Metatranscriptomic Sequencing of Medically Important Mosquitoes Reveals Extensive Diversity of RNA Viruses and Other Microbial Communities in Western Australia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mosquito Samples
2.2. Sample Processing and Sequencing
2.3. Virus Discovery
2.4. Viral Genome Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Identification of Non-Viral Microbes
2.6. Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. Mosquito Virome
3.2. Characterization of Virus Diversity
3.2.1. Double-Stranded RNA Viruses
3.2.2. Positive-Sense Single-Stranded RNA Viruses
3.2.3. Negative-Sense Single-Stranded RNA Viruses
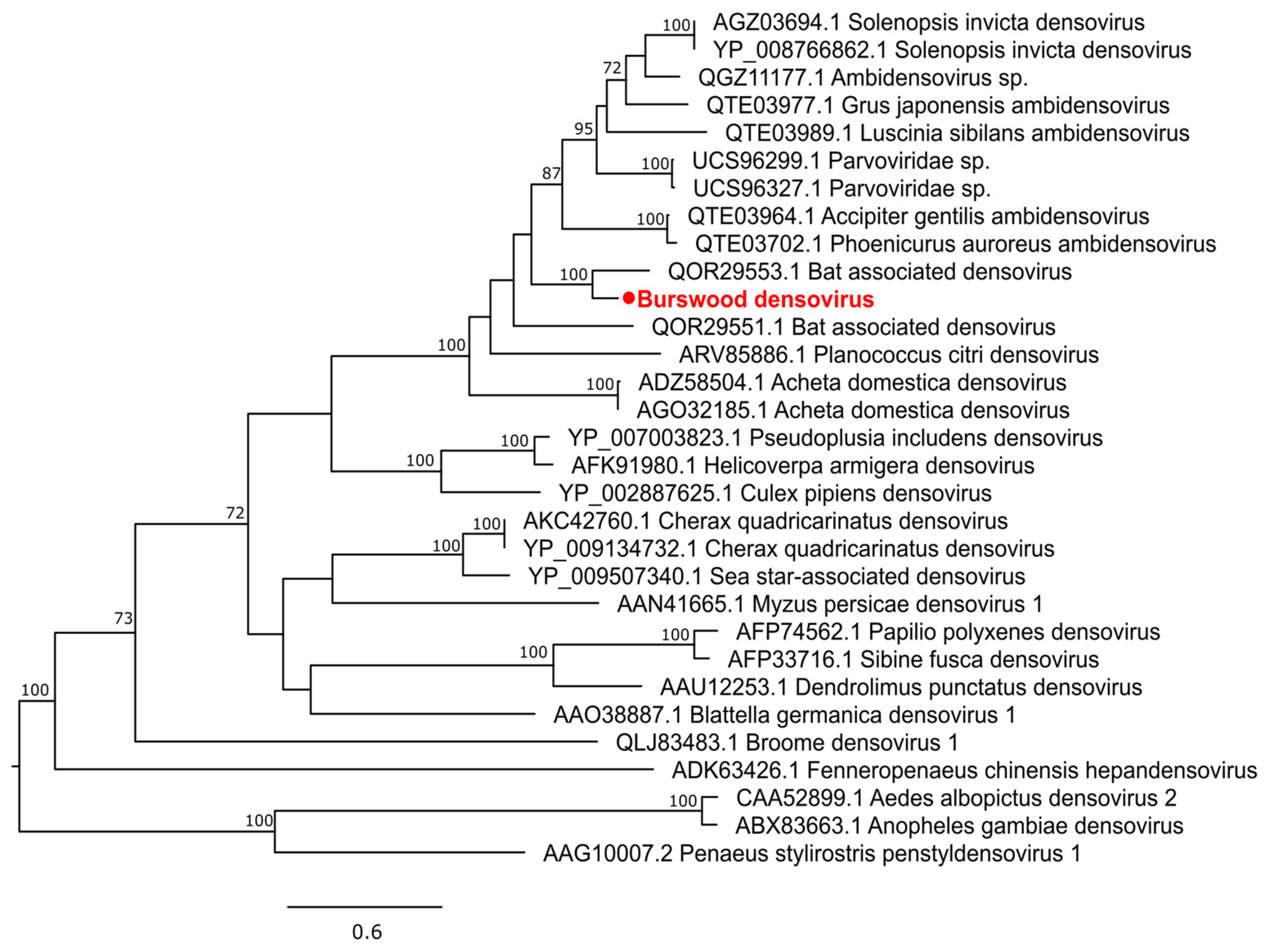
3.2.4. Single-Stranded DNA Virus
3.3. Geographical Differences in Aedes vigilax and Culex annulirostris Virome
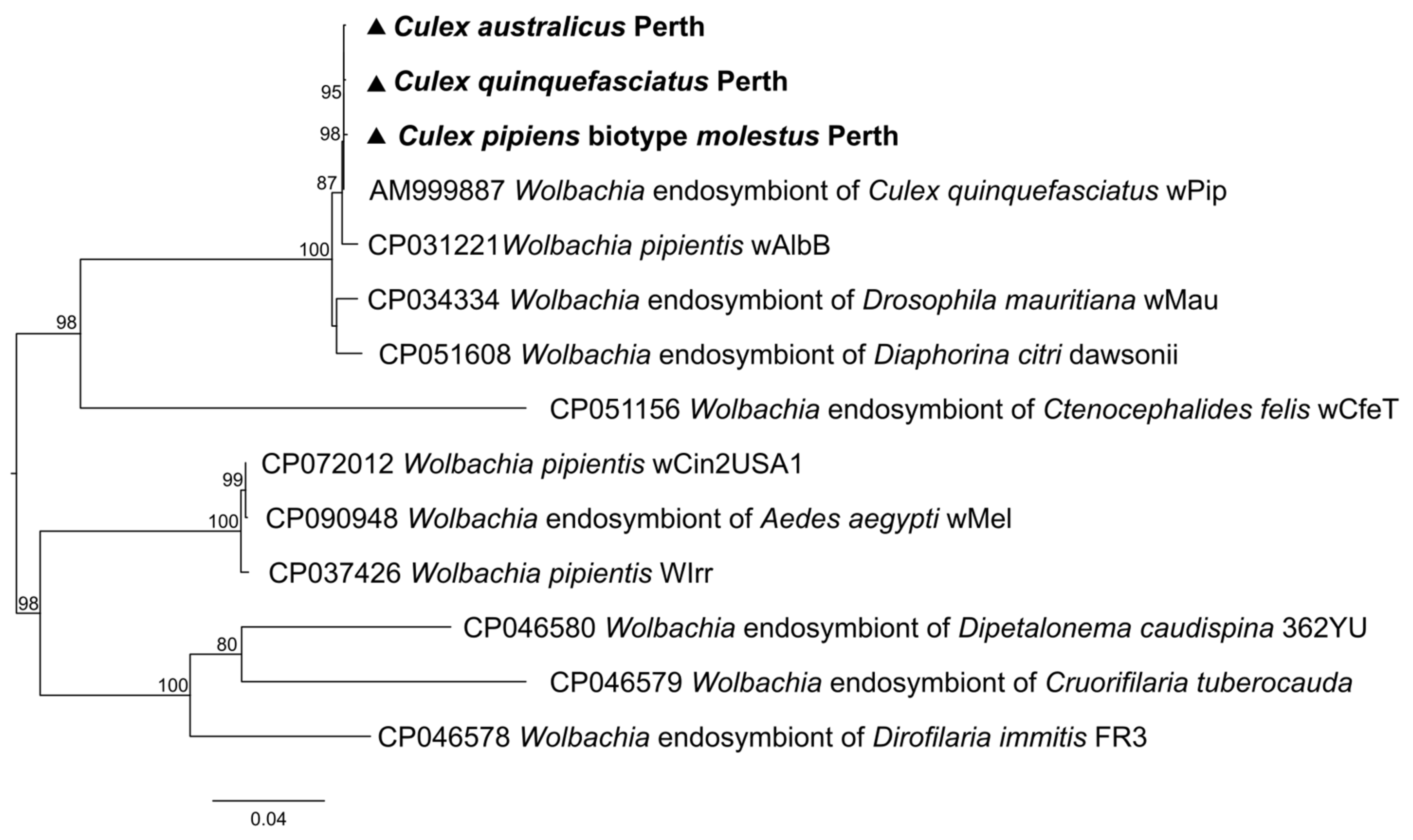
3.4. Non-Viral Microorganisms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dahmana, H.; Mediannikov, O. Mosquito-Borne Diseases Emergence/Resurgence and How to Effectively Control It Biologically. Pathogens 2020, 9, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakis, N.; Tesh, R.B. Insect-specific viruses and their potential impact on arbovirus transmission. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 15, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, V.L.; Long, M.T. Insect-Specific Viruses: An overview and their relationship to arboviruses of concern to humans and animals. Virology 2021, 557, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.; Henrion-Lacritick, A.; Frangeul, L.; Saleh, M.-C. Interactions of the Insect-Specific Palm Creek Virus with Zika and Chikungunya Viruses in Aedes Mosquitoes. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, B.J.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Webb, C.E.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Ritchie, S.A.; Hobson-Peters, J.; Hall, R.A.; Hurk, A.F.v.D. The Insect-Specific Parramatta River Virus Is Vertically Transmitted by Aedes vigilax Mosquitoes and Suppresses Replication of Pathogenic Flaviviruses In Vitro. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021, 21, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, E.I.; Villinger, J.; Muthoni, J.N.; Dobel-Ober, L.; Hughes, G.L. Exploiting insect-specific viruses as a novel strategy to control vector-borne disease. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2020, 39, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batson, J.; Dudas, G.; Haas-Stapleton, E.; Kistler, A.L.; Li, L.M.; Logan, P.; Ratnasiri, K.; Retallack, H. Single mosquito metatranscriptomics identifies vectors, emerging pathogens and reservoirs in one assay. eLife 2021, 10, 68353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongsripong, P.; Chandler, J.A.; Kittayapong, P.; Wilcox, B.A.; Kapan, D.D.; Bennett, S.N. Metagenomic shotgun sequencing reveals host species as an important driver of virome composition in mosquitoes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gou, Q.-Y.; Luo, G.-Y.; Hou, X.; Liang, G.; Shi, M. Total RNA sequencing of Phlebotomus chinensis sandflies in China revealed viral, bacterial, and eukaryotic microbes potentially pathogenic to humans. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 2080–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.-D.; Tian, J.-H.; Chen, L.-J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.-X.; Qin, X.-C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.-P.; Eden, J.-S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Neville, P.; Nicholson, J.; Eden, J.-S.; Imrie, A.; Holmes, E.C. High-Resolution Metatranscriptomics Reveals the Ecological Dynamics of Mosquito-Associated RNA Viruses in Western Australia. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00680-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, C.A.; Susai, V.; Hall, R.A.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Clark, D.C.; May, F.J.; Hemmerter, S.; Smith, D.W.; Broom, A.K. Genetic and phenotypic differences between isolates of Murray Valley encephalitis virus in Western Australia, 1972–2003. Virus Genes 2007, 35, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.J.; Johansen, C.A.; Lindsay, M.D.A.; Selvey, L.; Jardine, A. Mosquito and Virus Surveillance as a Predictor of Human Ross River Virus Infection in South-West Western Australia: How Useful Is It? Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.H.; Levy, A.; Yates, R.A.; Somaweera, N.; Neville, P.J.; Nicholson, J.; Lindsay, M.D.A.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Jain, K.; Imrie, A.; et al. The Diversity and Distribution of Viruses Associated with Culex annulirostris Mosquitoes from the Kimberley Region of Western Australia. Viruses 2020, 12, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Selvey, L.; A Johansen, C.; Broom, A.K.; Antão, C.; Lindsay, M.D.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Smith, D.W. Rainfall and sentinel chicken seroconversions predict human cases of Murray Valley encephalitis in the north of Western Australia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.L.; Hurk, A.F.v.D.; Meyer, D.B.; Ritchie, S.A. Searching for the proverbial needle in a haystack: Advances in mosquito-borne arbovirus surveillance. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, C.; Schielke, A.; Ellerbroek, L.; Johne, R. PCR inhibitors—occurrence, properties and removal. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batovska, J.; Mee, P.T.; Sawbridge, T.I.; Rodoni, B.C.; Lynch, S.E. Enhanced Arbovirus Surveillance with High-Throughput Metatranscriptomic Processing of Field-Collected Mosquitoes. Viruses 2022, 14, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, L.L.; Page, B.L.; Greninger, A.L.; Herring, B.L.; Russell, R.C.; Doggett, S.L.; Haniotis, J.; Wang, C.; Deng, X.; Delwart, E.L. Enhanced arbovirus surveillance with deep sequencing: Identification of novel rhabdoviruses and bunyaviruses in Australian mosquitoes. Virology 2014, 448, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, A.T.; A Shivas, M.; Darbro, J.M.; Onn, M.B.; Johnson, P.H.; Crunkhorn, A.; Montgomery, I.; Burtonclay, P.; Jansen, C.C.; Hurk, A.F.v.D. Uncovering the genetic diversity within the Aedes notoscriptus virome and isolation of new viruses from this highly urbanised and invasive mosquito. