Cerebral Cryptococcomas: A Systematic Scoping Review of Available Evidence to Facilitate Diagnosis and Treatment
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction Process
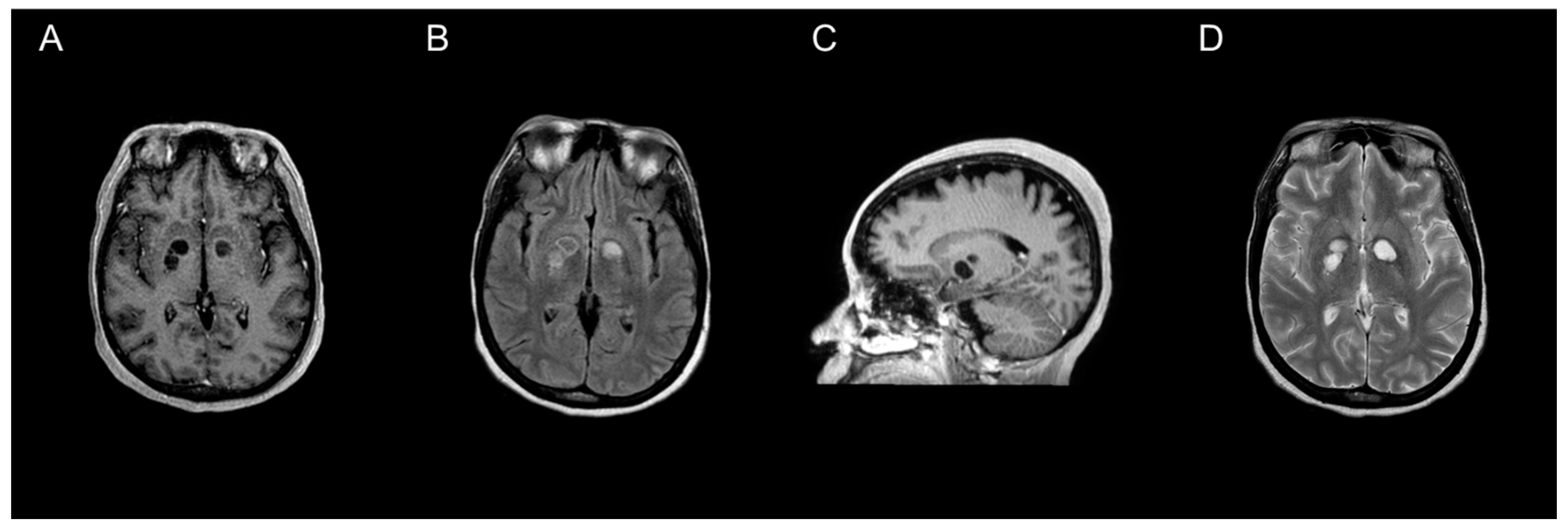
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Causative Pathogens
3.3. Clinical Manifestations
3.4. Site and Description of Lesion(s)
3.5. Treatment Details
3.6. Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajasingham, R.; Smith, R.M.; Park, B.J.; Jarvis, J.N.; Govender, N.P.; Chiller, T.M.; Denning, D.W.; Loyse, A.; Boulware, D.R. Global Burden of Disease of HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis: An Updated Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- George, I.A.; Spec, A.; Powderly, W.G.; Santos, C.A.Q. Comparative Epidemiology and Outcomes of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Non-HIV Non-Transplant, and Solid Organ Transplant Associated Cryptococcosis: A Population-Based Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamilos, G.; Lionakis, M.S.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Call for Action: Invasive Fungal Infections Associated with Ibrutinib and Other Small Molecule Kinase Inhibitors Targeting Immune Signaling Pathways. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 66, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hevey, M.A.; George, I.A.; Raval, K.; Powderly, W.G.; Spec, A. Presentation and Mortality of Cryptococcal Infection Varies by Predisposing Illness: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 977–983.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.A.; Felsen, U.; Wang, T.; Pirofski, L.-A. Cryptococcus Neoformans Infection in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-Infected and HIV-Uninfected Patients at an Inner-City Tertiary Care Hospital in the Bronx. Med. Mycol. 2019, 58, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marr, K.A.; Sun, Y.; Spec, A.; Lu, N.; Panackal, A.; Bennett, J.; Pappas, P.; Ostrander, D.; Datta, K.; Zhang, S.X.; et al. A Multicenter, Longitudinal Cohort Study of Cryptococcosis in Human Immunodeficiency Virus–Negative People in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 70, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, L.B.; Freeman, A.F.; Yang, L.M.; Jutivorakool, K.; Olivier, K.N.; Angkasekwinai, N.; Suputtamongkol, Y.; Bennett, J.E.; Pyrgos, V.; Williamson, P.R.; et al. Anti–GM-CSF Autoantibodies in Patients with Cryptococcal Meningitis. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3959–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pappas, P.G.; Perfect, J.R.; Cloud, G.A.; Larsen, R.A.; Pankey, G.A.; Lancaster, D.J.; Henderson, H.; Kauffman, C.A.; Haas, D.W.; Saccente, M.; et al. Cryptococcosis in Human Immunodeficiency Virus–Negative Patients in the Era of Effective Azole Therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sitapati, A.M.; Kao, C.L.; Cachay, E.R.; Masoumi, H.; Wallis, R.S.; Mathews, W.C. Treatment of HIV-Related Inflammatory Cerebral Cryptococcoma with Adalimumab. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, e7–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tien, R.D.; Chu, P.K.; Hesselink, J.R.; Duberg, A.; Wiley, C. Intracranial Cryptococcosis in Immunocompromised Patients: CT and MR Findings in 29 Cases. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1991, 12, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, A.C.; Rodrigues, M.L. Fungal Colonization of the Brain: Anatomopathological Aspects of Neurological Cryptococcosis. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2015, 87, 1293–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Paredes, C.; Chastain, D.B.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Marcos, L.A. Cryptococcal Meningoencephalitis in HIV/AIDS: When to Start Antiretroviral Therapy? Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2017, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DHHS. Panel on Opportunistic Infections in HIV-Infected Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Opportunistic Infections in HIV-Infected Adults and Adolescents: Recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Available online: https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/sites/default/files/guidelines/documents/Adult_OI.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Perfect, J.R.; Dismukes, W.E.; Dromer, F.; Goldman, D.L.; Graybill, J.R.; Hamill, R.J.; Harrison, T.S.; Larsen, R.A.; Lortholary, O.; Nguyen, M.-H.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Cryptococcal Disease: 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 291–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- >World Health Organization Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee. In Guidelines for The Diagnosis, Prevention and Management of Cryptococcal Disease in HIV-Infected Adults, Adolescents and Children: Supplement to the 2016 Consolidated Guidelines on the Use of Antiretroviral Drugs for Treating and Preventing HIV Infection; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H.; McInerney, P.; Parker, D.; Soares, C.B. Guidance for Conducting Systematic Scoping Reviews. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amburgy, J.W.; Miller, J.H.; Ditty, B.J.; Lune, P.V.; Muhammad, S.; Fisher, W.S. Cryptococcus Gattiiin an Immunocompetent Patient in the Southeastern United States. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2016, 2016, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bayardelle, P.; Giard, N.; Maltais, R.; Delorme, J.; Brazeau, M. Success with Amphotericin B and 5-Fluorocytosine in Treating Cerebral Cryptococcoma Accompanying Cryptococcal Meningitis. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1982, 127, 732–733. [Google Scholar]
- Brunasso, L.; Costanzo, R.; Cascio, A.; Florena, A.; Sparacia, G.; Iacopino, D.G.; Grasso, G. Seizure in Isolated Brain Cryptococcoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colom, M.F.; Frasés, S.; Ferrer, C.; Jover, A.; Andreu, M.; Reus, S.; Sánchez, M.; Torres-Rodríguez, J.M. First Case of Human Cryptococcosis due to Cryptococcus Neoformans Var. Gattii in Spain. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3548–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppens, Y.; Kalala, J.-P.; Van Roost, D.; Broecke, C.V.D.; Vogelaers, D. Cryptococcoma Unresponsive to Antifungal Treatment in a 63-Year-Old Non-Hiv-Infected Male. Acta Clin. Belg. 2006, 61, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Merchen, L. Cerebral Cryptococcoma-Why? J. Kuwait Med. Assoc. 2015, 47, 346–347. [Google Scholar]
