Nuclear Morphofunctional Organization and Epigenetic Characteristics in Somatic Cells of T. infestans (Klug, 1834)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
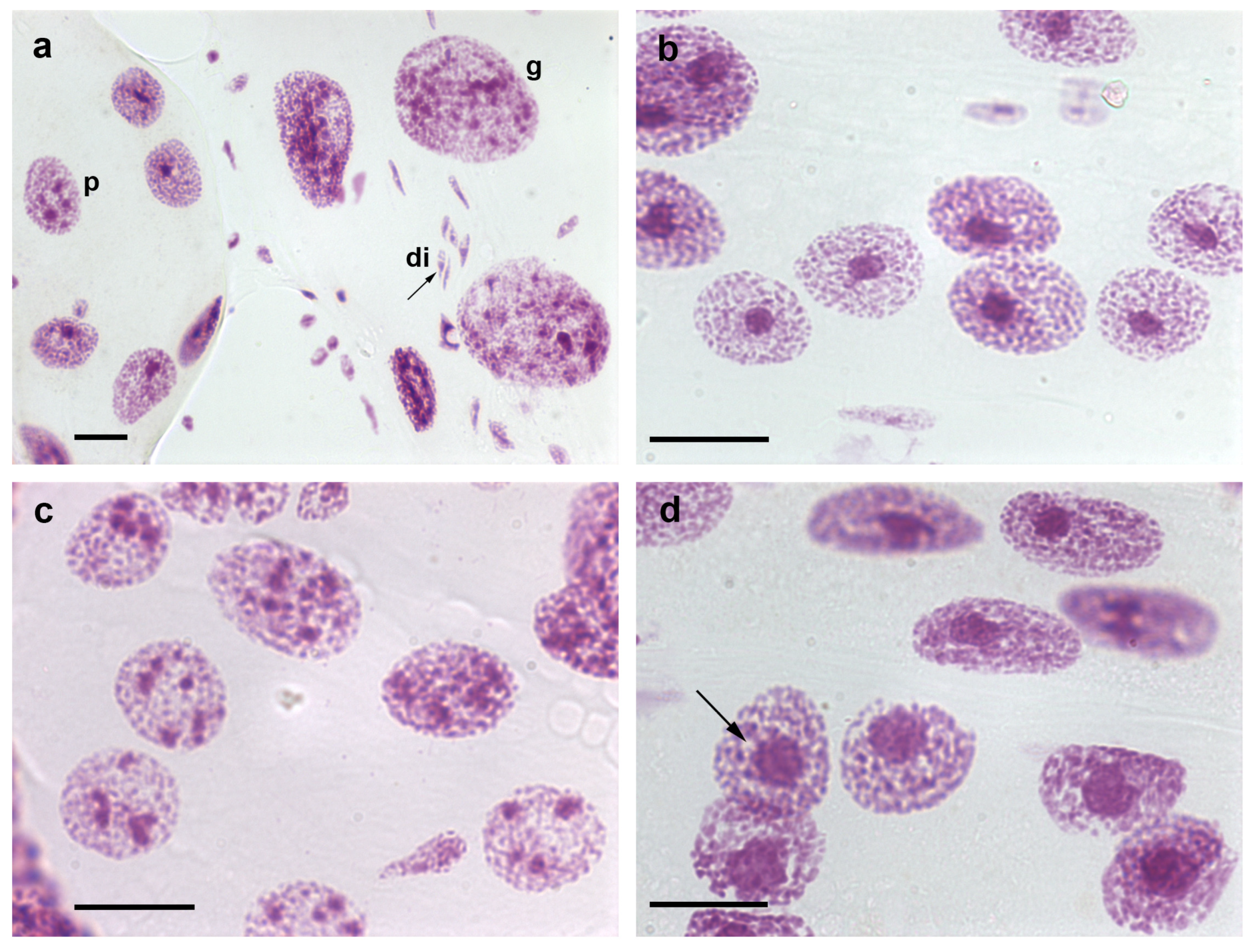
2. Somatic Polyploidy
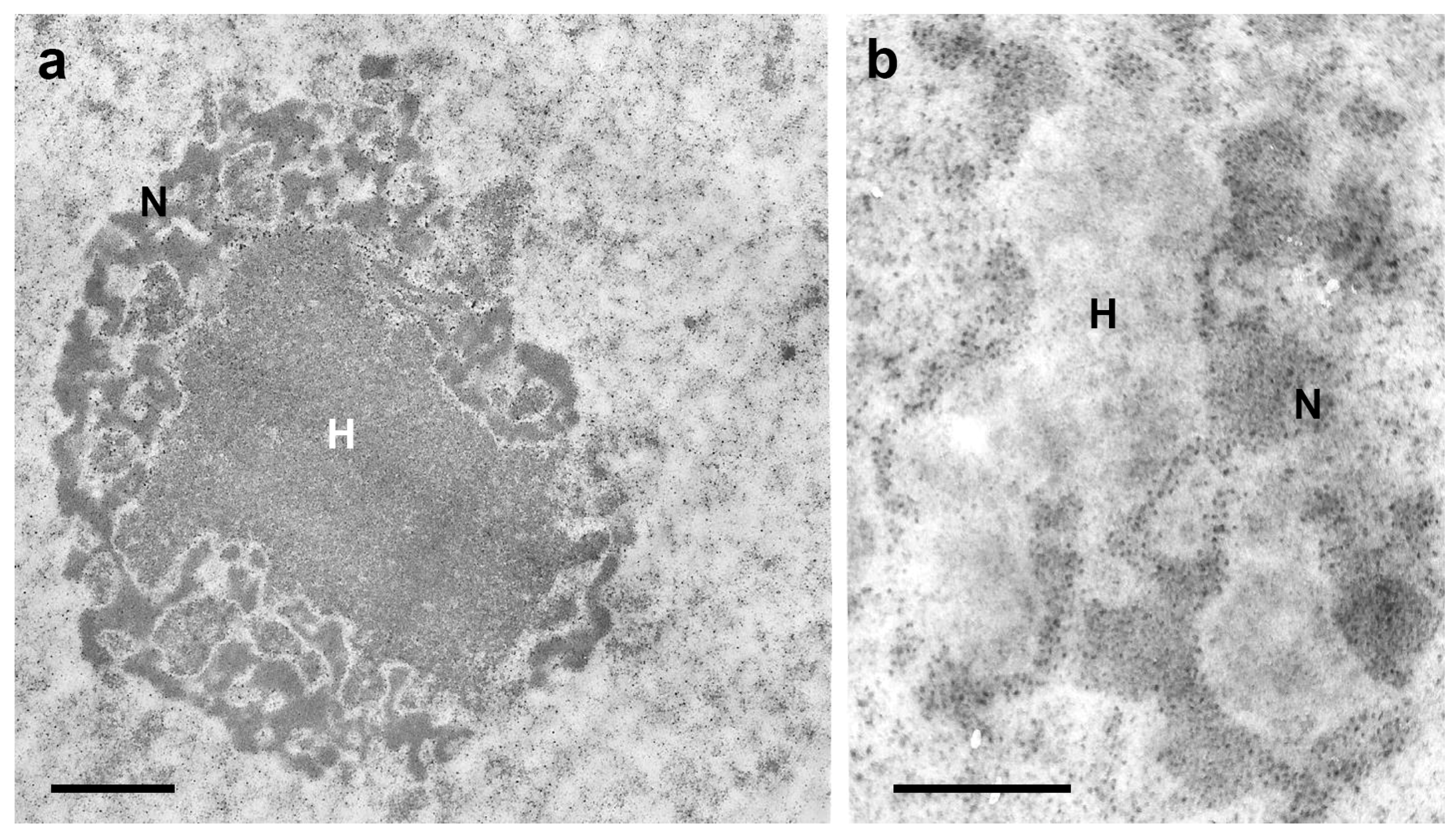
3. Heterochromatin and Nuclear Phenotypes
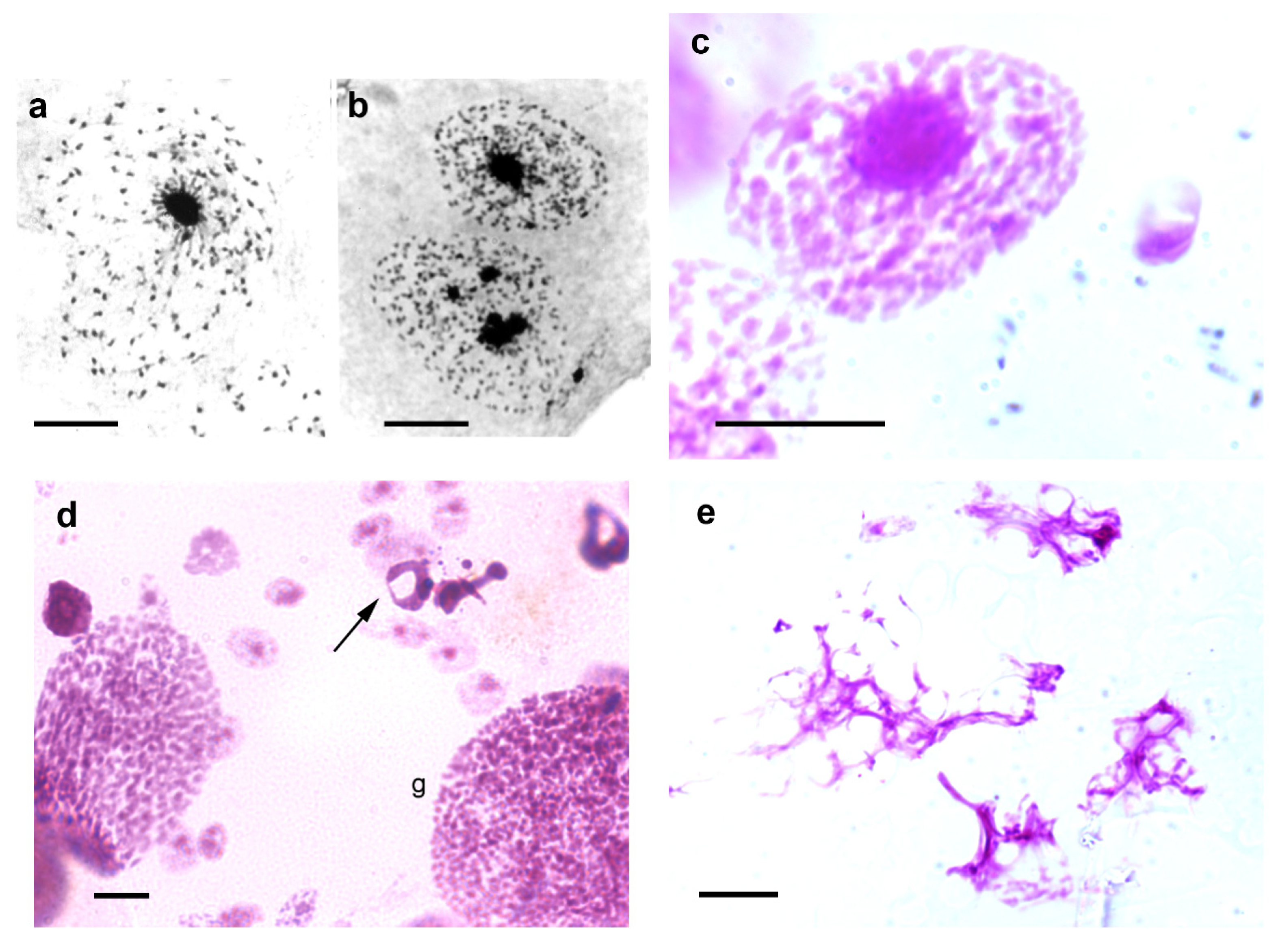
4. Response to Stress Agents
5. Epigenetic Markers: DNA and Histone Methylation
6. Response to Epigenetic Modulators
7. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bargues, M.D.; Kiisiowicz, D.R.; Panzera, F.; Noireau, F.; Marcilla, A.; Perez, R.; Rojas, M.G.; O’Connor, J.E.; Gonzales-Candelas, F.; Galvao, C.; et al. Origin and phylogeography of the Chagas disease main vector Triatoma infestans based on nuclear rDNA sequences and genome size. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2006, 6, 436–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pita, S.; Panzera, F.; Mora, P.; Vel, J.; Cuadrado, A.; Sanchez, A.; Palomeque, T.; Lorite, P. Comparative repeatome analysis on Triatoma infestans Andean and Non-Andean lineages, main vector of Chagas disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mello, M.L.S. Somatic polyploidy in insects. Ciênc. Cult. 1970, 22, 348–350. [Google Scholar]
- Frawley, L.E.; Orr-Weaver, T.L. Polyploidy. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R353–R358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anatskaya, O.V.; Vinogradov, A.E. Somatic polyploidy promotes cell function under stress and energy depletion: Evidence from tissue-specific mammal transcriptome. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2010, 10, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anatskaya, O.V.; Vinogradov, A.E. Polyploidy as a fundamental phenomenon in Evolution, Development, Adaptation and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, M.L.S. Nuclear behavior in the Malpighian tubes of Triatoma infestans (Reduv., Hemiptera). Cytologia 1971, 36, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mello, M.L.S. Feulgen-DNA values and ploidy degrees in the Malpighian tubes of some triatomids. Rev. Bras. Pesq. Méd. Biol. 1975, 8, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, M.L.S.; Vidal, B.C. The Feulgen reaction: A brief review and new perspectives. Acta Histochem. 2017, 119, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, M.L.S.; Tavares, M.C.H.; Dantas, M.M.; Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Maria-Engler, S.S.; Campos, S.P.; Garcia, N.L. Cell death and survival alterations in Malpighian tubules of Triatoma infestans following heat shock. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 79, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, M.L.S. Nuclear fusion and change in chromatin packing state in response to starvation in Triatoma infestans. Rev. Bras. Genét. 1989, 12, 485–498. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, C.G.T.J.; Mello, M.L.S. Phenotypes and number of Malpighian tubule nuclei in Triatoma infestans Klug along development and starvation. Rev. Bras. Genét. 