Abstract
Saprolegnia infections are among the main parasitic diseases affecting farmed salmonids. The distribution and potential transfer of Saprolegnia spp. between farms and the natural environment has been scarcely investigated. Therefore, this work aimed to study the diversity and abundance of oomycete species in salmonid farms, tributary water, and effluent water systems. Four trout farms in Italy and two Atlantic salmon farms in Scotland were considered. In Italian farms, 532 isolates of oomycetes were obtained from fish and water, at upstream, inside, and downstream the farms. In Scottish farms, 201 oomycetes isolates were obtained from water outside the farm and from fish and water inside the farming units. Isolates were identified to the species level through amplification and sequencing of the ITS rDNA region. In Italy, S. parasitica was significantly more present in farmed than in wild fish, while in water it was more frequently isolated from the wild, particularly in effluent systems, not associated with more frequent isolation of S. parasitica in wild fish downstream the farm. In Scotland, S. parasitica was the most prevalent species isolated from fish, while isolates from water were mostly Pythium spp. with few S. parasitica isolates from upstream and downstream the farms.
1. Introduction
Parasites of wild fish pose a potential threat to aquaculture [1]. One of the main issues related to intensive aquaculture is the proliferation of parasites, particularly those with direct life cycles, and other infectious agents due to high farming densities [2], which can subsequently spread outside the farm into the natural environment. Therefore, the risk of diseases spreading from wild to farmed fish, with subsequent proliferation within the farm and transmission into the environment, generates great concern.
In salmonid aquaculture, severe problems with respect to parasite exchange between farmed and wild fish have been reported [3,4,5]. Salmonid farming is mainly based on open aquaculture systems (open-net pens, raceways), which exchange water together with other materials, such as chemicals, waste, and a wide range of potential infectious agents with the natural environment (sea, natural streams).
Many oomycetes seem to be ubiquitous in freshwater environments, where they contribute to the structural and functional organization of aquatic ecosystems [6]. However, the introduction of potentially pathogenic oomycete species into lakes and ponds through fish stocking and other anthropogenic activities has been associated with the decline of amphibian [7] and crustacean [8,9] populations.
Infections with oomycetes of the genus Saprolegnia represent one of the main parasitic diseases affecting freshwater-farmed salmonids. Saprolegnia parasitica is of primary importance with respect to infections in fish, while other Saprolegnia species such as S. diclina and S. australis infect fish and their eggs [10,11,12,13]. Saprolegnia species can cause heavy losses in salmonid farming [10,14] and are responsible for the ‘winter kill’ in catfish aquaculture [15]. Although infections are usually more severe in farmed fish than in wild fish [16], Saprolegnia outbreaks have also been reported in the latter [17,18,19,20]. Particularly, high mortality rates were reported in wild populations of brown trout, Salmo trutta, in Spanish rivers [18]. This evidence raised concern about the possible spread of potentially pathogenic Saprolegnia strains from farmed fish to wild populations.
Despite the widespread occurrence of Saprolegnia spp. in wild and aquaculture environments [21], little attention has been directed to understand the distribution and potential transfer of these agents between the farm and its tributary and effluent systems. A recent study [22] on the distribution of Saprolegnia in selected trout farms in Croatia indicated a possible role of trout farms as a source of spreading Saprolegnia spp. into the environment.
Until recently, difficulties in identifying oomycetes up to species level with morphological methods contributed to the lack of knowledge concerning their circulation in different farmed and wild fish [13,23]. The use of molecular techniques, based on amplification and sequencing of the ITS region, and phylogenetic approaches allowed to resolve problems in the identification of oomycetes and to establish DNA-based molecular operational taxonomic units (MOTU) for species delimitation [13].
The aim of this work is to study the distribution and species composition of oomycete assemblage through molecular identification of strains isolated in two different types of salmonid breeding and in their tributary and effluent water systems (trout farms located in Italy and Atlantic salmon farms located in Scotland), in order to: (i) study the diversity and abundance of oomycete species; (ii) evaluate the potential transfer of pathogenic species of Saprolegnia, specifically Saprolegnia parasitica, between wild and farmed fish, and (iii) determine whether there is an impact of salmonid farms on the diffusion of S. parasitica to wild fish in two different types of fish farming.
2. Results
Due to differences in the farmed species and the farming system/environment, the results will be described separately for Italy and Scotland.
2.1. Environmental Parameters
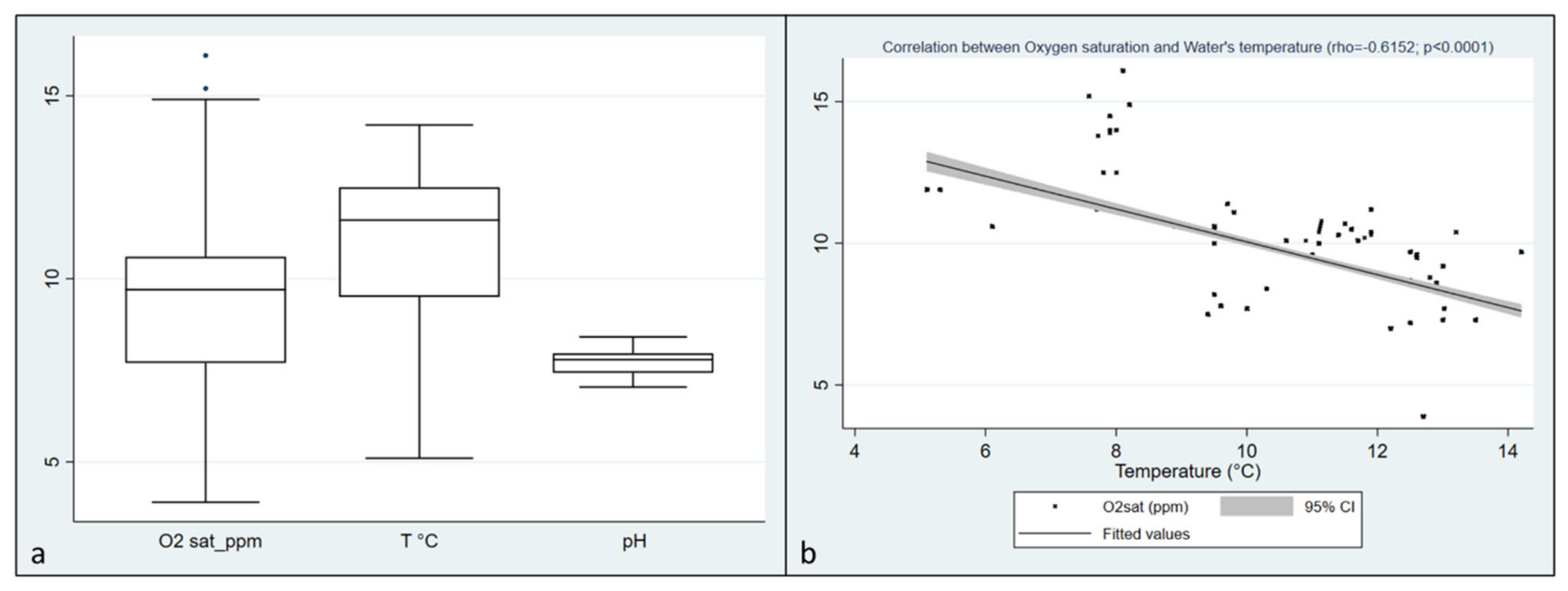
In Italian trout farms, recorded values of Dissolved Oxygen (DO) ranged from 3.9 to 16.8, with a median of 9.7 ppm (IQRs: 7.7–10.6), water temperatures ranged from a minimum of 5.1 to a maximum of 14.2 °C with a median of 11.6 °C (IQRs: 9.5–12.5). Finally, the pH observation revealed a median of 7.79, ranging from 7.05 to 8.41 (IQRs: 7.43–7.96). (Table 1; Figure 1a). A negative correlation was found between Oxygen saturation and water’s temperature (rho = 0.6152, p < 0.0001) (Figure 1b). From the 239 collected fish, 458 single inocula were obtained, and 120 oomycetes strains were isolated. Additionally, 412 isolates were obtained from baits.

Table 1.
Characteristic of the farms considered in Italy and number of samples collected. Coordinates: A = 45°42′57.2” N, 11°40′49.2” E, 84 m a.s.l.; B = 46°32′644” N, 11°12′448” E, 250 m a.s.l; C = 45°54′53” N, 13°4′35” E, 30 m a.s.l.; D = 46°0′34” N, 12°29′38” E, 42 m a.s.l. farmed species: 1 = Oncorhynchus mykiss; 2 = Salmo marmoratus and Salmo trutta water supply: 3 = river; 4 = mixed (river/spring).
