Differential Gene Expression in the Upper Respiratory Tract following Acute COVID-19 Infection in Ambulatory Patients That Develop Long COVID
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cohort Description
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction and Viral Load Quantification
2.3. RNA Sequencing
2.4. Serology
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Description
3.2. Quantification of Viral RNA in Respiratory Specimens
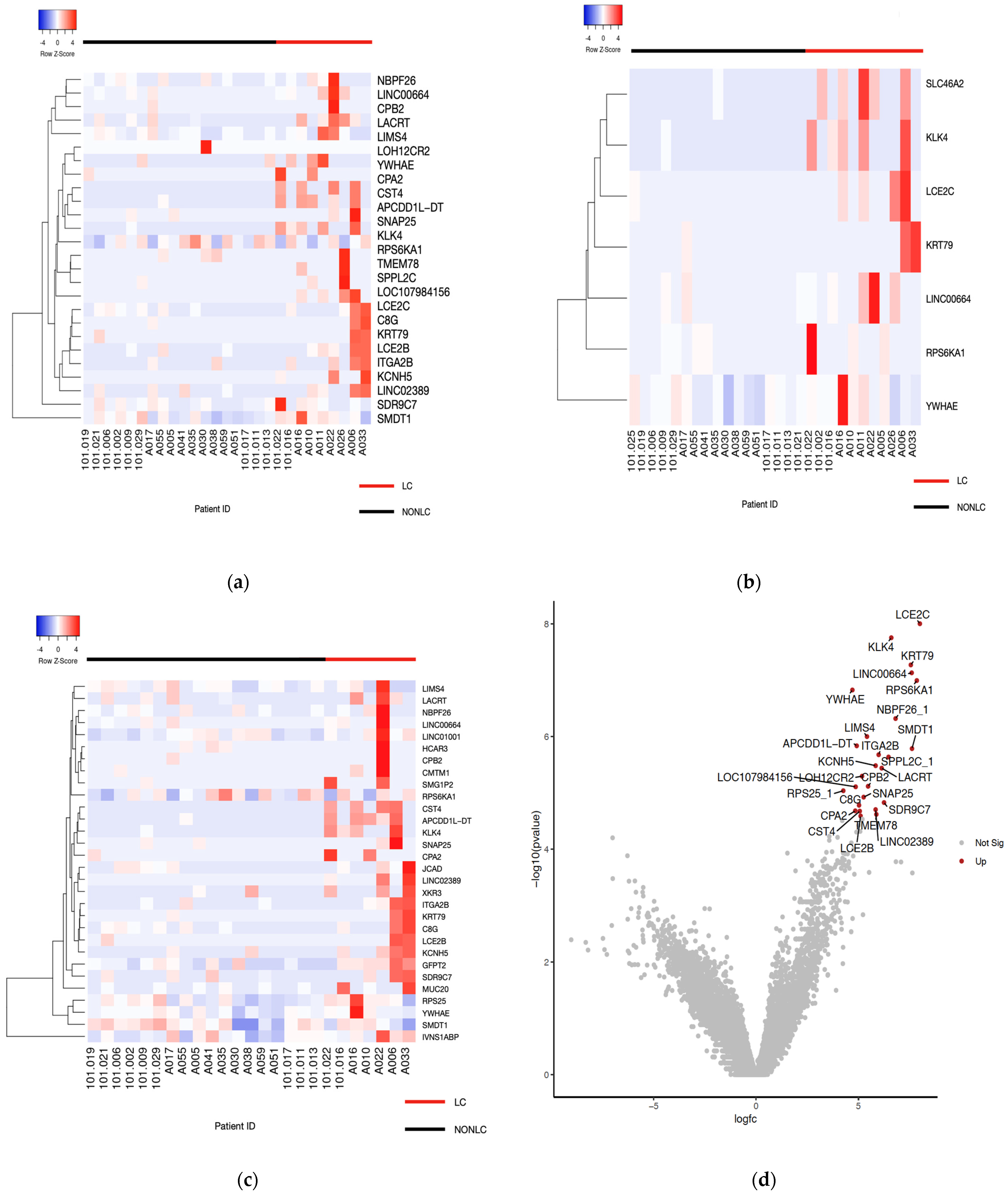
3.3. Distinct Gene Expression Patterns and Pathways Associated with Long COVID
3.4. Dysregulated Pathways in LC Patients
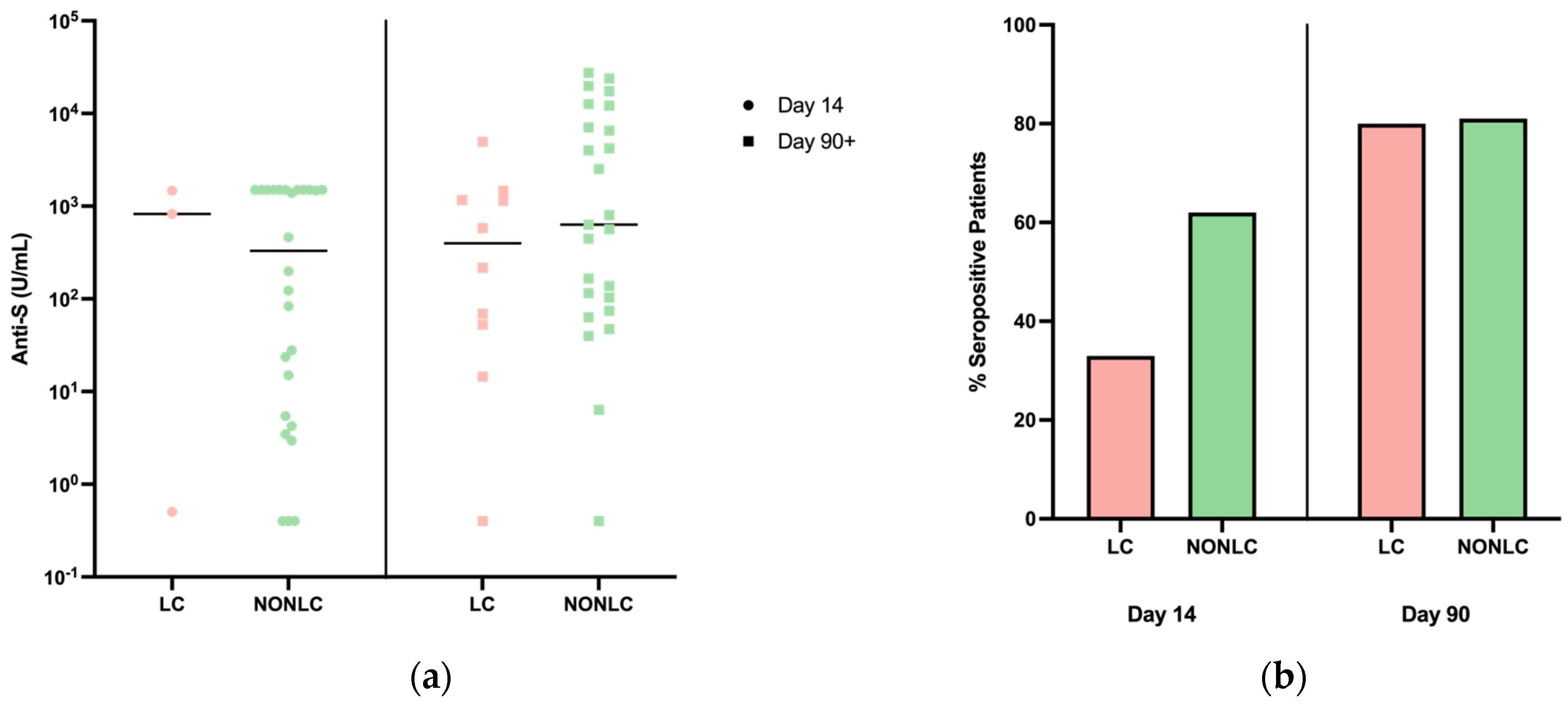
3.5. Serology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altmann, D.M.; Whettlock, E.M.; Liu, S.; Arachchillage, D.J.; Boyton, R.J. The immunology of long COVID. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 618–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowe, B.; Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Postacute sequelae of COVID-19 at 2 years. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2347–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, M.; Pujol, J.C.; Spector, T.D.; Ourselin, S.; Steves, C.J. Risk of long COVID associated with delta versus omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2. Lancet 2022, 399, 2263–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowe, B.; Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Acute and postacute sequelae associated with SARS-CoV-2 reinfection. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2398–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Yuan, D.; Chen, D.G.; Ng, R.H.; Wang, K.; Choi, J.; Li, S.; Hong, S.; Zhang, R.; Xie, J.; et al. Multiple early factors anticipate post-acute COVID-19 sequelae. Cell 2022, 185, 881–895.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.C.; Devason, A.S.; Umana, I.C.; Cox, T.O.; Dohnalova, L.; Litichevskiy, L.; Perla, J.; Lundgren, P.; Etwebi, Z.; Izzo, L.T.; et al. Serotonin reduction in post-acute sequelae of viral infection. Cell 2023, 186, 4851–4867.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervia-Hasler, C.; Bruningk, S.C.; Hoch, T.; Fan, B.; Muzio, G.; Thompson, R.C.; Ceglarek, L.; Meledin, R.; Westermann, P.; Emmenegger, M.; et al. Persistent complement dysregulation with signs of thromboinflammation in active Long Covid. Science 2024, 383, eadg7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, R.A.; Salvant, E.; Chang, V.; Oikonomou, A.; Biondi, M.J.; Feld, J.J.; Armstrong, S.; Wasif, S.; Mubareka, S.; Nirmalarajah, K.; et al. Host Expression Profiling From Diagnostic Coronavirus Disease 2019 Swabs Associates Upper Respiratory Tract Immune Responses with Radiologic Lung Pathology and Clinical Severity. