Corynebacteria in Bovine Quarter Milk Samples—Species and Somatic Cell Counts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Detected Corynebacterium spp. and Their Mastitis Diagnosis
2.2. Group Distribution of Mastitis Status
2.3. Species Distribution on Different Farms
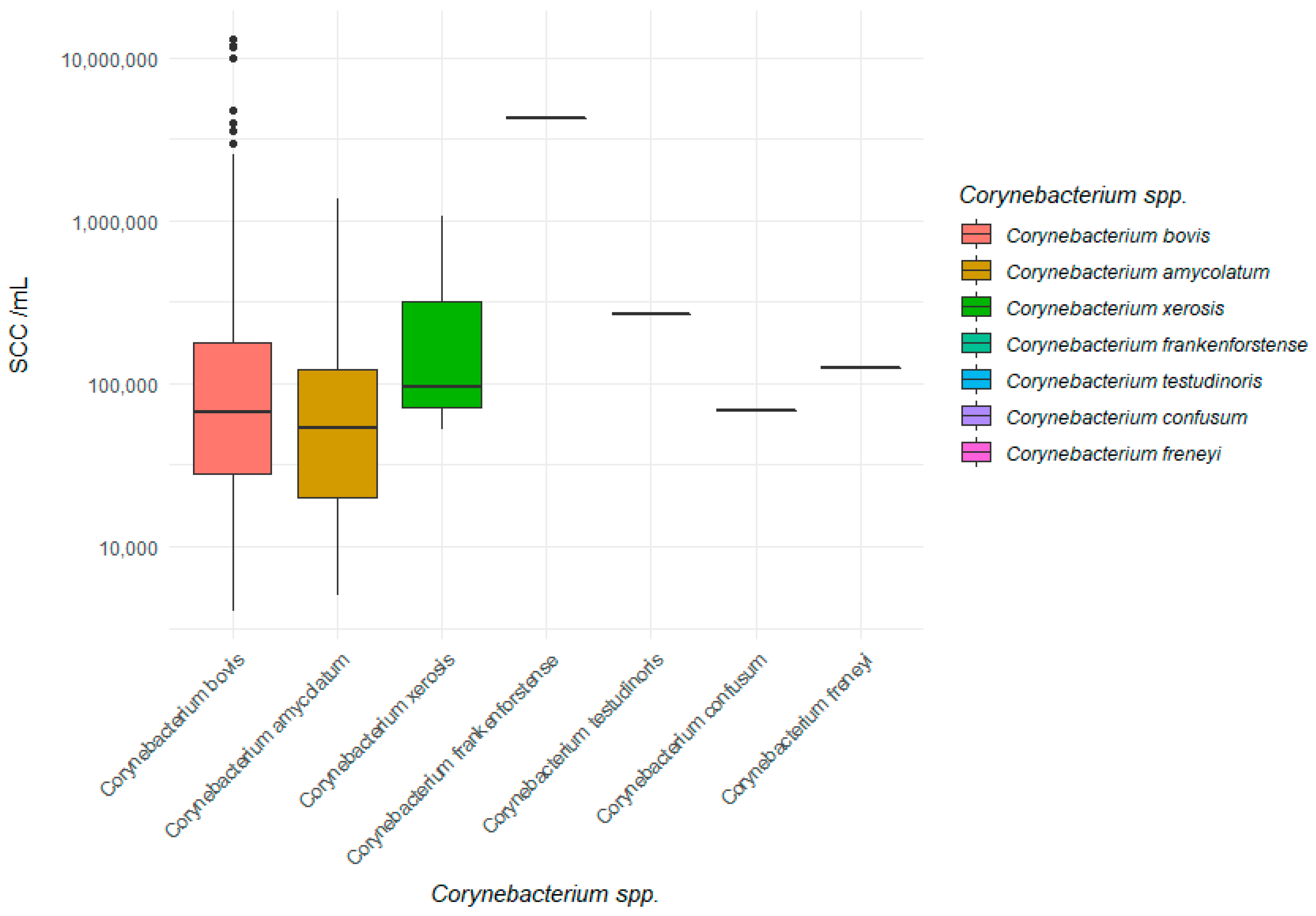
2.4. Somatic Cell Count (SCC)
3. Discussion
Species Identification
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Origin of Samples
4.2. Cytomicrobiological Examination and Species Differentiation
4.3. Somatic Cell Count (SCC) and Definitions
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heikkilä, A.-M.; Liski, E.; Pyörälä, S.; Taponen, S. Pathogen-specific production losses in bovine mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9493–9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tenhagen, B.-A.; Köster, G.; Wallmann, J.; Heuwieser, W. Prevalence of Mastitis Pathogens and Their Resistance against Antimicrobial Agents in Dairy Cows in Brandenburg, Germany. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 2542–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krömker, V.; Paduch, J.H.; Klocke, D.; Zinke, C. Microbiological investigation of culture negative milk samples of clinical mastitis cows. Milchwissenschaft 2010, 65, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bexiga, R.; Pereira, H.; Pereira, O.; Leitão, A.; Carneiro, C.; Ellis, K.A.; Vilela, C.L. Observed reduction in recovery of Corynebacterium spp. from bovine milk samples by use of a teat cannula. J. Dairy Res. 2011, 78, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, T.J.; Schukken, Y.H.; van Vliet, J.H.; Grommers, F.J.; Tielen, M.J.; Brand, A. Effect of natural infection with minor pathogens on susceptibility to natural infection with major pathogens in the bovine mammary gland. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1997, 58, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, J.L.; Tomazi, T.; Barreiro, J.R.; Beuron, D.C.; Arcari, M.A.; Lee, S.H.I.; Martins, C.M.d.M.R.; Araújo Junior, J.P.; dos Santos, M.V. Effects of bovine subclinical mastitis caused by Corynebacterium spp. on somatic cell count, milk yield and composition by comparing contralateral quarters. Vet. J. 2016, 209, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watts, J.L.; Lowery, D.E.; Teel, J.F.; Rossbach, S. Identification of Corynebacterium bovis and other Coryneforms Isolated from Bovine Mammary Glands. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 2373–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillmann, T. Beziehungen zwischen dem Nachweis von coryneformen Bakterien und Entzündungsparametern in Viertelanfangsgemelkproben von Milchkühen; Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover: Hannover, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, J.L.; Tomazi, T.; Barreiro, J.R.; Braga, P.A.d.C.; Ferreira, C.R.; Araújo Junior, J.P.; Eberlin, M.N.; dos Santos, M.V. Identification of Corynebacterium spp. isolated from bovine intramammary infections by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzdil, J. Corynebacteria and coryneform microorganisms isolated from bovine milk with symptomps of mastitis. Veterinářství 2017, 67, 806–810. [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson Unnerstad, H.; Lindberg, A.; Persson Waller, K.; Ekman, T.; Artursson, K.; Nilsson-Ost, M.; Bengtsson, B. Microbial aetiology of acute clinical mastitis and agent-specific risk factors. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 137, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taponen, S.; Liski, E.; Heikkilä, A.-M.; Pyörälä, S. Factors associated with intramammary infection in dairy cows caused by coagulase-negative staphylococci, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus uberis, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Corynebacterium bovis, or Escherichia coli. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- German Veterinary Association. Leitlinien zur Bekämpfung der Mastitis des Rindes als Bestandsproblem, 4th ed.; GVA e.V.: Gießen, German, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, A.; Green, M. Use and interpretation of somatic cell count data in dairy cows. Practice 2005, 27, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theel, E.S.; Schmitt, B.H.; Hall, L.; Cunningham, S.A.; Walchak, R.C.; Patel, R.; Wengenack, N.L. Formic acid-based direct, on-plate testing of yeast and Corynebacterium species by Bruker Biotyper matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3093–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- German Veterinary Association. Leitlinien der Labordiagnostik der Mastitis—Probennahme und Mikrobiologische Untersuchung, 3rd ed.; GVA e.V.: Gießen, German, 2018. [Google Scholar]



| Species | No. of Isolates (% of Total Isolates Number) | No. of Isolates from Latent Infections (% of All Isolates within One Species) | No. of Isolates from Subclinical Mastitis (% of All Isolates within One Species) | No. of Isolates from Clinical Mastitis (% of All Isolates within One Species) | No. of Other Isolates (% of All Isolates within One Species) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. bovis | 448 (90.1) 94/203/145 b | 249 (55.6) 46/101/99 | 152 (33.9) 30/80/39 | 26 (5.8) 13/11/2 | 21 (4.7) 5/11/5 |
| C. amycolatum | 38 (7.7) 6/16/16 | 25 (65.8) 5/7/13 | 10 (26.3) 1/6/3 | - | 3 (7.9) -/3/- |
| C. confusum | 2 (0.4) 1/1/- | 1 (50) 1/-/- | - | 1 (50) -/1/- | - |
| C. frankenforstense | 1 (0.2) -/1/- | - | 1 (100) -/1/- | - | - |
| C. freneyi | 1 (0.2) 1/-/- | - | 1 (100) 1/-/- | - | - |
| C. kroppenstedtii | 1 (0.2) -/1/- | - | - | - | 1 (100) -/1/- |
