Mice as an Animal Model for Japanese Encephalitis Virus Research: Mouse Susceptibility, Infection Route, and Viral Pathogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Virus
3. Clinical Features in Humans
3.1. Central Nervous System Disorders
3.2. Peripheral Nervous System Disorders
3.3. Reproductive Disorders
4. Mice: A Reliable Small-Animal Model for JEV Research
4.1. Mouse Susceptibility
4.1.1. Mouse Strain-Dependent Variation
4.1.2. Mouse Age-Dependent Variation
4.2. Infection Route
4.2.1. Peripheral vs. Intracerebral Inoculation
4.2.2. Inoculation into a Cephalic Cavity
4.2.3. Peripheral Inoculation during Pregnancy
4.3. Viral Pathogenesis
4.3.1. Viral Replication in the Mononuclear Phagocyte System
4.3.2. Viral Entry into the Central Nervous System
4.3.3. Viral Replication in the Central Nervous System
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simmonds, P.; Becher, P.; Bukh, J.; Gould, E.A.; Meyers, G.; Monath, T.; Muerhoff, S.; Pletnev, A.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Smith, D.B.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Flaviviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, E.A.; de Lamballerie, X.; Zanotto, P.M.; Holmes, E.C. Origins, evolution, and vector/host coadaptations within the genus Flavivirus. Adv. Virus Res. 2003, 59, 277–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Barrett, A.D.; Deubel, V. The Japanese encephalitis serological group of flaviviruses: A brief introduction to the group. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 267, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pearce, J.C.; Learoyd, T.P.; Langendorf, B.J.; Logan, J.G. Japanese encephalitis: The vectors, ecology and potential for expansion. J. Travel Med. 2018, 25, S16–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, L. The natural history of Japanese encephalitis virus. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1986, 40, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, L.; Tesh, R.B.; Lien, J.C.; Cross, J.H. Transovarial transmission of Japanese encephalitis virus by mosquitoes. Science 1978, 199, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, L.; Lien, J.C.; Shroyer, D.A.; Baker, R.H.; Lu, L.C. Experimental vertical transmission of Japanese encephalitis virus by Culex tritaeniorhynchus and other mosquitoes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1989, 40, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, K.L.; Hernandez-Triana, L.M.; Banyard, A.C.; Fooks, A.R.; Johnson, N. Japanese encephalitis virus infection, diagnosis and control in domestic animals. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 201, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, J.S.; Gurley, E.S.; Pulliam, J.R. Rethinking Japanese encephalitis virus transmission: A framework for implicating host and vector species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.R.S.; Cohnstaedt, L.W.; Cernicchiaro, N. Japanese encephalitis virus: Placing disease vectors in the epidemiologic triad. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2018, 111, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Palinski, R.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cao, S.; Geng, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wen, Y.; Huang, X.; Yan, Q.; et al. Aerosol and contact transmission following intranasal infection of mice with Japanese encephalitis virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, A.C.; Huang, Y.S.; Park, S.L.; Ayers, V.B.; Hettenbach, S.M.; Higgs, S.; McVey, D.S.; Noronha, L.; Hsu, W.W.; Vanlandingham, D.L. Shedding of Japanese encephalitis virus in oral fluid of infected swine. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Nicolas, O.; Braun, R.O.; Milona, P.; Lewandowska, M.; Dijkman, R.; Alves, M.P.; Summerfield, A. Targeting of the nasal mucosa by Japanese encephalitis virus for non-vector-borne transmission. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01091-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, M.E.; Garcia-Nicolas, O.; Brechbuhl, D.; Python, S.; Zumkehr, B.; Nougairede, A.; Charrel, R.N.; Posthaus, H.; Oevermann, A.; Summerfield, A. Vector-free transmission and persistence of Japanese encephalitis virus in pigs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, E.W.; Dominik, J.W.; Slone, T.W. Aerosol stability and respiratory infectivity of Japanese B encephalitis virus. Infect. Immun. 1980, 30, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, A.; Arora, K.L.; Chaturvedi, U.C. Transplacental Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) infection in mice during consecutive pregnancies. J. Gen. Virol. 1982, 59, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapagain, S.; Pal Singh, P.; Le, K.; Safronetz, D.; Wood, H.; Karniychuk, U. Japanese encephalitis virus persists in the human reproductive epithelium and porcine reproductive tissues. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, A.; Arora, K.L.; Chaturvedi, U.C. Congenital infection of mice with Japanese encephalitis virus. Infect. Immun. 1981, 34, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.L.; Huang, Y.S.; Vanlandingham, D.L. Re-examining the importance of pigs in the transmission of Japanese encephalitis virus. Pathogens 2022, 11, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulkin, S.E.; Sims, R.; Allen, R. Studies of arthropod-borne virus infections in Chiroptera. II. Experiments with Japanese B and St. Louis encephalitis viruses in the gravid bat. Evidence of transplacental transmission. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 13, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, D.; Van Soom, A.; Appeltant, R.; Arsenakis, I.; Nauwynck, H. Porcine semen as a vector for transmission of viral pathogens. Theriogenology 2016, 85, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althouse, G.C.; Rossow, K. The potential risk of infectious disease dissemination via artificial insemination in swine. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2011, 46 (Suppl. S2), 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, T. Control of Japanese encephalitis--within our grasp? N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turtle, L.; Solomon, T. Japanese encephalitis—The prospects for new treatments. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, U.K.; Kalita, J. Overview: Japanese encephalitis. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 91, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, M. The pathology of Japanese encephalitis. Bull. World Health Organ. 1964, 30, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Tiroumourougane, S.V.; Raghava, P.; Srinivasan, S. Japanese viral encephalitis. Postgrad. Med. J. 2002, 78, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.I.; Lee, Y.M. Japanese encephalitis virus: Molecular biology and vaccine development. In Molecular Biology of the Flavivirus; Kalitzky, M., Borowski, P., Eds.; Horizon Scientific Press: Norwich, UK, 2006; pp. 225–271. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, K.; McCarthy, J.S.; Pearson, M.; Loukas, A.; Hotez, P.J. Neglected tropical diseases of Oceania: Review of their prevalence, distribution, and opportunities for control. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endy, T.P.; Nisalak, A. Japanese encephalitis virus: Ecology and epidemiology. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 267, 11–48. [Google Scholar]
- Erlanger, T.E.; Weiss, S.; Keiser, J.; Utzinger, J.; Wiedenmayer, K. Past, present, and future of Japanese encephalitis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hurk, A.F.; Ritchie, S.A.; Mackenzie, J.S. Ecology and geographical expansion of Japanese encephalitis virus. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2009, 54, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Williams, D.T. The zoonotic flaviviruses of southern, south-eastern and eastern Asia, and Australasia: The potential for emergent viruses. Zoonoses Public Health 2009, 56, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Li, M.H.; Fu, S.H.; Chen, W.X.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Da, W.; Hu, S.L.; Mu, S.D.; Bai, J.; et al. Japanese encephalitis, Tibet, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Liang, G. Japanese encephalitis and Japanese encephalitis virus in mainland China. Rev. Med. Virol. 2012, 22, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Fu, S.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Liang, X.F.; Cheng, J.X.; Jing, H.M.; Cai, G.L.; Li, X.W.; Ze, W.Y.; Lv, X.J.; et al. Japanese encephalitis outbreak, Yuncheng, China, 2006. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Fu, S.; Wang, H.; Lu, Z.; Cao, Y.; He, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, T.; et al. Vaccine strategies for the control and prevention of Japanese encephalitis in Mainland China, 1951–2011. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xufang, Y.; Huanyu, W.; Shihong, F.; Xiaoyan, G.; Shuye, Z.; Chunting, L.; Minghua, L.; Yougang, Z.; Guodong, L. Etiological spectrum of clinically diagnosed Japanese encephalitis cases reported in Guizhou Province, China, in 2006. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Luo, H.; Li, Y.; Hadler, S.C.; Sandhu, H.S.; Fischer, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Japanese encephalitis disease burden and clinical features of Japanese encephalitis in four cities in the People’s Republic of China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Luo, H.; Ur Rehman, M.; Nabi, F.; Li, K.; Lan, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, L.; Mehmood, K.; Shahzad, M.; et al. Evidence of JEV in Culex tritaeniorhynchus and pigs from high altitude regions of Tibet, China. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2017, 54, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Johansen, C.A.; van den Hurk, A.F.; Ritchie, S.A.; Zborowski, P.; Nisbet, D.J.; Paru, R.; Bockarie, M.J.; Macdonald, J.; Drew, A.C.; Khromykh, T.I.; et al. Isolation of Japanese encephalitis virus from mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) collected in the Western Province of Papua New Guinea, 1997–1998. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 62, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.P.; Taylor, C.T.; Richards, A.R.; Smith, I.L.; Boutlis, C.S. Japanese encephalitis acquired near Port Moresby: Implications for residents and travellers to Papua New Guinea. Med. J. Aust. 2004, 181, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, J.N.; Ritchie, S.A.; Phillips, D.A.; Lee, J.M.; Hills, S.L.; van den Hurk, A.F.; Pyke, A.T.; Johansen, C.A.; Mackenzie, J.S. Japanese encephalitis in north Queensland, Australia, 1998. Med. J. Aust. 1999, 170, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, J.N.; Ritchie, S.A.; Phillips, D.A.; Shield, J.; Bailey, M.C.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Poidinger, M.; McCall, B.J.; Mills, P.J. An outbreak of Japanese encephalitis in the Torres Strait, Australia, 1995. Med. J. Aust. 1996, 165, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, S.A.; Phillips, D.; Broom, A.; Mackenzie, J.; Poidinger, M.; van den Hurk, A. Isolation of Japanese encephalitis virus from Culex annulirostris in Australia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 56, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, S.A.; Rochester, W. Wind-blown mosquitoes and introduction of Japanese encephalitis into Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Hurk, A.F.; Montgomery, B.L.; Northill, J.A.; Smith, I.L.; Zborowski, P.; Ritchie, S.A.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Smith, G.A. Short report: The first isolation of Japanese encephalitis virus from mosquitoes collected from mainland Australia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hurk, A.F.; Ritchie, S.A.; Johansen, C.A.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Smith, G.A. Domestic pigs and Japanese encephalitis virus infection, Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1736–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hurk, A.F.; Johansen, C.A.; Zborowski, P.; Phillips, D.A.; Pyke, A.T.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Ritchie, S.A. Flaviviruses isolated from mosquitoes collected during the first recorded outbreak of Japanese encephalitis virus on Cape York Peninsula, Australia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 64, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammon, W.M.; Tigertt, W.D.; Sather, G.E.; Berge, T.O.; Meiklejohn, G. Epidemiologic studies of concurrent virgin epidemics of Japanese B encephalitis and of mumps on Guam, 1947–1948, with subsequent observations including dengue, through 1957. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1958, 7, 441–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgren, D.C.; Palladino, V.S.; Arnold, A. Japanese B and mumps encephalitis: A clinicopathological report of simultaneous outbreaks on the island of Guam. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1958, 7, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, W.C.; Rudnick, A. A survey of the mosquitoes of Guam in two periods in 1948 and 1949 and its epidemiological implications. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1951, 31, 633–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, W.S.; Moore, P.S.; Karabatsos, N.; Flood, S.P.; Yamada, S.; Jackson, T.; Tsai, T.F. Outbreak of Japanese encephalitis on the island of Saipan, 1990. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 167, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.J.; Savage, H.M.; Smith, G.C.; Flood, S.P.; Castro, L.T.; Roppul, M. Japanese encephalitis on Saipan: A survey of suspected mosquito vectors. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 48, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagasabai, K.; Joshua, V.; Ravi, M.; Sabarinathan, R.; Kirubakaran, B.K.; Ramachandran, V.; Murhekar, M.V. Epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis in India: Analysis of laboratory surveillance data, 2014–2017. J. Infect. 2018, 76, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baruah, A.; Hazarika, R.A.; Barman, N.N.; Islam, S.; Gulati, B.R. Mosquito abundance and pig seropositivity as a correlate of Japanese encephalitis in human population in Assam, India. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2018, 55, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, A.; Tanaka, M.; Morita, K.; Takasu, T.; Ahmed, A.; Ahmed, A.; Akram, D.S.; Waqar, M.A. Detection of West Nile and Japanese encephalitis viral genome sequences in cerebrospinal fluid from acute encephalitis cases in Karachi, Pakistan. Microbiol. Immunol. 1994, 38, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, M.A.; Hoogstraal, H.; Roberts, T.J.; Ahmed, I.P.; Omar, F. A sero-epidemiological survey for certain arboviruses (Togaviridae) in Pakistan. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1983, 77, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, G. Epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis: Past, present, and future prospects. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 435–448. [Google Scholar]