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023, 10, ofad190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, D.; Mozsary, C.; Meydan, C.; Foox, J.; Rosiene, J.; Shaiber, A.; Mason, C.E.; Bhattacharya, C.; Young, B.; Ryon, K.; et al. Shotgun transcriptome, spatial omics, and isothermal profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals unique host responses, viral diversification, and drug interactions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Dean, L.S.; Jiyarom, B.; Khadka, V.; Deng, Y.; Nerurukar, V.R.; Park, J.; Koh, Y.; Devendra, G.; Shikuma, C.M.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals characteristics of myeloid cells in pulmonary post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Frere, J.J.; Serafini, R.A.; Pryce, K.D.; Zazhytska, M.; Oishi, K.; Golynker, I.; Tenoever, B.R.; Zachariou, V.; Lomvardas, S.; Schwartz, R.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in hamsters and humans results in lasting and unique systemic perturbations after recovery. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabq3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaweethai, T.; Jolley, S.E.; Karlson, E.W.; Levitan, E.B.; Levy, B.; McComsey, G.A.; Donohue, S.E.; Atchley-Challenner, R.; Shinnick, D.J.; Selvaggi, C.A.; et al. Development of a Definition of Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA 2023, 329, 1934–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, J.J.; Kandel, C.; Biondi, M.J.; Kozak, R.A.; Zahoor, M.A.; Lemieux, C.; Borgia, S.M.; Boggild, A.K.; Powis, J.; McCready, J.; et al. Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of outpatients with COVID-19: A phase 2, placebo-controlled randomised trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, G.; Moreira Silva, E.A.S.; Medeiros Silva, D.C.; Thabane, L.; Campos, V.H.S.; Ferreira, T.S.; Santos, C.V.; Nogueira, A.M.; Almeida, A.P.; Savassi, L.C.; et al. Early Treatment with Pegylated Interferon Lambda for COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Meo, A.; Ma, L.; Yau, K.; Abe, K.T.; Colwill, K.; Gingras, A.C.; Yip, P.M.; Hladunewich, M.A. Evaluation of commercial assays for the assessment of SARS-CoV-2 antibody response in hemodialysis patients. Clin. Biochem. 2023, 121–122, 110681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afgan, E.; Nekrutenko, A.; Grüning, B.A.; Blankenberg, D.; Goecks, J.; Schatz, M.C.; Ostrovsky, A.E.; Mahmoud, A.; Lonie, A.J.; Syme, A.; et al. Correction to ‘The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2022 update’. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 8999. [Google Scholar]
