A Novel Jeilongvirus from Florida, USA, Has a Broad Host Cell Tropism Including Human and Non-Human Primate Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Source
2.2. Preliminary Virus Isolation Attempt in Vero E6 Cells
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic and Genetic Analyses
2.5. Real-Time RT-PCR Assay
2.6. Host Species Tropism Studies
2.7. Plaque Assays
3. Results
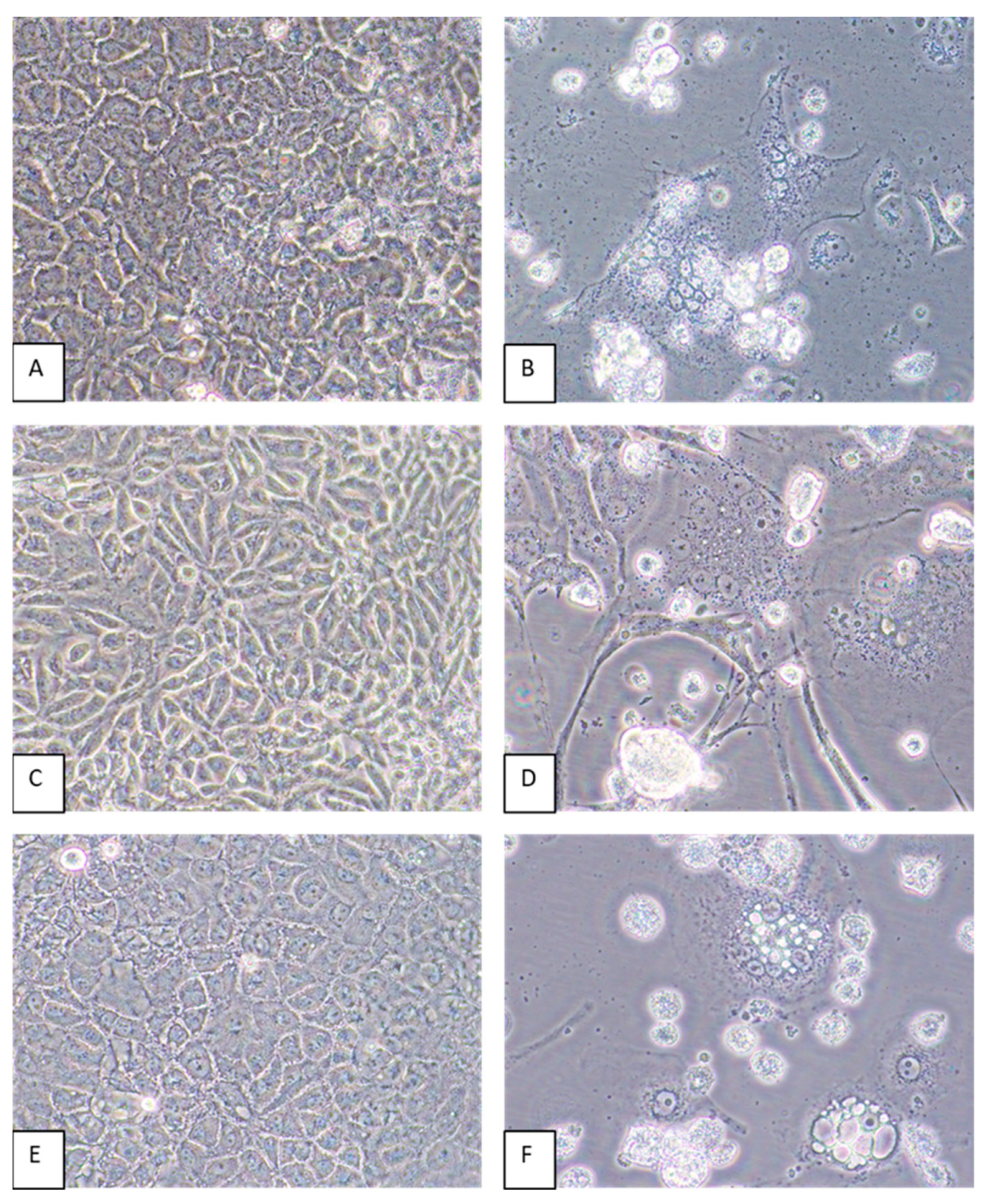
3.1. Initial Isolation of Virus in Vero E6 Cells
3.2. Sequencing Results
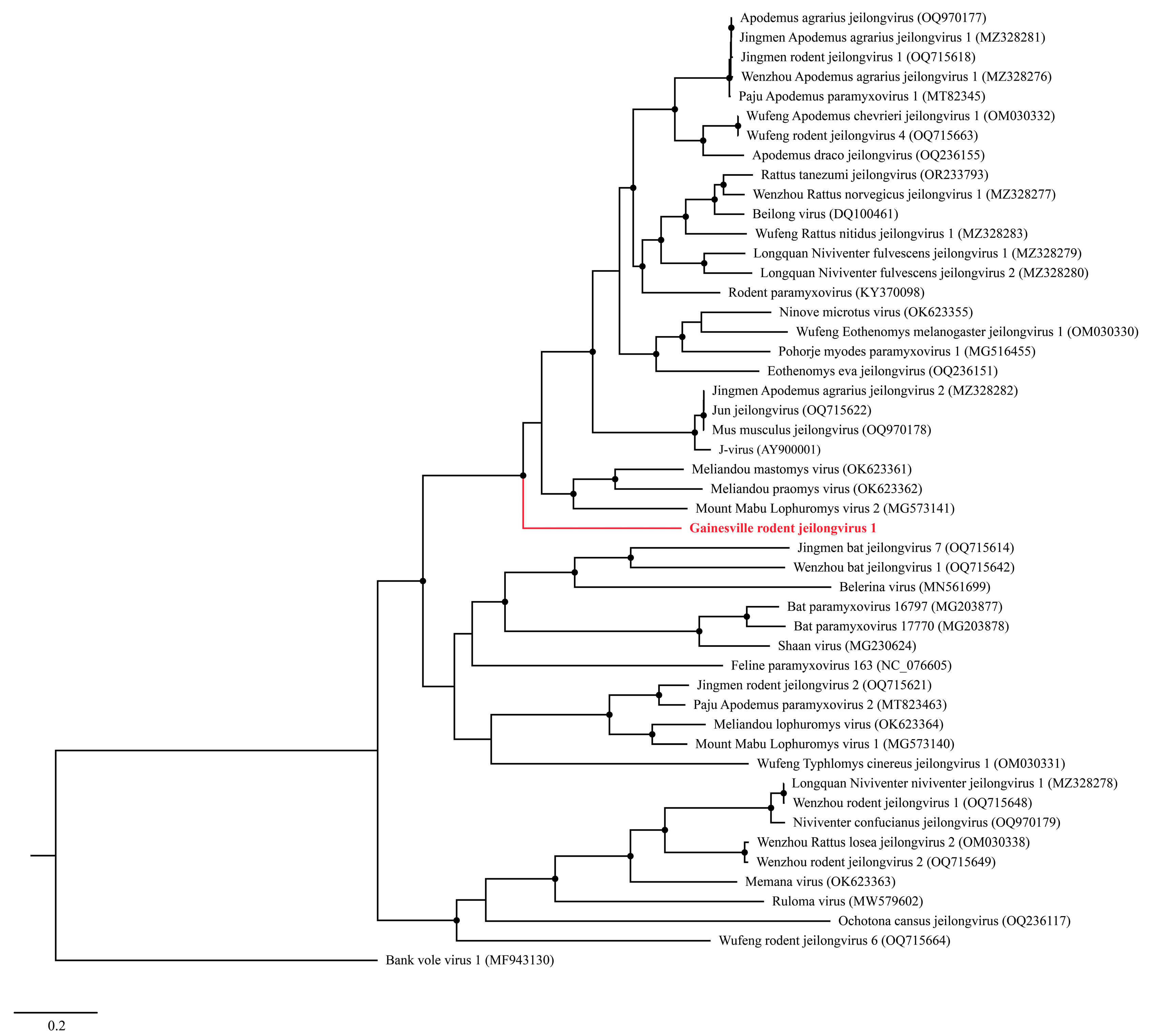
3.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
3.4. Host Cell Tropism and Virus Yields
3.5. rRT-PCR Assay
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B

References
- Vanmechelen, B.; Bletsa, M.; Laenen, L.; Lopes, A.R.; Vergote, V.; Beller, L.; Deboutte, W.; Korva, M.; Avšič Županc, T.; Goüy de Bellocq, J.; et al. Discovery and Genome Characterization of Three New Jeilongviruses, a Lineage of Paramyxoviruses Characterized by Their Unique Membrane Proteins. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, C.J.; Halvorson, D.A.; Newman, J.A.; Senne, D.A. Isolation of Avian Paramyxoviruses from Sentinel Ducks and Turkeys in Minnesota. Avian Dis. 1985, 29, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamendin, K.; Kydyrmanov, A.; Kasymbekov, Y.; Daulbayeva, K.; Khan, E.; Seidalina, A.; Sayatov, M.; Gavrilov, A.; Fereidouni, S. Cormorants as Potential Victims and Reservoirs of Velogenic Newcastle Disease Virus (Orthoavulavirus-1) in Central Asia. Avian Dis. 2019, 63, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.C. The Ecology of Viral Emergence. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2022, 9, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.B.; Gryseels, S.; Otto, H.W.; Worobey, M. Evolution and Diversity of Bat and Rodent Paramyxoviruses from North America. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0109821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rima, B.; Collins, P.; Easton, A.; Fouchier, R.; Kurath, G.; Lamb, R.A.; Lee, B.; Maisner, A.; Rota, P.; Wang, L.