- Guhjjar, M.K.; Ghazanfar, H.; Ashraf, S.; Gaddam, M.; Matela, A. Disseminated Cryptococcal Disease in a Patient with Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance and Polycythemia Vera: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Cureus 2021, 13, e1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, J.E.; Dias, J.S.; Villasboas-Bisneto, J.C.; Falcão, M.B.; Ko, A.I.; Ribeiro, G.S. Puerperal Brain Cryptococcoma in an HIV-Negative Woman Successfully Treated with Fluconazole: A Case Report. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2014, 47, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiraga, A.; Yatomi, M.; Ozaki, D.; Kamitsukasa, I.; Kuwabara, S. Cryptococcosis Mimicking Lung Cancer with Brain Metastasis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 135, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.; Lee, H.; Lee, K.; Chen, W. Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cerebral Cryptococcoma. Acta Radiol. 2005, 46, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Wei, H.; Meng, F.; Xu, C.; Cheng, C.; Yang, Y. Recurrent Cryptococcal Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in an HIV-Infected Patient after Anti-Retroviral Therapy: A Case Report. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2013, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, A.; Mpanza, P.; Lekgwara, P.; Otto, D.; Otto, D. Multicentric Cryptococcomas Mimicking Neoplasia in Immunocompetent Patient. World Neurosurg. 2018, 118, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.; Lekgwara, P.; Otto, D. Recurring Multicentric Granulomatous Cryptococcomas in the Contralateral Cerebral Hemisphere in an Adult Immunocompetent Patient with Known Previous Disease. World Neurosurg. 2020, 140, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, V.S.S.; Winder, M.J. Multiple Cerebral Cryptococcomas in an Immunocompetent Man: An Unlikely Diagnosis. ANZ J. Surg. 2013, 84, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Corbett, A. Intracranial and Dermatological Cryptococcal Infection in an Immunocompetent Man. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2004, 11, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Bajaj, A.; Tewari, M.K.; Singh, P.; Das Radotra, B. Cerebellar Cryptococcoma in an Immunocompetent Adult: A Rare Occurrence Report of a Case and Review of Literature. Indian J. Neurosurg. 2020, 9, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; You, C.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y. Central Nervous System Cryptococcoma in Immunocompetent Patients: A Short Review Illustrated by a New Case. Acta Neurochir. 2009, 152, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, J.H.; Grayson, M.L. Torsades de Pointes in a Patient Receiving Fluconazole for Cerebral Cryptococcosis. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2008, 65, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musubire, A.K.; Boulware, D.R.; Meya, D.; Rhein, J. Diagnosis and Management of Cryptococcal Relapse. J. AIDS Clin. Res. 2013, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadkarni, T.; Menon, R.K.; Desai, K.I.; Goel, A. A Solitary Cryptococcal Granuloma in an Immunocompetent Host. Neurol. India 2005, 53, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakwan, N.; Songjamrat, A.; Tungsinmonkong, K.; Nakwan, N. Cerebellar Cryptococcoma in an Immunocompetent Adult Patient. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2009, 40, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Nucci, A.; Maciel, J.A., Jr.; Queiroz, L.D.S.; Montenegro, M.A.; De Carvalho, R.B. Pseudocystic Form of Neurocryptococcosis in Pregnancy: Case Report. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 1999, 57, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, F.D.M.; Severo, C.B.; Guazzelli, L.S.; Severo, L.C. Cryptococcus Gattii Fungemia: Report of a Case with Lung and Brain Lesions Mimicking Radiological Features of Malignancy. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2007, 49, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.L.C.; De Aguiar, G.B.; Lovato, R.M.; Zanetti, A.V.D.; Panagopoulos, A.T.; Veiga, J.C.E. Cryptococcoma Mimicking a Brain Tumor in an Immunocompetent Patient: Case Report of an Extremely Rare Presentation. São Paulo Med. J. 2017, 136, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettersen, K.D.; Pappas, P.G.; Chin-Hong, P.; Baxi, S.M. A Paradoxical Decline: Intracranial Lesions in Two HIV-Positive Patients Recovering from Cryptococcal Meningitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2015212108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovich, M.J.; Arthur, R.H.; Helmer, E. CT of Intracranial Cryptococcosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1990, 154, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rai, S.; Marak, R.; Jain, S.; Dhole, T. Posterior Fossa Midline Cryptococcoma in a Patient with Idiopathic CD4 Lymphocytopenia. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 30, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbatani, S.; Manfredi, R.; Pavoni, M.; Consales, A.; Chiodo, F. Voriconazole Proves Effective in Long-Term Treatment of a Cerebral Cryptococcoma in a Chronic Nephropathic HIV-Negative Patient, after Fluconazole Failure. Mycopathologia 2004, 158, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saigal, G.; Post, M.J.; Lolayekar, S.; Murtaza, A. Unusual Presentation of Central Nervous System Cryptococcal Infection in an Immunocompetent Patient. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 2522–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Santander, X.A.; Gutiérrez-González, R.; Cotúa, C.; Tejerina, E.; Rodríguez, G.-B. Intraventricular Cryptococcoma Mimicking a Neoplastic Lesion in an Immunocompetent Patient with Hydrocephalus: A Case Report. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2019, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, B.; Hall, P.; Cine-Gowdie, S.; Hays, A.L.; Patel, K.; Lockhart, S.R.; Franco-Paredes, C. Cryptococcus Gattii: An Emerging Fungal Pathogen in the Southeastern United States. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 343, 510–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, W.G.; Hansen, M. Fluorescence in a Cryptococcoma Following Administration of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Hydrochloride (Gliolan). BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso, A.; Fumagalli, J.; Shinzato, R.; Gulotta, H.; Toller, M.; Bava, J. CNS Cryptococcoma in an HIV-Positive Patient. J. Int. Assoc. Physicians AIDS Care 2002, 1, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulett, K.B.; Cockburn, J.W.J.; Jeffree, R.; Woods, M.L. Cerebral Cryptococcoma Mimicking Glioblastoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr2016218824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppar, A.; Raj, A.P.; Konar, S.; Kandregula, S.; Shukla, D.; Somanna, S.; Devi, B.; Yasha, C.; Chandrashekar, N. Intracranial Cryptococcoma—Clinicopathologic Correlation and Surgical Outcome: A Single-Institution Experience. World Neurosurg. 