In the Dawn of an Early Invasion: No Genetic Diversity of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Ecuador?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parasites and Experimental Infection
2.2. Molecular Phylogenetic and Phylogeographic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Phylogenetic Analyses
3.2. Phylogeographic Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.-T. Un Nouveau Nématode Pulmonaire, Pulmonema Cantonensis, n. g., n. Sp. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1935, 13, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eamsobhana, P. Eosinophilic Meningitis Caused by Angiostrongylus Cantonensis—A Neglected Disease with Escalating Importance. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 31, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martins, Y.C.; Tanowitz, H.B.; Kazacos, K.R. Central Nervous System Manifestations of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis Infection. Acta Trop. 2015, 141, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.P.; Wu, Z.D.; Wei, J.; Owen, R.L.; Lun, Z.R. Human Angiostrongylus Cantonensis: An Update. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alicata, J.E. Biology and Distribution of the Rat Lungworm, Angiostrongylus Cantonensis, and Its Relationship to Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis and Other Neurological Disorders of Man and Animals**Paper Presented at the First International Congress of Parasitology, Rome, Italy, 19–26 September 1964. In Advances in Parasitology; Dawes, B., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: London, UK, 1965; Volume 3, pp. 223–248. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado-Júnior, A.; Simões, R.O.; Oliveira, A.P.M.; Motta, E.M.; Fernandez, M.A.; Pereira, Z.M.; Monteiro, S.S.; Torres, E.J.L.; Thiengo, S.C. First Report of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis (Nematoda: Metastrongylidae) in Achatina Fulica (Mollusca: Gastropoda) from Southeast and South Brazil. Memórias Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2010, 105, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, R.H.; Ansdell, V.; Panosian Dunavan, C.; Rollins, R.L. Neuroangiostrongyliasis: Global Spread of an Emerging Tropical Disease. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 107, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federspiel, F.; Skovmand, S.; Skarphedinsson, S. Eosinophilic Meningitis Due to Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in Europe. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.P.; Lai, D.H.; Zhu, X.Q.; Chen, X.G.; Lun, Z.R. Human Angiostrongyliasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansdell, V.; Wattanagoon, Y. Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in Travelers: Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solorzano, L.F.; Martini Robles, L.; Hernandez, H.; Sarracent, J.; Muzzio, J.; Rojas, L. Angiostrongylus cantonensis: Un parásito emergente en Ecuador. Rev. Cuba. Med. Trop. 2014, 66, 20–33. [Google Scholar]
- Martini-Robles, L.; Gómez-Landires, E.; Muzzio-Aroca, J.; Solórzano-Álava, L. Descripcion Del Primer Foco de Transmision Natural de Angiostrongylus Cantonensis En Ecuador. In Angiostrongylus cantonensis—Emergencia en América; Martini-Robles, L., Dorta-Contreras, A.J., Eds.; Editorial Academia La Habana: La Habana, Cuba, 2016; pp. 209–220. ISBN 978-959-270-368-1. [Google Scholar]
