Interactome Profiling of N-Terminus-Truncated NS1 Protein of Influenza A Virus Reveals Role of 14-3-3γ in Virus Replication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
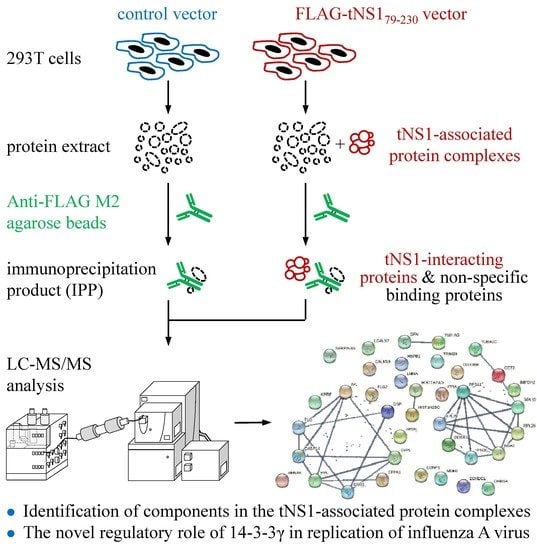
2.1. Interactome Analysis of N-Terminus-Truncated NS1 Proteins of Influenza A Virus
2.2. Spectral Counting-Based Identification of Proteins Interacting with tNS179-230 Protein
2.3. Determination of Biological Pathways Involved with the tNS1-Interacting Partners
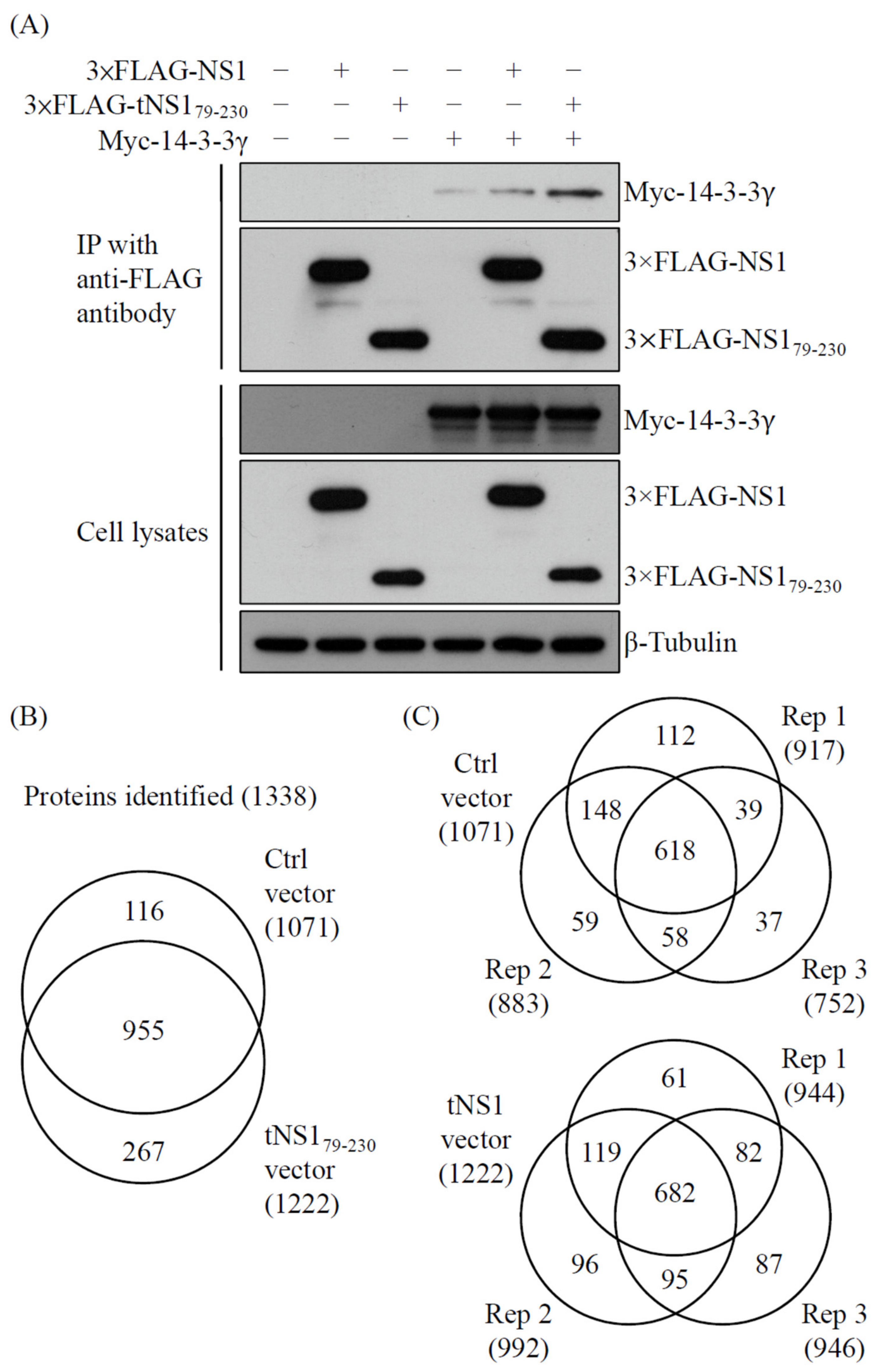
2.4. N-Terminus-Truncated NS1 of PR8 Virus Interacts with 14-3-3γ Protein
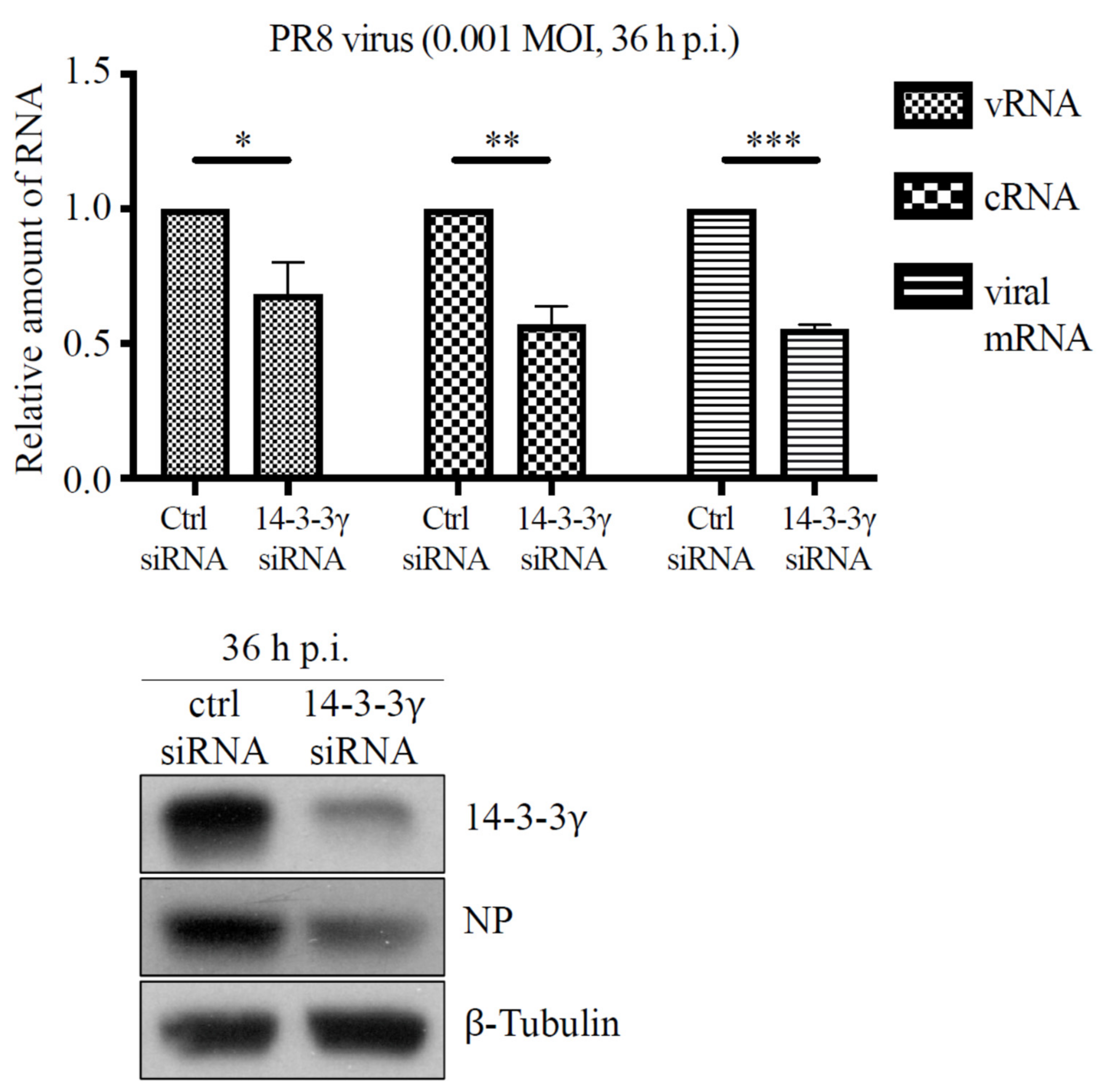
2.5. Knockdown of 14-3-3γ Expression Reduces Replication of Influenza A PR8 Virus
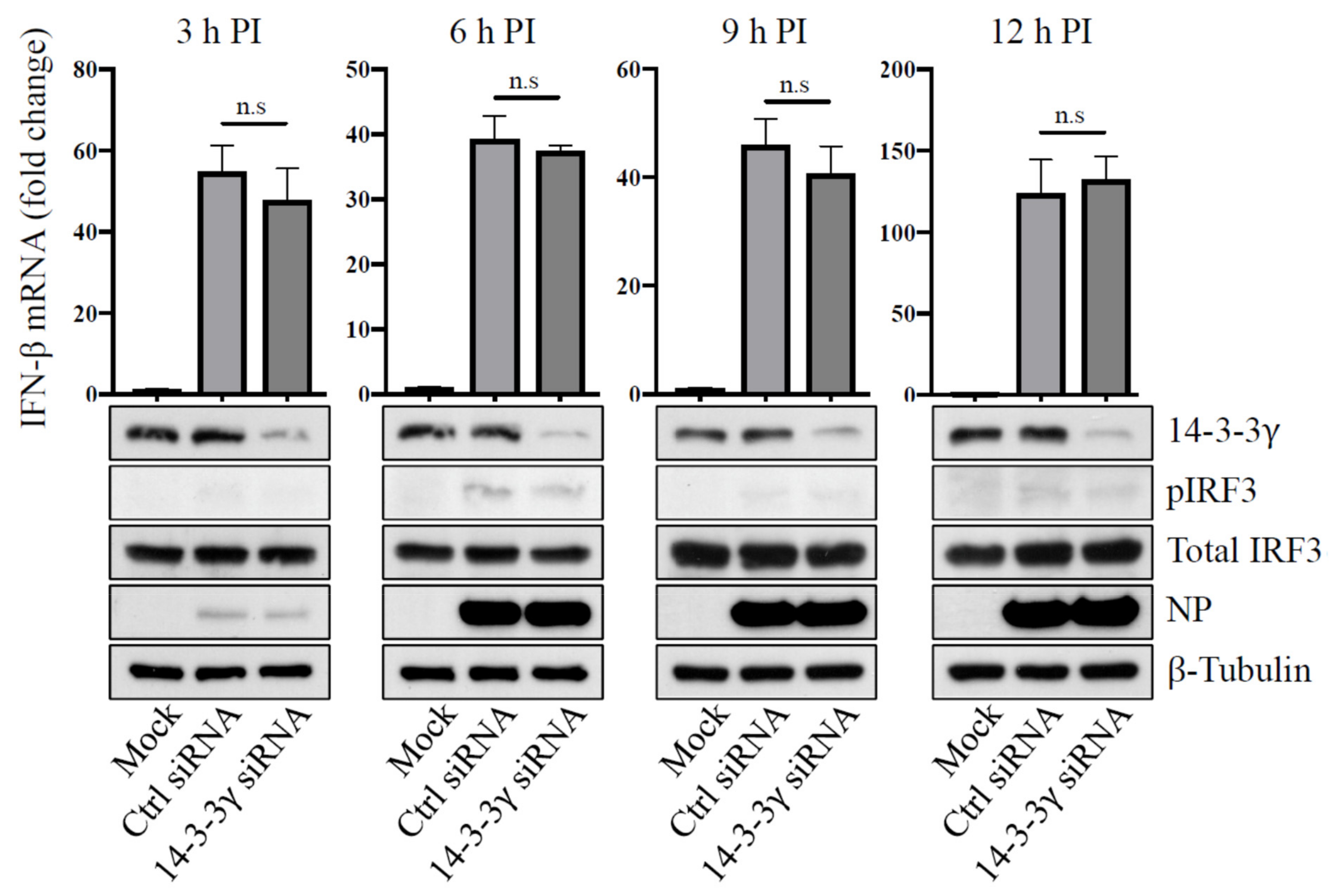
2.6. Knockdown of 14-3-3γ Did Not Affect Influenza A Virus RNA Polymerase Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells, Plasmids, and Viruses
4.2. Immunoprecipitation, Immunoblotting, and Antibodies
4.3. Reverse-Phase LC-MS/MS Analysis and Protein Identification
4.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.5. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative PCR
4.6. RNA Interference
4.7. Minigenome Polymerase Activity Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kilbourne, E.D. Influenza pandemics of the 20th century. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario-Ferreira, N.; Preto, A.J.; Melo, R.; Moreira, I.S.; Brito, R.M.M. The central role of non-structural protein 1 (NS1) in influenza biology and infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1511. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Z.X.; Wang, X.Q.; Liu, X.F. NS1: A key protein in the "game" between influenza A virus and host in innate immunity. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 670177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.Y.; Alonso-Caplen, F.; Krug, R.M. Two functional domains of the influenza virus NS1 protein are required for regulation of nuclear export of mRNA. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 2433–2441. [Google Scholar]
