Improving African Swine Fever Surveillance Using Fluorescent Rapid Tests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood and Serum Samples
2.2. Generation of the Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (rMAb)18BG3 from the Hybridoma Cells
2.3. Fluorescent Lateral Flow Assays for Antigen Detection of ASFV (Ag-LFA) or Antibody Detection (Ab-LFA)
2.3.1. Capture Reagents
2.3.2. Detector Reagents
2.3.3. Assembling of LFA Strips
2.3.4. Test Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Recombinant Antibody Production
3.2. Fluorescent Double-Antibody Sandwich LFA for Detection of ASFV Antigen, Ag-LFA
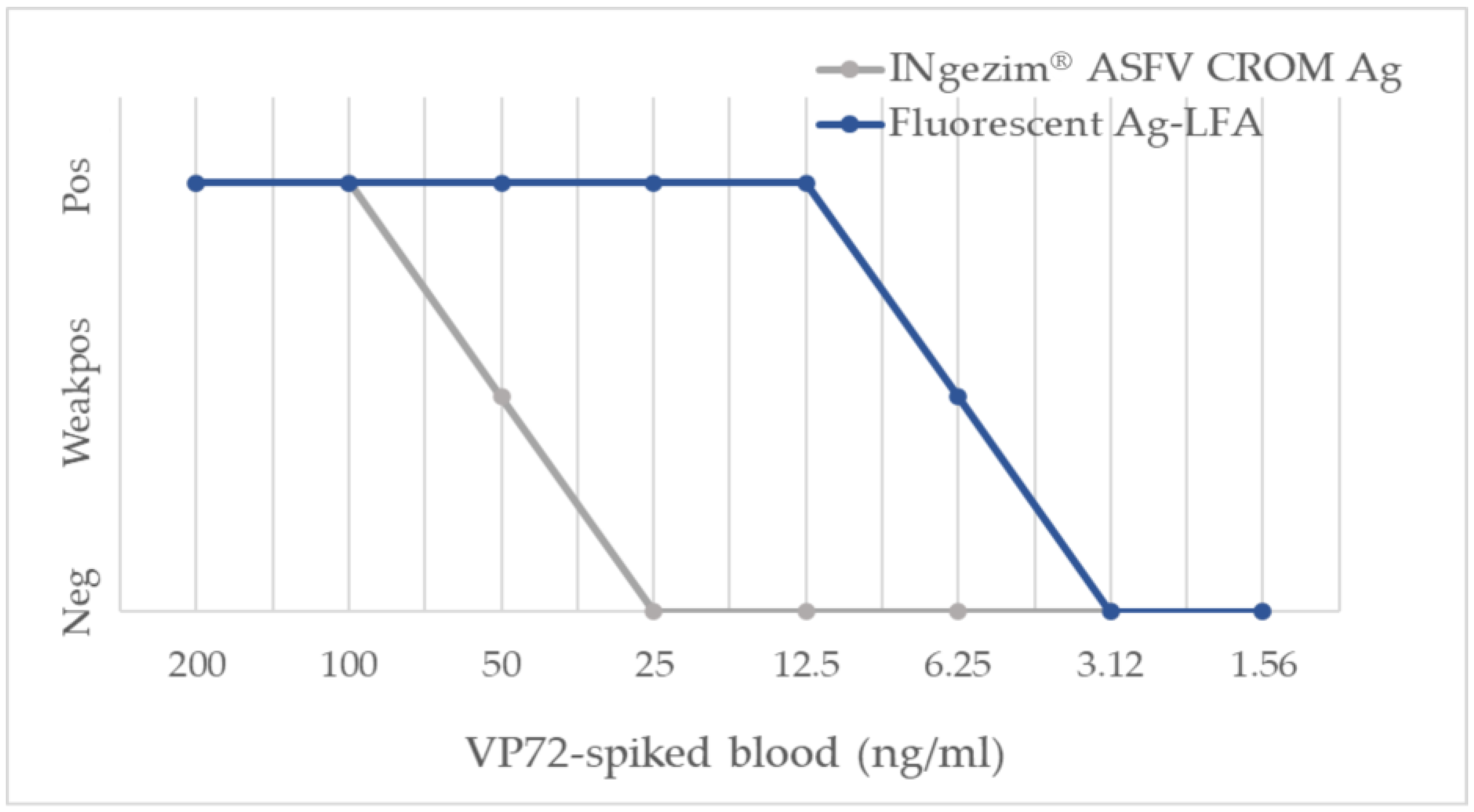
3.2.1. Analytical Sensitivity
3.2.2. Diagnostic Performance
3.3. Fluorescent Double Recognition LFA for Detection of ASFV p72-Specific Antibodies
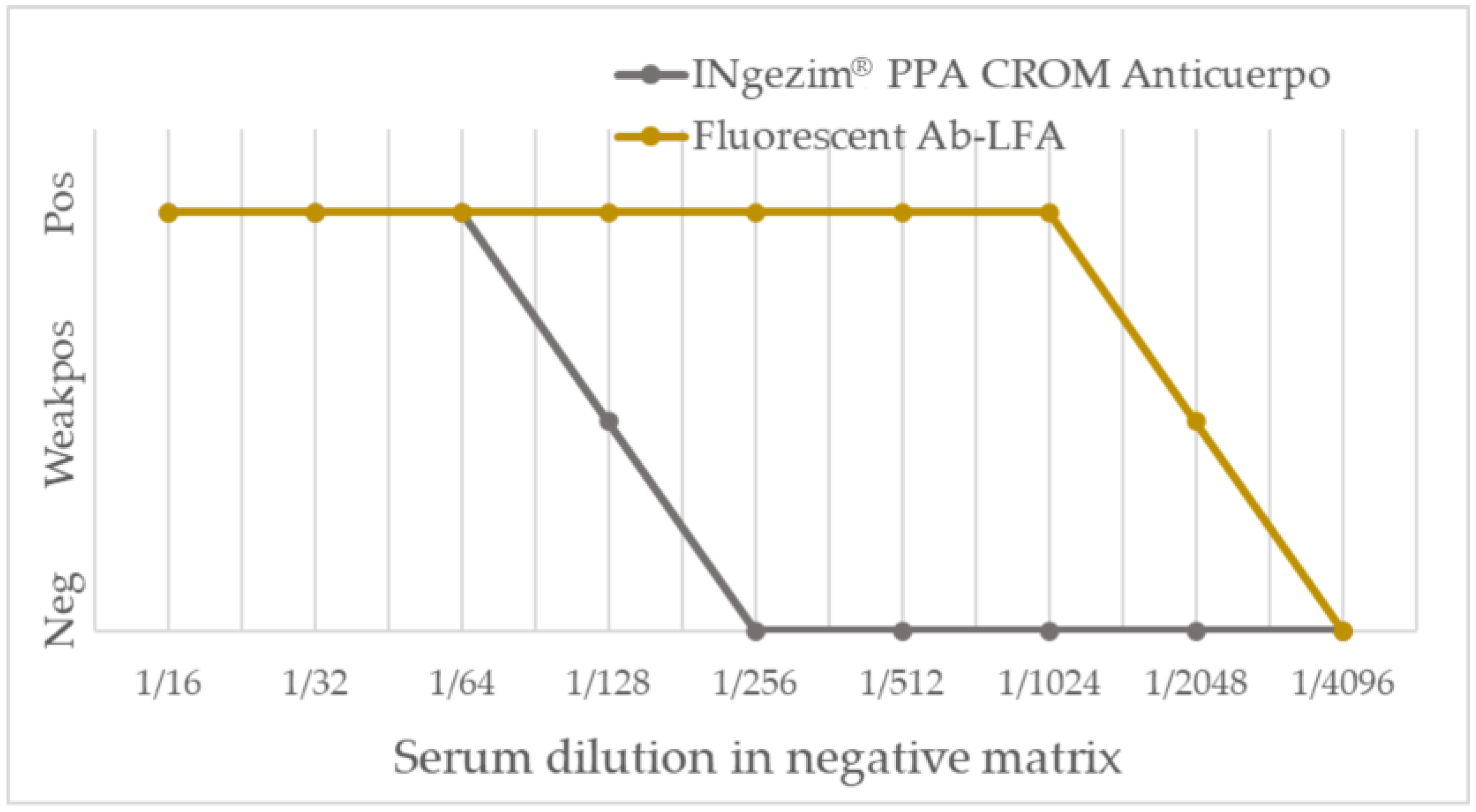
3.3.1. Analytical Performance
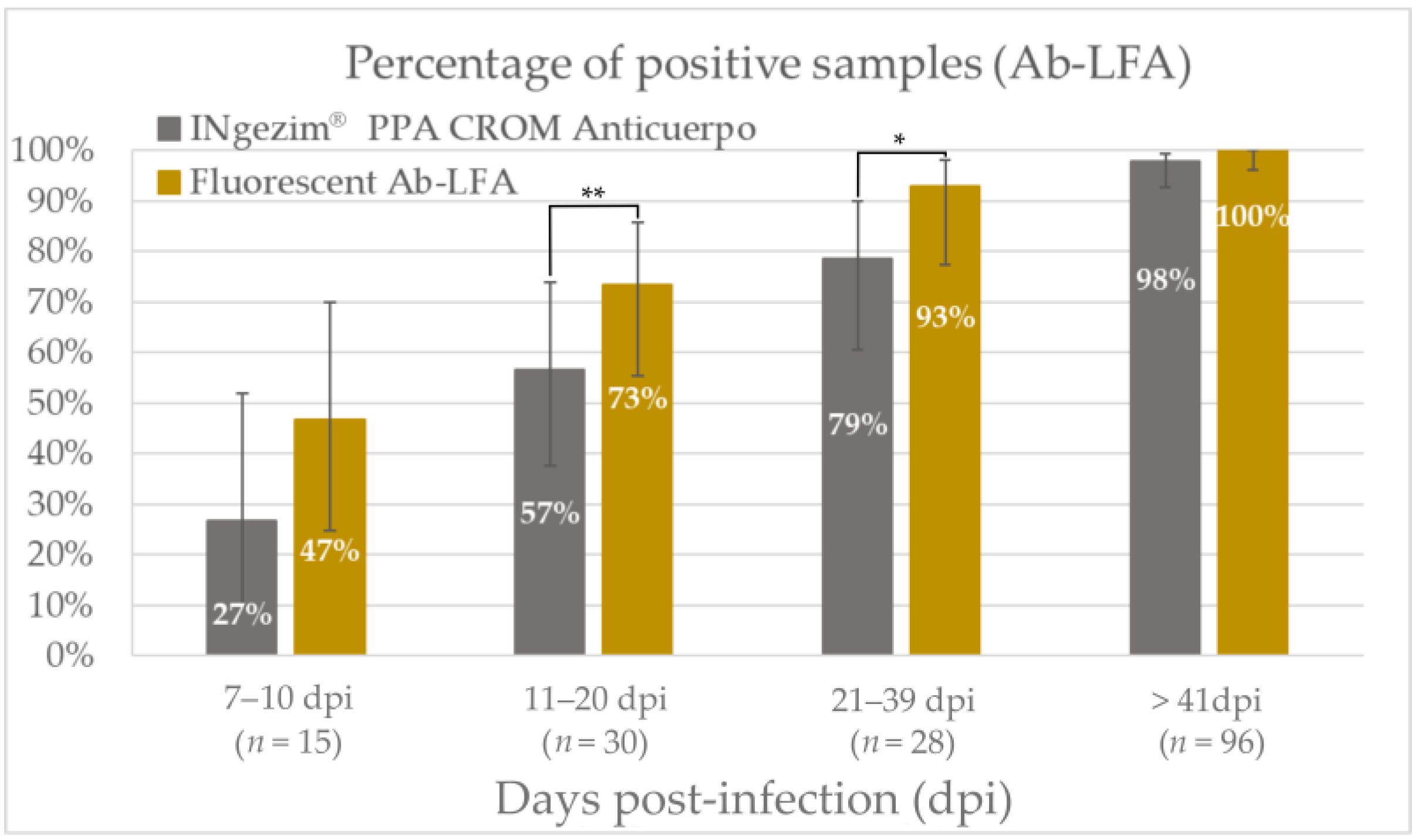
3.3.2. Diagnostic Performance
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallardo, M.C.; de la Torre Reoyo, A.; Fernández-Pinero, J.; Iglesias, I.; Muñoz, M.J.; Arias, M.L. African Swine Fever: A Global View of the Current Challenge. Porc. Health Manag. 2015, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M.; Mur, L.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Carrasco, L. An Update on the Epidemiology and Pathology of African Swine Fever. J. Comp. Pathol. 2015, 152, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter-Louis, C.; Conraths, F.J.; Probst, C.; Blohm, U.; Schulz, K.; Sehl, J.; Fischer, M.; Forth, J.H.; Zani, L.; Depner, K.; et al. African Swine Fever in Wild Boar in Europe—A Review. Viruses 2021, 13, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Montoya, M.; Reis, A.L.; Dixon, L.K. African Swine Fever: A Re-Emerging Viral Disease Threatening the Global Pig Industry. Vet. J. 2018, 233, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ata, E.B.; Li, Z.-J.; Shi, C.-W.; Yang, G.-L.; Yang, W.-T.; Wang, C.-F. African Swine Fever Virus: A Raised Global Upsurge and a Continuous Threaten to Pig Husbandry. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 167, 105561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organisation for Animal Health, WOAH.; World Animal Health Information System, WAHIS. Available online: https://wahis.woah.org/#/home (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Blome, S.; Franzke, K.; Beer, M. African Swine Fever—A Review of Current Knowledge. Virus Res. 2020, 287, 198099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, I.; Alonso, C. African Swine Fever Virus: A Review. Viruses 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arias, M.; Jurado, C.; Gallardo, C.; Fernández-Pinero, J.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. Gaps in African Swine Fever: Analysis and Priorities. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65 (Suppl. S1), 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz, A.L.; Tabarés, E. Characteristics of the Major Structural Proteins of African Swine Fever Virus: Role as Antigens in the Induction of Neutralizing Antibodies. A Review. Virology 2022, 571, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, L.K.; Chapman, D.A.G.; Netherton, C.L.; Upton, C. African Swine Fever Virus Replication and Genomics. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejo, A.; Matamoros, T.; Guerra, M.; Andrés, G. A Proteomic Atlas of the African Swine Fever Virus Particle. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01293-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, H.; Ge, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z. A Systematic Review of Genotypes and Serogroups of African Swine Fever Virus. Virus Genes 2022, 58, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudreault, N.N.; Madden, D.W.; Wilson, W.C.; Trujillo, J.D.; Richt, J.A. African Swine Fever Virus: An Emerging DNA Arbovirus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, X.H.; Phuong, L.T.; Huy, N.Q.; Thuy, D.T.; Nguyen, V.D.; Quang, P.H.; Ngôn, Q.V.; Rai, A.; Gay, C.G.; Gladue, D.P.; et al. Evaluation of the Safety Profile of the ASFV Vaccine Candidate ASFV-G-ΔI177L. Viruses 2022, 14, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CÔNG TY CỔ PHẦN AVAC VIỆT NAM. AVAC ASF LIVE. Available online: http://www.avac.com.vn/en/products-for-pigs/avac-asf-live/ (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- Gallardo, C.; Fernández-Pinero, J.; Arias, M. African Swine Fever (ASF) Diagnosis, an Essential Tool in the Epidemiological Investigation. Virus Res. 2019, 271, 197676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organisation for Animal Health, WOAH. African Swine Fever. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2021; Chapter 3.9.1; Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/terrestrial-code-online-access/ (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral Flow Assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, K.; Gallardo, C.; Portugal, R.; Dixon, L.K.; Baton, C.; Williams, D. The OIE ASF Reference Laboratory Network’s Overview of African Swine Fever Diagnostic Tests for Field Application; World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Xu, H.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y. Membrane-Based Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Strip with Nanoparticles as Reporters for Detection: A Review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, T.; Knuutila, A.; Barkoff, A.-M.; Mertsola, J.; He, Q. A Rapid Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Serological Diagnosis of Pertussis. Vaccine 2018, 36, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, A.; Wang, R.; Hou, T.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Li, C.; Ding, J. Lateral Flow Immunoassay Strips Based on Europium(III) Chelate Microparticle for the Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Trichinella Spiralis Infection in Whole Blood Samples of Pigs. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, H.; Cong, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Z.; et al. Development of a Rapid and Sensitive Europium (III) Chelate Microparticle-Based Lateral Flow Test Strip for the Detection and Epidemiological Surveillance of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradbury, A.R.M.; Trinklein, N.D.; Thie, H.; Wilkinson, I.C.; Tandon, A.K.; Anderson, S.; Bladen, C.L.; Jones, B.; Aldred, S.F.; Bestagno, M.; et al. When Monoclonal Antibodies Are Not Monospecific: Hybridomas Frequently Express Additional Functional Variable Regions. mAbs 2018, 10, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lua, W.-H.; Ling, W.-L.; Yeo, J.Y.; Poh, J.