- Sayers, E.W.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; Funk, K.; Kelly, C.; Kim, S.; et al. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D20–D26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’Ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Bailey, A.; Kuleshov, M.V.; Clarke, D.J.; Evangelista, J.E.; Jenkins, S.L.; Ma’ayan, A.; Jeon, M.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Kropiwnicki, E.; et al. Gene Set Knowledge Discovery with Enrichr. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, J.B.; Murthy, S.; Marshall, J.C.; Relan, P.; Diaz, J.V. A clinical case definition of post-COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafran, N.; Shafran, I.; Ben-Zvi, H.; Sofer, S.; Sheena, L.; Krause, I.; Shlomai, A.; Goldberg, E.; Sklan, E.H. Secondary bacterial infection in COVID-19 patients is a stronger predictor for death compared to influenza patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babicki, S.; Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.R.; Maciejewski, A.; Wishart, D.S. Heatmapper: Web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W147–W153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavougios, G.D. SARS-CoV-2 dysregulation of PTBP1 and YWHAE/Z gene expression: A primer of neurodegeneration. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 110212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leenaerts, D.; Loyau, S.; Mertens, J.C.; Boisseau, W.; Michel, J.B.; Lambeir, A.M.; Hendriks, D.; Jandrot-Perrus, M. Carboxypeptidase U (CPU, carboxypeptidase B2, activated thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor) inhibition stimulates the fibrinolytic rate in different in vitro models. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 2057–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, Y.; Sui, Y.; Berzofksy, J.A. IL-7 in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and as a Potential Vaccine Adjuvant. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 737406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LC Patients (n = 9) | Non-LC Patients (n = 18) | |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 29 | 23 |
| Age, mean age SD | 45 ± 10.38 | 48 ± 14.89 |
| Maximum | 56 | 72 |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 2 (22%) | 9 (50%) |
| Female | 7 (77%) | 9 (50%) |
| Mean LC Score | 15 | 1.8 |
| Symptoms | ||
| Smell/Taste | 8 (88%) | 4 (22%) |
| Post-Exertional Malaise | 6 (66%) | 2 (11%) |
| Chronic Cough | 2 (22%) | 0 |
| Brain Fog | 7 (77%) | 1 (5%) |
| Thirst | 0 | 0 |
| Palpitations | 4 (44%) | 0 |
| Chest Pain | 2 (22%) | 0 |
| Fatigue | 4 (44%) | 3 (16%) |
| Loss of Sexual Desire/Capacity | 0 | 0 |
