Lactoferrin and Lysozyme Inhibit the Proteolytic Activity and Cytopathic Effect of Naegleria fowleri Enzymes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Viability Assays
2.3. Growth Curves
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.5. Zymography Assays
2.6. Protease Inhibition
2.7. Cytopathic Effect of N. fowleri on MDCK Cells
3. Results
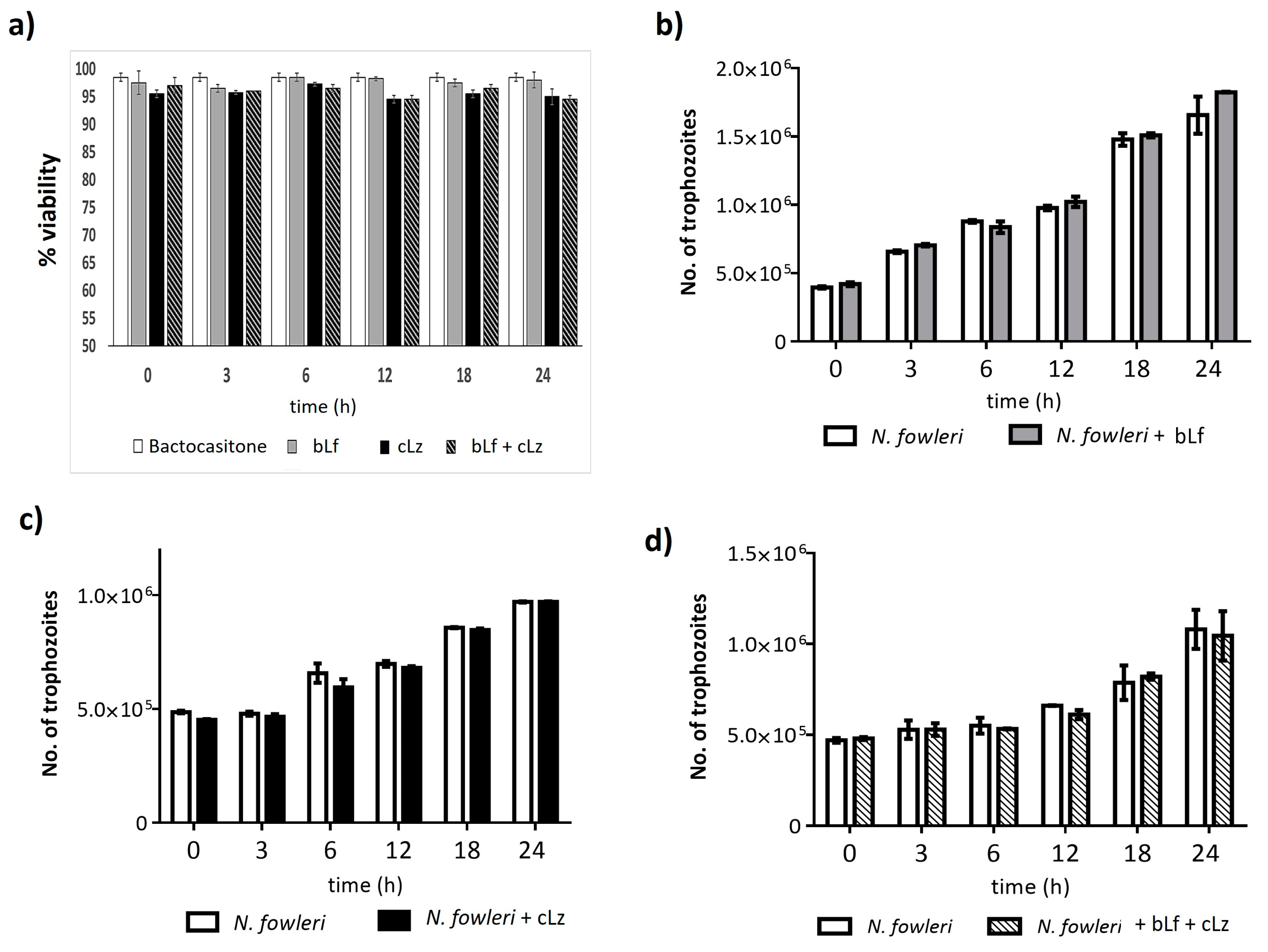
3.1. bLf and cLz Did Not Have an Amoebicidal Effect over N. fowleri Trophozoites
3.2. bLf and cLz Did Not Affect the Growth of N. fowleri Trophozoites
3.3. Ultrastructural Analysis of Trophozoites
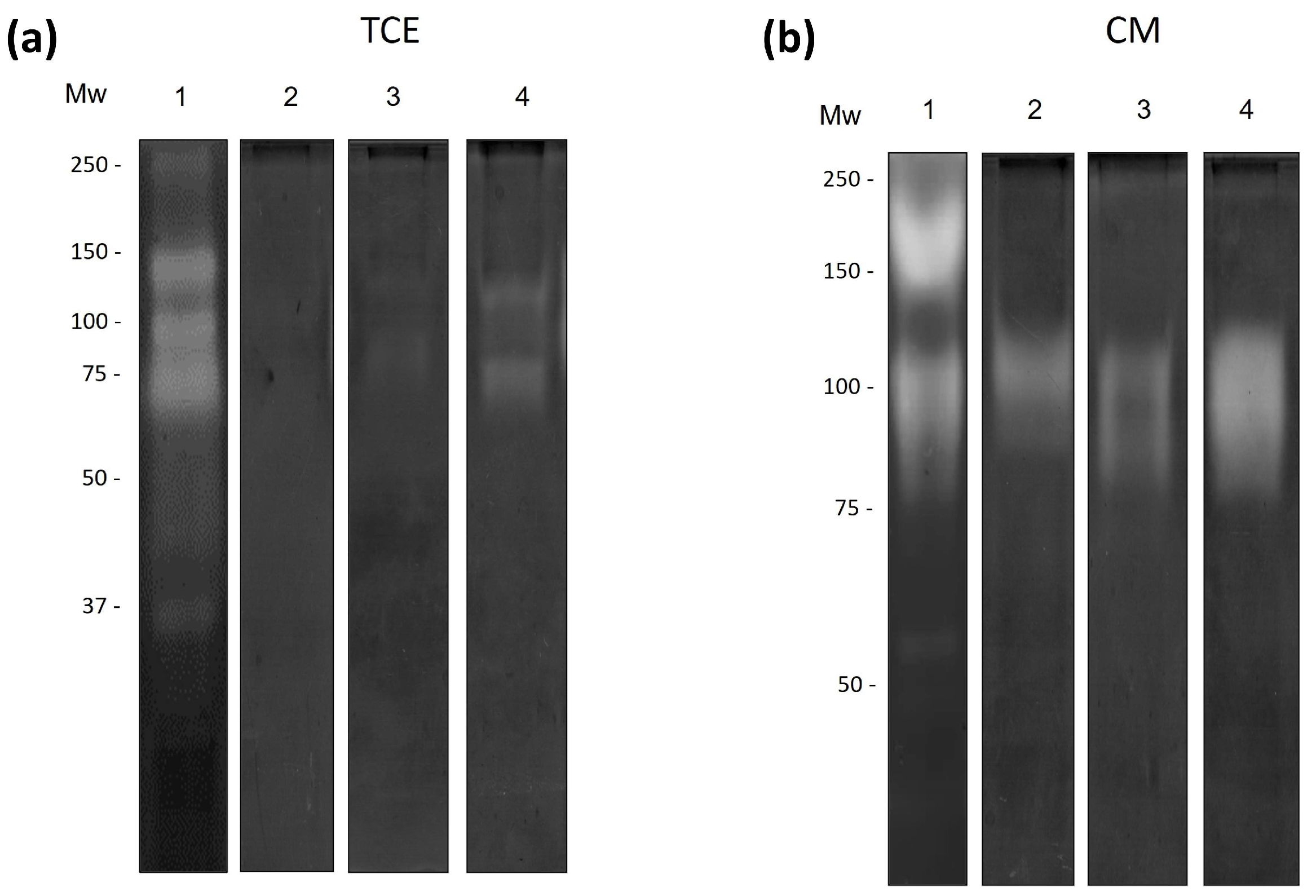
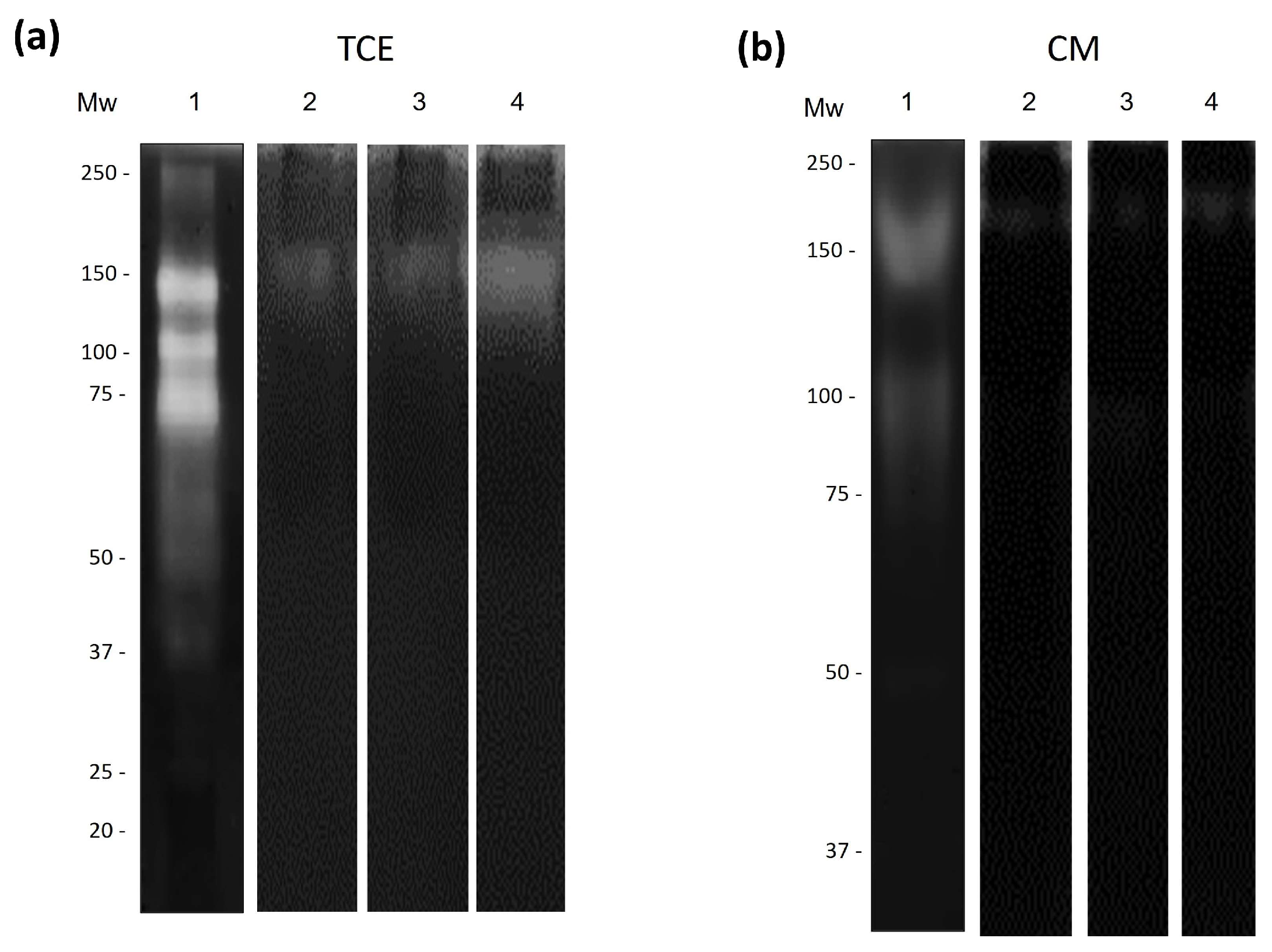
3.4. Regulation of Amoebic Proteases by the Antimicrobial Proteins
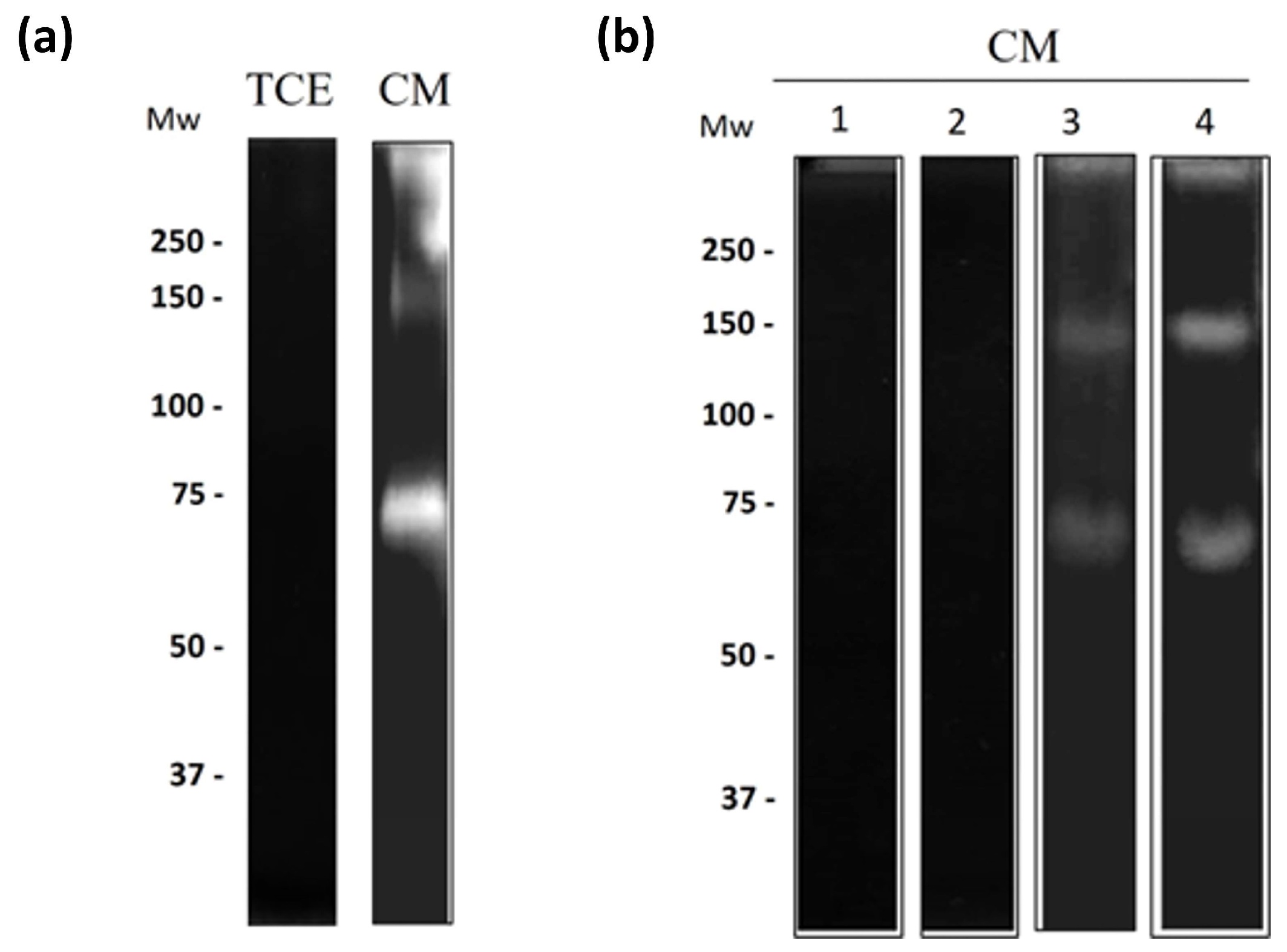
3.5. Cysteine Proteases from N. fowleri Degrade Bovine Lactoferrin
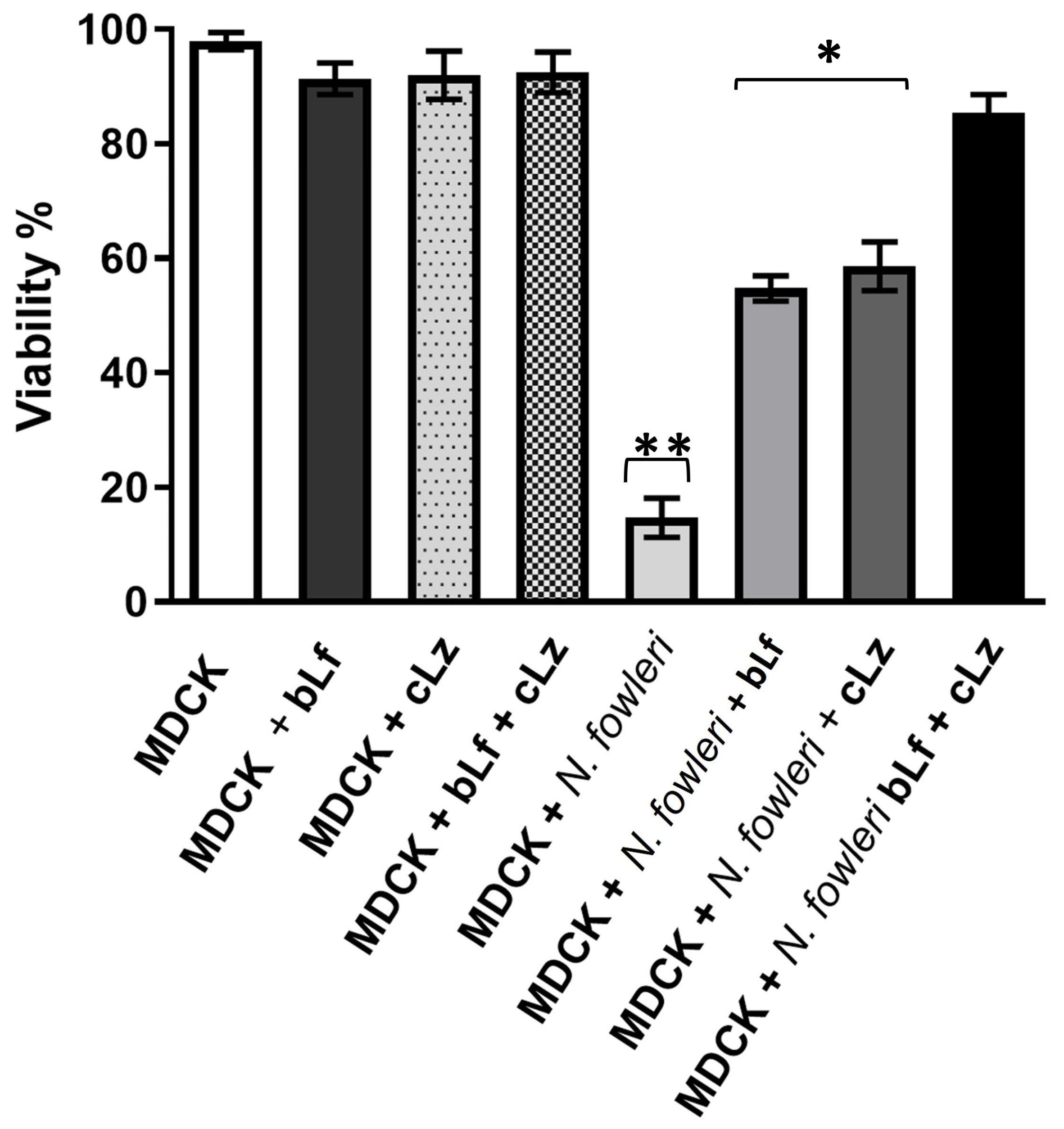
3.6. Inhibition of Cytopathic Effect of N. fowleri by bLf and cLz
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez-Castillo, M.; Cardenas-Zuniga, R.; Coronado-Velazquez, D.; Debnath, A.; Serrano-Luna, J.; Shibayama, M. Naegleria fowleri after 50 years: Is it a neglected pathogen? J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedan, H.; Janosova, V.; Hajtman, A.; Calkovsky, V. Non-Reflex Defense Mechanisms of Upper Airway Mucosa: Possible Clinical Application. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, S55–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quraishi, M.S.; Jones, N.S.; Mason, J. The rheology of nasal mucus: A review. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1998, 23, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, A. Free-living amoebae: Pathogenicity and immunity. Parasite Immunol. 