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, C.C.; Williams, C.R.; Hurk, A.F.v.D. The Usual Suspects: Comparison of the Relative Roles of Potential Urban Chikungunya Virus Vectors in Australia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurk, A.F.v.D.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Pyke, A.T.; Smith, G.A.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Nicholson, J.; Beebe, N.W.; Davis, J.; Muzari, O.M.; Russell, R.C.; et al. Vector Competence of Australian Mosquitoes for Chikungunya Virus. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.C. A Review of the Status and Significance of the Species within the Culex pipiens Group in Australia. J. Am. Mosq. Control. Assoc. 2012, 28, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholomay, L.C.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Mayhew, G.F.; Campbell, C.L.; Michel, K.; Zou, Z.; Ramirez, J.L.; Das, S.; Alvarez, K.; Arensburger, P.; et al. Pathogenomics of Culex quinquefasciatus and Meta-Analysis of Infection Responses to Diverse Pathogens. Science 2010, 330, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurchenko, A.A.; Masri, R.A.; Khrabrova, N.V.; Sibataev, A.K.; Fritz, M.L.; Sharakhova, M.V. Genomic differentiation and intercontinental population structure of mosquito vectors Culex pipiens pipiens and Culex pipiens molestus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohe, D.L.; Fall, R.P. A miniature battery powered CO2 baited light trap for mosquito borne encephalitis surveillance. Bull. Soc. Vector Ecol. 1979, 4, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liehne, P.F.S. An Atlas of The Mosquitoes of Western Australia; Health Department of Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2014, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, J.H.-O.; Shi, M.; Eden, J.-S.; Holmes, E.C.; Hesson, J.C. Meta-Transcriptomic Comparison of the RNA Viromes of the Mosquito Vectors Culex pipiens and Culex torrentium in Northern Europe. Viruses 2019, 11, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. ProtTest 3: Fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1164–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Míguez, A.; Beghini, F.; Cumbo, F.; McIver, L.J.; Thompson, K.N.; Zolfo, M.; Manghi, P.; Dubois, L.; Huang, K.D.; Thomas, A.M.; et al. Extending and improving metagenomic taxonomic profiling with uncharacterized species using MetaPhlAn. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, M.; Bordenstein, S.R.; Baldo, L.; Lo, N.; Beninati, T.; Wernegreen, J.J.; Werren, J.H.; Bandi, C. Phylogeny of Wolbachia pipientis based on gltA, groEL and ftsZ gene sequences: Clustering of arthropod and nematode symbionts in the F supergroup, and evidence for further diversity in the Wolbachia tree. Microbiology 2005, 151, 4015–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Sadiq, S.; Tian, J.-H.; Chen, X.; Lin, X.-D.; Shen, J.-J.; Chen, H.; Hao, Z.-Y.; Wille, M.; Zhou, Z.-C.; et al. RNA viromes from terrestrial sites across China expand environmental viral diversity. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, B.J.; Hobson-Peters, J.; Webb, C.E.; Watterson, D.; Prow, N.A.; Nguyen, H.D.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Warrilow, D.; Johansen, C.A.; Jansen, C.C.; et al. A novel insect-specific flavivirus replicates only in Aedes-derived cells and persists at high prevalence in wild Aedes vigilax populations in Sydney, Australia. Virology 2015, 486, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, P.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Ayllón, M.A.; Basler, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Blasdell, K.R.; Briese, T.; Brown, P.A.; Bukreyev, A.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; et al. Taxonomy of the order Mononegavirales: Second update Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-X.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.-H.; Lin, X.-D.; Kang, Y.-J.; Chen, L.-J.; Qin, X.-C.; Xu, J.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Unprecedented genomic diversity of RNA viruses in arthropods reveals the ancestry of negative-sense RNA viruses. eLife 2015, 4, 05378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Mushegian, A.R.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Alfenas-Zerbini, P.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dutilh, B.E.; García, M.L.; Hendrickson, R.C.; et al. Recent changes to virus taxonomy ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2022). Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 2429–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.T.; Culverwell, C.L.; Suvanto, M.T.; Korhonen, E.M.; Uusitalo, R.; Vapalahti, O.; Smura, T.; Huhtamo, E. Characterisation of the RNA Virome of Nine Ochlerotatus Species in Finland. Viruses 2022, 14, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liehne, P.; Anderson, S.; Stanley, N.; Liehne, C.; Wright, A.; Chan, K.; Leivers, S.; Britten, D.; Hamilton, N. Isolation of Murray Valley encephalitis virus and other arboviruses in the Ord River Valley 1972–1976. Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 1981, 59, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.W.; A Wright, S.; Eldridge, B.F.; A Brown, D. Cost effectiveness of three arbovirus surveillance methods in northern California. J. Am. Mosquito Contr. 2001, 17, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Z. A Metagenomic Survey of Viral Abundance and Diversity in Mosquitoes from Hubei Province. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, L.M.S.; Pinto, A.Z.d.L.; de Carvalho, M.S.; de Melo, F.L.; Ribeiro, B.M.; Slhessarenko, R.D. Novel Viruses in Mosquitoes from Brazilian Pantanal. Viruses 2019, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Altan, E.; Deng, X.; Barker, C.M.; Fang, Y.; Coffey, L.L.; Delwart, E. Virome of > 12 thousand Culex mosquitoes from throughout California. Virology 2018, 523, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faizah, A.N.; Kobayashi, D.; Isawa, H.; Amoa-Bosompem, M.; Murota, K.; Higa, Y.; Futami, K.; Shimada, S.; Kim, K.S.; Itokawa, K.; et al. Deciphering the Virome of Culex vishnui Subgroup Mosquitoes, the Major Vectors of Japanese Encephalitis, in Japan. Viruses 2020, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thannesberger, J.; Rascovan, N.; Eisenmann, A.; Klymiuk, I.; Zittra, C.; Fuehrer, H.