Screening of Toxoplasmosis in Owned and Stray Dogs of District Faisalabad, Pakistan through Latex Agglutination and Indirect ELISA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Size Estimation and Sampling
2.3. Serological Investigations
2.4. Statistical Analyses
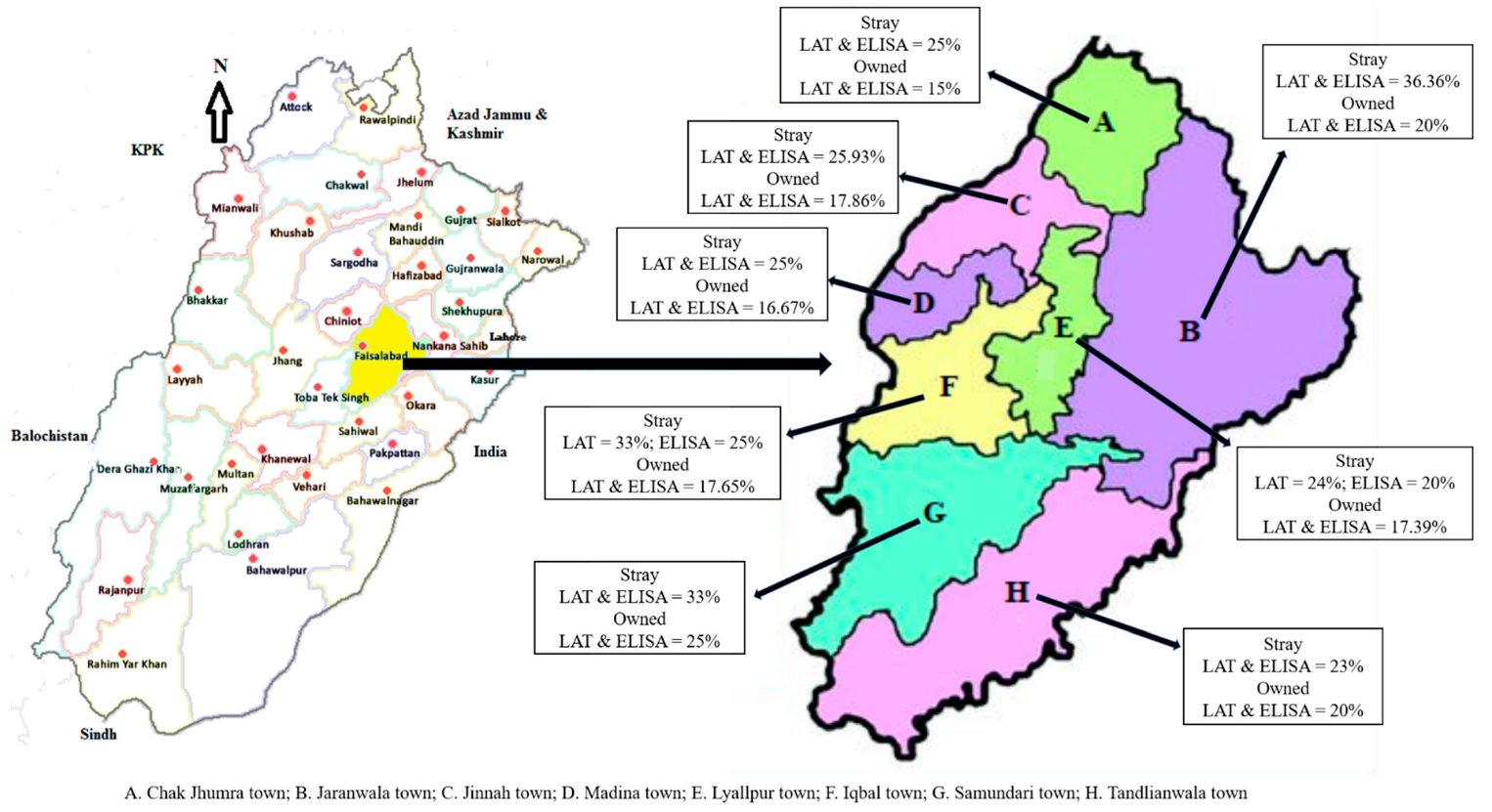
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feitosa, T.F.; Brasil, A.W.L.; Parentoni, R.N.; Vilela, V.L.R.; Nety, T.F.L.; Pena, H.F.D.J. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in mammals, birds and reptiles at the zoological-botanical park in João Pessoa, Paraíba, Brazil. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2018, 84, e0022016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis in Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii from animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saadatnia, G.; Golkar, G. A review on human toxoplasmosis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 44, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, C.N.; Linam, W.M.; Gadde, J.A.; Wolf, D.S.; Walson, K.; Montoya, J.G.; Rostad, C.A. Congenital toxoplasmosis presenting as eosinophilic encephalomyelitis with spinal cord hemorrhage. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20191425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attias, M.; Teixeira, D.E.; Benchimol, M.; Vommaro, R.C.; Crepaldi, P.H.; Souza, W.D. The life-cycle of Toxoplasma gondii reviewed using animations. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Ahmed, H.; Irum, S.; Qayyum, M. Seroprevalence of IgG and IgM antibodies and associated risk factors for toxoplasmosis in cats and dogs from subtropical arid parts of Pakistan. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 31, 777–784. [Google Scholar]
- Zarra-Nezhad, F.; Borujeni, M.P.; Mosallanejad, B.; Hamidinejat, H. A seroepidemiological survey of Toxoplasma gondii infection in referred dogs to Veterinary hospital of Ahvaz, Iran. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2017, 5, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huertas-López, A.; Sukhumavasi, W.; Álvarez-García, G.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cano-Terriza, D.; Almería, S.; Dubey, J.P.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Cerón, J.J.; Martínez-Carrasco, C. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in outdoor dogs and cats in Bangkok, Thailand. Parasitology 2021, 148, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Yang, Y.R.; Su, C. Toxoplasma gondii infections in dogs: 2009-2020. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 287, 109223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fábrega, L.; Restrepo, C.M.; Torres, A.; Smith, D.; Chan, P.; Pérez, D.; Cumbrera, A.; Caballero, Z. Frequency of Toxoplasma gondii and risk factors associated with the infection in stray dogs and cats of Panama. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ding, J.; Xia, Z.; Lin, D.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.; Liu, Q. Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii in pet dogs and cats in Beijing, China. Acta Parasitol. 2008, 53, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Maqbool, A.; Mahfooz, A.; Hayat, S. Serological survey of Toxoplasma gondii in dogs and cats. Pak. Vet. J. 2001, 21, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, C.N.; Harris, J.A.; Watkins, J.D.; Adesiyun, A.A. Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii in dogs in Trinidad and Tobago. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 113, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.P.; de Sordi, D.; Müller, H.H.O.; Lamn, M.C.; Carl, A.; Kohse, K.P.; Philipsen, A. Aggravation of symptom severity in adult attention-eficit/hyperactivity disorder by latent Toxoplasma gondii infection: A case–control study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, C.; Maier, S.; Walker, R.A.; Rehrauer, H.; Joekel, D.E.; Winiger, R.R.; Basso, W.U.; Grigg, M.E.; Hehl, A.B.; Deplazes, P.; et al. An experimental genetically attenuated live vaccine to prevent transmission of Toxoplasma gondii by cats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atail, H.B.; Ibrahaem, H.H.; Shuaib, Y.A.; Mohamed, A.K.; Suliman, S.E.; Idris, S.H.; Abdalla, M.A. Sero-prevalence of toxoplasmosis in sheep and goats in El-Gadarif state. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2017, 4, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Ashraf, T.; Rahman, A. Tracking trends of Toxoplasma gondii transmission from environment to animal to human. J. Adv. Parasitol. 2021, 8, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijlstra, A.; Jongert, E. Control of the risk of human toxoplasmosis transmitted by meat. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, R.; Bretagne, S.; Einsele, H.; Maertens, J.; Ullmann, A.J.; Parody, R.; Schumacher, U.; Pautas, C.; Theunissen, K.; Schindel, C.; et al. Infectious disease working party of the European group for blood and marrow transplantation. Early detection of Toxoplasma infection by molecular monitoring of Toxoplasma gondii in peripheral blood samples after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Thekisoe, O.M.; Aboge, G.O.; Kyan, H.; Yamagishi, J.; Inoue, N.; Nishikawa, Y.; Zakimi, S.; Xuan, X. Toxoplasma gondii: Sensitive and rapid detection of infection by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 122, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkat, A.; Kabiri, M.; Tligui, H.; Bouazzaoui, L.N. Seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis in Morocco. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 68, 486–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinek, P.; Nowakowska, D.; Szaflik, K.; Spiewak, E.; Malafiej, E.; Wilczynski, J. Analysis of complications during pregnancy in women with serological features of acute toxoplasmosis or acute parvovirosis. Ginekol. Pol. 2008, 79, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barratt, J.L.; Harkness, J.; Marriott, D.; Ellis, J.T.; Stark, D. Importance of non-enteric protozoan infections in immunocompromised people. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 795–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, R.C.; Souza, L.C.; Langoni, H.; Tanaka, E.M.; Lima, V.Y.; Silva, A.V. Risk factors and presence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in dogs from the coast of Sao Paulo State, Brazil. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2010, 30, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sedlak, K.; Bartova, E. The prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii IgM and IgG antibodies in dogs and cats from the Czech Republic. Vet. Med. 2006, 51, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oncel, T.; Handemir, E.; Kamburgil, K.; Yurtalan, S. Determination of seropositivity for Toxoplasma gondii in stray dogs in Istanbul, Turkey. Rev. Med. Vet. 2007, 158, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Ortuno, A.; Castella, J.; Almeria, S. Seroprevalence of antibodies to Neospora caninum in dogs from Spain. J. Parasitol. 2002, 88, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanha, K.; Edelhofer, R.; Gabler-Eduardo, C.; Prosl, H. Prevalence of antibodies against Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii in dogs and foxes in Austria. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 128, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukthana, Y. Toxoplasmosis: Beyond animals to humans. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, A.; Ahmad, N.; Haleem, S.; Akbar, N.; Zareen, S.; Taib, M.; Khan, S.; Hussain, R.; Sohail. Detection of toxoplasmosis in pets and stray cats through molecular and serological techniques in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, A.D.N.; Martins, F.D.C.; Mareze, M.; Santos, N.J.R.; Ferreira, F.P.; Martins, C.M.; Garcia, J.L.; Mitsuka-Breganó, R.; Freire, R.L.; Biondo, A.W.; et al. Spatial and simultaneous representative seroprevalence of anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in owners and their domiciled dogs in a major city of southern Brazil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, W.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhou, N.; Peng, P.; Qin, S.Y.; Meng, Q.F.; Qian, A.D. Prevalence of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in pets and their owners in Shandong province, Eastern China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.S.; Fei, A.C.Y.; Mar, P.H.; Pong, Y.M. Seroprevalences of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in stray dogs in Taipei. BioFormos 2004, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.-C.; Yang, N.; He, J.-B.; Mu, M.-Y.; Yang, M.; Sun, N.; Li, H.-K. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in police dogs in Shenyang, Northeastern China. Kor. J. Parasitol. 2013, 5, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.S. Seroprevalences to Toxoplasma gondii in privately-owned dogs in Taiwan. Prev. Vet. Med. 1898, 35, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseininejad, M.; Malmasi, A.; Hosseini, F.; Selk-Ghaffari, M.; Khorrami, N.; Mohebali, M.; Shojaee, S.; Mirani, A.; Azizzadeh, M.; Mirshokraei, P.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in dogs in Tehran, Iran. Iranian J. Parasitol. 2011, 6, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Dong-Hui, Y.; Hui-Qun, Z.; Chao, S.; Min, Y.; Feng-Cai, Z. Sero-prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in dogs in Jinzhou City, Northeast China. African J. Microbiol. 2013, 7, 3479–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waladjo, A.R.K.; Allanonto, V.; Gbati, O.B.; Kone, P.S.; Koffi, J.F.A.; Coulibaly, F.; Ndour, A.P.N.; Efoua-Tomo, N.; Kante, S.; Syll, M.; et al. Seroprevalence of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii in dogs and risk of infection of dogs and women in the city Saint Louis, Senegal. Sci. Parasitol. 2013, 14, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseininejad, M.; Hosseini, F. Seroprevalence of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii infection in dogs from west and central parts of Iran using two indirect ELISA tests and assessment of associate risk factors. Iran J. Vet. Res. 2011, 12, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, T.H.; Barkema, H.W.; Eysker, M.; Hesselink, J.W.; Wouda, W. Natural transmission routes of Neospora caninum between farm dogs and cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 105, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhin, E.Z.; Sarba, E.J.; Tola, G.K.; Endalew, S.S.; Marami, L.M.; Melkamsew, A.T.; Presti, V.D.M.L.; Vitale, M. Prevalence and risk factors of Toxoplasma gondii and Leishmania spp. infections in apparently healthy dogs in west Shewa zone, Oromia, Ethiopia. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, K.; Bahia-Oliveira, L.; Dixon, B.; Dumètre, A.; de Wit, L.; VanWormer, E.; Villena, I. Environmental transmission of Toxoplasma gondii: Oocysts in water, soil and food. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, M.A.; Mehdi, M.; Aslam, F.; Ashraf, K.; Aleem, M.T.; Khalid, A.R.; Sattar, A.; Waheed, S.F.; Alouffi, A.; Alharbi, O.O.; et al. Molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in cats and its zoonotic potential for public health significance. Pathogens 2022, 11, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, A.; Khan, M.S.; Ashraf, K.; Avais, M.; Pervez, K.; Khan, J.A. Sero-epidemiological and haematological studies on toxoplasmosis in cats, dogs and their owners in Lahore, Pakistan. J. Protozool. Res. 2006, 16, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Examined | Infected | Prevalence | p-Value | Chi-Square (χ2) | Examined | Infected | Prevalence | p-Value | Chi-Square (χ2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxoplasmosis in Stray Dogs | |||||||||||
