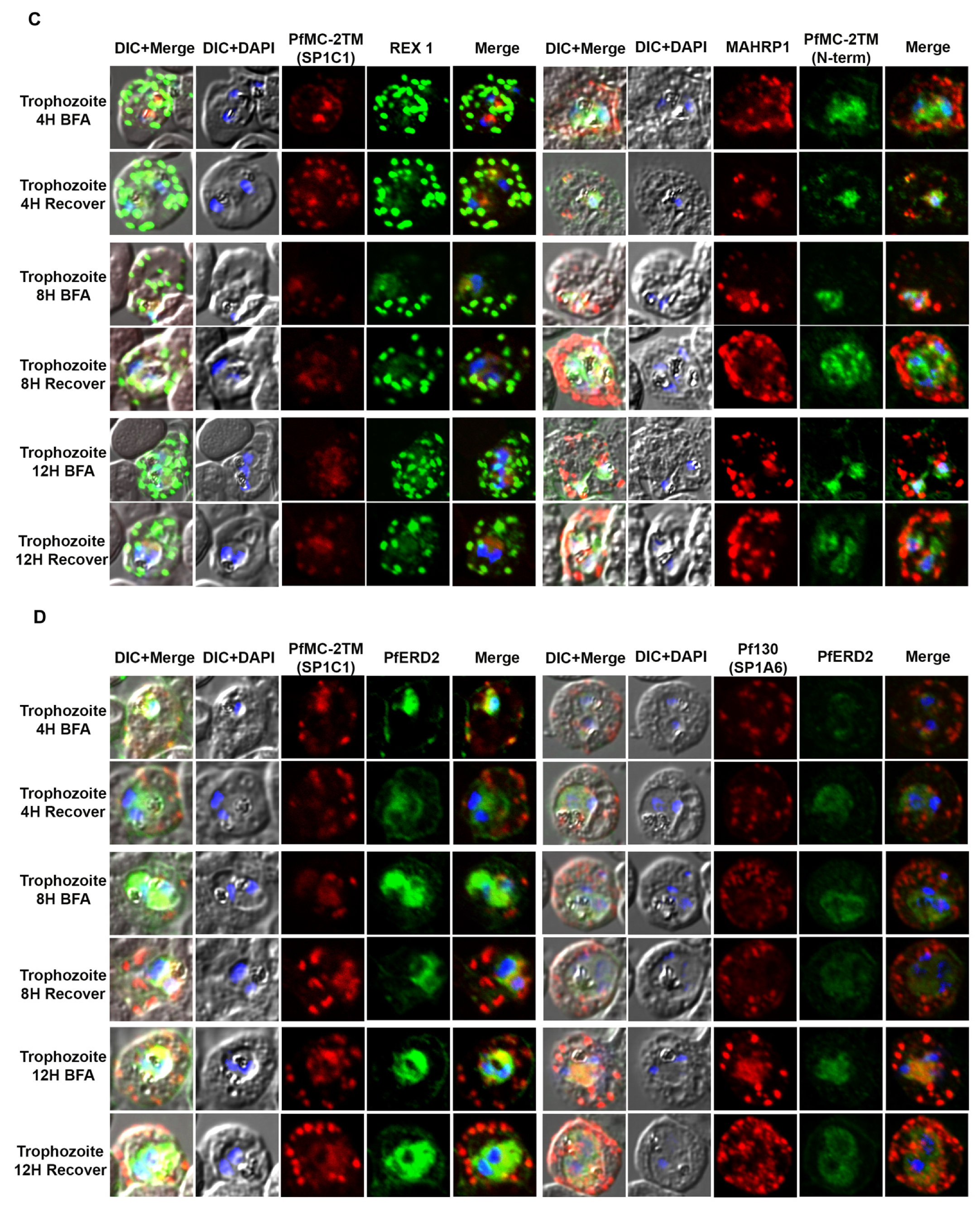
2.3. PfMC-2TM Is Exported Using the Classical Secretory Pathway
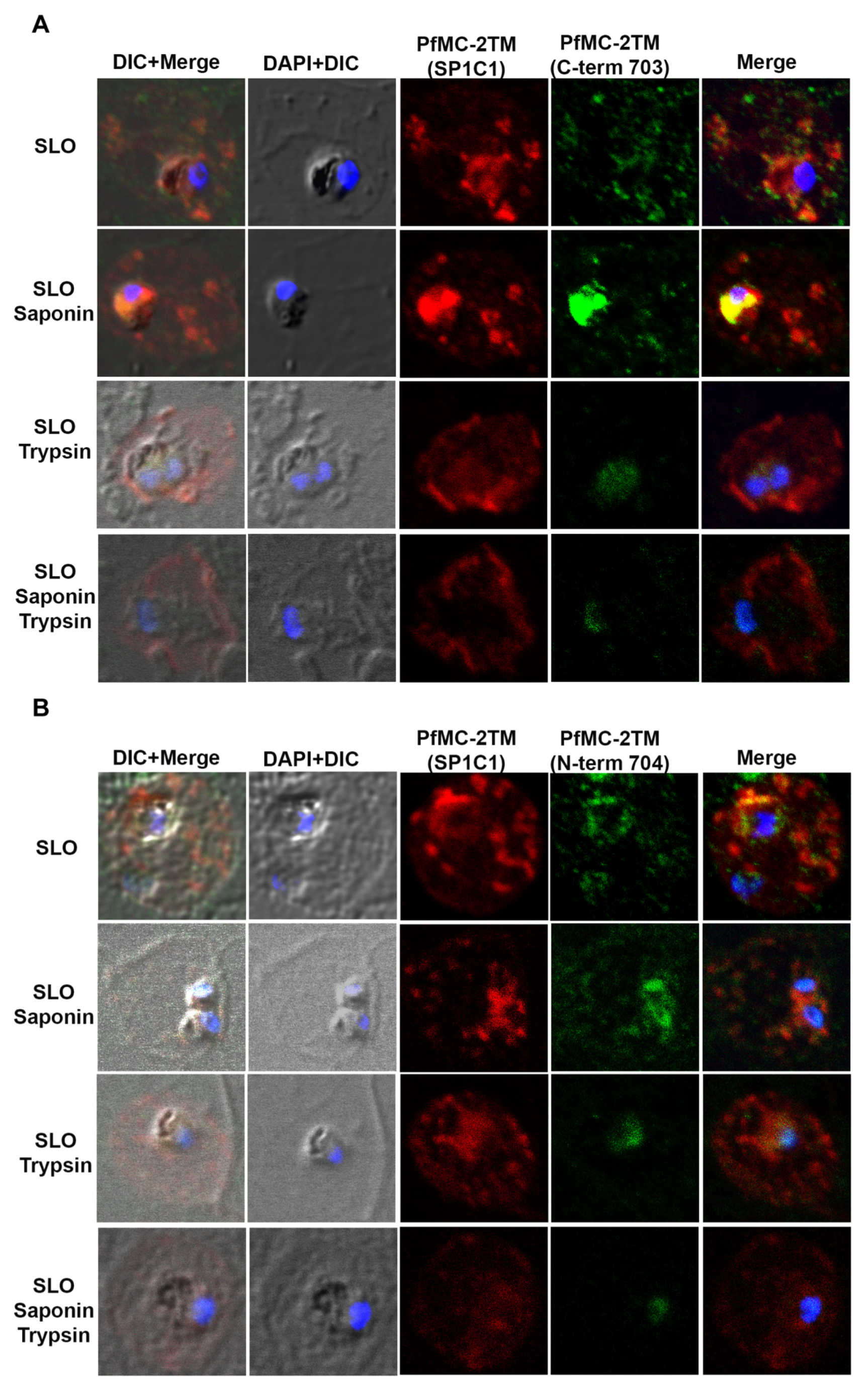
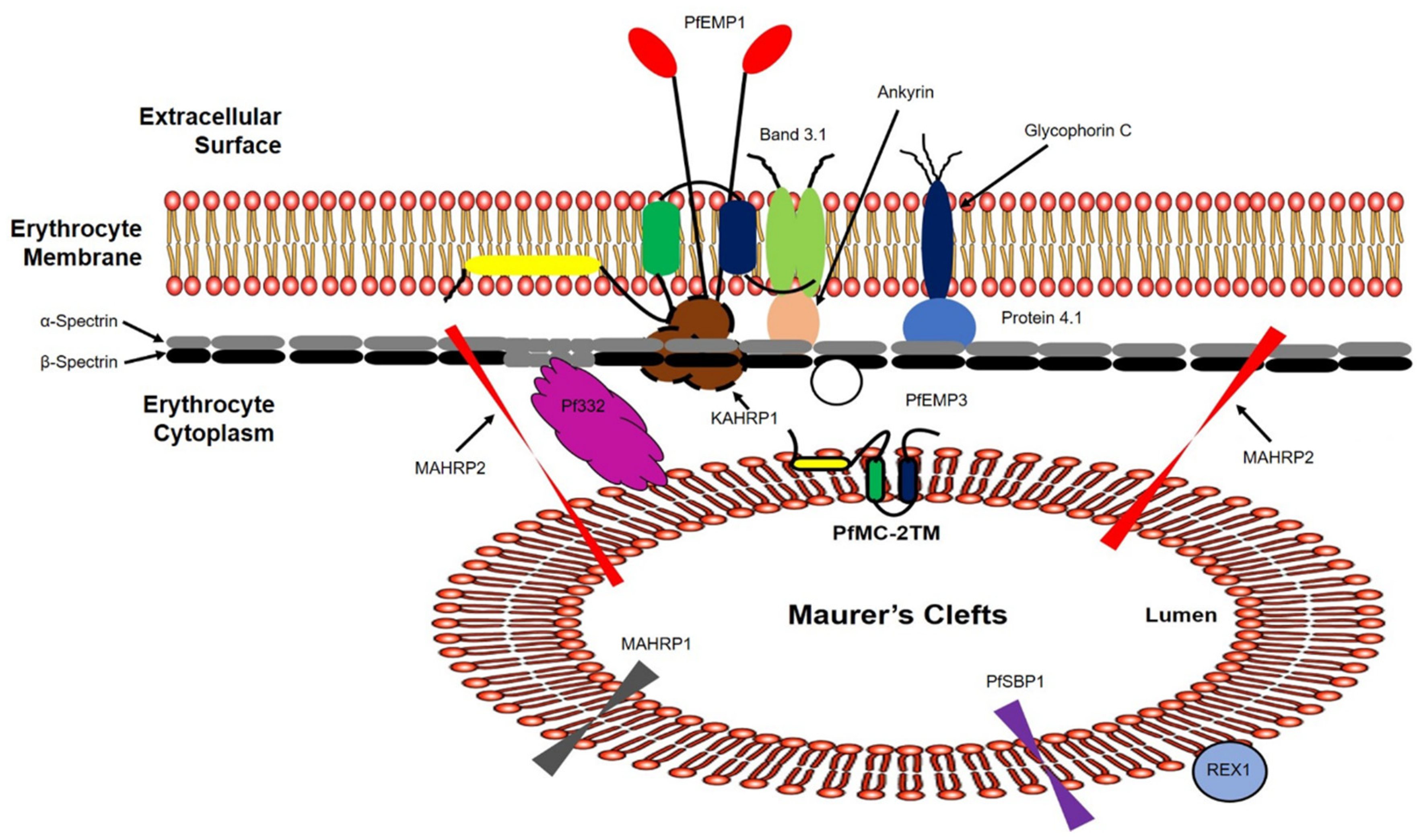
2.4. PfMC-2TM Is Associated with the MC Membrane with the N- and C-termini Exposed to the Erythrocyte Cytoplasm
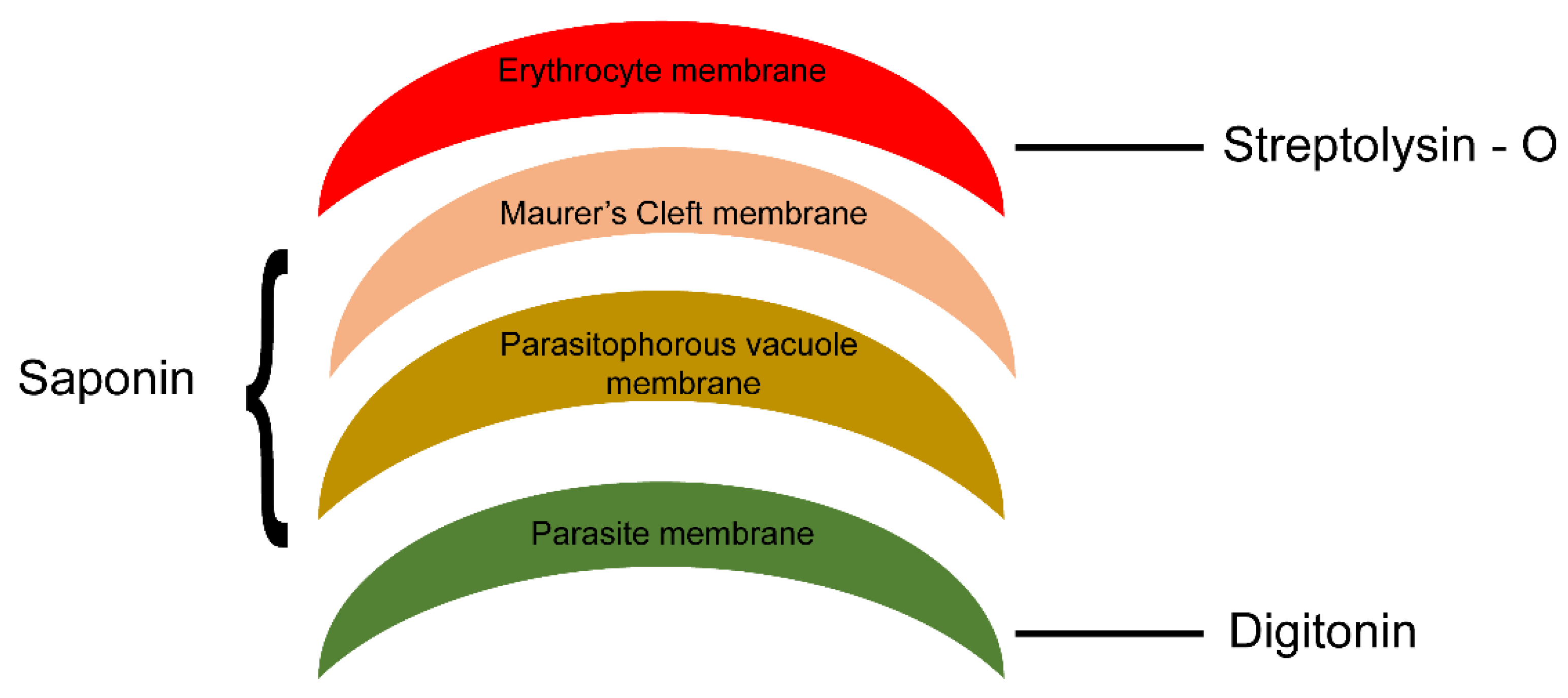
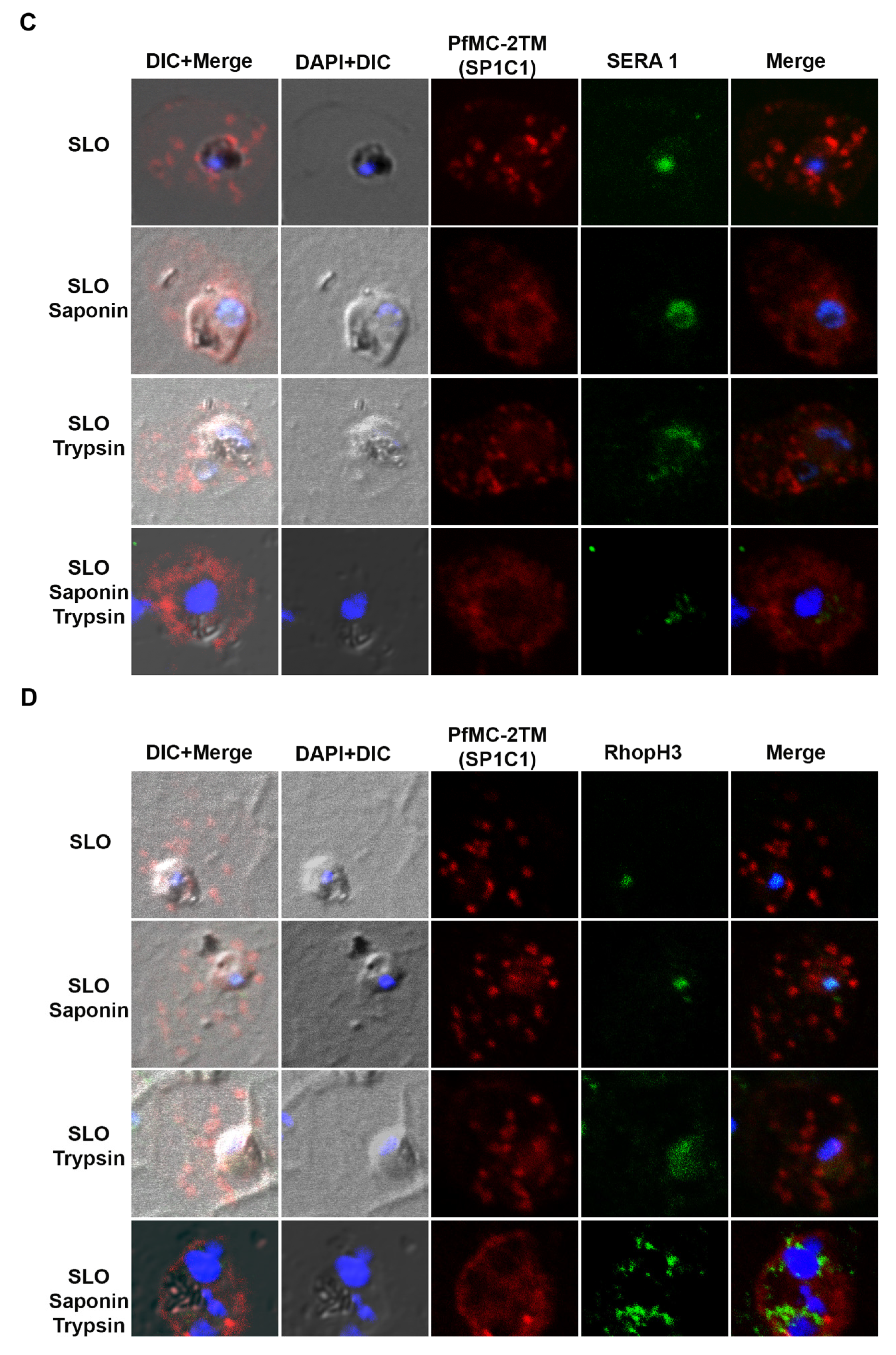
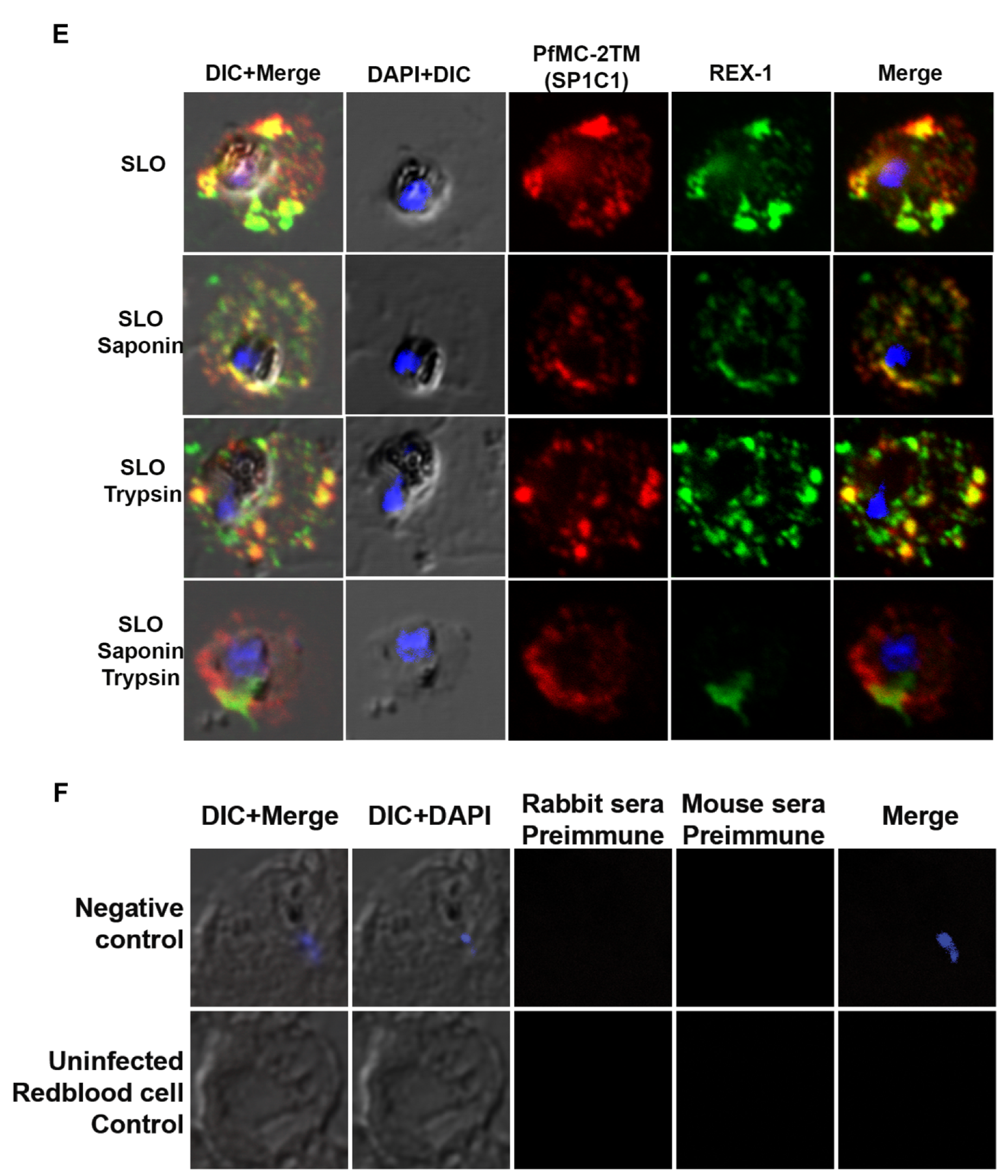
2.5. PfMC-2TM in the MC Is Accessible to Protease in the Erythrocyte Cytoplasm
2.6. PfMC-2TM Remains an Integral Membrane Protein upon Association with the Erythrocyte Membrane
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmodium Falciparum Cultures
4.2. Stage Specific Protein Expression
4.3. Brefeldin A Treatment
4.4. Permeabilization of Schizont-Infected Erythrocytes with Streptolysin O, Saponin and Trypsin
4.5. PfMC-2TM Solubility Assays and Proteinase K Digestion of Infected Erythrocyte Membrane Ghosts
4.6. Antibodies
4.7. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
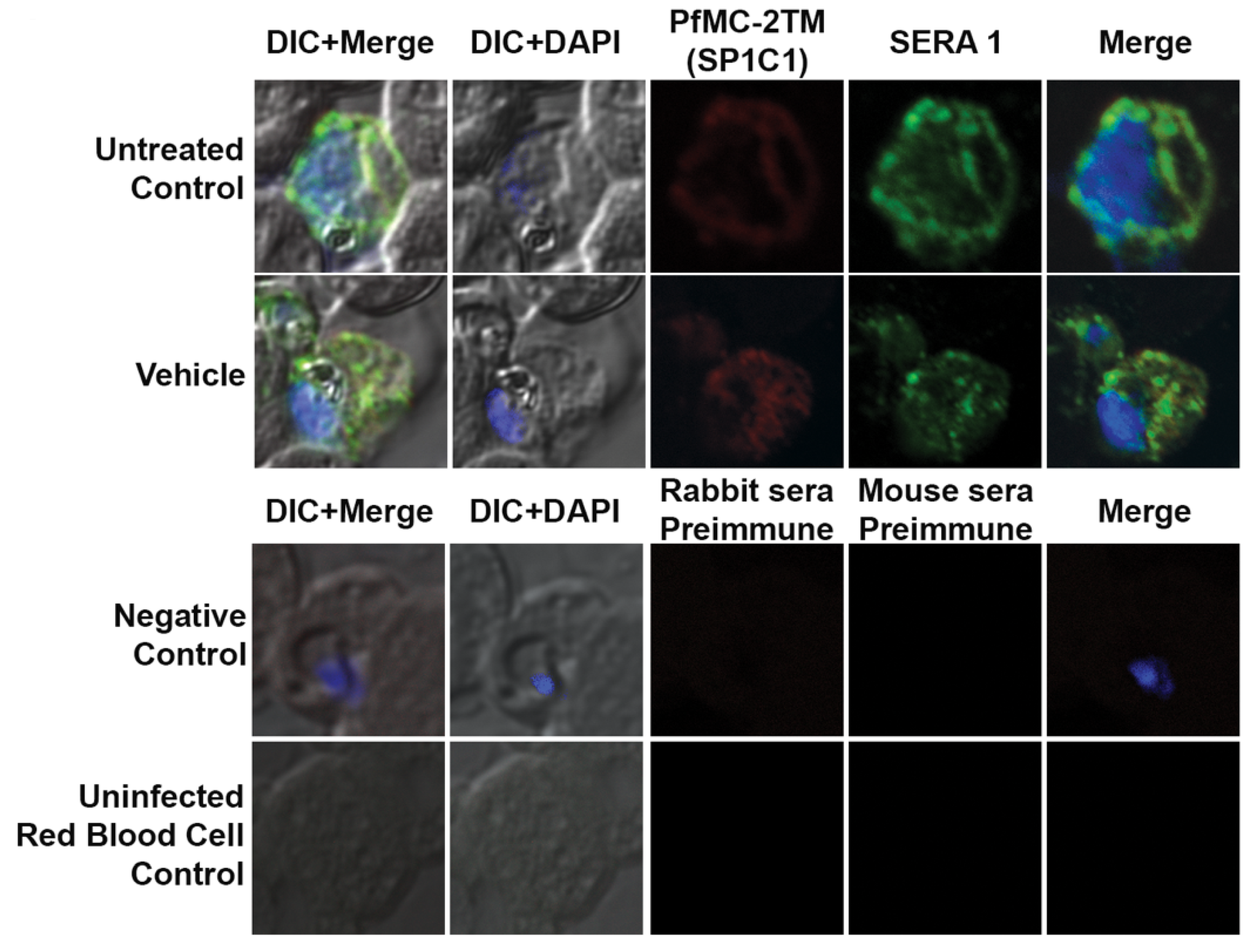
4.8. Immunofluorescence and Confocal Microscopy
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pachlatko, E.; Rusch, S.; Muller, A.; Hemphill, A.; Tilley, L.; Hanssen, E.; Beck, H.-P. MAHRP2, an exported protein of Plasmodium falciparum, is an essential component of Maurer’s. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, K. Membrane transport in the malaria-infected erythrocyte. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 495–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzer, M.; Wickert, H.; Krohne, G.; Vincensini, L.; Breton, C.B. Maurer’s clefts: A novel multi-functional organelle in the cytoplasm of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, L.; Hanssen, E. A 3D view of the host cell compartment in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2008, 15, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batinovic, S.; Mchugh, E.; Chisholm, S.A.; Matthews, K.; Liu, B.; Dumont, L.; Tilley, L. An exported protein-interacting complex involved in the trafficking of virulence determinants in Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klausner, R.D.; Donaldson, J.G.