1987, 10, 449–457. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, M.L.S.; Pudney, M. Polyploidization of the BTC-32 cell line from Triatoma infestans (Hemiptera, Reduviidae). Genetica 1987, 74, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigglesworth, V.B. Polyploidy and nuclear fusion in the fat body of Rhodnius (Hemiptera). J. Cell Sci. 1967, 2, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolder, H.; Mello, M.L.S. Dados preliminares sobre partículas semelhantes a vírus em células de triatomíneos (Preliminary data on virus-like particles in triatomini cells). Rev. Saúde Públ. 1978, 12, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolder, H.; Mello, M.L.S. Virus-like particles in the Malpighian tubes of blood-sucking insects. Cell. Mol. Biol. 1978, 23, 299–310. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, M.L.S. Patterns of lability towards acid hydrolysis in heterochromatin and euchromatin of Triatoma infestans Klug. Cell. Mol. Biol. 1979, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarenga, E.M.; Mondin, M.; Martins, J.A.; Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Vidal, B.C.; Mello, M.L.S. Spatial distribution of AT- and GC-rich DNA within interphase cell nuclei of Triatoma infestans Klug. Micron 2011, 42, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, G.; Bogliolo, A.R.; Pinto, A.C. Cytogenetics of Triatominae: Karyotype, DNA content, nuclear size and heteropyknosis of autosomes. Braz. J. Biol. 1972, 32, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Solari, J. Autosomal synaptonemal complexes and sex chromosomes without axes in Triatoma infestans (Reduviidae, Hemiptera). Chromosoma 1979, 72, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morielle-Souza, A.; Azeredo-Oliveira, M.T.V. Differential characterization of holocentric chromosomes in triatomines (Heteroptera, Triatominae) using different staining techniques and fluorescent in situ hybridization. Genet. Mol. Res. 2007, 6, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirai, H.; Shomo, Y.; Arias, A.R.; Tada, I. Constitutive heterochromatin polymorphism of a Triatoma infestans strain, a main vector insect of Chagas disease. Jpn. J. Sant. Zool. 1991, 42, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzera, F.; Perez, R.; Panzera, Y.; Ferrandis, I.; Ferreiro, M.J.; Calleros, L. Cytogenetics and genome evolution in the subfamily Triatominae (Hemiptera, Reduviidae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2010, 128, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardella, V.B.; da Rosa, J.A.; Vanzela, A.L.L. Origin and distribution of AT-rich repetitive DNA families in Triatoma infestans (Heteroptera). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 23, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imperador, C.H.L.; Bardella, V.B.; dos Anjos, E.H.; Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C.; Mello, M.L.S. Spatial distribution of heterochromatin bodies in the nuclei of Triatoma infestans (Klug). Microsc. Microanal. 