-P.; Scantlebury-Manning, T.; Gittens-St. Hilaire, M.; Austin, S.; Landis, R.C.; et al. Highly Sensitive Virome Characterization of Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens Complex from Central Europe and the Caribbean Reveals Potential for Interspecies Viral Transmission. Pathogens 2020, 9, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Beller, L.; Deboutte, W.; Yinda, K.C.; Delang, L.; Vega-Rúa, A.; Failloux, A.-B.; Matthijnssens, J. Stable distinct core eukaryotic viromes in different mosquito species from Guadeloupe, using single mosquito viral metagenomics. Microbiome 2019, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, R.A.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; McLean, B.J.; O’Brien, C.A.; Colmant, A.M.; Piyasena, T.B.; Harrison, J.J.; Newton, N.D.; Barnard, R.T.; Prow, N.A.; et al. Commensal Viruses of Mosquitoes: Host Restriction, Transmission, and Interaction with Arboviral Pathogens. Evol. Bioinform. 2016, 12, EBO.S40740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trammell, C.E.; Goodman, A.G. Host Factors That Control Mosquito-Borne Viral Infections in Humans and Their Vector. Viruses 2021, 13, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batovska, J.; Blacket, M.J.; Brown, K.; Lynch, S.E. Molecular identification of mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in southeastern Australia. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 3001–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Yin, Q.; Zhou, L.; Meng, L.; Hu, W.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Han, K.; Zhang, S.; Fu, S.; et al. Metagenomic sequencing reveals viral abundance and diversity in mosquitoes from the Shaanxi-Gansu-Ningxia region, China. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Gou, Q.-Y.; Yang, W.-H.; Wu, W.-C.; Wang, J.; Holmes, E.C.; Liang, G.; Shi, M. A time-series meta-transcriptomic analysis reveals the seasonal, host, and gender structure of mosquito viromes. Virus Evol. 2022, 8, veac006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atyame, C.M.; Delsuc, F.; Pasteur, N.; Weill, M.; Duron, O. Diversification of Wolbachia Endosymbiont in the Culex pipiens Mosquito. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2761–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, A.; Hesson, J.C. Wolbachia prevalence in the vector species Culex pipiens and Culex torrentium in a Sindbis virus-endemic region of Sweden. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, E.; Atyame, C.M.; Milesi, P.; Fonseca, D.M.; Shaikevich, E.V.; Unal, S.; Makoundou, P.; Weill, M.; Duron, O. Population structure of Wolbachia and cytoplasmic introgression in a complex of mosquito species. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasgon, J.L.; Scott, T.W. Wolbachia and Cytoplasmic Incompatibility in the California Culex pipiens Mosquito Species Complex: Parameter Estimates and Infection Dynamics in Natural Populations. Genetics 2003, 165, 2029–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-J.