- Platonov, A.; Rossi, G.; Karan, L.; Mironov, K.; Busani, L.; Rezza, G. Does the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) represent a threat for human health in Europe? Detection of JEV RNA sequences in birds collected in Italy. Eurosurveillance 2012, 17, 20241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preziuso, S.; Mari, S.; Mariotti, F.; Rossi, G. Detection of Japanese encephalitis virus in bone marrow of healthy young wild birds collected in 1997–2000 in Central Italy. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravanini, P.; Huhtamo, E.; Ilaria, V.; Crobu, M.G.; Nicosia, A.M.; Servino, L.; Rivasi, F.; Allegrini, S.; Miglio, U.; Magri, A.; et al. Japanese encephalitis virus RNA detected in Culex pipiens mosquitoes in Italy. Eurosurveillance 2012, 17, 20221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon-Loriere, E.; Faye, O.; Prot, M.; Casademont, I.; Fall, G.; Fernandez-Garcia, M.D.; Diagne, M.M.; Kipela, J.M.; Fall, I.S.; Holmes, E.C.; et al. Autochthonous Japanese encephalitis with yellow fever coinfection in Africa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1483–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nett, R.J.; Campbell, G.L.; Reisen, W.K. Potential for the emergence of Japanese encephalitis virus in California. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009, 9, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.R.S.; Cohnstaedt, L.W.; Noronha, L.E.; Mitzel, D.; McVey, D.S.; Cernicchiaro, N. Perspectives regarding the risk of introduction of the Japanese encephalitis virus in the United States. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Gubler, D.J.; Petersen, L.R. Emerging flaviviruses: The spread and resurgence of Japanese encephalitis, West Nile and dengue viruses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S98–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, A.P.; Bhatia, R.; Sunyoto, T.; Mourya, D.T. Emerging and re-emerging arboviral diseases in Southeast Asia. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2013, 50, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Johansen, C.A.; Ritchie, S.A.; van den Hurk, A.F.; Hall, R.A. Japanese encephalitis as an emerging virus: The emergence and spread of Japanese encephalitis virus in Australasia. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 267, 49–73. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, D.S.; Leake, C.J. Japanese encephalitis. In The Arboviruses: Epidemiology and Ecology; Monath, T.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; pp. 63–92. [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn, D.W.; Hoke, C.H., Jr. The epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis: Prospects for prevention. Epidemiol. Rev. 1992, 14, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Flohic, G.; Porphyre, V.; Barbazan, P.; Gonzalez, J.P. Review of climate, landscape, and viral genetics as drivers of the Japanese encephalitis virus ecology. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.H.; Masuoka, P.; Klein, T.A.; Kim, H.C.; Somer, T.; Grieco, J. Ecological niche modeling to estimate the distribution of Japanese encephalitis virus in Asia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T.; Ni, H.; Beasley, D.W.; Ekkelenkamp, M.; Cardosa, M.J.; Barrett, A.D. Origin and evolution of Japanese encephalitis virus in southeast Asia. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3091–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.L.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.Y.; Fu, S.H.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhang, H.L.; Li, M.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Sun, X.H.; et al. Emergence of genotype I of Japanese encephalitis virus as the dominant genotype in Asia. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9847–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Fu, S.; Cao, L.; Shao, N.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Lei, W.; et al. Changing geographic distribution of Japanese encephalitis virus genotypes, 1935–2017. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Fu, S.; Guo, Z.; Liang, G. Southernmost Asia is the source of Japanese encephalitis virus (genotype 1) diversity from which the viruses disperse and evolve throughout Asia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, A.J.; Ward, M.J.; Leigh Brown, A.J.; Barrett, A.D. Dynamics of the emergence and establishment of a newly dominant genotype of Japanese encephalitis virus throughout Asia. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4522–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Fu, S.; Liang, G. Insights into the evolutionary history of Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) based on whole-genome sequences comprising the five genotypes. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Takasaki, T.; Fu, S.H.; Sun, X.H.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, Z.X.; Hao, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.K.; Tang, Q.; Kotaki, A.; et al. Molecular epidemiological analysis of Japanese encephalitis virus in China. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nga, P.T.; Parquet, M.D.C.; Cuong, V.D.; Ma, S.P.; Hasebe, F.; Inoue, S.; Makino, Y.; Takagi, M.; Nam, V.S.; Morita, K. Shift in Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) genotype circulating in northern Vietnam: Implications for frequent introductions of JEV from Southeast Asia to East Asia. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.T.; Wang, L.F.; Daniels, P.W.; Mackenzie, J.S. Molecular characterization of the first Australian isolate of Japanese encephalitis virus, the FU strain. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, A.J.; Li, L.; Tesh, R.B.; Innis, B.L.; Barrett, A.D. Genetic characterization of early isolates of Japanese encephalitis virus: Genotype II has been circulating since at least 1951. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, A.J.; Tesh, R.B.; Barrett, A.D. Genetic characterization of Japanese encephalitis virus genotype II strains isolated from 1951 to 1978. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuh, A.J.; Guzman, H.; Tesh, R.B.; Barrett, A.D. Genetic diversity of Japanese encephalitis virus isolates obtained from the Indonesian archipelago between 1974 and 1987. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Fu, S.H.; Chen, W.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Guo, Y.H.; Liu, Q.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Luo, H.M.; Da, W.; Duo Ji, D.Z.; et al. Genotype V Japanese encephalitis virus is emerging. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.H.; Fu, S.H.; Chen, W.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Cao, Y.X.; Liang, G.D. Molecular characterization of full-length genome of Japanese encephalitis virus genotype V isolated from Tibet, China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2014, 27, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takhampunya, R.; Kim, H.C.; Tippayachai, B.; Kengluecha, A.; Klein, T.A.; Lee, W.J.; Grieco, J.; Evans, B.P. Emergence of Japanese encephalitis virus genotype V in the Republic of Korea. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Cha, G.W.; Jeong, Y.E.; Lee, W.G.; Chang, K.S.; Roh, J.Y.; Yang, S.C.; Park, M.Y.; Park, C.; Shin, E.H. Detection of Japanese encephalitis virus genotype V in Culex orientalis and Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae) in Korea. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monath, T.P. Japanese encephalitis vaccines: Current vaccines and future prospects. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 267, 105–138. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, T.; Vaughn, D.W. Pathogenesis and clinical features of Japanese encephalitis and West Nile virus infections. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 267, 171–194. [Google Scholar]
- Heffelfinger, J.D.; Li, X.; Batmunkh, N.; Grabovac, V.; Diorditsa, S.; Liyanage, J.B.; Pattamadilok, S.; Bahl, S.; Vannice, K.S.; Hyde, T.B.; et al. Japanese encephalitis surveillance and immunization—Asia and Western Pacific Regions, 2016. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.L.; Hills, S.L.; Fischer, M.; Jacobson, J.A.; Hoke, C.H.; Hombach, J.M.; Marfin, A.A.; Solomon, T.; Tsai, T.F.; Tsu, V.D.; et al. Estimated global incidence of Japanese encephalitis: A systematic review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2011, 89, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Hong, Z.; Zhao, S.J.; Clemens, J.D.; Zhou, B.; Wang, B.; Huang, M.S.; Zeng, J.; Guo, Q.H.; Liu, W.; et al. Long-term disability from acute childhood Japanese encephalitis in Shanghai, China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Hills, S.; Staples, E.; Johnson, B.; Yaich, M.; Solomon, T. Japanese encephalitis prevention and control: Advances, challenges, and new initiatives. In Emerging Infections 8; Scheld, W.M., Hammer, S.M., Hughes, J.M., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 93–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ooi, M.H.; Lewthwaite, P.; Lai, B.F.; Mohan, A.; Clear, D.; Lim, L.; Krishnan, S.; Preston, T.; Chieng, C.H.; Tio, P.H.; et al. The epidemiology, clinical features, and long-term prognosis of Japanese encephalitis in Central Sarawak, Malaysia, 1997–2005. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.I.; Lee, Y.M. Japanese encephalitis: The virus and vaccines. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2014, 10, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, S.L.; Walter, E.B.; Atmar, R.L.; Fischer, M.; ACIP Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Work Group. Japanese encephalitis vaccine: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2019, 68, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, N.R.; Gore, M.M. Japanese encephalitis vaccines: Immunogenicity, protective efficacy, effectiveness, and impact on the burden of disease. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 1320–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, T.M.; Thao, T.T.N.; Duy, N.M.; Nhat, T.M.; Clapham, H. Estimates of the global burden of Japanese encephalitis and the impact of vaccination from 2000–2015. eLife 2020, 9, e51027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.I.; Lee, Y.M. Japanese encephalitis virus. In Encyclopedia of Virology, 4th ed.; Bamford, D., Zuckerman, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 583–597. [Google Scholar]