2018, 115, e349–e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velamakanni, S.S.; Bahr, N.C.; Musubire, A.K.; Boulware, D.R.; Rhein, J.; Nabeta, H.W. Central Nervous System Cryptococcoma in a Ugandan Patient with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2014, 6, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y. Central Nervous System Cryptococcoma Mimicking Demyelinating Disease: A Case Report. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.-H.; Lin, S.-F.M.; Chiu, M.-C.; Kuo, C.-L.; Huang, H.-T.; Shoung, H.-M. Cerebral Cryptococcoma in an HIV-Negative Patient: Experience Learned from a Case. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 26, E34–E35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.X.; De Zhi, K. Multiple Cerebellar Abscess and Pneumonia Caused by Cryptococcus in an Immunocompetent Adult Patient. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 27, 448–450. [Google Scholar]
- Hagen, F.; Khayhan, K.; Theelen, B.; Kolecka, A.; Polacheck, I.; Sionov, E.; Falk, R.; Parnmen, S.; Lumbsch, T.; Boekhout, T. Recognition of Seven Species in the Cryptococcus Gattii/Cryptococcus Neoformans Species Complex. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015, 78, 16–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyrgos, V.; Seitz, A.E.; Steiner, C.A.; Prevots, D.R.; Williamson, P.R. Epidemiology of Cryptococcal Meningitis in the US: 1997–2009. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maziarz, E.K.; Perfect, J.R. Cryptococcosis. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2016, 30, 179–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.C.-A.; Slavin, M.A.; Heath, C.H.; Playford, E.G.; Byth, K.; Marriott, D.; Kidd, S.E.; Bak, N.; Currie, B.; Hajkowicz, K.; et al. Clinical Manifestations of Cryptococcus Gattii Infection: Determinants of Neurological Sequelae and Death. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charlier, C.; Dromer, F.; Lévêque, C.; Chartier, L.; Cordoliani, Y.-S.; Fontanet, A.; Launay, O.; Lortholary, O.; for the French Cryptococcosis Study Group. Cryptococcal Neuroradiological Lesions Correlate with Severity during Cryptococcal Meningoencephalitis in HIV-Positive Patients in the HAART Era. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gologorsky, Y.; DeLaMora, P.; Souweidane, M.M.; Greenfield, J. Cerebellar Cryptococcoma in an Immunocompetent Child. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2007, 107, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospenthal, D.R.; Bennett, J.E. Persistence of Cryptococcomas on Neuroimaging. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case | Location | Age (Years) | Sex | Medical, Surgical, or Social History | Causative Pathogen | Clinical Manifestations, Duration | Number and Location of Lesion(s) | Treatment Course | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amburgy et al., 2016 [18] | U.S. | Middle age † | M | Cocaine use, travel to Hawaii, Philippines, Thailand, Australia, Japan, and China over the last 30 years, otherwise unremarkable | C. gattii | Fevers, chills, headache, back pain, vomiting, 28 days | Multiple: basal ganglia, and subcortical white matter (also had evidence of a T11-12 cryptococcoma) |
|
|
| Bayardelle, et al., 1982 [19] | Canada | 42 | M | Unremarkable | C. neoformans | Headache, seizure, 30 days | 3: upper L parietal region, R rolandic area, cerebral parenchyma posterior to the frontal opercular region |
|
|
| Brunasso et al., 2021 [20] | Italy | 32 | F | Tonic-clonic seizures | Cryptococcus spp. | Asymptomatic | 1: R temporo-mesial lesion |
