Abstract
Studies of marine fish have revealed distant relatives of viruses important to global fish and animal health, but few such studies exist for freshwater fish. To investigate whether freshwater fish also host such viruses, we characterized the viromes of five wild species of freshwater fish in Wisconsin, USA: bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus), brown trout (Salmo trutta), lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens), northern pike (Esox lucius), and walleye (Sander vitreus). We analyzed 103 blood serum samples collected during a state-wide survey from 2016 to 2020 and used a metagenomic approach for virus detection to identify known and previously uncharacterized virus sequences. We then characterized viruses phylogenetically and quantified prevalence, richness, and relative abundance for each virus. Within these viromes, we identified 19 viruses from 11 viral families: Amnoonviridae, Circoviridae, Coronaviridae, Hepadnaviridae, Peribunyaviridae, Picobirnaviridae, Picornaviridae, Matonaviridae, Narnaviridae, Nudnaviridae, and Spinareoviridae, 17 of which were previously undescribed. Among these viruses was the first fish-associated coronavirus from the Gammacoronavirus genus, which was present in 11/15 (73%) of S. vitreus. These results demonstrate that, similar to marine fish, freshwater fish also harbor diverse relatives of viruses important to the health of fish and other animals, although it currently remains unknown what effect, if any, the viruses we identified may have on fish health.
1. Introduction
Much of our current understanding of viruses infecting fish is based on the study of pathogenic viruses in symptomatic hosts. However, the recent rise of metagenomic sequencing has led to the discovery that fish harbor a greater number of viruses than any other class of vertebrates [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Most families of RNA viruses once thought to infect mammals have been described in bony fishes [1]. For example, a survey of dead/moribund chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) revealed the first coronavirus (Coronaviridae) associated with fish, pacific salmon nidovirus [8]. Subsequent transcriptome analyses of publicly available sequence data identified additional distinct sub-families of coronaviruses in fish and amphibian transcriptomes [9,10]. Similarly, filoviruses (Filoviridae), previously thought to exclusively infect mammals, were discovered in European perch (Perca fluviatilis) and marine greenfin horse-faced filefish (Thamnaconus septentrionalis) [2,11]. Whilst these viruses retain a number of key features of other filoviruses, they are genetically distinct from the ebolaviruses and marburgviruses (renowned for causing lethal disease in humans) [12]. Likewise, hepadnaviruses, once known only from mammals and birds, infect amphibians and fish [13].
Despite rapid advances in our understanding of fish viromes, most knowledge to date has been obtained from studies of wild marine fish. Novel viruses from families known to infect marine fish [6,14], as well as families previously only associated with mammals, have been described [1,2]. One such study was Geoghegan et al. (2021), who identified the first fish-associated matonavirus (f. Matonaviridae), tiger flathead matonavirus, sharing only 28% amino acid identity (RDRP gene) with its famous relative, rubella virus, the causative agent of rubella in humans. They speculated that this family, as well as other viral families such as Hantaviridae and Filoviridae, may have originated in fish, evidenced by their basal phylogenetic positions [15]. They also hypothesized that vertebrate-associated viromes of fish were shaped by phylogenetic history of their hosts, with cross-species transmission also a common occurrence throughout virus evolution [15]. In general, it is clear that further examination of viral diversity in fish could deepen our understanding of the evolutionary origins of many viral families [16].
Viromes of wild freshwater fish are comparatively less studied than those of their marine counterparts. In most instances, such studies have been conducted in response to mortality events in wild fish [17,18] or in aquaculture settings [11]. We could only find a handful of broad virome surveys targeting wild freshwater fish, and none that had been conducted in the USA, to our knowledge [5,7,19,20,21]. This lack of data on wild freshwater fish viromes represents a potentially substantial knowledge gap. Lundberg et al. (2000) estimated that 10,000 fish species reside in freshwater bodies, making up 40% of all fish species [22]. Given this information, and the finding that the alpha diversity of vertebrate-associated viruses may be greater in freshwater fish than in their marine counterparts [5], studies examining viral diversity in wild freshwater fish would likely prove informative.
We conducted a study of the blood viromes of five species of sport fish across the state of Wisconsin, USA, collected from 2016 to 2020. Sport fishing in Wisconsin holds great cultural and economic significance [23], and viral diseases have previously impacted wild fish populations in the state, sometimes dramatically [18,24]. We performed a metagenomic survey of apparently healthy fish to (1) examine the total virome composition of these fish, (2) describe the phylogenetic relationships of potentially novel viruses, and (3) investigate whether viral prevalence, richness, or abundance varies between factors such as host species, location, or viral family. Our results support the notion that freshwater fish harbor highly diverse viromes, extending our knowledge of the geographical and host range over which such fish viruses occur.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Collection and Preparation
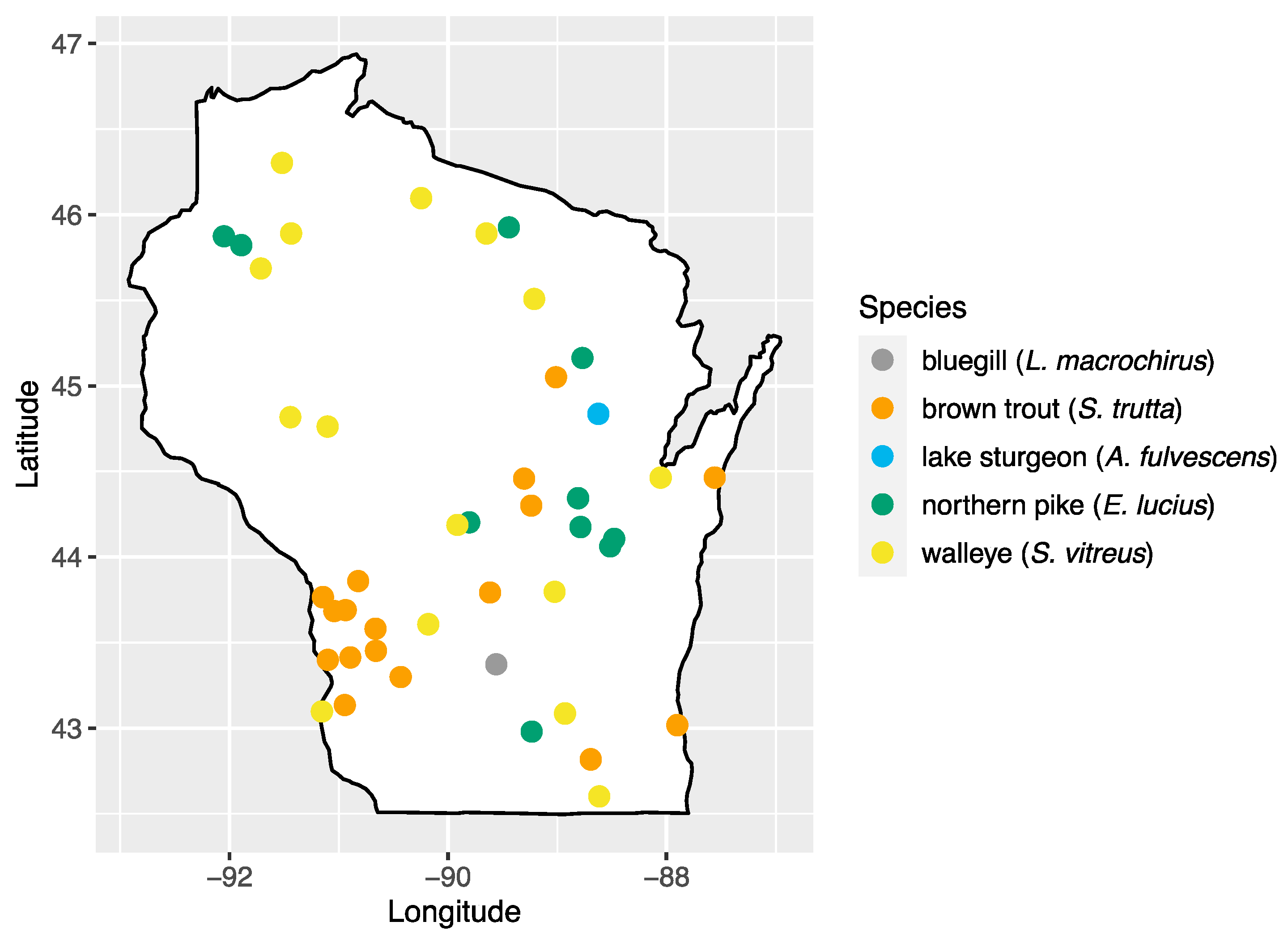
We analyzed 103 serum samples collected from five species of fish during a previous study of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (Rhabdoviridae: Novirhabdovirus) [24]. Fish species were chosen based on their importance to sport fishing in the state: walleye (Sander vitreus; n = 17), bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus; n = 14), brown trout (Salmo trutta; n = 18), northern pike (Esox lucius; n = 23), and lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens; n = 31). Sampling locations consisted of 43 inland waterbody sites across the state of Wisconsin, with multiple species present at 20 of these sites (Figure 1, Table S1). Samples were collected by the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources as part of surveys of fish health across Wisconsin and were made available for this study [24]. Briefly, fish were captured using a number of methods (fyke netting, boom shocking, stream shocking, and capture via spawning weir), blood samples were collected from the caudal vein using an 18–22 gauge needle and 3–5 mL syringe and transferred to no-additive, red top glass blood tubes. Samples were stored at 4 °C to encourage clotting and, after 24 h, samples were centrifuged at 3200× g for 15 min, and the sera transferred to sterile 2 mL cryovials and stored at −80 °C until processing.
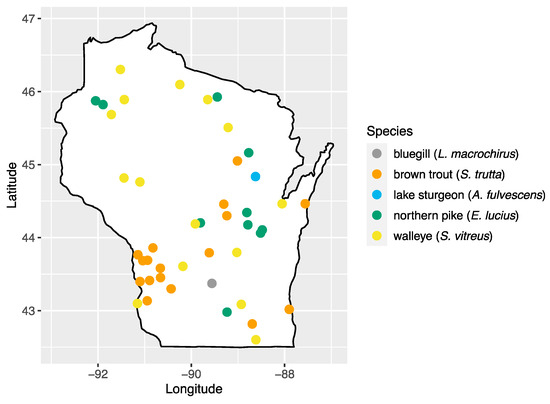
Figure 1.