| Dizziness | 3 (33%) | 1 (5%) |
| Gastrointestinal | 1 (11%) | 0 |
| Abnormal Movements | 1 (11%) | 0 |
| Hair Loss | 0 | 0 |
| Gene ID | Gene Name | logFC | logPCM | p Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thaweethai Criteria | |||||
| LCE2C | Late Cornified Envelope 2C | 7.99818236 | 1.02581422 | 9.96 × 10−9 | 0.00044157 |
| KLK4 | Kallikrein-related peptidase 4 | 6.60280809 | −0.4530804 | 1.77 × 10−8 | 0.00044157 |
| KRT79 | Keratin 79 | 7.55570871 | 0.45248437 | 5.37 × 10−8 | 0.0008943 |
| LINC00664 | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 664 | 7.59844381 | 1.53093465 | 7.41 × 10−8 | 0.00092692 |
| RPS6KA1 | Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase A1 | 7.84846419 | 1.81682067 | 1.02 × 10−7 | 0.00101709 |
| YWHAE | Tyrosine 3-Monooxygenase/Tryptophan 5-Monooxygenase Activation Protein Epsilon | 4.70372922 | 4.33485505 | 1.50 × 10−7 | 0.00124748 |
| NBPF26_1 | NBPF Member 26 | 6.81095407 | 1.81382749 | 4.81 × 10−7 | 0.00343671 |
| LIMS4 | LIM Zinc Finger Domain Containing 4 | 5.41592334 | 2.52669888 | 1.00 × 10−6 | 0.00628014 |
| APCDD1L-DT | APCDD1L Divergent Transcript | 4.91514328 | −1.3918229 | 1.47 × 10−6 | 0.00814973 |
| SMDT1 | Single-Pass Membrane Protein with Aspartate Rich Tail 1 | 7.61332542 | 3.90907796 | 1.64 × 10−6 | 0.00822243 |
| ITGA2B | Integrin Subunit Alpha 2b | 5.98646273 | 0.29497006 | 2.11 × 10−6 | 0.00959703 |
| SPPL2C_1 | Signal Peptide Peptidase Like 2C | 6.46793059 | 0.27990204 | 2.32 × 10−6 | 0.0096583 |
| KCNH5 | Potassium Voltage-Gated Channel Subfamily H Member 5 | 5.83849379 | −0.4084643 | 3.31 × 10−6 | 0.01271414 |
| LACRT | Lacritin | 6.13395019 | 1.79756093 | 3.66 × 10−6 | 0.01305873 |
| LOH12CR2 | Loss Of Heterozygosity On Chromosome 12, Region 2 | 5.17501683 | −1.2807788 | 5.08 × 10−6 | 0.01693806 |
| CPB2 | Carboxypeptidase B2 | 5.46949369 | −1.1090355 | 7.67 × 10−6 | 0.02306396 |
| LOC107984156 | ADP-Ribosylation Factor-Like Protein 17 | 4.86443002 | −1.5030954 | 7.84 × 10−6 | 0.02306396 |
| RPS25_1 | 4.26012384 | 5.18739973 | 9.21 × 10−6 | 0.02558409 | |
| SNAP25 | Synaptosome Associated Protein 25 | 5.2533259 | −0.8910211 | 1.20 × 10−5 | 0.03148975 |
| SDR9C7 | Short Chain Dehydrogenase/Reductase Family 9C Member 7 | 6.24842783 | 2.17718851 | 1.49 × 10−5 | 0.0373324 |
| C8G | Complement C8 Gamma Chain | 5.02875954 | 0.0675793 | 1.67 × 10−5 | 0.03967669 |
| LINC02389 | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 2389 | 5.83746521 | −1.2208943 | 1.99 × 10−5 | 0.0441908 |
| CPA2 | Carboxypeptidase A2 | 4.84490407 | −1.2458497 | 2.10 × 10−5 | 0.0441908 |
| CST4 | Cystatin S | 5.06387008 | −1.58686 | 2.12 × 10−5 | 0.0441908 |
| TMEM78 | Transmembrane Protein 78 | 5.8739541 | 0.04196411 | 2.42 × 10−5 | 0.04839646 |