2020, 26, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, M.; Cummings, R.; Yamashita, Y.M. A conserved function for pericentromeric satellite DNA. eLife 2018, 7, e34122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, C.G.T.J. Fenótipos Nucleares com ênfase na Heterocromatina, e Frequências Nucleares, em Algumas Espécies de Triatomíneos. (Nuclear Phenotypes with Emphasis in Heterochromatin, and Nuclear Frequencies in Some Triatomine Species). Masters’ Thesis, University of Campinas, Campinas, Brazil, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, M.L.S.; Vidal, B.C. Critical electrolyte concentration of the heterochromatin and euchromatin of Triatoma infestans. Cytobios 1989, 59, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, R.; Brero, A.; von Hase, J.; Schroeder, T.; Cremer, T.; Dietzel, S. Common themes and cell type specific variations of higher order chromatin arrangements in the mouse. BMC Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jost, K.L.; Bertulat, B.; Rapp, A.; Brero, A.; Hardt, T.; Domaing, P.; Gösele, C.; Schulz, H.; Hübner, N.; Cardoso, M.C. Gene repositioning within the cell nucleus is not random and is determined by its genomic neighborhood. Epigenetics Chromatin 2015, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poulet, A.; Duc, C.; Voisin, M.; Desset, S.; Tutois, S.; Vanrobays, E.; Benoit, M.; Evans, D.E.; Probst, A.V.; Tatout, C. The LINC complex contributes to heterochromatin organization and transcriptional gene silencing in plants. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 590–601. [Google Scholar]
- Brändle, F.; Frühbauer, B.; Jagannathan, M. Principles and functions of pericentromeric satellite DNA clustering into chromocenters. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 128, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperador, C.H.L.; Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Mello, M.L.S. The topological distribution of the chromocenter in Panstrongylus megistus (Burmeister) Malpighian tubule cells examined by confocal microscopy. Cytologia 2021, 86, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allshire, R.C.; Madhani, H.D. Ten principles of heterochromatin formation and function. Nat. Rev. 2018, 19, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bártova, E.; Krejci, J.; Harnicarová, A.; Galiová, G.; Kozubek, S. Histone modifications and nuclear architecture: A review. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2008, 56, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Politz, J.C.R.; Scalzo, D.; Groudine, M. Something silent this way forms: The functional organization of the repressive nuclear compartment. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 29, 241–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mello, M.L.S.; Dolder, H.; Dias, C.A. Nuclear ultrastructure of Malpighian tubule cells in Triatoma infestans (Hemiptera, Reduviidae) under conditions of full nourishment and starvation. Braz. J. Genet. 