Map of sampling areas throughout Wisconsin where bluegill, brown trout, northern pike, lake sturgeon, and walleye were collected in this study.
2.2. Next-Generation Sequencing
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing was performed as previously described [6,18,25,26]. In brief, samples were centrifuged at 10,000× g (4 °C) for 10 min to remove debris, then supernatants were transferred to a new tube and centrifuged further at 25,000× g (4 °C) for 3 h to pellet viruses. Nucleic acids were extracted from the resulting viral pellets using the QIAamp MinElute Virus Spin Kit (Qiagan, Germantown, MD, USA), and viral RNA was converted to double-stranded complementary DNA (cDNA) using the SuperScript IV First-Strand Synthesis System (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) and NEBNext® Ultra™ II Non-Directional RNA Second Strand Synthesis (New England BioLabs, Ipswich, MA, USA). Samples then underwent purification using AmpureXP beads (Beckman Coulter, Indianapolis, IN, USA), and libraries were prepared using the Nextera XT DNA sample preparation kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) for sequencing on a MiSeq instrument using the MiSeq Reagent Kit, V3 chemistry, for 600 cycles (Illumina, USA).
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
Sequence data from all fish species were initially processed using CLC Genomics Workbench v.23.0.2 (Qiagen). Sequence data were trimmed to remove low-quality (<Q30) and short-length (<50 bp) reads. For each fish species, sequences mapping to host DNA and known contaminants were removed and the remaining reads underwent de novo assembly using the metagenomic assembler metaSPAdes v.3.15.5 [27], with resulting contiguous sequences (contigs) shorter than 500 bp discarded. Putative viral contigs were then queried against the NCBI non-redundant (nr) database at the protein level using DIAMOND v.2.0.14.152 (blastx, --very-sensitive), with the subsequent DIAMOND alignment archive (DAA) file processed by MEGAN v.6.25.3 to produce taxonomic assignments with reference to the NCBI taxonomy, using the lowest common ancestor (LCA) algorithm [28,29,30]. To confirm the putative viral contigs thus identified, we conducted homology searches against the NCBI nucleotide database (nt) and Conserved Domains Search Database [31].
Viruses were described based on their closest match in GenBank, with information on the natural hosts of each virus family identified from the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) and ViralZone [32,33]. Viral families unlikely to infect fish (e.g., environmental viruses or viruses with non-vertebrate host ranges) were recorded but not analyzed further. For the resulting putative fish-infecting viruses, protein functions encoded by the sequence of each contig were inferred using a combination of the annotation software, Cenote-taker2 v.2.1.2 [34], ORFfinder, and the NCBI Conserved Domains Search Database [35].
To calculate viral abundance, reads from each fish were mapped to each viral target sequence (length fraction = 1, similarity = 0.9). A virus was considered present if a fish had ≥2 overlapping viral reads of 50 bp or more. Reads that mapped to each virus, or any of the viruses examined (total viral load), were then normalized for sequencing depth and viral sequence length and log-transformed to become log10 viral reads per million per kilobase of target sequence (Log10vRPM/kb) [6,25,26].
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