-F. Problems of Classification in the Family Paramyxoviridae. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genus: Jeilongvirus|ICTV. Available online: https://ictv.global/report/chapter/paramyxoviridae/paramyxoviridae/jeilongvirus (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Calain, P.; Roux, L. The Rule of Six, a Basic Feature for Efficient Replication of Sendai Virus Defective Interfering RNA. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4822–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rima, B.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; Dundon, W.G.; Duprex, P.; Easton, A.; Fouchier, R.; Kurath, G.; Lamb, R.; Lee, B.; Rota, P.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Paramyxoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1593–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayler, K.A.; Subramaniam, K.; Jacob, J.M.; Loeb, J.C.; Craft, W.F.; Farina, L.L.; Stacy, N.I.; Moussatche, N.; Cook, L.; Lednicky, J.A.; et al. Characterization of Mule Deerpox Virus in Florida White-Tailed Deer Fawns Expands the Known Host and Geographic Range of This Emerging Pathogen. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An Ultra-Fast Single-Node Solution for Large and Complex Metagenomics Assembly via Succinct de Bruijn Graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ORFfinder Home-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- Douglas, J.; Drummond, A.J.; Kingston, R.L. Evolutionary History of Cotranscriptional Editing in the Paramyxoviral Phosphoprotein Gene. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, R.; Kaelin, K.; Baczko, K.; Billeter, M.A. Measles Virus Editing Provides an Additional Cysteine-Rich Protein. Cell 1989, 56, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, R. Different Types of Messenger RNA Editing. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1991, 25, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audsley, M.D.; Marsh, G.A.; Lieu, K.G.; Tachedjian, M.; Joubert, D.A.; Wang, L.