- Pincay, T.; García, L.; Narváez, E.; Decker, O.; Martini, L.; Moreira, J.M. Angiostrongiliasis Por Parastrongylus (Angiostrongylus) Cantonensis En Ecuador. Primer Informe En Sudamérica. Trop. Med. Int Health 2009, 14, S37. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero, M.; Vargas, F.M.; Rosero, A.R.; Nuques, M.L.; Bolaños, E.S.; Briones, M.T.; Martínez, W.Z.; Gómez, A.O. Meningitis eosinofílica por angiostrongylus cantonensis. Reporte de caso de autopsia. Medicina 2008, 13, 312–318. [Google Scholar]
- Solórzano, L.; Sánchez-Amador, F.; Valverde, T. Angiostrongylus (Parastrongylus) cantonensis en huéspedes intermediarios y definitivos en Ecuador, 2014–2017. Biomédica 2019, 39, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzio, J. Hospederos Intermediarios de Angiostrongylus Cantonensis en Ecuador; Editorial Academica Española: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Thiengo, S.C.; Faraco, F.A.; Salgado, N.C.; Cowie, R.H.; Fernandez, M.A. Rapid Spread of an Invasive Snail in South America: The Giant African Snail, Achatina Fulica, in Brasil. Biol. Invasions 2007, 9, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.L.C.; Giese, E.G.; Melo, F.T.V.; Simões, R.O.; Thiengo, S.C.; Maldonado-Júnior, A.; Santos, J.N. Endemic Angiostrongyliasis in the Brazilian Amazon: Natural Parasitism of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in Rattus Rattus and R. Norvegicus, and Sympatric Giant African Land Snails, Achatina Fulica. Acta Trop. 2013, 125, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qvarnstrom, Y.; Sullivan, J.J.; Bishop, H.S.; Hollingsworth, R.; da Silva, A.J. PCR-Based Detection of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in Tissue and Mucus Secretions from Molluscan Hosts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qvarnstrom, Y.; da Silva, A.J.C.A.; Teem, J.L.; Hollingsworth, R.; Bishop, H.S.; Graeff-Teixeira, C.; Aramburu Da Silva, A.C. Improved Molecular Detection of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in Mollusks and Other Environmental Samples with a Species-Specific Internal Transcribed Spacer Based TaqMan Assay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5287–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qvarnstrom, Y.; Xayavong, M.; da Silva, A.C.A.; Park, S.Y.; Whelen, A.C.; Calimlim, P.S.; Sciulli, R.H.; Honda, S.A.A.; Higa, K.; Kitsutani, P.; et al. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Detection of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis DNA in Cerebrospinal Fluid from Patients with Eosinophilic Meningitis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qvarnstrom, Y.; Bishop, H.S.; da Silva, A.J. Detection of Rat Lungworm in Intermediate, Definitive, and Paratenic Hosts Obtained from Environmental Sources. Hawaii J. Med. Public Health 2013, 72, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sears, W.J.; Qvarnstrom, Y.; Nutman, T.B. RPAcan3990: An Ultrasensitive Recombinase Polymerase Assay To Detect Angiostrongylus Cantonensis DNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0118521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Song, H.-Q.; Zhang, R.-L.; Chen, M.-X.; Xu, M.-J.; Ai, L.; Chen, X.-G.; Zhan, X.-M.; Liang, S.-H.; Yuan, Z.-G.; et al. Specific Detection of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in the Snail Achatina Fulica Using a Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Assay. Mol. Cell Probes 2011, 25, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Steinmann, P.; Utzinger, J.; Zhou, X.