|
|
| Colom et al., 2005 [21] | Spain | 60 | M | Diabetes mellitus | C. gattii | Headaches, somnolence, several days | 1: basal ganglia |
|
|
| Coppens, et al., 2006 [22] | Belgium | 63 | M | Diabetes mellitus | C. neoformans | Weight loss, fatigue, headache, somnolence, hemianopsia, disorientation to time and place, 210 days | 3: R parietal, R frontal, and L occipital lobes |
|
|
| Guha, et al., 2015 [23] | U.S. | 66 | F | Hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia | C. neoformans | Global limb weakness, anorexia, cough, seizures, night sweats, 7 days | 1: postcentral gyrus (1.1 cm) |
|
|
| Guhjjar et al., 2021 [24] | U.S. | 58 | M | JAK2 positive polycythemia vera, MGUS, hypertension | C. neoformans | Confusion, drowsiness, auditory hallucinations, L sided weakness, 7 days | 1: R basal ganglia (0.8 × 0.5 cm) |
|
|
| Hagan et al., 2014 [25] | Brazil | 25 | F | Unremarkable | Cryptococcus spp. | Word-finding difficulty, R sided numbness and weakness | 1: L thalamus (3 × 2 cm) |
|
|
| Hiraga et al., 2015 [26] | Japan | 71 | F | Hypertension, hyperthyroidism | C. neoformans | R lower limb weakness, headache, loss of appetite, diplopia, 3 days | 1: L frontal lobe |
|
|
| Ho et al., 2005 [27] | Taiwan | 55 | F | Unremarkable | C. neoformans | Headache, facial palsy, 365 days | 1: R frontal lobe |
|
|
| Hu et al., 2013 [28] | China | 19 | M | HIV-infected (CD4 0 cells/μL) | C. neoformans | Headache, confusion, 14 days | Bilateral basal ganglia |
|
|
| Kelly et al., 2018 [29] and Kelly et al., 2020 [30] | South Africa | 19 | M | Unremarkable | C. neoformans | Headache, blurry vision, R upper extremity weakness, tonic-clonic seizure | 2: L frontal lobe, temporal lobe |
|
|
| King et al., 2014 [31] | Australia | 59 | M | Unremarkable | C. gattii | Flashing lights and intermittent blindness in R eye, 270 days | 2: R temporal lobe, L occipital lobe |
|
|
| Krishnan et al., 2004 [32] | Australia | 72 | M | Parkinson’s disease, diabetes mellitus | C. neoformans | Depression, confusion, falls, 42 days | 2: L parietal lobe, R superior cerebellar peduncle |
|
|
| Kumar et al., 2020 [33] | India | 48 | M | Unremarkable | Cryptococcus spp. | Headache, giddiness, vomiting, bilateral papilledema, 90 days | 1: cerebellar hemisphere (3 × 3 × 4 cm) |
|
|
| Li et al., 2010 [34] | China | 49 | F | Unremarkable | C. neoformans | Headache, dizziness, vomiting, 30 days | 1: R occipital lobe (5 × 4 × 4.5 cm) |
|
|
| McMahon et al., 2008 [35] | Australia | 68 | F | Hypertension | C. gattii | Falls, 30 days | 2: L pons and middle cerebellar peduncle |
|
|
| Musubire et al., 2012 [36] | Uganda | 35 | M | HIV-infected on ART (VL UD, CD4 89 cells/μL), treated for CM 7 months prior | C. neoformans | Headache, photophobia, dizziness, anorexia, behavioral changes | 1: R parietal lobe |
|
|
| Nadkarni et al., 2005 [37] | India | 22 | M | Seizures | C. neoformans | Seizures, L hemiparesis, bilateral papilledema | 1: R parietal lobe |
|
|
| Nakwan et al., 2009 [38] | Thailand | 23 | M | Migraine headaches | Cryptococcus spp. | Headache, vomiting, ataxia, dysmetria, dysdiadochokinesia, 365 days | Multiple: cerebellum |
|
|
| Nucci et al., 1999 [39] | Brazil | 29 | F | Pregnant (2nd trimester) | C. neoformans | Sleepiness, vomiting, bilateral 6th nerve palsy, nuchal rigidity, papilledema, 120 days | Multiple: basal ganglia, R lateral ventricle |
|
|
