Isolation of a New Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) Variant from Genetically Resistant Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) during 2021–2022
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Gross Pathology
2.2. Histopathology
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR
2.5. IPNV Isolation and Cell Culture
2.6. DNA Sequencing
2.7. Data Analysis
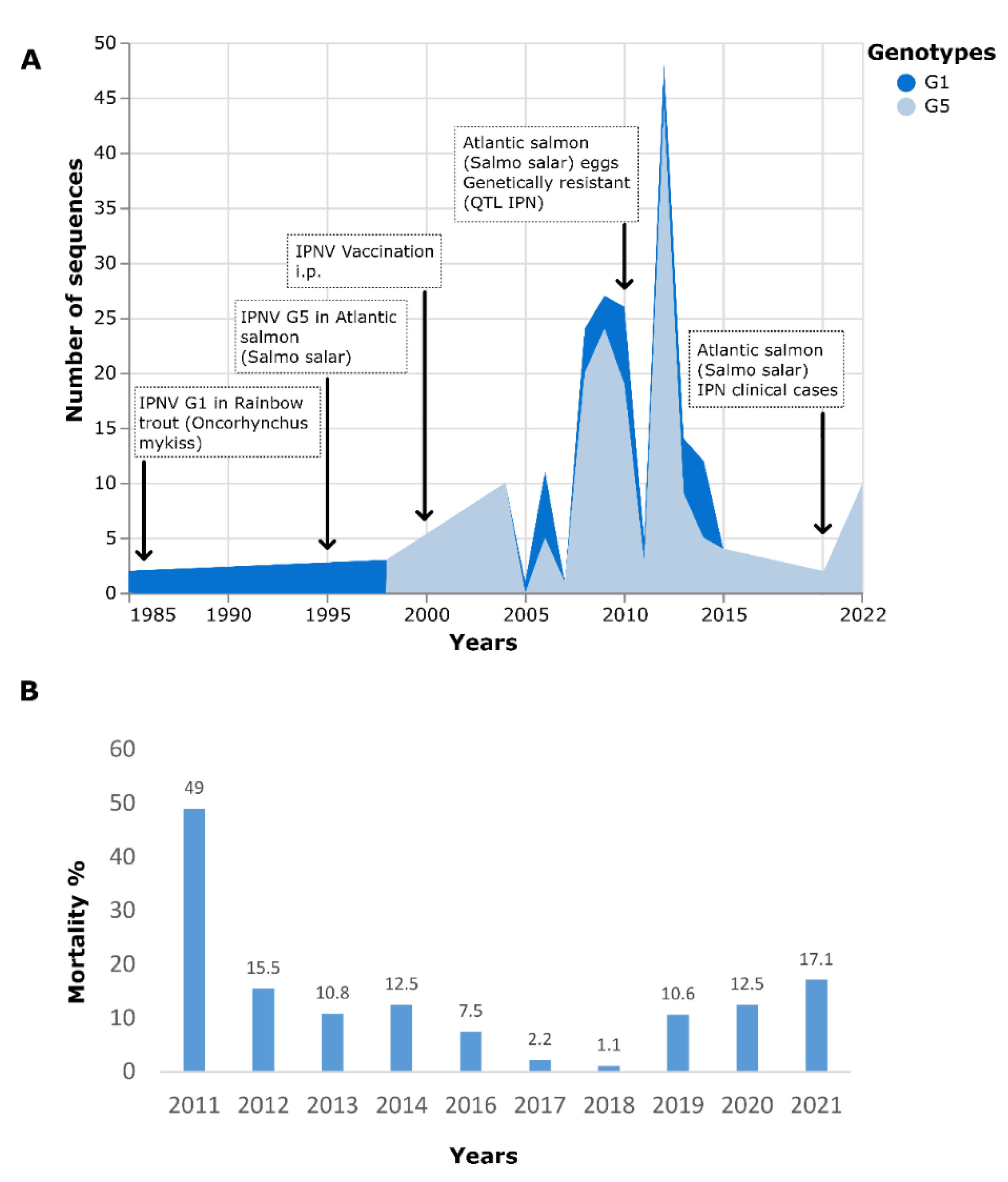
3. Results
3.1. Gross Pathology
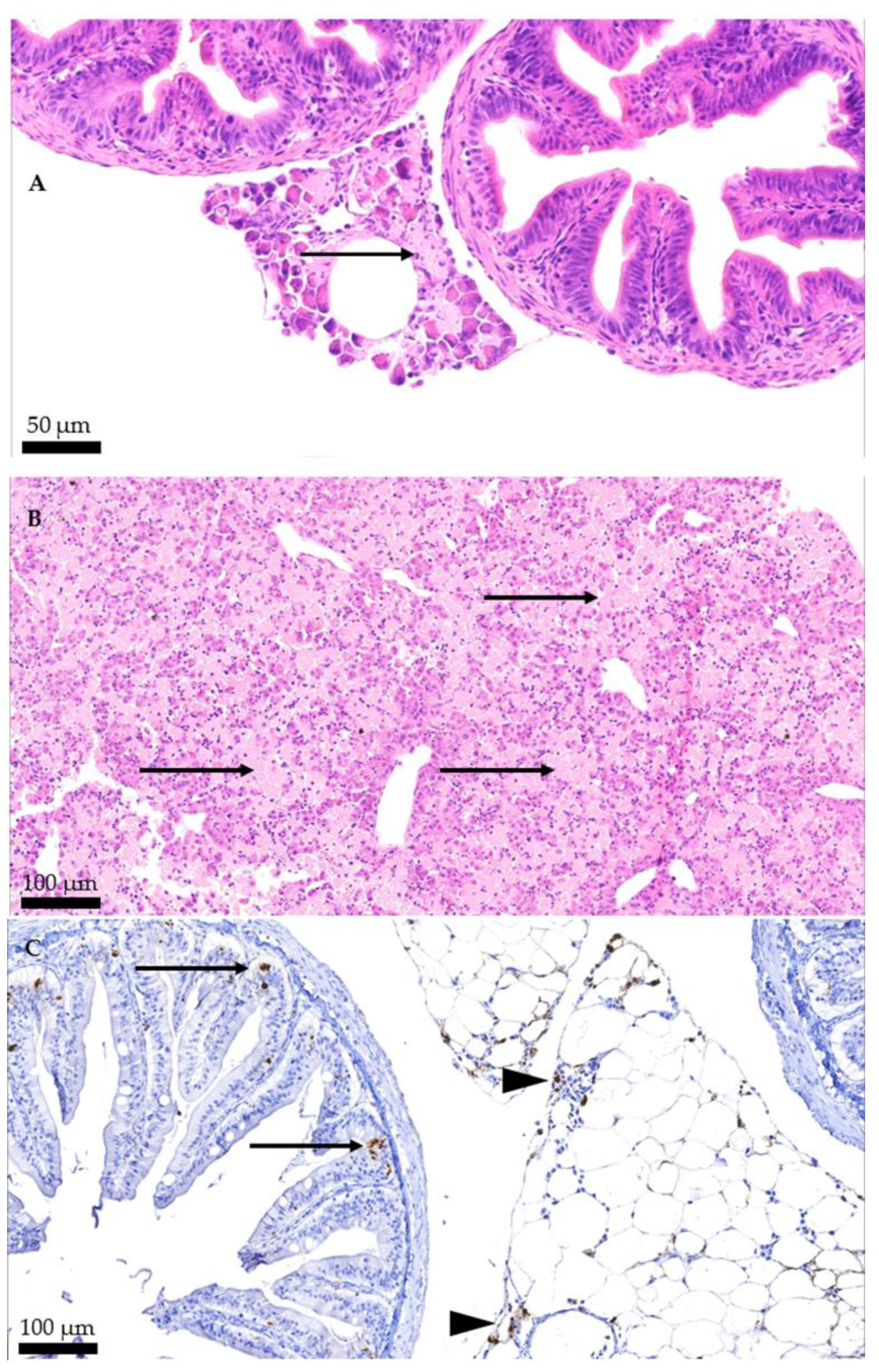
3.2. Histopathology
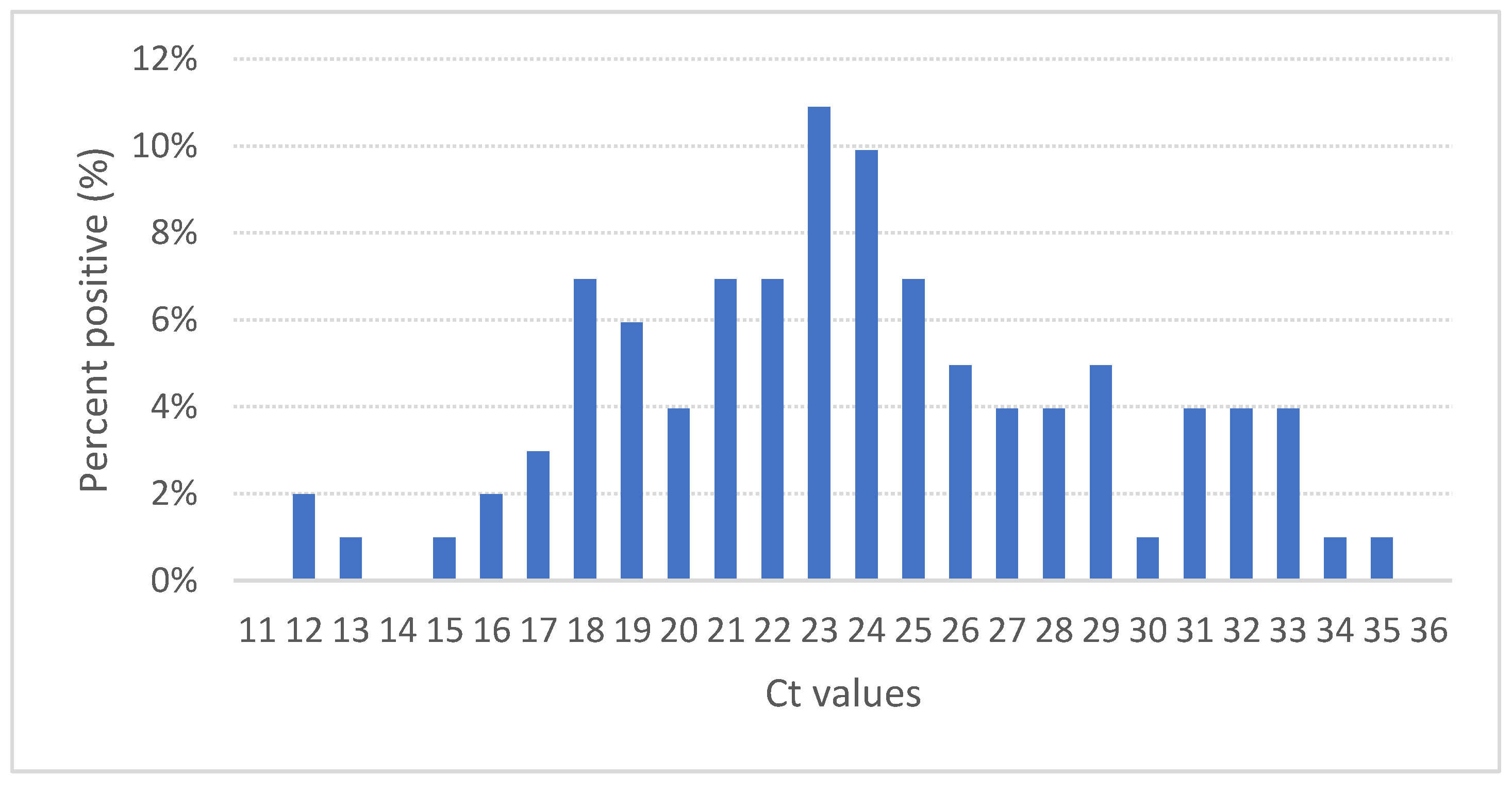
3.3. IPNV PCR
3.4. Cell Culture
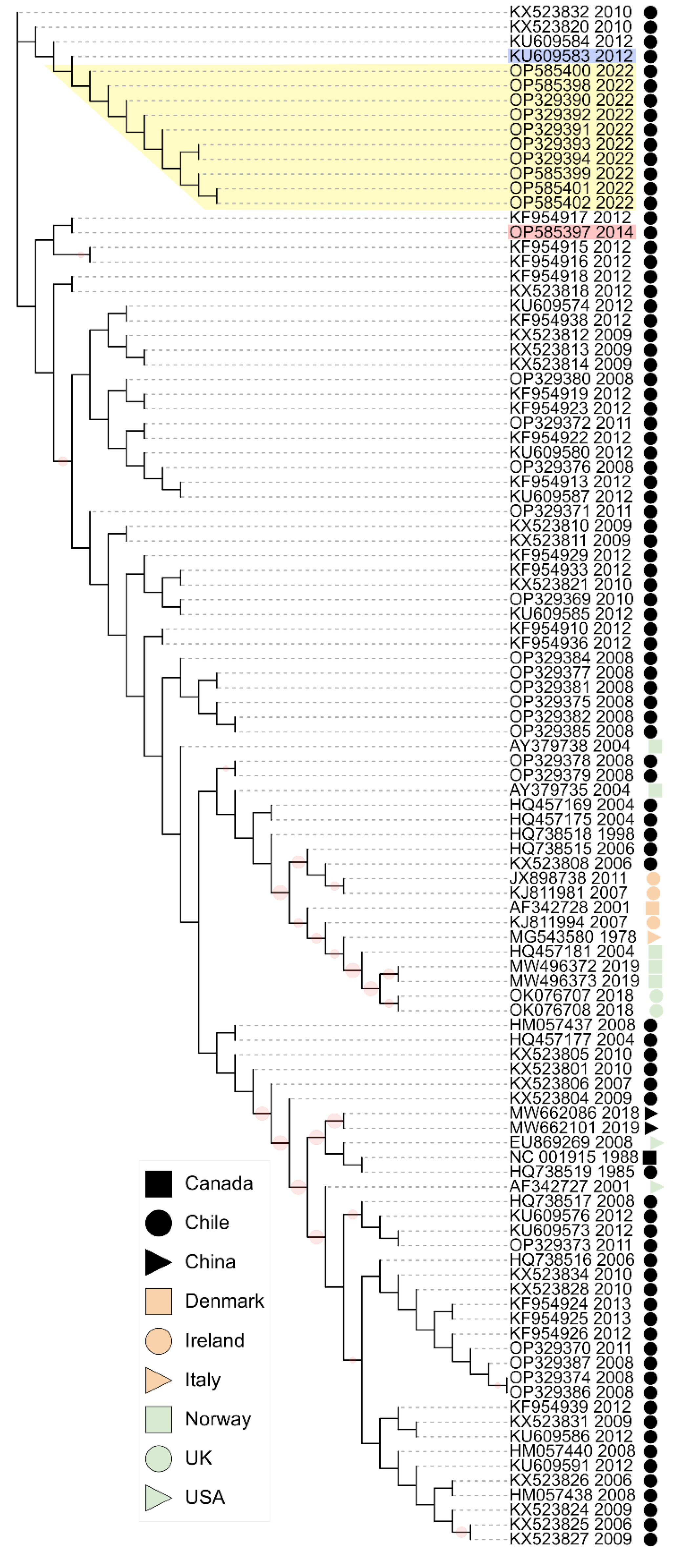
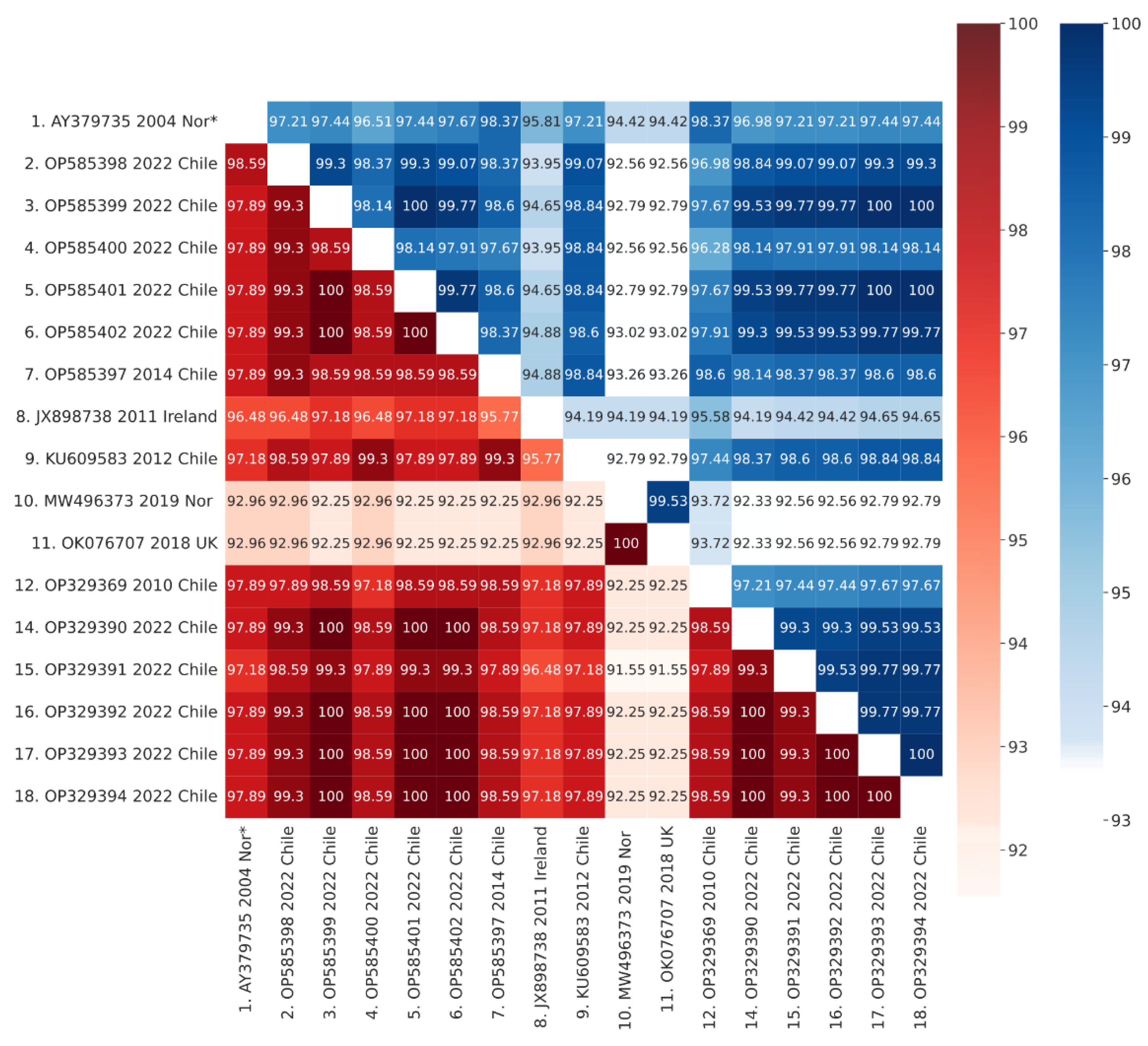
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
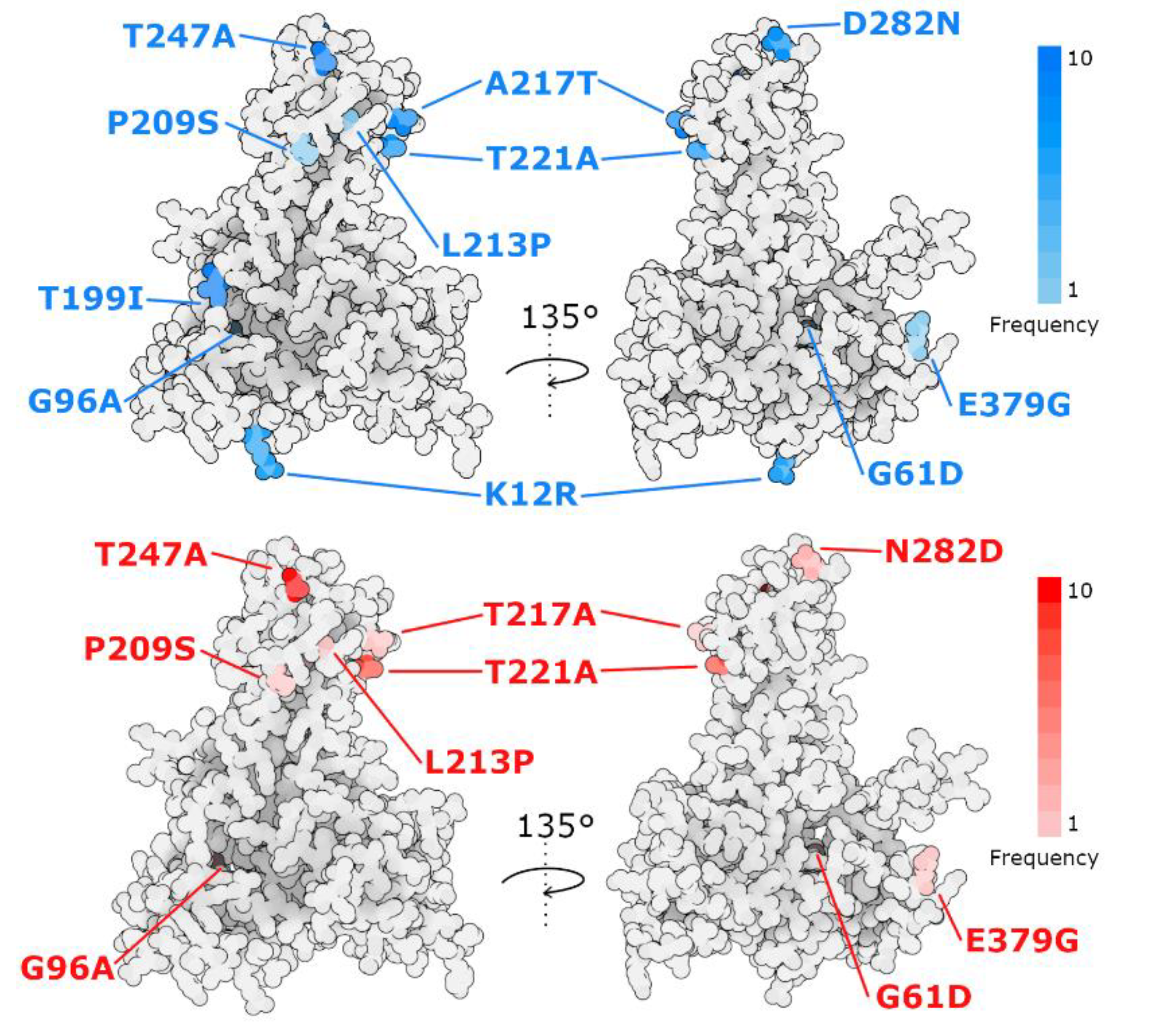
3.6. VP2 Mutations
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lefkowitz, E.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Orton, R.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Smith, D.B. Virus Taxonomy: The Database of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D708–D717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delmas, B.; Attoui, H.; Ghosh, S.; Malik, Y.S.; Mundt, E.; Vakharia, V.N. ICTV Report Consortium ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Birnaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argot, J.; Malsberger, R.G. Intracellular Replication of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus. Can. J. Microbiol. 