First Report of Aeromonas veronii as an Emerging Bacterial Pathogen of Farmed Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Fish Sampling
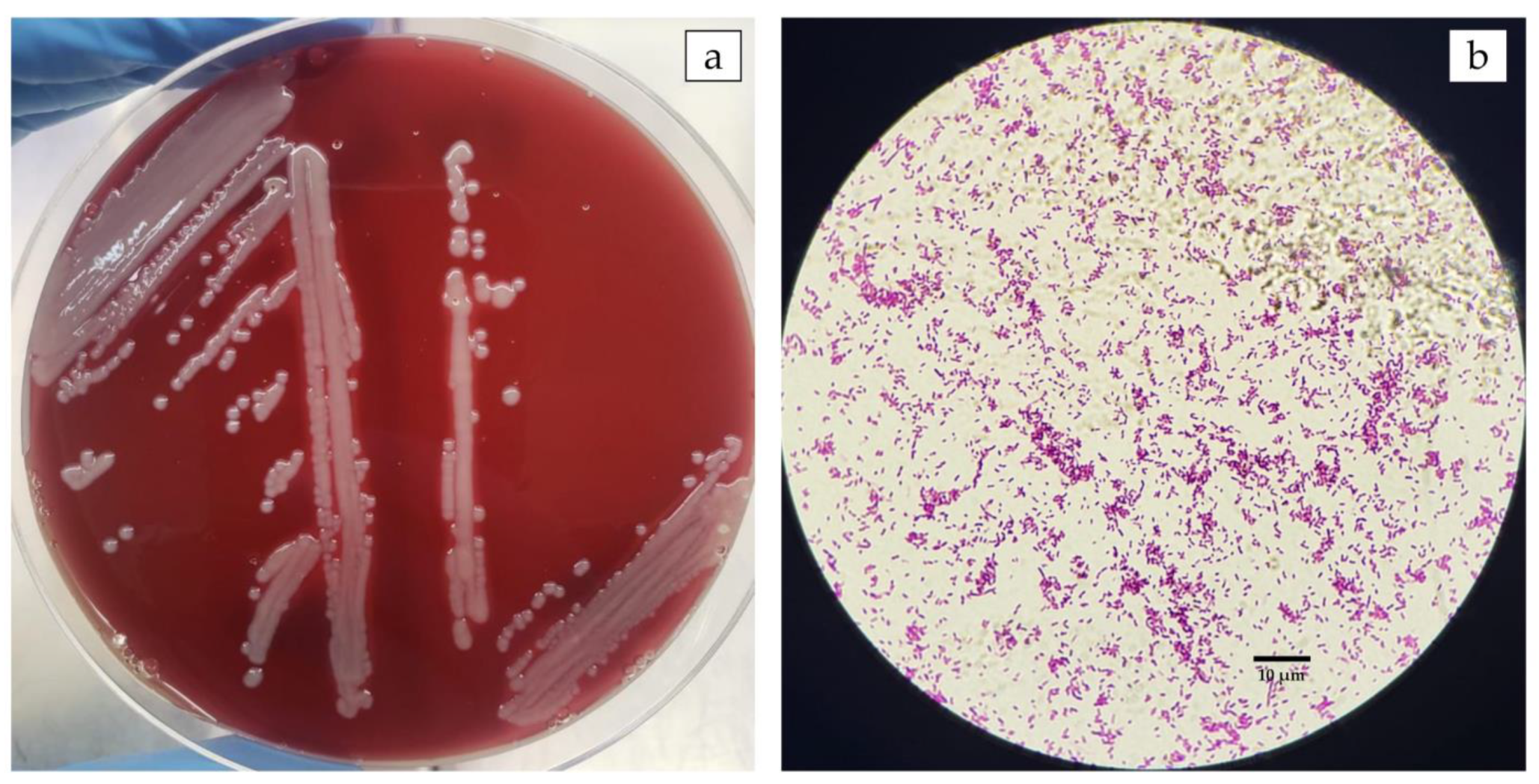
2.2. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.3. Molecular Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
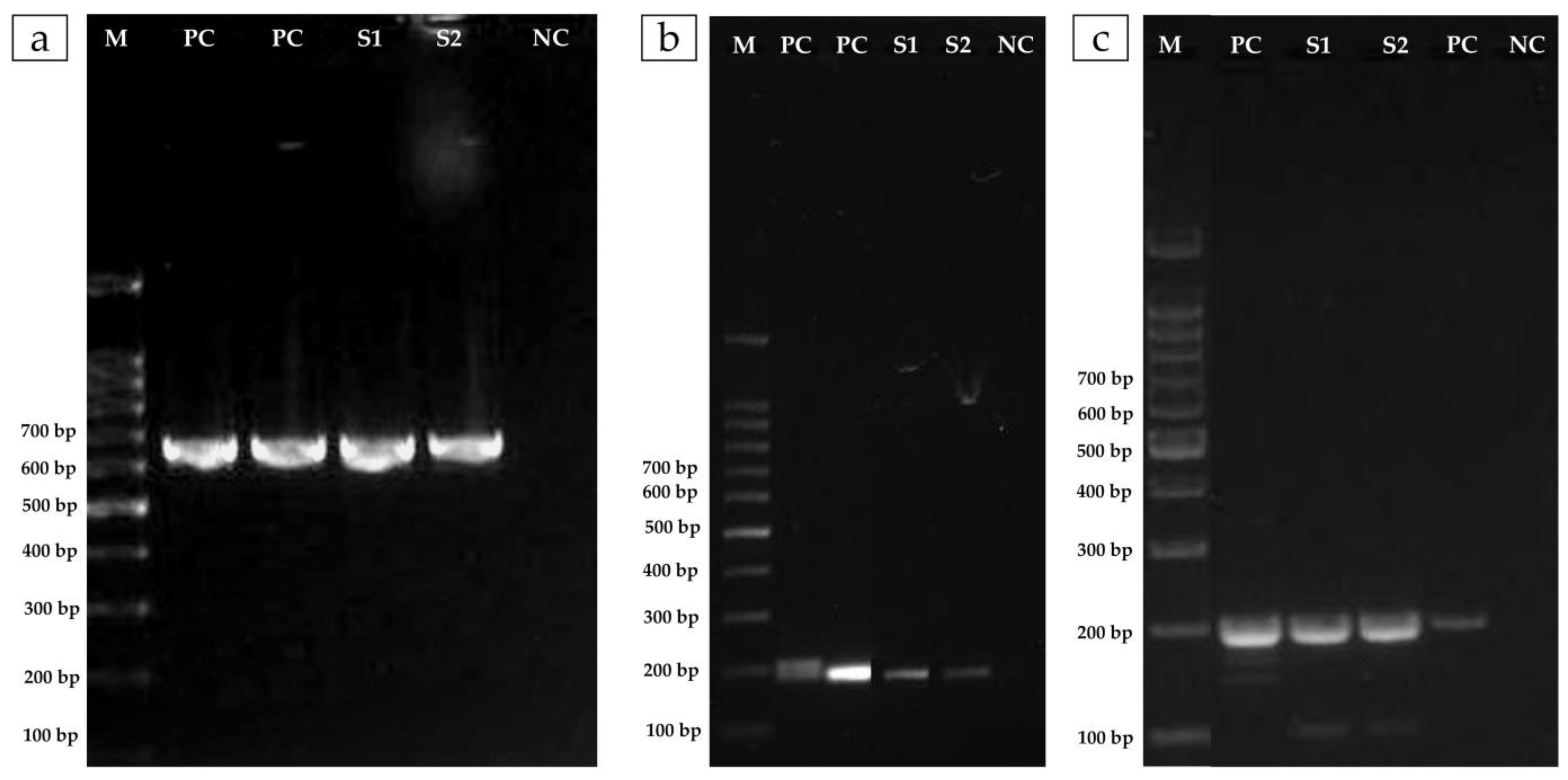
2.5. Molecular Detection of Resistance Genes
2.6. Experimental Challenge
2.6.1. Preparation of Bacterial Inoculum
2.6.2. Challenge Trial
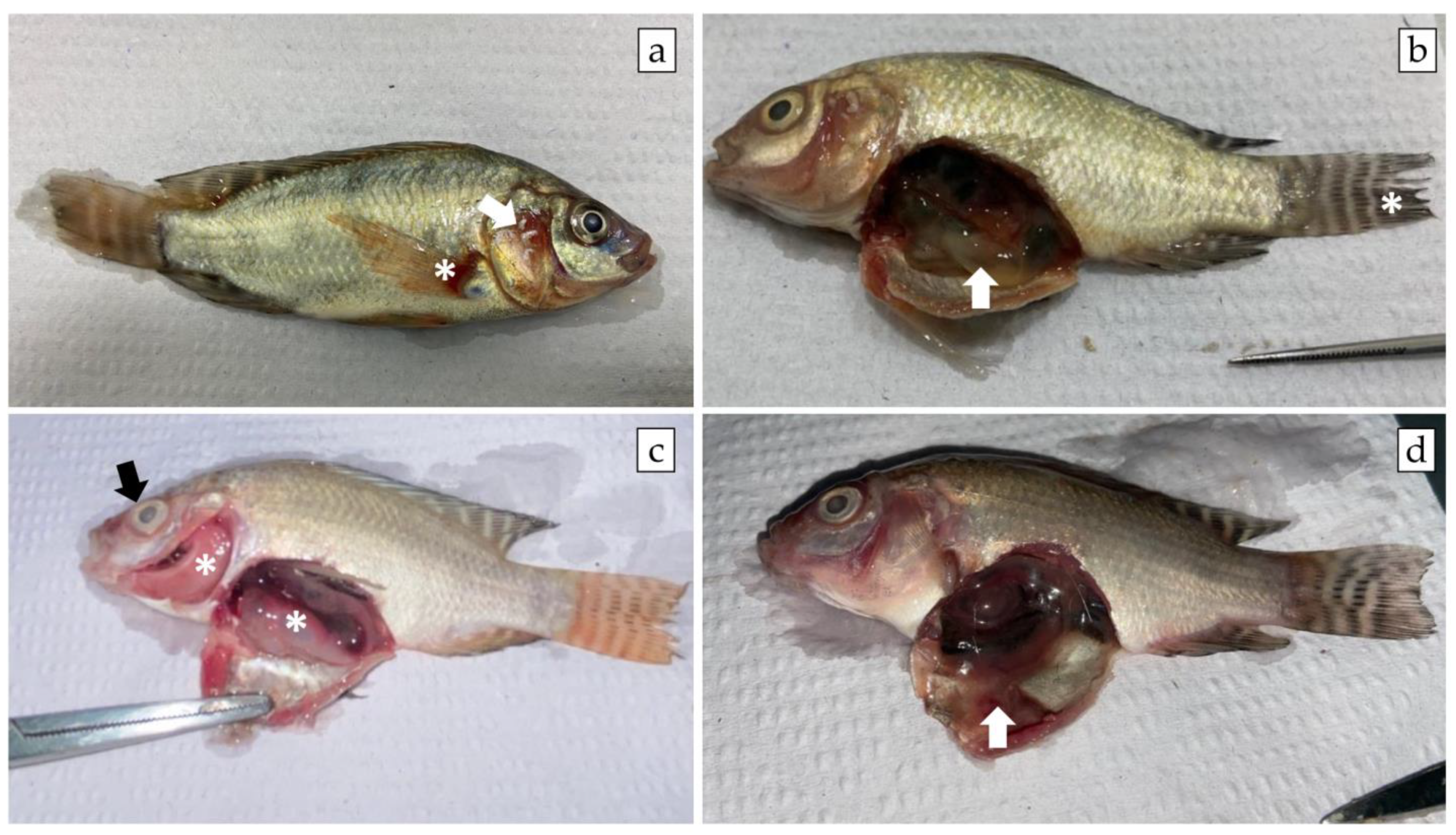
2.6.3. Histopathology
3. Results
3.1. The Outbreak in Farmed Nile Tilapia in Brazil Was Caused by A. veronii
3.2. The Isolate of A. veronii Showed Multidrug Resistance to the Most Used Antibacterial Drugs in Nile Tilapia Farmed in Brazil
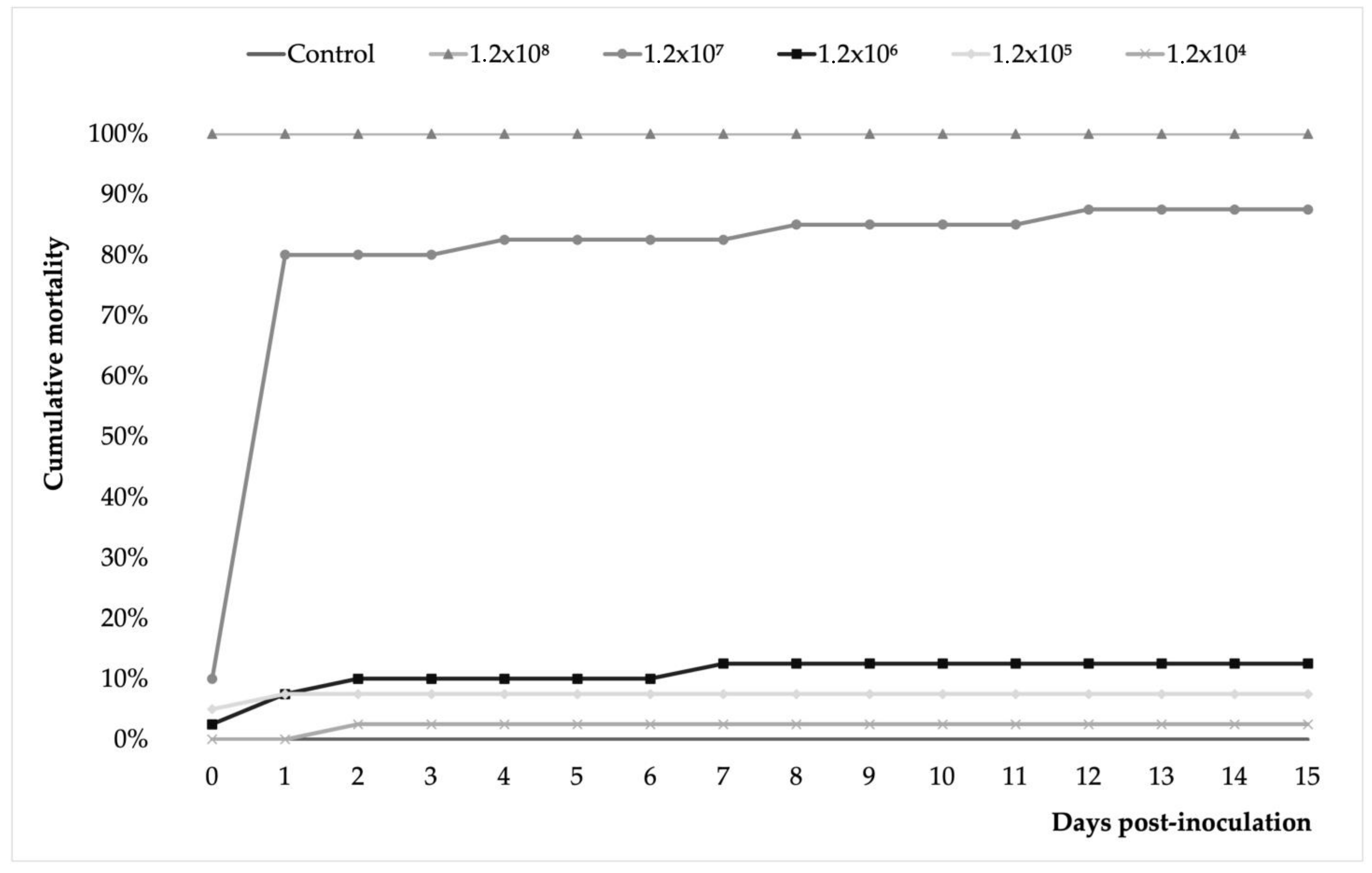
3.3. A. veronii Showed High In Vivo Pathogenicity and Koch’s Postulates Were Fulfilled
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castilho-Barros, L.; Owatari, M.S.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Silva, B.C.; Seiffert, W.Q. Economic feasibility of tilapia culture in southern Brazil: A small-scale farm model. Aquaculture 2020, 515, 734551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Tavares, G.C.; Dorella, F.A.; Rosa, J.C.C.; Marcelino, S.A.C.; Pierezan, F.; Pereira, F.L. First report of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus in Nile tilapia in Brazil. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 3008–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.F.M.; Fontana, H.; Moreira, B.M.; Bonelli, R.R. Draft Genome Sequence of a Tetracycline-Resistant Plesiomonas shigelloides Strain Isolated from Aquaculture-Reared Tilapia. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7, e00832-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assane, I.M.; de Sousa, E.L.; Valladão, G.M.R.; Tamashiro, G.D.; Criscoulo-Urbinati, E.; Hashimoto, D.T.; Pilarski, F. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Aeromonas jandaei involved in mass mortalities of cultured Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) in Brazil. Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaneci-Silva, D.; Assane, I.M.; de Oliveira Alves, L.; Gomes, F.C.; Moro, E.B.; Kotzent, S.; Pitondo-Silva, A.; Pilarski, F. Klebsiella pneumoniae causing mass mortality in juvenile Nile tilapia in Brazil: Isolation, characterization, pathogenicity and phylogenetic relationship with other environmental and pathogenic strains from livestock and human sources. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, R.C.; Rosa, J.C.C.; Resende, L.F.L.; de Pádua, S.B.; de Oliveira Barbosa, F.; Zerbini, M.T.; Tavares, G.C.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Emerging fish pathogens Lactococcus petauri and L. garvieae in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) farmed in Brazil. Aquaculture 2023, 565, 739093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.T.; Techatanakitarnan, C.; Jindakittikul, P.; Thaiprayoon, A.; Taengphu, S.; Charoensapsri, W.; Khunrae, P.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Senapin, S. Aeromonas jandaei and Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An Update on the Genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, Epidemiology, and Pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.A.; Noureldin, E.A.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Fita, N.A. Molecular identification and epizootiology of Aeromonas veronii infection among farmed Oreochromis niloticus in Eastern Province, KSA. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2017, 43, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, N.S.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Dharmaratnam, A.; Raja, S.A.; Ramraj, D.; Lal, K.K. Aeromonas veronii caused bilateral exophthalmia and mass mortality in cultured Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) in India. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, I.; El-Lamei, M.; Sherif, M.; Desuky, E.; Zaki, M.; Bakry, M. Aeromonas veronii biovar sobria a causative agent of mass mortalities in cultured Nile tilapia in El-Sharkia governorate, Egypt. Life Sci. J. 2015, 12, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zepeda-Velázquez, A.P.; Vega-Sánchez, V.; Salgado-Miranda, C.; Soriano-Vargas, E. Histopathological findings in farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) naturally infected with 3 different Aeromonas species. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2015, 79, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoai, T.D.; Trang, T.T.; Van Tuyen, N.; Giang, N.T.H.; Van Van, K. Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in channel catfish in Vietnam. Aquaculture 2019, 513, 734425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, A.A.; Sung, K.; Tran, Q.; Kerdahi, K.; Steele, R. Detection and characterization of virulence genes and integrons in Aeromonas veronii isolated from catfish. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.-H.; Wu, Z.-H.; Jian, J.-C.; Lu, Y.-S.; Tang, J.-F. Characterization of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii bv. veronii associated with ulcerative syndrome from Chinese longsnout catfish (Leiocassis longirostris Günther). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Sun, J.; Han, Z.; Yang, X.; Xian J-a Lv, A.; Hu, X.; Shi, H. Isolation, Identification and Characteristics of Aeromonas veronii from Diseased Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, T.; Song, G.; Yue, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Q. Whole-genome sequencing and antimicrobial resistance analysis of multidrug-resistant Aeromonas veronii strain JC529 from a common carp. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 27, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, X.R.; Li, J.; Li, G.Y.; Liu, Z.P.; Mo, Z.L. Identification and virulence properties of Aeromonas veronii bv. sobria isolates causing an ulcerative syndrome of loach Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wei, W.; Zhang, X. Pathogenicity of Aeromonas veronii causing mass mortalities of Odontobutis potamophila and its induced host immune response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 125, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, M.; Popowska, M. The prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes among Aeromonas species in aquatic environments. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, A.; Riesner, D. Purification of nucleic acids by selective precipitation with polyethylene glycol 6000. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 354, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals, 4th ed.; CLSI supplement VET08; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kahlmeter, G.; Brown, D.; Goldstein, F.; MacGowan, A.; Mouton, J.; Odenholt, I.; Rodloff, A.; Soussy, C.J.; Steinbakk, M.; Soriano, F.; et al. European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) technical notes on antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodford, N.; Fagan, E.J.; Ellington, M.J. Multiplex PCR for rapid detection of genes encoding CTX-M extended-spectrum (beta)-lactamases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogaerts, P.; Rezende de Castro, R.; de Mendonça, R.; Huang, T.D.; Denis, O.; Glupczynski, Y. Validation of carbapenemase and extended-spectrum β-lactamase multiplex endpoint PCR assays according to ISO 15189. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattoir, V.; Poirel, L.; Rotimi, V.; Soussy, C.J.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for detection of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance qnr genes in ESBL-producing enterobacterial isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaco, L.M.; Hasman, H.; Xia, S.; Aarestrup, F.M. qnrD, a novel gene conferring transferable quinolone resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky and Bovismorbificans strains of human origin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Guo, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Ye, X.; Wu, S.; Hooper, D.C.; Wang, M. New plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance gene, qnrC, found in a clinical isolate of Proteus mirabilis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, A.; Fortini, D.; Veldman, K.; Mevius, D.; Carattoli, A. Characterization of plasmids harbouring qnrS1, qnrB2 and qnrB19 genes in Salmonella. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.K.; Martin, I.; Alfa, M.; Mulvey, M. Multiplex PCR for the detection of tetracycline resistant genes. Mol. Cell. Probes 2001, 15, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André Fernando Nascimento, G.; Elane Cristine Correia, S.; João Batista Kochenborger, F.; Leonardo Susumu, T. Mentol e eugenol como substitutos da benzocaína na indução anestésica de juvenis de pacu. Acta Sci. Anim. Sci. 2008, 30, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sudheesh, P.S.; Al-Ghabshi, A.; Al-Mazrooei, N.; Al-Habsi, S. Comparative Pathogenomics of Bacteria Causing Infectious Diseases in Fish. Int. J. Evol. Biol. 2012, 2012, 457264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delphino, M.K.V.C.; Leal, C.A.G.; Gardner, I.A.; Assis, G.B.N.; Roriz, G.D.; Ferreira, F.