-F.; Jans, D.A.; Moseley, G.W. The Immune Evasion Function of J and Beilong Virus V Proteins Is Distinct from That of Other Paramyxoviruses, Consistent with Their Inclusion in the Proposed Genus Jeilongvirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT Online Service: Multiple Sequence Alignment, Interactive Sequence Choice and Visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, M.; Hu, B.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, N.; Wei, J.; Nie, T.; Cai, K.; Zheng, Z. Discovery and Characterization of Novel Jeilongviruses in Wild Rodents from Hubei, China. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Ding, H.; Hu, Z.; Liu, W.; et al. Genetic Diversity and Expanded Host Range of J Paramyxovirus Detected in Wild Small Mammals in China. Viruses 2023, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchipudi, S.V.; Nelli, R.K.; Gontu, A.; Satyakumar, R.; Surendran Nair, M.; Subbiah, M. Sialic Acid Receptors: The Key to Solving the Enigma of Zoonotic Virus Spillover. Viruses 2021, 13, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisfeld, A.J.; Biswas, A.; Guan, L.; Gu, C.; Maemura, T.; Trifkovic, S.; Wang, T.; Babujee, L.; Dahn, R.; Halfmann, P.J.; et al. Pathogenicity and Transmissibility of Bovine H5N1 Influenza Virus. Nature 2024, 633, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Oligonucleotide ID | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| RodparamyxF | CCT CCA TGG TTT GGA ACA CAT GCC |
| RodparamyxP | 6-FAM-CCT GGG GGA GGG ATC AGG GGC AAT GC-BHQ-1 |
| RodparamyxR | GCC TCA GAA GGG TAG ACA TGG TG |
| Gene | Length (Ribonucleotides) | Genomic Positions | Gene Product | Amino Acid Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leader sequence | 93 | 1–3 | N/A a | N/A |
| N | 1647 | 31–1677 | Nucleocapsid protein | 548 |
| TIS b | 3 | 1774–1776 | N/A | N/A |
| P | 1470 | 1863–3332 | Phosphoprotein | 489 |
| P/V/C editing site | 16 | 2551–2566 | N/A | N/A |
| V | 894 c | 1863–2755 | V protein | 298 |
| C | 456 | 1906–2364 | C protein | 152 |
| W | 924 d | 1863–2784 | W protein | 308 |
| TIS | 3 | 3509–3511 | N/A | N/A |