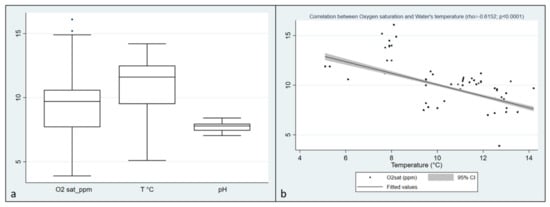
Figure 1.
(a) distribution of Dissolved Oxygen, temperature, and pH values collected during the visits in Italian farms; (b) Correlation between Oxygen saturation and water temperature in Italian farms (rho = 0.6152, p < 0.0001).
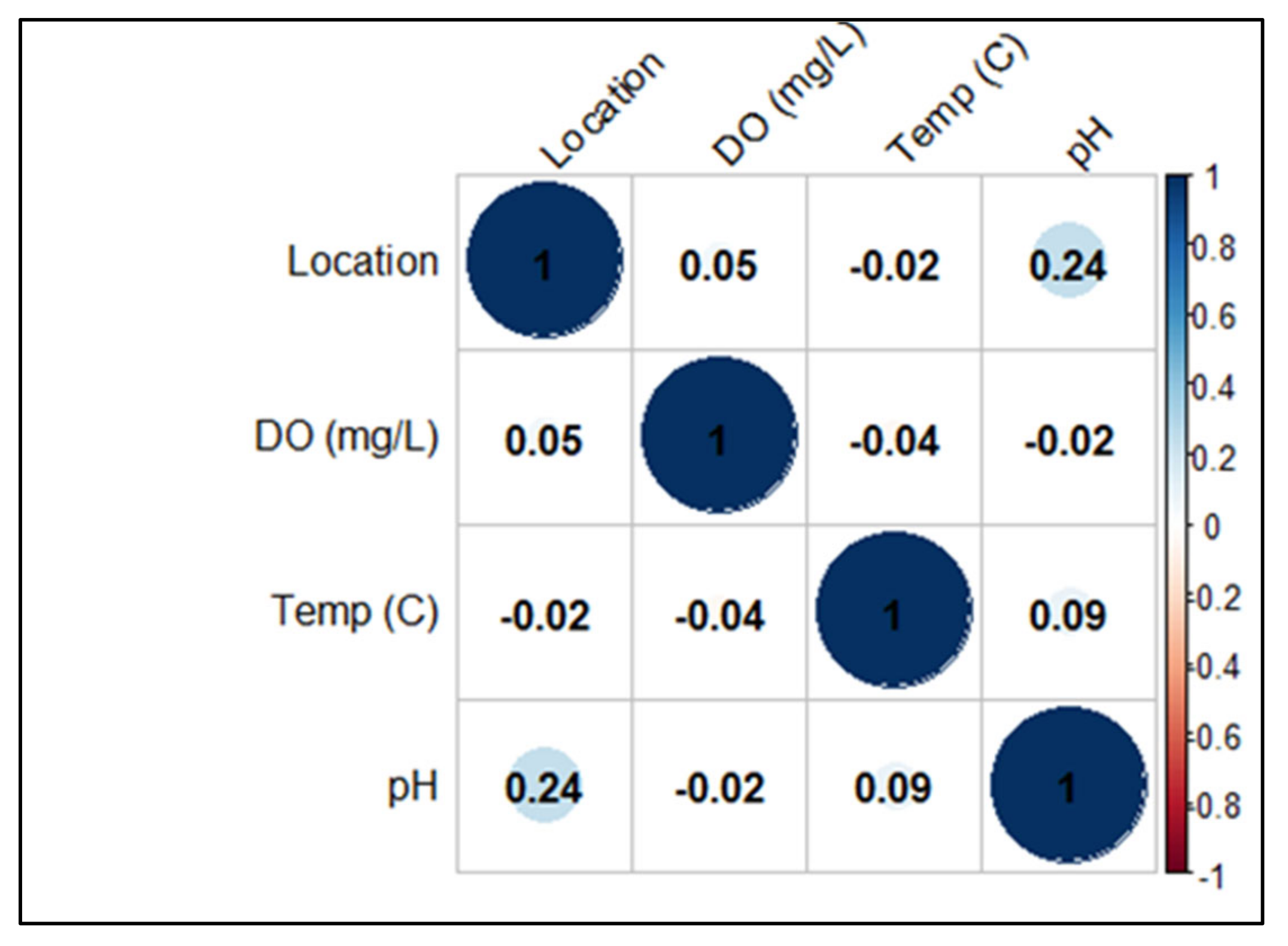
In Scottish salmon farms, water temperature values ranged from 6.1 to 16.7 °C with a median of 10.3 °C (IQRs: 7.3–14.3), pH ranged from 4.5 to 7.9 with a median of 6.9 (IQRs: 6.6–7.2), being more constant at farm G (6.5–7.6), and dissolved oxygen values ranged from 90 to 94 mg/L (IQRs: 91–93) with a median of 92mg/L (Table 2). A negative correlation was found between DO and water temperature (p = 0.04) and between DO and pH (p = 0.02) (Figure 2).

Table 2.
Characteristics of the farms considered in Scotland and number of samples collected. Coordinates: F = 56.966° N 5.134° W, G = 56°58′07″ N 4°54′38″ W; Farmed species: Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar).
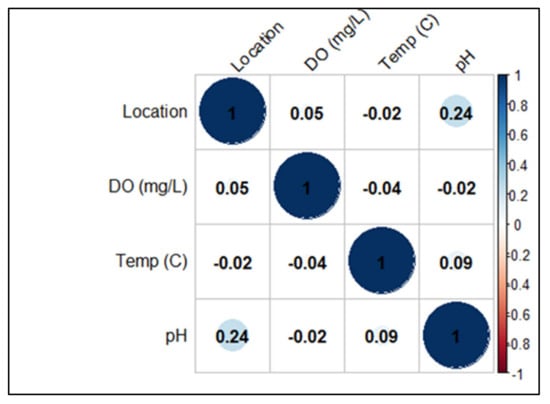
Figure 2.
Pearson’s correlation coefficients calculated considering environmental data from Scottish farms.
From the 200 fish samples collected, 128 oomycetes were obtained. Moreover, 73 oomycetes were collected from hempseeds.