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Lv, N.; Shi, P.-Q.; Wang, X.-M.; Huang, J.-L.; Qiu, B.-L. Plant–mediated horizontal transmission of Wolbachia between whiteflies. ISME J. 2016, 11, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.N.; Lloyd, V.K. Evidence for horizontal transfer of Wolbachia by a Drosophila mite. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 66, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graña-Miraglia, L.; Sikutova, S.; Vancová, M.; Bílý, T.; Fingerle, V.; Sing, A.; Castillo-Ramírez, S.; Margos, G.; Rudolf, I. Spirochetes isolated from arthropods constitute a novel genus Entomospira genus novum within the order Spirochaetales. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Nino, M.E.; Fitzpatrick, D.M.; Eckstrom, K.M.; Tighe, S.; Hattaway, L.M.; Hsueh, A.N.; Stone, D.M.; Dragon, J.A.; Cheetham, S. Metagenomic analysis of Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus mosquitoes from Grenada, West Indies. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osei-Poku, J.; Mbogo, C.M.; Palmer, W.J.; Jiggins, F.M. Deep sequencing reveals extensive variation in the gut microbiota of wild mosquitoes from Kenya. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 5138–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, S.; Komagata, O.; Tomita, T.; Sawabe, K.; Tsuda, Y.; Kurahashi, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Motoki, M.; Takahashi, T.; Tanikawa, T.; et al. PCR-Based Identification of Culex pipiens Complex Collected in Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Fonseca, D.M. Rapid assays for identification of members of the culex (Culex) pipiens complex, their hybrids, and other sibling species (Diptera: Culicidae). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 70, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


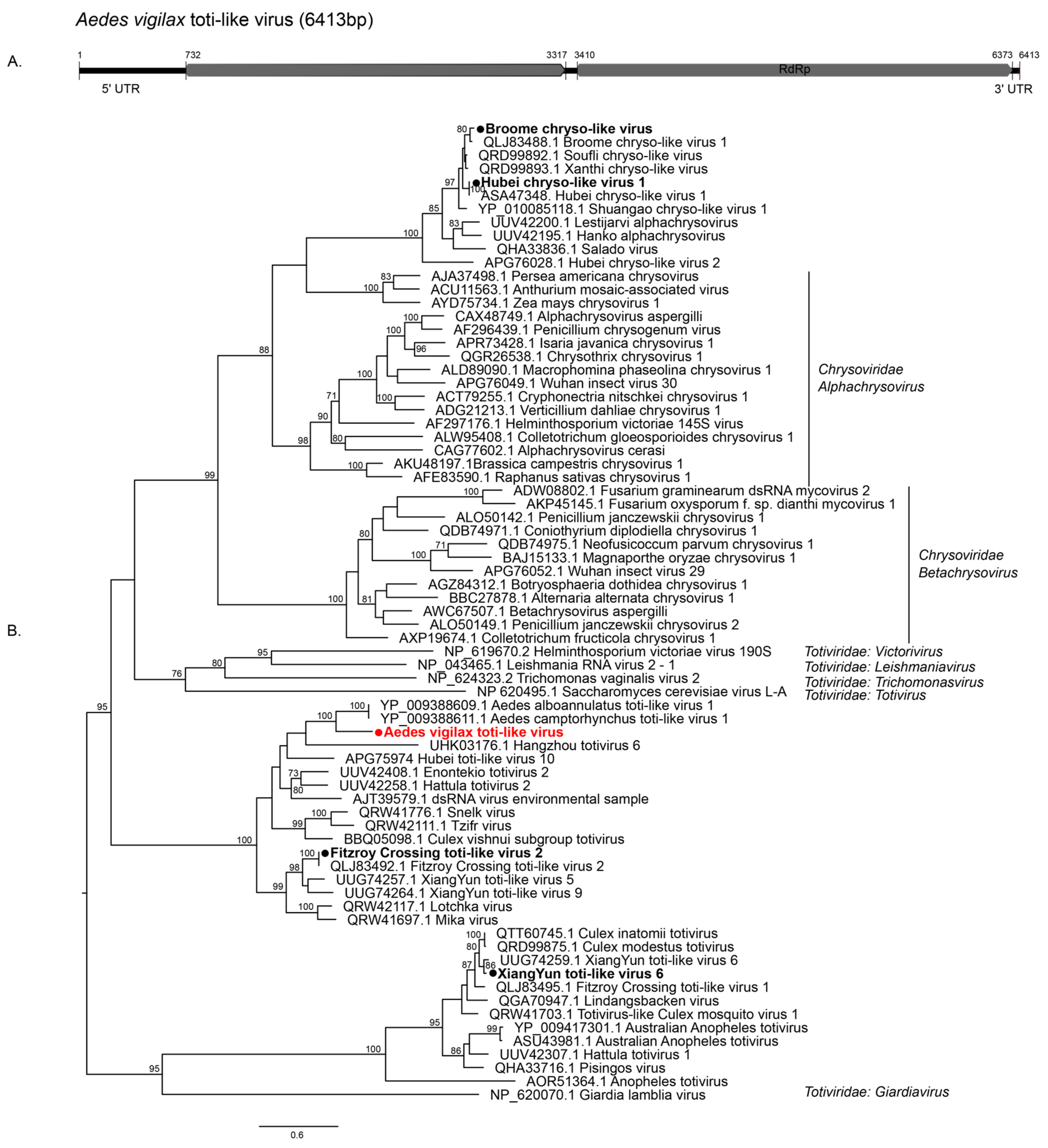

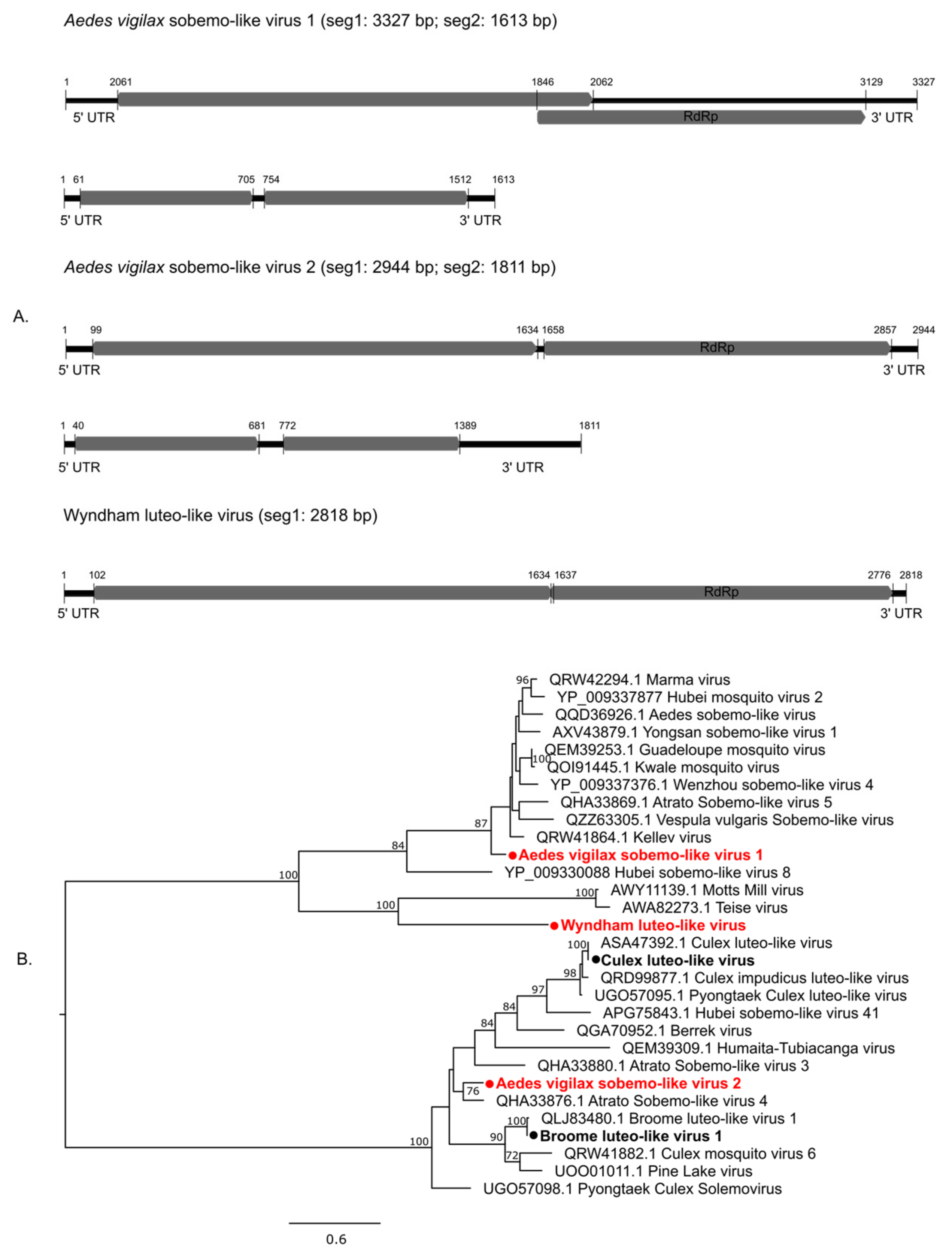

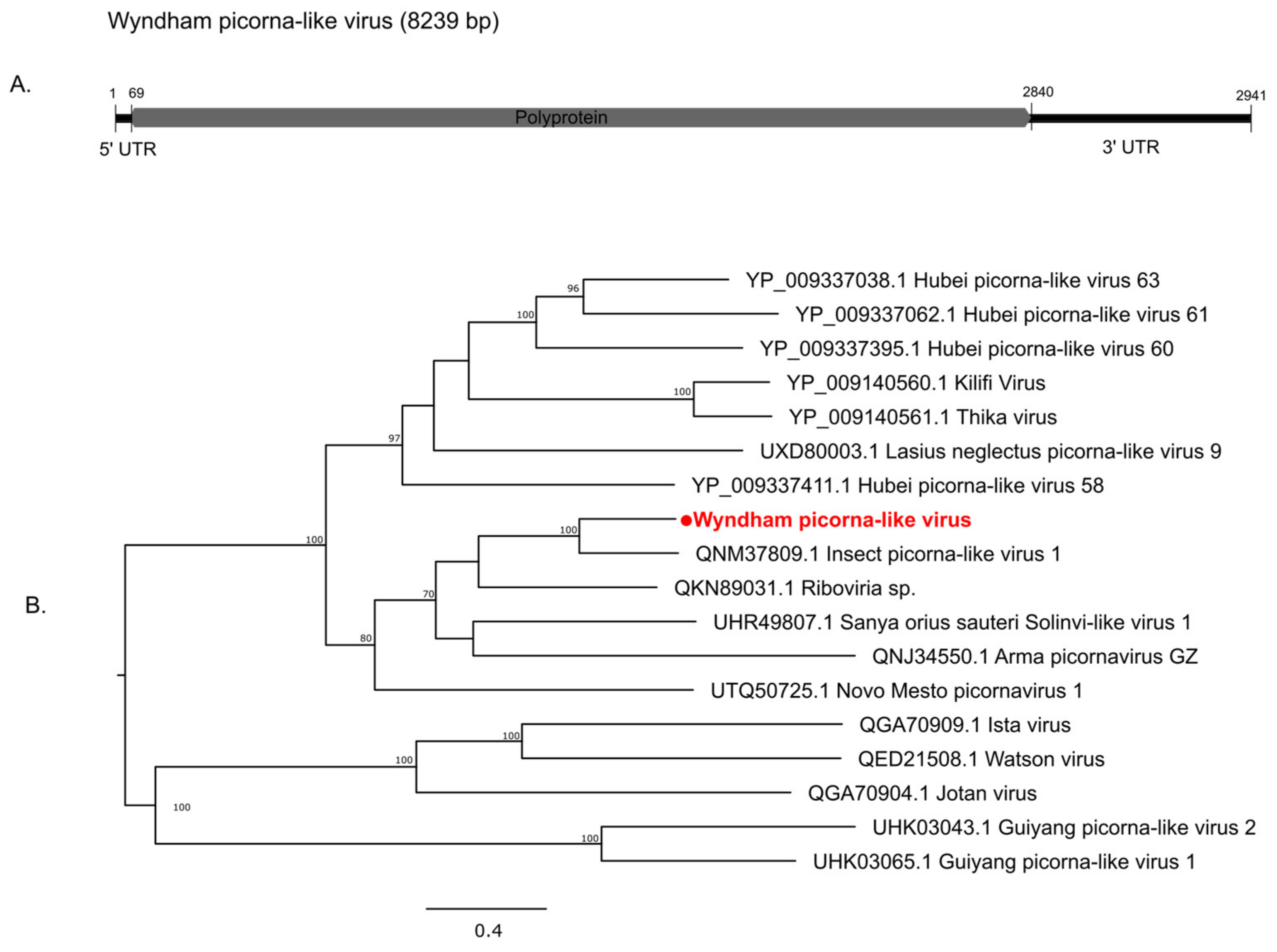
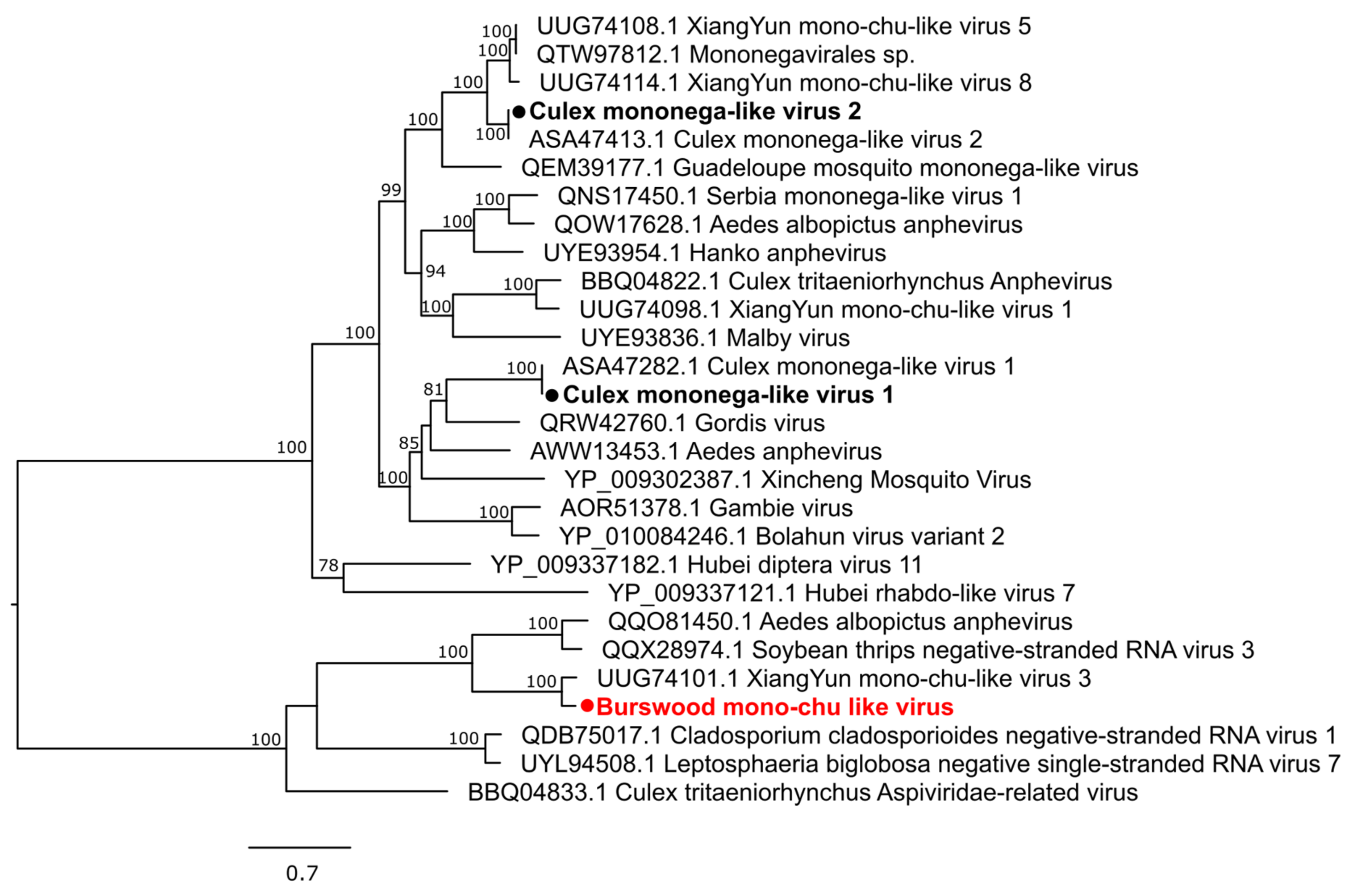

| Mosquito Species | City | Location Code | GPS Coordinates | Number of Mosquitoes | Year of Collection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ae. vigilax | Wyndham | L1 | −15.4967, 128.1432 | 50 | 2018 |
| Ae. vigilax | Perth | L6 | −31.9863, 115.8272 | 50 | 2021 |
| Cx. annulirostris | Wyndham | L2 | −15.7143, 128.2558 | 50 | 2018 |
| Cx. annulirostris | Karratha | L3 | −20.7214, 116.83 | 50 | 2020 |
| Cx. australicus | Perth | L4 | −31.9797, 115.9501 | 20 | 2018 |
| Cx. globocoxitus | Perth | L5 | −31.9483, 115.8885 | 20 | 2018 |
| Cx. quinquefasciatus | Perth | L5 | −31.9483, 115.8885 | 20 | 2018 |
| Cx. pipiens biotype molestus | Perth | L4 | −31.9797, 115.9501 | 20 | 2018 |
| Classification | Virus | Aedes vigilax | Culex annulirostris | Culex quinquefasciatus | Culex pipiens biotype molestus | Culex australicus | Culex globocoxitus | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perth | Wyndham | Karratha | Wyndham | Perth | Perth | Perth | Perth | ||
