Contribution of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies to the Understanding of Cerebral Malaria Pathogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Murine Model of CM
3. MRI and MRS Findings in ECM
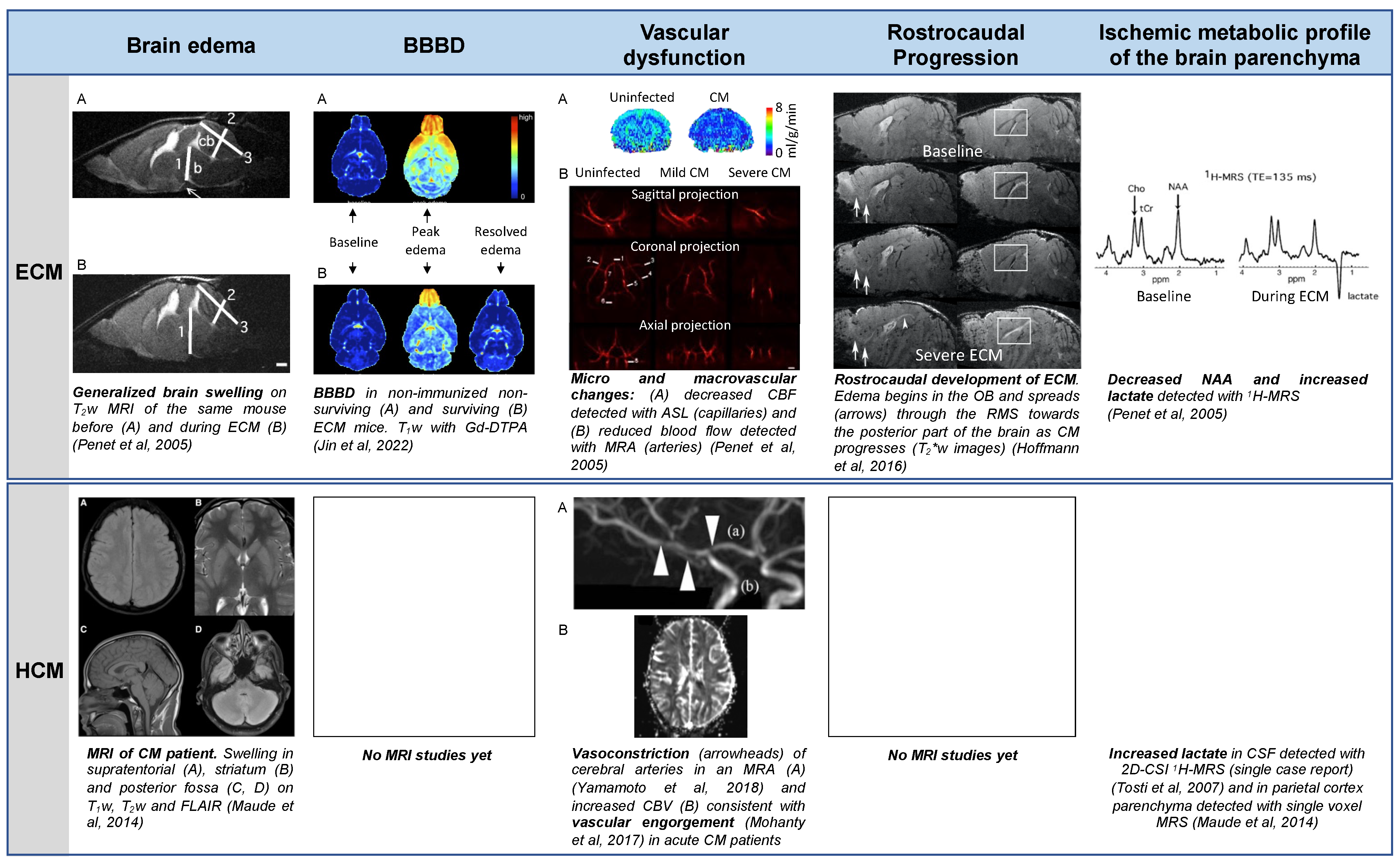
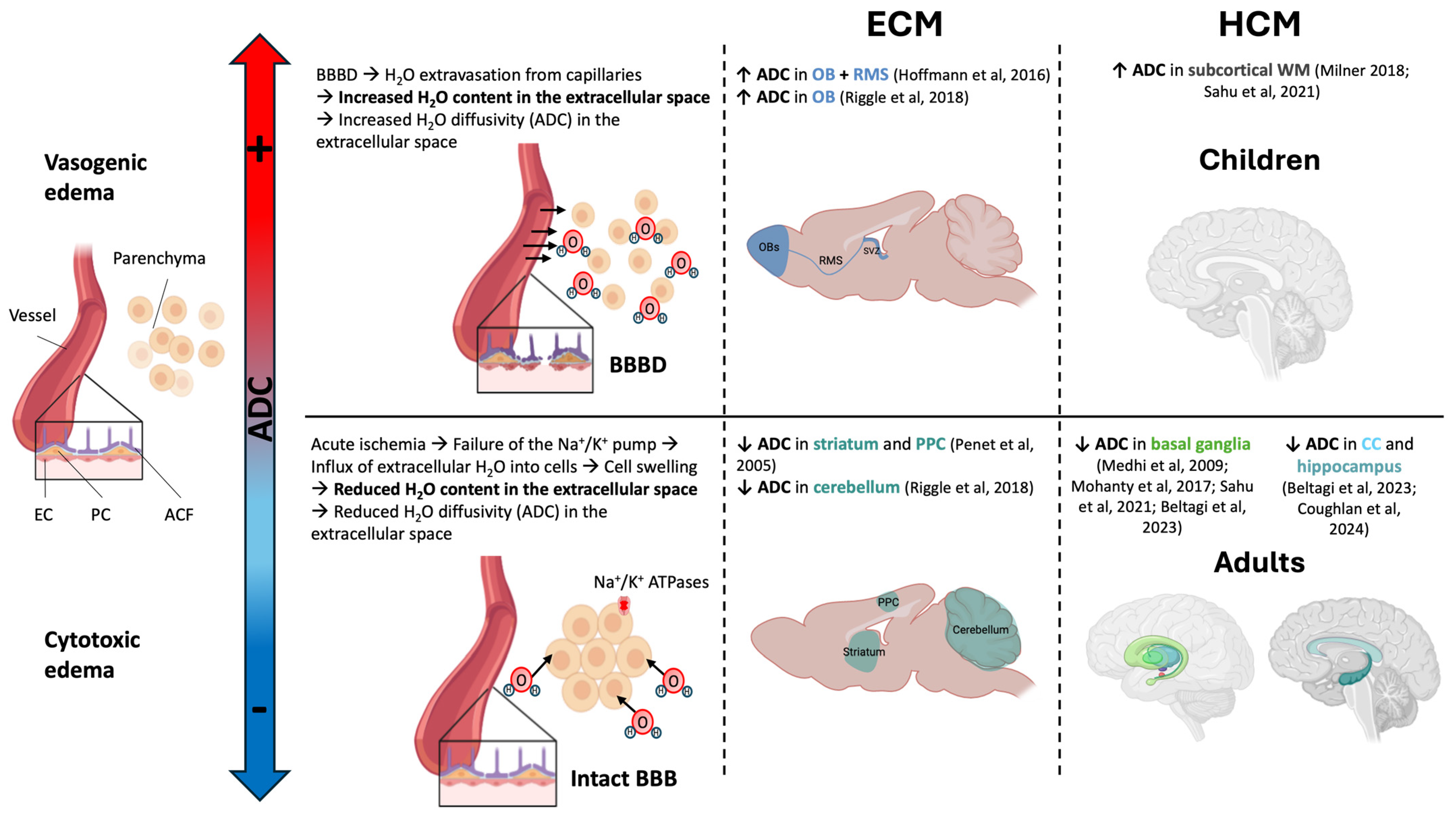
3.1. Brain Edema
3.2. Blood Brain Barrier Disruption
3.3. Vascular Dysfunction
3.4. Spatiotemporal Development of the Disease
3.5. Metabolic Changes
4. Relevance of ECM and MRI/MRS Method
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACF | Astrocyte endfeet. |
| ADC | Apparent diffusion coefficient (of water). |
| ASL | Arterial spin labeling (perfusion MRI method without contrast agent injection). |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate. |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier. |
| BBBD | Blood–brain barrier disruption. |
| CBF | Cerebral blood flow. |
| CC | Corpus callosum. |
| Cho | Choline-containing compounds. |
| CM | Cerebral malaria. |
| Cr | Creatine + phosphocreatine. |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid. |
| 2D-CSI | Two-dimensional chemical shift imaging (method combining MRI and MRS). |
| DMS | Dorsal migratory stream. |
| DWI | Diffusion weighted imaging. |
| EC | Endothelial cell. |
| ECM | Experimental cerebral malaria. |
| FLAIR | Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (pulse sequence enabling the suppression of the signal from liquids such as CSF in brain). |
| GBCA | Gadolinium-based contrast agents. |
| Gd-DTPA | Gadopentetic acid (contrast agent). |
| Glx | Glutamine + glutamate. |
| GM | Gray matter. |
| MRA | Magnetic resonance angiography. |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging. |
| MRS | Magnetic resonance spectroscopy. |
| NAA | N-acetylaspartate. |
| OB | Olfactory bulb. |
| PbA | Plasmodium berghei ANKA. |
| PC | Pericyte. |
| PCr | Phosphocreatine. |
| PPC | Posterior parietal cortex. |
| ppm | Parts per million. |
| pRBC | Parasitized red blood cell. |
| RMS | Rostral migration stream. |
| TE | Time of echo (one of the basic MRI/MRS pulse sequence parameters). |
| T1w | T1-weighted MRI. |
| T2w | T2-weighted MRI. |
| T2*w | T2*-weighted MRI. |
| SVZ | Subventricular zone. |
| WM | White matter. |
References
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2023; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Hoffmann, A.; Pfeil, J.; Mueller, A.-K.; Jin, J.; Deumelandt, K.; Helluy, X.; Wang, C.; Heiland, S.; Platten, M.; Chen, J.W.; et al. MRI of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Myeloperoxidase Activity Links Inflammation to Brain Edema in Experimental Cerebral Malaria. Radiology 2019, 290, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Severe Malaria: WHO. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2014, 19, 7–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht-Schgoer, K.; Lackner, P.; Schmutzhard, E.; Baier, G. Cerebral Malaria: Current Clinical and Immunological Aspects. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 863568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idro, R.; Otieno, G.; White, S.; Kahindi, A.; Fegan, G.; Ogutu, B.; Mithwani, S.; Maitland, K.; Neville, B.G.; Newton, C.R. Decorticate, Decerebrate and Opisthotonic Posturing and Seizures in Kenyan Children with Cerebral Malaria. Malar. J. 2005, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idro, R.; Jenkins, N.E.; Newton, C.R. Pathogenesis, Clinical Features, and Neurological Outcome of Cerebral Malaria. Lancet Neurol. 2005, 4, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydel, K.B.; Kampondeni, S.D.; Valim, C.; Potchen, M.J.; Milner, D.A.; Muwalo, F.W.; Birbeck, G.L.; Bradley, W.G.; Fox, L.L.; Glover, S.J.; et al. Brain Swelling and Death in Children with Cerebral Malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idro, R.; Marsh, K.; John, C.C.; Newton, C.R.J. Cerebral Malaria: Mechanisms of Brain Injury and Strategies for Improved Neurocognitive Outcome. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 68, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, M.; Elphinstone, R.E.; Conroy, A.L.; Kain, K.C. Contrasting Pediatric and Adult Cerebral Malaria: The Role of the Endothelial Barrier. Virulence 2013, 4, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochman, S.E.; Madaline, T.F.; Wassmer, S.C.; Mbale, E.; Choi, N.; Seydel, K.B.; Whitten, R.O.; Varughese, J.; Grau, G.E.R.; Kamiza, S.; et al. Fatal Pediatric Cerebral Malaria Is Associated with Intravascular Monocytes and Platelets That Are Increased with HIV Coinfection. mBio 2015, 6, e01390-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.T.; Hollingsworth, T.D.; Reyburn, H.; Drakeley, C.J.; Riley, E.M.; Ghani, A.C. Gradual Acquisition of Immunity to Severe Malaria with Increasing Exposure. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20142657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.; Driss, A.; Solomon, W.; Dickinson-Copeland, C.; Salifu, H.; Jain, V.; Singh, N.; Stiles, J. CXCL10 Gene Promoter Polymorphism -1447A>G Correlates with Plasma CXCL10 Levels and Is Associated with Male Susceptibility to Cerebral Malaria. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggle, B.A.; Sinharay, S.; Schreiber-Stainthorp, W.; Munasinghe, J.P.; Maric, D.; Prchalova, E.; Slusher, B.S.; Powell, J.D.; Miller, L.H.; Pierce, S.K.; et al. MRI Demonstrates Glutamine Antagonist-Mediated Reversal of Cerebral Malaria Pathology in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E12024–E12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varo, R.; Crowley, V.M.; Sitoe, A.; Madrid, L.; Serghides, L.; Kain, K.C.; Bassat, Q. Adjunctive Therapy for Severe Malaria: A Review and Critical Appraisal. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Patnaik, R.; Dutt, A.K.; Pradhan, S.; Das, B.; Patnaik, J.; Mohanty, A.K.; Lee, S.J.; Dondorp, A.M. Brain Swelling and Mannitol Therapy in Adult Cerebral Malaria: A Randomized Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Anbalagan, L.C.; Pannu, A.K. Towards Eradication of Malaria: Is the WHO’s RTS,S/AS01 Vaccination Effective Enough? Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2021, 14, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RTS,S Clinical Trials Partnership. Efficacy and Safety of RTS,S/AS01 Malaria Vaccine with or without a Booster Dose in Infants and Children in Africa: Final Results of a Phase 3, Individually Randomised, Controlled Trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datoo, M.S.; Dicko, A.; Tinto, H.; Ouédraogo, J.-B.; Hamaluba, M.; Olotu, A.; Beaumont, E.; Ramos Lopez, F.; Natama, H.M.; Weston, S.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Malaria Vaccine Candidate R21/Matrix-M in African Children: A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2024, 403, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rénia, L.; Howland, S.W.; Claser, C.; Charlotte Gruner, A.; Suwanarusk, R.; Hui Teo, T.; Russell, B.; Ng, L.F.P. Cerebral Malaria: Mysteries at the Blood-Brain Barrier. Virulence 2012, 3, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmer, S.C.; Taylor, T.; Maclennan, C.A.; Kanjala, M.; Mukaka, M.; Molyneux, M.E.; Grau, G.E. Platelet-Induced Clumping of Plasmodium Falciparum-Infected Erythrocytes from Malawian Patients with Cerebral Malaria-Possible Modulation in Vivo by Thrombocytopenia. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierro, F.; Grau, G.E.R. The Ins and Outs of Cerebral Malaria Pathogenesis: Immunopathology, Extracellular Vesicles, Immunometabolism, and Trained Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, C.N.; Aggrey, A.A.; Chapman, L.M.; Modjeski, K.L. Emerging Roles for Platelets as Immune and Inflammatory Cells. Blood 2014, 123, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, N.H.; Ball, H.J.; Hansen, A.M.; Khaw, L.T.; Guo, J.; Bakmiwewa, S.; Mitchell, A.J.; Combes, V.; Grau, G.E.R. Cerebral Malaria: Gamma-Interferon Redux. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, S.N.; Deshmukh, R.; Trivedi, V. Severe Malaria: Biology, Clinical Manifestation, Pathogenesis and Consequences. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2020, 57, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armah, H.; Dodoo, A.K.; Wiredu, E.K.; Stiles, J.K.; Adjei, A.A.; Gyasi, R.K.; Tettey, Y. High-Level Cerebellar Expression of Cytokines and Adhesion Molecules in Fatal, Paediatric, Cerebral Malaria. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2005, 99, 629–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, T.F.; Karnad, D.R.; Shetty, P.G.; Desai, A.P.; Prasad, S.R. Adult Cerebral Malaria: Prognostic Importance of Imaging Findings and Correlation with Postmortem Findings. Radiology 2002, 224, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potchen, M.J.; Kampondeni, S.D.; Seydel, K.B.; Birbeck, G.L.; Hammond, C.A.; Bradley, W.G.; DeMarco, J.K.; Glover, S.J.; Ugorji, J.O.; Latourette, M.T.; et al. Acute Brain MRI Findings in 120 Malawian Children with Cerebral Malaria: New Insights into an Ancient Disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maude, R.J.; Barkhof, F.; Hassan, M.U.; Ghose, A.; Hossain, A.; Abul Faiz, M.; Choudhury, E.; Rashid, R.; Sayeed, A.A.; Charunwatthana, P.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain in Adults with Severe Falciparum Malaria. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potchen, M.J.; Kampondeni, S.D.; Seydel, K.B.; Haacke, E.M.; Sinyangwe, S.S.; Mwenechanya, M.; Glover, S.J.; Milner, D.A.; Zeli, E.; Hammond, C.A.; et al. 1.5 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Investigate Potential Etiologies of Brain Swelling in Pediatric Cerebral Malaria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, U. Magnetic Resonance Features of Cerebral Malaria. Acta Radiol. 2008, 49, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampondeni, S.D.; Potchen, M.J.; Beare, N.A.V.; Seydel, K.B.; Glover, S.J.; Taylor, T.E.; Birbeck, G.L. MRI Findings in a Cohort of Brain Injured Survivors of Pediatric Cerebral Malaria. Am. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhi, N.; Das, S.B.; Das, R.R.; Medhi, S.; Sarma, P.; Duwara, R.; Das, P.; Saikia, R. MRI Findings of Cerebral Malaria: A Report of Two Cases. Neuroradiol. J. 2009, 22, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasalkar, D.D.; Paunipagar, B.K.; Sanghvi, D.; Sonawane, B.D.; Loniker, P. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cerebral Malaria: A Report of Four Cases. Br. J. Radiol. 2011, 84, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosti, C.L.; Petersen, E.T.; Laothamatas, J.; Golay, X.; Swaminathan, S.V.; Cauteren, M.V.; Murdoch, J.; Lekprasert, V.; Tangpukdee, N.; Krudsood, S.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Lactate in P. Falciparum Malaria: Measurement by Chemical Shift Imaging at 3 Tesla. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 2007, 15, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, D.J.; Lucas, T.C.D.; Nguyen, M.; Nandi, A.K.; Bisanzio, D.; Battle, K.E.; Cameron, E.; Twohig, K.A.; Pfeffer, D.A.; Rozier, J.A.; et al. Mapping the Global Prevalence, Incidence, and Mortality of Plasmodium Falciparum, 2000–2017: A Spatial and Temporal Modelling Study. Lancet 2019, 394, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanfari, N.; Mueller, S.N.; Heath, W.R. Cerebral Malaria in Mouse and Man. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.B.; Hafalla, J.C.R.; Riley, E.M.; Couper, K.N. Cerebral Malaria: Why Experimental Murine Models Are Required to Understand the Pathogenesis of Disease. Parasitology 2010, 137, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, N.H.; Grau, G.E. Cytokines: Accelerators and Brakes in the Pathogenesis of Cerebral Malaria. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penet, M.-F.; Viola, A.; Confort-Gouny, S.; Le Fur, Y.; Duhamel, G.; Kober, F.; Ibarrola, D.; Izquierdo, M.; Coltel, N.; Gharib, B.; et al. Imaging Experimental Cerebral Malaria In Vivo: Significant Role of Ischemic Brain Edema. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 7352–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postels, D.G.; Li, C.; Birbeck, G.L.; Taylor, T.E.; Seydel, K.B.; Kampondeni, S.D.; Glover, S.J.; Potchen, M.J. Brain MRI of Children with Retinopathy-Negative Cerebral Malaria. Am. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Ba, M.A.; Wai, C.H.; Mohanty, S.; Sahu, P.K.; Pattnaik, R.; Pirpamer, L.; Fischer, M.; Heiland, S.; Lanzer, M.; et al. Transcellular Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in Malaria-Induced Reversible Brain Edema. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202201402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.; Pfeil, J.; Alfonso, J.; Kurz, F.T.; Sahm, F.; Heiland, S.; Monyer, H.; Bendszus, M.; Mueller, A.-K.; Helluy, X.; et al. Experimental Cerebral Malaria Spreads along the Rostral Migratory Stream. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Kato, Y.; Shinohara, K.; Kutsuna, S.; Takeshita, N.; Hayakawa, K.; Iwagami, M.; Kano, S.; Watanabe, S.; Ohmagari, N. Case Report: Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome in Cerebral Malaria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.; Benjamin, L.A.; Majhi, M.; Panda, P.; Kampondeni, S.; Sahu, P.K.; Mohanty, A.; Mahanta, K.C.; Pattnaik, R.; Mohanty, R.R.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Cerebral Malaria Patients Reveals Distinct Pathogenetic Processes in Different Parts of the Brain. mSphere 2017, 2, e00193-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmer, L.; Martins, Y.C.; Zanini, G.M.; Frangos, J.A.; Carvalho, L.J.M. Artemether and Artesunate Show the Highest Efficacies in Rescuing Mice with Late-Stage Cerebral Malaria and Rapidly Decrease Leukocyte Accumulation in the Brain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Singh, P.; Kar, S.K. An Overview of Cerebral Malaria: Lessons Learnt from Observations in Humans and Experimental Models. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2021, 35, 27276–27284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, S.; Sugiyama, M. Imaging Analysis of the Brain in a Primate Model of Cerebral Malaria. Acta Trop. 2010, 114, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopp, S.E.R.; Ramachandran, V.; Henson, K.; Luzader, A.; Lindstrom, M.; Spooner, M.; Steffy, B.M.; Suzuki, O.; Janse, C.; Waters, A.P.; et al. Genome Wide Analysis of Inbred Mouse Lines Identifies a Locus Containing Ppar-γ as Contributing to Enhanced Malaria Survival. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Lucas, R.; Grau, G.E. Pathogenesis of Cerebral Malaria: Recent Experimental Data and Possible Applications for Humans. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, V.; Souza, J.B.D.; Rénia, L.; Hunt, N.H.; Grau, G.E. Cerebral Malaria: Which Parasite? Which Model? Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2005, 2, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, L.M.; Amante, F.H.; McSweeney, K.A.; Zhou, Y.; Stanley, A.C.; Haque, A.; Jones, M.K.; Hill, G.R.; Boyle, G.M.; Engwerda, C.R. Common Strategies to Prevent and Modulate Experimental Cerebral Malaria in Mouse Strains with Different Susceptibilities. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 3312–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Liu, J.; Pan, Y.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-J.; Shang, H.; Cao, Y.-M. Age-Related CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Regulatory T-Cell Responses during Plasmodium Berghei ANKA Infection in Mice Susceptible or Resistant to Cerebral Malaria. Korean J. Parasitol. 