Closely related amino acid sequences to the viral open-reading frames (ORFs) of interest were identified through a blastp search against GenBank [35]. These, in addition to member species of each viral family under investigation, were used in phylogenetic analysis of viral sequences identified as described above [36]. Amino acid sequences were aligned using MUSCLE v.3.8, and multiple codon alignments were constructed from the aligned proteins using PAL2NAL v.14 [37,38]. The codon alignment was then trimmed using trimAL v.1.4.1 (default settings), with minor manual adjustments made as needed. A suitable nucleotide evolutionary model was selected for each alignment using ModelTest-NG and a Bayesian approach to inferring phylogenetic relationships was performed using MrBayes v.3.2.7 (ngen = 100,000, samplefreq = 500, burninfrac = 0.25) implemented in NGPhylogeny [39,40,41]. The resulting trees with posterior probability values were rooted at the midpoint and visualized using Figtree v.1.4.4 [42].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The proportion of positive individuals for each virus was used to indicate viral prevalence, with 95% confidence intervals calculated using the modified Wald method [43]. We compared prevalence, richness (number of viruses per fish), and normalized abundance among species, location (region of Wisconsin), and viral family using Kruskal–Wallis tests (Kruskal.test) and Wilcoxon rank-sum tests with Benjamini–Hochberg adjustment for pairwise comparisons (pairwise.wilcox.test, p.adjest.method = “BH”; [44]) in R studio v.1.2.5 [45].
3. Results
A total of 7552 contigs were assembled from all fish samples; 1753 from walleye, 1262 from bluegill, 197 from brown trout, 3700 from northern pike, and 640 from lake sturgeon. Of these contigs, 42 were viral in origin, 17 of which were thought to have originated from environmental contamination and so were not analyzed further (Table S2). The remaining 23 sequences represented viruses comprising five Baltimore classes: II (ssDNA), III (dsRNA), IV (ssRNA[+]), V (ssRNA[-]), and VII (dsDNA-RT). These sequences were most closely related to known viruses from 11 taxonomic groups, and one sequence most closely related to a currently unclassified known virus (Table 1).

Table 1.
Contigs representing viruses in Wisconsin sport fish.
Viruses closely related to those originating from fish hosts or other vertebrates and thus likely infecting fish were analyzed further. This included 19 viruses in total, representing the following viral families: Amnoonviridae, Circoviridae, Coronaviridae, Hepadnaviridae, Matonaviridae, Narnaviridae, Nudnaviridae, Peribunyaviridae, Picobirnaviridae, Picornaviridae, and Spinareoviridae.
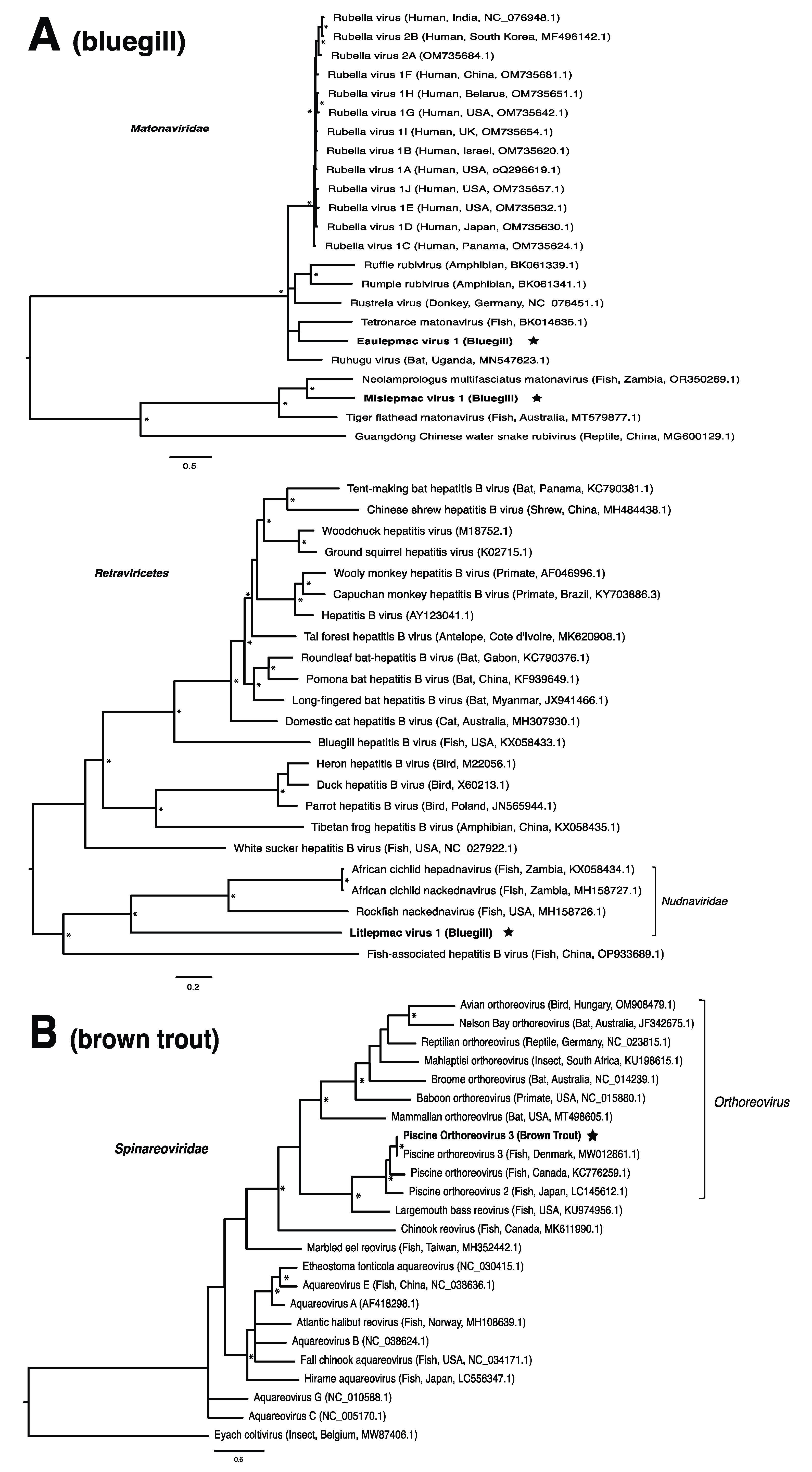
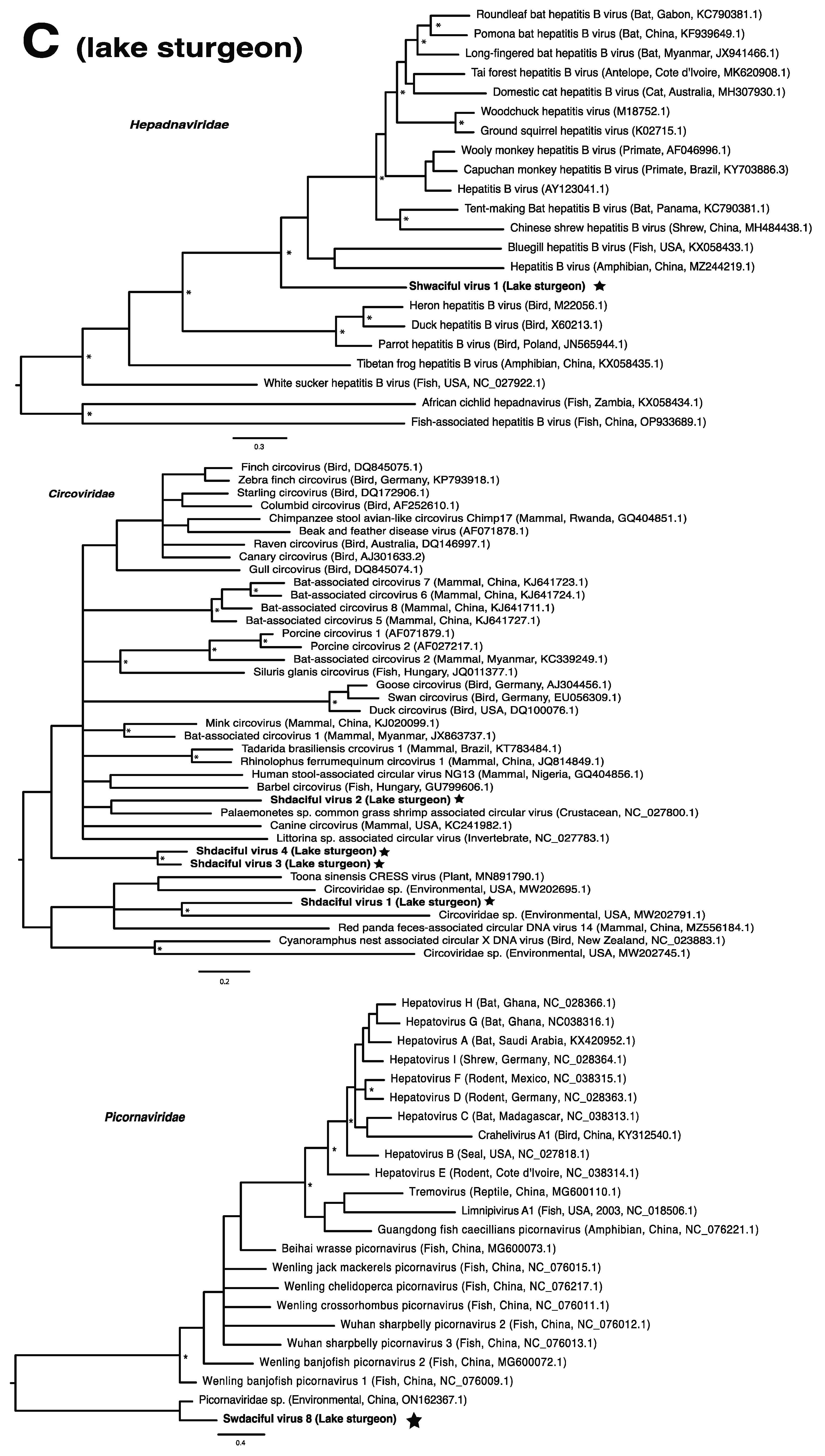
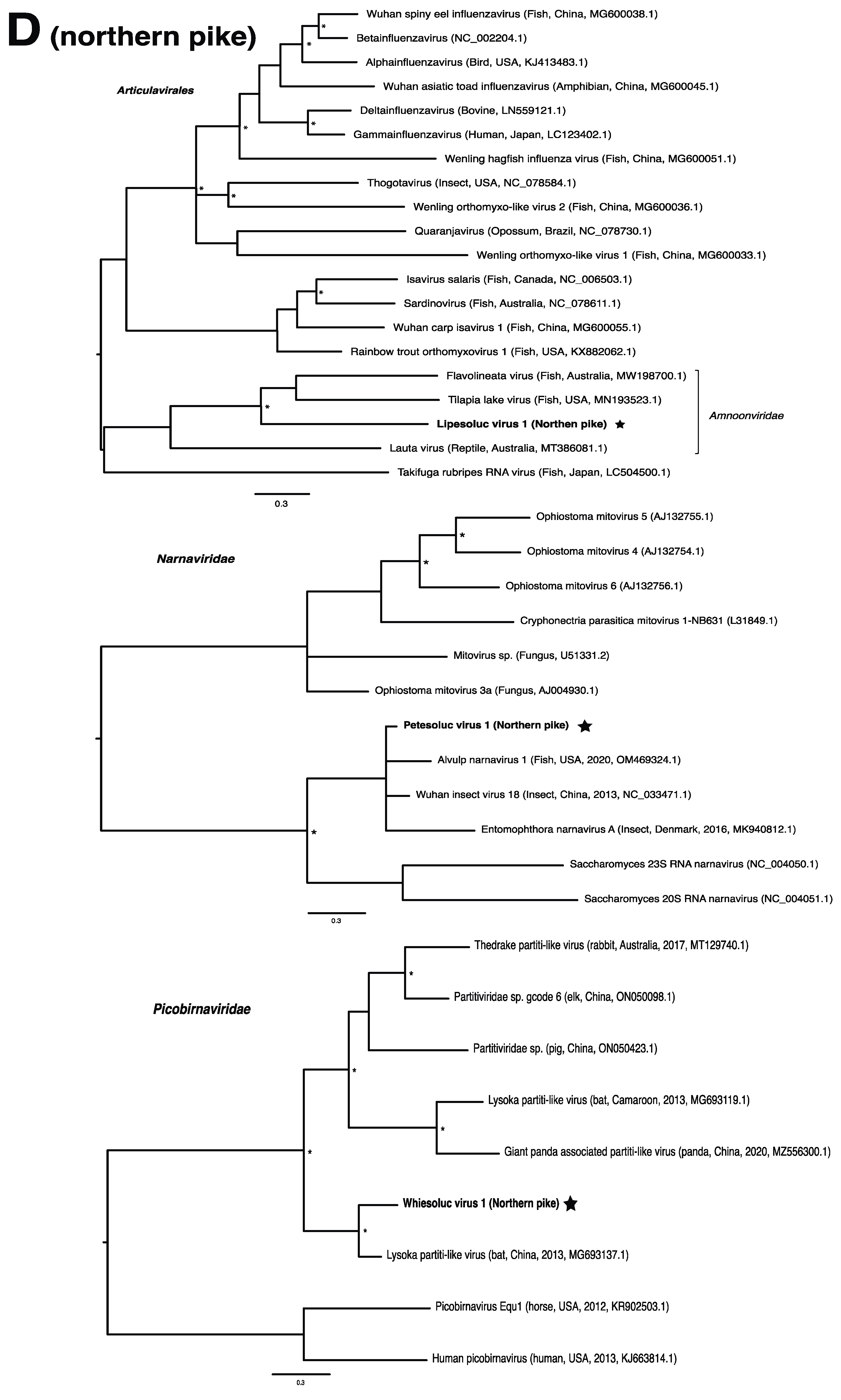
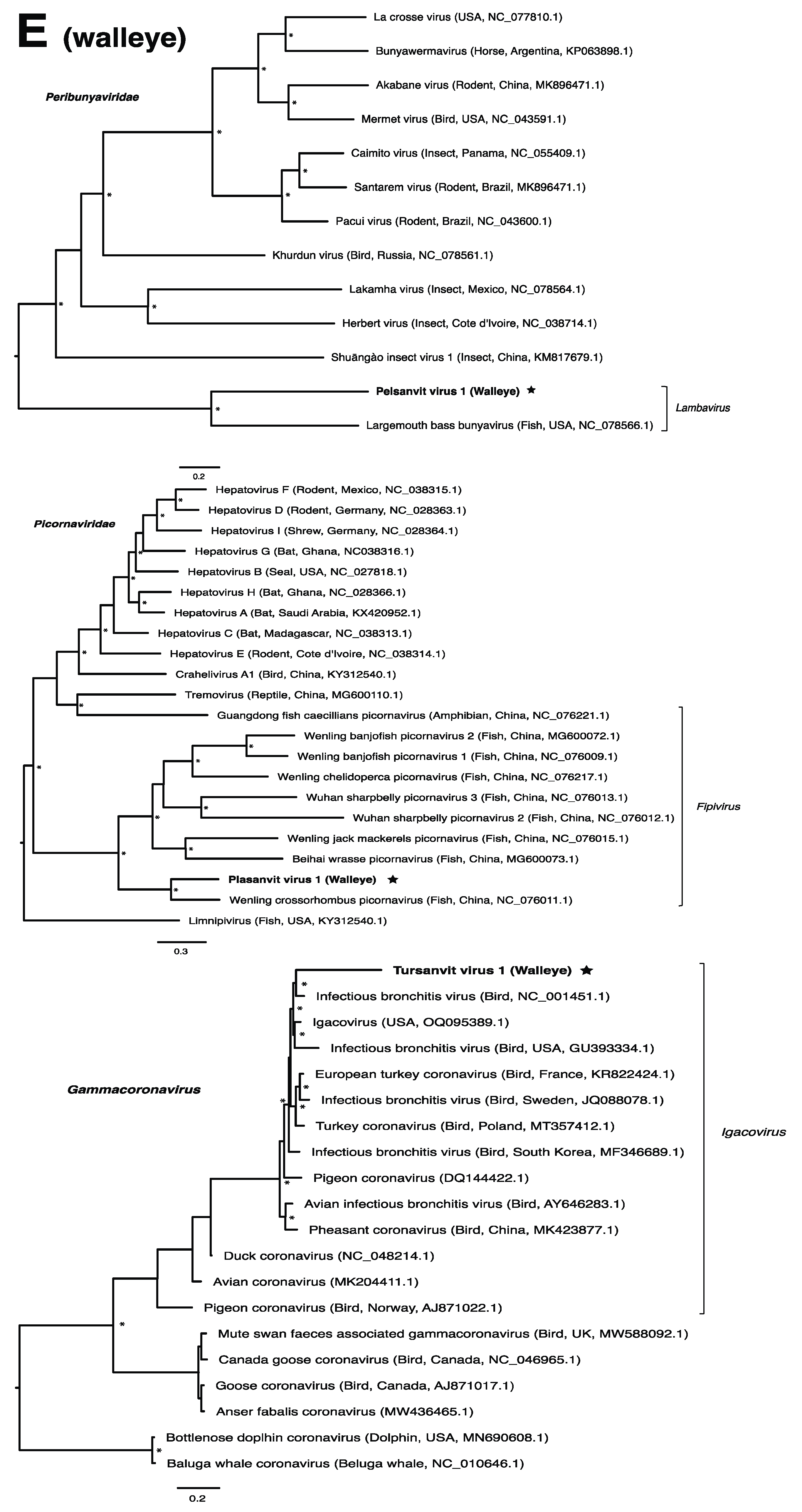
These viruses showed approximately 25% to more than 95% amino acid identity with their closest matches in GenBank (Table 1). Two viral contigs contained complete open reading frames (ORFs), and the remainder contained partial ORFs (Table S3). Phylogenetic analyses showed that most viruses investigated, excluding some belonging to the families Circoviridae, Coronaviridae, Picornaviridae (lake sturgeon only), and Picobirnaviridae, were most closely related to viruses previously identified in fish (Figure 2). Of these, all but piscine orthoreovirus 3 are previously undescribed members of their taxonomic group. Within the genus Gammacoronavirus (f. Coronaviridae), phylogenetic analysis revealed the virus under investigation (designated Tursanvit virus 1 by the authors) to be most closely related (94% amino acid identity within the nucleocapsid region) to infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) [46], an avian coronavirus belonging to the Igacovirus subgenus, for which the natural hosts are birds [47].