1972, 18, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, R.D.; Roy, K.L.; Yamamoto, T.; Chang, N. Oligonucleotide Fingerprints of the RNAs from Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus. Arch. Virol. 1977, 54, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobos, P. Virus-Specific Protein Synthesis in Cells Infected by Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus. J. Virol. 1977, 21, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santi, N.; Song, H.; Vakharia, V.N.; Evensen, Ø. Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus VP5 Is Dispensable for Virulence and Persistence. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9206–9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, R.; Mason, C.L.; Nagy, E.; Leong, J.-A.; Dobos, P. Sequence Analysis of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Genome Segment B and Its Encoded VP1 Protein: A Putative RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Lacking the Gly-Asp-Asp Motif. Virology 1991, 181, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, F.; Chevalier, C.; Delmas, B.; Rey, F.A. Crystal Structure of an Aquabirnavirus Particle: Insights into Antigenic Diversity and Virulence Determinism. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Havarstein, L.S.; Kalland, K.H.; Christie, K.E.; Endresen, C. Sequence of the Large Double-Stranded RNA Segment of the N1 Strain of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus: A Comparison with Other Birnaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell-Reno, P.; Reno, P.W.; Nicholson, B.L. Monoclonal Antibodies to Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus: Analysis of Viral Epitopes and Comparison of Different Isolates. J. Gen. Virol. 1986, 67, 2193–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, N.; Vakharia, V.N.; Evensen, Ø. Identification of Putative Motifs Involved in the Virulence of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus. Virology 2004, 322, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivappa, R.; Song, H.; Yao, K.; Aas-Eng, A.; Evensen, Ø.; Vakharia, V. Molecular Characterization of Sp Serotype Strains of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Exhibiting Differences in Virulence. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 61, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.; Santi, N.; Evensen, Ø.; Vakharia, V.N. Molecular Determinants of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Virulence and Cell Culture Adaptation. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10289–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smail, D.A.; Bain, N.; Bruno, D.W.; King, J.A.; Thompson, F.; Pendrey, D.J.; Morrice, S.; Cunningham, C.O. Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus in Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar L., Post-Smolts in the Shetland Isles, Scotland: Virus Identification, Histopathology, Immunohistochemistry and Genetic Comparison with Scottish Mainland Isolates. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoloki, S.; Jøssund, T.B.; Ritchie, G.; Munang’andu, H.M.; Evensen, Ø. Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Causing Clinical and Subclinical Infections in Atlantic Salmon Have Different Genetic Fingerprints. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holopainen, R.; Eriksson-Kallio, A.M.; Gadd, T. Molecular Characterisation of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Viruses Isolated from Farmed Fish in Finland. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3459–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guy, D.R.; Bishop, S.C.; Brotherstone, S.; Hamilton, A.; Roberts, R.J.; McAndrew, B.J.; Woolliams, J.A. Analysis of the Incidence of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Mortality in Pedigreed Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar L., Populations. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, R.D.; Haley, C.S.; Hamilton, A.; Guy, D.R.; Tinch, A.E.; Taggart, J.B.; McAndrew, B.J.; Bishop, S.C. Major Quantitative Trait Loci Affect Resistance to Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar). Genetics 2008, 178, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houston, R.D.; Haley, C.S.; Hamilton, A.; Guy, D.R.; Mota-Velasco, J.C.; Gheyas, A.A.; Tinch, A.E.; Taggart, J.B.; Bron, J.E.; Starkey, W.G.; et al. The Susceptibility of Atlantic Salmon Fry to Freshwater Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Is Largely Explained by a Major QTL. Heredity 2010, 105, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moen, T.; Baranski, M.; Sonesson, A.K.; Kjøglum, S. Confirmation and Fine-Mapping of a Major QTL for Resistance to Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar): Population-Level Associations between Markers and Trait. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, T.; Torgersen, J.; Santi, N.; Davidson, W.S.; Baranski, M.; Ødegård, J.; Kjøglum, S.; Velle, B.; Kent, M.; Lubieniecki, K.P.; et al. Epithelial Cadherin Determines Resistance to Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus in Atlantic Salmon. Genetics 2015, 200, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benkaroun, J.; Muir, K.F.; Allshire, R.; Tamer, C.; Weidmann, M. Isolation of a New Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) Variant from a Fish Farm in Scotland. Viruses 2021, 13, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillestad, B.; Johannessen, S.; Melingen, G.O.; Moghadam, H.K. Identification of a New Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) Variant in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar L.) That Can Cause High Mortality Even in Genetically Resistant Fish. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 635185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, P.E.; Reyes, X. Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus: Isolation from Rainbow Trout, Salmo Gairdneri Richardson, Imported into Chile. J. Fish Dis. 1984, 7, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, E.; Farías, G.; Soler, M.; Kuznar, J. Identity between Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus VR-299 and a Chilean Isolate. Intervirology 1985, 24, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M. Estudio Epidemiológico del Virus de la Necrosis Pancreática Infecciosa en Salmones: Tipificación Molecular de los Distintos Serotipos Existentes en Chile; Universidad Austral de Chile: Valdivia, Chile, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Eissler, Y.; Pavlov, M.S.; Conejeros, P.; Espinoza, J.C.; Kuznar, J. Detection and Quantification of Chilean Strains of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus by Real-Time RT-PCR Assays Using Segment B as a Target. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2011, 39, 544–552. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, S.; Midtlyng, P.J. The Use of Fish Vaccines in the Chilean Salmon Industry 1999–2003. Aquaculture 2007, 270, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; Funk, K.; Kelly, C.; Kim, S.; et al. Database Resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D20–D26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Fisheries Service. Private communication. 2022.