2013, 51, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legorreta-Herrera, M.; Nava-Castro, K.E.; Palacios-Arreola, M.I.; Hernández-Cervantes, R.; Aguilar-Castro, J.; Cervantes-Candelas, L.A.; Morales-Montor, J. Sex-Associated Differential mRNA Expression of Cytokines and Its Regulation by Sex Steroids in Different Brain Regions in a Plasmodium Berghei ANKA Model of Cerebral Malaria. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, M.M.; Gros, P.; Olivier, M.; Fortin, A.; Serghides, L. Cerebral Malaria: Human versus Mouse Studies. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 274–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, D.S.; Bernard, N.J.; Nie, C.Q.; Schofield, L. NK Cells Stimulate Recruitment of CXCR3 + T Cells to the Brain during Plasmodium Berghei -Mediated Cerebral Malaria. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5779–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belnoue, E.; Potter, S.M.; Rosa, D.S.; Mauduit, M.; Grüner, A.C.; Kayibanda, M.; Mitchell, A.J.; Hunt, N.H.; Rénia, L. Control of Pathogenic CD8+ T Cell Migration to the Brain by IFN-γ during Experimental Cerebral Malaria. Parasite Immunol. 2008, 30, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.R.; Heyde, H.C.V.D.; Sun, G.; Specian, R.D.; Granger, D.N. Regulation of Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Expression in an Experimental Model of Cerebral Malaria. Microcirculation 2002, 9, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.; Rogerson, S.; Taylor, T.; Tembo, M.; Mwenechanya, J.; Molyneux, M.; Turner, G. Blood-Brain Barrier Function in Cerebral Malaria in Malawian Children. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 64, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, P.A.; Hart, G.T.; Russo, M.V.; Nayak, D.; Yazew, T.; Peña, M.; Khan, S.M.; Janse, C.J.; Pierce, S.K.; McGavern, D.B. CD8+ T Cells Induce Fatal Brainstem Pathology during Cerebral Malaria via Luminal Antigen-Specific Engagement of Brain Vasculature. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1006022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, N.H.; Grau, G.E.; Engwerda, C.; Barnum, S.R.; van der Heyde, H.; Hansen, D.S.; Schofield, L.; Golenser, J. Murine Cerebral Malaria: The Whole Story. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, G.E.; Tacchini-Cottier, F.; Vesin, C.; Milon, G.; Lou, J.N.; Piguet, P.F.; Juillard, P. TNF-Induced Microvascular Pathology: Active Role for Platelets and Importance of the LFA-1/ICAM-1 Interaction. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 1993, 4, 415–419. [Google Scholar]
- Rénia, L.; Grüner, A.C.; Snounou, G. Cerebral Malaria: In Praise of Epistemes. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassmer, S.C.; Combes, V.; Candal, F.J.; Juhan-Vague, I.; Grau, G.E. Platelets Potentiate Brain Endothelial Alterations Induced by Plasmodium Falciparum. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassmer, S.C.; Combes, V.; Grau, G.E.R. Platelets and Microparticles in Cerebral Malaria: The Unusual Suspects. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2011, 8, e15–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strangward, P.; Haley, M.J.; Shaw, T.N.; Schwartz, J.-M.; Greig, R.; Mironov, A.; de Souza, J.B.; Cruickshank, S.M.; Craig, A.G.; Milner, D.A.; et al. A Quantitative Brain Map of Experimental Cerebral Malaria Pathology. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, J.; Rayment, N.; Landon, D.N.; Katz, D.R.; de Souza, J.B. de Immunopathology of Cerebral Malaria: Morphological Evidence of Parasite Sequestration in Murine Brain Microvasculature. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 5364–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggu, R.; Faille, D.; Grau, G.E.; Cozzone, P.J.; Viola, A. In the Eye of Experimental Cerebral Malaria. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von zur Muhlen, C.; Sibson, N.R.; Peter, K.; Campbell, S.J.; Wilainam, P.; Grau, G.E.; Bode, C.; Choudhury, R.P.; Anthony, D.C. A Contrast Agent Recognizing Activated Platelets Reveals Murine Cerebral Malaria Pathology Undetectable by Conventional MRI. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Aoshi, T.; Kawai, S.; Mori, Y.; Konishi, A.; Ozkan, M.; Fujita, Y.; Haseda, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Kohyama, M.; et al. Olfactory Plays a Key Role in Spatiotemporal Pathogenesis of Cerebral Malaria. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennan, R.P.; Machado, F.S.; Lee, S.C.; Desruisseaux, M.S.; Wittner, M.; Tsuji, M.; Tanowitz, H.B. Reduced Cerebral Blood Flow and N-Acetyl Aspartate in a Murine Model of Cerebral Malaria. Parasitol. Res. 2005, 96, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.K.; Hoffmann, A.; Majhi, M.; Pattnaik, R.; Patterson, C.; Mahanta, K.C.; Mohanty, A.K.; Mohanty, R.R.; Joshi, S.; Mohanty, A.; et al. Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Reveals Different Courses of Disease in Pediatric and Adult Cerebral Malaria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e2387–e2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looareesuwan, S.; Wilairatana, P.; Krishna, S.; Kendall, B.; Vannaphan, S.; Viravan, C.; White, N.J. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain in Patients with Cerebral Malaria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 21, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfitt, J.T.; McDermott, M.P.; Brim, R.; Mboma, S.; Potchen, M.J.; Kampondeni, S.D.; Seydel, K.B.; Semrud-Clikeman, M.; Taylor, T.E. Neurodevelopmental Impairments 1 Year After Cerebral Malaria. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20181026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltagi, A.E.; Elsotouhy, A.; Al-Warqi, A.; Aker, L.; Ahmed, M. Imaging Features of Fulminant Cerebral Malaria: A Case Report. Radiol. Case Rep. 2023, 18, 3642–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, S.M.; Birbeck, G.L.; Taylor, T.E.; Seydel, K.B.; Kampondeni, S.D.; Potchen, M.J. Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in a Prospective Cohort of Children with Cerebral Malaria Offers Insights into Pathophysiology and Prognosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, C.; Jäger, H.R.; Brealey, D.; Carletti, F.; Hyare, H.; Pattnaik, R.; Sahu, P.K.; Mohanty, S.; Logan, S.; Hoffmann, A.; et al. Adult Cerebral Malaria: Acute and Subacute Imaging Findings, Long-Term Clinical Consequences. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 78, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.; Silva, T.M.; Conceição, C.; Vieira, J.P.; Gouveia, C.; Varandas, L. Cerebral Malaria and Cytotoxic Lesions of the Corpus Callosum. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 42, e358–e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoliani, Y.-S.; Sarrazin, J.-L.; Felten, D.; Caumes, E.; Leveque, C.; Fisch, A. MR of Cerebral Malaria. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1998, 19, 871–874. [Google Scholar]
- Brim, R.; Mboma, S.; Semrud-Clikeman, M.; Kampondeni, S.; Magen, J.; Taylor, T.; Langfitt, J. Cognitive Outcomes and Psychiatric Symptoms of Retinopathy-Positive Cerebral Malaria: Cohort Description and Baseline Results. Am. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, O.; Barest, G.D. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Cerebral Malaria. J. Neuroimaging 2005, 15, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmer, S.C.; Grau, G.E.R. Severe Malaria: What’s New on the Pathogenesis Front? Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, M.-C.; Waiczies, S.; Niendorf, T.; Pohlmann, A. Assessment of Blood Brain Barrier Leakage with Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1718, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, C.; DeAguero, J.; Brearley, A.; Trejo, X.; Howard, T.; Escobar, G.P.; Wagner, B. Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent Use, Their Safety, and Practice Evolution. Kidney360 2020, 1, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunon-Ortiz, A.; Lamb, T.J. Blood Brain Barrier Disruption in Cerebral Malaria: Beyond Endothelial Cell Activation. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.; Hien, T.T.; Day, N.; Mai, N.T.; Chuong, L.V.; Chau, T.T.; Loc, P.P.; Phu, N.H.; Bethell, D.; Farrar, J.; et al. Evidence of Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Human Cerebral Malaria. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1999, 25, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, M.P.; Agalliu, D.; Cutforth, T. Hello from the Other Side: How Autoantibodies Circumvent the Blood–Brain Barrier in Autoimmune Encephalitis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanni, L.A.; Rae, C.; Maitland, A.; Stocker, R.; Hunt, N.H. Is Ischemia Involved in the Pathogenesis of Murine Cerebral Malaria? Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawat, H.M.; Sharma, S. Host Responses in Malaria Disease Evaluated Through Nuclear Magnetic Resonance–Based Metabonomics. Clin. Lab. Med. 2012, 32, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penet, M.-F.; Kober, F.; Confort-Gouny, S.; Le Fur, Y.; Dalmasso, C.; Coltel, N.; Liprandi, A.; Gulian, J.-M.; Grau, G.E.; Cozzone, P.J.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Reveals an Impaired Brain Metabolic Profile in Mice Resistant to Cerebral Malaria Infected with Plasmodium Berghei ANKA. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14505–14514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, J.R.; Ross, B.; Arun, P.; Madhavarao, C.N.; Namboodiri, A.M.A. N-Acetylaspartate in the CNS: From Neurodiagnostics to Neurobiology. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 89–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N.; Looareesuwan, S.; Phillips, R.; Warrell, D.; Chanthavanich, P.; Pongpaew, P. Pathophysiological and Prognostic Significance of Cerebrospinal-Fluid Lactate in Cerebral Malaria. Lancet 1985, 325, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dkhil, M.A.; Al-Shaebi, E.M.; Lubbad, M.Y.; Al-Quraishy, S. Impact of Sex Differences in Brain Response to Infection with Plasmodium Berghei. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadanga, S.; Thatoi, P.K.; Mohapatra, B.N.; Mohapatra, N.; Mohanty, C.; Karuna, T. Severe Falciparum Malaria-Difference in Mortality among Male and Nonpregnant Females. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2014, 8, MC01–MC04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Taylor, T.E.; Kampondeni, S.; Potchen, M.J.; Panda, P.; Majhi, M.; Mishra, S.K.; Wassmer, S.C. Magnetic Resonance Imaging during Life: The Key to Unlock Cerebral Malaria Pathogenesis? Malar. J. 2014, 13, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| PATHOGENIC FEATURE | FINDINGS | REFERENCES |
|---|---|---|
| Brain swelling and vasogenic edema | Increased brain volume | [2,39,41,67] |
| Cerebellum crushing | [13,39,67] | |
| Brainstem engulfment | [39,67] | |
| Increased diffusion in OB, WM and RMS | [13,42] | |
| Cytotoxic edema (restricted diffusion) | Striatum | [39] |
| Parietal cortex | [39] | |
| Cerebellum | [13] | |
| Changes in ventricle volume | [39] | |
| BBBD | OB, CC, external capsule | [2,13,39,41,42,68] |
| Blood–CSF disruption | [2,13,39] | |
| Lesions | WM | [39,67] |
| Caudate putamen | [39,67] | |
| Brainstem | [67] | |
| OB | [13,42,67] | |
| Cranial nerves | [67] | |
| (Micro)hemorrhages | Cerebrum | [39,67] |
| Cerebellum, brainstem | [67] | |
| OB | [41,67,69] | |
| Vascular function | Reduced blood flow in cerebral arteries | [39] |
| Reduced CBF (capillaries) | [39,70] | |
| Vascular inflammation | [2] | |
| Neurometabolic changes | Reduced NAA | [39,70] |
| Increased Glx | [39] | |
| Decreased (PCr + β-ATP)/Pi | [39] | |
| Decrease in pH | [39] | |
| Increased lactate | [39] | |