1990, 13, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sandritter, W.; Kiefer, G.; Salm, R.; Moore, G.W.; Grimm, H.; Kiefer, R. DNA in heterochromatin cytophotometric pattern recognition image analysis among cell nuclei in duct epithelium and in carcinoma of the human breast. Beitr. Pathol. 1974, 151, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, L.C.G.; Cestari, A.N. Cromossomos politênicos: Sistemas experimentais in vivo e in vitro. (Polytene chromosomes: In vivo and in vitro experimental systems). Ciênc. Cult. 1982, 34, 480–485. [Google Scholar]
- Jagannathan, M.; Cummings, R.; Yamashita, Y.M. The modular mechanism of chromocenter formation in Drosophila. eLife 2019, 8, e43938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, B.C.; Mello, M.L.S. Toluidine blue staining for cell and tissue biology applications. Acta Histochem. 2019, 121, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, M.L.S. Apoptosis in polyploid cells of the blood-sucking hemipteran, Triatoma infestans Klug. Caryologia 2005, 58, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Dantas, M.M.; Mello, M.L.S. Changes in the nuclear phenotypes of Triatoma infestans Klug induced by thermal shocks. Rev. Bras. Genét. 1992, 15, 509–519. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Mello, M.L.S.; Ferraz Filho, A.N.; Dantas, M.M. Sobrevivência e ocorrência de muda em Triatoma infestans Klug (Hemiptera, Reduviidae) após choque de temperatura (Survival and molting incidence in Triatoma infestans Klug (Hemiptera, Reduviidae) after temperature shocks). Rev. Saúde Públ. 1991, 25, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, S.G.P.; Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Wada, C.Y.; Mello, M.L.S. Effect of sequential cold shocks on survival and molting rate in Triatoma infestans Klug. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2002, 97, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, S.L.; Garcia, N.L.; Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Mello, M.L.S. Effect of sequential cold shocks on survival and molting incidence in Panstrongylus megistus (Burmeister) (Hemiptera, Reduviidae). Cryobiology 2001, 42, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, S.G.P.; Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Mello, M.L.S. Changes in nuclear phenotype frequencies following sequential cold shocks in Triatoma infestans (Hemiptera, Reduviidae). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2002, 97, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mello, M.L.S.; Kubrusly, F.S.; Randi, M.A.F.; Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Ferraz Filho, A.N. Effect of heavy metals on chromatin supraorganization, nuclear phenotypes, and survival of Triatoma infestans. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1995, 74, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Anjos, E.H.M.; Rocha, M.A.; Vidal, B.C.; Mello, M.L.S. Exploration of DNA methylation in the chromatin of Triatoma infestans (Klug). Cytologia, 2023; 88, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Bongiorni, S.; Cintio, O.; Prantera, C. The relationship between DNA methylation and chromosome imprinting in the coccid Planococcus citri. Genetics 1999, 151, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrioli, M.; Azzoni, P.; Lombardo, G.; Manicardi, G.C. Composition and epigenetic markers of heterochromatin in the aphid Aphis neri (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2011, 133, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, E.M.; Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Moraes, A.S.; Naves, L.S.; Mondin, M.; Felisbino, M.B.; Mello, M.L.S. Histone epigenetic marks in heterochromatin and euchromatin of the Chagas disease vector, Triatoma infestans. Acta Histochem. 2016, 118, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Terry, A.V.; Singh, P.B.; Gilbert, D.M. Differential subnuclear localization and replication timing of histone H3 lysine 9 methylation states. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 2872–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barski, A.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.Y.; Schones, D.E.; Wang, Z.; Wei, G.; Chepelev, I.; Zhao, K. High-resolution profile of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 2007, 129, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balakrishnan, L.; Milavetz, B. Decoding the histone H4 lysine 20 methylation mark. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 45, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.A.; Vidal, B.C.; Mello, M.L.S. Sodium valproate modulates the methylation status of lysine residues 4, 9 and 27 in histone H3 of HeLa cells. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2023, 16, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rice, J.C.; Briggs, S.D.; Ueberheide, B.; Barber, C.M.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F.; Shinkai, Y.; Allis, C.D. Histone methyltransferases direct different degrees of methylation to define distinct chromatin domains. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suka, N.; Luo, K.; Grunstein, M. Sir2p and Sas2p opposingly regulate acetylation of histone H4 lysine 16 and spreading of heterochromatin. Nature Genet. 2002, 32, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.J.J.; Na, W.; Routh, A.; Martino, F.; Chapman, L.; Roeder, R.G.; Rhodes, D. 30 nm chromatin fibre decompaction requires both H4-K16 acetylation and linker histone eviction. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 381, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Grummt, I. The PHD finger/bromodomain of NoRC interacts with acetylated histone H4K16 and is sufficient for rDNA silencing. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1434–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herz, H.M.; Garruss, A.; Shilatifard, A. SET for life: Biochemical activities and biological functions of SET domain-containing proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 621–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corvalan, A.Z.; Coller, H.A. Methylation of histone 4’s lysine 20: A critical analysis of the state of the field. Physiol. Genom. 