Aspergillus-SARS-CoV-2 Coinfection: What Is Known?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aspergillus Features Influencing Susceptibility to COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CAPA) Development
3. Host Factors Affecting Susceptibility to CAPA Development
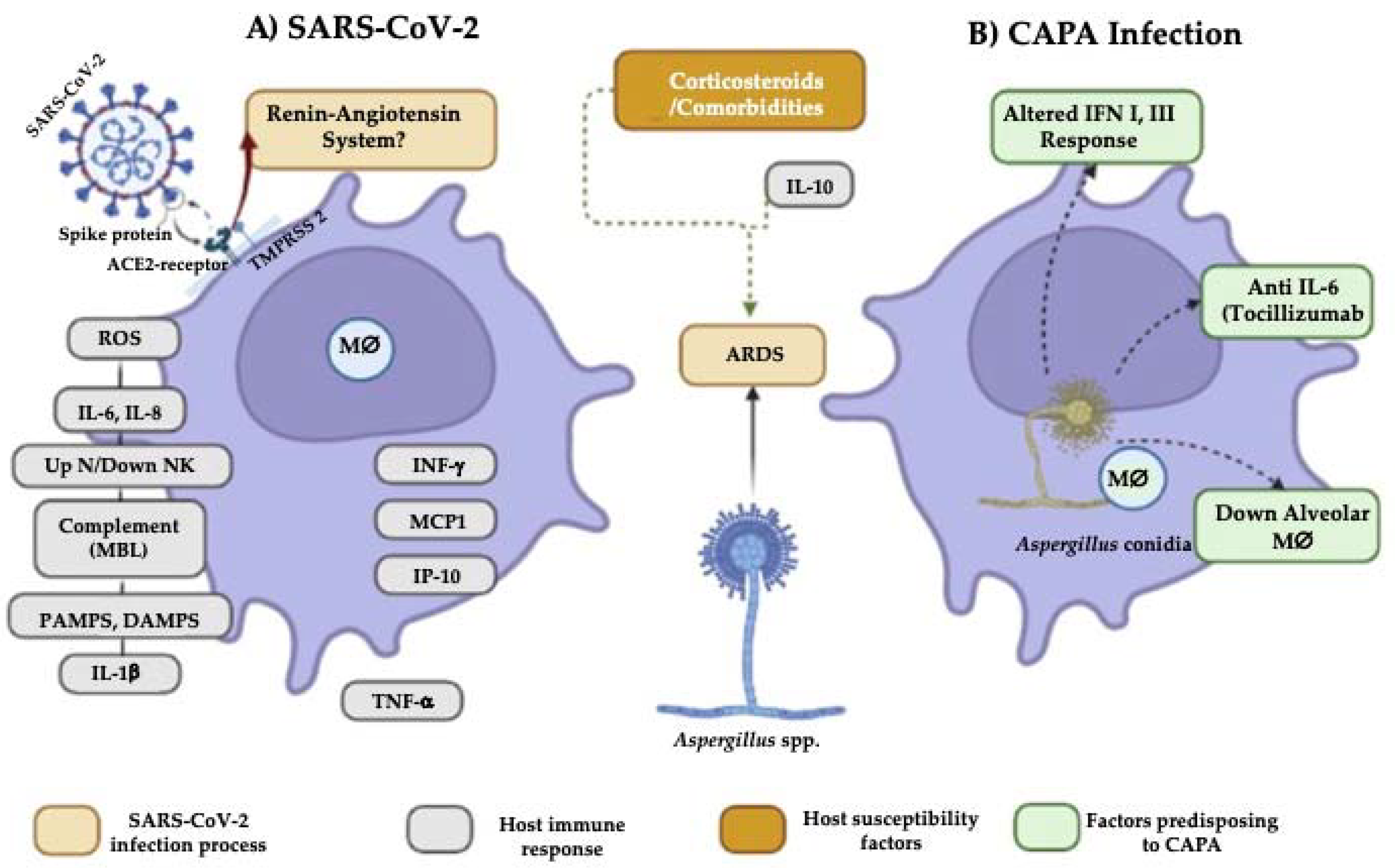
3.1. Comorbidities
3.2. Changes in the Immune Response That Predispose to CAPA
3.3. Influence of Antifungals on the Aspergillus-SARS-CoV-2 Interaction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borges-Vélez, G.; Rosario-Rodriguez, L.J.; Rosado-Philippi, J.E.; Cartagena, L.J.; Garcia-Requena, L.; Gonzalez, A.; Perez, J.; Melendez, M.L. SARS-CoV-2: Biology, detection, macrophage mediated pathogenesis and potential treatments. Virol. Immunol. J. 2020, 4, 242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Lu, X.; Xu, C.; Sun, W.; Pan, B. Understanding of COVID-19 based on current evidence. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naserghandi, A.; Allameh, S.; Saffarpour, R. All about COVID-19 in brief. New Microbes New Infect. 2020, 35, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worldometers. Info. Dover, Delaware, USA. 2022. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- Tortorici, M.A.; Veesler, D. Structural insights into coronavirus entry. Adv. Virus Res. 2019, 105, 93–116. [Google Scholar]
- Podder, S.; Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, T. Mutations in membrane-fusion subunit of spike glycoprotein play crucial role in the recent outbreak of COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 93, 2790–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, J.; Zhou, C.; Chen, B.; Fang, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. A Review of SARS-CoV2: Compared with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 628370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canedo-Marroquín, G.; Saavedra, F.; Andrade, C.A.; Berrios, R.V.; Rodríguez-Guilarte, L.; Opazo, M.C.; Riedel, C.A.; Kalergis, A.M. SARS-CoV-2: Immune response elicited by infection and development of vaccines and treatments. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 569760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, J.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, function, and dntigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 180, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrobaa, I.H.; New, K.J. COVID-19: Pulmonary and extra pulmonary manifestations. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 711616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansbury, L.; Lim, B.; Baskaran, V.; Lim, W.S. Co-infections in people with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Narayan, R.K.; Prasoon, P.; Kumari, C.; Kaur, G.; Kumar, S.; Kulandhasamy, M.; Sesham, K.; Pareek, V.; Faiq, M.A.; et al. COVID-19 mechanisms in the human body—What we know so far. Front Immunol. 2021, 3, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arastehfar, A.; Carvalho, A.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Jenks, J.D.; Koehler, P.; Krause, R.; Cornely, O.A.; SPerlin, D.; Lass-Flör, C.; Hoenig, M. COVID-19 associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA)-From Immunology to Treatment. J. Fungi Basel Switz. 2020, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horby, P.; Lim, W.; Emberson, J.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Brightling, C.; Ustianowski, A.; Elmahi, E.; et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.; Kontoyiannis, D. Invasive aspergillosis in glucocorticoid-treated patients. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47, S271–S281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.C.; Yu, W.L. Covid-19 associated with pulmonary aspergillosis: A literature review. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanio, A.; Delliere, S.; Fodil, S.; Bretagne, S.; Megarbane, B. Prevalence of putative invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients with COVID19. Lancet Respir Med. 2020, 8, e48–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, P.; Cornely, O.A.; Böttiger, B.W.; Dusse, F.; Eichenauer, D.A.; Fuchs, F.; Hallek, M.; Jung, N.; Klein, F.; Persigehl, T.; et al. COVID-19 associated pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses 2020, 63, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmanton-García, J.; Sprute, R.; Stemler, J.; Bartoletti, M.; Dupont, D.; Valerio, M.; García Vidal, C.; Falces-Romero, I.; Machado, M.; de la Villa, S.; et al. COVID-19–Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis, March–August 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schein, F.; Munoz-Pons, H.; Mahinc, C.; Grange, R.; Cathébras, P.; Flori, P. Fatal aspergillosis complicating severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: A case report. J. Mycol. Med. 2020, 30, 101039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Arkel, A.L.E.; Rijpstra, T.A.; Belderbos, H.N.A.; van Wijngaarden, P.; Verweij, P.E.; Bentvelsen, R.G. COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antinori, S.; Rech, R.; Galimberti, L.; Castelli, A.; Angeli, E.; Fossali, T.; Bernasconi, D.; Covizzi, A.; Bonazzetti, C.; Torre, A.; et al. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis complicating SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: A diagnostic challenge. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 38, 101752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoletti, M.; Pascale, R.; Cricca, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Maccaro, A.; Bussini, L.; Fornaro, G.; Tonetti, T.; Pizzilli, G.; Francalanci, E.; et al. Epidemiology of invasive pulmonary Aspergillosis among intubated patients with COVID-19: A prospective study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3606–e3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaize, M.; Mayaux, J.; Nabet, C.; Lampros, A.; Marcelin, A.G.; Thellier, M.; Piarroux, R.; Demoule, A.; Fekkar, A. Fatal invasive aspergillosis and coronavirus disease in an immunocompetent patient. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1636–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borman, A.M.; Palmer, M.D.; Fraser, M.; Patterson, Z.; Mann, C.; Oliver, D.; Linton, C.J.; Gough, M.; Brown, P.; Dzietczyk, A.; et al. COVID-19-Associated invasive aspergillosis: Data from the UK National Mycology Reference Laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauvet, P.; Mallat, J.; Arumadura, C.; Vangrunderbeek, N.; Dupre, C.; Pauquet, P.; Orfi, A.; Granier, M.; Lemyze, M. Risk factors for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care Explor. 2020, 2, e0244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellière, S.; Dudoignon, E.; Fodil, S.; Voicu, S.; Collet, M.; Oillic, P.A.; Salmona, M.; Dépret, F.; Ghelfenstein-Ferreira, T.; Plaud, B.; et al. Risk factors associated with COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in ICU patients: A French multicentric retrospective cohort. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 27, 790.e1–790.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Menotti, J.; Turc, J.; Miossec, C.; Wallet, F.; Richard, J.C.; Argaud, L.; Paulus, S.; Wallon, M.; Ader, F.; et al. Pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Med. Mycol. 2020, 59, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelfenstein-Ferreira, T.; Saade, A.; Alanio, A.; Bretagne, S.; de Castro, R.A.; Hamane, S.; Azoulay, E.; Bredin, S.; Dellieère, S. Recovery of a triazole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus in respiratory specimen of COVID-19 patient in ICU-A case report. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2020, 31, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangneux, J.P.; Reizine, F.; Guegan, H.; Pinceaux, K.; Le Balch, P.; Prat, E.; Pelletier, R.; Belaz, S.; Le Souhaitier, M.; Le Tulzo, Y.; et al. Is the COVID-19 pandemic a good time to include Aspergillus molecular detection to categorize aspergillosis in ICU patients? A monocentric experience. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helleberg, M.; Steensen, M.; Arendrup, M.C. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmer, T.; Kriescher, S.; Herner, A.; Rothe, K.; Spinner, C.D.; Schneider, J.; Mayer, U.; Neuenhahn, M.; Hoffmann, D.; Geisler, F.; et al. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: Results from the prospective AspCOVID-19 study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0238825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoth, F.; Glampedakis, E.; Boillat-Blanco, N.; Oddo, M.; Pagani, J.L. Incidence of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis among critically ill COVID-19 patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1706–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescure, F.X.; Bouadma, L.; Nguyen, D.; Parisey, M.; Wicky, P.H.; Behillil, S.; Gaymard, A.; Bouscambert-Duchamp, M.; Donati, F.; Le Hingrat, Q.; et al. Clinical and virological data of the first cases of COVID-19 in Europe: A case series. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.; Valerio, M.; Álvarez-Uría, A.; Olmedo, M.; Veintimilla, C.; Padilla, B.; De la Villa, S.; Guinea, J.; Escribano, P.; Ruiz-Serrano, M.J.; et al. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in the COVID-19 era: An expected new entity. Mycoses 2020, 64, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, E.F.J.; Dofferhoff, A.S.M.; Hoiting, O.; Meis, J.F. COVID-19–associated pulmonary aspergillosis: A prospective single-center dual case series. Mycoses 2021, 64, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Hassan, T.; Trzos-Grzybowska, M.; Thomas, J.; Quinn, A.; O’Sullivan, M.; Griffin, A.; Rogers, T.R.; Talento, A.F. Multi-triazole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus and SARS-CoV-2 co-infection: A lethal combination. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2021, 31, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, N.; Farooqi, J.; Mahmood, S.F.; Jabeen, K. COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA) in patients admitted with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: An observational study from Pakistan. Mycoses 2020, 63, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prattes, J.; Valentin, T.; Hoenigl, M.; Talakic, E.; Reisinger, A.C.; Eller, P. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis complicating COVID-19 in the ICU—A case report. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2020, 31, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Montes, C.M.; Martinez-Gamboa, A.; Diaz-Lomelí, P.; Cervantes-Sanchez, A.; Rangel-Cordero, A.; Sifuentes-Osornio, J. Accuracy of galactomannan testing on tracheal aspirates in COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses 2020, 64, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutsaert, L.; Steinfort, N.; Van Hunsel, T.; Bomans, P.; Naesens, R.; Mertes, H.; Dits, H.; Van Regenmortel, N. COVID-19-associated invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.F.; Pivoto, G.; Alexandre, M.A.A.; Baía-da-Silva, D.C.; Borba, M.G.d.S.; Val, F.A.; Brito-Sousa, J.D.; Cardoso Melo, G.; Marcelo Monteiro, W.; Braga Souza, J.V.; et al. Confirmed invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and COVID-19: The value of postmortem findings to support antemortem management. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2020, 53, e20200401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segrelles-Calvo, G.; Araújo, G.R.S.; Llopis-Pastor, E.; Carrillo, J.; Hernández-Hernández, M.; Rey, L.; Rodríguez Melean, N.; Escribano, I.; Antón, E.; Zamarro, C.; et al. Prevalence of opportunistic invasive aspergillosis in COVID-19 patients with severe pneumonia. Mycoses 2021, 64, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Hofmeyr, A.; Bansal, A.; Thakkar, D.; Lam, L.; Harrington, Z.; Bhonagiri, D. COVID-19 associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA): An Australian case report. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2020, 31, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Biesen, S.; Kwa, D.; Bosman, R.J.; Juffermans, N.P. Detection of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in COVID-19 with nondirected BAL. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 1171–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez Pintado, M.; Camiro-Zúñiga, A.; Aguilar Soto, M.; Cuenca, D.; Mercado, M.; Crabtree-Ramirez, B.; ARMII Study Group. COVID-19-associated invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in a tertiary care center in Mexico City. Med. Mycol. 2021, 59, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versyck, M.; Zarrougui, W.; Lambiotte, F.; Elbeki, N.; Saint-Leger, P. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in COVID-19 critically ill patients: Results of a French monocentric cohort. J. Mycol. Med. 2021, 31, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoth, F.; Lewis, R.E.; Walsh, T.J.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Navigating the uncertainties of COVID-19 associated aspergillosis (CAPA): A comparison with influenza associated aspergillosis (IAPA). J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquier, G.; Bounhiol, A.; Robert Gangneux, F.; Zahar, J.; Gangneux, J.P.; Novara, A.; Bougnoux, M.; Dannaoui, E. A review of significance of Aspergillus detection in airways of ICU COVID-19 patients. Mycoses 2021, 64, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekkar, A.; Neofytos, D.; Nguyen, M.H.; Clancy, C.J.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Lamoth, F. COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA): How big a problem is it? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1376–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kula, B.E.; Clancy, C.J.; Hong Nguyen, M.; Schwartz, I.S. Invasive mould disease in fatal COVID-19: A systematic review of autopsies. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e405–e414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, T.F.; Thompson, G.R.; Denning, D.W.; Fishman, J.A.; Hadley, S.; Herbrecht, R.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Marr, K.A.; Morrison, V.A.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of Aspergillosis: 2016 update by the infectious diseases society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e1–e60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thompson, G.R., III; Young, J.H. Aspergillus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Gorman, C. Airborne Aspergillus fumigatus conidia: A risk factor for aspergillosis. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2021, 25, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latgé, J.P. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 310–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakhage, A.A.; Langfelder, K. Menacing mold: The molecular biology of Aspergillus fumigatus. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagenais, T.R.; Keller, N.P. Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in invasive aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, A.; Loeffler, J.; Ebel, F. Aspergillus fumigatus: Contours of an opportunistic human pathogen. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Brüggemann, R.J.; Vos, S.; De Hertogh, G.; Wauters, J.; Reijers, M.H.; Netea, M.G.; Schouten, J.A.; Verweij, P.E. COVID-19-associated Aspergillus tracheobronchitis: The interplay between viral tropism, host defence, and fungal invasion. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.; Morenoa, L.; Yagüea, G.; Andreu, E.; Jara, R.; Segovia, M. Colonization by multidrug-resistant microorganisms in ICU patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. Med. Intensiva 2021, 45, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichai, P.; Saliba, F.; Baune, P.; Daoud, A.; Coilly, A.; Samuel, D. Impact of negative air pressure in ICU rooms on the risk of pulmonary aspergillosis in COVID-19 patients. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddley, J.W.; Thompson, G.R., III; Chen, S.C.; White, P.L.; Johnson, M.D.; Nguyen, M.H.; Schwartz, I.S.; Spec, A.; OstroskyZeichner, L.; Jackson, B.R.; et al. Coronavirus disease 2019-associated invasive fungal infection. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellanger, A.P.; Lallemand, S.; Tumasyan Horikian, A.; Navellou, J.C.C.; Barrera, A.; Rouzet, E.; Scherer, G.; Reboux, G.; Piton, L. Millon investigation of the value of precipitins in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) patients with a positive marker for Aspergillus species. Med. Mycol. 2022, 60, myac031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregoire, E.; Pirotte, B.F.; Moerman, F.; Altdorfer, A.; Gaspard, L.; Firre, E.; Moonen, M.; Fraipont, V.; Ernst, M.; Darcis, G. Incidence and risk factors of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in intensive care unit-A monocentric retrospective observational study. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Lv, Z.; Zhou, T.; Liu, H.; Zou, X.; Cao, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Chen, W.; et al. Risk factors for invasive aspergillosis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit with coronavirus disease 2019: A multicenter retrospective study. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 753659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prattes, J.; Wauters, J.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Salmanton-García, J.; Maertens, J.; Bourgeois, M.; Reynders, M.; Rutsaert, L.; Regenmortel, N.V.; Lormans, P.; et al. Risk factors and outcome of pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill coronavirus disease 2019 patients-a multinational observational study by the European Confederation of Medical Mycology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, G.; Almyroudi, M.; Myrianthefs, P.; Rello, J. COVID-19-Associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA). J. Intensive Med. 2021, 1, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Shokohi, T.; Lass Florl, C.; Hedayati, M.T.; Hoenig, M. Immunological response to COVID-19 and its role as a predisposing factor in invasive aspergillosis. Curr. Med. Mycol. 2020, 6, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, C.; Anderson, R. The role of co-infections and secondary infections in patients with COVID-19. Pneumonia 2021, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, P.; Bassetti, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Chen, S.C.A.; Lopes Colombo, A.; Hoenigl, M.; Klimko, N.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Oladele, R.O.; Vinh, D.C.; et al. Defining and managing COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: The 2020 ECMM/ISHAM consensus criteria for research and clinical guidance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e149–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, S.; Almyroudi, M.P.; Braspenning, R.; Lagrou, K.; Spriet, I.; Dimopoulos, G.; Wauters, J.A. Visual and comprehensive review on COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CAPA). J. Fungi 2021, 7, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, N.A.F.; Nyga, R.; Vanderbeke, L.; Jacobs, C.; Ergün, M.; Buil, J.B.; van Dijk, K.; Altenburg, J.; Bouman, C.S.C.; van der Spoel, H.I.; et al. Multinational observational cohort study of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2892–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagris, D.; Papanikolaou, A.; Kvernland, A.; Korompok Frontera, E.J.A.; Troxe, A.B.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Milionis, H.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Michel, P.; Yaghi, S.; et al. COVID-19 and ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 3826–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videla, C.G.; Agustina, M.; de la Iglesia Niveyro, P.X.; Ciarrocchi Nicolas, M. Muerte cerebral debida a aspergilosis cerebral en un paciente de COVID-19. Rev. Esp. Anestesiol. Y Reanim. 2022; 69, 592–596. [Google Scholar]