2.2. Oomycetes Diversity
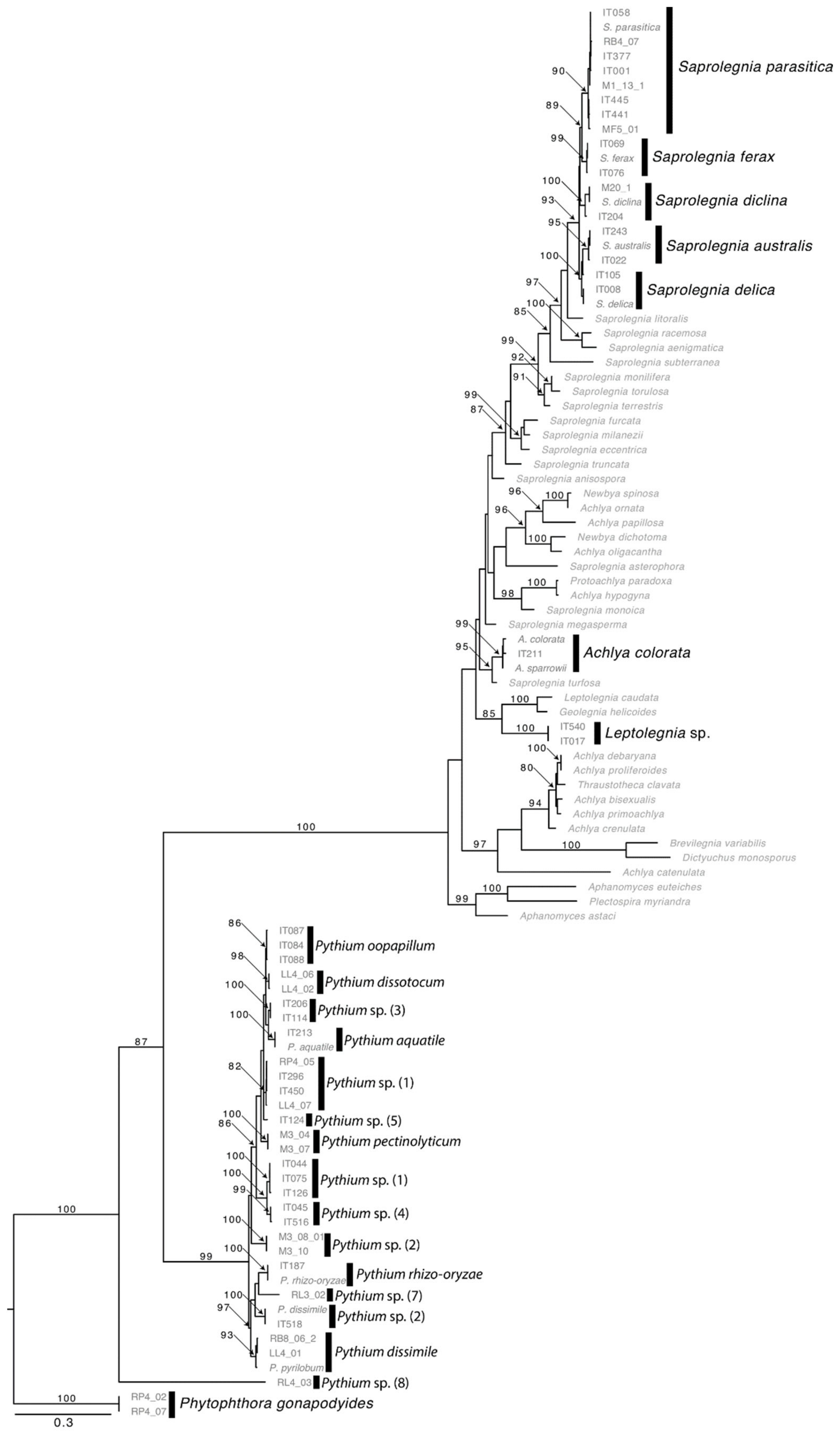
A total of 532 oomycetes isolates from Italy, and 201 from Scotland were identified by phylogenetic and molecular taxonomic analyses; the sequences obtained corresponded to the following MOTUs (Figure 3): Achlya colorata, Saprolegnia australis, Saprolegnia delica, Saprolegnia diclina, Saprolegnia ferax, Saprolegnia parasitica, Pythium aquatile, Pythium dissimile, Pythium rhizooryzae, P. dissotocum, P. oopapillum, P. pectinolyticum and other could only be identified to genus level, e.g., Saprolegnia sp., Leptolegnia sp., Pythium sp.
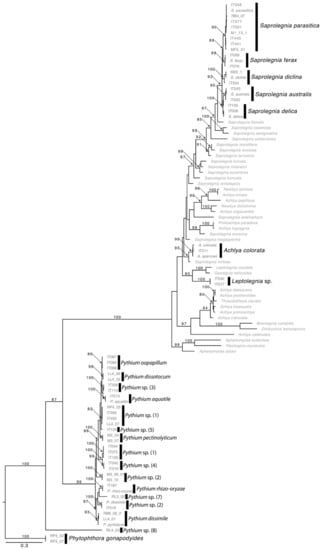
Figure 3.
Maximum Likelihood tree based on ITS nrDNA sequences of oomycetes isolated during the present study with indication of the MOTUs (in bold) identified.
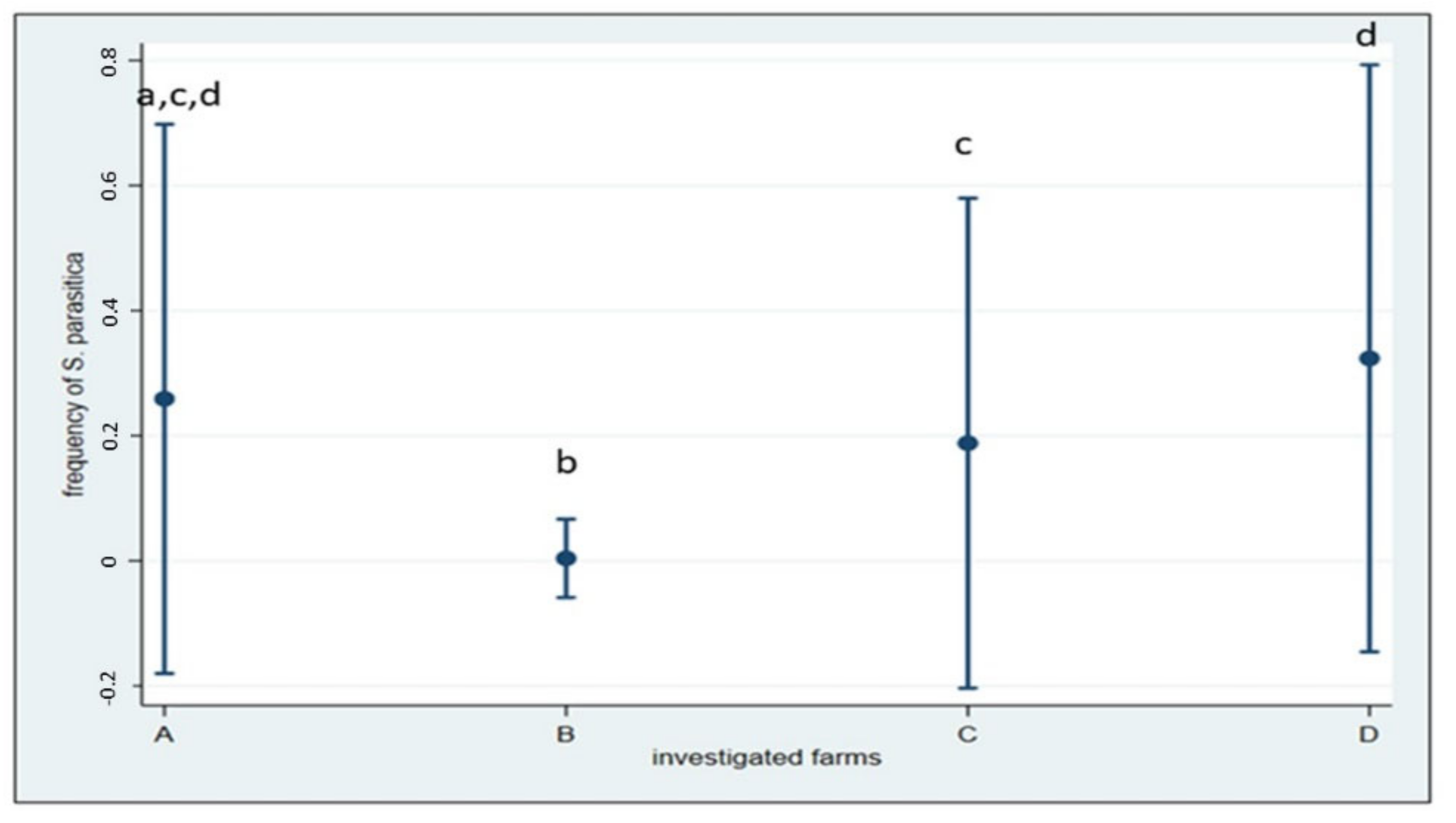
In Italian farms and connected aquatic systems, S. parasitica was isolated from 156 samples (17.9%). The frequency of S. parasitica, both from fish and water, was significantly different among the four surveyed farms (including their surrounding waters) (χ2(3) = 87.58; p < 0.001). Detection proportion ranged from 0.39% (1 positive sample) in farm B to a maximum of 32.4% (58 positive samples) in farm D. In particular, in farm B, where saprolegniosis is not considered a significant problem in farmed O. mykiss, S. parasitica was not isolated from fish upstream and inside the farm, but only from a wild S. trutta without lesions collected about 1 km downstream. Figure 4 shows the distribution of frequencies by farm.
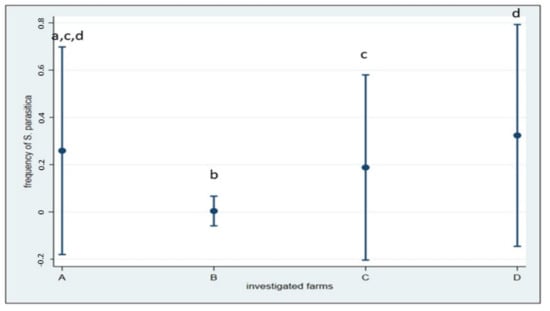
Figure 4.