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Gonçalves, V.S.P. Seasonal dynamics of bacterial pathogens of Nile tilapia farmed in a Brazilian reservoir. Aquaculture 2019, 498, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakingking, R., Jr.; Palma, P.; Usero, R. Aeromonas load and species composition in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultured in earthen ponds in the Philippines. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4736–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.V.; Dias, M.F.; Francisco, C.J.; David, G.S.; Silva RJd Júnior, J.P.A. Aeromonas hydrophila in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) from Brazilian aquaculture: A public health problem. Emergent Life Sci. Res. 2019, 5, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam-Sayuti, M.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Yusof, M.T.; Annas, S.; Najihah, M.Y.; Liles, M.R.; Monir, M.S.; Zaidi, Z.; Amal, M.N.A. The prevalence, putative virulence genes and antibiotic resistance profiles of Aeromonas spp. isolated from cultured freshwater fishes in peninsular Malaysia. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.T.; Nguyen, V.V.; Le, H.D.; Sangsuriya, P.; Jitrakorn, S.; Saksmerprome, V.; Senapin, S.; Rodkhum, C. Naturally concurrent infections of bacterial and viral pathogens in disease outbreaks in cultured Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) farms. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.P.; Bu, D.P.; Carrique-Mas, J.; Fèvre, E.M.; Gilbert, M.; Grace, D.; Hay, S.I.; Jiwakanon, J.; Kakkar, M.; Kariuki, S.; et al. Antibiotic resistance is the quintessential One Health issue. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, B.; Baron, S.; Barraud, O. Aeromonas: The multifaceted middleman in the One Health world. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2022, 65, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakulworakan, R.; Chokmangmeepisarn, P.; Dinh-Hung, N.; Sivaramasamy, E.; Hirono, I.; Chuanchuen, R.; Kayansamruaj, P.; Rodkhum, C. Insight into Whole Genome of Aeromonas veronii Isolated from Freshwater Fish by Resistome Analysis Reveal Extensively Antibiotic Resistant Traits. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 733668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A. Resistance plasmid families in Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayatgheib, N.; Calvez, S.; Fournel, C.; Pineau, L.; Pouliquen, H.; Moreau, E. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles and Resistance Genes in Genus Aeromonas spp. Isolated from the Environment and Rainbow Trout of Two Fish Farms in France. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Wang, K.Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Wang, E.L.; Liu, T.; Chen, D.-F.; Lai, W. Multidrug-Resistant Aeromonas veronii Recovered from Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) in China: Prevalence and Mechanisms of Fluoroquinolone Resistance. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, A.H.; Kassab, A.S. Multidrug-resistant Aeromonas bacteria prevalence in Nile tilapia broodstock. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.-J.; Kim, M.-S.; Jeong, M.-G.; Do, M.-Y.; Hwang, S.-D.; Kim, W.-J. Establishment of Epidemiological Cut-Off Values and the Distribution of Resistance Genes in Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas veronii Isolated from Aquatic Animals. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusunur, A.B.; Mogilipuri, S.S.; Moturu, D.; Benala, M.; Vaiyapuri, M.; Panda, S.K.; George, J.C.; Badireddy, M.R. Tetracycline resistance potential of heterotrophic bacteria isolated from freshwater fin-fish aquaculture system. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbu, S.M.; Zhou, L.; Sun, S.X.; Zhang, M.L.; Du, Z.Y. Chronic exposure to low environmental concentrations and legal aquaculture doses of antibiotics cause systemic adverse effects in Nile tilapia and provoke differential human health risk. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Choudhury, A.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Choi, J.; Acharya, S.; Park, J.