- Poonsiri, T.; Wright, G.S.A.; Solomon, T.; Antonyuk, S.V. Crystal structure of the Japanese encephalitis virus capsid protein. Viruses 2019, 11, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.H.; Zhu, L.; Nian, Q.G.; Yuan, S.; Gao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Ye, Q.; Li, X.F.; Xie, D.Y.; et al. Near-atomic structure of Japanese encephalitis virus reveals critical determinants of virulence and stability. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.I.; Song, B.H.; Polejaeva, I.A.; Davies, C.J.; White, K.L.; Lee, Y.M. Comparison of the live-attenuated Japanese encephalitis vaccine SA14-14-2 strain with its pre-attenuated virulent parent SA14 strain: Similarities and differences in vitro and in vivo. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2575–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Fink, K.; Zust, R.; Lim, S.P.; Qin, C.F.; Shi, P.Y. Flavivirus RNA methylation. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, A.E.; Atkins, J.F. A conserved predicted pseudoknot in the NS2A-encoding sequence of West Nile and Japanese encephalitis flaviviruses suggests NS1′ may derive from ribosomal frameshifting. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, C.S.; Hahn, Y.S.; Rice, C.M.; Lee, E.; Dalgarno, L.; Strauss, E.G.; Strauss, J.H. Conserved elements in the 3′ untranslated region of flavivirus RNAs and potential cyclization sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 1987, 198, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.I.; Choi, Y.J.; Song, B.H.; Lee, Y.M. 3′ Cis-acting elements that contribute to the competence and efficiency of Japanese encephalitis virus genome replication: Functional importance of sequence duplications, deletions, and substitutions. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7909–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.H.; Yun, S.I.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, Y.M. A complex RNA motif defined by three discontinuous 5-nucleotide-long strands is essential for flavivirus RNA replication. RNA 2008, 14, 1791–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.I.; Lee, Y.M. Zika virus: An emerging flavivirus. J. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinton, M.A.; Basu, M. Functions of the 3′ and 5′ genome RNA regions of members of the genus Flavivirus. Virus Res. 2015, 206, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.C.; Soto-Acosta, R.; Bradrick, S.S.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A.; Ooi, E.E. The 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions of the flaviviral genome. Viruses 2017, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villordo, S.M.; Carballeda, J.M.; Filomatori, C.V.; Gamarnik, A.V. RNA structure duplications and flavivirus host adaptation. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; et al. Universal RNA secondary structure insight into mosquito-borne flavivirus (MBFV) cis-acting RNA biology. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Kim, J.M.; Song, B.H.; Yun, S.I.; Yun, G.N.; Byun, S.J.; Lee, Y.M. Profiling of viral proteins expressed from the genomic RNA of Japanese encephalitis virus using a panel of 15 region-specific polyclonal rabbit antisera: Implications for viral gene expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melian, E.B.; Hinzman, E.; Nagasaki, T.; Firth, A.E.; Wills, N.M.; Nouwens, A.S.; Blitvich, B.J.; Leung, J.; Funk, A.; Atkins, J.F.; et al. NS1’ of flaviviruses in the Japanese encephalitis virus serogroup is a product of ribosomal frameshifting and plays a role in viral neuroinvasiveness. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Li, X.F.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.H.; Deng, Y.Q.; Cao, R.Y.; Song, K.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Hua, R.H.; Yu, Y.X.; et al. A single nucleotide mutation in NS2A of Japanese encephalitis live vaccine virus (SA14-14-2) ablates NS1′ formation and contributes to attenuation. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assenberg, R.; Mastrangelo, E.; Walter, T.S.; Verma, A.; Milani, M.; Owens, R.J.; Stuart, D.I.; Grimes, J.M.; Mancini, E.J. Crystal structure of a novel conformational state of the flavivirus NS3 protein: Implications for polyprotein processing and viral replication. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12895–12906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Xu, T.; Hunke, C.; Gruber, G.; Vasudevan, S.G.; Lescar, J. Crystal structure of the NS3 protease-helicase from dengue virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sahili, A.; Lescar, J. Dengue virus non-structural protein 5. Viruses 2017, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, D.S.; Ruiz-Arroyo, V.M.; Soler, N.; Uson, I.; Guarne, A.; Verdaguer, N. Supramolecular arrangement of the full-length Zika virus NS5. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, T.; Olieric, V.; Waltersperger, S.; Panepucci, E.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, D.; Rose, J.; Ebihara, A.; Kuramitsu, S.; et al. Fast native-SAD phasing for routine macromolecular structure determination. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Unno, H.; Mori, Y.; Tani, H.; Moriishi, K.; Takamizawa, A.; Agoh, M.; Tsukihara, T.; Matsuura, Y. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of Japanese encephalitis virus NS3 helicase/nucleoside triphosphatase at a resolution of 1.8 A. Virology 2008, 373, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Gong, P. Crystal structure of the full-length Japanese encephalitis virus NS5 reveals a conserved methyltransferase-polymerase interface. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.C. Viral membrane fusion. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Sevvana, M.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. Structural biology of Zika virus and other flaviviruses. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, E.R.A.; Mohana-Borges, R.; de Alencastro, R.B.; Horta, B.A.C. The flavivirus capsid protein: Structure, function and perspectives towards drug design. Virus Res. 2017, 227, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, T.J.; Hahn, C.S.; Galler, R.; Rice, C.M. Flavivirus genome organization, expression, and replication. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1990, 44, 649–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinton, M.A. Replication cycle and molecular biology of the West Nile virus. Viruses 2013, 6, 13–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjape, S.M.; Harris, E. Control of dengue virus translation and replication. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 338, 15–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bollati, M.; Alvarez, K.; Assenberg, R.; Baronti, C.; Canard, B.; Cook, S.; Coutard, B.; Decroly, E.; de Lamballerie, X.; Gould, E.A.; et al. Structure and functionality in flavivirus NS-proteins: Perspectives for drug design. Antivir. Res. 2010, 87, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diosa-Toro, M.; Prasanth, K.R.; Bradrick, S.S.; Garcia Blanco, M.A. Role of RNA-binding proteins during the late stages of flavivirus replication cycle. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.L.; Jones, C.T.; Rice, C.M. Architects of assembly: Roles of Flaviviridae non-structural proteins in virion morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.J.; Mitzel, D.N.; Taylor, R.T.; Best, S.M.; Bloom, M.E. Tick-borne flaviviruses: Dissecting host immune responses and virus countermeasures. Immunol. Res. 2009, 43, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, J.; Aguirre, S.; Fernandez-Sesma, A. Innate immunity evasion by dengue virus. Viruses 2012, 4, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miorin, L.; Maestre, A.M.; Fernandez-Sesma, A.; Garcia-Sastre, A. Antagonism of type I interferon by flaviviruses. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 492, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gack, M.U.; Diamond, M.S. Innate immune escape by dengue and West Nile viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 20, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.I.; Lee, Y.M. Early events in Japanese encephalitis virus infection: Viral entry. Pathogens 2018, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Wu, Z.; Wu, S.; Chen, S.; Cheng, A. The key amino acids of E protein involved in early flavivirus infection: Viral entry. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Verma, A.; Yadav, P.; Dubey, S.K.; Azhar, E.I.; Maitra, S.S.; Dwivedi, V.D. Molecular pathogenesis of Japanese encephalitis and possible therapeutic strategies. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 1739–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puerta-Guardo, H.; Glasner, D.R.; Espinosa, D.A.; Biering, S.B.; Patana, M.; Ratnasiri, K.; Wang, C.; Beatty, P.R.; Harris, E. Flavivirus NS1 triggers tissue-specific vascular endothelial dysfunction reflecting disease tropism. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1598–1613 e1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, K.E.; Lessler, J.; Moloney, R.M.; Kmush, B.; Cummings, D.A. Incubation periods of mosquito-borne viral infections: A systematic review. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatus, B.J.; Rose, M.R. Japanese B encephalitis: Epidemiological, clinical and pathological aspects. J. Infect. 1983, 6, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwayama, M.; Ito, M.; Takao, S.; Shimazu, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Miyazaki, K.; Kurane, I.; Takasaki, T. Japanese encephalitis virus in meningitis patients, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 471–473. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, P.W.; Truong, D.H.; Hinh, L.D.; Ladinsky, J.L.; Karabatsos, N.; Cropp, C.B.; Martin, D.; Gubler, D.J. Japanese encephalitis among hospitalized pediatric and adult patients with acute encephalitis syndrome in Hanoi, Vietnam 1995. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1998, 58, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, G.; Jongsakul, K. Acute undifferentiated fever caused by infection with Japanese encephalitis virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 68, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhaori, G.; Vene, S.; Shen, K.; Zhou, Y.; Magnius, L.O.; Wahren, B.; Linde, A. Viral etiology of acute childhood encephalitis in Beijing diagnosed by analysis of single samples. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1996, 15, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poneprasert, B. Japanese encephalitis in children in northern Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1989, 20, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Tripathi, P.; Singh, S.; Bannerji, G. Clinical features in children hospitalized during the 2005 epidemic of Japanese encephalitis in Uttar Pradesh, India. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K. Markedly severe dystonia in Japanese encephalitis. Mov. Disord. 2000, 15, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayamajhi, A.; Singh, R.; Prasad, R.; Khanal, B.; Singhi, S. Clinico-laboratory profile and outcome of Japanese encephalitis in Nepali children. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2006, 26, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T.; Dung, N.M.; Kneen, R.; Thao le, T.T.; Gainsborough, M.; Nisalak, A.; Day, N.P.; Kirkham, F.J.; Vaughn, D.W.; Smith, S.; et al. Seizures and raised intracranial pressure in Vietnamese patients with Japanese encephalitis. Brain 2002, 125, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, U.K.; Kalita, J. Seizures in Japanese encephalitis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 190, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T.; Dung, N.M.; Kneen, R.; Gainsborough, M.; Vaughn, D.W.; Khanh, V.T. Japanese encephalitis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 68, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, S.; Lagier, J.C.; Charrel, R.; Querat, G.; Vanhomwegen, J.; Despres, P.; Pelletier, J.; Kaphan, E. Japanese encephalitis in a French traveler to Nepal. J. Neurovirol. 2014, 20, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoti, G.; Dutta, P.; Ram Das, B.; Borah, J.; Mahanta, J. Clinical profile and outcome of Japanese encephalitis in children admitted with acute encephalitis syndrome. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 152656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borah, J.; Dutta, P.; Khan, S.A.; Mahanta, J. A comparison of clinical features of Japanese encephalitis virus infection in the adult and pediatric age group with acute encephalitis syndrome. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 52, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, U.K.; Kalita, J. Movement disorders in Japanese encephalitis. J. Neurol. 1997, 244, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, U.K.; Kalita, J. Prognosis of Japanese encephalitis patients with dystonia compared to those with parkinsonian features only. Postgrad. Med. J. 2002, 78, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, U.K.; Kalita, J. Anterior horn cells are also involved in Japanese encephalitis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1997, 96, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T.; Kneen, R.; Dung, N.M.; Khanh, V.C.; Thuy, T.T.; Ha, D.Q.; Day, N.P.; Nisalak, A.; Vaughn, D.W.; White, N.J. Poliomyelitis-like illness due to Japanese encephalitis virus. Lancet 1998, 351, 1094–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Misra, U.K.; Kalita, J.; Salwani, V.; Gupta, R.K.; Gujral, R. MRI in Japanese encephalitis. Neuroradiology 1997, 39, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Ning, P.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, Y. Acute flaccid paralysis as the initial manifestation of Japanese encephalitis: A case report. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, 381–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K. Comparison of CT scan and MRI findings in the diagnosis of Japanese encephalitis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2000, 174, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.C.; Lee, S.S.; Chen, Y.S.; Tsai, H.C.; Wann, S.R.; Kao, C.H.; Liu, Y.C. Acute flaccid paralysis as an unusual presenting symptom of Japanese encephalitis: A case report and review of the literature. Infection 2007, 35, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basumatary, L.J.; Raja, D.; Bhuyan, D.; Das, M.; Goswami, M.; Kayal, A.K. Clinical and radiological spectrum of Japanese encephalitis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 325, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, L. Japanese encephalitis can trigger anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Han, W.; Jiang, L. Japanese encephalitis-induced anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor encephalitis: A hospital-based prospective study. Brain Dev. 2020, 42, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Li, J.; Lei, W.; Shu, X. Japanese encephalitis virus-induced anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis: A case report and review of literature. Neuropediatrics 2019, 50, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Praharaj, H.N.; Patil, T.B.; Giri, P. Acute transverse myelitis following Japanese encephalitis viral infection: An uncommon complication of a common disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2012, 2012, bcr2012007094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankur Nandan, V.; Nilesh, K.; Dibyaranjan, B.; Ashutosh, T.; Ravi, A.; Arvind, A. Acute transverse myelitis (ascending myelitis) as the initial manifestation of Japanese encephalitis: A rare presentation. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2013, 2013, 487659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.L.; Liao, M.F.; Chiang, H.L.; Lin, S.K. A possible case of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis after Japanese encephalitis. Acta Neurol. Taiwan. 2013, 22, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtaki, E.; Matsuishi, T.; Hirano, Y.; Maekawa, K. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis after treatment with Japanese B encephalitis vaccine (Nakayama-Yoken and Beijing strains). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1995, 59, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, A.F.; Sivertson, S.E. Acute phase of Japanese B encephalitis; two hundred and one cases in American soldiers, Korea, 1950. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1952, 150, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkari, N.B.; Thacker, A.K.; Barthwal, S.P.; Mishra, V.K.; Prapann, S.; Srivastava, D.; Sarkari, M. Japanese encephalitis (JE) part I: Clinical profile of 1282 adult acute cases of four epidemics. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.S.; Nisalak, A.; Ussery, M.A.; Laorakpongse, T.; Chantavibul, S. Kinetics of IgM and IgG responses to Japanese encephalitis virus in human serum and cerebrospinal fluid. J. Infect. Dis. 1985, 151, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagana, M.; Preux, P.M.; Dumas, M. Japanese encephalitis revisited. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 262, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Jiang, L. Outcome of children with Japanese encephalitis and predictors of outcome in southwestern China. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 107, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.H.; Tang, H.J.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, J.C.; Liu, J.W.; Ko, W.C.; Chang, K.; Lee, C.Y.; Chang, Y.T.; Lu, P.L. Determining the clinical characteristics and prognostic factors for the outcomes of Japanese encephalitis in adults: A multicenter study from southern Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huy, B.V.; Tu, H.C.; Luan, T.V.; Lindqvist, R. Early mental and neurological sequelae after Japanese B encephalitis. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1994, 25, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schneider, R.J.; Firestone, M.H.; Edelman, R.; Chieowanich, P.; Pornpibul, R. Clinical sequelae after Japanese encephalitis: A one year follow-up study in Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1974, 5, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayxay, M.; Douangdala, P.; Vilayhong, C.; Phommasone, K.; Chansamouth, V.; Vongsouvath, M.; Rattanavong, S.; Chang, K.; Sengvilaipaseuth, O.; Chanthongthip, A.; et al. Outcome of Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) infection in pediatric and adult patients at Mahosot Hospital, Vientiane, Lao PDR. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkari, N.B.; Thacker, A.K.; Barthwal, S.P.; Mishra, V.K.; Prapann, S.; Srivastava, D.; Sarkari, M. Japanese encephalitis (JE) part II: 14 years’ follow-up of survivors. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtle, L.; Easton, A.; Defres, S.; Ellul, M.; Bovill, B.; Hoyle, J.; Jung, A.; Lewthwaite, P.; Solomon, T. ‘More than devastating’-patient experiences and neurological sequelae of Japanese encephalitis section sign. J. Travel Med. 2019, 26, taz064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Tan, Z.R.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.W. Guillain-Barre syndrome associated with Japanese encephalitis virus infection in China. Viral Immunol. 2014, 27, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Guo, T.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, H.; Hou, X.; Ding, X.; Dou, C.; et al. Guillain-Barre syndrome associated with JEV infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, V.; Taly, A.B.; Shankar, S.K.; Shenoy, P.K.; Desai, A.; Nagaraja, D.; Gourie-Devi, M.; Chandramuki, A. Association of Japanese encephalitis virus infection with Guillain-Barre syndrome in endemic areas of south India. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1994, 90, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, S.; Longo, M.R. Guillain-Barre syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, N.; Piccione, E.A. Guillain-Barre syndrome triggered by West Nile virus: A rare case scenario. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2019, 21, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Libman, R.; Wesson, K.; Ahmed, F.; Einberg, K. Guillain-Barre syndrome: An unusual presentation of West Nile virus infection. Neurology 2000, 55, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauer, F.; Riesen, M.; Reveiz, L.; Oladapo, O.T.; Martinez-Vega, R.; Porgo, T.V.; Haefliger, A.; Broutet, N.J.; Low, N.; WHO Zika Causality Working Group. Zika virus infection as a cause of congenital brain abnormalities and Guillain-Barre syndrome: Systematic review. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, O.J.M.; da Silva, I.R.F. Guillain-Barre syndrome and Zika virus outbreaks. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carod-Artal, F.J.; Wichmann, O.; Farrar, J.; Gascon, J. Neurological complications of dengue virus infection. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Ning, Z.J.; Liu, Y.M.; Li, X.H. Neurological manifestations of dengue infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides-Lara, A.; la Paz Barboza-Arguello, M.; Gonzalez-Elizondo, M.; Hernandez-deMezerville, M.; Brenes-Chacon, H.; Ramirez-Rojas, M.; Ramirez-Hernandez, C.; Arjona-Ortegon, N.; Godfred-Cato, S.; Valencia, D.; et al. Zika virus-associated birth defects, Costa Rica, 2016–2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, U.C.; Mathur, A.; Chandra, A.; Das, S.K.; Tandon, H.O.; Singh, U.K. Transplacental infection with Japanese encephalitis virus. J. Infect. Dis. 1980, 141, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patgiri, S.J.; Borthakur, A.K.; Borkakoty, B.; Saikia, L.; Dutta, R.; Phukan, S.K. An appraisal of clinicopathological parameters in Japanese encephalitis and changing epidemiological trends in upper Assam, India. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2014, 57, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, A.; Tandon, H.O.; Mathur, K.R.; Sarkari, N.B.; Singh, U.K.; Chaturvedi, U.C. Japanese encephalitis virus infection during pregnancy. Indian J. Med. Res. 1985, 81, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mathur, A.; Chaturvedi, U.C.; Tandon, H.O.; Agarwal, A.K.; Mathur, G.P.; Nag, D.; Prasad, A.; Mittal, V.P. Japanese encephalitis epidemic in Uttar Pradesh, India during 1978. Indian J. Med. Res. 1982, 75, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T.; Kawakami, Y.; Fukuhara, S.; Matumoto, M. Experimental stillbirth in pregnant swine infected with Japanese encephalitis virus. Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 1954, 24, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burns, K.F. Congenital Japanese B encephalitis infection of swine. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1950, 75, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, H.; Matumoto, M.; Iwasa, S. Epizootiological studies on stillbirth of swine occurred in Japan during summer months of 1948. Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 1950, 20, 587–595. [Google Scholar]
- Tsubaki, S.; Masu, S.; Obata, Y.; Shimada, F. Studies on Japanese B encephalitis on swine encephalitis and abortion (1947–1949). Kitasato Arch. Exp. Med. 1950, 23, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Desingu, P.A.; Ray, P.K.; Patel, B.H.; Singh, R.; Singh, R.K.; Saikumar, G. Pathogenic and genotypic characterization of a Japanese encephalitis virus isolate associated with reproductive failure in an Indian pig herd. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Heise, M.T. Mouse models as resources for studying infectious diseases. Clin. Ther. 2019, 41, 1912–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydell-Tormanen, K.; Johnson, J.R. The applicability of mouse models to the study of human disease. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1940, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perlman, R.L. Mouse models of human disease: An evolutionary perspective. Evol. Med. Public Health 2016, 2016, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, J.; Warren, H.S.; Cuenca, A.G.; Mindrinos, M.N.; Baker, H.V.; Xu, W.; Richards, D.R.; McDonald-Smith, G.P.; Gao, H.; Hennessy, L.; et al. Genomic responses in mouse models poorly mimic human inflammatory diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3507–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangarajan, A.; Weinberg, R.A. Comparative biology of mouse versus human cells: Modelling human cancer in mice. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, A.C.; Myint, K.S.; Mai, N.T.; Pomeroy, I.; Phu, N.H.; Tzartos, J.; Winter, P.; Collett, J.; Farrar, J.; Barrett, A.; et al. A preliminary neuropathological study of Japanese encephalitis in humans and a mouse model. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 100, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Sasaki, M.; Okumura, M.; Kim, E.; Sawa, H. Flavivirus encephalitis: Pathological aspects of mouse and other animal models. Vet. Pathol. 2010, 47, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.C.; Brault, A.C.; Hunsperger, E. The contribution of rodent models to the pathological assessment of flaviviral infections of the central nervous system. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1423–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Basu, A. Japanese encephalitis-A pathological and clinical perspective. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharucha, T.; Cleary, B.; Farmiloe, A.; Sutton, E.; Hayati, H.; Kirkwood, P.; Al Hamed, L.; van Ginneken, N.; Subramaniam, K.S.; Zitzmann, N.; et al. Mouse models of Japanese encephalitis virus infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis using a meta-regression approach. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Goto, N.; Suzuki, H.; Fujisaki, Y. Strain difference of mouse in susceptibility to Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Jikken Dobutsu 1988, 37, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, S.; Morita, K.; Bundo-Morita, K.; Igarashi, A. Differences in susceptibility to peripheral infection with Japanese encephalitis virus among inbred strains of mouse. Uirusu 1994, 44, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Onodera, T.; Nishida, A.; Goto, N.; Fujisaki, Y. A single gene controls resistance to Japanese encephalitis virus in mice. Arch. Virol. 1990, 112, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Deubel, V. Mice with different susceptibility to Japanese encephalitis virus infection show selective neutralizing antibody response and myeloid cell infectivity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacoby, R.O.; Bhatt, P.N. Genetic resistance to lethal flavivirus encephalitis. I. Infection of congenic mice with Banzi virus. J. Infect. Dis. 1976, 134, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.N.; Kent, K.A.; Bennett, C.J.; Bernard, K.A. Tissue tropism and neuroinvasion of West Nile virus do not differ for two mouse strains with different survival rates. Virology 2007, 368, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, M.B.; Koprowski, H.; Lagerspetz, K. Genetically determined resistance to infection with group B arboviruses. I. Distribution of the resistance gene among various mouse populations and characteristics of gene expression in vivo. J. Infect. Dis. 1974, 129, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabin, A.B. Nature of inherited resistance to viruses affecting the nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1952, 38, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manet, C.; Roth, C.; Tawfik, A.; Cantaert, T.; Sakuntabhai, A.; Montagutelli, X. Host genetic control of mosquito-borne flavivirus infections. Mamm. Genome 2018, 29, 384–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Uyangaa, E.; Patil, A.M.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.; Han, Y.W.; Eo, S.K. Amelioration of Japanese encephalitis by blockage of 4-1BB signaling is coupled to divergent enhancement of type I/II IFN responses and Ly-6C(hi) monocyte differentiation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Uyangaa, E.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, K.; Eo, S.K. Distinct dictation of Japanese encephalitis virus-induced neuroinflammation and lethality via triggering TLR3 and TLR4 signal pathways. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.K.; Paterson, S. Wild rodents as a model to discover genes and pathways underlying natural variation in infectious disease susceptibility. Parasite Immunol. 