- Drappier, M.; Michiels, T. Inhibition of the OAS/RNase L pathway by viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 15, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.Y.; Krug, R.M. The primary function of RNA binding by the influenza A virus NS1 protein in infected cells: Inhibiting the 2′-5′ oligo (A) synthetase/RNase L pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7100–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jureka, A.S.; Kleinpeter, A.B.; Cornilescu, G.; Cornilescu, C.C.; Petit, C.M. Structural basis for a novel interaction between the NS1 protein derived from the 1918 influenza virus and RIG-I. Structure 2015, 23, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jureka, A.S.; Kleinpeter, A.B.; Tipper, J.L.; Harrod, K.S.; Petit, C.M. The influenza NS1 protein modulates RIG-I activation via a strain-specific direct interaction with the second CARD of RIG-I. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, C.H.; Zhou, L.; Krug, R.M. Cellular DDX21 RNA helicase inhibits influenza A virus replication but is counteracted by the viral NS1 protein. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Song, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, H.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Q.; Kang, T.; Chen, S.; Huang, W. Influenza A virus-encoded NS1 virulence factor protein inhibits innate immune response by targeting IKK. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1849–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marazzi, I.; Ho, J.S.; Kim, J.; Manicassamy, B.; Dewell, S.; Albrecht, R.A.; Seibert, C.W.; Schaefer, U.; Jeffrey, K.L.; Prinjha, R.K.; et al. Suppression of the antiviral response by an influenza histone mimic. Nature 2012, 483, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Krug, R.M. Influenza A virus NS1 protein targets poly(A)-binding protein II of the cellular 3’-end processing machinery. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2273–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, K.; Ma, L.C.; Xiao, R.; Radvansky, B.; Aramini, J.; Zhao, L.; Marklund, J.; Kuo, R.L.; Twu, K.Y.; Arnold, E.; et al. Structural basis for suppression of a host antiviral response by influenza A virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13093–13098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Twu, K.Y.; Noah, D.L.; Rao, P.; Kuo, R.L.; Krug, R.M. The CPSF30 binding site on the NS1A protein of influenza A virus is a potential antiviral target. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 3957–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemeroff, M.E.; Barabino, S.M.; Li, Y.; Keller, W.; Krug, R.M. Influenza virus NS1 protein interacts with the cellular 30 kDa subunit of CPSF and inhibits 3’end formation of cellular pre-mRNAs. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, R.L.; Li, L.H.; Lin, S.J.; Li, Z.H.; Chen, G.W.; Chang, C.K.; Wang, Y.R.; Tam, E.H.; Gong, Y.N.; Krug, R.M.; et al. Role of N terminus-truncated NS1 proteins of influenza A virus in inhibiting IRF3 activation. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 4696–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, R.L.; Li, Z.H.; Li, L.H.; Lee, K.M.; Tam, E.H.; Liu, H.M.; Liu, H.P.; Shih, S.R.; Wu, C.C. Interactome analysis of the NS1 protein encoded by influenza A H1N1 virus reveals a positive regulatory role of host protein PRP19 in viral replication. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, E.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Woung, C.H.; Liu, H.M.; Wu, G.H.; Wu, C.C.; Kuo, R.L. Role of the chaperone protein 14-3-3ε in the regulation of influenza A virus-activated beta interferon. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0023121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Tinti, M.; Wood, N.T.; Campbell, D.G.; Toth, R.; Dubois, F.; Geraghty, K.M.; Wong, B.H.; Brown, L.J.; Tyler, J.; et al. Visualization and biochemical analyses of the emerging mammalian 14-3-3-phosphoproteome. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2011, 10, M110.005751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darling, D.L.; Yingling, J.; Wynshaw-Boris, A. Role of 14-3-3 proteins in eukaryotic signaling and development. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2005, 68, 281–315. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Cao, S.; Ding, G.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, Q.; Feng, J.; Liu, S.; Qin, L.; et al. The role of 14-3-3 proteins in cell signalling pathways and virus infection. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 4173–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Subramanian, R.R.; Masters, S.C. 14-3-3 proteins: Structure, function, and regulation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2000, 40, 617–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghazadeh, Y.; Papadopoulos, V. The role of the 14-3-3 protein family in health, disease, and drug development. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, M.K.; Morrison, D.K. Unlocking the code of 14-3-3. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Heusden, G.P. 14-3-3 proteins: Regulators of numerous eukaryotic proteins. IUBMB Life 2005, 57, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.M.; Loo, Y.M.; Horner, S.M.; Zornetzer, G.A.; Katze, M.G.; Gale, M., Jr. The mitochondrial targeting chaperone 14-3-3ε regulates a RIG-I translocon that mediates membrane association and innate antiviral immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riedl, W.; Acharya, D.; Lee, J.H.; Liu, G.; Serman, T.; Chiang, C.; Chan, Y.K.; Diamond, M.S.; Gack, M.U. Zika virus NS3 mimics a cellular 14-3-3-binding motif to antagonize RIG-I- and MDA5-mediated innate immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 493–503 e496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.P.; Fan, Y.K.; Liu, H.M. The 14-3-3η chaperone protein promotes antiviral innate immunity via facilitating MDA5 oligomerization and intracellular redistribution. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falcon, A.M.; Marion, R.M.; Zurcher, T.; Gomez, P.; Portela, A.; Nieto, A.; Ortin, J. Defective RNA replication and late gene expression in temperature-sensitive influenza viruses expressing deleted forms of the NS1 protein. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3880–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, J.Y.; Li, S.; Sen, G.C.; Krug, R.M. A site on the influenza A virus NS1 protein mediates both inhibition of PKR activation and temporal regulation of viral RNA synthesis. Virology 2007, 363, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aitken, A.; Collinge, D.B.; van Heusden, B.P.; Isobe, T.; Roseboom, P.H.; Rosenfeld, G.; Soll, J. 14-3-3 proteins: A highly conserved, widespread family of eukaryotic proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1992, 17, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardino, A.K.; Smerdon, S.J.; Yaffe, M.B. Structural determinants of 14-3-3 binding specificities and regulation of subcellular localization of 14-3-3-ligand complexes: A comparison of the X-ray crystal structures of all human 14-3-3 isoforms. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2006, 16, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babula, J.J.; Liu, J.Y. Integrate omics data and molecular dynamics simulations toward better understanding of human 14-3-3 interactomes and better drugs for cancer therapy. J. Genet. Genomics 2015, 42, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acevedo, S.F.; Tsigkari, K.K.; Grammenoudi, S.; Skoulakis, E.M. In vivo functional specificity and homeostasis of Drosophila 14-3-3 proteins. Genetics 2007, 177, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoenwaelder, S.M.; Darbousset, R.; Cranmer, S.L.; Ramshaw, H.S.; Orive, S.L.; Sturgeon, S.; Yuan, Y.; Yao, Y.; Krycer, J.R.; Woodcock, J.; et al. 14-3-3ζ regulates the mitochondrial respiratory reserve linked to platelet phosphatidylserine exposure and procoagulant function. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pennington, K.L.; Chan, T.Y.; Torres, M.P.; Andersen, J.L. The dynamic and stress-adaptive signaling hub of 14-3-3: Emerging mechanisms of regulation and context-dependent protein-protein interactions. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5587–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, T.P.; Vuong, L.T.; Kim, A.R.; Hsu, Y.C.; Choi, K.W. 14-3-3 proteins regulate Tctp-Rheb interaction for organ growth in Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, A.; Anhlan, D.; Ferrando, V.; Mecate-Zambrano, A.; Mellmann, A.; Wixler, V.; Boergeling, Y.; Ludwig, S. Phosphorylation of influenza A virus NS1 at serine 205 mediates its viral polymerase-enhancing function. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02369-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.K.; Chen, C.J.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, S.W.; Shih, S.R.; Kuo, R.L. Cellular hnRNP A2/B1 interacts with the NP of influenza A virus and impacts viral replication. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0188214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, R.L.; Chen, C.J.; Tam, E.H.; Huang, C.G.; Li, L.H.; Li, Z.H.; Su, P.C.; Liu, H.P.; Wu, C.C. Interactome analysis of NS1 protein encoded by influenza A H7N9 virus reveals an inhibitory role of NS1 in host mRNA maturation. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Protein Name (Accession Number, Gene Name) | Spectral Counts (SCs) in Replicates 1/2/3 | tNS1/VC Ratio a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vector Control (VC) | N-Terminus-Truncated NS1 (tNS1) | ||