-H. Exposure to Oxy-Tetracycline Changes Gut Bacterial Community Composition in Rainbow Trout: A Preliminary Study. Animals 2021, 11, 3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Fejzic, N.; MacKinnon, B.; Huchzermeyer, D.; Seric-Haracic, S.; Mardones, F.O.; Mohan, C.V.; Taylor, N.; Jansen, M.D.; Tavornpanich, S.; et al. A 12-point checklist for surveillance of diseases of aquatic organisms: A novel approach to assist multidisciplinary teams in developing countries. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1469–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Primers | Sequences (5′ - 3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Amplicon (pb) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| blaCTX-M-1 | CTX-M1 f CTX-M1 r | AAAAATCACTGCGCCAGTTC AGCTTATTCATCGCC ACGTT | 52 | 415 | [28] |
| blaCTX-M-2 | CTX-M2 f CTX-M2 r | CGACGCTACCCCTGCTAT CCAGCGTCAGATTTTTCAGG | 52 | 552 | |
| blaCTX-M-8 | CTX-M8 f CTX-M8 r | TCGCGTTAAGCGGATGATGC AACCCACGATGTGGGTAGC | 52 | 666 | |
| blaCTX-M-9 | CTX-M9 f CTX-M9 r | CAAAGAGAGTGCAACGGATG ATTGGAAAGCGTTCATCACC | 52 | 205 | |
| blaCTX-M-25 | CTX-M25 f CTX-M25 r | GCACGATGACATTCGGG AACCCACGATGTGGGTAGC | 52 | 327 | |
| blaNDM | IsoCarba_NDM f IsoCarba_NDM r | ACTTGGCCTTGCTGTCCTT CATTAGCCGCTGCATTGAT | 66 | 603 | [29] |
| blaVIM | IsoCarba _VIM f IsoCarba_VIM r | TGTCCGTGATGGTGATGAGT ATTCAGCCAGATCGGCATC | 66 | 437 | |
| blaIMP | IsoCarba_IMP f IsoCarba _IMP r | ACAYGGYTTRGTDGTKCTTG GGTTTAAYAAARCAACCACC | 66 | 387 | |
| blaKPC | IsoCarba_KPC f IsoCarba_KPC r | TCGCCGTCTAGTTCTGCTGTCTTG ACAGCTCCGCCACCGTCAT | 66 | 353 | |
| blaOXA-48 | IsoCarba_OXA-48 f IsoCarba_OXA-48 r | ATGCGTGTATTAGCCTTATCG CATCCTTAACCACGCCCAAATC | 66 | 265 | |
| qnrA1 a qnrA6 | QnrAm-f QnrAm-r | AGAGGATTTCTCACGCCAGG TGCCAGGCACAGATCTTGAC | 54 | 580 | [30] |
| qnrB1 a qnrB6 | QnrBm-f QnrBm-r | GGMATHGAAATTCGCCACTG TTTGCYGYYCGCCAGTCGAA | 54 | 264 | |
| qnrS1 a qnrS2 | QnrSm-f QnrSm-r | GCAAGTTCATTGAACAGGGT TCTAAACCGTCGAGTTCGGCG | 54 | 428 | |
| qnrD | QnrD-f | CGAGATCAATTTACGGGGAATA | 62 | 581 | [31] |
| QnrD-r | AACAAGCTGAAGCGCCTG | ||||
| qnrC | QnrC-f | GGGTTGTACATTTATTGAATC | 50 | 447 | [32] |
| QnrC-r | TCCACTTTACGAGGTTCT | ||||
| ColE plasmid | ColE-f | GTTCGTGCATACAGTCCA | 60 | 187 | [33] |
| ColE-r | GGCGAAACCCGACAGGACT | ||||
| tetB | tetB f | TTGGTTAGGGGCAAGTTTTG | 55 | 659 | [34] |
| tetB r | GTAATGGGCCAATAACACCG | ||||
| tetC | tetC f | CTTGAGAGCCTTCAACCCAG | 418 | ||
| tetC r | ATGGTCGTCATC TACCTGCC | ||||