- Bhotla, H.K.; Balasubramanian, B.; Meyyazhagan, A.; Pushparaj, K.; Easwaran, M.; Pappusamy, M.; Robert, A.A.; Arumugam, V.A.; Tsibizova, V.; Alfalih, A.M.; et al. Opportunistic mycoses in COVID-19 patients/survivors: Epidemic inside a pandemic. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, P.E.; Brüggemann, R.J.M.; Azoulay, E.; Bassetti, M.; Blot, S.; Buil, J.B.; Calandra, T.; Chiller, T.; Clancy, C.J.; Cornely, O.A.; et al. Taskforce report on the diagnosis and clinical management of COVID-19 associated pulmonary aspergillosis. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, F.; Bignell, E.; Brown, G.D.; Cook, P.C.; Warris, A. Pathogenesis of respiratory viral and fungal coinfections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e00094-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, A.; Farzaneh, F.; Candore, G.; Caruso, C.; Davinelli, S.; Gambino, C.M.; Ligotti, M.E.; Zareian, N.; Accardi, G. Immunosenescence and its hallmarks: How to oppose aging strategically? A review of potential options for therapeutic intervention. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadambari, S.; Klenerman, P.; Pollard, A.J. Why the elderly appear to be more severely affected by COVID-19: The potential role of immunosenescence and CMV. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, e2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pang, S.C.; Yang, Y. A potential association between immunosenescence and high COVID-19 related mortality among elderly patients with cardiovascular diseases. Immun. Ageing 2021, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, N.; Knighton, P.; Kar, P.; O’Keefe, J.; Curley, M.; Weaver, A.; Barron, E.; Bakhai, C.; Khunti, K.; Wareham, N.J.; et al. Risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in England: A population-based cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Bae, J.H.; Kwon, H.S.; Nauck, M.A. COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: From pathophysiology to clinical management. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, M.; Winfred, S.B.; Meiyazhagan, G.; Venkatachalam, D.P. Mechanisms contributing to adverse outcomes of COVID-19 in obesity. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2022, 477, 1155–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Li, R.; Lu, Z.; Huang, Y. Does comorbidity increase the risk of patients with COVID-19: Evidence from meta-analysis. Aging 2020, 12, 6049–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, W.H.; Saha, B.K.; Neu, K.P. Comparing the clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19-associate pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infection 2022, 50, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulou, A.; Garrigos, Z.E.; Vijayvargiya, P.; Lerner, A.H.; Farmakiotis, D. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review of the literature. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borger, P.; Koeter, G.H.; Timmerman, A.J.; Vellenga, A.; Tomee, J.F.; Kauffman, H.F. Protease from Aspergillus fumigatus induce interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 producin in airway epithelial cell lines by transcriptional mechanisms. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuri-Cervantes, L.; Pampena, M.B.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; Ittner, C.A.G.; Weisman, A.R.; Agyekum, R.S.; Mathew, D.; Baxter, A.E.; Vella, L.A.; et al. Comprehensive mapping of immune perturbations associated with severe COVID-19. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabd7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozada-Requena, I.; Núñez Ponce, C. COVID-19: Respuesta inmune y perspectivas terapéuticas. Rev. Peru Med. Exp. Salud Pública 2020, 37, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudicessi, J.R.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Friedman, P.A.; Ackerman, M.J. Urgent guidance for navigating and circumventing the QTc-prolonging and torsadogenic potential of possible pharmaco-therapies for Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID-19). Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshneya, M.; Irurzun-Arana, I.; Campana, C.; Dariolli, R.; Gutierrez, A.; Pullinger, T.K.; Sobie, E.A. Investigational treatments for COVID-19 may increase ventricular arrhythmia risk through drug interactions. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2021, 10, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, J.D.; Mehta, S.R.; Hoenigl, M. Broad spectrum triazoles for invasive mould infections in adults: Which drug and when? Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, S168–S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, S.S.; Stchigel, A.; Cano, J.; Guarro, J.; Colombo, A.L. In vitro antifungal susceptibility of clinically relevant species belonging to Aspergillus section Flavi. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1944–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruanno, M.; Glampedakis, E.; Lamoth, F. Echinocandins for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis: From laboratory to bedside. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00399-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergün, M.; Brüggemann, R.J.M.; Alanio, A.; Delliére, S.; van Arkel, A.; Bentvelsen, R.G.; Rijpstra, T.; van der Sar-van der Brugge, S.; Lagrou, K.; Janssen, N.A.F.; et al. Aspergillus test profiles and mortality in critically Ill COVID-19 patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e01229-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Tsutani, H.; Iwasaki, H. Multifaceted efficacy of caspofungin against fungal infections in COVID-19 patients. Med. Hypotheses 2022, 164, 110876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.; Rogers, T.R.; Talento, A.F. COVID-19 Associated invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. J. Fungi. 2020, 6, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzl, S.; Reisinger, A.C.; Posch, F.; Prattes, J.; Stradner, M.; Pilz, S.; Eller, P.; Schoerghuber, M.; Toller, W.; Gorkiewicz, G.; et al. Antifungal prophylaxis 815 for prevention of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients: An observational study. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Country (Cases Number) | Identification Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | Italy (9) | Culture from BAL and AT | [14] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | Germany (4) | Culture from BAL, AT, and PCR | [18] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | Netherlands (6) | Culture from BAL, AT, and sputum | [21] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | Italy (1) | Culture from BAL | [22] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati, A. niger/A. section Nigri, A. flavus/A. section Flavi | Italy (NA) | Culture from BAL | [23] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | France (1) | Culture from AT (X2) | [24] |
| A. fumigatus | United Kingdom (NA) | Respiratory secretions (BAL fluids, NBL fluids, TA, and secretions) were subjected to GM testing, Aspergillus-specific PCR, microscopic examination, and mycological culture. A limited selection of serum or BAL fluid samples was also subjected to Aspergillus-specific LFD testing. | [25] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | France (NA) | Culture from BAL and AT | [26] |
| Aspergillus spp. | France (NA) | Culture from BAL and AT | [27] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati, A. flavus/A. section Flavi, A. calidoustus/A. section Usti | France (NA) | Culture from BAL, AB, and AT | [28] |
| A. fumigatus (TR34/L98H mutation)/A. section Fumigati | France (1) | Culture from AT | [29] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | France (NA) | Culture from BAL and AT | [30] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | Denmark (NA) | Culture from BAL and AT | [31] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | Germany (2) | Culture from BAL | [32] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | Swiss (NA) | Culture from AT | [33] |
| A. flavus/A. section Flavi | France (1) | Culture from AT | [34] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati, A. citrinoterreus/A. section Terrei, A. lentulus/A. section Fumigati | Spain (NA) | Culture from BAL | [35] |
| A. fumigatus (TR32/L98H mutation)/A. section Fumigati | Netherlands (1) | Culture from BAL and AT | [36] |
| A. fumigatus (TR34/L98H mutation)/A. section Fumigati | Ireland (1) | Culture from AT | [37] |