2013, 35, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokutanda, H.K. Relationship between viremia and interferon production of Japanese encephalitis virus. J. Immunol. 1969, 102, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, A.; Nagashima, K.; Hall, W.W.; Ichikawa, M.; Kimura-Kuroda, J.; Yasui, K. Japanese encephalitis virus neurotropism is dependent on the degree of neuronal maturity. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monath, T.P.; Myers, G.A.; Beck, R.A.; Knauber, M.; Scappaticci, K.; Pullano, T.; Archambault, W.T.; Catalan, J.; Miller, C.; Zhang, Z.X.; et al. Safety testing for neurovirulence of novel live, attenuated flavivirus vaccines: Infant mice provide an accurate surrogate for the test in monkeys. Biologicals 2005, 33, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Higgs, S.; Horne, K.M.; Vanlandingham, D.L. Flavivirus-mosquito interactions. Viruses 2014, 6, 4703–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.L.; Ong, K.C.; Wong, K.T. Pathological findings in a mouse model of Japanese encephalitis infected via the footpad. Neurol. Asia 2015, 20, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Larena, M.; Regner, M.; Lee, E.; Lobigs, M. Pivotal role of antibody and subsidiary contribution of CD8+ T cells to recovery from infection in a murine model of Japanese encephalitis. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5446–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.L.; Ong, K.C.; Tan, S.H.; Wong, K.T. Japanese encephalitis virus infects the thalamus early followed by sensory-associated cortex and other parts of the central and peripheral nervous systems. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 78, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, U.K.; Kalita, J.; Jain, S.K.; Mathur, A. Radiological and neurophysiological changes in Japanese encephalitis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 1484–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handique, S.K.; Das, R.R.; Barman, K.; Medhi, N.; Saharia, B.; Saikia, P.; Ahmed, S.A. Temporal lobe involvement in Japanese encephalitis: Problems in differential diagnosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Siddharthan, V.; Hall, J.O.; Morrey, J.D. West Nile virus preferentially transports along motor neuron axons after sciatic nerve injection of hamsters. J. Neurovirol. 2009, 15, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunsperger, E.A.; Roehrig, J.T. Temporal analyses of the neuropathogenesis of a West Nile virus infection in mice. J. Neurovirol. 2006, 12, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeha, L.E.; Sila, C.A.; Lederman, R.J.; Prayson, R.A.; Isada, C.M.; Gordon, S.M. West Nile virus infection: A new acute paralytic illness. Neurology 2003, 61, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Hui, J.S.; Bartt, R.E. Acute anterior radiculitis associated with West Nile virus infection. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 823–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvert, A.E.; Dixon, K.L.; Delorey, M.J.; Blair, C.D.; Roehrig, J.T. Development of a small animal peripheral challenge model of Japanese encephalitis virus using interferon deficient AG129 mice and the SA14-14-2 vaccine virus strain. Vaccine 2014, 32, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Shimada, S.; Simantini, D.S.; Tun, M.M.; Buerano, C.C.; Morita, K.; Hayasaka, D. Type-I interferon response affects an inoculation dose-independent mortality in mice following Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishna, C.; Ravi, V.; Desai, A.; Subbakrishna, D.K.; Shankar, S.K.; Chandramuki, A. T helper responses to Japanese encephalitis virus infection are dependent on the route of inoculation and the strain of mouse used. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayasaka, D.; Shirai, K.; Aoki, K.; Nagata, N.; Simantini, D.S.; Kitaura, K.; Takamatsu, Y.; Gould, E.; Suzuki, R.; Morita, K. TNF-alpha acts as an immunoregulator in the mouse brain by reducing the incidence of severe disease following Japanese encephalitis virus infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Dutta, K.; Kumawat, K.L.; Ghoshal, A.; Adhya, D.; Basu, A. Abrogated inflammatory response promotes neurogenesis in a murine model of Japanese encephalitis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.I.; Song, B.H.; Kim, J.K.; Yun, G.N.; Lee, E.Y.; Li, L.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G.; Morrey, J.D.; Lee, Y.M. A molecularly cloned, live-attenuated Japanese encephalitis vaccine SA14-14-2 virus: A conserved single amino acid in the ij hairpin of the viral E glycoprotein determines neurovirulence in mice. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Ogata, A.; Tashiro, K.; Nagashima, K.; Tamura, M.; Yasui, K.; Nishihira, J. Japanese encephalitis virus up-regulates expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) mRNA in the mouse brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1517, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, G.; Tiwari, S.; Kumar, A. CCR2 inhibition reduces neurotoxic microglia activation phenotype after Japanese encephalitis viral infection. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kalita, J.; Saxena, V.; Khan, M.Y.; Khanna, V.K.; Sharma, S.; Dhole, T.N.; Misra, U.K. Some observations on the tropism of Japanese encephalitis virus in rat brain. Brain Res. 2009, 1268, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hase, T.; Dubois, D.R.; Summers, P.L. Comparative study of mouse brains infected with Japanese encephalitis virus by intracerebral or intraperitoneal inoculation. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 1990, 71, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Nakamura, K.; Yoshii, M.; Kaku, Y.; Narita, M. Brain lesions induced by experimental intranasal infection of Japanese encephalitis virus in piglets. J. Comp. Pathol. 2009, 141, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.L.; Huang, Y.S.; Lyons, A.C.; Ayers, V.B.; Hettenbach, S.M.; McVey, D.S.; Burton, K.R.; Higgs, S.; Vanlandingham, D.L. North American domestic pigs are susceptible to experimental infection with Japanese encephalitis virus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, A.O.I.; Chevalier, V.; Cappelle, J.; Duong, V.; Fontenille, D.; Duboz, R. How much does direct transmission between pigs contribute to Japanese encephalitis virus circulation? A modelling approach in Cambodia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, I.; Watanabe, T.; Ouchi, N.; Hashimoto, N. Ecological studies of Japanese encephalitis virus in Hokkaido: Interepidemic outbreaks of swine abortion and evidence for the virus to overwinter locally. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1988, 38, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, D.G.; Hilmas, D.E.; Elwell, M.R.; Whitmire, R.E.; Stephen, E.L. Intranasal infection of monkeys with Japanese encephalitis virus: Clinical response and treatment with a nuclease-resistant derivative of poly (I).poly (C). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1977, 26, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, K.S.; Raengsakulrach, B.; Young, G.D.; Gettayacamin, M.; Ferguson, L.M.; Innis, B.L.; Hoke, C.H., Jr.; Vaughn, D.W. Production of lethal infection that resembles fatal human disease by intranasal inoculation of macaques with Japanese encephalitis virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, R.J.; Whiting, T.L.; Anderson, R.A.; Drebot, M.A. An outbreak of West Nile virus-associated disease in domestic geese (Anser anser domesticus) upon initial introduction to a geographic region, with evidence of bird to bird transmission. Can. Vet. J. 2004, 45, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swayne, D.E.; Beck, J.R.; Smith, C.S.; Shieh, W.J.; Zaki, S.R. Fatal encephalitis and myocarditis in young domestic geese (Anser anser domesticus) caused by West Nile virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komar, N.; Langevin, S.; Hinten, S.; Nemeth, N.; Edwards, E.; Hettler, D.; Davis, B.; Bowen, R.; Bunning, M. Experimental infection of North American birds with the New York 1999 strain of West Nile virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. West Nile virus infection among turkey breeder farm workers—Wisconsin, 2002. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2003, 52, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Nir, Y.D. Airborne West Nile virus infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1959, 8, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.Q.; Zhang, N.N.; Li, X.F.; Wang, Y.Q.; Tian, M.; Qiu, Y.F.; Fan, J.W.; Hao, J.N.; Huang, X.Y.; Dong, H.L.; et al. Intranasal infection and contact transmission of Zika virus in guinea pigs. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Schlaberg, R.; Lewis, J.; Hanson, K.E.; Couturier, M.R. Fatal Zika virus infection with secondary nonsexual transmission. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1907–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillpotts, R.J.; Brooks, T.J.; Cox, C.S. A simple device for the exposure of animals to infectious microorganisms by the airborne route. Epidemiol. Infect. 1997, 118, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Wilson, M.E. Transmission of dengue virus without a mosquito vector: Nosocomial mucocutaneous transmission and other routes of transmission. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, e56–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.E.; Haig, D.A.; Alexander, R.A. Wesselsbron virus—A virus not previously described, associated with abortion in domesticated animals. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1956, 27, 183–195. [Google Scholar]
- Llorente, F.; Perez-Ramirez, E.; Fernandez-Pinero, J.; Elizalde, M.; Figuerola, J.; Soriguer, R.C.; Jimenez-Clavero, M.A. Bagaza virus is pathogenic and transmitted by direct contact in experimentally infected partridges, but is not infectious in house sparrows and adult mice. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Teng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Z. Airborne transmission of a novel Tembusu virus in ducks. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2734–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishna, C.; Desai, A.; Shankar, S.K.; Chandramuki, A.; Ravi, V. Oral immunisation of mice with live Japanese encephalitis virus induces a protective immune response. Vaccine 1999, 17, 3102–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, M.; Das, T.; Tomar, N.; John, J.K.; Dubal, Z.B.; Rajak, K.K.; Singh, R.; Saikumar, G. Japanese encephalitis virus-induced neuropathology in mouse model infected through the conjunctival route. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 150, 498–503. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya, T. Intrabulbar inoculation of Japanese encephalitis virus to mice. Kurume Med. J. 1968, 15, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaki, Y.; Miura, Y.; Sugimori, T.; Morimoto, T.; Ino, T. Experimental studies on vertical infection of mice with Japanese encephalitis virus. I. Effect of mouse strain on placental and fetal infection. Natl. Inst. Anim. Health Q. 1976, 16, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisaki, Y.; Miura, Y.; Sugimori, T.; Murakami, Y.; Miura, K. Experimental studies on vertical infection of mice with Japanese encephalitis virus. IV. Effect of virus strain on placental and fetal infection. Natl. Inst. Anim. Health Q. 1983, 23, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisaki, Y.; Miura, Y.; Sugimori, T.; Morimoto, T.; Ino, T. Experimental studies on vertical infection of mice with Japanese encephalitis virus. II. Effect of inoculation route on placental and fetal infection. Natl. Inst. Anim. Health Q. 1977, 17, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisaki, Y.; Miura, Y.; Sugimori, T.; Murakami, Y.; Ino, T.; Miura, K. Experimental studies on vertical infection of mice with Japanese encephalitis virus III. Effect of gestation days at the time of inoculation on placental and fetal infection. Natl. Inst. Anim. Health Q. 1982, 22, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Intrauterine West Nile virus infection—New York, 2002. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2002, 51, 1135–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, F.M.E.; Pietrobon, A.J.; Oliveira, L.M.; Oliveira, L.M.S.; Sato, M.N. Maternal-fetal interplay in Zika virus infection and adverse perinatal outcomes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouliot, S.H.; Xiong, X.; Harville, E.; Paz-Soldan, V.; Tomashek, K.M.; Breart, G.; Buekens, P. Maternal dengue and pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2010, 65, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paixao, E.S.; Teixeira, M.G.; Costa, M.; Rodrigues, L.C. Dengue during pregnancy and adverse fetal outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sips, G.J.; Wilschut, J.; Smit, J.M. Neuroinvasive flavivirus infections. Rev. Med. Virol. 2012, 22, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, T.J.; Diamond, M.S. Pathogenesis of flavivirus encephalitis. Adv. Virus Res. 2003, 60, 273–342. [Google Scholar]
- Maximova, O.A.; Pletnev, A.G. Flaviviruses and the central nervous system: Revisiting neuropathological concepts. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2018, 5, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velandia, M.L.; Castellanos, J.E. Flavivirus neurotropism, neuroinvasion, neurovirulence and neurosusceptibility: Clues to understanding flavivirus- and dengue-induced encephalitis. In Viral Genomes—Molecular Structure, Diversity, Gene Expression Mechanisms and Host-Virus Interactions; Garcia, M., Ed.; InTech Open Access: Shanghai, China, 2012; pp. 219–240. [Google Scholar]