1991, 13, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciano-Cabral, F.; Cabral, G.A. The immune response to Naegleria fowleri amebae and pathogenesis of infection. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 51, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Hernandez, S.; Jarillo-Luna, A.; Rodriguez-Monroy, M.; Moreno-Fierros, L.; Campos-Rodriguez, R. Immunohistochemical characterization of the initial stages of Naegleria fowleri meningoencephalitis in mice. Parasitol. Res. 2004, 94, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanes, P.A.; Wallet, F.; Pringuez, E.; Pernin, P. Assessing the risk of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis from swimming in the presence of environmental Naegleria fowleri. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2927–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerva, L.; Novak, K. Amoebic meningoencephalitis: 16 fatalities. Science 1968, 160, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, K.; Weir, M.H.; Mitchell, J. Development of a dose-response model for Naegleria fowleri. J. Water Health 2019, 17, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowerby, L.J.; Wright, E.D. Tap water or “sterile” water for sinus irrigations: What are our patients using? Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2012, 2, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Actor, J.K.; Hwang, S.A.; Kruzel, M.L. Lactoferrin as a natural immune modulator. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 1956–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drago-Serrano, M.E.; Campos-Rodriguez, R.; Carrero, J.C.; de la Garza, M. Lactoferrin: Balancing Ups and Downs of Inflammation Due to Microbial Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, P.P.; Paz, E.; Conneely, O.M. Multifunctional roles of lactoferrin: A critical overview. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2540–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, R.T., 3rd; Giehl, T.J.; LaForce, F.M. Damage of the outer membrane of enteric gram-negative bacteria by lactoferrin and transferrin. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 2774–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainard, P. Bacteriostatic activity of bovine lactoferrin in mastitic milk. Vet. Microbiol. 1987, 13, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.G.; Gold, M.R.; Hancock, R.E. Interaction of cationic peptides with lipoteichoic acid and gram-positive bacteria. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 6445–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levay, P.F.; Viljoen, M. Lactoferrin: A general review. Haematologica 1995, 80, 252–267. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, A.M.; Dewan, P.; Ganz, T. Innate antimicrobial activity of nasal secretions. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 3267–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragland, S.A.; Criss, A.K. From bacterial killing to immune modulation: Recent insights into the functions of lysozyme. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalfa, V.C.; Spector, S.L.; Ganz, T.; Cole, A.M. Lysozyme levels in the nasal secretions of patients with perennial allergic rhinitis and recurrent sinusitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004, 93, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Sicairos, N.; Lopez-Soto, F.; Reyes-Lopez, M.; Godinez-Vargas, D.; Ordaz-Pichardo, C.; de la Garza, M. Amoebicidal activity of milk, apo-lactoferrin, sIgA and lysozyme. Clin. Med. Res. 2006, 4, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchany, J.M.; Aley, S.B.; Gillin, F.D. Giardicidal activity of lactoferrin and N-terminal peptides. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4550–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Omata, Y.; Saito, A.; Shimazaki, K.; Igarashi, I.; Suzuki, N. Growth inhibitory effects of bovine lactoferrin to Toxoplasma gondii parasites in murine somatic cells. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1996, 58, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiewcharoen, S.; Phurttikul, W.; Rabablert, J.; Auewarakul, P.; Roytrakul, S.; Chetanachan, P.; Atithep, T.; Junnu, V. Effect of synthetic antimicrobial peptides on Naegleria fowleri trophozoites. Southeast. Asian J. Trop. Med. Public. Health 2014, 45, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Luna, J.; Cervantes-Sandoval, I.; Tsutsumi, V.; Shibayama, M. A biochemical comparison of proteases from pathogenic naegleria fowleri and non-pathogenic Naegleria gruberi. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2007, 54, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesner, J.; Vilcinskas, A. Antimicrobial peptides: The ancient arm of the human immune system. Virulence 2010, 1, 440–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrade, F.B.; de Oliveira, J.C.; Yoshie, M.T.; Guimaraes, B.M.; Goncalves, R.B.; Schwarcz, W.D. Antimicrobial activity and synergism of lactoferrin and lysozyme against cariogenic microorganisms. Braz. Dent. J. 2014, 25, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Nakaoka, C.; Hiratani, T.; Abe, S.; Uchida, K.; Yamaguchi, H. Synergy of lysozyme and lanoconazole on the morphology of Candida albicans. J. Electron. Microsc. 