| Filaggrin (FILA_HUMAN, FLG) | 0/0/0 | 46/32/0 | 28.634 |
| Filaggrin-2 (FILA2_HUMAN, FLG2) | 0/0/0 | 34/27/0 | 22.367 |
| Prelamin-A/C (LMNA_HUMAN, LMNA) | 0/0/0 | 22/24/0 | 16.767 |
| Calmodulin-like protein 5 (CALL5_HUMAN, CALML5) | 0/0/0 | 21/24/0 | 16.384 |
| Inosine-5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase 2 (IMDH2_HUMAN, IMPDH2) | 0/0/0 | 18/13/11 | 15.678 |
| 14-3-3 protein gamma (1433G_HUMAN, YWHAG) | 0/0/0 | 13/14/14 | 15.307 |
| Desmoglein-1 (DSG1_HUMAN, DSG1) | 0/0/0 | 18/22/0 | 14.567 |
| Galectin-7 (LEG7_HUMAN, LGALS7) | 0/0/0 | 21/18/0 | 14.384 |
| Keratinocyte proline-rich protein (KPRP_HUMAN, KPRP) | 0/0/0 | 8/9/17 | 12.935 |
| 14-3-3 protein sigma (1433S_HUMAN, SFN) | 0/0/0 | 15/20/0 | 12.750 |
| Neuroblast differentiation-associated protein AHNAK (AHNK_HUMAN, AHNAK) | 0/0/0 | 13/20/0 | 11.983 |
| Involucrin (INVO_HUMAN, IVL) | 0/0/0 | 15/16/0 | 11.417 |
| Envoplakin (EVPL_HUMAN, EVPL) | 0/0/0 | 13/17/0 | 10.983 |
| Periplakin (PEPL_HUMAN, PPL) | 0/0/0 | 12/17/0 | 10.600 |
| Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I (H2B1C_HUMAN, HIST1H2BC) | 0/0/0 | 12/12/4 | 10.216 |
| Histone H2A type 1-D (H2A1D_HUMAN, HIST1H2AD) | 0/0/0 | 13/11/0 | 8.983 |
| 60S ribosomal protein L26 (RL26_HUMAN, RPL26) | 0/0/0 | 5/9/10 | 8.957 |
| Suprabasin (SBSN_HUMAN, SBSN) | 0/0/0 | 12/12/0 | 8.933 |
| 60S ribosomal protein L12 (RL12_HUMAN, RPL12) | 0/0/0 | 10/8/6 | 8.924 |
| Desmoplakin (DESP_HUMAN, DSP) | 20/20/0 | 159/160/23 | 8.532 |
| 40S ribosomal protein S11 (RS11_HUMAN, RPS11) | 3/0/0 | 12/11/14 | 8.166 |
| Serine/threonine-protein kinase 38 (STK38_HUMAN, STK38) | 0/0/0 | 9/7/5 | 7.804 |
| Ethylmalonyl-CoA decarboxylase (ECHD1_HUMAN, ECHDC1) | 0/0/0 | 6/8/7 | 7.795 |
| Heat shock protein beta-1 (HSPB1_HUMAN, HSPB1) | 4/2/0 | 28/18/5 | 7.684 |
| Spliceosome RNA helicase DDX39B (DX39B_HUMAN, DDX39B) | 0/0/0 | 9/5/6 | 7.541 |
| Unconventional myosin-Ib (MYO1B_HUMAN, MYO1B) | 0/0/0 | 7/12/2 | 7.491 |
| Hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase, mitochondrial (GLO2_HUMAN, HAGH) | 0/0/0 | 5/7/7 | 7.078 |
| Tubulin alpha-1C chain (TBA1C_HUMAN, TUBA1C) | 0/0/0 | 10/8/0 | 6.833 |
| Epiplakin (EPIPL_HUMAN, EPPK1) | 0/0/0 | 8/10/0 | 6.733 |
| Caspase-14 (CASPE_HUMAN, CASP14) | 0/0/0 | 7/11/0 | 6.683 |
| Protein POF1B (POF1B_HUMAN, POF1B) | 0/0/0 | 7/11/0 | 6.683 |
| Malate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial (MDHM_HUMAN, MDH2) | 0/0/0 | 7/7/4 | 6.633 |
| Lon protease homolog, mitochondrial (LONM_HUMAN, LONP1) | 0/0/0 | 8/7/3 | 6.612 |
| DNA ligase 3 (DNLI3_HUMAN, LIG3) | 0/0/0 | 6/9/3 | 6.512 |
| tRNA selenocysteine 1-associated protein 1 (TSAP1_HUMAN, TRNAU1AP) | 0/0/0 | 7/4/6 | 6.441 |
| T-complex protein 1 subunit beta (TCPB_HUMAN, CCT2) | 0/0/0 | 6/6/5 | 6.320 |
| Ribosome biogenesis protein NSA2 homolog (NSA2_HUMAN, NSA2) | 0/0/0 | 6/0/9 | 6.270 |
| Dehydrogenase/reductase SDR family member 4 (DHRS4_HUMAN, DHRS4) | 0/0/0 | 0/10/6 | 6.091 |
| Serpin B3 (SPB3_HUMAN, SERPINB3) | 0/0/0 | 8/8/0 | 6.067 |
| Tripartite motif-containing protein 29 (TRI29_HUMAN, TRIM29) | 0/0/0 | 8/8/0 | 6.067 |
| RNA-binding protein PNO1 (PNO1_HUMAN, PNO1) | 0/0/0 | 9/3/4 | 6.066 |
| Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX47 (DDX47_HUMAN, DDX47) | 0/0/0 | 3/6/7 | 5.978 |
| 60S ribosomal protein L28 (RL28_HUMAN, RPL28) | 0/0/0 | 5/6/5 | 5.937 |
| Zinc finger CCCH-type antiviral protein 1-like (ZCCHL_HUMAN, ZC3HAV1L) | 0/0/0 | 7/0/7 | 5.845 |
| 2-Methoxy-6-polyprenyl-1,4-benzoquinol methylase, mitochondrial (COQ5_HUMAN, COQ5) | 0/0/0 | 0/9/6 | 5.758 |
| Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A (PPIA_HUMAN, PPIA) | 0/0/0 | 6/9/0 | 5.633 |
| Biological Process a | Identified Proteins Involved in Process | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Cornification | FLG, DSP, CASP14, DSG1, PPL, EVPL, IVL | 8.23 × 10−8 |
| Keratinization | DSP, CASP14, DSG1, SFN, PPL, EVPL, IVL | 2.44 × 10−6 |
| Intermediate filament cytoskeleton organization | DSP, EPPK1, PPL, EVPL | 9.07 × 10−6 |
| Neutrophil degranulation | DSP, SERPINB3, CCT2, FLG2, CALML5, IMPDH2, DSG1, PPIA | 3.68 × 10−5 |
| Negative regulation of protein kinase activity | HSPB1, SFN, PPIA, YWHAG | 3.35 × 10−4 |
| rRNA processing | NSA2, DDX47, RPL12, RPL26, RPL28 | 5.33 × 10−4 |