-J.; Lane, D.P.; Gan, S.K.-E. The Effects of Antibody Engineering CH and CL in Trastuzumab and Pertuzumab Recombinant Models: Impact on Antibody Production and Antigen-Binding. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hermanson, G.T. Microparticles and Nanoparticles. In Bioconjugate Techniques, 2nd ed.; Hermanson, G.T., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Chapter 14; pp. 582–626. ISBN 978-0-12-370501-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, H.; Dups-Bergmann, J.; Schulz, K.; Probst, C.; Zani, L.; Fischer, M.; Gethmann, J.; Denzin, N.; Blome, S.; Conraths, F.J.; et al. Identification of Risk Factors for African Swine Fever: A Systematic Review. Viruses 2022, 14, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Park, B.; Kang, H.E. Control Measures to African Swine Fever Outbreak: Active Response in South Korea, Preparation for the Future, and Cooperation. J. Vet. Sci. 2021, 22, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, S.; Casadei, G.; De Lorenzi, G.; Tamba, M. A Review of Risk Factors of African Swine Fever Incursion in Pig Farming within the European Union Scenario. Pathogens 2021, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juntunen, E.; Myyryläinen, T.; Salminen, T.; Soukka, T.; Pettersson, K. Performance of Fluorescent Europium(III) Nanoparticles and Colloidal Gold Reporters in Lateral Flow Bioaffinity Assay. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 428, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, S.; Saatçi, E.; Joseph, J. Development and Evaluation of Europium-Based Quantitative Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Chronic Kidney Disease Marker Cystatin-C. J. Fluoresc. 2022, 32, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastre, P.; Gallardo, C.; Monedero, A.; Ruiz, T.; Arias, M.; Sanz, A.; Rueda, P. Development of a Novel Lateral Flow Assay for Detection of African Swine Fever in Blood. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Group of Samples | Result from INgezim® ASFV CROM Ag (No. of Samples) | Result from Fluorescent Ag-LFA (No. of Samples) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | ||
| Positive samples (n = 56) | 7–10 dpi | 10 | 5 | 13 | 2 |