| M | 1017 | 3550–4566 | Matrix protein | 339 |
| TIS | 3 | 4829–4831 | N/A | N/A |
| F | 1641 | 4975–6615 | Fusion protein | 546 |
| TIS | 3 | 6631–6633 | N/A | N/A |
| tM | 777 | 6745–7521 | Transmembrane protein | 258 |
| TIS | 3 | 7701–7703 | N/A | N/A |
| RBP | 2352 | 7753–10,104 | Receptor-binding protein | 783 |
| TIS | 3 | 10,290–10,292 | N/A | N/A |
| L; RdRp | 6759 | 10,363–16,941 | Large; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | 2192 |
| Trailer sequence | 530 | 16,492–17,021 | N/A | N/A |
| Cell Line | Virus Titer, Log10PFU/mL * |
|---|---|
| A549 | 5.3 ± 0.3 |
| BHK-21 | 5.9 ± 0.4 |
| Caco-2 | 5.3 ± 0.7 |
| CV-1 | 6.8 ± 0.1 |
| HeLa | 4.6 ± 0.7 |
| LLC-MK2 | 7.1 ± 0.1 |
| MDCK | 4.0 ± 0.3 |
| MRC-5 | 6.4 ± 0.7 |
| Neuro-2a | 3.5 ± 1.5 |
| OHH1k | 2.9 ± 0.1 |
| SAEC | 6.0 ± 0.6 |
| Vero E6 | 7.2 ± 0.3 |
| Tb1Lu | 2.6 ± 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
DeRuyter, E.; Subramaniam, K.; Wisely, S.M.; Morris, J.G., Jr.; Lednicky, J.A. A Novel Jeilongvirus from Florida, USA, Has a Broad Host Cell Tropism Including Human and Non-Human Primate Cells. Pathogens 2024, 13, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100831
DeRuyter E, Subramaniam K, Wisely SM, Morris JG Jr., Lednicky JA. A Novel Jeilongvirus from Florida, USA, Has a Broad Host Cell Tropism Including Human and Non-Human Primate Cells. Pathogens. 2024; 13(10):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100831
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeRuyter, Emily, Kuttichantran Subramaniam, Samantha M. Wisely, J. Glenn Morris, Jr., and John A. Lednicky. 2024. "A Novel Jeilongvirus from Florida, USA, Has a Broad Host Cell Tropism Including Human and Non-Human Primate Cells" Pathogens 13, no. 10: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100831
APA StyleDeRuyter, E., Subramaniam, K., Wisely, S. M., Morris, J. G., Jr., & Lednicky, J. A. (2024). A Novel Jeilongvirus from Florida, USA, Has a Broad Host Cell Tropism Including Human and Non-Human Primate Cells. Pathogens, 13(10), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13100831