- Noga, E.J. Fish Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-0-8138-0697-6. [Google Scholar]
- Prophet, E.B.; Mills, B.; Arrington, J.B.; Sobin, L.H. Laboratory methods in histotechnology. Armed Forces Inst. Pathol. 1992, 56, 151–164. [Google Scholar]
- Ingerslev, H.-C.; Rønneseth, A.; Pettersen, E.F.; Wergeland, H.I. Differential Expression of Immune Genes in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar L.) Challenged Intraperitoneally or by Cohabitation with IPNV. Scand. J. Immunol. 2009, 69, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, G.; Lovoll, M.; Tengs, T.; Hornig, M.; Hutchison, S.; Hui, J.; Kongtorp, R.-T.; Savji, N.; Bussetti, A.V.; Solovyov, A.; et al. Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation of Farmed Salmon Is Associated with Infection with a Novel Reovirus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, M.; McKay, P.; McBeath, A.J.A.; Black, J.; Doig, F.; Kerr, R.; Cunningham, C.O.; Nylund, A.; Devold, M. Development, Application and Validation of a Taqman Real-Time RT-PCR Assay for the Detection of Infectious Salmon Anaemia Virus (ISAV) in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar). Dev. Biol. 2006, 126, 133–145, discussion 325–326. [Google Scholar]
- USFWS and AFS-FHS (U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and American Fisheries Society-Fish Health Section). Standard procedures for aquatic animal health inspections. In Suggested Procedures for the Detection and Identification of Certain Finfish and Shellfish Pathogens, 2020th ed.; AFS-FHS: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2014; Available online: https://units.fisheries.org/fhs/fish-health-section-blue-book-2020/ (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, Scalable Generation of High-quality Protein Multiple Sequence Alignments Using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML Version 8: A Tool for Phylogenetic Analysis and Post-Analysis of Large Phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (ITOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making Protein Folding Accessible to All. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, G.; Armenia, I.; Molla, G. The Protein Imager: A Full-Featured Online Molecular Viewer Interface with Server-Side HQ-Rendering Capabilities. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2909–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A.E.; Cavaco, A.; Petrie, A.; Lockhart, K.; Snow, M.; Collet, B. Histology, Immunocytochemistry and QRT-PCR Analysis of Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar L., Post-Smolts Following Infection with Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV): Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) in Atlantic Salmon. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKnight, I.J.; Roberts, R.J. The Pathology of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis. I. The Sequential Histopathology of the Naturally Occurring Condition. Br. Vet. J. 1976, 132, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, P.A.; Bruno, D.W. Liver Involvement in Post-Smolt Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar L., Infected with Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV): A Retrospective Histopathological Study: Liver Involvement in IPNV Infected Salmon. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.J.; McKnight, I.J. The Pathology of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis. II. Stress-Mediated Recurrence. Br. Vet. J. 1976, 132, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.J.; Pearson, M.D. Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis in Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar L. J. Fish Dis. 2005, 28, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Fan, J.; Yu, F.; Feng, B.; Lou, B.; Zou, Q.; Xie, G.; Lin, S.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.; et al. Viral Load Dynamics and Disease Severity in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Zhejiang Province, China, January–March 2020: Retrospective Cohort Study. BMJ 2020, 369, m1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruslind, L.; Reno, P. Virulence Comparison of Three Buhl-Subtype Isolates of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus in Brook Trout Fry. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2000, 12, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadar, M.; Peyghan, R.; Memari, H.R.; Shapouri, M.R.S.A.; Hasanzadeh, R.; Goudarzi, L.M.; Vakharia, V.N. Sequence Analysis of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Isolated from Iranian Reared Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) in 2012. Virus Genes 2013, 47, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Case ID | 3987 | 3759 | 4258 | 4257 | 4579 | 5117 | 5126 | 7023 | 7036 | 7027 | 7061 | 3746 | 7150 | 7190 | 7189 | 7176 | 95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | 01-2020 | 09-2020 | 05-2021 | 05-2021 | 10-2021 | 05-2022 | 05-2022 | 06-2022 | 06-2022 | 06-2022 | 06-2022 | 08-2020 | 08-2022 | 08-2022 | 08-2022 | 08-2022 | 2014 |
| Region | IX | X | X | IX | X | XI | X | X | XI | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Salinity | FW | BW | BW | FW | BW | FW | BW | BW | FW | BW | BW | FW | FW | FW | BW | FW | FW |
| Development stage | Fry | Pre Smolt | Pre Smolt | Fry | Pre Smolt | Fry | Pre Smolt | Pre Smolt | Fry | Pre Smolt | Pre Smolt | Fry | Pre Smolt | Pre Smolt | Pre Smolt | Pre Smolt | NA |