| Totiviridae | AVTLV | 445.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| FCTLV2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 74.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| XYTLV6 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 36.67 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Chrysoviridae | BCLV1 | 3374.37 | 331.94 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| HCLV1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 114.29 | 1166.24 | |
| Partitiviridae | BPLV1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 9645.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| WYPLV1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 10.30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| WYPLV2 | 0.00 | 323.44 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| WYPLV3 | 0.00 | 304.67 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| WPLV1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 128.81 | |
| WPLV2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 310.23 | |
| Reoviridae | BRLV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 148.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Flaviviridae | PARV | 19,106.13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Mesoniviridae | AMNV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2301.93 |
| Iflaviridae | CILV1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 301.64 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Luteo-like | AVSLV1 | 36,925.01 | 5035.38 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| AVSLV2 | 75,784.76 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| WYLLV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 6.90 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| CLLV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 399.07 | |
| BLLV1 a | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 402.30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Narnaviridae | BNLV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 224.80 |
| WYNLV1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 5.60 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| WYNLV2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 9.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| PDNLV a | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 515.69 | |
| Picornaviridae | WYPILV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 83.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Tombusviridae | CATLV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 8038.81 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 13,463.94 |
| Tymoviridae | GCTLV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 43.23 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Negev-like | CNLV1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 11,188.65 |
| CNLV2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 81,237.81 | |
| CNLV3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 49,987.88 | |
| CV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 16,348.41 | |
| Xinmoviridae | BMCLV a | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 236.76 |