2001, 50, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Sandoval, I.; Serrano-Luna Jde, J.; Garcia-Latorre, E.; Tsutsumi, V.; Shibayama, M. Characterization of brain inflammation during primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. Parasitol. Int. 2008, 57, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Sicairos, N.; Reyes-Lopez, M.; Ordaz-Pichardo, C.; de la Garza, M. Microbicidal action of lactoferrin and lactoferricin and their synergistic effect with metronidazole in Entamoeba histolytica. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 84, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsam, S.; Jeong, S.R.; Dudley, R.; Khan, N.A. Role of human tear fluid in Acanthamoeba interactions with the human corneal epithelial cells. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 298, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzitko, K.; Dziadek, B.; Dziadek, J.; Dlugonska, H. Toxoplasma gondii: Inhibition of the intracellular growth by human lactoferrin. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikadai, H.; Tanaka, T.; Shibahara, N.; Tanaka, H.; Matsuu, A.; Kudo, N.; Shimazaki, K.; Igarashi, I.; Oyamada, T. Inhibitory effect of lactoferrin on in vitro growth of Babesia caballi. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leboffe, L.; Giansanti, F.; Antonini, G. Antifungal and Antiparasitic Activities of Lactoferrin. Anti-Infect. Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 8, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguila, A.; Herrera, A.G.; Morrison, D.; Cosgrove, B.; Perojo, A.; Montesinos, I.; Perez, J.; Sierra, G.; Gemmell, C.G.; Brock, J.H. Bacteriostatic activity of human lactoferrin against Staphylococcus aureus is a function of its iron-binding properties and is not influenced by antibiotic resistance. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 31, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.A.; Preston, T.M. Studies of anionic sites on the cell surface of the amoeba Naegleria gruberi using cationized ferritin. J. Cell Sci. 1977, 28, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Samaranayake, Y.H.; Samaranayake, L.P.; Nikawa, H. In vitro susceptibility of Candida species to lactoferrin. Med. Mycol. 