| LAT | ELISA | ||||||||||
| Breed | Bhakarwal dog | 28 | 11 | 39.29 | 0.51 | 3.30 | 28 | 11 | 39.29 | 0.36 | 4.826 |
| Bulldog | 34 | 9 | 26.47 | 34 | 9 | 26.47 | |||||
| Bully Kutta | 39 | 8 | 20.51 | 39 | 7 | 17.95 | |||||
| Bhagyari dog | 16 | 5 | 31.25 | 16 | 5 | 31.25 | |||||
| Indian Pariah dog | 22 | 5 | 22.73 | 22 | 4 | 18.18 | |||||
| Age | Young | 65 | 15 | 23.08 | 0.29 | 1.12 | 65 | 14 | 21.54 | 0.27 | 1.210 |
| Adult | 74 | 23 | 31.08 | 74 | 22 | 29.73 | |||||
| Sex | Male | 45 | 8 | 17.78 | 0.08 | 3.06 | 45 | 8 | 17.78 | 0.13 | 2.287 |
| Female | 94 | 30 | 31.91 | 94 | 28 | 29.79 | |||||
| Total | 139 | 38 | 27.34 | 139 | 36 | 25.90 | |||||
| Toxoplasmosis in owned dogs | |||||||||||
| Breed | Bulldog | 53 | 15 | 28.30 | 0.20 | 4.69 | 53 | 15 | 28.30 | 0.20 | 4.69 |
| Greyhound | 32 | 4 | 12.50 | 32 | 4 | 12.50 | |||||
| German Shepherd | 38 | 5 | 13.16 | 38 | 5 | 13.16 | |||||
| Labrador | 12 | 2 | 16.67 | 12 | 2 | 16.67 | |||||
| American Bullterrier | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | |||||
| Alsatian | 4 | 1 | 25.00 | 4 | 1 | 25.00 | |||||
| Cocker spaniel | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | |||||
| Belgium shepherd | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | |||||
| Rottweiler | 3 | 0 | 0.00 | 3 | 0 | 0.00 | |||||
| Pointer | 2 | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 0 | 0.00 | |||||
| Mixed | 3 | 0 | 0.00 | 3 | 0 | 0.00 | |||||
| Age | Young | 62 | 15 | 24.19 | 0.10 | 2.75 | 62 | 15 | 24.19 | 0.10 | 2.75 |
| Adult | 88 | 12 | 13.64 | 88 | 12 | 13.64 | |||||
| Sex | Male | 113 | 17 | 15.04 | 0.10 | 2.71 | 113 | 17 | 15.04 | 0.10 | 2.71 |
| Female | 37 | 10 | 27.03 | 37 | 10 | 27.03 | |||||
| Animal keeping | Remain indoor | 23 | 3 | 13.04 | 0.50 | 0.452 | 23 | 3 | 13.04 | 0.50 | 0.452 |
| Go for walk | 127 | 24 | 18.90 | 127 | 24 | 18.90 | |||||
| Total | 150 | 27 | 18.00 | 150 | 27 | 18.00 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamidullah; Saqib, M.; Sajid, M.S.; Hussain, S.; Rizwan, H.M.; Ashfaq, K.; Ghazanfer, S.; Butt, A.A.; Maqbool, M.; Ahmad, S.; et al. Screening of Toxoplasmosis in Owned and Stray Dogs of District Faisalabad, Pakistan through Latex Agglutination and Indirect ELISA. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111307
Hamidullah, Saqib M, Sajid MS, Hussain S, Rizwan HM, Ashfaq K, Ghazanfer S, Butt AA, Maqbool M, Ahmad S, et al. Screening of Toxoplasmosis in Owned and Stray Dogs of District Faisalabad, Pakistan through Latex Agglutination and Indirect ELISA. Pathogens. 2022; 11(11):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111307
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamidullah, Muhammad Saqib, Muhammad Sohail Sajid, Sabir Hussain, Hafiz Muhammad Rizwan, Khurram Ashfaq, Sadia Ghazanfer, Asif Ali Butt, Mahvish Maqbool, Sibtain Ahmad, and et al. 2022. "Screening of Toxoplasmosis in Owned and Stray Dogs of District Faisalabad, Pakistan through Latex Agglutination and Indirect ELISA" Pathogens 11, no. 11: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111307
APA StyleHamidullah, Saqib, M., Sajid, M. S., Hussain, S., Rizwan, H. M., Ashfaq, K., Ghazanfer, S., Butt, A. A., Maqbool, M., Ahmad, S., & Sparagano, O. A. (2022). Screening of Toxoplasmosis in Owned and Stray Dogs of District Faisalabad, Pakistan through Latex Agglutination and Indirect ELISA. Pathogens, 11(11), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111307