| CMLV1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 298.40 | 0.00 | 160.76 | 1623.34 | |
| CMLV2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 39.35 | |
| Orthomyxoviridae | WMV3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3523.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| WMV4 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 8295.23 | 225.96 | 0.00 | |
| WMV6 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 14,885.72 | 85,573.19 | 14,975.02 | 13,039.50 | |
| Phasmaviridae | CPLV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 16,355.87 | 0.00 | 9495.19 | 19,896.30 |
| Qinviridae | FCQV1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 17.60 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| WQLV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 4843.81 | |
| Rhabdoviridae | CRLV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 684.93 | 0.00 |
| Parvoviridae | BDNV a | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 808.23 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Host COI | 20,256.85 | 32,205.12 | 17,267.12 | 9052.50 | 10,366.23 | 12,927.79 | 11,573.13 | 5356.84 | |
| Wolbachia | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2953.62 | 3341.82 | 997.00 | 0.00 | |
| Entomospira culicis | 0.00 | 0.00 | 85.99 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 39.09 | 0.00 | |
| Zymobacter palmae | 0.00 | 0.00 | 158.38 | 210.50 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Cystoisospora sp. | 0.00 | 36.89 | 17.90 | 11.31 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Trypanosoma sp. | 0.00 | 6.79 | 2.54 | 13.31 | 11.47 | 1.69 | 19.07 | 41.27 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamichhane, B.; Brockway, C.; Evasco, K.; Nicholson, J.; Neville, P.J.; Levy, A.; Smith, D.; Imrie, A. Metatranscriptomic Sequencing of Medically Important Mosquitoes Reveals Extensive Diversity of RNA Viruses and Other Microbial Communities in Western Australia. Pathogens 2024, 13, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13020107
Lamichhane B, Brockway C, Evasco K, Nicholson J, Neville PJ, Levy A, Smith D, Imrie A. Metatranscriptomic Sequencing of Medically Important Mosquitoes Reveals Extensive Diversity of RNA Viruses and Other Microbial Communities in Western Australia. Pathogens. 2024; 13(2):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13020107
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamichhane, Binit, Craig Brockway, Kimberly Evasco, Jay Nicholson, Peter J. Neville, Avram Levy, David Smith, and Allison Imrie. 2024. "Metatranscriptomic Sequencing of Medically Important Mosquitoes Reveals Extensive Diversity of RNA Viruses and Other Microbial Communities in Western Australia" Pathogens 13, no. 2: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13020107
APA StyleLamichhane, B., Brockway, C., Evasco, K., Nicholson, J., Neville, P. J., Levy, A., Smith, D., & Imrie, A. (2024). Metatranscriptomic Sequencing of Medically Important Mosquitoes Reveals Extensive Diversity of RNA Viruses and Other Microbial Communities in Western Australia. Pathogens, 13(2), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13020107