-N. The Genetic Variation of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in the People’s Republic of China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, R.L.; Chen, M.X.; Li, J.; Ai, L.; Wu, C.Y.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Lin, Q. Characterisation of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis Isolates from China by Sequences of Internal Transcribed Spacers of Nuclear Ribosomal DNA. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011, 10, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, S.; Lun, Z.; Wu, Z.; Fan, C.-K.; Brown, C.L.; Cheng, P.; Peng, S.; Yang, T. Phylogeography of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis (Nematoda: Angiostrongylidae) in Southern China and Some Surrounding Areas. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontanilla, I.K.C.; Wade, C.M. The Small Subunit (SSU) Ribosomal (r) RNA Gene as a Genetic Marker for Identifying Infective 3rd Juvenile Stage Angiostrongylus Cantonensis. Acta Trop. 2008, 105, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eamsobhana, P.; Lim, P.E.; Yong, H.S. Phylogenetics and Systematics of Angiostrongylus Lungworms and Related Taxa (Nematoda: Metastrongyloidea) Inferred from the Nuclear Small Subunit (SSU) Ribosomal DNA Sequences. J. Helminthol. 2015, 89, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galtier, N.; Nabholz, B.; Glémin, S.; Hurst, G.D.D. Mitochondrial DNA as a Marker of Molecular Diversity: A Reappraisal. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 4541–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, M.S. Molecular Prospecting for Cryptic Species of Nematodes: Mitochondrial DNA versus Internal Transcribed Spacer. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.S.; Eamsobhana, P.; Song, S.-L.; Prasartvit, A. Molecular Phylogeography of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis (Nematoda: Angiostrongylidae) and Genetic Relationships with Congeners Using Cytochrome b Gene Marker. Acta Trop. 2015, 148, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, L.R.; de Souza, J.G.R.; Santos, H.A.; Torres, E.J.L.; do Val Vilela, R.; Cruz, O.M.S.; Rodrigues, L.; de Jesus Pereira, C.A.; Maldonado-Júnior, A.; dos Santos Lima, W. Angiostrongylus Minasensis n. Sp.: New Species Found Parasitizing Coatis (Nasua Nasua) in an Urban Protected Area in Brazil. Rev. Bras. De Parasitol. Veterinária 2020, 29, e018119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eamsobhana, P.; Lim, P.-E.; Solano, G.; Zhang, H.; Gan, X.; Yong, H.S. Molecular Differentiation of Angiostrongylus Taxa (Nematoda: Angiostrongylidae) by Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit I (COI) Gene Sequences. Acta Trop. 2010, 116, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, R.L.; Carvalho, O.S.; Mendonça, C.L.G.F.; Graeff-Teixeira, C.; Silva, M.C.; Ben, R.; Maurer, R.; Lima, W.S.; Lenzi, H.L. Molecular Differentiation of Angiostrongylus Costaricensis, A. Cantonensis, and A. Vasorum by Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism. Memórias Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2003, 98, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentyne, H.; Spratt, D.M.; Aghazadeh, M.; Jones, M.K.; Šlapeta, J. The Mitochondrial Genome of Angiostrongylus Mackerrasae Is Distinct from A. Cantonensis and A. Malaysiensis. Parasitology 2020, 147, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitta, A.; Srisongcram, N.; Thiproaj, J.; Wongma, A.; Polsut, W.; Fukruksa, C.; Yimthin, T.; Mangkit, B.; Thanwisai, A.; Dekumyoy, P. Phylogeny of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in Thailand Based on Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit I Gene Sequence. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2016, 47, 377–386. [Google Scholar]