| 11–20 dpi | 5 | 19 | 20 | 4 | |
| 21–39 dpi | 0 | 14 | 9 | 5 | |
| >41 dpi | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | |
| Negative samples (n = 100) | Field bloods | 2 | 98 | 2 | 98 |
| Group of Samples | Result from INgezim® PPA CROM Anticuerpo (No. of Samples) | Result from Fluorescent Ab-LFA (No. of Samples) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | ||
| Positive samples (n = 141) | 7–10 dpi | 4 | 11 | 7 | 8 |
| 11–20 dpi | 17 | 13 | 22 | 8 | |
| 21–39 dpi | 22 | 6 | 26 | 2 | |
| > 41 dpi | 94 | 2 | 96 | 0 | |
| Negative samples (n = 114) | Field sera | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| Experimental sera | 0 | 40 | 0 | 40 | |
| Field bloods | 0 | 34 | 0 | 34 | |
| CSFV-positive sera | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 | |
| TB-positive sera | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 | |
| PRRSV-positive sera | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aira, C.; Monedero, A.; Hernández-Antón, S.; Martínez-Cano, J.; Camuñas, A.; Casado, N.; Nieto, R.; Gallardo, C.; García-Durán, M.; Rueda, P.; et al. Improving African Swine Fever Surveillance Using Fluorescent Rapid Tests. Pathogens 2023, 12, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060811
Aira C, Monedero A, Hernández-Antón S, Martínez-Cano J, Camuñas A, Casado N, Nieto R, Gallardo C, García-Durán M, Rueda P, et al. Improving African Swine Fever Surveillance Using Fluorescent Rapid Tests. Pathogens. 2023; 12(6):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060811
Chicago/Turabian StyleAira, Cristina, Alejandro Monedero, Sonia Hernández-Antón, Juan Martínez-Cano, Ana Camuñas, Nadia Casado, Raquel Nieto, Carmina Gallardo, Marga García-Durán, Paloma Rueda, and et al. 2023. "Improving African Swine Fever Surveillance Using Fluorescent Rapid Tests" Pathogens 12, no. 6: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060811
APA StyleAira, C., Monedero, A., Hernández-Antón, S., Martínez-Cano, J., Camuñas, A., Casado, N., Nieto, R., Gallardo, C., García-Durán, M., Rueda, P., & Fresco-Taboada, A. (2023). Improving African Swine Fever Surveillance Using Fluorescent Rapid Tests. Pathogens, 12(6), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060811