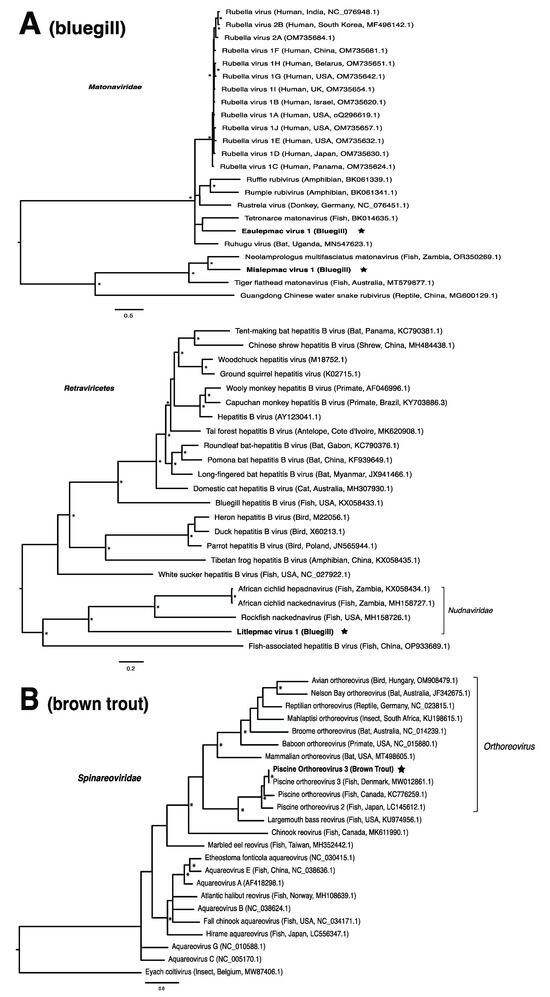
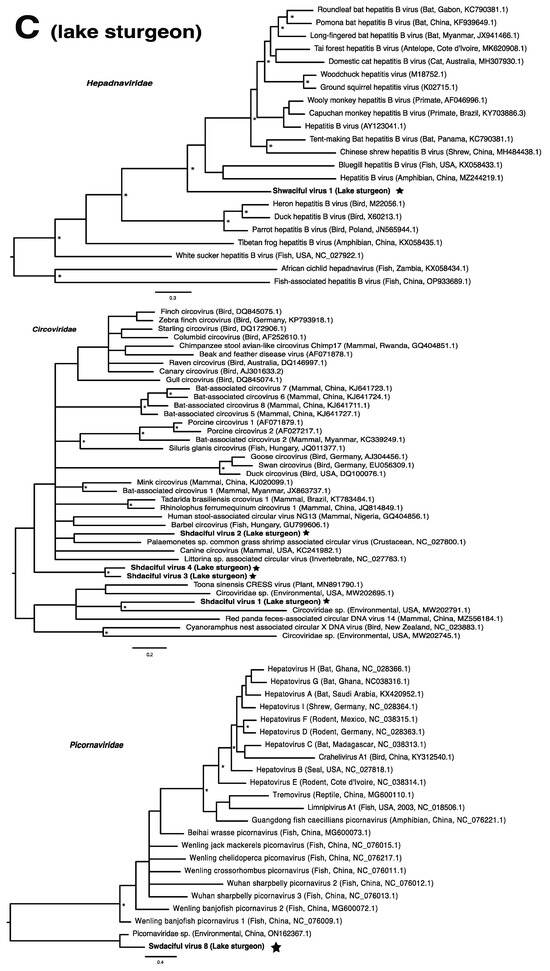
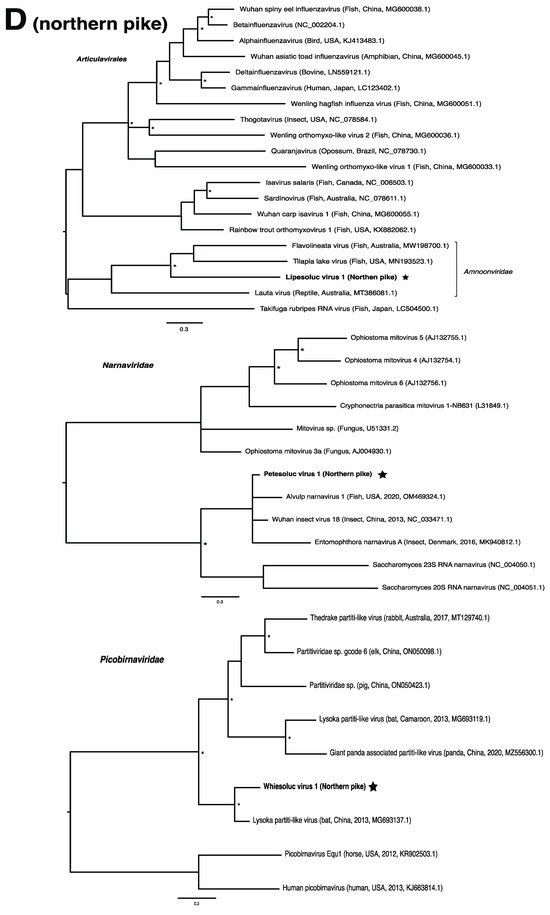
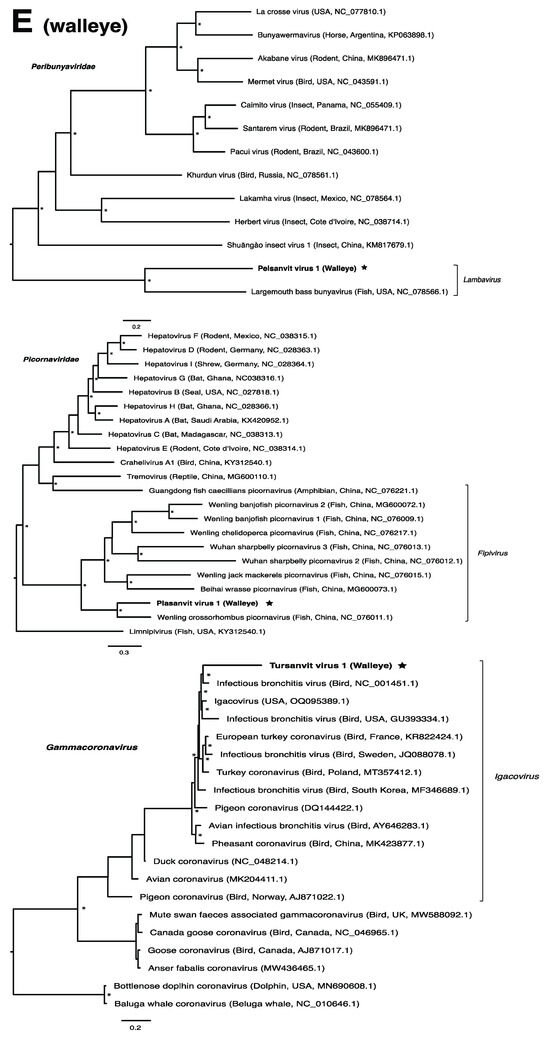
Figure 2.
Bayesian inference of phylogenetic relationships for viruses in (A) bluegill (L. macrochirus), (B) brown trout (S. trutta), (C) lake sturgeon (A. fulvescens), (D) northern pike (E. lucius), (E) walleye (S. vitreus), and their relatives. Where available, virus names are followed by host, country, and GenBank accession number in parentheses. * indicates posterior probabilities ≥95%. Scale bar = substitutions per site. ORFs and substitution models used for each tree are given in Table S4. Star next to virus name indicates viruses originating from this study.
Viruses from the family Picornaviridae were identified in both lake sturgeon and walleye (Table 2), which was the only family present in more than one species. Lake sturgeon, northern pike, and walleye contained the highest viral diversity among the fish species analyzed, spanning three viral taxonomic groups each (with northern pike containing a further unclassified virus), followed by bluegill (two) and brown trout (one) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Percentage viral prevalence in five wild fish species sampled from the Wisconsin fish survey (L. macrochirus, S. trutta, A. fulvescens, E. Lucius, and S. vitreus). Displayed is the proportion of individuals within each species that were positive for at least one virus from each viral taxonomic group. 95% confidence interval is shown in parentheses.
Prevalence of infection with any virus was highest in lake sturgeon (96.77%), followed by walleye (70.59%), bluegill (42.86%), northern pike (39.13%), and brown trout (5.56%). Total viral prevalence did not vary significantly among species (p = 0.406), virus family (p = 0.443), or region of Wisconsin (p = 0.391; determined using the Kruskal–Wallis test). Viruses with particularly high prevalence included the circoviruses, shdaciful virus 2, 3, and 4, present in lake sturgeon at 83.87% (26/31), 64.51% (20/31), and 80.65% (25/31), respectively, followed by tursanvit virus 1 (TURSV-1), a coronavirus (f. Coronaviridae: g. Gammacoronavirus) found in 11/17 (64.71%) of walleye examined. Prevalence values of remaining viruses ranged from around 5% to 39% (Table S4).