- Monte, T.C.C.; Simões, R.O.; Oliveira, A.P.M.; Novaes, C.F.; Thiengo, S.C.; Silva, A.J.; Cordeiro-Estrela, P.; Maldonado-Júnior, A. Phylogenetic Relationship of the Brazilian Isolates of the Rat Lungworm Angiostrongylus Cantonensis (Nematoda: Metastrongylidae) Employing Mitochondrial COI Gene Sequence Data. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eamsobhana, P.; Song, S.L.; Yong, H.S.; Prasartvit, A.; Boonyong, S.; Tungtrongchitr, A. Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit I Haplotype Diversity of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis (Nematoda: Angiostrongylidae). Acta Trop. 2017, 171, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokiwa, T.; Harunari, T.; Tanikawa, T.; Komatsu, N.; Koizumi, N.; Tung, K.-C.; Suzuki, J.; Kadosaka, T.; Takada, N.; Kumagai, T.; et al. Phylogenetic Relationships of Rat Lungworm, Angiostrongylus Cantonensis, Isolated from Different Geographical Regions Revealed Widespread Multiple Lineages. Parasitol. Int. 2012, 61, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legislation for the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes—Environment—European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/chemicals/lab_animals/legislation_en.htm (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Aguiar, P.H.; Morera, P.; Pascual, J. First Record of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in Cuba. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 963–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubelaker, J.E. Systematics of Species Referred to the Genus Angiostrongylus. J. Parasitol. 1986, 72, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An Integrated and Extendable Desktop Software Platform for the Organization and Analysis of Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple Sequence Alignment with High Accuracy and High Throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maddison, W.P.; Maddison, D.R. Mesquite: A Modular System for Evolutionary Analysis. 2021. Available online: https://www.mesquiteproject.org (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Corander, J.; Marttinen, P.; Sirén, J.; Tang, J. Enhanced Bayesian Modelling in BAPS Software for Learning Genetic Structures of Populations. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corander, J.; Sirén, J.; Arjas, E. Bayesian Spatial Modeling of Genetic Population Structure. Comput. Stat. 2008, 23, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hohna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice Across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for Inference of Large Phylogenetic Trees. In Proceedings of the 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-Feature Software for Haplotype Network Construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelt, H.-J.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-Joining Networks for Inferring Intraspecific Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, F. Statistical Method for Testing the Neutral Mutation Hypothesis by DNA Polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.