| Oliveira et al., 2007 [40] | Brazil | 64 | M | Unremarkable | C. gattii | Fever, anorexia, disorientation, weakness, bilateral papilledema, 7 days | 1: R temporal lobe, multiple nodules throughout brain parenchyma |
|
|
| Paiva et al., 2017 [41] | Brazil | 54 | F | Hypertension, direct contact with several bird species including pigeons | C. neoformans | Behavioral disturbances, confusion, weakness, 60 days | 2: L occipital lobe |
|
|
| Pettersen et al., 2015 [42] | U.S. | 30 | M | HIV-infected on ART (CD4 157 cells/µL), treated for recurrent CM 2 months prior | Cryptococcus spp. | Headache, fever, nuchal rigidity, night sweats, seizures | Multiple: R caudate, R temporal lobe |
|
|
| Pettersen et al., 2015 [42] | U.S. | 40 | M | HIV-infected on ART (CD4 84 cells/µL), treated for CM 3 months prior | Cryptococcus spp. | Headache, expressive aphasia, R facial weakness, weight loss | 2: L frontotemporal region |
|
|
| Popovich et al., 1990 [43] | U.S. | 52 | M | HIV-infected | Cryptococcus spp. | Headache, altered mental status, photophobia, nausea, vomiting, 1 day | Multiple: bilateral cerebral hemispheres |
|
|
| Popovich et al., 1990 [43] | U.S. | 47 | F | Unremarkable | Cryptococcus spp. | Headache, nausea, vomiting, somnolence, L hemianopsia, 3 days | 1: temporal horn of R lateral ventricle |
|
|
| Popovich et al., 1990 [43] | U.S. | 30 | M | HIV-infected, previously treated for CM | Cryptococcus spp. | Headache, nausea, vomiting, 28 days | Multiple: bilateral basal ganglia |
|
|
| Popovich et al., 1990 [43] | U.S. | 50 | M | HIV-infected, treated for CM 2 months prior | Cryptococcus spp. | Not specified | Multiple: bilateral thalamus and basal ganglia |
|
|
| Rai et al., 2012 [44] | India | 50 | M | Idiopathic CD4 lymphocytopenia (CD4 204 cells/µL) | C. neoformans | Headache, dysmetria, dysdiadochokinesia, impaired gait, impaired gag reflex, weak hand grip, 365 days | 2: vermis (largest 3.25 × 3.18 × 3.16 cm) |
|
|
| Sabbatani, et al., 2004 [45] | Italy | 46 | M | Homocystinuria, renal dysfunction, anemia | C. neoformans | Time–space disorientation | 1: R frontal lobe |
|
|
| Saigal et al., 2005 [46] | U.S. | 49 | M | Cleaned pigeon droppings from coop 1 month prior to presentation, otherwise unremarkable | C. neoformans | Headache, syncope, confusion, mental status changes, 30 days | Multiple: bilateral basal ganglia |
|
|
| Santander et al., 2019 [47] | Spain | 41 | F | Unremarkable | C. neoformans | Gait disturbance, urinary incontinence, impaired memory, 120 days | 1: biventricular mass (1.6 cm diameter) |
|
|
| Sellers et al., 2012 [48] | U.S. | 70 | M | Unremarkable | C. gattii | Stupor, lethargy, 3 days | Multiple: bilateral basal ganglia |
|
|
| Sitapati et al., 2010 [9] | U.S. | 28 | M | HIV-infected (CD4 149 cells/μL), treated for CM 22 months prior | Cryptococcus spp. | Seizures, expressive aphasia, R sided weakness | 1: L temporal lobe (6.0 × 3.4 × 3.3 cm) |
|
|
| Solis et al., 2017 [49] | Australia | 54 | M | Worked with timber in New South Wales, Australia, otherwise unremarkable | C. gattii | Dysarthria, L facial droop | 1: R frontal lobe (1.9 × 3.0 × 2.5 cm) |
|
|
| Troncoso, et al., 2002 [50] | Argentina | 28 | M | HIV-infected (CD4 28 cells/μL) | C. neoformans | Fever, headache, hallucinations, altered mental status, seizures, 14 days | 1: L occipital lobe (2 cm) |
|
|
| Ulett et al., 2017 [51] | Australia | 55 | M | Hypertension, gout, diabetes mellitus | C. gattii | Headache, R papilledema, L pronator drift, 30 days | 1: R frontoparietal (4 × 5 × 4.8 cm) |
|
|