| Epidermis development | DSP, CASP14, CALML5, EVPL | 5.56 × 10−4 |
| Cytoplasmic translation | RPL12, RPL26, RPS11, RPL28 | 6.83 × 10−4 |
| Peptide cross-linking | FLG, DSP, EVPL, IVL | 9.07 × 10−4 |
| Wound healing | DSP, EPPK1, PPL, EVPL | 9.62 × 10−4 |
| Reactome Pathway a | Identified Proteins Involved in Pathway | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Keratinization | FLG, DSP, CASP14, DSG1, PPL, EVPL, IVL | 3.15 × 10−5 |
| rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol | DDX47, PNO1, RPL12, RPL26, RPS11, RPL28 | 1.81 × 10−4 |
| Developmental biology | FLG, DSP, TUBA1C, CASP14, RPL12, DSG1, RPL26, RPS11, PPL, EVPL, RPL28, IVL | 2.23 × 10−4 |
| Neutrophil degranulation | DSP, SERPINB3, CCT2, FLG2, CALML5, IMPDH2, DSG1, PPIA | 3.95 × 10−4 |
| Programmed cell death | DSP, LMNA, DSG1, SFN, YWHAG | 1.81 × 10−3 |
| Eukaryotic translation termination/elongation | RPL12, RPL26, RPS11, RPL28 | 2.50 × 10−3 |
| Rho GTPase signaling | DSP, CCT2, TUBA1C, DDX39B, STK38, DSG1, SFN, YWHAG | 3.78 × 10−3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuo, R.-L.; Tam, E.-H.; Woung, C.-H.; Hung, C.-M.; Liu, H.-P.; Liu, H.M.; Wu, C.-C. Interactome Profiling of N-Terminus-Truncated NS1 Protein of Influenza A Virus Reveals Role of 14-3-3γ in Virus Replication. Pathogens 2022, 11, 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070733
Kuo R-L, Tam E-H, Woung C-H, Hung C-M, Liu H-P, Liu HM, Wu C-C. Interactome Profiling of N-Terminus-Truncated NS1 Protein of Influenza A Virus Reveals Role of 14-3-3γ in Virus Replication. Pathogens. 2022; 11(7):733. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070733
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuo, Rei-Lin, Ee-Hong Tam, Chian-Huey Woung, Chu-Mi Hung, Hao-Ping Liu, Helene Minyi Liu, and Chih-Ching Wu. 2022. "Interactome Profiling of N-Terminus-Truncated NS1 Protein of Influenza A Virus Reveals Role of 14-3-3γ in Virus Replication" Pathogens 11, no. 7: 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070733
APA StyleKuo, R.-L., Tam, E.-H., Woung, C.-H., Hung, C.-M., Liu, H.-P., Liu, H. M., & Wu, C.-C. (2022). Interactome Profiling of N-Terminus-Truncated NS1 Protein of Influenza A Virus Reveals Role of 14-3-3γ in Virus Replication. Pathogens, 11(7), 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11070733