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Brefeldin A: Insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 116, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakrivos, J.; Newbold, C.I.; Lingelbach, K. A potential novel mechanism for the insertion of a membrane protein revealed by a biochemical analysis of the Plasmodium falciparum cytoadherence molecule PfEMP-1. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1272–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnwell, J.W.; Asch, A.S.; Nachman, R.L.; Yamaya, M.; Aikawa, M.; Ingravallo, P. A human 88-kD membrane glycoprotein (CD36) functions in vitro as a receptor for a cytoadherence ligand on Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendt, A.R.; Simmon, D.L.; Tansey, J.; Newbold, C.I.; Marsh, K. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is an endothelial cell adhesion receptor for Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 1989, 341, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howitt, C.A.; Wilinski, D.; Llinas, M.; Templeton, T.J.; Dzikowski, R.; Deitsch, K.W. Clonally variant gene families in Plasmodium falciparum share a common activation factor. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 73, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ockenhouse, C.F.; Tegoshi, T.; Maeno, Y.; Benjamin, C.; Ho, M.; Kan, K.E.; Lobb, R.R. Human vascular endothelial cell adhesion receptors for Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes: Roles for endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, A.; Petter, M.; Tilly, A.-K.; Biller, L.; Uliczka, K.A.; Duffy, M.F.; Bruchhaus, I. Temporal expression and localization patterns of variant surface antigens in clinical Plasmodium falciparum isolates during erythrocyte schizogony. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawthorne, P.L.; Trenholme, K.R.; Skinner-Adams, T.S.; Spielmann, T.; Fischer, K.; Dixon, M.W.A.; Gardiner, D.L. A novel Plasmodium falciparum ring stage protein, REX, is located in Maurer’s clefts. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2004, 136, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.W.A.; Hawthorne, P.L.; Spielmann, T.; Anderson, K.L.; Trenholme, K.R.; Gardiner, D.L. Targeting of the ring exported protein 1 to the Maurer’s clefts is mediated by a two-phase process. Traffic 2008, 9, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, E.; Carlton, P.; Deed, S.; Klonis, N.; Sedat, J.; Derisi, J.; Tilley, L. Whole cell imaging reveals novel modular features of the exomembrane system of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blisnick, T.; Morales Betoulle, M.E.; Barale, J.C.; Uzureau, P.; Berry, L.; Desoroses, S.; Fujioka, H.; Mattei, D.; Braun Breton, C. Pfsbp1, a Maurer’s cleft Plasmodium falciparum protein is associated with the erythrocyte skeleton. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2000, 111, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulangara, C.; Luedin, S.; Dietz, O.; Rusch, S.; Frank, G.; Mueller, D.; Felger, I. Cell biological characterization of the malaria vaccine candidate trophozoite exported protein 1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, S.; Angeletti, D.; Wahlgren, M.; Chen, Q.; Moll, K. Plasmodium falciparum antigen 332 is a resident peripheral membrane protein of Maurer’s clefts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spycher, C.; Rug, M.; Pachlatko, E.; Hanssen, E.; Ferguson, D.; Cowman, A.F.; Beck, H.-P. The Maurer’s cleft protein MAHRP1 is essential for trafficking of PfEMP1 to the surface of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 68, 1300–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flick, K.; Chen, Q. Var genes, PfEMP1 and the human host. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2004, 134, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriek, N.; Tilley, L.; Horrocks, P.; Pinches, R.; Elford, B.C.; Ferguson, D.J.P.; Newbold, C.I. Characterization of the pathway for transport of the cytoadherence-mediating protein, PfEMP1, to the host cell surface in malaria parasite-infected erythrocytes. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przyborski, J.M.; Nyboer, B.; Lanzer, M. Ticket to ride: Export of proteins to the Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocyte. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 101, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templeton, T.J.; Deitsch, K.W. Targeting malaria parasite proteins to the erythrocyte. Trends Parasitol. 2005, 21, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsarukyanova, I.; Drazba, J.A.; Fujioka, H.; Yadav, S.P.; Sam-Yellowe, T.Y. Proteins of the Plasmodium falciparum two transmembrane Maurer’s cleft protein family, PfMC-2TM, and the 130 kDa Maurer’s cleft protein define different domains of the infected erythrocyte intramembranous network. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 104, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, E.; Hawthorne, P.; Dixon, M.W.A.; Trenholme, K.R.; Mcmillan, P.J.; Spielmann, T.; Tilley, L. Targeted mutagenesis of the ring-exported protein-1 of Plasmodium falciparum disrupts the architecture of Maurer’s cleft organelles. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 69, 938–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbengue, A.; Audiger, N.; Vialla, E.; Dubremetz, J.-F.; Braun-Breton, C. Novel Plasmodium falciparum Maurer’s clefts protein families implicated in the release of infectious merozoites. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 88, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincensini, L.; Richert, S.; Blisnick, T.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Leize-Wagner, E.; Rabilloud, T.; Braun, B.C. Proteomic analysis identifies novel proteins of the Maurer’s clefts, a secretory compartment delivering Plasmodium falciparum proteins to the surface of its host cell. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, A.; Scholz, J.A.M.; Jansen, M.; Klinkert, M.-Q.; Tannich, E.; Bruchhaus, I.; Petter, M. A comparative study of the localization and membrane topology of members of the RIFIN, STEVOR and PfMC-2TM protein families in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saridaki, T.; Frohlich, K.S.; Braun-Breton, C.; Lanzer, M. Export of PfSBP1 to the Plasmodium falciparum Maurer’s clefts. Traffic 2009, 10, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam-Yellowe, T.Y.; Florens, L.; Johnson, J.R.; Wang, T.; Drazba, J.A.; Le Roch, K.G.; Yates, J.R., 3rd. A Plasmodium gene family encoding Maurer’s cleft membrane proteins: Structural properties and expression profiling. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam-Yellowe, T.Y.; Shio, H.; Perkins, M.E. Secretion of Plasmodium falciparum rhoptry protein into the plasma membrane of host erythrocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 106, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sam-Yellowe, T.Y.; Ndengele, M.M. Monoclonal antibody epitope mapping of Plasmodium falciparum rhoptry proteins. Exp. Parasitol. 1993, 76, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoneim, A.M. Trafficking of Plasmodium falciparum chimeric rhoptry protein with Brefeldin, A. Folia Parasitol. 2013, 60, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmendorf, H.G.; Haldar, K. 1993: Identification and localization of ERD2 in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum: Separation from sites of sphingomyelin synthesis and implications for organization of the Golgi. EMBO J. 2008, 12, 4763–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansorge, I.; Benting, J.; Bhakdi, S.; Lingelbach, K. Protein sorting in Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells permeabilized with the pore-forming protein streptolysin O. Biochem. J. 1996, 315, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ebine, K.; Hirai, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Yahata, K.; Kaneko, O.; Saito-Nakano, Y. Plasmodium Rab5b is secreted to the cytoplasmic face of the tubovesicular network in infected red blood cells together with N-acetylated adenylate kinase 2. Malar. J. 2016, 17, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulzer, S.; Bittl, V.; Przyborski, J.M. Fractionation of Plasmodium-infected human red blood cells to study protein trafficking. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1270, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Gruring, C.; Heiber, A.; Kruse, F.; Ungefehr, J.; Gilberger, T.-W.; Spielmann, T. Development and host cellmodification of Plasmodium falciparum blood stages in four dimensions. Nat. Commun. 