| tetD | tetD f | AAACCATTACGGCATTCTGC | 787 | ||
| tetD r | GACCGGATACACCATCCATC | ||||
| tetA | tetA f | GCTACATCCTGCTTGCCTTC | 55 | 210 | |
| tetA r | CATAGATCGCCGTGAAGAGG | ||||
| tetE | tetE f | AAACCACATCCTCCATACGC | 278 | ||
| tetE r | AAATAGGCCACAACCGTCAG |
| Antibiotic Drugs | Classification Ranges (mm) | Inhibition Zone (mm) | Result | CIM (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild-Type (WT) | Non-Wild Type (NWT) | ||||
| Oxitetracycline (OTC) | ≥23 | ≤22 | 18 | NWT | 32 |
| Enrofloxacin (ENR) | ≥32 | ≤31 | 18 | NWT | 4 |
| Amoxycillin (AML) | * | * | 10 | * | ≥256 |
| Florfenicol (FFC) | ≥25 | ≤24 | 35 | WT | ≤0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dos Santos, S.B.; Alarcon, M.F.; Ballaben, A.S.; Harakava, R.; Galetti, R.; Guimarães, M.C.; Natori, M.M.; Takahashi, L.S.; Ildefonso, R.; Rozas-Serri, M. First Report of Aeromonas veronii as an Emerging Bacterial Pathogen of Farmed Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Brazil. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081020
dos Santos SB, Alarcon MF, Ballaben AS, Harakava R, Galetti R, Guimarães MC, Natori MM, Takahashi LS, Ildefonso R, Rozas-Serri M. First Report of Aeromonas veronii as an Emerging Bacterial Pathogen of Farmed Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Brazil. Pathogens. 2023; 12(8):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081020
Chicago/Turabian Styledos Santos, Sandie Bispo, Miguel Fernandez Alarcon, Anelise Stella Ballaben, Ricardo Harakava, Renata Galetti, Mateus Cardoso Guimarães, Mariene Miyoko Natori, Leonardo Susumu Takahashi, Ricardo Ildefonso, and Marco Rozas-Serri. 2023. "First Report of Aeromonas veronii as an Emerging Bacterial Pathogen of Farmed Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Brazil" Pathogens 12, no. 8: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081020
APA Styledos Santos, S. B., Alarcon, M. F., Ballaben, A. S., Harakava, R., Galetti, R., Guimarães, M. C., Natori, M. M., Takahashi, L. S., Ildefonso, R., & Rozas-Serri, M. (2023). First Report of Aeromonas veronii as an Emerging Bacterial Pathogen of Farmed Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Brazil. Pathogens, 12(8), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081020