Frequencies of S. parasitica detected within the four Italian farms and the relative 95% CIs. Pairwise comparisons showed differences between farm A and B; B and C and B and D (Fischer’s exact p < 0.001), and between farm C and D (p = 0.002). Different letters indicate significant difference.
DO did not significantly affect the probability of detecting S. parasitica. On the contrary, it was more frequently detected when water temperatures were colder (H = 10.48; p = 0.001) and with higher pH values (H = 45.58; p < 0.001). Quantitative analysis showed that there was 13% more chance to isolate S. parasitica for each Celsius degree decreased (p = 0.001).
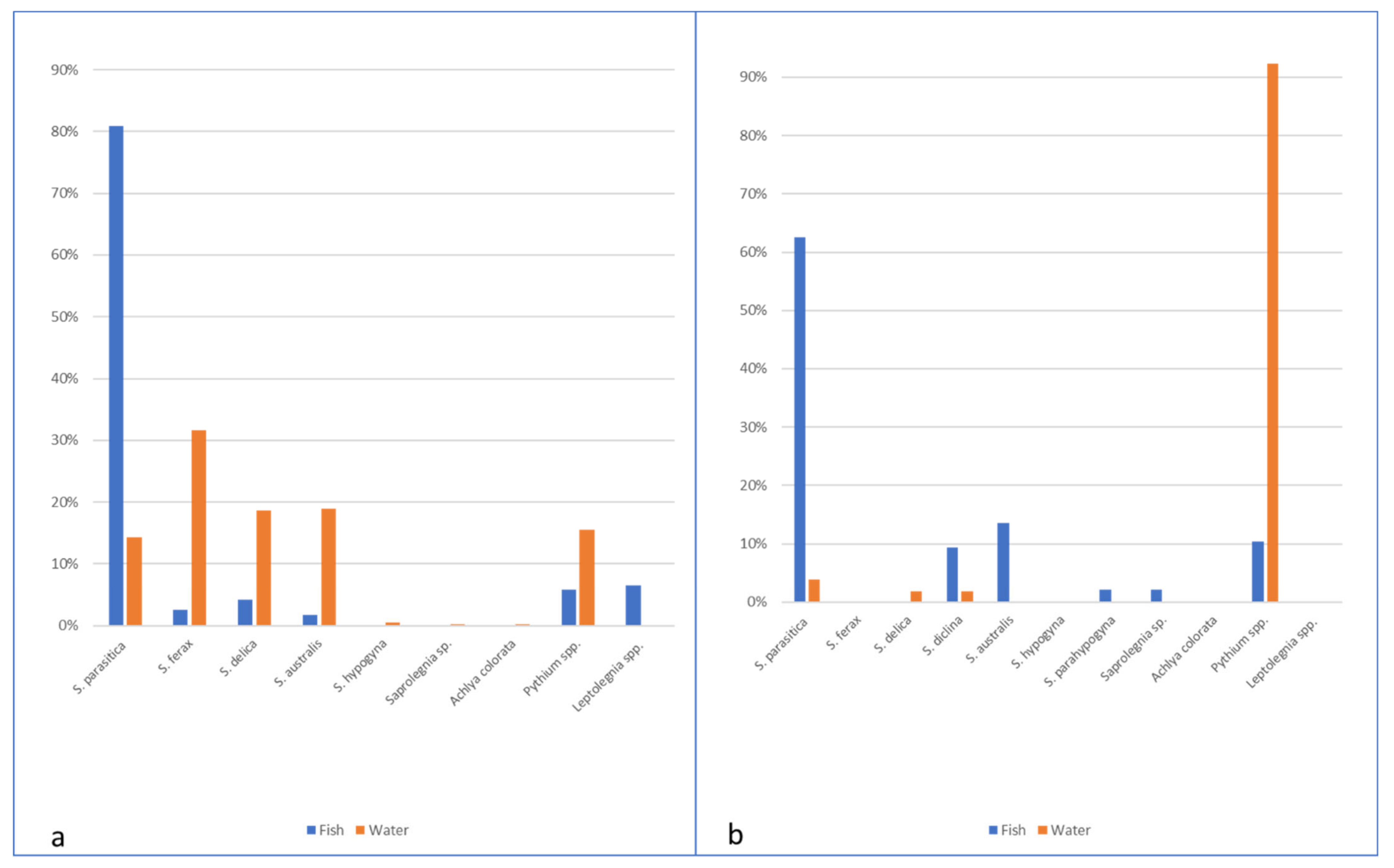
S. parasitica was significantly more frequently isolated from fish (21.2% of the samples) compared to 14.3% of isolates from water baits (χ2 = 6.933, p = 0.008). Indeed, S. parasitica represented 80.8% of the oomycetes isolates from fish, while other species of oomycetes (e.g., S. ferax, S. delica, and S. australis) were more rarely found from different fish species (O. mykiss, S. trutta, and Sq. cephalus) alone or in association with S. parasitica. In eight farmed and wild fish (O. mykiss, S. trutta, Sq. cephalus, and P. fluviatilis), species of the genus Pythium were obtained. Particularly, in one wild S. trutta sampled downstream the farm, Pythium sp. was isolated from fin lesions. Isolates identified as Leptolegnia sp. were obtained in wild fish without lesions (1 O. mykiss, 4 S. trutta, and 1 S. cephalus) sampled downstream in one of the monitored farms. Using baits, a more heterogeneous variety of species was isolated (either from farm, upstream, and downstream water), and S. ferax was predominant (31.6% of the isolates), followed by S. delica and S. australis, while S. parasitica represented only 14.3% of the isolates). In particular, in farm B, Pythium spp. and S. ferax seemed to be prevalent in the aquatic environment, and Pythium sp. was also isolated from fish without lesions (2 farmed O. mykiss, 3 S. cephalus, and 1 P. fluviatilis downstream the farm) (Table 3; Figure 5a).

Table 3.
Oomycete isolates in Italy from water and fish samples.
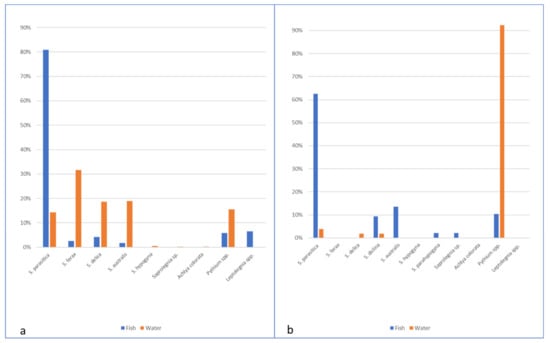
Figure 5.
Species composition of oomycetes isolated from fish and water in Italian (a) and Scottish (b) farms.
In Scottish farms and connected aquatic systems, S. parasitica was significantly more frequently isolated from fish compared to isolates from water baits (p < 0.0001). Indeed, S. parasitica represented 62.5% of the oomycetes isolates from fish, while other species of oomycetes, such as S. diclina or S. australis, were less found (9.3% and 13.54%, respectively). Pythium spp. were also found in fish (10.4%). In contrast with the Italian farms, no S. delica or S. ferax were isolated from fish. Farm F, although without reported saprolegniosis problems, presented a statistically significantly higher number of S. parasitica isolates (41) when compared to Farm G (20) with p = 0.006. This is probably the result of an intensive treatment regime from Farm G. In addition, the species distribution pattern was different between farms, with unique isolates of Saprolegnia sp1 being isolated from farm F and unique S. delica and S. parahypogyna isolates from farm G. Furthermore, a significant number of Pythium spp. isolates was obtained at farm G compared to farm F. In water, a diversity of Pythium spp. was isolated, representing 92.30%, followed by S. parasitica, S. delica and S. diclina. A reduced number of isolates was obtained at fish farms with only Pythium spp.; this is possibly due to the treatments carried out at the farm and the daily removal of mort’s. Upstream the fish farms, the only Saprolegnia species isolated was S. parasitica, while downstream only S. delica and S. diclina were isolated (Figure 5b, Table 4). No statistically significant difference was found between the water collection sites.

Table 4.
Oomycete isolates in Scotland from water and fish samples.
