First Isolation of Virulent Tenacibaculum maritimum Isolates from Diseased Orbicular Batfish (Platax orbicularis) Farmed in Tahiti Island
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Microscopic Examination and Isolation of Bacteria
2.2. Genomic and Serological Characterisation
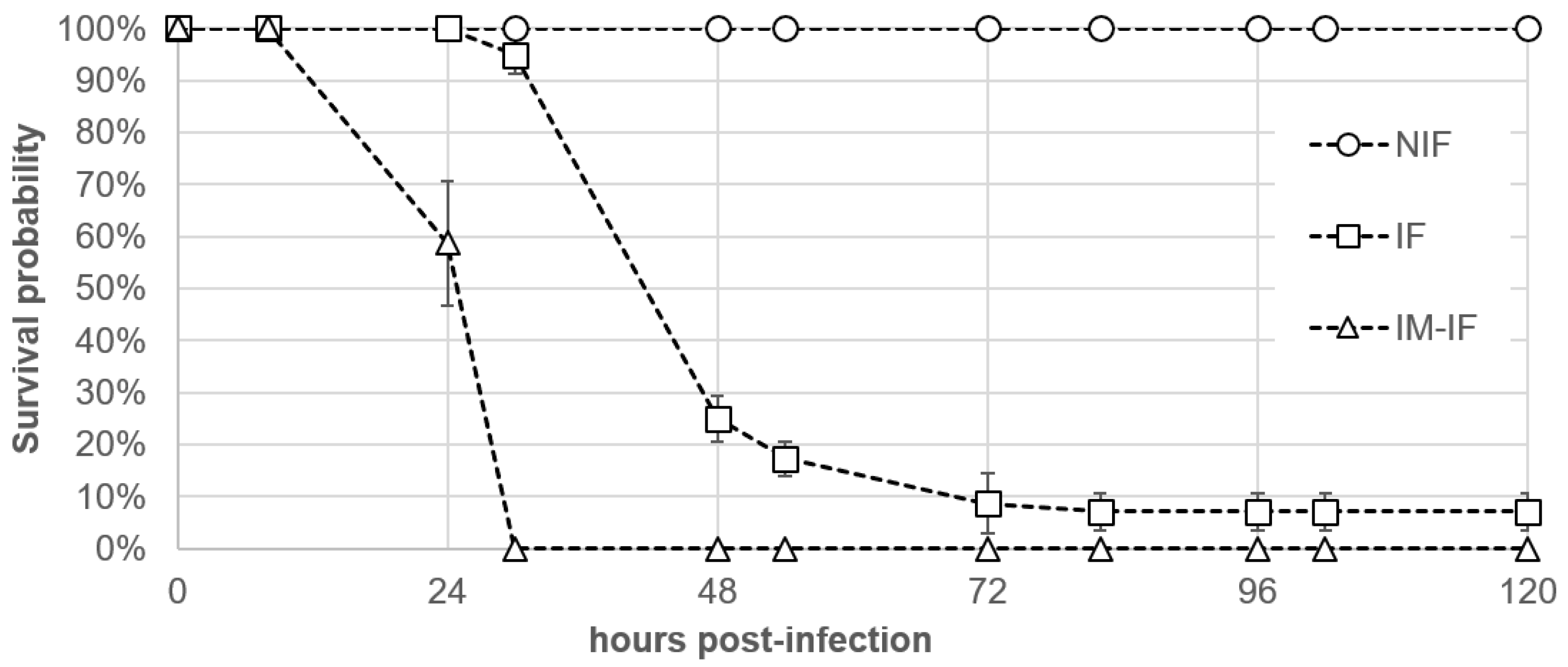
2.3. Pathogenicity Assays Using an Immersion Challenge
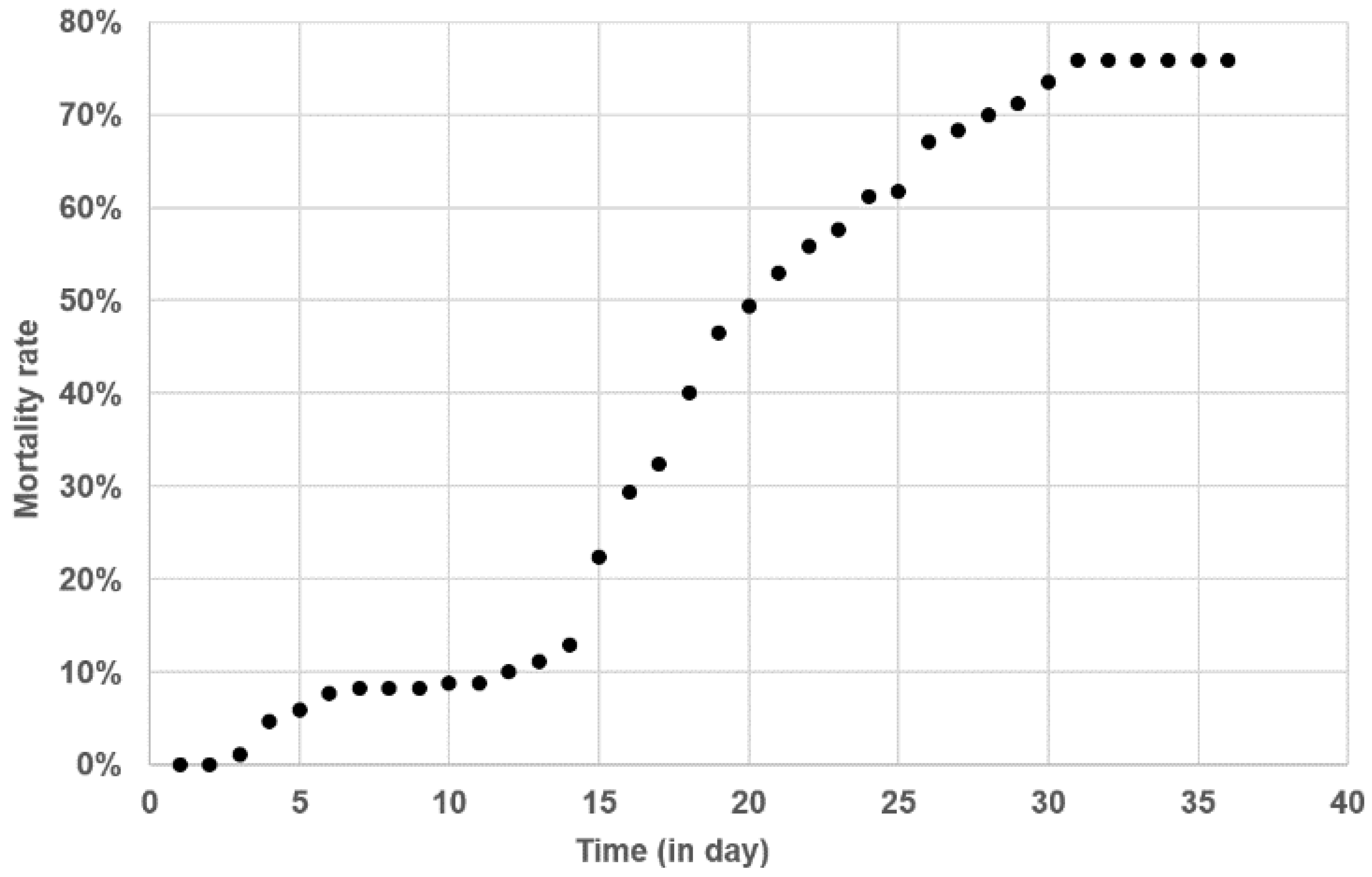
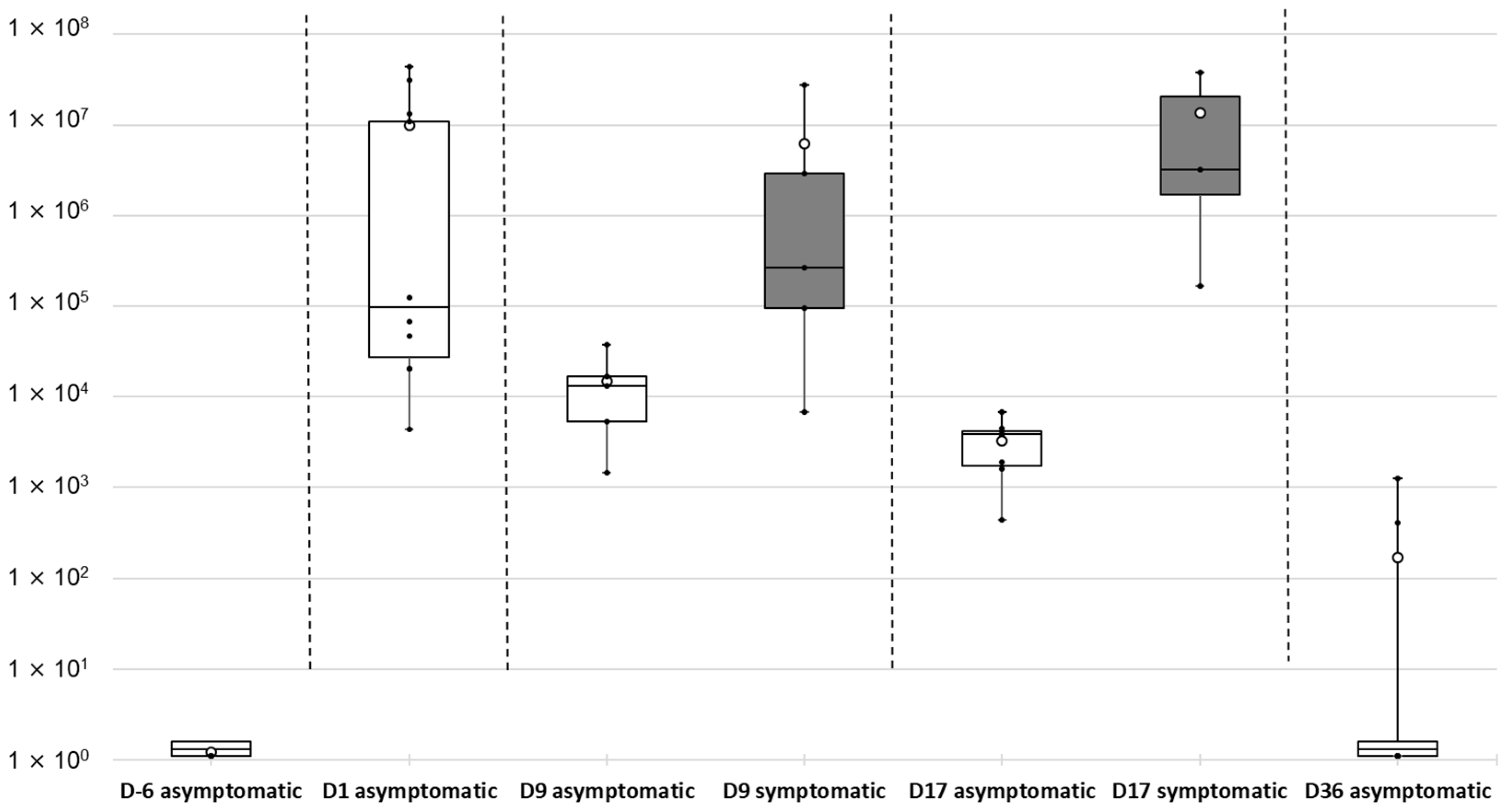
2.4. Kinetics of Tenacibaculum maritimum Infection during a Field Episode of Tenacibaculosis
3. Discussion
| Isolate | Source and Date of Isolation | GPS Location | 16S rDNA GenBank Accession Number | Bacterial Species | Virulence | ST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFA4 | Skin lesions, Tautira lagoon, Tahiti, 2013 | 17°47′50″ S, 149°07′14″ W | MW690171 | T. maritimum | yes | ST168 |
| Aq 9–66 | Skin lesions, Tautira lagoon, Tahiti, 2013 | 17°47′50″ S, 149°07′14″ W | MW690177 | T. mesophilum | no | |
| Aq 9–67 | Skin lesions, Tautira lagoon, Tahiti, 2013 | 17°47′50″ S, 149°07′14″ W | MW690178 | T. mesophilum | no | |
| Aq 16–83 | Skin lesions, Vairao lagoon, Tahiti, 2016 | 17°48′22″ S, 149°17′36″ W | MW690172 | T. maritimum | n/a | n/a |
| Aq 16–84 | Skin lesions, Vairao lagoon, Tahiti, 2016 | 17°48′22″ S, 149°17′36″ W | MW690173 | T. maritimum | yes | n/a |
| Aq 16–85 | Skin lesions, Vairao lagoon, Tahiti, 2016 | 17°48′22″ S, 149°17′36″ W | MW690174 | T. maritimum | n/a | ST167 |
| Aq 16–87 | Skin lesions, Vairao lagoon, Tahiti, 2016 | 17°48′22″ S, 149°17′36″ W | MW690175 | T. maritimum | yes | n/a |
| Aq 16–88 | Skin lesions, Vairao lagoon, Tahiti, 2016 | 17°48′22″ S, 149°17′36″ W | MW690176 | T. maritimum | n/a | ST167 |
| Aq 16–89 | Skin lesions, Vairao lagoon, Tahiti, 2016 | 17°48′22″ S, 149°17′36″ W | MW690180 | T. maritimum | n/a | ST167 |
| Aq 16–91 | Skin lesions, Vairao lagoon, Tahiti, 2016 | 17°48′22″ S, 149°17′36″ W | MW690179 | T. mesophilum | n/a |
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling of Diseased Fish
4.2. Direct Microscopic Examination and Isolation of Bacteria
4.3. Histopathological Examination
4.4. Molecular and Serological Studies