| Uppar, et al., 2018 [52] | India | 55 | M | Unremarkable | C. neoformans | Fever, altered sensorium, headache, vomiting, behavioral changes, hemiparesis, papilledema, L 6th nerve palsy, L upper motor neuron facial palsy | 1: R parieto-occipital lobe |
|
|
| Uppar, et al., 2018 [52] | India | 45 | M | Unremarkable | C. neoformans | Giddiness, headache, vomiting, cerebellar signs | 1: R cerebellum |
|
|
| Uppar, et al., 2018 [52] | India | 74 | M | Unremarkable | C. gattii | Headache, reduced appetite, vomiting, cerebellar signs | 1: R cerebellum |
|
|
| Uppar, et al., 2018 [52] | India | 30 | M | Unremarkable | C. neoformans | Headache, vomiting, fever, visual disturbances, papilledema | 1: R frontal lobe |
|
|
| Uppar, et al., 2018 [52] | India | 24 | M | Unremarkable | C. neoformans | Headache, vomiting, fever, behavioral changes, altered sensorium, visual disturbances, papilledema, bilateral 6th nerve palsy | 1: R caudate region |
|
|
| Velamakanni et al., 2014 [53] | Uganda | 45 | M | HIV-infected (CD4 4 cells/µL), treated for CM 2 months prior | C. neoformans | Headache, cough, vomiting, fever, seizures, R-sided hemiparesis, 7 days | 1: occipital lobe |
|
|
| Wei, et al., 2020 [54] | China | 40 | M | Unremarkable | C. neoformans | Altered consciousness, apathy, 7 days | Multiple: corpus callosum, centrum ovale |
|
|
| Yeh, et al., 2014 [55] | Taiwan | 75 | M | Unremarkable | Cryptococcus spp. | R sided weakness, several days | 1: L parietal lobe |
|
|
| Zheng et al., 2011 [56] | China | 53 | F | Poultry farmer, otherwise unremarkable | Cryptococcus spp. | Headache, vomiting, ataxia, wide-based gait, dysmetria, 180 days | Multiple: posterior fossa |
|
|
| C. neoformans | C. gattii | |
|---|---|---|
| Prevalence * | 74% | 26% |
| Clinical manifestations | ||
| 56% | 50% |
| 52% | 25% |
| 16% | 13% |
| 16% | 0% |
| 20% | 25% |
| 0% | 13% |
| 16% | 25% |
| 4% | 13% |
| 20% | 25% |
| 20% | 13% |
| 30 (3–365) | 29 (3–270) |
| Radiographic findings | ||
| 40% | 56% |
| 77% | 47% |
| 71% | 33% |
| Treatment regimens | ||
| 88% | 100% |
| 57% | 89% |
| 42 (10–60) | 38 (7–84) |
| 126 (60–730) | 317.5 (12–365) |
| Follow-up, median (range) | 302.5 (30–4380) | 279 (7–1460) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chastain, D.B.; Rao, A.; Yaseyyedi, A.; Henao-Martínez, A.F.; Borges, T.; Franco-Paredes, C. Cerebral Cryptococcomas: A Systematic Scoping Review of Available Evidence to Facilitate Diagnosis and Treatment. Pathogens 2022, 11, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020205
Chastain DB, Rao A, Yaseyyedi A, Henao-Martínez AF, Borges T, Franco-Paredes C. Cerebral Cryptococcomas: A Systematic Scoping Review of Available Evidence to Facilitate Diagnosis and Treatment. Pathogens. 2022; 11(2):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020205
Chicago/Turabian StyleChastain, Daniel B., Amy Rao, Armaan Yaseyyedi, Andrés F. Henao-Martínez, Thomas Borges, and Carlos Franco-Paredes. 2022. "Cerebral Cryptococcomas: A Systematic Scoping Review of Available Evidence to Facilitate Diagnosis and Treatment" Pathogens 11, no. 2: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020205
APA StyleChastain, D. B., Rao, A., Yaseyyedi, A., Henao-Martínez, A. F., Borges, T., & Franco-Paredes, C. (2022). Cerebral Cryptococcomas: A Systematic Scoping Review of Available Evidence to Facilitate Diagnosis and Treatment. Pathogens, 11(2), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020205