| Mortality (%) | 8.1 | 0.83 | 1.2 | 5 | 0.95 | 9.7 | 0.7 | 0.45 | 4.3 | 1.15 | 0.78 | 3.1 | 0.8 | 0.93 | 2.7 | 1.2 | NA |
| Outbreak time (weeks) | 4 to 5 | 3 | 3 to 4 | 4 to 5 | 3 to 4 | 4 to 5 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 to 4 | 3 | 3 to 4 | 2 to 3 | 3 to 4 | 3 to 4 | 3 to 4 | NA |
| Fish sampled | 8 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 13 | 3 | 5 | 17 | 15 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 19 | 13 | 10 | NA |
| Average IPNV Ct | 20.5 | 28.1 | 23.2 | 25.4 | 25.6 | 13.3 | 27.4 | 25.4 | 21.2 | 21.5 | 17.4 | 30.5 | 26.5 | 20.2 | 20.2 | 27.6 | 21.9 |
| Cell culture | CPE | NA | CPE | NA | NA | NA | NA | CPE | NA | NA | NA | CPE | NA | NA | CPE | NA | NA |
| GenBank accession | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | OP329390 | NA | NA | NA | OP585398 | OP329391 OP329392 OP329393 OP329394 | NA | NA | OP585401OP585402 | OP585399OP585400 | NA | OP585397 |
| Tissue | Histopathological Description | Diagnosis | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pancreas | Structural loss of the acinar cells of the pancreas, forming amorphous eosinophilic mass areas. | Diffuse, severe, pancreas necrosis. | 37/46 |
| Liver | Structural loss of multiple coalescent areas of hepatocytes, in some cases, it presents as ballooning degeneration, characterized by enlarged and swollen hepatocytes with granular material in the cytoplasm. In some, a loss of cell integrity is observed, and pyknotic nuclei and eosinophilic bodies are consistent with apoptosis. | Diffuse, severe, hepatic necrosis. | 36/46 |
| Pyloric ceca/intestine | Necrosis and sloughing of epithelium. Eosinophilic content in the lumen of the pyloric ceca. | Diffuse, mild to severe, intestinal necrosis. NA | 5/46 6/46 |
| Peripiloric fat | Multiple hemorrhagic foci, fat cell boundary loss and loss of their peripheral nuclei. In some cases, their cytoplasm has become a pink amorphous mass of necrotic material. | Moderate to severe focal to multifocal hemorrhagic fat necrosis. | 3/46 |
| Kidney | Presence of basophilic amorphous deposits in lumen of tubules and ureters. | Renal calcinosis, mild to moderate. | 3/46 |
| Heart | Multifocal to diffuse infiltration of mononuclear cells of myocardium and epicardium. | Multifocal to diffuse, subacute, mild to moderate, epicarditis and myocarditis. | 8/46 |
| 12 | 61 | 96 | 199 | 209 | 213 | 217 | 221 | 247 | 282 | 379 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AY379735 2004 Norway | K | G | G | I | P | L | T | T | A | N | E |
| OP585398 2022 Chile | R | G | A | I | S | L | T | T | A | D | E |
| OP585399 2022 Chile | R | G | G | I | P | L | T | A | A | N | G |
| OP585400 2022 Chile | R | G | G | I | P | L | A | T | A | D | E |
| OP585401 2022 Chile | R | G | G | I | P | L | T | A | A | N | E |
| OP585402 2022 Chile | R | G | G | I | P | L | T | A | A | N | E |
| OP585397 2014 Chile | R | G | G | I | P | L | T | T | T | N | E |
| JX880108 1999 Ireland | - | S | G | I | P | L | P | T | P | A | E |
| KU609583 2012 Chile | K | G | G | T | P | L | A | T | T | D | E |
| MW496373 2019 Norway | K | G | G | I | P | L | P | T | A | T | E |
| OK076707 2018 UK | K | G | G | I | P | L | P | T | A | T | E |
| OP329369 2010 Chile | R | G | G | I | P | L | T | A | T | N | E |
| OP329387 2008 Chile | R | G | G | I | P | L | A | T | A | A | D |
| OP329390 2022 Chile | R | G | G | I | P | L | T | A | A | N | E |
| OP329391 2022 Chile | - | G | G | I | P | P | T | A | A | N | E |
| OP329392 2022 Chile | - | G | G | I | P | L | T | A | A | N | E |
| OP329393 2022 Chile | - | D | G | I | P | L | T | A | A | N | E |
| OP329394 2022 Chile | - | G | G | I | P | L | T | A | A | N | E |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godoy, M.; Kibenge, M.J.T.; Montes de Oca, M.; Pontigo, J.P.; Coca, Y.; Caro, D.; Kusch, K.; Suarez, R.; Burbulis, I.; Kibenge, F.S.B. Isolation of a New Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) Variant from Genetically Resistant Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) during 2021–2022. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111368
Godoy M, Kibenge MJT, Montes de Oca M, Pontigo JP, Coca Y, Caro D, Kusch K, Suarez R, Burbulis I, Kibenge FSB. Isolation of a New Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) Variant from Genetically Resistant Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) during 2021–2022. Pathogens. 2022; 11(11):1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111368
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodoy, Marcos, Molly J. T. Kibenge, Marco Montes de Oca, Juan Pablo Pontigo, Yoandy Coca, Diego Caro, Karina Kusch, Rudy Suarez, Ian Burbulis, and Frederick S. B. Kibenge. 2022. "Isolation of a New Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) Variant from Genetically Resistant Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) during 2021–2022" Pathogens 11, no. 11: 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111368
APA StyleGodoy, M., Kibenge, M. J. T., Montes de Oca, M., Pontigo, J. P., Coca, Y., Caro, D., Kusch, K., Suarez, R., Burbulis, I., & Kibenge, F. S. B. (2022). Isolation of a New Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) Variant from Genetically Resistant Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) during 2021–2022. Pathogens, 11(11), 1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111368







