Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia—The First Case Report and Brief Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
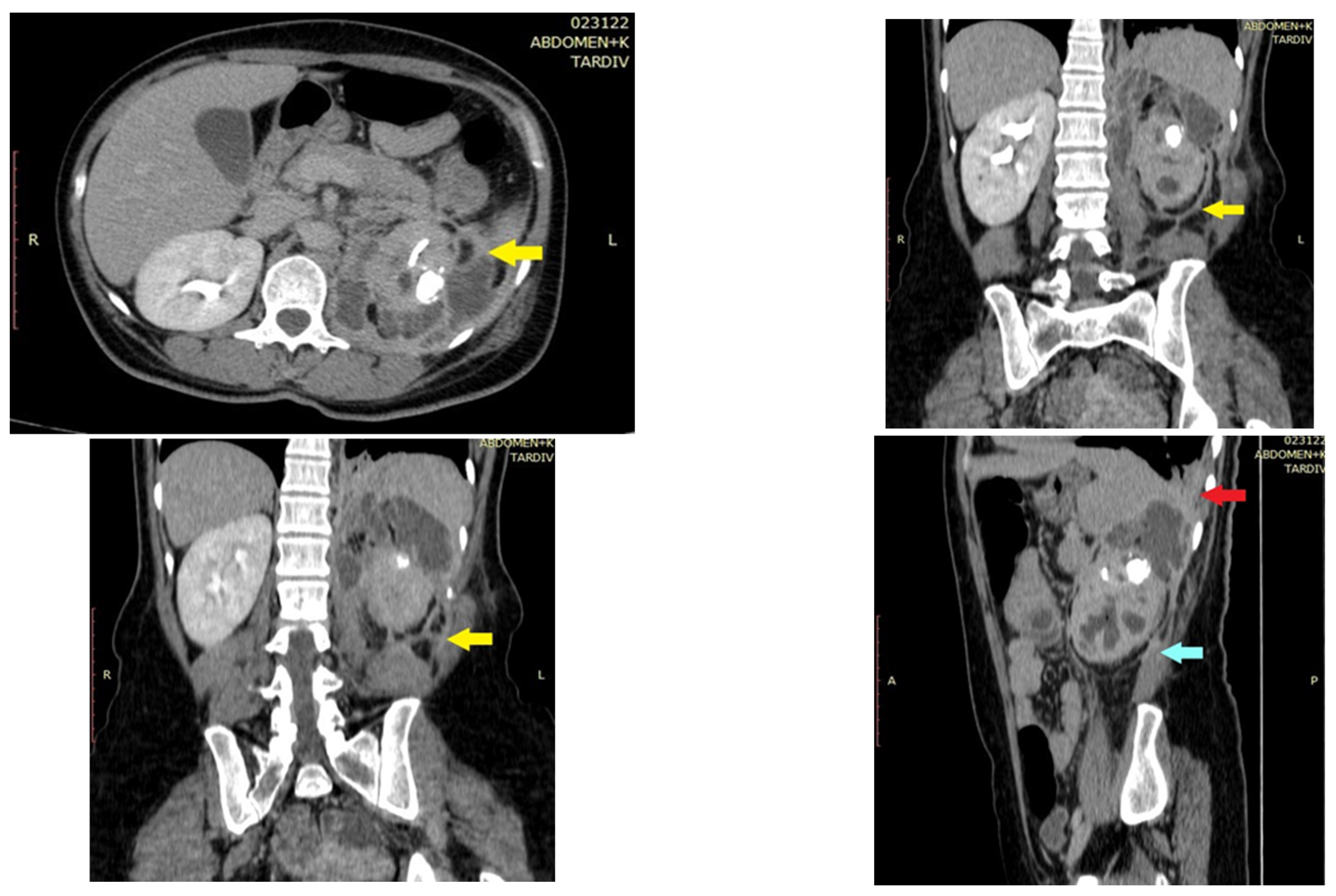
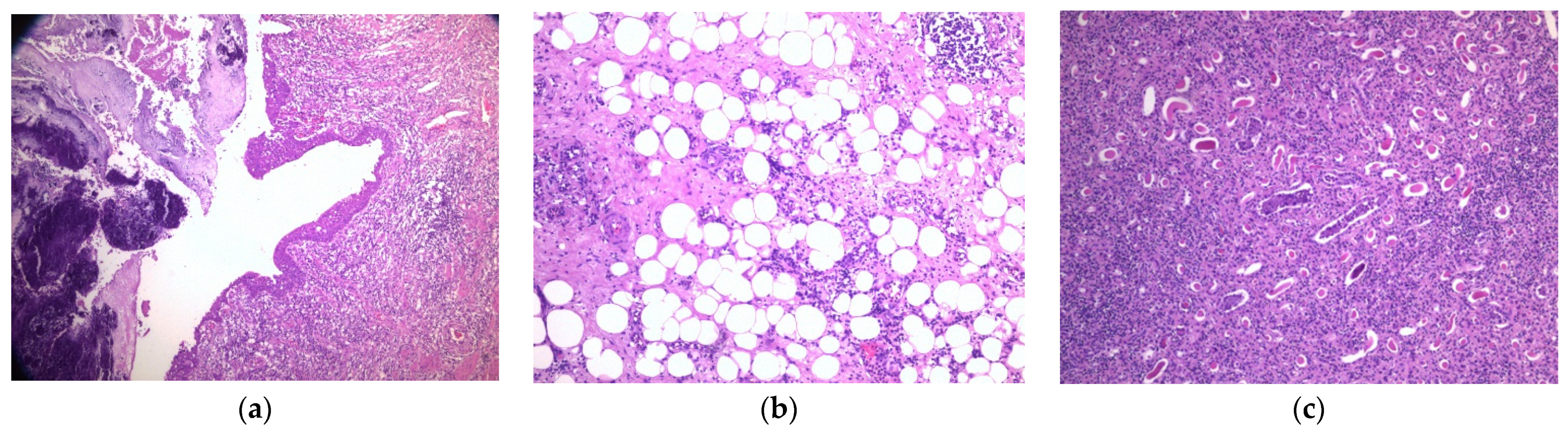
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abadi, A.T.B.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Haertlé, T.; Blatt, N.L. World Health Organization report: Current crisis of antibiotic resistance. BioNanoScience 2019, 9, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calza, L.; Manfredi, R.; Chiodo, F. Stenotrophomonas (Xanthomonas) maltophilia as an emerging opportunistic pathogen in association with HIV infection: A 10-year surveillance study. Infection 2003, 31, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muder, R.R.; Harris, A.P.; Muller, S.; Edmond, M.; Chow, J.W.; Papadakis, K.; Wagener, M.W.; Bodey, G.P.; Steckelberg, J.M. Bacteremia due to Stenotrophomonas (Xanthomonas) maltophilia: A prospective, multicenter study of 91 episodes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, M.W.; Anderson, D.E.; Campbell, D.M.; Carroll, K.C.; Malone, C.L.; Anderson, J.D.; Hollis, R.J.; Pfaller, M.A. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Emergence of multidrug-resistant strains during therapy and in an in vitro pharmacodynamic chamber model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 2859–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vartivarian, S.; Anaissie, E.; Bodey, G.; Sprigg, H.; Rolston, K. A changing pattern of susceptibility of Xanthomonas maltophilia to antimicrobial agents: Implications for therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Looney, W.J.; Narita, M.; Mühlemann, K. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: An emerging opportunist human pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, A.A.; Stenström, T.A.; Okoh, A.I. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia as an emerging ubiquitous pathogen: Looking beyond contemporary antibiotic therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales, C.; Opazo, V.; Bassa, C.; López, L.; Araos, F.; Madrid, P.; Morales, I. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A case report. Urol. Case Rep. 2018, 19, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlagenhauefer, F. Uber eigentumliche staphylmkosen der nieven und der pararenalen bindegewebes. Frankf. Z. Pathol. 1916, 19, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, R.; Baliyan, A.; Dhingra, H.; Bhalla, V.; Punia, R.S. Clinicopathological spectrum of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. Indian J. Nephrol. 2019, 29, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çaliskan, S.; Özsoy, E.; Kaba, S.; Koca, O.; Öztürk, M.I. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis. Arch. Iran. Med. 2016, 19, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marinacci, L.X.; Rosales, I. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Abad, P.; Rodríguez-Cabello, M.Á.; Vera-Berón, R.; Platas-Sancho, A. Bear Paw Sign: Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis. J. Radiol. Case Rep. 2018, 12, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkes, F.; Favoretto, R.L.; Bróglio Silva, C.A.; Castro, M.G.; Perez, M.D.C. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: Clinical experience with 41 cases. Urology 2008, 71, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, U.S.; Goyal, N.K.; Saxena, V.; Acharya, R.L.; Trivedi, S.; Singh, P.B.; Vyas, N.; Datta, B.; Kumar, A.; Das, S. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: Our experience with review of published reports. ANZ J. Surg. 2006, 76, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petca, R.C.; Popescu, R.I.; Mares, C.; Mehedintu, C.; Mastalier, B.; Badiu, D.C.; Maru, N.; Constantin, V.D.; Petca, A. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis: Presentation and management. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2019, 6, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute® (CLSI). M 100 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed. Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m100/ (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Gajdács, M.; Urbán, E. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in respiratory tract samples: A 10-year epidemiological snapshot. Health Serv. Res. Manag. Epidemiol. 2019, 6, 2333392819870774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gajdács, M.; Ábrók, M.; Lázár, A.; Burián, K. Urinary tract infections in elderly patients: A 10-year study on their epidemiology and antibiotic resistance based on the WHO Access, Watch, Reserve (AWaRe) classification. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.H.; Lai, M.Y.; Shen, S.H.; Yang, A.H.; Su, N.W.; Ng, Y.Y. Bilateral xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2008, 71, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddappa, S.; Ramprasad, K.; Muddegowda, M.K. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A retrospective review of 16 cases. Korean J. Urol. 2011, 52, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papadopoulos, I.; Wirth, B.; Wand, H. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis associated with renal cell carcinoma. Report on two cases and review of the literature. Eur. Urol. 1990, 18, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titus, B.; Gupta, S.; Edpao, P.; Psutka, S.P.; Limaye, A.P.; Bakthavatsalam, R.; Rakita, R.M. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis with direct extension into the liver. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 1054–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, R.S.; Elder, J.S. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A critical analysis of 26 cases and of the literature. J. Urol. 1978, 119, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdale, A.; Mittal, S.; Patel, K.; Azhar, S.; Prasla, S. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A case review of two cases. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2016, 4, 4198–4201. [Google Scholar]
- Hugh, R.; Leifson, E. A description of the type strain of Pseudomonas maltophilia. Int. Bull. Bacteriol. Nomencl. Taxon. 1963, 13, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovaleva, J.; Degener, J.E.; van der Mei, H.C. Mimicking disinfection and drying of biofilms in contaminated endoscopes. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 76, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, J.; Yamadori, I.; Xu, G.; Hojo, S.; Negayama, K.; Miyawaki, H.; Yamaji, Y.; Takahara, J. Clinical features of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia pneumonia in immunocompromised patients. Respir. Med. 1996, 90, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydin, K.; Koksal, I.; Kaygusuz, S.; Kaklikkaya, I.; Caylan, R.; Ozdemir, R. Endocarditis caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 32, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.H.; Murder, R.R. Meningitis due to Xanthomonas maltophilia: Case report and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 19, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartivarian, S.E.; Papadakis, K.A.; Anaissie, E.J. Stenotrophomonas (Xanthomonas) maltophilia urinary tract infection. A disease that is usually severe and complicated. Arch. Int. Med. 1996, 156, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, J.; Marco, F. Lectura interpretada del antibiograma de bacilos gramnegativos no fermentadores [Interpretive reading of the non-fermenting Gram-negative bacilli antibiogram]. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2010, 28, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Ni, W.; Cai, X.; Zhao, J.; Cui, J. Evaluation of Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole (SXT), Minocycline, Tigecycline, Moxifloxacin, and Ceftazidime Alone and in Combinations for SXT-Susceptible and SXT-Resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia by In Vitro Time-Kill Experiments. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdács, M.; Urbán, E. Epidemiological trends and resistance associated with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia: A 10-year retrospective cohort study in a tertiary-care hospital in hungary. Diseases 2019, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.H.; Yu, C.M.; Hsu, S.T.; Wu, R.X. Levofloxacin-resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Risk factors and antibiotic susceptibility patterns in hospitalized patients. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 104, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, E.; Davis, H.; Kim, T.; Duhon, B. Monotherapy with Minocycline or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole for treatment of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemoter. 2016, 71, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsueh, S.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Huang, Y.T.; Liao, C.H.; Tsuji, M.; Hsueh, P.R. In vitro activities of cefiderocol, ceftolozane/tazobactam, ceftazidime/avibactam and other comparative drugs against imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, all associated with bloodstream infections in Taiwan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 380–386. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzo, T.J.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Pierorazio, P.M.; Varkarakis, J.; Schaeffer, E.M.; Allaf, M.E. Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: Presentation and management in the era of laparoscopy. BJU Int. 2009, 104, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, W.D.; Wagner, B.J.; Travis, M.D. Pyelonephritis: Radiologic-pathologic review. Radiographics 2008, 28, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petca, R.-C.; Dănău, R.-A.; Popescu, R.-I.; Damian, D.; Mareș, C.; Petca, A.; Jinga, V. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia—The First Case Report and Brief Review. Pathogens 2022, 11, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010081
Petca R-C, Dănău R-A, Popescu R-I, Damian D, Mareș C, Petca A, Jinga V. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia—The First Case Report and Brief Review. Pathogens. 2022; 11(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010081
Chicago/Turabian StylePetca, Răzvan-Cosmin, Răzvan-Alexandru Dănău, Răzvan-Ionuț Popescu, Daniel Damian, Cristian Mareș, Aida Petca, and Viorel Jinga. 2022. "Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia—The First Case Report and Brief Review" Pathogens 11, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010081
APA StylePetca, R.-C., Dănău, R.-A., Popescu, R.-I., Damian, D., Mareș, C., Petca, A., & Jinga, V. (2022). Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia—The First Case Report and Brief Review. Pathogens, 11(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010081