| LCE2B | Late Cornified Envelope 2B | 5.1047095 | −0.7940237 | 2.58 × 10−5 | 0.04970391 |
| WHO Criteria | |||||
| LCE2C | Late Cornified Envelope 2C | 7.4653423 | 1.02571863 | 32.0434816 | 8.67 × 10−7 |
| KLK4 | Kallikrein-related peptidase 4 | 6.12355248 | −0.4532072 | 30.2043019 | 1.53 × 10−6 |
| SLC46A2 | Solute Carrier Family 46 Member 2 | 6.19933981 | −0.4248683 | 30.1165666 | 1.58 × 10−6 |
| KRT79 | KRT79 | 7.03842812 | 0.45240021 | 28.0903087 | 3.01 × 10−6 |
| LINC00664 | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 664 | 7.17192834 | 1.53114803 | 27.9724926 | 3.54 × 10−6 |
| RPS6KA1 | Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase A1 | 7.73153057 | 1.81676322 | 28.5427881 | 3.95 × 10−6 |
| YWHAE | Tyrosine 3-Monooxygenase/Tryptophan 5-Monooxygenase Activation Protein Epsilon | 4.39133048 | 4.33486381 | 26.6236527 | 6.23 × 10−6 |
| Software | Pathway | Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| BioCarta (2016) | Classical Complement Pathway | 0.04 |
| BioCarta (2016) | Fibrinolysis Pathway | 0.04 |
| BioCarta (2016) | IL-7 Signal Transduction | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biondi, M.J.; Addo, M.; Zahoor, M.A.; Salvant, E.; Yip, P.; Barber, B.; Smookler, D.; Wasif, S.; Gaete, K.; Kandel, C.; et al. Differential Gene Expression in the Upper Respiratory Tract following Acute COVID-19 Infection in Ambulatory Patients That Develop Long COVID. Pathogens 2024, 13, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13060510
Biondi MJ, Addo M, Zahoor MA, Salvant E, Yip P, Barber B, Smookler D, Wasif S, Gaete K, Kandel C, et al. Differential Gene Expression in the Upper Respiratory Tract following Acute COVID-19 Infection in Ambulatory Patients That Develop Long COVID. Pathogens. 2024; 13(6):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13060510
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiondi, Mia J., Mary Addo, Muhammad Atif Zahoor, Elsa Salvant, Paul Yip, Bethany Barber, David Smookler, Sumaiyah Wasif, Kayla Gaete, Christopher Kandel, and et al. 2024. "Differential Gene Expression in the Upper Respiratory Tract following Acute COVID-19 Infection in Ambulatory Patients That Develop Long COVID" Pathogens 13, no. 6: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13060510
APA StyleBiondi, M. J., Addo, M., Zahoor, M. A., Salvant, E., Yip, P., Barber, B., Smookler, D., Wasif, S., Gaete, K., Kandel, C., Feld, J. J., Tsui, H., & Kozak, R. A. (2024). Differential Gene Expression in the Upper Respiratory Tract following Acute COVID-19 Infection in Ambulatory Patients That Develop Long COVID. Pathogens, 13(6), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13060510