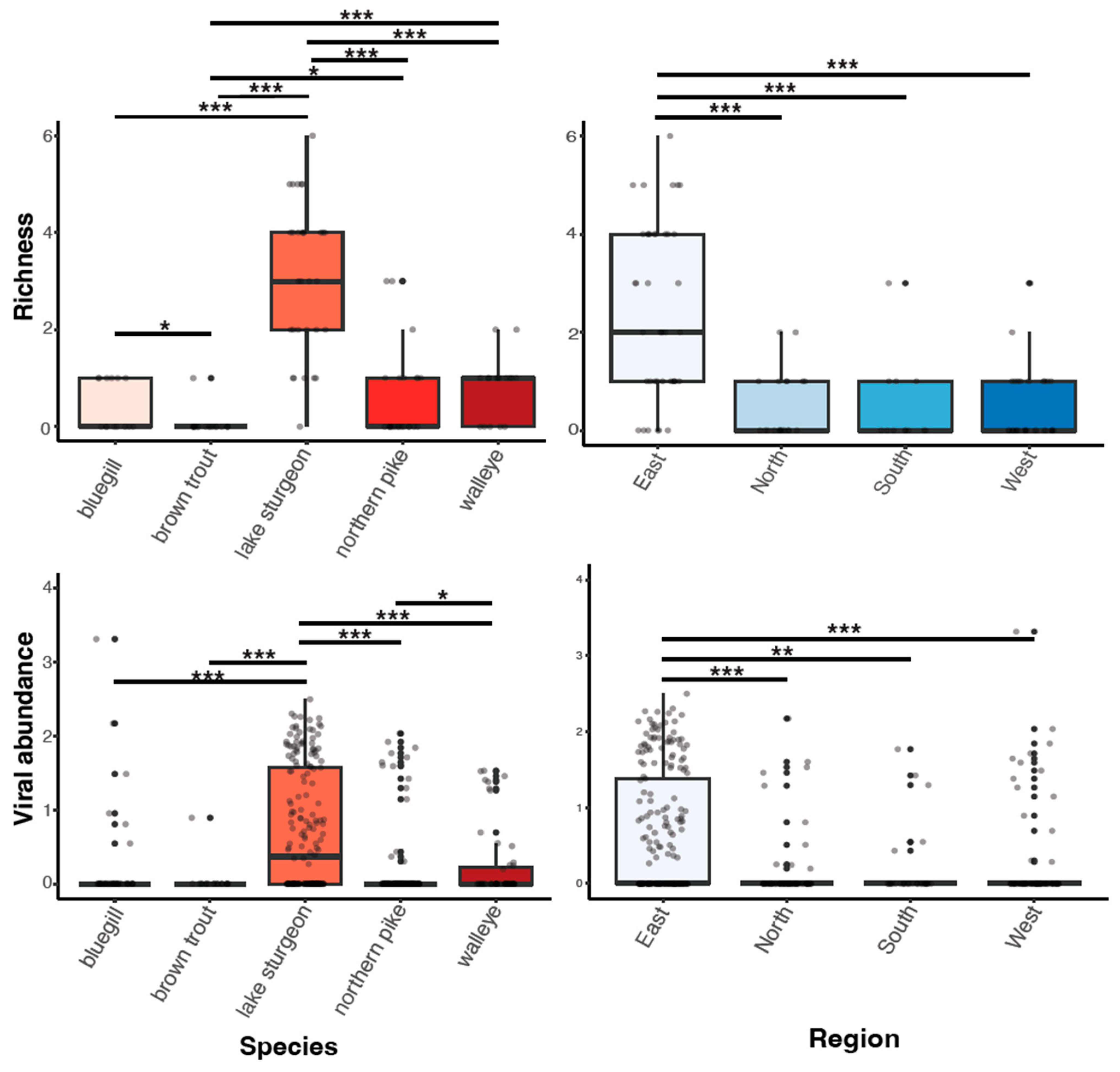
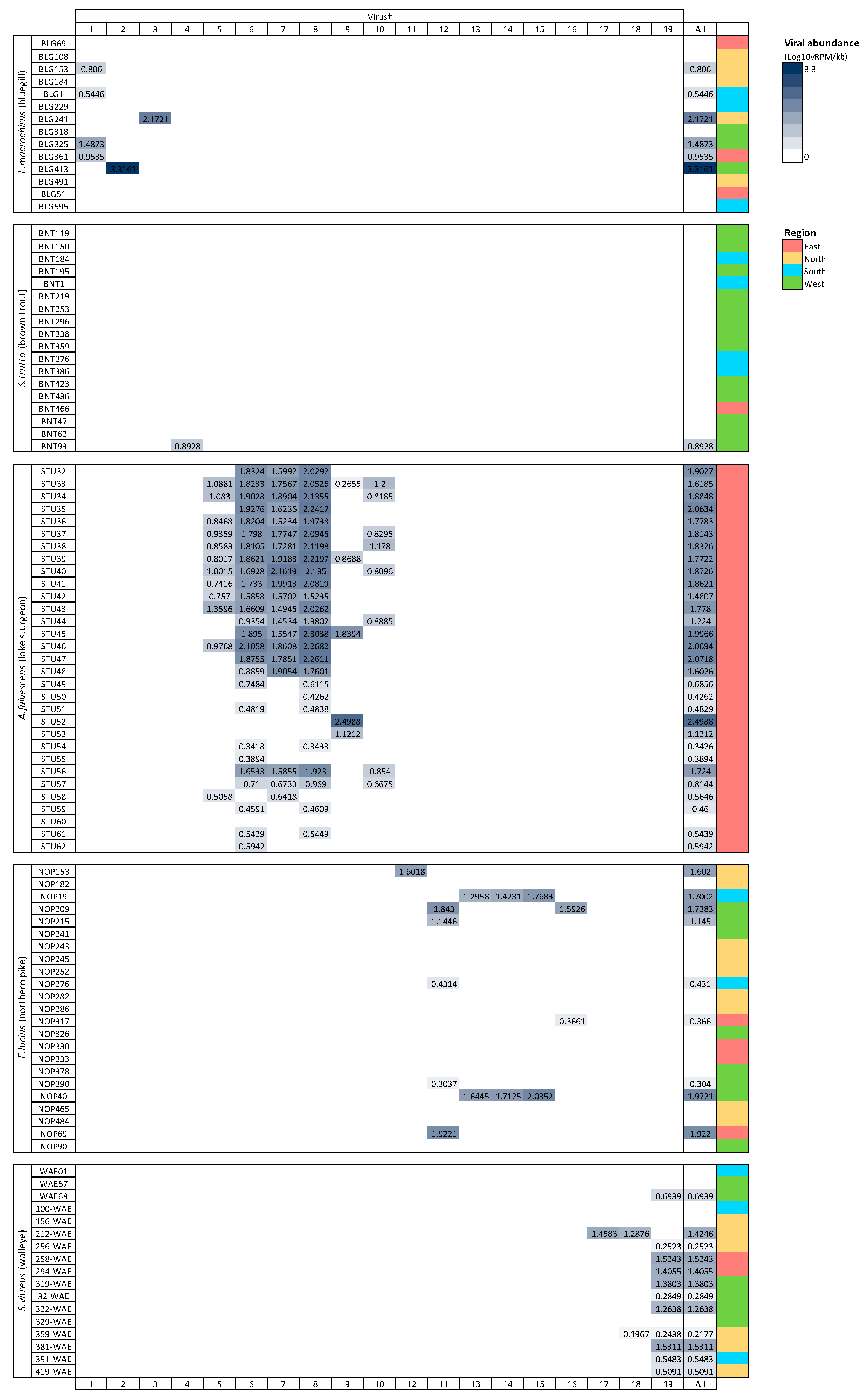
Viral richness (number of viruses per fish) ranged from 0 to 6 and differed significantly among fish species (Kruskal–Wallis chi-squared = 60.55, df = 4, p ≤ 0.0001; Figure 3). This trend was predominantly driven by the significantly higher richness in lake sturgeon, and to a lesser extent, northern pike and walleye, when compared to the other species. Viral abundance also varied significantly among species (Kruskal–Wallis chi-squared = 78.08, df = 4, p ≤ 0.0001; Figure 3). Again, this was driven by high viral abundance in lake sturgeon. Sampling region had a significant effect on both viral abundance (Kruskal–Wallis chi-squared = 50.57, df = 3, p ≤ 0.0001) and richness (Kruskal–Wallis chi-squared = 36.79, df = 3, p ≤ 0.0001), though this may be due to the large sampling numbers from the eastern region of Wisconsin. The virome of each fish species was unique, in that no individual virus was shared among fish species (Figure 4).
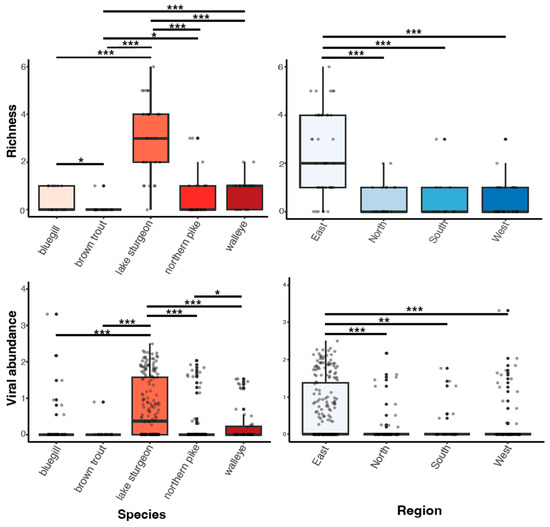
Figure 3.
Boxplots of viral richness and viral abundance (log10vRPM/kb) for each species and regional location. p < 0.05(*), 0.01(**), 0.001(***) as determined by Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a Benjamini–Hochberg adjustment.