- Briant, L.; Despres, P.; Choumet, V.; Misse, D. Role of skin immune cells on the host susceptibility to mosquito-borne viruses. Virology 2014, 464, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischknecht, F. The skin as interface in the transmission of arthropod-borne pathogens. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, H. Japanese encephalitis virus wild strain infection suppresses dendritic cells maturation and function, and causes the expansion of regulatory T cells. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, K.; Dutta, K.; Nazmi, A.; Basu, A. Japanese encephalitis virus infection modulates the expression of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) in macrophages: Implications for the hosts’ innate immune response. Cell. Immunol. 2013, 285, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.D.; Yeh, W.T.; Chen, R.F.; Chuon, H.L.; Tsai, H.P.; Yao, C.W.; Shaio, M.F. A model to study neurotropism and persistency of Japanese encephalitis virus infection in human neuroblastoma cells and leukocytes. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleyas, A.G.; George, J.A.; Han, Y.W.; Rahman, M.M.; Kim, S.J.; Han, S.B.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, K.; Eo, S.K. Functional modulation of dendritic cells and macrophages by Japanese encephalitis virus through MyD88 adaptor molecule-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2462–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, M.; Chen, L.; Mei, L.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Cao, S. Infection of mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells by live attenuated Japanese encephalitis virus induces cells maturation and triggers T cells activation. Vaccine 2011, 29, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Hegde, P.; Lecerf, M.; Nain, M.; Kaur, M.; Kalia, M.; Vrati, S.; Bayry, J.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Kaveri, S.V. Japanese encephalitis virus expands regulatory T cells by increasing the expression of PD-L1 on dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooryanarain, H.; Ayachit, V.; Gore, M. Activated CD56(+) lymphocytes (NK+NKT) mediate immunomodulatory and anti-viral effects during Japanese encephalitis virus infection of dendritic cells in vitro. Virology 2012, 432, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myint, K.S.; Kipar, A.; Jarman, R.G.; Gibbons, R.V.; Perng, G.C.; Flanagan, B.; Mongkolsirichaikul, D.; Van Gessel, Y.; Solomon, T. Neuropathogenesis of Japanese encephalitis in a primate model. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Rathore, D.K.; Sachan, S.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Gupta, N.; Awasthi, A.; Vrati, S.; Kalia, M. Japanese encephalitis virus infected human monocyte-derived dendritic cells activate a transcriptional network leading to an antiviral inflammatory response. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 638694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, K.; Mishra, M.K.; Nazmi, A.; Kumawat, K.L.; Basu, A. Minocycline differentially modulates macrophage mediated peripheral immune response following Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Immunobiology 2010, 215, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Satake, Y.; Kobayashi, Y. Effect of cytokines on Japanese encephalitis virus production by human monocytes. Microbiol. Immunol. 1990, 34, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Choi, J.Y.; Uyangaa, E.; Patil, A.M.; Hossain, F.M.; Hur, J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.; Eo, S.K. Blockage of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase regulates Japanese encephalitis via enhancement of type I/II IFN innate and adaptive T-cell responses. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooryanarain, H.; Sapkal, G.N.; Gore, M.M. Pathogenic and vaccine strains of Japanese encephalitis virus elicit different levels of human macrophage effector functions. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1905–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.T.; Liu, R.S.; Wu, M.F.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Tan, D.T.; Chou, T.Y.; Tsai, I.S.; Li, L.; Hsieh, S.L. CLEC5A regulates Japanese encephalitis virus-induced neuroinflammation and lethality. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissmann, F.; Manz, M.G.; Jung, S.; Sieweke, M.H.; Merad, M.; Ley, K. Development of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Science 2010, 327, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, L.J.; Halliday, G.M.; King, N.J. Langerhans cells migrate to local lymph nodes following cutaneous infection with an arbovirus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Devery, J.M.; King, N.J. Adherence status regulates the primary cellular activation responses to the flavivirus West Nile. Immunology 1995, 84, 254–264. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, A.W.; Wu, W.; Freewan, M.; Stocker, R.; King, N.J.; Thomas, S.R. Flavivirus infection induces indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in human monocyte-derived macrophages via tumor necrosis factor and NF-kappaB. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, M.; Zhang, M.J.; Grinev, A.; Srinivasan, K.; Daniel, S.; Wood, O.; Hewlett, I.K.; Dayton, A.I. Monocytes-macrophages are a potential target in human infection with West Nile virus through blood transfusion. Transfusion 2006, 46, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quicke, K.M.; Bowen, J.R.; Johnson, E.L.; McDonald, C.E.; Ma, H.; O’Neal, J.T.; Rajakumar, A.; Wrammert, J.; Rimawi, B.H.; Pulendran, B.; et al. Zika virus infects human placental macrophages. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Grouard-Vogel, G.; Sun, W.; Mascola, J.R.; Brachtel, E.; Putvatana, R.; Louder, M.K.; Filgueira, L.; Marovich, M.A.; Wong, H.K.; et al. Human skin Langerhans cells are targets of dengue virus infection. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.J.; Wang, J.J.; Shaio, M.F.; Kao, C.L.; Chang, D.M.; Han, S.W.; Lai, J.H. Infection of human dendritic cells by dengue virus causes cell maturation and cytokine production. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassaneetrithep, B.; Burgess, T.H.; Granelli-Piperno, A.; Trumpfheller, C.; Finke, J.; Sun, W.; Eller, M.A.; Pattanapanyasat, K.; Sarasombath, S.; Birx, D.L.; et al. DC-SIGN (CD209) mediates dengue virus infection of human dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba-Spaeth, G.; Longman, R.S.; Albert, M.L.; Rice, C.M. Live attenuated yellow fever 17D infects human DCs and allows for presentation of endogenous and recombinant T cell epitopes. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingen, M.; Schmid, M.A.; Harris, E.; McKimmie, C.S. Mosquito biting modulates skin response to virus infection. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labuda, M.; Austyn, J.M.; Zuffova, E.; Kozuch, O.; Fuchsberger, N.; Lysy, J.; Nuttall, P.A. Importance of localized skin infection in tick-borne encephalitis virus transmission. Virology 1996, 219, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, P.Y.; Behr, M.J.; Chadwick, C.M.; Shi, P.Y.; Bernard, K.A. Keratinocytes are cell targets of West Nile virus in vivo. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5197–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.; Wehbe, M.; Leveque, N.; Bodet, C. Skin innate immune response to flaviviral infection. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2017, 28, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Wong, C. Relation of the peripheral multiplication of Japanese B encephalitis virus to the pathogenesis of the infection in mice. Acta Virol. 1963, 7, 322–330. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, A.; Bharadwaj, M.; Kulshreshtha, R.; Rawat, S.; Jain, A.; Chaturvedi, U.C. Immunopathological study of spleen during Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mice. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1988, 69, 423–432. [Google Scholar]
- Nagata, N.; Iwata-Yoshikawa, N.; Hayasaka, D.; Sato, Y.; Kojima, A.; Kariwa, H.; Takashima, I.; Takasaki, T.; Kurane, I.; Sata, T.; et al. The pathogenesis of 3 neurotropic flaviviruses in a mouse model depends on the route of neuroinvasion after viremia. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, S.B.; Uyangaa, E.; Patil, A.M.; Han, Y.W.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.; Eo, S.K. CD11c(hi) dendritic cells regulate Ly-6C(hi) monocyte differentiation to preserve immune-privileged CNS in lethal neuroinflammation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkal, G.N.; Wairagkar, N.S.; Ayachit, V.M.; Bondre, V.P.; Gore, M.M. Detection and isolation of Japanese encephalitis virus from blood clots collected during the acute phase of infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swami, R.; Ratho, R.K.; Mishra, B.; Singh, M.P. Usefulness of RT-PCR for the diagnosis of Japanese encephalitis in clinical samples. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 40, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Cao, S.; Wang, K.; Yuan, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Cui, M.; Fu, Z.F. Viral infection of the central nervous system and neuroinflammation precede blood-brain barrier disruption during Japanese encephalitis virus infection. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5602–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, T. Flavivirus encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurane, I. Immune responses to Japanese encephalitis virus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 267, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Innate immune recognition of viral infection. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. MDA5/RIG-I and virus recognition. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.S.; Lorsomrudee, W.; Leake, C.J.; Hoke, C.H.; Nisalak, A.; Chongswasdi, V.; Laorakpongse, T. Fatal outcome in Japanese encephalitis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 34, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, M.D.; Salimi, H.; Diamond, M.S.; Klein, R.S. Mechanisms of pathogen invasion into the central nervous system. Neuron 2019, 103, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, N.J.; Getts, D.R.; Getts, M.T.; Rana, S.; Shrestha, B.; Kesson, A.M. Immunopathology of flavivirus infections. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dando, S.J.; Mackay-Sim, A.; Norton, R.; Currie, B.J.; St John, J.A.; Ekberg, J.A.; Batzloff, M.; Ulett, G.C.; Beacham, I.R. Pathogens penetrating the central nervous system: Infection pathways and the cellular and molecular mechanisms of invasion. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 691–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, A.; Shankar, S.K.; Ravi, V.; Chandramuki, A.; Gourie-Devi, M. Japanese encephalitis virus antigen in the human brain and its topographic distribution. Acta Neuropathol. 1995, 89, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherji, A.K.; Biswas, S.K. Histopathological studies of brains (and other viscera) from cases of JE virus encephalitis during 1973 epidemic at Bankura. Indian J. Med. Res. 1976, 64, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.T.; Burke, D.S.; Elwell, M.; Leake, C.J.; Nisalak, A.; Hoke, C.H.; Lorsomrudee, W. Japanese encephalitis: Immunocytochemical studies of viral antigen and inflammatory cells in fatal cases. Ann. Neurol. 1985, 18, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.H.; Liang, L.C.; Wang, C.C.; Liu, H.C.; Chen, W.J. The blood-brain barrier in the cerebrum is the initial site for the Japanese encephalitis virus entering the central nervous system. J. Neurovirol. 2008, 14, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Zhao, Z.; Montagne, A.; Nelson, A.R.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-brain barrier: From physiology to disease and back. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 21–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Patabendige, A.A.; Dolman, D.E.; Yusof, S.R.; Begley, D.J. Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabh, P.; Braun, A.; Nedergaard, M. The blood-brain barrier: An overview: Structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneman, R.; Prat, A. The blood-brain barrier. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Ronda, J.; Weintraub, M.; Jain, K.; Silver, R.; Silverman, A.J. Brain mast cell relationship to neurovasculature during development. Brain Res. 2007, 1171, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.T.; St John, A.L. Japanese encephalitis virus and its mechanisms of neuroinvasion. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, Y.M.; Meuren, L.M.; Coelho, S.V.A.; de Arruda, L.B. Pathways exploited by flaviviruses to counteract the blood-brain barrier and invade the central nervous system. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, G. Immune response and blood-brain barrier dysfunction during viral neuroinvasion. Innate Immun. 