2010, 2, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickert, H.; Gottler, W.; Krohne, G.; Lanzer, M. Maurer’s cleft organization in the cytoplasm of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes: New insights from three-dimensional reconstruction of serial ultrathin sections. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 83, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhiel, M.; Bittl, V.; Tribensky, A.; Charnaud, S.C.; Strecker, M.; Muller, S.; Przyborski, J.M. Trafficking of the exported Plasmodium falciparum chaperone PfHsp70x. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oquendo, P.; Hundt, E.; Lawler, J.; Seed, B. CD36 directly mediates cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum parasitized erythrocytes. Cell 1989, 58, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przyborski, J.M.; Miller, S.K.; Pfahler, J.M.; Henrich, P.P.; Rohrbach, P.; Crabb, B.S.; Lanzer, M. Trafficking of STEVOR to the Maurer’s clefts in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 2306–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yam, X.Y.; Niang, M.; Madnani, K.G.; Preiser, P.R. Three is a crowd—New insights into rosetting in Plasmodium falciparum. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, F.G.; Lanke, K.; Nebie, I.; Schildkraut, J.A.; Goncalves, B.P.; Tiono, A.B.; Rijpma, S.R. Molecular markers for sensitive detection of plasmodium falciparum asexual stage parasites and their application in a malaria clinical trial. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crary, J.L.; Haldar, K. Brefeldin A inhibits protein secretion and parasite maturation in the ring stage of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1992, 53, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddey, J.A.; Carvalho, T.G.; Hodder, A.N.; Sargeant, T.J.; Sleebs, B.E.; Marapana, D.; Cowman, A.F. Role of plasmepsin V in export of diverse protein families from the Plasmodium falciparum exportome. Traffic 2013, 14, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddey, J.A.; O’neill, M.T.; Lopaticki, S.; Carvalho, T.G.; Hodder, A.N.; Nebl, T.; Cowman, A.F. Export of malaria proteins requires co-translational processing of the PEXEL motif independent of phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Hora, R. “2TM proteins”: An antigenically diverse superfamily with variable functions and export pathways. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Nagaoka, H.; Ntege, E.H.; Kanoi, B.N.; Ito, D.; Nakata, T.; Takashima, E. PV1, a novel Plasmodium falciparum merozoite dense granule protein, interacts with exported protein in infected erythrocytes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, D.; Schureck, M.A.; Desai, S.A. An essential dual-function complex mediates erythrocyte invasion and channel-mediated nutrient uptake in malaria parasites. ELife 2017, 6, e23485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherling, E.S.; Knuepfer, E.; Brzostowski, J.A.; Miller, L.H.; Blackman, M.J.; Van Ooij, C. The Plasmodium falciparum rhoptry protein RhopH3 plays essential roles in host cell invasion and nutrient uptake. Elife 2017, 6, e23239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trager, W.; Jensen, J.B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science 1976, 193, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasvol, G.; Wilson, R.J.; Smalley, M.E.; Brown, J. Separation of viable schizont-infected red cells of Plasmodium falciparum from human blood. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1978, 72, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambros, C.; Vanderberg, J.P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J. Parasitol. 1979, 65, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam-Yellowe, T.Y.; Fujioka, H.; Aikawa, M.; Hall, T.; Drazba, J.A.A. Plasmodium falciparum protein located in Maurer’s clefts underneath knobs and protein localization in association with Rhop-3 and SERA in the intracellular network of infected erythrocytes. Parasitol. Res. 2001, 87, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spycher, C.; Klonis, N.; Spielmann, T.; Kump, E.; Steiger, S.; Tilley, L.; Beck, H.-P. MAHRP-1, a novel Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein, binds ferriprotoporphyrin IX and localizes to the Maurer’s clefts. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 35373–35383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Blanton, R.E.; King, C.L.; Fujioka, H.; Aikawa, M.; Sam-yellowe, T.Y. Seroprevalence and specificity of human responses to the Plasmodium falciparum rhoptry protein Rhop-3 determined by using a C-terminal recombinant protein. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 3584–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Time Point | Hours Post Infection (hpi) | Parasite Stage | Parasitemia Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0–4 | Segmenters Rings | Shizonts (1%) Rings (4%) |
| 2 | 5–8 | Rings | Rings (5 %) Schizonts (0.1%) |
| 3 | 9–12 | Rings | Rings (6 %) Schizonts (<0.1%) |
| 4 | 13–16 | Rings | 5% Rings 1% Early trophozoites |
| 5 | 18–30 | Late rings Early trophozoites | 0.5% Late Rings 5–6% Trophozoites |
| 6 | 31–40 | Late trophozoites Early schizonts | 5% Early schizonts 1.5% Late trophozoites |
| 7 | 42–51 | Schizonts Segmenters | 5 % Schizonts |
| 8 | 51–3 (second cycle) | Segmenters Rings | 3% rings 5% Segmented schizont |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yadavalli, R.; Peterson, J.W.; Drazba, J.A.; Sam-Yellowe, T.Y. Trafficking and Association of Plasmodium falciparum MC-2TM with the Maurer’s Clefts. Pathogens 2021, 10, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10040431
Yadavalli R, Peterson JW, Drazba JA, Sam-Yellowe TY. Trafficking and Association of Plasmodium falciparum MC-2TM with the Maurer’s Clefts. Pathogens. 2021; 10(4):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10040431
Chicago/Turabian StyleYadavalli, Raghavendra, John W. Peterson, Judith A. Drazba, and Tobili Y. Sam-Yellowe. 2021. "Trafficking and Association of Plasmodium falciparum MC-2TM with the Maurer’s Clefts" Pathogens 10, no. 4: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10040431
APA StyleYadavalli, R., Peterson, J. W., Drazba, J. A., & Sam-Yellowe, T. Y. (2021). Trafficking and Association of Plasmodium falciparum MC-2TM with the Maurer’s Clefts. Pathogens, 10(4), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10040431