2.3. Transfer of Saprolegnia parasitica between Wild and Farmed Fish and Impact of Salmonid Farms on the Spread of S. parasitica to Wild Fish
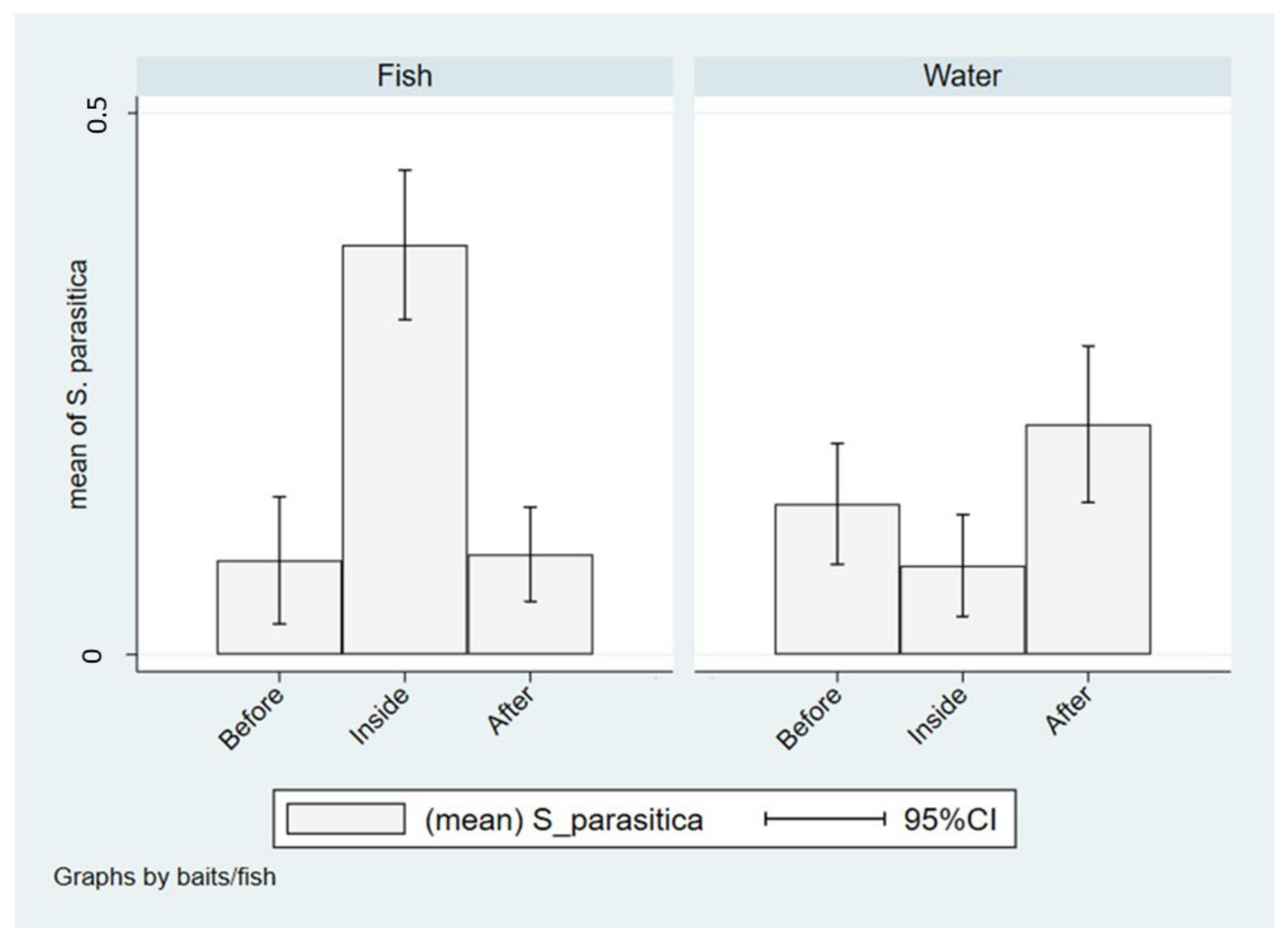
In Italian farms, the isolation of S. parasitica was significantly higher in farmed fish than in wild fish from both upstream and downstream waters (χ2(2) = 55.37, p < 0.001), while no differences were found between wild fish captured upstream and downstream. On the contrary, the presence of S. parasitica in water, assessed through the use of baits, was significantly lower in farms compared to outside (χ2(2) = 9.085; p = 0.011) with particular references to downstream (Figure 6).
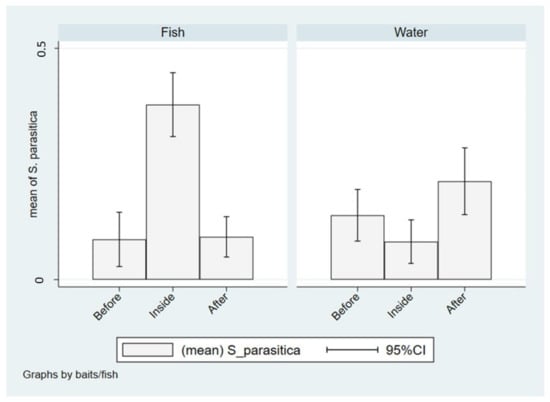
Figure 6.
Isolation of S. parasitica in fish and water from upstream (before), in-farm (inside) or downstream (after) sampling sites in Italy.
The quantitative analysis remarks these differences, showing six times less chance to isolate S. parasitica in wild fish from upstream and downstream compared to farmed fish (p < 0.001), while when the isolation was made from waters using baits, it was three times more likely to detect S. parasitica downstream compared to in-farm (OR: 3.02; p = 0.004), whereas no significant difference was found when in-farm and upstream were considered (p = 0.132). These results are also summarized in Table 5.

Table 5.
Probability to isolate S. parasitica upstream or downstream the Italian farms compared to the in-farms baseline based on different sources and how the chance to isolate S. parasitica changes as a function of the water temperature. * Odds ratio is reported as the inverse (1/OR).
3. Discussion
3.1. Oomycetes Diversity
Overall, a high number of oomycete isolates were obtained from fish and baits in the Italian and Scottish farms under study.
Particularly, for Italian farms, the results obtained by culture/isolation of Oomycetes from water showed that hempseed baits allow the isolation of Saprolegnia spp., including S. parasitica, and other oomycete species from water in a very efficient way. Although S. parasitica is more frequently isolated from fish, our findings highlight the usefulness of environmental baits to isolate Saprolegnia spp. and other oomycetes during epidemiological studies, allowing to reduce the sampling of fish. Besides representing a useful tool to avoid invasive techniques in fish, the use of hempseed baits allows overcoming problems deriving from difficulties in sampling wild fish. For example, in Italy, in the upstream water system of farm B, only a few specimens of protected fish species were present; in farm A, in rainy periods the use of electrofishing was not feasible, and angling is difficult; in farm C, that receives the water from a spring, very few wild fish were present upstream.
Saprolegnia species other than S. parasitica isolated in the present study (S. delica, S. australis, S. ferax, and S. turfosa), mainly through the use of baits, are often considered as part of the aquatic ecosystem and of lower importance for farming activities [21]. However, these species may also affect the aquatic fauna: particularly, S. ferax was involved, together with S. diclina, in mortalities of amphibian embryos [24]. Results of an experimental study [25] suggested that the transfer of S. ferax from restocked rainbow trout to wild amphibians was a possible cause of the decline of Bufo boreas populations, although few scientific data are available to support this hypothesis.
Leptolegnia species are often isolated from arthropods exuviae or from mosquito larvae [26]. Interestingly, in the present study, Leptolegnia was only found in six wild fish collected downstream the farm A; its isolation might be linked to the abundant presence of amphipod crustaceans in this environment. These amphipods are intermediate hosts of the swim-bladder nematode Cystidicola farionis and several acanthocephalans, parasites often encountered in trout cultured in farm A and may also be vectors of Leptolegnia spp. for other crustaceans and fish. However, no lesions associated with Leptolegnia were detected in the six positive fish.
Among all the farms taken into consideration in this survey, farm B was unique since it has a constant temperature of around 12 °C throughout the year, since the water originates from a brook approximately 600 m long, with particular environmental conditions (shallow water, constant temperature, abundant presence of algae, and low amount of dissolved oxygen), populated mainly by crayfish. The species composition of the oomycete assemblage may also be peculiar to this specific environment since, in this farm, a higher proportion of Pythium spp. was isolated. This genus, included within the order Peronosporales, comprises more than 200 species that are ubiquitous in soil or represent important plant pathogens [27]. However, they are also found in the aquatic environment [6], where they are isolated from animal and vegetal organisms. Particularly, several species of Pythium are found growing on dead specimens of freshwater crustaceans, where they contribute to the decomposition of chitin carapaces [28].