| Development of the disease | Rostrocaudal (via RMS to DMS) | [2,42] |
| PATHOGENIC FEATURE | FINDINGS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADULT CM | PEDIATRIC CM | |||
| Brain edema | Mild and diffuse | [28,32,41,43,71] | Severe | [10,27,40,41,71] |
| Resolved in survivors | [71,72] | Resolved in survivors | [7,71] | |
| Uncal, cerebellum or brainstem herniation | [7,27,71] | |||
| Associated with morbidity | [7,40] | |||
| Persistent in survivors with neurological sequelae | [31,73] | |||
| Vasogenic edema (increased diffusion) | Cortex, posterior | [44] | Cortex | [27,44] |
| Basal ganglia | [7,27] | |||
| Corpus callosum | [7,27] | |||
| Subcortical WM | [27,71] | |||
| Posterior fossa | [7] | |||
| Cytotoxic edema (restricted diffusion) | Cortex | [28,74] | Cortex | [75] |
| Basal ganglia | [32,44,71,74,76] | Basal ganglia | [29,44,75] | |
| Corpus callosum | [74,76] | Corpus callosum | [75,77] | |
| Thalamus | [33] | Subcortical WM | [29,71,75] | |
| Periaqueductal GM | [33] | Resolved in survivors | [71] | |
| Cerebellum | [33] | |||
| Brainstem | [33] | |||
| Hippocampus | [76] | |||
| Resolved in survivors | [71] | |||
| White matter lesions | Focal | [78] | Persistent in survivors and correlating with long term neurological sequelae | [31,73,79] |
| Periventricular WM | [30,80] | Periventricular WM | [27,73] | |
| Subcortical WM | [76,80] | Subcortical WM | [7,27,29,40,73] | |
| Corpus callosum | [28,30,74] | Corpus callosum | [27,29] | |
| Corona radiata | [33,76] | |||
| Cortical lesions | Focal | [28] | Focal | [7,27,29,40] |
| Persistent in survivors | [73] | |||
| Subcortical lesions | Thalamus | [30,32,33] | Thalamus | [7,27,40] |
| Basal ganglia | [28,32,74] | Basal ganglia | [7,27,29,40,73] | |
| Cerebellum | [28,32,33] | Cerebellum | [27,73] | |
| Brainstem | [28,33] | Brainstem | [7,29,40,73] | |
| Hippocampus | [33] | Posterior fossa | [7,40] | |
| (Micro)hemorrhages | Cortex | [78] | ||
| Basal ganglia | [41,74,76] | Basal ganglia | [41] | |
| Corpus callosum | [41,74,76] | Corpus callosum | [41] | |
| GM-WM junction | [41] | GM-WM junction | [41] | |
| Cerebellum | [41] | Cerebellum | [41] | |
| Brainstem | [33] | |||
| Thalamus | [33] | |||
| Frequency correlates with disease severity | [41] | Frequency correlates with disease severity | [41] | |
| Vascular function (congestion) | Basal ganglia | [44] | Basal ganglia | [29,44] |
| Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome | [43] | |||
| Neurometabolic changes | Increased lactate/Cre in CSF | [34] | ||
| Increased lactate/Cre in parietal cortex | [28] | |||
| Increased Cho/Cre in parietal cortex | [28] | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Comino Garcia-Munoz, A.; Varlet, I.; Grau, G.E.; Perles-Barbacaru, T.-A.; Viola, A. Contribution of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies to the Understanding of Cerebral Malaria Pathogenesis. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121042
Comino Garcia-Munoz A, Varlet I, Grau GE, Perles-Barbacaru T-A, Viola A. Contribution of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies to the Understanding of Cerebral Malaria Pathogenesis. Pathogens. 2024; 13(12):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121042
Chicago/Turabian StyleComino Garcia-Munoz, Alicia, Isabelle Varlet, Georges Emile Grau, Teodora-Adriana Perles-Barbacaru, and Angèle Viola. 2024. "Contribution of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies to the Understanding of Cerebral Malaria Pathogenesis" Pathogens 13, no. 12: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121042
APA StyleComino Garcia-Munoz, A., Varlet, I., Grau, G. E., Perles-Barbacaru, T.-A., & Viola, A. (2024). Contribution of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies to the Understanding of Cerebral Malaria Pathogenesis. Pathogens, 13(12), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121042