2021, 53, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttlicher, M.; Minucci, S.; Zhu, P.; Kramer, O.H.; Schinpf, A.; Giavara, S.; Sleeman, J.P.; LoCoco, F.; Nervi, C.; Pelicci, P.G.; et al. Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6969–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phiel, C.J.; Zhang, F.; Huang, E.Y.; Guenther, M.G.; Lazar, M.A.; Klein, P.S. Histone deacetylase is a direct target of valproic acid, a potent anticonvu lsant, mood stabilizer, and teratogene. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36734–36741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Detich, N.; Bovenzi, V.; Szyf, M. Valproate induces replication-independent active DNA demethylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 27586–27592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marchion, D.C.; Bicaku, E.; Daud, A.I.; Sullivan, D.M.; Munster, P.N. Valproic acid alters chromatin structure by regulation of chromatin modulation proteins. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3815–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felisbino, M.B.; Tamashiro, W.M.S.C.; Mello, M.L.S. Chromatin remodeling, cell proliferation and cell death in valproico acid-treated HeLa cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Felisbino, M.B.; Gatti, M.S.V.; Mello, M.L.S. Changes in chromatin structure in NIH 3T3 cells induced by valproic acid and trichostatin A. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.A.; Veronezi, G.M.B.; Felisbino, M.B.; Gatti, M.S.V.; Tamashiro, W.M.S.C.; Mello, M.L.S. Sodium valproate and 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine differentially modulate DNA demethylation in G1 phase-arrested and proliferative HeLa cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sargolzaei, J.; Rabbani-Chadegani, A.; Mollaei, H.; Deezagi, A. Spectroscopic analysis of the interaction of valproic acid with histone H1 in solution and in chromatin structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, B.C.; Mello, M.L.S. Sodium valproate (VPA) interactions with DNA and histones. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Fan, Y.; De La Fuente, R. Changes in chromatin accessibility lasndscape and histone H3 core acetylation during valproic acid-induced differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Epigenetics Chromatin 2021, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, M.L.S. Sodium valproate-induced chromatin remodeling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 645518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duenas-Gonzalez, A.; Candelaria, M.; Perez-Plascencia, C.; Perez-Cardenas, E.; de la Cruz-Hernandez, E.; Herrera, L.A. Valproic acid as epigenetic cancer drug: Preclinical, clinical and transcriptional effects on solid tumors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2008, 34, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chateauvieux, S.; Morceau, F.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Molecular and therapeutical potential and toxicity of valproic acid. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 479364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Coy, D.H. Anti-convulsant drug valproic acid in cancers and in combination anti-cancer therapeutics. Mod. Chem. Appl. 2014, 2, 1000118. [Google Scholar]