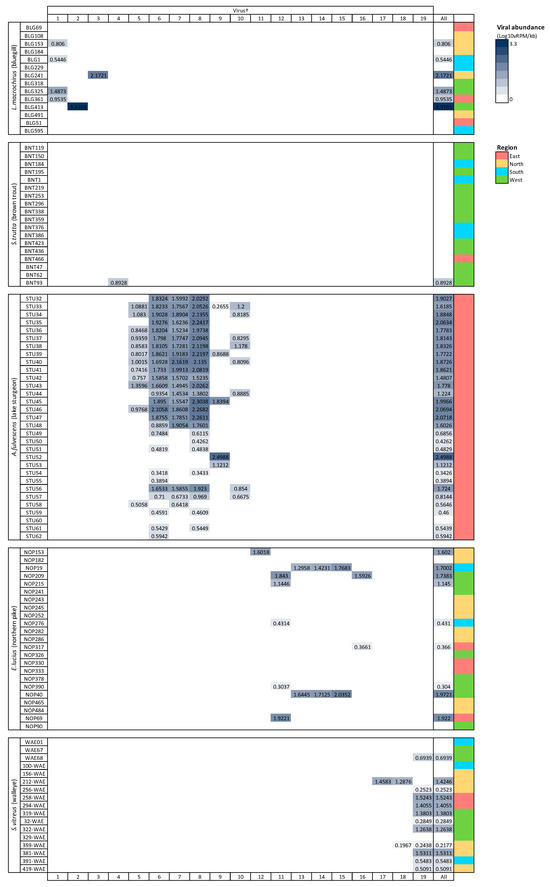
Figure 4.
Heatmap of viral abundance across species of fish. Cells are shaded in proportion to the normalized abundance of each virus and total viral abundance for all viruses. † refers to ID in Table 1. Viral abundance unit (Log10vRPM/kb) = log10 viral reads per million per kilobase of target sequence.
4. Discussion
In this study, we described the blood virome of five freshwater species of sport fish found in Wisconsin, USA. We identified 19 likely fish-infecting viruses, 17 of which are novel, with closest known relatives spanning nine viral families (Amnoonviridae, Circoviridae, Coronaviridae, Hepadnaviridae, Peribunyaviridae, Picobirnaviridae, Picornaviridae, Matonaviridae, and Nudnaviridae). We also identified a previously undescribed virus of which the family was unassigned.
4.1. Wisconsin Fish Harbor Diverse Novel Viruses
Wisconsin fish harbor viruses spanning five Baltimore classes (II, III, IV, V, VII), with RNA viruses most common and group IV predominant. This is not unexpected; there have been far more RNA virus families identified in fish than DNA viruses [2,48]. Although members of the families Circoviridae, Coronaviridae, Hepadnaviridae, Picornaviridae, and Spinareoviridae have also been found in previous metagenomic studies of wild freshwater fish [7,19,20,21], viruses from Amnoonviridae, Matonaviridae, Narnaviridae, Nudnaviridae, and Peribunyaviridae have, to our knowledge, not previously been described. Some members of these families have been detected in freshwater species previously, mostly through investigation of mortality events (e.g., tilapia lake virus; [49]), or by mining GenBank to study virus evolution [16].
Viruses in the Picornaviridae family were the only ones present in more than one species examined in this study. Picornaviruses are globally distributed and infect vertebrates of all classes. The family is extremely diverse, spanning 63 genera and 147 species [50,51]. Multiple picornaviruses have been associated with mortality in fish, causing hemorrhaging at the base of the fins and skin [17,52,53,54]. Whilst the majority of picornaviruses in the study are postulated to have originated from the environment, one virus, plasanvit virus 1 (PLASV-1), was discovered in walleye, of which the closest relative was Wenling crossorhombus picornavirus (pathogenicity unknown; [2]).
We also found piscine orthoreovirus 3 (PRV-3; brown trout) belonging to the genus Orthoreovirus within the family Spinareoviridae. PRV-3, a segmented double-stranded DNA virus, is known for causing heart inflammation in rainbow trout [55], and is currently being debated as to its association with proliferative darkening syndrome in brown trout [56,57]. Although numerous disease outbreaks have been associated with PRV-3 [55,56,58,59], there have also been reports of asymptomatic infections in brown trout [60,61]. Asymptomatic infections are often responsible for the persistence and spread of pathogens [62,63]. For example, the non-virulent infectious salmon anemia virus (ISAV-HPR0), detected in Canada since 1998 in the absence of virulent strains, has also been implicated in disease outbreaks through the transition of ISAV-HPR0 to ISAV-HPRΔ, its virulent form [64,65]. Similarly, the survivors of an infectious pancreatic necrosis virus outbreak became carriers of the virus, allowing the virus to persist and spread, sometimes over years [66]. We note that largemouth bass reovirus, an orthoreovirus, was previously discovered in Wisconsin following a fish kill of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides; [18]).
Members of the family Amnoonviridae, to which lipesoluc virus 1 in northern pike identified in this study putatively belongs, have also been associated with disease in fish. Tilapia lake virus, for instance, is the causative agent of a disease which induces lethargy, ocular alterations and skin erosion, and has resulted in mass mortalities of both wild and cultured Tilapia [67]. Together with flavolineata virus, which is not known to cause disease [68], tilapia lake virus is the known closest relative of LIPEV-1. Whether LIPEV-1 or the other aforementioned viruses cause disease in the fish in which we found them remains unknown.
We note that viruses from the families Narnaviridae and Picobirnaviridae may not directly infect their animal hosts, but rather the fungi and/or bacteria residing within them [69,70]. As members of the Narnaviridae family, for instance, infect a diverse array of hosts such as fungi, plants and protists, they may be useful indicators of other threats to fish health such as from endoparasites or disease-associated fungi [15,71]. We also note that viruses from the family Circoviridae were particularly abundant within this study, driven by lake sturgeon. Circoviruses have only recently been discovered in fish and amphibians, but it is becoming clear that circoviruses may be common in fish [72,73,74]. Whether these viruses are associated with disease in fish has yet to be determined.
4.2. Viromes of Wild Freshwater Fish Reveal Further Insights into Evolutionary Histories of Viral Families
Until recently, the only known species within the family Matonaviridae was rubella virus, a pathogen of global concern to human health [75,76]. More recently, this has been expanded to include matonaviruses in other mammals, as well as amphibians, reptiles, and fish [10,77,78,79,80]. In this study, we identified two putative matonaviruses in bluegill; the first, to our knowledge, to be identified in a freshwater species. Mislepmac virus 1 (MISLV-1) clustered with a distinct group of fish/reptile-associated matonaviruses, whereas eaulepmac virus 1 (EAULV-1) was most closely related to tetronarce matonavirus (TeMV) found in a Pacific eel ray (Tetronarce, tetronarca californica). It is intriguing that both MISLV-1 and EAULV-1, representing the two basally diverging lineages within the matonavirus phylogeny (Figure 2A), were found in bluegill in the same geographic location. This finding suggests that the evolutionary diversification of fish viruses may not depend on geographic separation, but rather the long-term virus–host co-divergence [1,9,21]. Our results are consistent with the notion that viruses from fish tend to form basally diverging lineages compared to viruses from other vertebrates, reflecting a longer evolutionary relationship with fish [2].
In the case of the hepadnaviruses, shwaciful virus 1 (SHWAV-1) is most closely related to an amphibian hepatitis B virus (sharing 40% amino acid identity), both of which form a group that is sister to the known hepadnaviruses of mammals, and more distantly related to known hepadnaviruses of non-mammalian vertebrates, including those of other fish (Figure 2C). This family is known to cause disease in a number of species. For instance, human-associated hepatitis B virus infects more than two billion people worldwide and can result in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma in approximately 105 million people globally [81]. Similar pathology is observed in woodchuck and duck hepatitis B virus, both of which have been identified as causative agents of liver necrosis in their respective hosts [13]. However, to our knowledge, no disease has been associated with hepadnaviruses in fish. Unlike matonaviruses, hepadnaviruses identified from fish are found not just basally, but throughout the phylogenetic tree (Figure 2C). Interestingly, hepadnaviruses have occasionally experienced cross-species jumps over large evolutionary distances of hosts, as revealed through cophylogenetic reconciliation analyses [1], which may help to explain their phylogenetic positioning. Certainly, the discovery of additional members of the Hepadnaviridae will shed more light on the contributions of host switches to the evolutionary origins of what could have, until recently, been considered a family of mammalian specialist viruses.
4.3. A Gammacoronavirus Detected in Walleye
The family Coronaviridae contains enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses with a broad host range. Most viruses within this family fall within the sub-family Orthovirinae, and predominantly infect mammals and birds, with the exception of a single virus from a reptilian host [2]. In recent years, the host range of this family has expanded to include another sub-family, Letovirinae, containing coronaviruses from both amphibian and fish hosts [8,82]. Mordecai et al. (2019) suggested that this sub-family was likely far larger than had been documented at the time [8], and indeed subsequent mining of transcriptomic data has revealed further viruses within this group.
The genus Gammacoronavirus within the Coronaviridae family predominantly infects birds, although gammacoronaviruses have been found in aquatic mammals, forming the subgenus Cegacovirus [47,83]. The discovery of tursanvit virus 1 (TURSV-1) in walleye, represents (to our knowledge) the first such gammacoronavirus identified in fish. TURSV-1 is most closely related to infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), exemplar member of the subgenus Igacovirus, all of which infect birds [84,85]. IBV, predominantly a pathogen of chickens, affects the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, kidney and reproductive systems of poultry, which has led to economic losses within the industry [46]. A fish-associated igacovirus would therefore significantly expand the host range of this subgenus. The replication ability and pathogenicity of TURSV-1 in walleye, however, remains unknown.
In summary, we identified a diverse assemblage of viruses in five wild freshwater species of fish in Wisconsin, USA. A number of these viruses are closely related to, or are known themselves to be, causative agents of disease in fish. Our virome profiles surely underestimate the full diversity of viruses in the fish we examined. Among other considerations, we examined viruses in blood, and research on wild marine fish has documented significant differences in virome composition among organs [4]. Nevertheless, our results show that freshwater fish host distant relatives of pathogens impacting global fish and animal health, including several viruses of importance to human health, which is a notion previously supported by research on marine fish. In addition to more studies of freshwater fish viromes in further geographic locations, we suggest that future research should focus on determining the pathogenicity of the viruses we have identified in fish and examining the genomes of novel viruses and their as-yet-undiscovered relatives in order to further examine the evolutionary histories of their respective families.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens13020150/s1, Table S1: Sampling locations for five fish species sampled during the Wisconsin fish survey; Table S2: Environmentally derived contigs present in samples; Table S3: ORFs and substitution models for each Bayesian phylogenetic tree; Table S4: Virus prevalence in each fish species.