2021, 27, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, K.Y.Y.; Fairn, G.D.; Lee, W.L. Transcellular vesicular transport in epithelial and endothelial cells: Challenges and opportunities. Traffic 2018, 19, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, M.L.; Hsu, C.Y. Japanese encephalitis virus is transported across the cerebral blood vessels by endocytosis in mouse brain. Cell Tissue Res. 1998, 293, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Zhao, J.X.; Yamamoto, T.; Konno, H. Immunohistochemical demonstration of viral antigens in Japanese encephalitis. Acta Neuropathol. 1986, 70, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.Y.; Ou, Y.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Pan, H.C.; Chang, C.J.; Liao, S.L.; Su, H.L.; Chen, C.J. Endothelial Japanese encephalitis virus infection enhances migration and adhesion of leukocytes to brain microvascular endothelia via MEK-dependent expression of ICAM1 and the CINC and RANTES chemokines. J. Neurochem. 2012, 123, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Chen, H.W.; Zhang, H.X.; Wang, K.; Su, J.; Chen, Y.R.; Wang, X.R.; Fu, Z.F.; Cui, M. EGFR activation impairs antiviral activity of interferon signaling in brain microvascular endothelial cells during Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 894356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, Y.; Qi, Z. Ezrin is essential for the entry of Japanese encephalitis virus into the human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patabendige, A.; Michael, B.D.; Craig, A.G.; Solomon, T. Brain microvascular endothelial-astrocyte cell responses following Japanese encephalitis virus infection in an in vitro human blood-brain barrier model. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 89, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, M.M.J.; Bahadoran, A.; Har, L.S.; Mui, W.S.; Rajarajeswaran, J.; Zandi, K.; Manikam, R.; Sekaran, S.D. Japanese encephalitis virus disrupts blood-brain barrier and modulates apoptosis proteins in THBMEC cells. Virus Res. 2017, 233, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shwetank; Date, O.S.; Kim, K.S.; Manjunath, R. Infection of human endothelial cells by Japanese encephalitis virus: Increased expression and release of soluble HLA-E. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Ou, Y.C.; Li, J.R.; Chang, C.Y.; Pan, H.C.; Lai, C.Y.; Liao, S.L.; Raung, S.L.; Chang, C.J. Infection of pericytes in vitro by Japanese encephalitis virus disrupts the integrity of the endothelial barrier. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Li, J.R.; Chen, W.Y.; Ou, Y.C.; Lai, C.Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Wu, C.C.; Chang, C.J.; Chen, C.J. Disruption of in vitro endothelial barrier integrity by Japanese encephalitis virus-infected astrocytes. Glia 2015, 63, 1915–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, N.J.C.; van Vreden, C.; Terry, R.L.; Getts, D.R.; Yeung, A.W.S.; Teague-Getts, M.; Davison, A.M.; Deffrasnes, C.; Munoz-Erazo, L. The immunopathogenesis of neurotropic flavivirus infection. In Flavivirus encephalitis; Ruzek, D., Ed.; InTech Open Access: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 25–52. [Google Scholar]
- Mladinich, M.C.; Schwedes, J.; Mackow, E.R. Zika virus persistently infects and is basolaterally released from primary human brain microvascular endothelial cells. mBio 2017, 8, e00952-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Lo, Y.; Chapagain, M.; Lum, S.; Kumar, M.; Gurjav, U.; Luo, H.; Nakatsuka, A.; Nerurkar, V.R. West Nile virus infection modulates human brain microvascular endothelial cells tight junction proteins and cell adhesion molecules: Transmigration across the in vitro blood-brain barrier. Virology 2009, 385, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, Y.; Malik, A.B. Regulation of endothelial permeability via paracellular and transcellular transport pathways. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 463–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, A.; Khanna, N.; Chaturvedi, U.C. Breakdown of blood-brain barrier by virus-induced cytokine during Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 1992, 73, 603–611. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, M.K.; Dutta, K.; Saheb, S.K.; Basu, A. Understanding the molecular mechanism of blood-brain barrier damage in an experimental model of Japanese encephalitis: Correlation with minocycline administration as a therapeutic agent. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 55, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Hossain, F.M.; Patil, A.M.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, S.B.; Uyangaa, E.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, B.; Kim, K.; et al. Ablation of CD11c(hi) dendritic cells exacerbates Japanese encephalitis by regulating blood-brain barrier permeability and altering tight junction/adhesion molecules. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.; Shakya, A.K.; Shukla, M.; Kumari, N.; Krishnani, N.; Dhole, T.N.; Misra, U.K. Circulating levels of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases during Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Virusdisease 2016, 27, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, V.; Mathur, A.; Krishnani, N.; Dhole, T.N. Kinetics of cytokine profile during intraperitoneal inoculation of Japanese encephalitis virus in BALB/c mice model. Microbes Infect. 2008, 10, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.M.; Kar, S.; Singh, R.; Chakraborty, D.; Vipat, V.; Raut, C.G.; Mishra, A.C.; Gore, M.M.; Ghosh, D. Immunomodulatory cytokines determine the outcome of Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mice. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Lomash, V.; Rao, P.V. Expression profile of Japanese encephalitis virus induced neuroinflammation and its implication in disease severity. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 49, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, P.M.; Dung, N.M.; Loan, H.T.; Kneen, R.; Wills, B.; Thu le, T.; House, D.; White, N.J.; Farrar, J.J.; Hart, C.A.; et al. Proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in humans with Japanese encephalitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, T.; Sharvani, V.; Nair, D.; Medigeshi, G.R. Japanese encephalitis virus disrupts cell-cell junctions and affects the epithelial permeability barrier functions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, W.J. The role of matrix metalloproteinase in inflammation with a focus on infectious diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, L.G.N.; Thode, H.; Eslambolchi, Y.; Chopra, S.; Young, D.; Gill, S.; Devel, L.; Dufour, A. Matrix metalloproteinases: From molecular mechanisms to physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2022, 74, 712–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Cen, J.; Huang, Y.; Shen, H.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 secreted by leukemic cells increase the permeability of blood-brain barrier by disrupting tight junction proteins. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.Y.; Yu, W.H.; Yeh, W.L.; Tang, C.H.; Leung, Y.M.; Wong, K.L.; Chen, Y.F.; Lai, C.H.; Fu, W.M. Hypoxia-induced matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in astrocytes enhances permeability of brain endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 220, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanabalasundaram, G.; Pieper, C.; Lischper, M.; Galla, H.J. Regulation of the blood-brain barrier integrity by pericytes via matrix metalloproteinases mediated activation of vascular endothelial growth factor in vitro. Brain Res. 2010, 1347, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, G.A. Matrix metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation. Glia 2002, 39, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, V.; Kumar Shakya, A.; Dhole, T.N.; Misra, U.K. Upregulated expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases in BALB/c mouse brain challenged with Japanese encephalitis virus. Neuroimmunomodulation 2012, 19, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, V.; Shakya, A.K.; Dhole, T.N.; Misra, U.K. Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of children with Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2561–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, W.H.; Tsai, H.W.; Lee, I.T.; Hsieh, H.L.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Yang, C.M. Japanese encephalitis virus induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 in rat brain astrocytes via NF-kappaB signalling dependent on MAPKs and reactive oxygen species. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 1566–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Lin, C.C.; Lee, I.T.; Lin, Y.H.; Yang, C.M.; Chen, W.J.; Jou, M.J.; Hsiao, L.D. Japanese encephalitis virus induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression via a ROS/c-Src/PDGFR/PI3K/Akt/MAPKs-dependent AP-1 pathway in rat brain astrocytes. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.T.; Rathore, A.P.S.; Soundarajan, G.; St John, A.L. Japanese encephalitis virus neuropenetrance is driven by mast cell chymase. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchougounova, E.; Lundequist, A.; Fajardo, I.; Winberg, J.O.; Abrink, M.; Pejler, G. A key role for mast cell chymase in the activation of pro-matrix metalloprotease-9 and pro-matrix metalloprotease-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9291–9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Dai, J.; Bai, F.; Kong, K.F.; Wong, S.J.; Montgomery, R.R.; Madri, J.A.; Fikrig, E. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 facilitates West Nile virus entry into the brain. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8978–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, K.; Kumar, M.; Lum, S.; Orillo, B.; Nerurkar, V.R.; Verma, S. West Nile virus-induced disruption of the blood-brain barrier in mice is characterized by the degradation of the junctional complex proteins and increase in multiple matrix metalloproteinases. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, B.T.; Davis, T.P. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persidsky, Y.; Ramirez, S.H.; Haorah, J.; Kanmogne, G.D. Blood-brain barrier: Structural components and function under physiologic and pathologic conditions. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2006, 1, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De la Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuna, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The roles of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in human diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkedal-Hansen, H.; Moore, W.G.; Bodden, M.K.; Windsor, L.J.; Birkedal-Hansen, B.; DeCarlo, A.; Engler, J.A. Matrix metalloproteinases: A review. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1993, 4, 197–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.S.; Jawdat, D.M. Mast cells in innate immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, L.; Heemskerk, N.; van Buul, J.D. Leukocyte transendothelial migration: A local affair. Small GTPases 2017, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Buul, J.D.; Hordijk, P.L. Signaling in leukocyte transendothelial migration. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.; Ubogu, E.E.; Ransohoff, R.M. Inflammatory cell migration into the central nervous system: A few new twists on an old tale. Brain Pathol. 2007, 17, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachter, J.S.; de Vries, H.E.; Fabry, Z. The blood-brain barrier and its role in immune privilege in the central nervous system. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 62, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larochelle, C.; Alvarez, J.I.; Prat, A. How do immune cells overcome the blood-brain barrier in multiple sclerosis? FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3770–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Chen, S.; Klebe, D.; Zhang, J.H.; Tang, J. Adhesion molecules in CNS disorders: Biomarker and therapeutic targets. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Rao, P.V. Transcriptomic profile of host response in Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, B.; Wolf, M.; Walz, A.; Loetscher, P. Chemokines: Multiple levels of leukocyte migration control. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Granata, T. Brain inflammation in epilepsy: Experimental and clinical evidence. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1724–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, J.; Yang, X.; Jiang, R.; Chen, H.; Cao, S. Japanese encephalitis virus infection induces changes of mRNA profile of mouse spleen and brain. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Duseja, R.; Das, S.; Appaiahgiri, M.B.; Vrati, S.; Basu, A. Induction of IP-10 (CXCL10) in astrocytes following Japanese encephalitis. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 414, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, N.; Agnihotri, M.; Mathur, A.; Chaturvedi, U.C. Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by Japanese encephalitis virus stimulated macrophages. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1991, 86, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempe, R.G.; Hartz, A.M.S.; Bauer, B. Matrix metalloproteinases in the brain and blood-brain barrier: Versatile breakers and makers. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 1481–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellebjerg, F.; Sorensen, T.L. Chemokines and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in leukocyte recruitment to the central nervous system. Brain Res. Bull. 2003, 61, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Avraham, H.; Lee, S.H.; Avraham, S. Vascular endothelial growth factor modulates neutrophil transendothelial migration via up-regulation of interleukin-8 in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10445–10451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapouly, C.; Tadesse Argaw, A.; Horng, S.; Castro, K.; Zhang, J.; Asp, L.; Loo, H.; Laitman, B.M.; Mariani, J.N.; Straus Farber, R.; et al. Astrocytic TYMP and VEGFA drive blood-brain barrier opening in inflammatory central nervous system lesions. Brain 2015, 138, 1548–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Goes, A.; Wouters, D.; Van Der Pol, S.M.; Huizinga, R.; Ronken, E.; Adamson, P.; Greenwood, J.; Dijkstra, C.D.; De Vries, H.E. Reactive oxygen species enhance the migration of monocytes across the blood-brain barrier in vitro. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 1852–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, A.; Das, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mishra, M.K.; Sharma, V.; Koli, P.; Sen, E.; Basu, A. Proinflammatory mediators released by activated microglia induces neuronal death in Japanese encephalitis. Glia 2007, 55, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrey, J.D.; Olsen, A.L.; Siddharthan, V.; Motter, N.E.; Wang, H.; Taro, B.S.; Chen, D.; Ruffner, D.; Hall, J.O. Increased blood-brain barrier permeability is not a primary determinant for lethality of West Nile virus infection in rodents. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzek, D.; Salat, J.; Singh, S.K.; Kopecky, J. Breakdown of the blood-brain barrier during tick-borne encephalitis in mice is not dependent on CD8+ T cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannes, N.; Summerfield, A.; Filgueira, L. Regulation of inflammation in Japanese encephalitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.S.; Zou, Q.C.; Xiong, W.J.; Cui, N.Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.X.; Lou, W.J.; Higazy, D.; Zhang, Y.G.; Cui, M. Brain microvascular endothelial cell-derived HMGB1 facilitates monocyte adhesion and transmigration to promote JEV neuroinvasion. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 701820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Zhen, Z.D.; Fan, D.Y.; Qin, C.F.; Han, D.S.; Zhou, H.N.; Wang, P.G.; An, J. Axl deficiency promotes the neuroinvasion of Japanese encephalitis virus by enhancing IL-1alpha production from pyroptotic macrophages. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00602-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raengsakulrach, B.; Nisalak, A.; Gettayacamin, M.; Thirawuth, V.; Young, G.D.; Myint, K.S.; Ferguson, L.M.; Hoke, C.H., Jr.; Innis, B.L.; Vaughn, D.W. An intranasal challenge model for testing Japanese encephalitis vaccines in rhesus monkeys. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.T.; Ng, K.Y.; Ong, K.C.; Ng, W.F.; Shankar, S.K.; Mahadevan, A.; Radotra, B.; Su, I.J.; Lau, G.; Ling, A.E.; et al. Enterovirus 71 encephalomyelitis and Japanese encephalitis can be distinguished by topographic distribution of inflammation and specific intraneuronal detection of viral antigen and RNA. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2012, 38, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Basu, A. Japanese encephalitis virus infects neural progenitor cells and decreases their proliferation. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1624–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura-Kuroda, J.; Ichikawa, M.; Ogata, A.; Nagashima, K.; Yasui, K. Specific tropism of Japanese encephalitis virus for developing neurons in primary rat brain culture. Arch. Virol. 1993, 130, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongtan, T.; Cheepsunthorn, P.; Chaiworakul, V.; Rattanarungsan, C.; Wikan, N.; Smith, D.R. Highly permissive infection of microglial cells by Japanese encephalitis virus: A possible role as a viral reservoir. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lannes, N.; Neuhaus, V.; Scolari, B.; Kharoubi-Hess, S.; Walch, M.; Summerfield, A.; Filgueira, L. Interactions of human microglia cells with Japanese encephalitis virus. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Ou, Y.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Pan, H.C.; Liao, S.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Raung, S.L.; Lai, C.Y. Glutamate released by Japanese encephalitis virus-infected microglia involves TNF-alpha signaling and contributes to neuronal death. Glia 2012, 60, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V.; Desai, A.S.; Shenoy, P.K.; Satishchandra, P.; Chandramuki, A.; Gourie-Devi, M. Persistence of Japanese encephalitis virus in the human nervous system. J. Med. Virol. 1993, 40, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mathur, A.; Prakash, V.; Kulshreshtha, R.; Kumar, R.; Chaturvedi, U.C. Japanese encephalitis virus latency in peripheral blood lymphocytes and recurrence of infection in children. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1991, 85, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, S.; Clarke, P.; Tyler, K.L. Pharmacologic depletion of microglia increases viral load in the brain and enhances mortality in murine models of flavivirus-induced encephalitis. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00525-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.K.; Basu, A. Minocycline neuroprotects, reduces microglial activation, inhibits caspase 3 induction, and viral replication following Japanese encephalitis. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 1582–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.L.; Lin, Y.L.; Wang, J.J.; Huang, Y.L.; Yeh, C.T.; Ma, S.H.; Chen, L.K. Effect of enforced expression of human bcl-2 on Japanese encephalitis virus-induced apoptosis in cultured cells. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5963–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, M.K.; Kumawat, K.L.; Basu, A. Japanese encephalitis virus differentially modulates the induction of multiple pro-inflammatory mediators in human astrocytoma and astroglioma cell lines. Cell Biol. Int. 2008, 32, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Jiang, R.; Cui, M.; Zhu, B.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Zohaib, A.; Dong, Q.; Ruan, X.; Song, Y.; et al. Etanercept reduces neuroinflammation and lethality in mouse model of Japanese encephalitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricker, M.; Tolkovsky, A.M.; Borutaite, V.; Coleman, M.; Brown, G.C. Neuronal cell death. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 813–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Das, A.; Ray, S.K.; Banik, N.L. Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Bull. 2012, 87, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Ou, Y.C.; Lin, S.Y.; Raung, S.L.; Liao, S.L.; Lai, C.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, J.H. Glial activation involvement in neuronal death by Japanese encephalitis virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazmi, A.; Dutta, K.; Das, S.; Basu, A. Japanese encephalitis virus-infected macrophages induce neuronal death. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2011, 6, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mishra, M.K.; Ghosh, J.; Basu, A. Japanese encephalitis virus infection induces IL-18 and IL-1beta in microglia and astrocytes: Correlation with in vitro cytokine responsiveness of glial cells and subsequent neuronal death. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 195, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarup, V.; Ghosh, J.; Das, S.; Basu, A. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated death domain mediated neuronal death contributes to the glial activation and subsequent neuroinflammation in Japanese encephalitis. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsini, A.; Zunszain, P.A.; Thuret, S.; Pariante, C.M. The role of inflammatory cytokines as key modulators of neurogenesis. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, N.P.; Eidem, T.M.; Peng, H.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, J.C. Inflammation mediates varying effects in neurogenesis: Relevance to the pathogenesis of brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders. J. Neurochem. 2009, 108, 1343–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ran, M.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Ma, K.; Yang, Y.; Fu, X.; Yang, S. New insight into neurological degeneration: Inflammatory cytokines and blood-brain barrier. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1013933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochfort, K.D.; Cummins, P.M. The blood-brain barrier endothelium: A target for pro-inflammatory cytokines. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, Y.; Ransohoff, R.M. Inflammatory cell trafficking across the blood-brain barrier: Chemokine regulation and in vitro models. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 248, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, E.H.; Weninger, W.; Hunter, C.A. Trafficking of immune cells in the central nervous system. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Liao, S.L.; Raung, S.L. Upregulation of RANTES gene expression in neuroglia by Japanese encephalitis virus infection. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12107–12119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kulshreshtha, R.; Mathur, A. Secretion of the chemokine interleukin-8 during Japanese encephalitis virus infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 49, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Kitaura, K.; Nakamichi, K.; Takasaki, T.; Suzuki, R.; Kurane, I. Accumulation of T cells with selected T-cell receptors in the brains of Japanese encephalitis virus-infected mice. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Ou, Y.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Pan, H.C.; Liao, S.L.; Raung, S.L.; Chen, S.Y. TNF-alpha and IL-1beta mediate Japanese encephalitis virus-induced RANTES gene expression in astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Patil, A.M.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, S.B.; Uyangaa, E.; Hossain, F.M.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.; Eo, S.K. CCL2, but not its receptor, is essential to restrict immune privileged central nervous system-invasion of Japanese encephalitis virus via regulating accumulation of CD11b(+) Ly-6C(hi) monocytes. Immunology 2016, 149, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Singh, R.K.; Tiwari, R.; Dhole, T.N. Japanese encephalitis: A review of the Indian perspective. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, M.D.; Scott, R.M.; Vaughn, D.W.; Rajbhandari, S.; Nisalak, A.; Shrestha, M.P. Short report: An outbreak of Japanese encephalitis in Kathmandu, Nepal. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 57, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, V.; Parida, S.; Desai, A.; Chandramuki, A.; Gourie-Devi, M.; Grau, G.E. Correlation of tumor necrosis factor levels in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid with clinical outcome in Japanese encephalitis patients. J. Med. Virol. 1997, 51, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, G.N.; Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K. Inflammatory markers in the patients of Japanese encephalitis. Neurol. Res. 2006, 28, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.S.; Morill, J.C. Levels of interferon in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acute Japanese encephalitis. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 155, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, U.; Ding, Z.; Deng, S.; Ye, J.; Cao, S.; Chen, Z. Pathogenicity and virulence of Japanese encephalitis virus: Neuroinflammation and neuronal cell damage. Virulence 2021, 12, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y. Development of Japanese encephalitis attenuated live vaccine virus SA14-14-2 and its characteristics. In Encephalitis; Tkachev, S., Ed.; InTech Open Access: Shanghai, China, 2013; pp. 181–206. [Google Scholar]
- Terry, R.L.; Getts, D.R.; Deffrasnes, C.; van Vreden, C.; Campbell, I.L.; King, N.J. Inflammatory monocytes and the pathogenesis of viral encephalitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

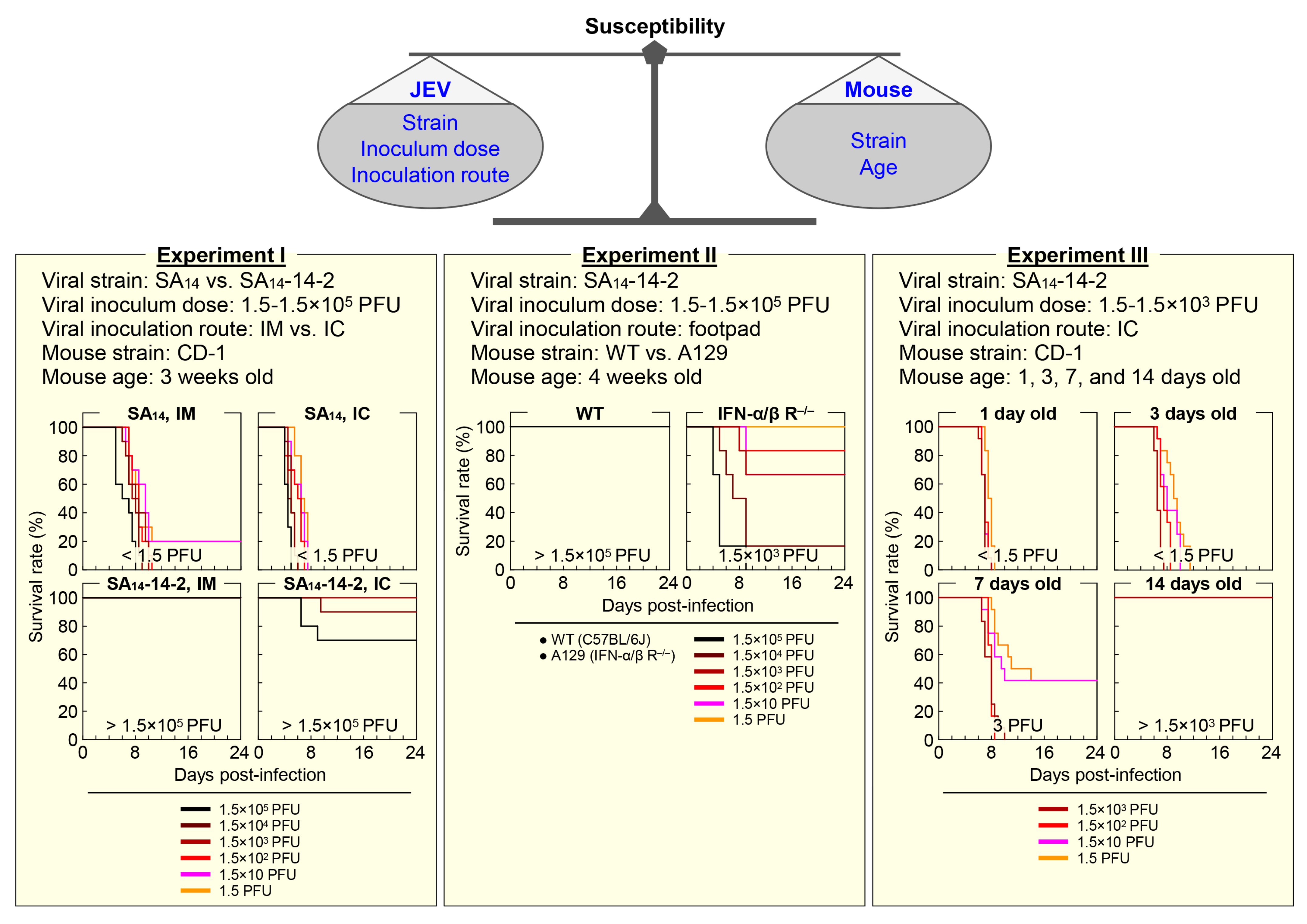
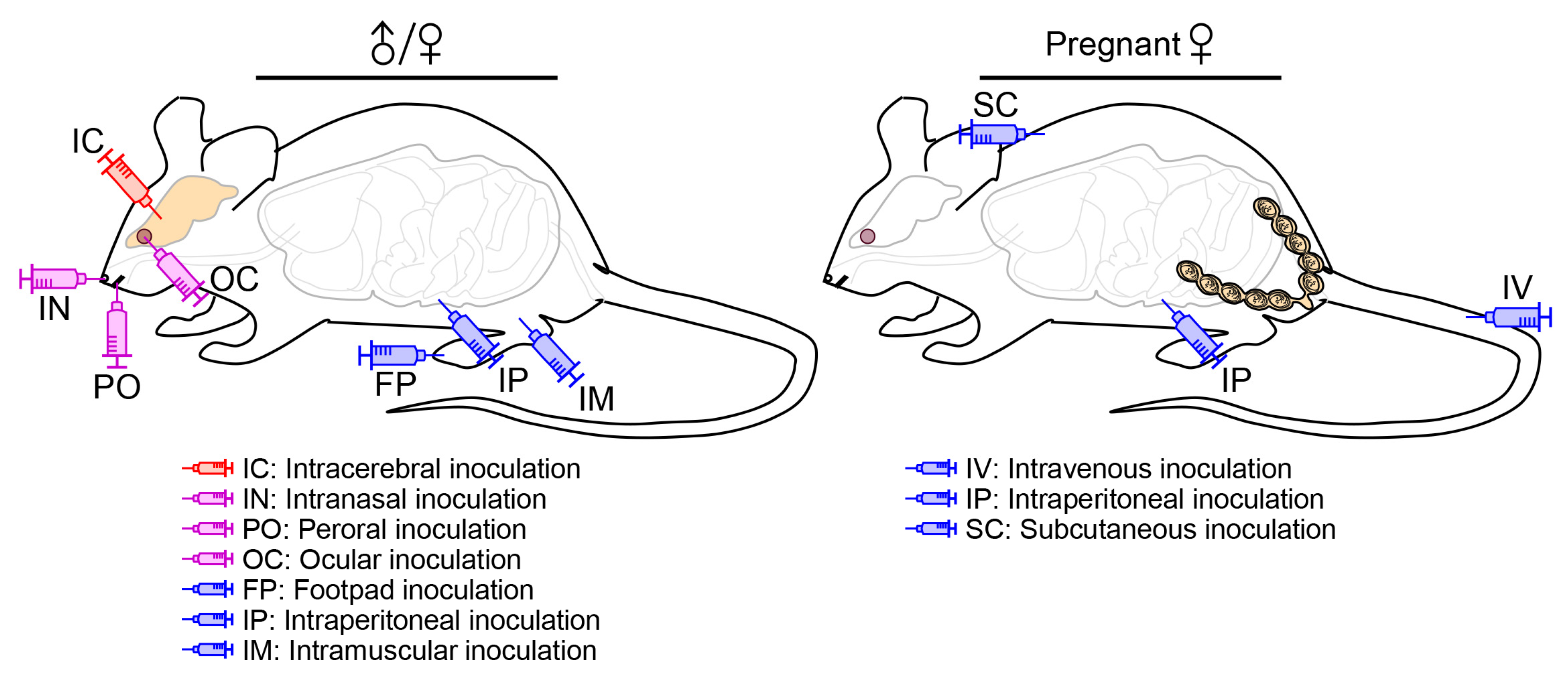
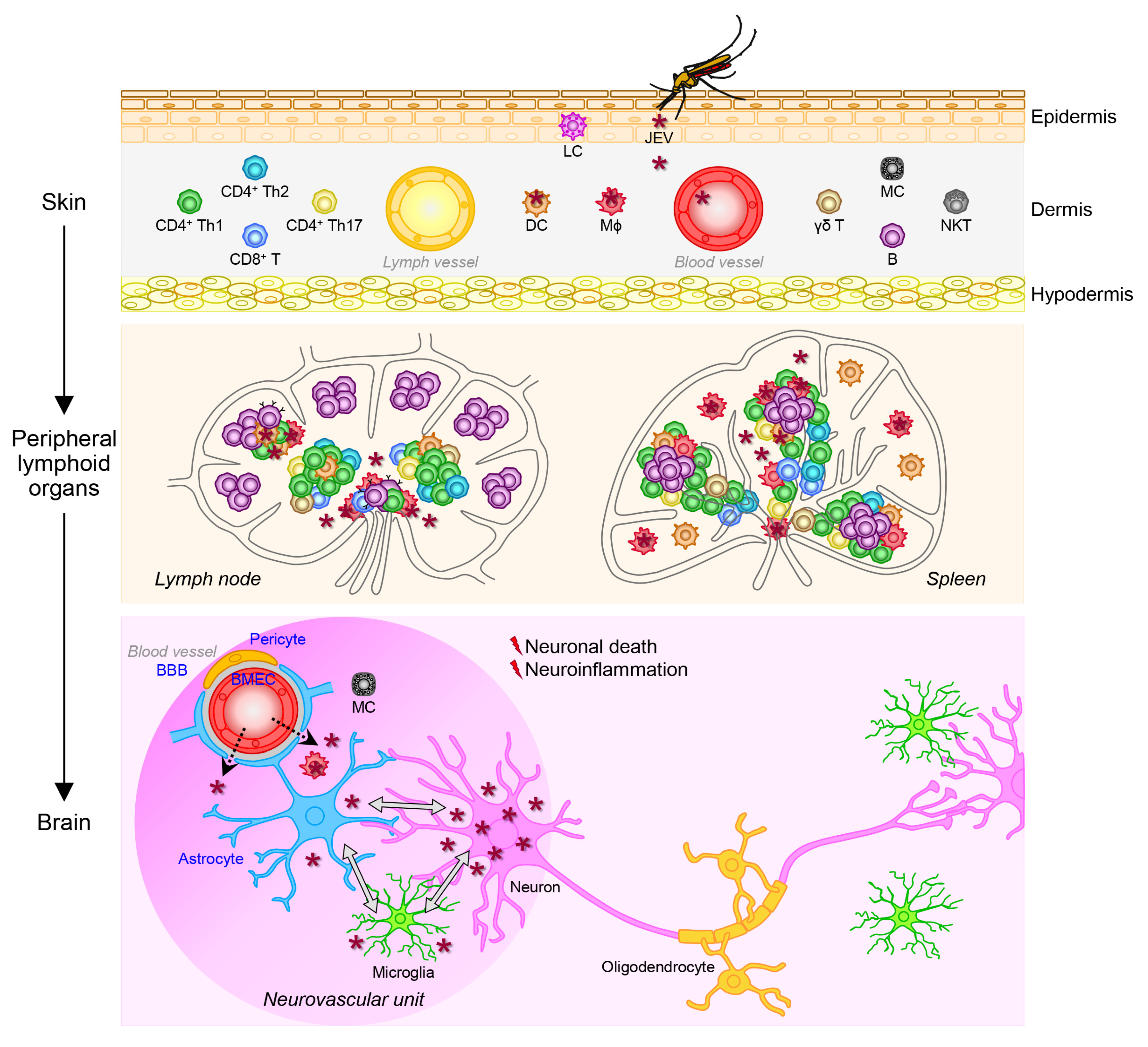
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frank, J.C.; Song, B.-H.; Lee, Y.-M. Mice as an Animal Model for Japanese Encephalitis Virus Research: Mouse Susceptibility, Infection Route, and Viral Pathogenesis. Pathogens 2023, 12, 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050715
Frank JC, Song B-H, Lee Y-M. Mice as an Animal Model for Japanese Encephalitis Virus Research: Mouse Susceptibility, Infection Route, and Viral Pathogenesis. Pathogens. 2023; 12(5):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050715
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrank, Jordan C., Byung-Hak Song, and Young-Min Lee. 2023. "Mice as an Animal Model for Japanese Encephalitis Virus Research: Mouse Susceptibility, Infection Route, and Viral Pathogenesis" Pathogens 12, no. 5: 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050715
APA StyleFrank, J. C., Song, B.-H., & Lee, Y.-M. (2023). Mice as an Animal Model for Japanese Encephalitis Virus Research: Mouse Susceptibility, Infection Route, and Viral Pathogenesis. Pathogens, 12(5), 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12050715