Both Scottish Atlantic salmon farms used in this study are loch sites with more than 60 m depth. Both areas are predominantly rural with moorland ridges, rocky outcrops, mosaics of heather, and grass with woodland, including forest plantations on some mid and lower slopes. Loch temperatures tend to be warmer in winter and colder in summer than adjacent rivers, showing the greatest variability in summer, taking longer to respond to seasonal temperature changes and rainfall events due to larger water volume. Lochs also have slightly acidic waters due to underlying geology. Due to all these adjacent conditions and Pythium spp. lifestyle (as mentioned above), the probability of isolating it from the water is high. Nevertheless, a variety of Pythium spp. were also isolated from fish. Its role in fish infection is unknown. Unique isolates of Saprolegnia sp1 were isolated from farm F, and unique S. delica and S. parahypogyna isolates from farm G. This might be due to host stage specificity of these pathogens since farm F possessed smolts, while farm G possessed parr and smolts. Interestingly, on farm F, which does not have recurrent saprolegniosis issues but treats fish prophylactically, a higher number of S. parasitica isolates were obtained from fish compared to farm G. Moreover, within the farms, S. parasitica was isolated almost exclusively from fish and not from water. At downstream sites, not many oomycetes’ isolates were obtained. Again, this might be due to the recurrent water treatment against saprolegniosis.
3.2. Transfer of Saprolegnia parasitica between Wild and Farmed Fish and Impact of Salmonid Farms on the Spread of S. parasitica to Wild Fish
Concerning the assessment of potential transfer and impact of salmonid farms on the spread of Saprolegnia to wild fish, the evaluation of the data collected in Italy must consider that the frequency of S. parasitica isolation, from both fish and water, was significantly different among the four surveyed farms, highlighting how the different environmental and managerial conditions can influence the presence and multiplication of this oomycete. A careful interpretation of the results of this survey should consider potential biases associated with the fact that several wild fish sampled upstream and downstream of the farms could have been introduced for restocking from other farms. In particular, farm A has affluent and effluent water within an irrigation channel system of Brenta River, where restocking with the allochthonous species O. mykiss is allowed because the channels are periodically drained and emptied. In this farm, although S. parasitica has always been isolated from cultured fish, it has never been isolated from wild fish downstream the farm but only from baits. It was isolated upstream from one “wild” O. mykiss with lesions that had been caught just before the grids of the farm. With respect to farm B, only one wild S. trutta without lesions was found positive to S. parasitica at about 1 km downstream the farm, in a channel where fish are often introduced for restocking. S. parasitica has never been isolated from O. mykiss in farm B, and no problems have been reported by the farm manager for several years. Concerning the sampling sites C and D, when S. parasitica was isolated from farmed fish, it was also always isolated from downstream fish. Upstream from these farms, Saprolegnia presence was almost always detected mainly through the hempseed baits, as some difficulties in sampling wild fish were often encountered at these sites. Nevertheless, the wild fish positive for S. parasitica, which were collected upstream and downstream the farms in most cases, were without lesions, except for one wild S. trutta upstream and one S. trutta downstream farm C and six wild S. trutta downstream farm D, which showed lesions with S. parasitica.
An interesting fact emerges from the statistical analysis of overall isolates obtained from Italian farms: S. parasitica was significantly more isolated in farmed fish than in wild fish, without differences between upstream and downstream sites; this is in accordance with the general principle that higher density of fish and other stressful factors associated with the farming environment may increase the colonization of S. parasitica in the fish host [29,30,31]. On the contrary, the presence of S. parasitica in water, determined by using baits, was significantly higher in the wild than within the farm and was particularly higher in downstream waters, although differences with upstream waters were not significant. Such finding would suggest that, with respect to the production systems surveyed in Italy, the farming of fish exhibiting overt signs of saprolegniosis could increase the dispersal of spores in water; on the other hand, this phenomenon does not seem to negatively affect wild fish populations, possibly due to the lack of potential predisposing factors (e.g., high stocking density, fish handling).
In Scotland, the frequency of S. parasitica isolation, from both fish and water, was significantly different among the two surveyed farms, highlighting how the different handling conditions can influence the presence and multiplication of this oomycete, namely treatment regime, and handling associated with it. Although farm G had recurrent saprolegniosis issues, only a few Saprolegnia spp. isolates were obtained downstream of it. S. parasitica seemed to be concentrated on the fish itself, suggesting that this species is attracted to Atlantic salmon, a more susceptible species to saprolegniosis than trout, and due to high fish densities and fish stressors, it multiplies. Since no wild fish was sampled, due to conservation restrictions, we cannot make conclusions regarding the possibility of S. parasitica spread from farmed to wild fish. Nevertheless, no significant difference was found between samples collected from the different water sites.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Areas
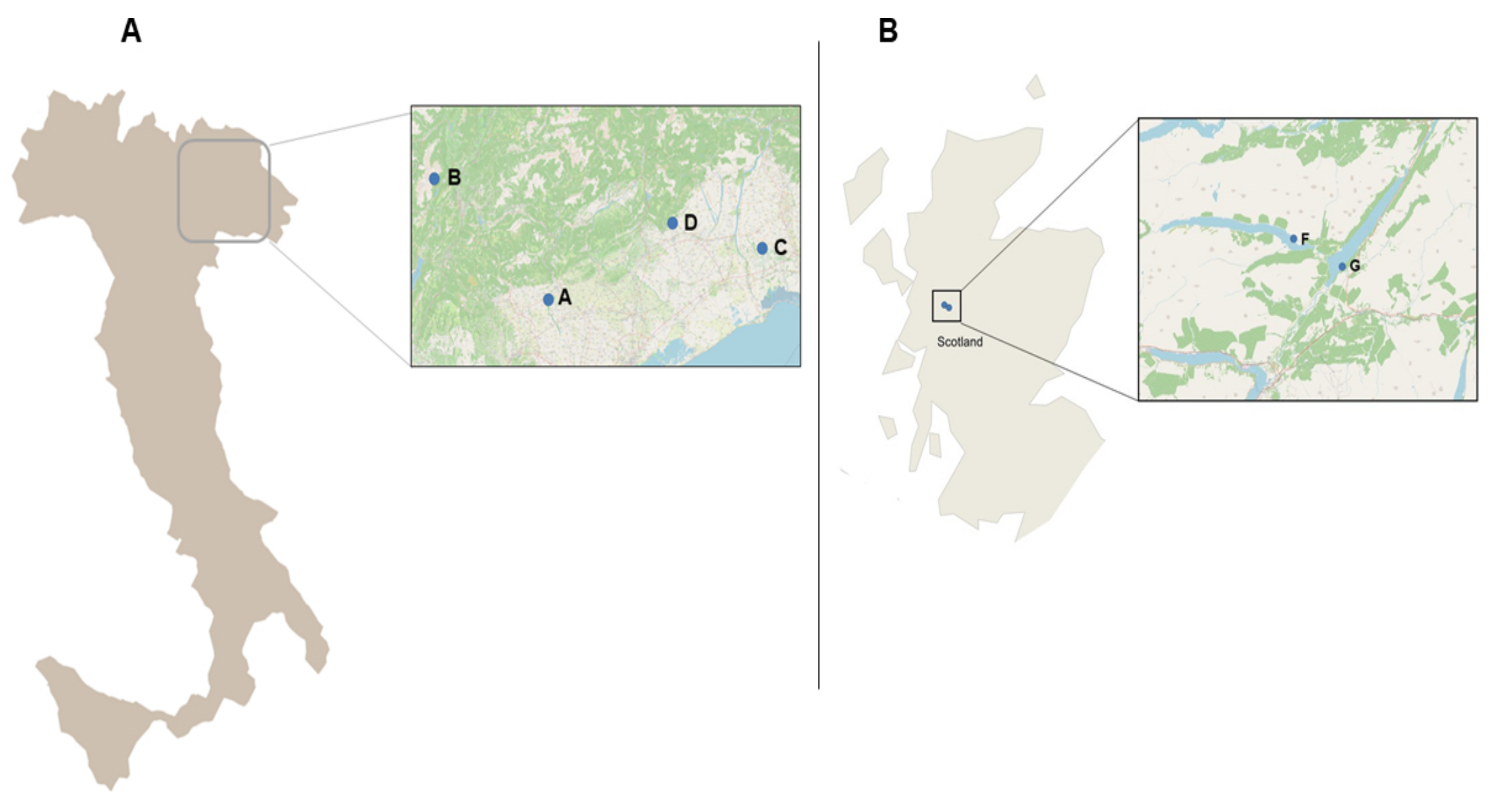
For the part of the study carried out in Italy, four trout farms were considered (Figure 7A). In these farms, fish is cultured in concrete tanks in raceway systems that collect water from natural water bodies (river, spring, mixed water source) and discharge untreated effluents back into the environment. Cultured species include the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (RBT), the brown trout Salmo trutta (BT), and the marble trout Salmo marmoratus (MT).