| C. testudinoris | 2 (0.4) 1/1/- | - | 1 (50) -/1/- | 1 (50) 1/-/- | - |
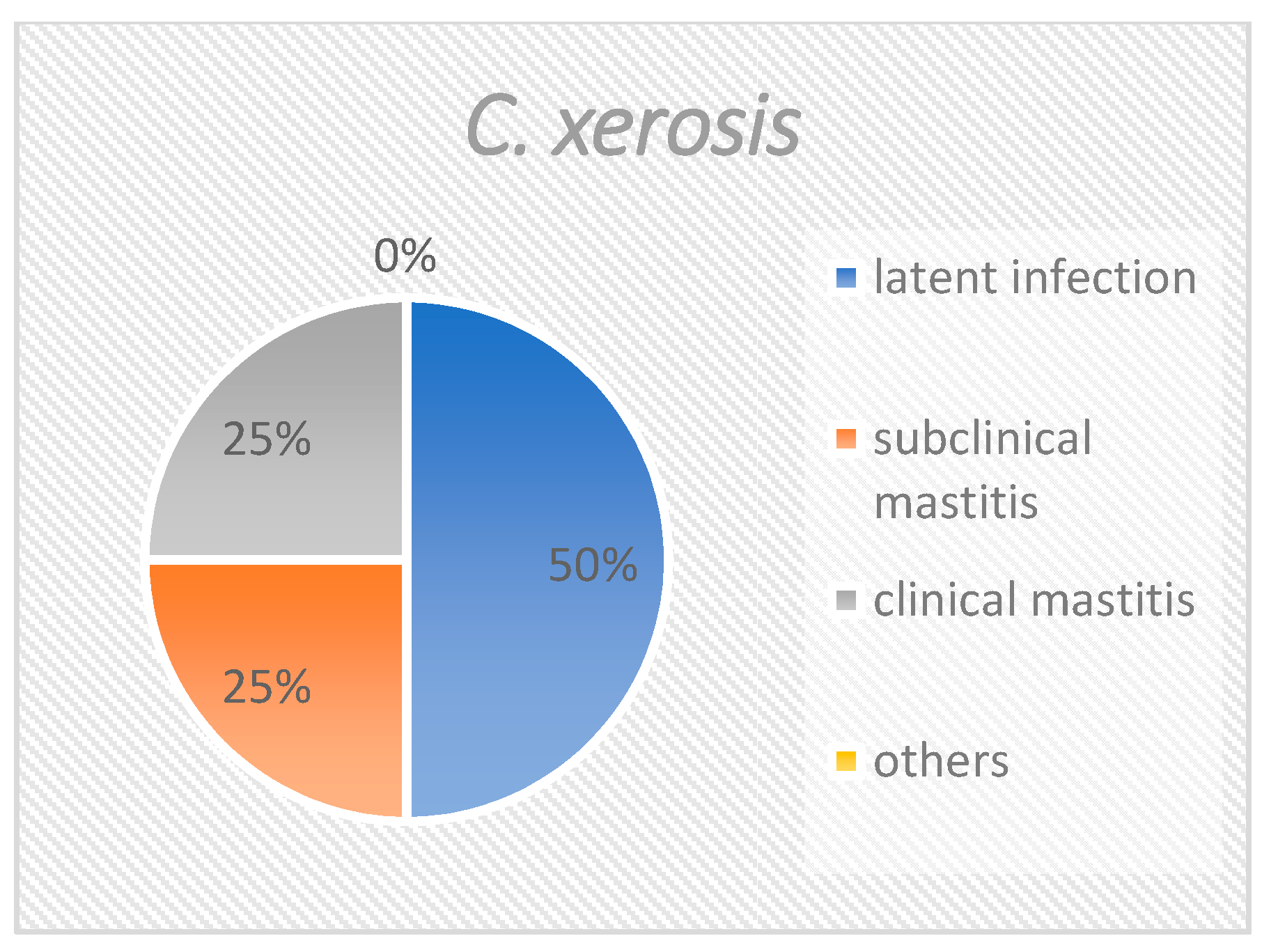
| C. xerosis | 4 (0.8) 3/1/- | 2 2/1/- | 1 (25) 1/-/- | 1 1/-/- | - |
| Total | 497 (100) | 277 (55.7) | 166 (33.4) | 29 (5.8) | 26 (5.2) |
| Present Species | Number of Farms |
|---|---|
| C. bovis | 30 |
| C. amycolatum | 5 |
| C. xerosis | 2 |
| C. bovis and C. amycolatum | 3 |
| C. bovis and C. xerosis | 1 |
| C. bovis and C. amycolatum and other species | 4 |
| Other species than C. bovis | 3 |
| Species | Median_SCC/mL | Median_Log(SCC) | GeoMean_SCC | GeoMean_Log(SCC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corynebacterium bovis (n = 401) | 66,000 | 4.82 | 78,000 | 4.69 |
| Corynebacterium amycolatum (n = 35) | 53,000 | 4.72 | 50,000 | 4.66 |
| Corynebacterium xerosis (n = 3) | 96,000 | 4.98 | 174,000 | 5.21 |
| Total (n = 443) a | 66,000 | 4.82 | 76,000 | 4.84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lücken, A.; Wente, N.; Zhang, Y.; Woudstra, S.; Krömker, V. Corynebacteria in Bovine Quarter Milk Samples—Species and Somatic Cell Counts. Pathogens 2021, 10, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070831
Lücken A, Wente N, Zhang Y, Woudstra S, Krömker V. Corynebacteria in Bovine Quarter Milk Samples—Species and Somatic Cell Counts. Pathogens. 2021; 10(7):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070831
Chicago/Turabian StyleLücken, Anneke, Nicole Wente, Yanchao Zhang, Svenja Woudstra, and Volker Krömker. 2021. "Corynebacteria in Bovine Quarter Milk Samples—Species and Somatic Cell Counts" Pathogens 10, no. 7: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070831
APA StyleLücken, A., Wente, N., Zhang, Y., Woudstra, S., & Krömker, V. (2021). Corynebacteria in Bovine Quarter Milk Samples—Species and Somatic Cell Counts. Pathogens, 10(7), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10070831