4.5. Experimental Infection by Immersion and Quantification of Tenacibaculum maritimum in Mucus Samples by Real-Time qPCR
4.6. Detection and Quantification of Tenacibaculum maritimum during a Field Episode of Tenacibaculosis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakabo, T. Fishes of the Japan: With Pictorial Keys to the Species, English Edition; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2002; ISBN 978-4-486-01570-3. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, B.; Sakai, Y.; Hashimoto, H.; Gushima, K. Feeding behavior of leaf-like juveniles of the round batfish Platax orbicularis (Ephippidae) on reefs of Kuchierabu-jima Island, southern Japan. J. Ethol. 2008, 26, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréfouët, S.; Adjeroud, M. French Polynesia. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 593–618. ISBN 978-0-08-100853-9. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Harayama, S.; Yamamoto, S. Phylogenetic analysis and taxonomic study of marine Cytophaga-like bacteria: Proposal for Tenacibaculum gen. nov. with Tenacibaculum maritimum comb. nov. and Tenacibaculum ovolyticum comb. nov., and description of Tenacibaculum mesophilum sp. nov. and Tenacibaculum amylolyticum sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1639–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowlan, J.P.; Lumsden, J.S.; Russell, S. Advancements in Characterizing Tenacibaculum Infections in Canada. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masumura, K.; Wakabayashi, H. An outbreak of gliding bacterial disease in hatchery-born red seabream (Pegrus major) and gilthead (Acanthopagrus schlegeli) fry in Hiroshima. Fish Pathol. 1977, 12, 171–177. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, H.; Hikida, M.; Masumura, K. Flexibacter maritimus sp. nov., a Pathogen of Marine Fishes. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1986, 36, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Handlinger, J.; Soltani, M.; Percival, S. The pathology of Flexibacter maritimus in aquaculture species in Tasmania, Australia. J. Fish Dis. 1997, 20, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, K.; Småge, S.B.; Johansen, R.; Duesund, H.; Brevik, Ø.J.; Nylund, A. Pathology of experimentally induced mouthrot caused by Tenacibaculum maritimum in Atlantic salmon smolts. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrok, M.; Machado, M.; Serra, C.R.; Afonso, A.; Valente, L.M.P.; Costas, B. Tenacibaculosis induction in the Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) and studies of Tenacibaculum maritimum survival against host mucus and plasma. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardet, J.-F.; Kerouault, B.; Michel, C. Comparative Study on Flexibacter maritimus Strains Isolated from Farmed Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) in France. Fish Pathol. 1994, 29, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, T.; Watanabe, K.-I.; Sano, M. A Bath Challenge Method with Tenacibaculum maritimum for Japanese Flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Pathol. 2009, 44, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasheim, M.H.M.; Haridy, M.H.M. Pathological Findings of Tenacibaculum maritimus Infection in Black Damselfish, Neoglyphieodon melas and Picasso Triggerfish, Rhinecanthus assasi in Red Sea, Egypt. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2014, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apablaza, P.; Frisch, K.; Brevik, Ø.J.; Småge, S.B.; Vallestad, C.; Duesund, H.; Mendoza, J.; Nylund, A. Primary Isolation and Characterization of Tenacibaculum maritimum from Chilean Atlantic Salmon Mortalities Associated with a Pseudochattonella spp. Algal Bloom. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2017, 29, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Småge, S.B.; Frisch, K.; Brevik, Ø.J.; Watanabe, K.; Nylund, A. First isolation, identification and characterisation of Tenacibaculum maritimum in Norway, isolated from diseased farmed sea lice cleaner fish Cyclopterus lumpus L. Aquaculture 2016, 464, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muniesa, A.; Basurco, B.; Aguilera, C.; Furones, D.; Reverté, C.; Sanjuan-Vilaplana, A.; Jansen, M.D.; Brun, E.; Tavornpanich, S. Mapping the knowledge of the main diseases affecting sea bass and sea bream in Mediterranean. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICES; Santos, I.; Pazos, F.; Barja, J.L. Tenacibaculum maritimum, Causal Agent of Tenacibaculosis in Marine Fish. Available online: www.vliz.be/imisdocs/publications/326136.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Bridel, S.; Bourgeon, F.; Marie, A.; Saulnier, D.; Pasek, S.; Nicolas, P.; Bernardet, J.-F.; Duchaud, E. Genetic diversity and population structure of Tenacibaculum maritimum, a serious bacterial pathogen of marine fish: From genome comparisons to high throughput MALDI-TOF typing. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Toranzo, A.E.; Magariños, B. A challenge model for Tenacibaculum maritimum infection in turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, T.; Suga, K.; Kanai, K.; Sugihara, Y. Biological and Serological Characterization of a Non-gliding Strain of Tenacibaculum maritimum Isolated from a Diseased Puffer Fish Takifugu rubripes. Fish Pathol. 2014, 49, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, T.; Kawai, K.; Oshima, S. Evaluation of an Experimental Immersion Infection Method with Tenacibaculum maritimum in Japanese Flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquac. Sci. 2010, 58, 481–489. [Google Scholar]
- Baxa, D.V.; Kawai, K.; Kusuda, R. Experimental infection of Flexibacter maritimus in black sea bream (Acanthopagrus schlegeli) fry. Fish Pathol. 1987, 22, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, K.; Småge, S.B.; Vallestad, C.; Duesund, H.; Brevik, Ø.J.; Klevan, A.; Olsen, R.H.; Sjaatil, S.T.; Gauthier, D.; Brudeseth, B.; et al. Experimental induction of mouthrot in Atlantic salmon smolts using Tenacibaculum maritimum from Western Canada. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, S.; MacKinnon, S.L.; Ross, N.W. A comparative study on innate immune parameters in the epidermal mucus of various fish species. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 148, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Hong, G.; Zhao, J. Degradation of malachite green dye by Tenacibaculum sp. HMG1 isolated from Pacific deep-sea sediments. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelderen, R.; Carson, J.; Gudkovs, N.; Nowak, B. Physical Characterisation of Tenacibaculum maritimum for Vaccine Development: T. maritimum for Vaccine Development. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Rodriguez, J.; Magarinos, B.; Romalde, J.; Toranzo, A. Intraspecific diversity of the marine fish pathogen Tenacibaculum maritimum as determined by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA-PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, Y.; Timur, G. Antigenic Characterisation of Tenacibaculum maritimum Isolates from Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) Farmed on the Aegean Sea Coasts of Turkey. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Toranzo, A.E.; Romalde, J.L.; Lemos, M.L.; Magariños, B. Iron Uptake Mechanisms in the Fish Pathogen Tenacibaculum maritimum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6947–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Ha, S.-M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix, M.; Gasset, E.; Bardon-Albaret, A.; Noel, J.; Pirot, N.; Perez, V.; Coves, D.; Saulnier, D.; Lignot, J.-H.; Cucchi, P.N. Description of the unusual digestive tract of Platax orbicularis and the potential impact of Tenacibaculum maritimum infection. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habib, C.; Houel, A.; Lunazzi, A.; Bernardet, J.-F.; Olsen, A.B.; Nilsen, H.; Toranzo, A.E.; Castro, N.; Nicolas, P.; Duchaud, E. Multilocus Sequence Analysis of the Marine Bacterial Genus Tenacibaculum Suggests Parallel Evolution of Fish Pathogenicity and Endemic Colonization of Aquaculture Systems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5503–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C. BIGSdb: Scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: An online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W242–W245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Magariños, B.; López-Romalde, S.; Romalde, J.; Toranzo, A.; Hartl-Meier, C.; Zang, C.; Dittmar, C.; Esper, J.; Göttlein, A.; et al. Phenotypic characterization and description of two major O-serotypes in Tenacibaculum maritimum strains from marine fishes. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2004, 58, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fringuelli, E.; Savage, P.D.; Gordon, A.; Baxter, E.J.; Rodger, H.D.; Graham, D.A. Development of a Quantitative Real-Time PCR for the Detection of Tenacibaculum Maritimum and Its Application to Field Samples: Real-Time PCR for Tenacibaculum Maritimum. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, B.; Banister, K.; Baumans, V.; Bernoth, E.-M.; Bromage, N.; Bunyan, J.; Erhardt, W.; Flecknell, P.; Gregory, N.; Hackbarth, H.; et al. Recommendations for euthanasia of experimental animals: Part 2. Lab. Anim. 1997, 31, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving Bioscience Research Reporting: The ARRIVE Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez, P.; Saulnier, D.; Swarup-Gaucher, S.; David, R.; Lau, C.; Taputuarai, R.; Belliard, C.; Basset, C.; Labrune, V.; Marie, A.; et al. First Isolation of Virulent Tenacibaculum maritimum Isolates from Diseased Orbicular Batfish (Platax orbicularis) Farmed in Tahiti Island. Pathogens 2022, 11, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020131
Lopez P, Saulnier D, Swarup-Gaucher S, David R, Lau C, Taputuarai R, Belliard C, Basset C, Labrune V, Marie A, et al. First Isolation of Virulent Tenacibaculum maritimum Isolates from Diseased Orbicular Batfish (Platax orbicularis) Farmed in Tahiti Island. Pathogens. 2022; 11(2):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020131
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez, Pierre, Denis Saulnier, Shital Swarup-Gaucher, Rarahu David, Christophe Lau, Revahere Taputuarai, Corinne Belliard, Caline Basset, Victor Labrune, Arnaud Marie, and et al. 2022. "First Isolation of Virulent Tenacibaculum maritimum Isolates from Diseased Orbicular Batfish (Platax orbicularis) Farmed in Tahiti Island" Pathogens 11, no. 2: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020131
APA StyleLopez, P., Saulnier, D., Swarup-Gaucher, S., David, R., Lau, C., Taputuarai, R., Belliard, C., Basset, C., Labrune, V., Marie, A., Bernardet, J. F., & Duchaud, E. (2022). First Isolation of Virulent Tenacibaculum maritimum Isolates from Diseased Orbicular Batfish (Platax orbicularis) Farmed in Tahiti Island. Pathogens, 11(2), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020131