Figure 7.
Farms considered for the study. (A) Farms’ location in Italy, (B) Farms’ location in Scotland.
For the part carried out in Scotland, two Atlantic salmon Salmo salar (AS) farms were considered (Figure 7B). In these farms, fish is cultured in an open-net pens system.
4.2. Collection of Fish and Water Samples
In Italian farms, sample collection was carried out in three periods: (i) November to December 2015, (ii) February to March 2016, and (iii) November to December 2016; these periods were selected due to the higher infection rates with Saprolegnia reported by fish farmers in the area. During each period, ten cultured fish, preferably with lesions referable to Saprolegnia, were collected in each farm, possibly from different tanks/earth ponds where affected batches were observed. At the same times, up to 10 wild fish upstream and downstream from each farm belonging to different species (RBT, BT, MT, Squalius cephalus, Perca fluviatilis, Scardinius erythrophthalmus) were collected by electrofishing or angling. Overall, 239 fish (46 from upstream, 105 from farms, 88 from downstream) were collected. During the first two sampling periods in each tank/earth pond or water system, upstream, inside, and downstream the farm where fish were sampled, five traps (homemade tea balls) were placed, each containing seven sterile halves of boiled hempseed as baits (prepared according to Seymour [32]). The traps were left for at least 10 days and then retrieved. In total, 412 baits (151 from upstream, 134 from farm, 127 from downstream) were collected and used for oomycetes isolation. Information about Dissolved Oxygen (DO) expressed in part per million (ppm), pH, temperature (°C) of the waters was collected, before, within, and after the farms at the time of sampling and at the time of traps retrieval.
In Scotland, sampling of the water and farmed AS was carried out on a monthly basis in the two farms for 10 months (Feb-Nov 2016). During each sampling, ten fish per farm were collected randomly from inside the pen. Water samples were collected in 24-well plates with one hempseed on each well in each pen where fish were sampled and in the upstream (2 m before) and downstream (2 m after) water systems.
Water temperature, pH, and DO expressed in mg/L were recorded in each sampling location at the time of sampling.
4.3. Oomycetes Isolation
Oomycete isolates from Italy were obtained from clinically infected fish (two tufts of mycelia from two different fish lesions) from fish without lesions (a piece of gills and a piece of skin at the base of the dorsal fin) and from each hempseed bait. Each sample was dipped briefly in absolute ethylic alcohol, washed with sterile saline solution, and placed onto glucose-yeast extract agar supplemented with penicillin G (6 mg/L) and oxolinic acid (10 mg/L) [33] (GY+P+OX) plates. Isolates were incubated at 18 °C and re-cultured until pure cultures were obtained.
A pectoral fin and skin close to the operculum were excised to obtain the Scottish fish isolates and placed into Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) supplemented with ampicillin (500 mg/L), vancomycin (100 mg/L), and pimaricin (20 mg/L) incubated at 12 °C and re-cultured until pure cultures were obtained. The water samples were distributed in 24-well plates with hempseeds and incubated at 12 °C for 2 weeks or until visible growth was observed. Colonized hemp seeds were then placed into PDA supplemented media and incubated at 12 °C and re-cultured until pure cultures were obtained.
4.4. DNA Extraction and PCR Conditions
Single spore isolates from both Italy and Scotland were obtained in order to carry out DNA extraction and amplification, as described in Sandoval-Sierra and Diéguez-Uribeondo [23]. DNA extraction was carried out by using the DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA). The internal transcribed spacer region (ITS) was amplified using universal primers for eukaryotes ITS5 and ITS4 [34] under the conditions illustrated in Sandoval-Sierra et al. [13]. Amplified products were sequenced using an automated sequencer (Applied Biosystems 3730xl DNA, Macrogen, The Netherlands). For each isolate, the consensus sequences for the ITS region were assembled and edited using the program Geneious v6.14 [35].
4.5. Molecular Identification of Species
For molecular identification of isolates to the species level, the ITS rDNA sequences obtained from all isolates were merged with Saprolegnia reference sequences according to Sandoval-Sierra et al. [13] using the software Geneious v10.0.9. The resulting sequences and Saprolegnia reference sequences were aligned using Mafft version 7.2 [36] and the algorithm G-INS-I [37,38]. The sequences were analyzed using the Maximum Likelihood model, and the isolates were assigned to species based on reference sequences for molecular operational taxonomic units (MOTUs) described by Sandoval-Sierra et al. [13]. Maximum Likelihood analysis was carried out using the software RaxML v8.1 [39]. For this analysis, the random starting tree was selected. Clade support was assessed with 1000 bootstrap replicates after selecting the best tree from 100 trees generated.
4.6. Statistical Analysis
In Italian farms where both fish and water samples were obtained from upstream, inside, and downstream sites, statistical analyses were carried out to evaluate the potential transfer of the pathogenic species S. parasitica, between wild and farmed fish and determine the potential impact of salmonid farms on the diffusion of S. parasitica to wild fish. The environmental data collected at the time of the visit and the results of oomycetes isolation and molecular identification were entered into a MS Excel spreadsheet and then imported into Stata 15 (StataCorp LLC, College Station, TX, USA) for statistical analyses. The distributions of environmental parameters were assessed by using the Shapiro–Wilk’s test for normality, median and interquartile ranges (IQRs) were reported as continuous variables were not normally distributed. Comparisons among S. parasitica isolates obtained from fish and baits in all the sampling sources (before, within, and after) and other categorical independent variables were computed by using Pearson’s χ2 considering the Fischer’s exact p-value when more than 20% of the cells had expected frequencies < 5 [40]. The Kruskal–Wallis non-parametric test was carried out when non-normally distributed continuous variables were involved. Odds Ratios (ORs) or inverse ORs (1/OR), when the OR is <1, and relative 95% Confidence Intervals (CIs) were also assessed to evaluate how the sampling sites, the sampling sources, and temperature affected the probability to isolate S. parasitica. The results were considered to be significant when p ≤ 0.05.
In Scottish farms, water samples were obtained from upstream, inside, and downstream sites, while fish were collected only from farms. The distributions of environmental parameters were assessed by using Shapiro–Wilk’s test for normality, median and interquartile ranges (IQRs) were reported as continuous variables were not normally distributed. Environmental parameters correlation was assessed by Pearson’s correlation using R. Comparisons among S. parasitica isolates obtained from fish and baits in all the sampling sources, and other categorical independent variables were computed by using Pearson’s χ2 using GraphPad. The Kruskal–Wallis non-parametric test was carried out when non-normally distributed continuous variables were involved.
5. Conclusions
Although genotyping of S. parasitica strains and other isolated oomycetes is necessary in order to assess their real circulation among upstream/farm/downstream systems, the results obtained in the present study seem to indicate that the interactions of Saprolegnia between wild and farmed fish are quite complex and might be influenced by anthropogenic interventions.
Specifically concerning S. parasitica, its occurrence seems mainly related to the presence of susceptible fish, as emerged from the results of isolations carried out in Italian farm B and the Scottish farms. When fish are present upstream of the farm, they can maintain the parasite in the environment and favor its spread to the farmed fish. In this regard, recommendations for reducing the transmission of oomycetes from wild fish to farms include avoiding the restocking in rivers with fish from infected farms. The typical conditions of salmonid farms, such as high biomass density, frequent handling of fish for grading and reproduction, and other predisposing factors, can favor Saprolegnia infection and pathology in the farmed population, with the multiplication of the parasite and increased release of spores into the wild. Therefore, although in our study we did not detect an effect of salmonid farms in increasing the spread of Saprolegnia to wild fish, such impact cannot be excluded, as pointed out also by Pavic et al. [22] in Croatia.
In order to avoid a massive spread of infective stages of Saprolegnia spp. to the downstream water environment and wild populations, general recommendations to salmonid farmers should mainly rely on the application of good management practices aimed at reducing the oomycete load in the farm (e.g., early and frequent removal of clinically infected fish from the tanks/cages).