-X. Statistical Tests of Neutrality of Mutations Against Population Growth, Hitchhiking and Background Selection. Genetics 1997, 147, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodpai, R.; Intapan, P.M.; Thanchomnang, T.; Sanpool, O.; Sadaow, L.; Laymanivong, S.; Aung, W.P.; Phosuk, I.; Laummaunwai, P.; Maleewong, W. Angiostrongylus Cantonensis and A. Malaysiensis Broadly Overlap in Thailand, Lao PDR, Cambodia and Myanmar: A Molecular Survey of Larvae in Land Snails. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Wit, L.A.; Ricketts, T.H. Trade and Deforestation Predict Rat Lungworm Disease, an Invasive-Driven Zoonosis, at Global and Regional Scales. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 680986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanol, J.; Fernandez, M.A.; de Oliveira, A.P.M.; de Moraes Russo, C.A.; Thiengo, S.C. O Caramujo Exótico Invasor Achatina Fulica (Stylommatophora, Mollusca) No Estado Do Rio de Janeiro (Brasil): Situação Atual. Biota Neotrop. 2010, 10, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Paiva Barçante, J.M.; Barçante, T.A.; Dias, S.R.C.; dos Santos Lima, W. Ocorrência de Achatina Fulica Bowdich, 1822 (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Achatinoidea) No Estado de Minas Gerais, Brasil. Bol. Mus. Biol. Mello Leitão 2005, 18, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Teles, H.M.S.; Fontes, L.R. Implicações Da Introdução e Dispersão de Achatina Fulica Bowdich, 1822 No Brasil. Bol. Inst. Adolfo Lutz 2002, 12, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Thiengo, S.C.; de Oliveira Simões, R.; Fernandez, M.A.; Maldonado-Júnior, A. Angiostrongylus Cantonensis and Rat Lungworm Disease in Brazil. Hawai’i J. Med. Public Health 2013, 72, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Arruda, J.O.; Santos, L. First Record of Achatina Fulica Bowdich, 1822 (Mollusca, Achatinidae), for the State of Rio Grande Do Sul, Brazil. Biotemas 2022, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrero, F.J.; Breure, A.S.H.; Christensen, C.C.; Correoso, M.; Avila, V.M. Into the Andes: Three New Introductions of Lissachatina Fulica (Gastropoda, Achatinidae) and Its Potential Distribution in South America. Tentacle 2009, 17, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Caldeira, R.L.; Mendonça, C.L.G.F.; Goveia, C.O.; Lenzi, H.L.; Graeff-Teixeira, C.; Lima, W.S.; Mota, E.M.; Pecora, I.L.; De Medeiros, A.M.Z.; Carvalho, O.D.S. First Record of Molluscs Naturally Infected with Angiostrongylus Cantonensis (Chen, 1935) (Nematoda: Metastrongylidae) in Brazil. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2007, 102, 887–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.-X.; Hu, L.; Yang, K.; Steinmann, P.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.-Y.; Utzinger, J.; Zhou, X.-N. Invasive Snails and an Emerging Infectious Disease: Results from the First National Survey on Angiostrongylus Cantonensis in China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tirira, S.D. Guía de Campo de Los Mamíferos Del Ecuador; Murciélago Blanco: Quito, Ecuador, 2007; ISBN 9978-44-651-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kosoy, M.; Khlyap, L.; Cosson, J.-F.; Morand, S. Aboriginal and Invasive Rats of Genus Rattus as Hosts of Infectious Agents. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species: A Selection From The Global Invasive Species Database. Aliens 2000, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowl, T.A.; Crist, T.O.; Parmenter, R.R.; Belovsky, G.; Lugo, A.E. The Spread of Invasive Species and Infectious Disease as Drivers of Ecosystem Change. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchio, E.; Crotta, M.; Romeo, C.; Drewe, J.A.; Guitian, J.; Ferrari, N. Invasive Alien Species and Disease Risk: An Open Challenge in Public and Animal Health. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Červená, B.; Modrý, D.; Fecková, B.; Hrazdilová, K.; Foronda, P.; Alonso, A.M.; Lee, R.; Walker, J.; Niebuhr, C.N.; Malik, R.; et al. Low Diversity of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis Complete Mitochondrial DNA Sequences from Australia, Hawaii, French Polynesia and the Canary Islands Revealed Using Whole Genome next-Generation Sequencing. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monte, T.C.C.; Gentile, R.; Garcia, J.S.; Mota, E.; dos Santos, J.N.; Maldonado-Júnior, A. Brazilian Angiostrongylus Cantonensis Haplotypes, Ac8 and Ac9, Have Two Different Biological and Morphological Profiles. Mem. Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2014, 109, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tokiwa, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Yabe, T.; Komatsu, N.; Akao, N.; Ohta, N. First Report of Angiostrongylus Cantonensis (Nematoda: Angiostrongylidae) Infections in Invasive Rodents from Five Islands of the Ogasawara Archipelago, Japan. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rael, R.C.; Peterson, A.C.; Ghersi-Chavez, B.; Riegel, C.; Lesen, A.E.; Blum, M.J. Rat Lungworm Infection in Rodents across Post-Katrina New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
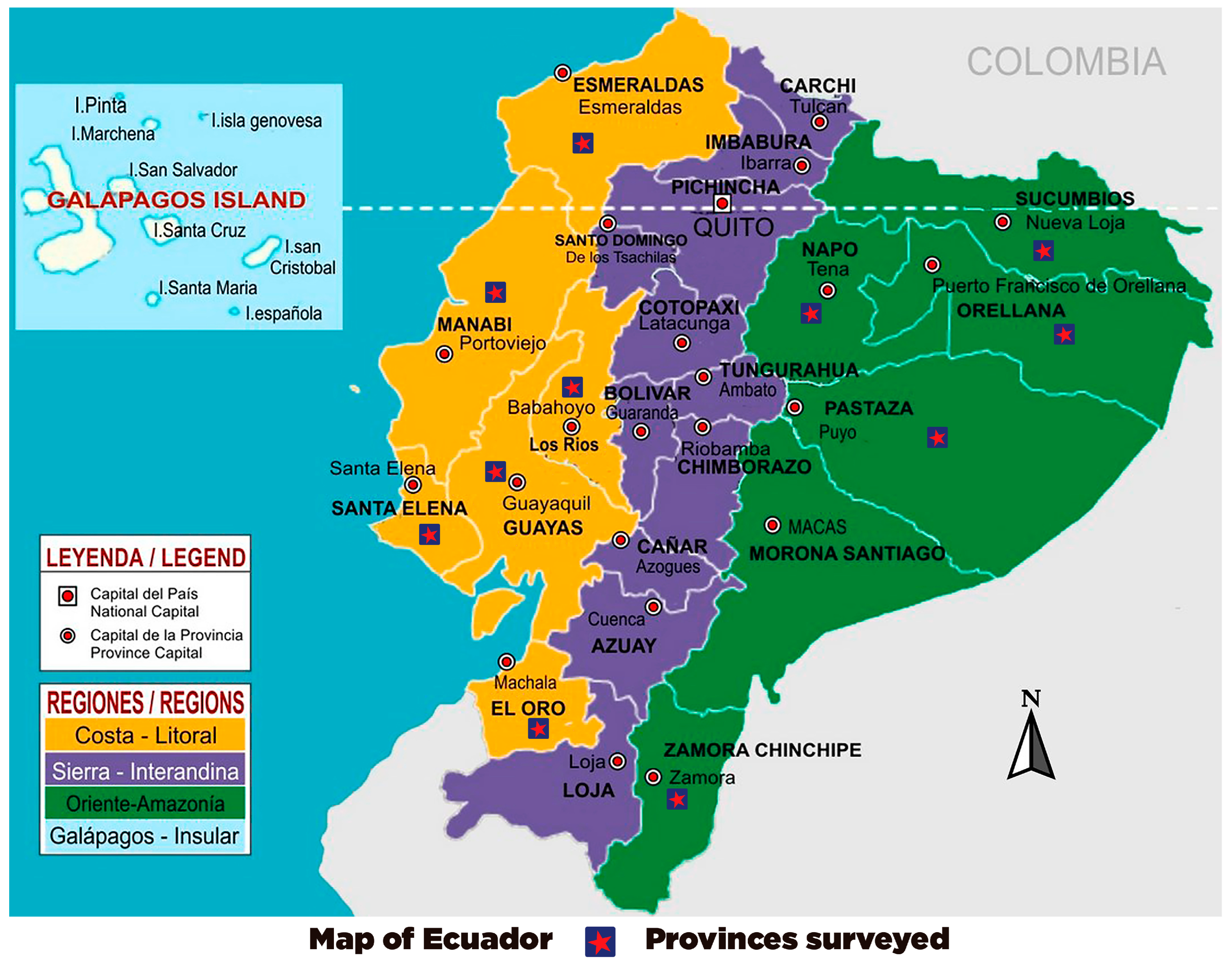


| Identification | GenBank Accession Number | Province |
|---|---|---|
| LSA-01 | MW391020 | Esmeraldas |
| LSA-02 | MW390970 | Santa Elena |
| LSA-03 | MW390971 | El Oro |
| LSA-04 | MW390972 | Guayas |
| LSA-05 | MW390967 | Zamora |
| LSA-06 | MW390974 | Pastaza |
| LSA-07 | MW390969 | Orellana |
| LSA-08 | MW390973 | Manabi |
| LSA-09 | MW390968 | Napo |
| LSA-10 | MW390966 | Los Rios |
| LSA-11 | MW390965 | Sucumbios |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solórzano Álava, L.; Bedoya Pilozo, C.; Hernandez Alvarez, H.; Rojas Rivera, L.; Rodriguez Ortega, M.; Fraga Nodarse, J.; Pereira, L.d.M.; Simões, R.d.O.; Vilela, R.d.V. In the Dawn of an Early Invasion: No Genetic Diversity of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Ecuador? Pathogens 2023, 12, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12070878
Solórzano Álava L, Bedoya Pilozo C, Hernandez Alvarez H, Rojas Rivera L, Rodriguez Ortega M, Fraga Nodarse J, Pereira LdM, Simões RdO, Vilela RdV. In the Dawn of an Early Invasion: No Genetic Diversity of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Ecuador? Pathogens. 2023; 12(7):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12070878
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolórzano Álava, Luis, Cesar Bedoya Pilozo, Hilda Hernandez Alvarez, Lazara Rojas Rivera, Misladys Rodriguez Ortega, Jorge Fraga Nodarse, Leandro de Mattos Pereira, Raquel de Oliveira Simões, and Roberto do Val Vilela. 2023. "In the Dawn of an Early Invasion: No Genetic Diversity of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Ecuador?" Pathogens 12, no. 7: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12070878
APA StyleSolórzano Álava, L., Bedoya Pilozo, C., Hernandez Alvarez, H., Rojas Rivera, L., Rodriguez Ortega, M., Fraga Nodarse, J., Pereira, L. d. M., Simões, R. d. O., & Vilela, R. d. V. (2023). In the Dawn of an Early Invasion: No Genetic Diversity of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Ecuador? Pathogens, 12(7), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12070878