1999, 37, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.H.; Sohn, H.J.; Yang, H.J.; Na, B.K.; Chwae, Y.J.; Park, S.; Kim, K.; Shin, H.J. Novel cathepsin B and cathepsin B-like cysteine protease of Naegleria fowleri excretory-secretory proteins and their biochemical properties. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2765–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Castillo, M.; Ramirez-Rico, G.; Serrano-Luna, J.; Shibayama, M. Iron-Binding Protein Degradation by Cysteine Proteases of Naegleria fowleri. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 416712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, I.K.; Jamerson, M.; Cabral, G.A.; Marciano-Cabral, F. Identification of peptidases in highly pathogenic vs. weakly pathogenic Naegleria fowleri amebae. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2015, 62, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alugupalli, K.R.; Kalfas, S. Degradation of lactoferrin by periodontitis-associated bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 145, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, M.; Wakabayashi, H.; Yamauchi, K.; Teraguchi, S.; Hayasawa, H. Bovine lactoferrin and lactoferricin derived from milk: Production and applications. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 80, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hooijdonk, A.C.; Kussendrager, K.D.; Steijns, J.M. In vivo antimicrobial and antiviral activity of components in bovine milk and colostrum involved in non-specific defence. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 84 (Suppl. S1), S127–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedstrom, L.; Lin, T.Y.; Fast, W. Hydrophobic interactions control zymogen activation in the trypsin family of serine proteases. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 4515–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Castillo, M.; Cardenas-Guerra, R.E.; Arroyo, R.; Debnath, A.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Sabanero, M.; Flores-Sanchez, F.; Navarro-Garcia, F.; Serrano-Luna, J.; Shibayama, M. Nf-GH, a glycosidase secreted by Naegleria fowleri, causes mucin degradation: An in vitro and in vivo study. Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 781–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; McKerrow, J.H. Cysteine proteases of parasitic organisms. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2002, 120, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldape, K.; Huizinga, H.; Bouvier, J.; McKerrow, J. Naegleria fowleri: Characterization of a secreted histolytic cysteine protease. Exp. Parasitol. 1994, 78, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, A.; Carter, R.F.; Lopez, A.F.; Rowan-Kelly, B.; Hill, N.L.; Vadas, M.A. Depression of immunity to Naegleria fowleri in mice by selective depletion of neutrophils with a monoclonal antibody. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, M.; Martinez-Castillo, M.; Silva-Olivares, A.; Galindo-Gomez, S.; Navarro-Garcia, F.; Escobar-Herrera, J.; Sabanero, M.; Tsutsumi, V.; Serrano-Luna, J. Disruption of MDCK cell tight junctions by the free-living amoeba Naegleria fowleri. Microbiology 2013, 159, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Soto, F.; Leon-Sicairos, N.; Reyes-Lopez, M.; Serrano-Luna, J.; Ordaz-Pichardo, C.; Pina-Vazquez, C.; Ortiz-Estrada, G.; de la Garza, M. Use and endocytosis of iron-containing proteins by Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Rico, G.; Martinez-Castillo, M.; Cardenas-Zuniga, R.; Coronado-Velazquez, D.; Silva-Olivares, A.; De la Garza, M.; Shibayama, M.; Serrano-Luna, J. Acanthamoeba castellanii Genotype T4: Inhibition of Proteases Activity and Cytopathic Effect by Bovine Apo-Lactoferrin. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado-Velazquez, D.; Silva-Olivares, A.; Castro-Munozledo, F.; Lares-Jimenez, L.F.; Rodriguez-Anaya, L.Z.; Shibayama, M.; Serrano-Luna, J. Acanthamoeba mauritaniensis genotype T4D: An environmental isolate displays pathogenic behavior. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 74, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinez-Castillo, M.; Ramírez-Rico, G.; Shibayama, M.; de la Garza, M.; Serrano-Luna, J. Lactoferrin and Lysozyme Inhibit the Proteolytic Activity and Cytopathic Effect of Naegleria fowleri Enzymes. Pathogens 2024, 13, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13010044
Martinez-Castillo M, Ramírez-Rico G, Shibayama M, de la Garza M, Serrano-Luna J. Lactoferrin and Lysozyme Inhibit the Proteolytic Activity and Cytopathic Effect of Naegleria fowleri Enzymes. Pathogens. 2024; 13(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinez-Castillo, Moises, Gerardo Ramírez-Rico, Mineko Shibayama, Mireya de la Garza, and Jesús Serrano-Luna. 2024. "Lactoferrin and Lysozyme Inhibit the Proteolytic Activity and Cytopathic Effect of Naegleria fowleri Enzymes" Pathogens 13, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13010044
APA StyleMartinez-Castillo, M., Ramírez-Rico, G., Shibayama, M., de la Garza, M., & Serrano-Luna, J. (2024). Lactoferrin and Lysozyme Inhibit the Proteolytic Activity and Cytopathic Effect of Naegleria fowleri Enzymes. Pathogens, 13(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13010044