Author Contributions
T.L.G. and E.M.L. designed the study; W.A.T. collected the samples; C.D.D. processed the samples; C.E.F. analyzed the data; C.E.F. prepared the manuscript with edits from all co-authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the University of Wisconsin Sea Grant Institute (grant.R/SFA-24).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The sequence reads generated in this study are available at the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database under BioProject accession PRJNA1053451. Viral sequences described in this study have been deposited in GenBank under accession numbers PP002545-PP002573. Details for individual fish sample locations, viruses described in this study, and phylogenetic information are provided in Supplementary Tables S1–S4.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the WI DNR Bureau of Fisheries Management for their efforts in the collection of samples used in this project. We would like to thank the reviewers for taking the necessary time and effort to review the manuscript. We sincerely appreciate all your valuable comments and suggestions, which helped us in improving the quality of the manuscript. Usage of trade names does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. The findings and conclusions in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Geoghegan, J.L.; Di Giallonardo, F.; Cousins, K.; Shi, M.; Williamson, J.E.; Holmes, E.C. Hidden Diversity and Evolution of Viruses in Market Fish. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Chen, X.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Li, K.; Wang, W.; Eden, J.S.; Shen, J.J.; Liu, L.; et al. The Evolutionary History of Vertebrate RNA Viruses. Nature 2018, 556, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipa-Silva, A.; Parreira, R.; Martínez-Puchol, S.; Bofill-Mas, S.; Barreto Crespo, M.T.; Nunes, M. The Unexplored Virome of Two Atlantic Coast Fish: Contribution of Next-Generation Sequencing to Fish Virology. Foods 2020, 9, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadoin, E.; Desnues, C.; Monteil-Bouchard, S.; Bouvier, T.; Auguet, J.-C.; d’Orbcastel, E.R.; Bettarel, Y. Fishing for the Virome of Tropical Tuna. Viruses 2021, 13, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, B.J.; Darestani, M.M.; Ara, M.G.; Hoste, A.; Jandt, J.M.; Dutoit, L.; Holmes, E.C.; Ingram, T.; Geoghegan, J.L. Viromes of Freshwater Fish with Lacustrine and Diadromous Life Histories Differ in Composition. Viruses 2022, 14, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.J.; Castillo, N.A.; Dunn, C.D.; Perez, A.; Schmitter-Soto, J.J.; Mejri, S.C.; Boucek, R.E.; Corujo, R.S.; Adams, A.J.; Rehage, J.S.; et al. Viruses of Atlantic Bonefish (Albula vulpes) in Florida and the Caribbean Show Geographic Patterns Consistent with Population Declines. Environ. Biol. Fish 2023, 106, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xie, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, H.; Qin, K.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Shen, Q.; et al. Viromics Reveals the High Diversity of Viruses from Fishes of the Tibet Highland. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00946-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordecai, G.J.; Miller, K.M.; Di Cicco, E.; Schulze, A.D.; Kaukinen, K.H.; Ming, T.J.; Li, S.; Tabata, A.; Teffer, A.; Patterson, D.A.; et al. Endangered Wild Salmon Infected by Newly Discovered Viruses. eLife 2019, 8, e47615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.K.; Mifsud, J.C.O.; Costa, V.A.; Grimwood, R.M.; Kitson, J.; Baker, C.; Brosnahan, C.L.; Pande, A.; Holmes, E.C.; Gemmell, N.J.; et al. Slippery When Wet: Cross-Species Transmission of Divergent Coronaviruses in Bony and Jawless Fish and the Evolutionary History of the Coronaviridae. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Taylor, J.; Lin, V.; Altman, T.; Barbera, P.; Meleshko, D.; Lohr, D.; Novakovsky, G.; Buchfink, B.; Al-Shayeb, B.; et al. Petabase-Scale Sequence Alignment Catalyses Viral Discovery. Nature 2022, 602, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierweger, M.M.; Koch, M.C.; Rupp, M.; Maes, P.; Di Paola, N.; Bruggmann, R.; Kuhn, J.H.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Seuberlich, T. Novel Filoviruses, Hantavirus, and Rhabdovirus in Freshwater Fish, Switzerland, 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 3082–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, A.J.; Mühlberger, E. Distinct Genome Replication and Transcription Strategies within the Growing Filovirus Family. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 4290–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dill, J.A.; Camus, A.C.; Leary, J.H.; Di Giallonardo, F.; Holmes, E.C.; Ng, T.F.F. Distinct Viral Lineages from Fish and Amphibians Reveal the Complex Evolutionary History of Hepadnaviruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7920–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltzek, T.B.; Subramaniam, K.; Leis, E.; Katona, R.; Fan Ng, T.F.; Delwart, E.; Barbknecht, M.; Rock, K.; Hoffman, M.A. Characterization of a Peribunyavirus Isolated from Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Virus Res. 2019, 273, 197761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoghegan, J.L.; Di Giallonardo, F.; Wille, M.; Ortiz-Baez, A.S.; Costa, V.A.; Ghaly, T.; Mifsud, J.C.O.; Turnbull, O.M.H.; Bellwood, D.R.; Williamson, J.E.; et al. Virome Composition in Marine Fish Revealed by Meta-Transcriptomics. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauber, C.; Seitz, S.; Mattei, S.; Suh, A.; Beck, J.; Herstein, J.; Börold, J.; Salzburger, W.; Kaderali, L.; Briggs, J.A.G.; et al. Deciphering the Origin and Evolution of Hepatitis B Viruses by Means of a Family of Non-Enveloped Fish Viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 387–399.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbknecht, M.; Sepsenwol, S.; Leis, E.; Tuttle-Lau, M.; Gaikowski, M.; Knowles, N.J.; Lasee, B.; Hoffman, M.A. Characterization of a New Picornavirus Isolated from the Freshwater Fish Lepomis Macrochirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, S.D.; Finley, M.A.; Baker, B.B.; Puzach, C.; Armién, A.G.; Giehtbrock, D.; Goldberg, T.L. Novel Reovirus Associated with Epidemic Mortality in Wild Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2482–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.A.; Mifsud, J.C.O.; Gilligan, D.; Williamson, J.E.; Holmes, E.C.; Geoghegan, J.L. Metagenomic Sequencing Reveals a Lack of Virus Exchange between Native and Invasive Freshwater Fish across the Murray–Darling Basin, Australia. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, G.; Boros, Á.; Mátics, R.; Altan, E.; Delwart, E.; Pankovics, P. A Novel Parvovirus (Family Parvoviridae) in a Freshwater Fish, Zander (Sander lucioperca). Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimwood, R.M.; Fortune-Kelly, G.; Holmes, E.C.; Ingram, T.; Geoghegan, J.L. Host Specificity Shapes Fish Viromes across Lakes on an Isolated Remote Island. Virology 2023, 587, 109884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.G.; Kottelat, M.; Smith, G.R.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; Gill, A.C. So Many Fishes, So Little Time: An Overview of Recent Ichthyological Discovery in Continental Waters. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2000, 87, 26–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, B.J.; Anderson, H.A.; Hanrahan, L.P.; Olson, L.J.; Sonzogni, W.C. Sport Fish Consumption and Body Burden Levels of Chlorinated Hydrocarbons: A Study of Wisconsin Anglers. Arch. Environ. Health 1989, 44, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, W.A.; Toohey-Kurth, K.L.; Giehtbrock, D.; Baker, B.B.; Finley, M.; Goldberg, T.L. Widespread Seropositivity to Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus (VHSV) in Four Species of Inland Sport Fishes in Wisconsin. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2021, 33, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.C.; Leis, E.M.; Dunn, C.D.; Harris, C.; Agbalog, R.E.; Campbell, L.J.; Knowles, S.; Waller, D.L.; Putnam, J.G.; Goldberg, T.L. Freshwater Mussels Show Elevated Viral Richness and Intensity during a Mortality Event. Viruses 2022, 14, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunay, E.; Owens, L.A.; Dunn, C.D.; Rukundo, J.; Atencia, R.; Cole, M.F.; Cantwell, A.; Emery Thompson, M.; Rosati, A.G.; Goldberg, T.L. Viruses in Sanctuary Chimpanzees across Africa. Am. J. Primatol. 2023, 85, e23452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurk, S.; Meleshko, D.; Korobeynikov, A.; Pevzner, P.A. metaSPAdes: A New Versatile Metagenomic Assembler. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huson, D.H.; Auch, A.F.; Qi, J.; Schuster, S.C. MEGAN Analysis of Metagenomic Data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and Sensitive Protein Alignment Using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, E.W.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Ostell, J.; Pruitt, K.D.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D94–D99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bryant, S.H. CD-Search: Protein Domain Annotations on the Fly. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W327–W331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulo, C.; de Castro, E.; Masson, P.; Bougueleret, L.; Bairoch, A.; Xenarios, I.; Le Mercier, P. ViralZone: A Knowledge Resource to Understand Virus Diversity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D576–D582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkowitz, E.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Orton, R.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Smith, D.B. Virus Taxonomy: The Database of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D708–D717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisza, M.J.; Belford, A.K.; Domínguez-Huerta, G.; Bolduc, B.; Buck, C.B. Cenote-Taker 2 Democratizes Virus Discovery and Sequence Annotation. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veaa100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Church, D.M.; Federhen, S.; Lash, A.E.; Madden, T.L.; Pontius, J.U.; Schuler, G.D.; Schriml, L.M.; Sequeira, E.; Tatusova, T.A.; et al. Database Resources of the National Center for Biotechnology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICTV Report Chapters|ICTV. Available online: https://ictv.global/report (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A Multiple Sequence Alignment Method with Reduced Time and Space Complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyama, M.; Torrents, D.; Bork, P. PAL2NAL: Robust Conversion of Protein Sequence Alignments into the Corresponding Codon Alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W609–W612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian Inference of Phylogenetic Trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, F.; Correia, D.; Lefort, V.; Doppelt-Azeroual, O.; Mareuil, F.; Cohen-Boulakia, S.; Gascuel, O. NGPhylogeny.Fr: New Generation Phylogenetic Services for Non-Specialists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W260–W265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Posada, D.; Kozlov, A.M.; Stamatakis, A.; Morel, B.; Flouri, T. ModelTest-NG: A New and Scalable Tool for the Selection of DNA and Protein Evolutionary Models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FigTree. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Agresti, A.; Coull, B.A. Approximate Is Better than “Exact” for Interval Estimation of Binomial Proportions. Am. Stat. 1998, 52, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Quinteros, J.; Noormohammadi, A.; Lee, S.; Browning, G.; Diaz-Méndez, A. Genomics and Pathogenesis of the Avian Coronavirus Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Aust. Vet. J. 2022, 100, 496–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; de Groot, R.J.; Haagmans, B.; Lau, S.K.P.; Neuman, B.W.; Perlman, S.; Sola, I.; van der Hoek, L.; Wong, A.C.P.; Yeh, S.-H. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Coronaviridae 2023. J. Gen. Virol. 2023, 104, 001843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, J.C. Fish Viruses. In Encyclopedia of Virology, 3rd ed.; Mahy, B.W.J., Van Regenmortel, M.H.V., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 227–234. ISBN 978-0-12-374410-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bacharach, E.; Mishra, N.; Briese, T.; Zody, M.C.; Kembou Tsofack, J.E.; Zamostiano, R.; Berkowitz, A.; Ng, J.; Nitido, A.; Corvelo, A.; et al. Characterization of a Novel Orthomyxo-like Virus Causing Mass Die-Offs of Tilapia. mBio 2016, 7, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zell, R. Picornaviridae—The Ever-Growing Virus Family. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zell, R.; Delwart, E.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Hovi, T.; King, A.M.Q.; Knowles, N.J.; Lindberg, A.M.; Pallansch, M.A.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Reuter, G.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Picornaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2421–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, P.E. Salmonid Fish Viruses. In Fish Medicine; Stoskopf, M.K., Ed.; W. B. Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993; pp. 380–408. [Google Scholar]
- McAllister, P.E. Freshwater Temperate Fish Viruses. In Fish Medicine; Stoskopf, M.K., Ed.; W. B. Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993; pp. 284–300. [Google Scholar]
- Mor, S.K.; Phelps, N.B.D. Chapter 21—Picornaviruses of Fish. In Aquaculture Virology; Kibenge, F.S.B., Godoy, M.G., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 337–348. ISBN 978-0-12-801573-5. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, A.B.; Hjortaas, M.; Tengs, T.; Hellberg, H.; Johansen, R. First Description of a New Disease in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum)) Similar to Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation (HSMI) and Detection of a Gene Sequence Related to Piscine Orthoreovirus (PRV). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, R.; Stoeckle, B.C.; Young, M.; Popp, L.; Taeubert, J.-E.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Geist, J. Identification of a Piscine Reovirus-Related Pathogen in Proliferative Darkening Syndrome (PDS) Infected Brown Trout (Salmo trutta fario) Using a next-Generation Technology Detection Pipeline. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, R.; Arndt, D.; Langenmayer, M.C.; Schwaiger, J.; Ferling, H.; Fischer, N.; Indenbirken, D.; Grundhoff, A.; Dölken, L.; Adamek, M.; et al. Piscine Orthoreovirus 3 Is Not the Causative Pathogen of Proliferative Darkening Syndrome (PDS) of Brown Trout (Salmo trutta fario). Viruses 2019, 11, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendramin, N.; Kannimuthu, D.; Olsen, A.B.; Cuenca, A.; Teige, L.H.; Wessel, Ø.; Iburg, T.M.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E.; Olesen, N.J. Piscine Orthoreovirus Subtype 3 (PRV-3) Causes Heart Inflammation in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, J.; Vendramin, N.; Priess, C.; Kannimuthu, D.; Henriksen, N.H.; Iburg, T.M.; Olesen, N.J.; Cuenca, A. Emergence and Spread of Piscine Orthoreovirus Genotype 3. Pathogens 2020, 9, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamotharan, K.; Vendramin, N.; Markussen, T.; Wessel, Ø.; Cuenca, A.; Nyman, I.B.; Olsen, A.B.; Tengs, T.; Krudtaa Dahle, M.; Rimstad, E. Molecular and Antigenic Characterization of Piscine Orthoreovirus (PRV) from Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Viruses 2018, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teige, L.H.; Kumar, S.; Johansen, G.M.; Wessel, Ø.; Vendramin, N.; Lund, M.; Rimstad, E.; Boysen, P.; Dahle, M.K. Detection of Salmonid IgM Specific to the Piscine Orthoreovirus Outer Capsid Spike Protein Sigma 1 Using Lipid-Modified Antigens in a Bead-Based Antibody Detection Assay. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenes, R.; Gray, M.J.; Waltzek, T.B.; Wilkes, R.P.; Miller, D.L. Transmission of Ranavirus between Ectothermic Vertebrate Hosts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, N.; Swali, P.; Houben, R.M.G.J. Asymptomatic but Infectious—The Silent Driver of Pathogen Transmission. A Pragmatic Review. Epidemics 2023, 44, 100704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagné, N.; LeBlanc, F. Overview of Infectious Salmon Anaemia Virus (ISAV) in Atlantic Canada and First Report of an ISAV North American-HPR0 Subtype. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas, C.; Carmona, M.; Gallardo, A.; Labra, A.; Marshall, S.H. Coexistence in Field Samples of Two Variants of the Infectious Salmon Anemia Virus: A Putative Shift to Pathogenicity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dopazo, C.P. The Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) and Its Virulence Determinants: What Is Known and What Should Be Known. Pathogens 2020, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyngor, M.; Zamostiano, R.; Kembou Tsofack, J.E.; Berkowitz, A.; Bercovier, H.; Tinman, S.; Lev, M.; Hurvitz, A.; Galeotti, M.; Bacharach, E.; et al. Identification of a Novel RNA Virus Lethal to Tilapia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 52, 4137–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, O.M.H.; Ortiz-Baez, A.S.; Eden, J.-S.; Shi, M.; Williamson, J.E.; Gaston, T.F.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Holmes, E.C.; Geoghegan, J.L. Meta-Transcriptomic Identification of Divergent Amnoonviridae in Fish. Viruses 2020, 12, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D. The Enigma of Picobirnaviruses: Viruses of Animals, Fungi, or Bacteria? Curr. Opin. Virol. 2022, 54, 101232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, B.I.; Cai, G. Chapter Six—The Family Narnaviridae: Simplest of RNA Viruses. In Advances in Virus Research; Ghabrial, S.A., Ed.; Mycoviruses; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 86, pp. 149–176. [Google Scholar]
- Fay, E.J.; Balla, K.M.; Roach, S.N.; Shepherd, F.K.; Putri, D.S.; Wiggen, T.D.; Goldstein, S.A.; Pierson, M.J.; Ferris, M.T.; Thefaine, C.E.; et al. Natural Rodent Model of Viral Transmission Reveals Biological Features of Virus Population Dynamics. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 219, e20211220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lőrincz, M.; Cságola, A.; Farkas, S.L.; Székely, C.; Tuboly, T. First Detection and Analysis of a Fish Circovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarján, Z.; Pénzes, J.; Tóth, R.; Benkő, M. First Detection of Circovirus-like Sequences in Amphibians and Novel Putative Circoviruses in Fishes. Acta Vet. Hung. 2013, 62, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuboly, T. Chapter 12—Circoviruses of Fish. In Aquaculture Virology; Kibenge, F.S.B., Godoy, M.G., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 183–190. ISBN 978-0-12-801573-5. [Google Scholar]
- Muscat, M.; Shefer, A.; Ben Mamou, M.; Spataru, R.; Jankovic, D.; Deshevoy, S.; Butler, R.; Pfeifer, D. The State of Measles and Rubella in the WHO European Region, 2013. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.K.; Moss, W.J. Rubella. Lancet 2022, 399, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.J.; Paskey, A.C.; Ebinger, A.; Pfaff, F.; Priemer, G.; Höper, D.; Breithaupt, A.; Heuser, E.; Ulrich, R.G.; Kuhn, J.H.; et al. Relatives of Rubella Virus in Diverse Mammals. Nature 2020, 586, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, F.; Breithaupt, A.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Nippert, S.; Baumbach, C.; Gerst, S.; Langner, C.; Wylezich, C.; Ebinger, A.; Höper, D.; et al. Revisiting Rustrela Virus: New Cases of Encephalitis and a Solution to the Capsid Enigma. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00103-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiasek, K.; Pfaff, F.; Weissenböck, H.; Wylezich, C.; Kolodziejek, J.; Tengstrand, S.; Ecke, F.; Nippert, S.; Starcky, P.; Litz, B.; et al. Mystery of Fatal ‘Staggering Disease’ Unravelled: Novel Rustrela Virus Causes Severe Meningoencephalomyelitis in Domestic Cats. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimwood, R.M.; Holmes, E.C.; Geoghegan, J.L. A Novel Rubi-Like Virus in the Pacific Electric Ray (Tetronarce Californica) Reveals the Complex Evolutionary History of the Matonaviridae. Viruses 2021, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.P.; Easterbrook, P.J.; McMahon, B.J. Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Impact of Vaccination on Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 607–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, K.; Mulley, G.; Gulyaeva, A.A.; Zhao, L.; Shu, G.; Jiang, J.; Neuman, B.W. Description and Initial Characterization of Metatranscriptomic Nidovirus-like Genomes from the Proposed New Family Abyssoviridae, and from a Sister Group to the Coronavirinae, the Proposed Genus Alphaletovirus. Virology 2018, 524, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütze, H. Coronaviruses in Aquatic Organisms. Aquac. Virol. 2016, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, M.; Holmes, E.C. Wild Birds as Reservoirs for Diverse and Abundant Gamma- and Deltacoronaviruses. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchenko, V.; Danilenko, A.; Kolosova, N.; Bragina, M.; Molchanova, M.; Bulanovich, Y.; Gorodov, V.; Leonov, S.; Gudymo, A.; Onkhonova, G.; et al. Diversity of Gammacoronaviruses and Deltacoronaviruses in Wild Birds and Poultry in Russia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).