The increased sustainability of fish farming activities and the protection of wild fish populations would benefit commercial and recreational fisheries. Particularly, a reduction in wild/farmed interactions would contribute to reducing the antagonism between wild fishery and aquaculture stakeholders emerging from the conflict of interests between different users. In this framework, the knowledge generated in the present study will inform the development of European policies aimed at protecting the health of wild aquatic animal populations while promoting responsible use of the aquatic environment for aquaculture purposes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization M.L.F., J.D.-U., R.G. and P.v.W.; methodology, M.L.F., J.D.-U., P.v.W. and R.G.; formal analysis B.M. and M.S.; investigation P.T., M.S., J.V.S.-S. and R.G.; resources, M.L.F., J.D.-U. and P.v.W.; data curation P.T., M.S., J.V.S.-S. and R.G.; writing—original draft preparation P.T., M.S., R.G. and B.M.; writing—review and editing All Authors; supervision M.L.F., J.D.-U., P.v.W. and R.G.; project administration M.L.F., J.D.-U. and P.v.W.; funding acquisition M.L.F., J.D.-U. and P.v.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 634429. This publication reflects the views only of the author, and the European Commission cannot be held responsible for any use, which may be made of the information contained therein.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the fish farmers/staff, veterinarians, biologists and local authorities who collaborated in the sample collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Johansen, L.H.; Jensen, I.; Mikkelsen, H.; Bjørn, P.A.; Jansen, P.A.; Bergh, Ø. Disease interaction and pathogens exchange between wild and farmed fish populations with special reference to Norway. Aquaculture 2011, 315, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krkošek, M. Host density thresholds and disease control for fisheries and aquaculture. Aquac. Environ. Int. 2010, 1, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krkošek, M.; Lewis, M.A.; Volpe, J.P. Transmission dynamics of parasitic sea lice from farm to wild salmon. Proc. R. Soc B Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krkošek, M.; Lewis, M.A.; Morton, A.; Frazer, L.N.; Volpe, J.P. Epizootics of wild fish induced by farm fish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15506–15510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krkošek, M.; Ford, J.S.; Morton, A.; Lele, S.; Myers, R.A.; Lewis, M.A. Declining wild salmon populations in relation to parasites from farm salmon. Science 2007, 318, 1772–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čomić, L.; Ranković, B.; Novevska, V.; Ostojić, A. Diversity and dynamics of the fungal community in Lake Ohrid. Aquat. Biol. 2010, 9, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaustein, A.R.; Wake, D.B.; Sousa, W.P. Amphibian declines: Judging stability, persistence, and susceptibility of populations to local and global extinctions. Conserv. Biol. 1994, 8, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestrup, Å.M.; Thomas, S.H.; van Rensburg, K.; Ricciardi, A.; Duffy, M.A. Differential infection of exotic and native freshwater amphipods by a parasitic water mold in the St. Lawrence River. Biol. Invasions 2011, 13, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezinciuc, S.; Sandoval-Sierra, J.V.; Oidtmann, B.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. The biology of crayfish plague pathogen Aphanomyces astaci: Current answers to most frequent questions. In Freshwater Crayfish—A Global Overview; Kawai, T., Faulkes, Z., Scholtz, G., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 182–204. [Google Scholar]
- Van West, P. Saprolegnia parasitica, an oomycete pathogen with a fishy appetite: New challenges for an old problem. Mycologist 2006, 20, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diéguez-Uribeondo, J.; Fregeneda-Grandes, J.M.; Cerenius, L.; Pérez-Iniesta, E.; Aller-Gancedo, J.M.; Tellería, M.T.; Söderhäll, K.; Martín, M.P. Re-evaluation of the enigmatic species complex Saprolegnia diclina–Saprolegnia parasitica based on morphological, physiological and molecular data. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2007, 44, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezinciuc, S.; Sandoval-Sierra, J.V.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. Molecular identification of a bronopol tolerant strain of Saprolegnia australis causing egg and fry mortality in farmed brown trout, Salmo trutta. Fungal Biol. 2014, 118, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval-Sierra, J.V.; Martín, M.P.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. Species identification in the genus Saprolegnia (Oomycetes): Defining DNA-based molecular operational taxonomic units. Fungal Biol. 2014, 118, 559–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatai, K.; Hoshiai, G. Mass mortality in cultured coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) due to Saprolegnia parasitica coker. J. Wildl. Dis. 1992, 28, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bly, J.E.; Lawson, L.A.; Dale, D.J.; Szalai, A.J.; Durburow, R.M.; Clem, L.W. Winter saprolegniosis in channel catfish. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1992, 13, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, R.H.; Pickering, A.D. Frequency and distribution patterns of Saprolegnia infection in wild and hatchery-reared brown trout Salmo trutta L. and char Salvelinus alpinus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 1978, 1, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.A. Ecology of an annual Saprolegnia sp. (Phycomycete) outbreak in wild brown trout. Verh. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. Verh. 1975, 19, 2456–2460. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, F.; Villena, A.; Zapata, A.; Razquin, B. Histopathology of the thymus in Saprolegnia-infected wild brown trout, Salmo trutta L. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1995, 47, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diéguez-Uribeondo, J.; Cerenius, L.; Söderhäll, K. Physiological characterization of Saprolegnia parasitica isolates from brown trout. Aquaculture 1996, 140, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Rodriguez, C.; Barberis, C.; Astoreca, A.; Brol, G. Registro de saprolegniasis en ejemplares silvestres de pejerrey Odontesthes bonariensis (Pisces: Atherinopsidae) de Argentina. Braz. J. Vet. Med. 2010, 32, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- De la Bastide, P.Y.; Leung, W.L.; Hintz, W.E. Species composition of the genus Saprolegnia in fin fish aquaculture environments, as determined by nucleotide sequence analysis of the nuclear rDNA ITS regions. Fungal. Biol. 2015, 119, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavić, A.; Miljanović, D.; Grbin, Š.L.; Vladušić, T.; Galuppi, R.; Tedesco, P.; Bielen, A. Identification and molecular characterization of oomycete isolates from trout farms in Croatia, and their upstream and downstream water environments. Aquaculture 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Sierra, J.V.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. A comprehensive protocol for improving the description of Saprolegniales (Oomycota): Two practical examples (Saprolegnia aenigmatica sp. nov. and Saprolegnia racemosa sp. nov.). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132999. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Benéitez, M.J.; Ortiz-Santaliestra, M.E.; Lizana, M.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. Saprolegnia diclina: Another species responsible for the emergent disease ‘Saprolegnia infections’ in amphibians. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 279, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesecker, J.M.; Blaustein, A.R.; Belden, L.K. Complex causes of amphibian population declines. Nature 2001, 410, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalva, C.; dos Santos, K.; Collier, K.; Rocha, L.F.; Fernandes, É.K.; Castrillo, L.A.; Luz, C.; Humber, R.A. First report of Leptolegnia chapmanii (Peronosporomycetes: Saprolegniales) affecting mosquitoes in central Brazil. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 136, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Plaats-Niterink, A.J. Monograph of the Genus Pythium; Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures: Baarn, NL, USA, 1981; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Czeczuga, B.; Kozłowska, M.; Godlewska, A. Zoosporic aquatic fungi growing on dead specimens of 29 freshwater crustacean species. Limnologica 2002, 32, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pickering, A.D.; Willoughby, L.G. Saprolegnia infections of salmonid fish. In Microbial Diseases of Fish; Roberts, R.J., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: London, UK, 1982; pp. 271–297. [Google Scholar]
- Toor, H.S.; Sehgal, H.; Sehdev, R.S. A case study of acute fish diseases in tanks loaded with high levels of organic manures. Aquaculture 1983, 35, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, M.; Muñoz, M.J. Effect of sublethal concentrations of four chemicals on susceptibility of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to saprolegniosis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, R.L. The genus Saprolegnia. Nova Hedwig. 1970, 19, 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Alderman, D.J.; Polglase, J.L. A comparative investigation of the effects of fungicides on Saprolegnia parasitica and Aphanomyces astaci. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1984, 83, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.D.; Lee, S.B.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Toh, H. Improved accuracy of multiple ncRNA alignment by incorporating structural information into a MAFFT-based framework. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Toh, H. Recent developments in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Brief. Bioinform. 2008, 9, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y. Statistical notes for clinical researchers: Chi-squared test and Fisher’s exact test. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2017, 42, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).