- Heers, H.; Stanislaw, J.; Harrelson, J.; Lee, M.W. Valproic acid as an adjunctive therapeutic agent for the treatment of breast cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 835, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.S.; Rocha, M.A.; Mello, M.L.S. Epigenetic studies in insects and the valproic acid perspective. Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 84, e256045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani, A.; Rocha, M.A.; Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Santos, D.S.; Nascimento, J.D.; da Rosa, J.A.; Mello, M.L.S. Effects of sodium valproate on the chromatin of Triatoma infestans (Klug, 1834) (Hemiptera, Reduviidae) under in vitro culture conditions. Acta Histochem. 2021, 123, 151695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannister, A.J.; Zegerman, P.; Partridge, J.F.; Miska, E.A.; Thomas, J.O.; Allshire, R.C.; Kouzarides, T. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 2001, 410, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachner, M.; O’Carroll, D.; Rea, S.; Mechtler, K.; Jenuwein, T. Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins. Nature 2001, 410, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, A.D.; Liu, P.Z.; Banigan, E.J.; Amassalha, L.M.; Bakman, V.; Adam, S.A.; Goldman, R.D.; Marko, J.F. Chromatin histone modifications and rigidity affect nuclear morphology independent of lamins. Mol. Biol. Cell 2018, 29, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, M.L.S.; Randi, M.A.F.; Giorgio, S.; Ferraz-Filho, A.N.; Rodrigues, V.L.C.C.; Rocha-e-Silva, E.O.; Cordeiro, J.E. Number of chromosomes, Feulgen-DNA content, and nuclear phenotypes in domestic and wild specimens of Panstrongylus megistus. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1986, 80, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mello, M.L.S. Nuclear Morphofunctional Organization and Epigenetic Characteristics in Somatic Cells of T. infestans (Klug, 1834). Pathogens 2023, 12, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081030
Mello MLS. Nuclear Morphofunctional Organization and Epigenetic Characteristics in Somatic Cells of T. infestans (Klug, 1834). Pathogens. 2023; 12(8):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081030
Chicago/Turabian StyleMello, Maria Luiza S. 2023. "Nuclear Morphofunctional Organization and Epigenetic Characteristics in Somatic Cells of T. infestans (Klug, 1834)" Pathogens 12, no. 8: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081030
APA StyleMello, M. L. S. (2023). Nuclear Morphofunctional Organization and Epigenetic Characteristics in Somatic Cells of T. infestans (Klug, 1834). Pathogens, 12(8), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12081030