| A. flavus/A. section Flavi, A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati, A. terreus/A. section Terrei | Pakistan (NA) | Culture from BAL, AT, and sputum | [38] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | Austria (1) | Culture from AT | [39] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati, Aspergillus spp., A. flavus/A. section Flavi, A. niger/A. section Nigri | Mexico (NA) | Culture from AT | [40] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati, A. flavus/A. section Flavi | Belgium (7) | Culture from BAL and AT | [41] |
| Unidentified | Brazil (1) | Sequencing identifying A. penicillioides | [42] |
| A. fumigatus, A. niger, A. flavus | Spain (NA) | ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 amplification by PCR and Sanger sequencing | [43] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | Australia (1) | Culture from AT (X3) | [44] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati, A. flavus/A. section Flavi, A. terreus/A. section Terrei | Netherlands (NA) | Culture from BAL | [45] |
| Aspergillus spp. | Mexico (NA) | Culture from BAL | [46] |
| A. fumigatus/A. section Fumigati | France (NA) | Culture from BAL and AT | [47] |
| Country | Number of Cases | Comorbidities |
|---|---|---|
| Italy | 108 | Obesity, AH, DM, coronary disease, COPD, CRF, hemodialysis, cerebrovascular disease, malignancies, solid organ transplant, chronic steroid treatment, and atrial fibrillation. |
| France | 615 | AH, obesity, DM, BA, cardiac disease, gout, thyroid cancer, MDS, Hashimoto disease, hyperlipidemia, cancer, hemopathy, CRF, kidney transplant recipient, HIV, steroid treatment, COPD, dialysis, stroke, CHF (NYHA classification 3–4), arrhythmias, CRF. |
| Belgium | 20 | AH, DM, hypercholesterolemia, CRF, obesity, AML, HIV. |
| China | 152 | DM, AH, heart disease, COPD, CRF. |
| Germany | 21 | AH, COPD, DM, obesity, OSA, pulmonary fibrosis. |
| Netherlands | 74 | Cardiomyopathy, COPD, BA, DM, AH, chronic steroid treatment, neutropenia, stem cell transplant, immunodeficiency, DM, CRF. |
| Austria | 1 | COPD, OSA, Obesity, DM, AH, and cardiac disease. |
| Netherland | 74 | Reflux, polyarthrosis. |
| Ireland | 1 | DM, AH, hyperlipidemia, obesity. |
| Brazil | 1 | AH, DM, CRF. |
| Pakistan | 23 | DM, AH, atrial myxoma, recent stroke. |
| Switzerland | 118 | AH, DM, obesity, pulmonary fibrosis, BA. |
| Spain | 239 | MDS, HIV, DM, COPD, ankylosing spondylitis, acquired hemophilia A, hypothyroidism, CLL, cardiac disease, AH, BA, obesity, CRF, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and CNS disease. |
| Denmark | 8 | AH, BA. |
| UK | 916 | DM, AH, CRF, obesity, cancer, CRF malignancy, hyperlipidemia, cardiac and vascular disease, and autoimmune disorders. |
| USA | 46 | Atrial fibrillation, COPD, AH, OSA, DM, CRF, coronary disease, CHD, ESRD, nephrectomy, vasculitis, junctional tachycardia, bipolar disorder, hypercholesterolemia, obesity, hypothyroidism, gastric ulcer, atherosclerosis, and sarcopenia. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castro-Fuentes, C.A.; Reyes-Montes, M.d.R.; Frías-De-León, M.G.; Valencia-Ledezma, O.E.; Acosta-Altamirano, G.; Duarte-Escalante, E. Aspergillus-SARS-CoV-2 Coinfection: What Is Known? Pathogens 2022, 11, 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111227
Castro-Fuentes CA, Reyes-Montes MdR, Frías-De-León MG, Valencia-Ledezma OE, Acosta-Altamirano G, Duarte-Escalante E. Aspergillus-SARS-CoV-2 Coinfection: What Is Known? Pathogens. 2022; 11(11):1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111227
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastro-Fuentes, Carlos Alberto, María del Rocío Reyes-Montes, María Guadalupe Frías-De-León, Omar E. Valencia-Ledezma, Gustavo Acosta-Altamirano, and Esperanza Duarte-Escalante. 2022. "Aspergillus-SARS-CoV-2 Coinfection: What Is Known?" Pathogens 11, no. 11: 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111227
APA StyleCastro-Fuentes, C. A., Reyes-Montes, M. d. R., Frías-De-León, M. G., Valencia-Ledezma, O. E., Acosta-Altamirano, G., & Duarte-Escalante, E. (2022). Aspergillus-SARS-CoV-2 Coinfection: What Is Known? Pathogens, 11(11), 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111227







