Evaluation of Primers OPF-01, P54, and 1253 to Identify A. fumigatus, A. flavus, and A. niger from Polymorphic Patterns Obtained by RAPD-PCR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Isolates
2.2. Identification of Sections of Aspergillus by Phenotypic and Genotypic Methods
Phenotypic Identification
2.3. Genotypic Identification
2.3.1. DNA Extraction
2.3.2. Amplification of the Partial Sequence of the BenA Gene
2.3.3. Sequence Analysis
2.3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Identification of A. fumigatus, A. flavus, and A. niger through Polymorphic Patterns Generated by RAPD-PCR with the Primers OPF-01, P54, and 1253, Respectively
Obtaining Polymorphic Patterns by RAPD-PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. UPGMA
2.5.2. Logistic Regression Model
3. Results
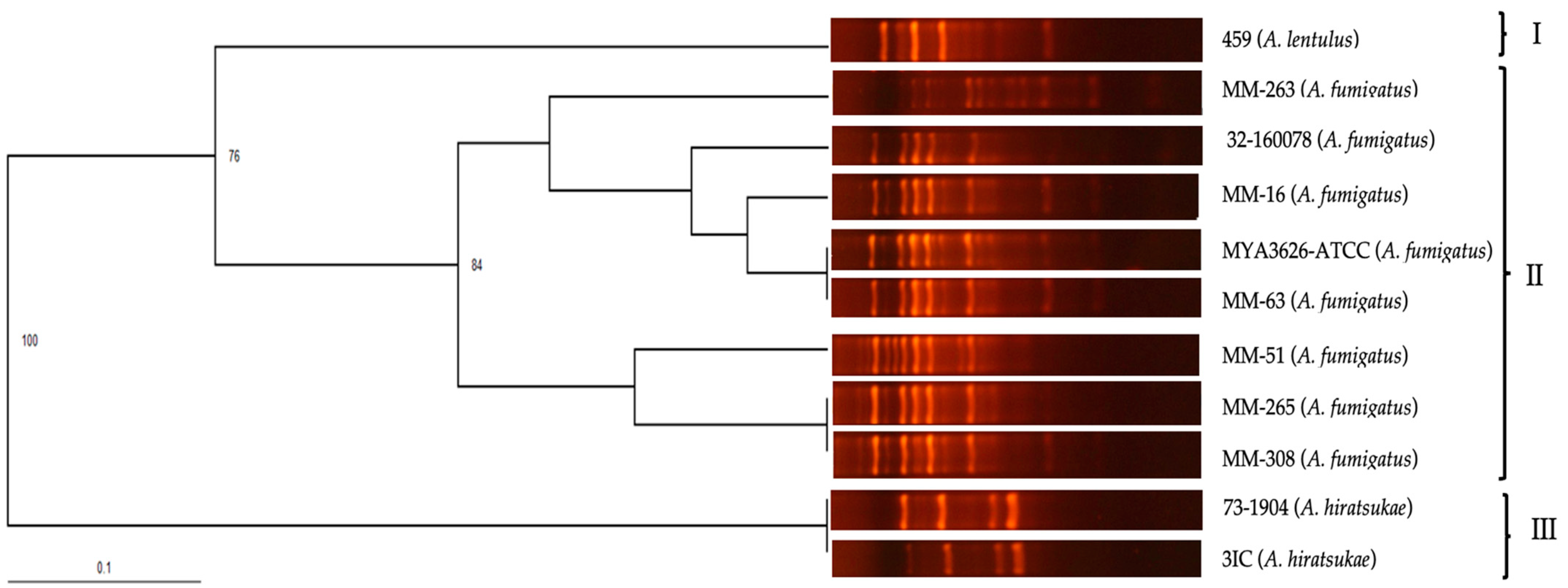
3.1. Identification of Aspergillus Species by Phenotypic and Genotypic Methods
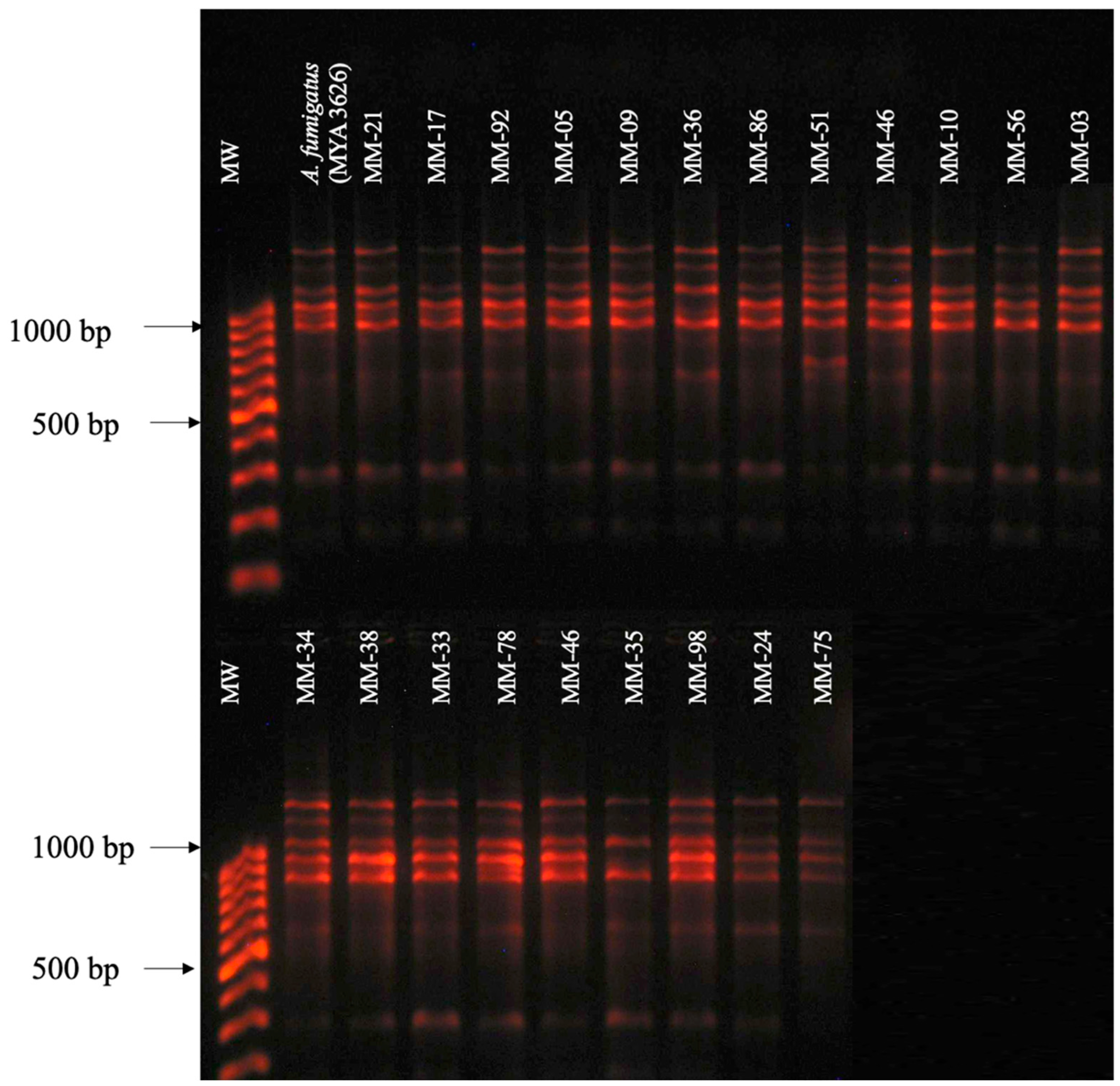
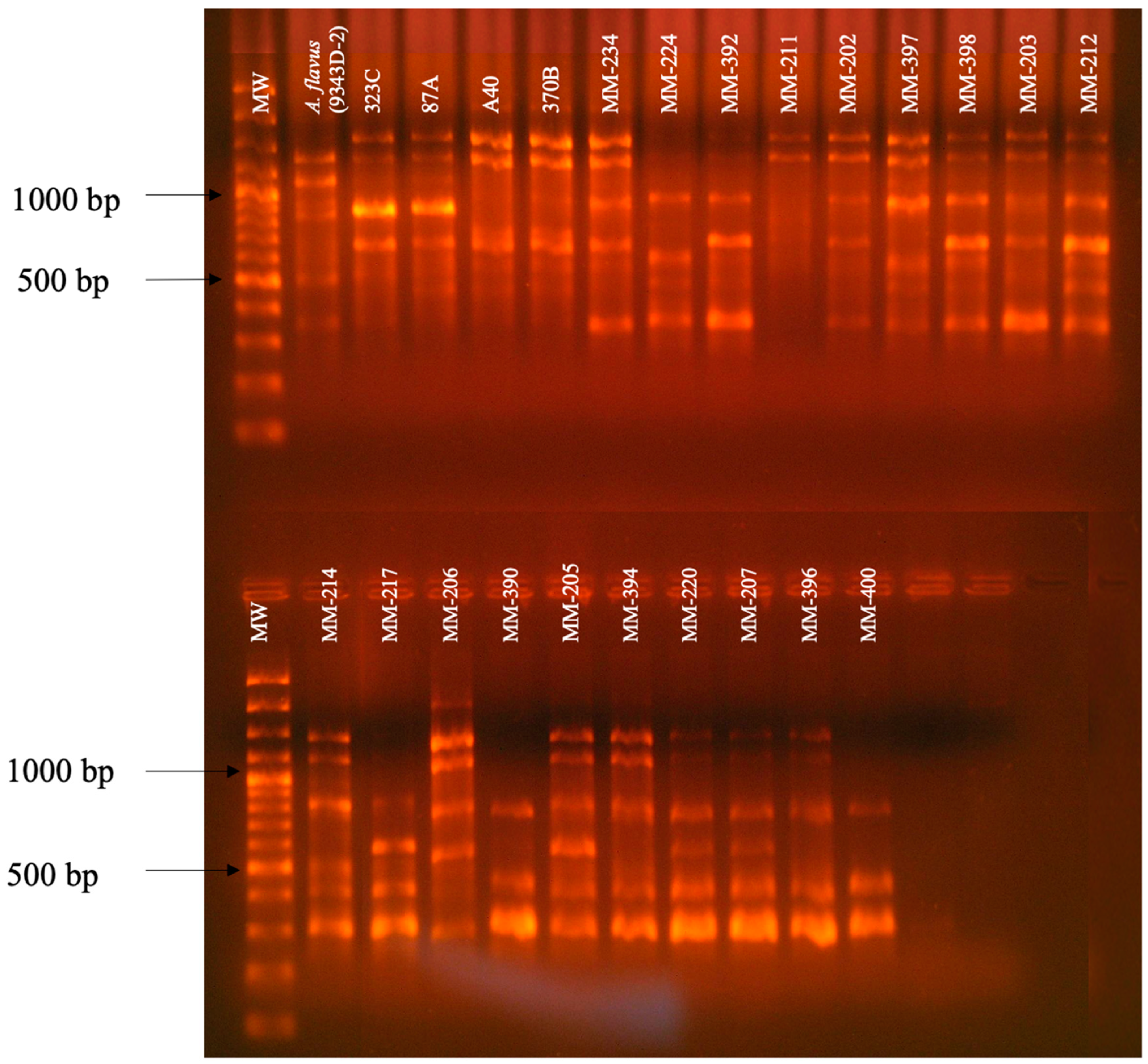
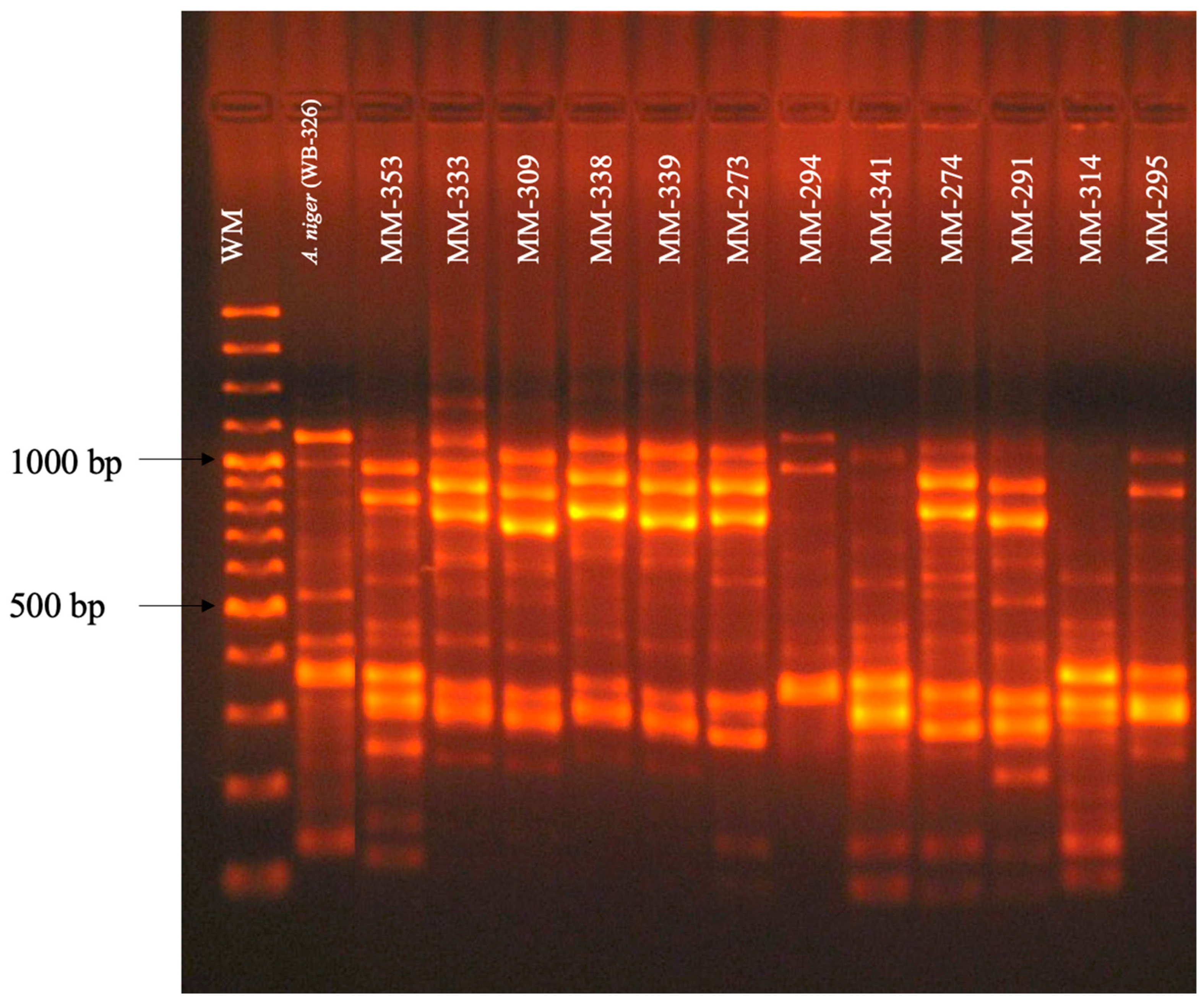
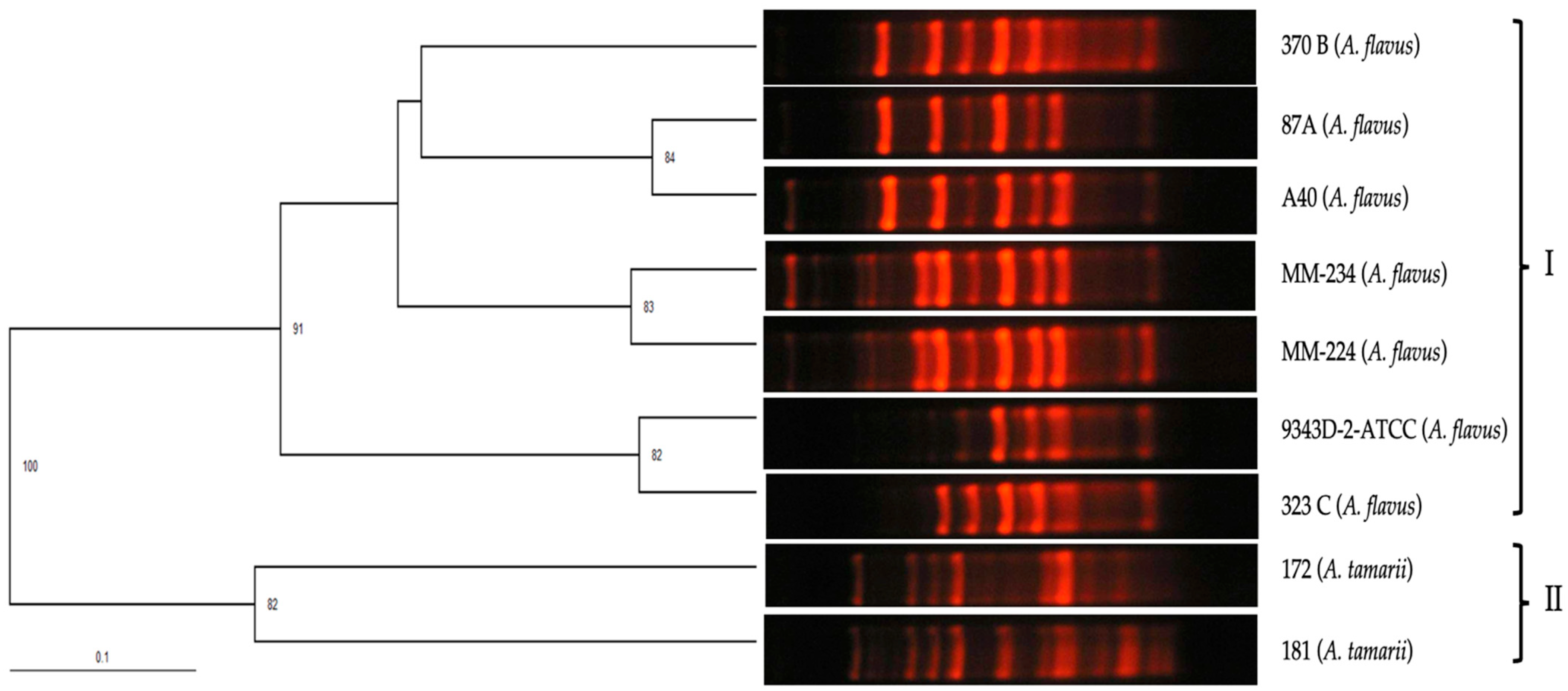
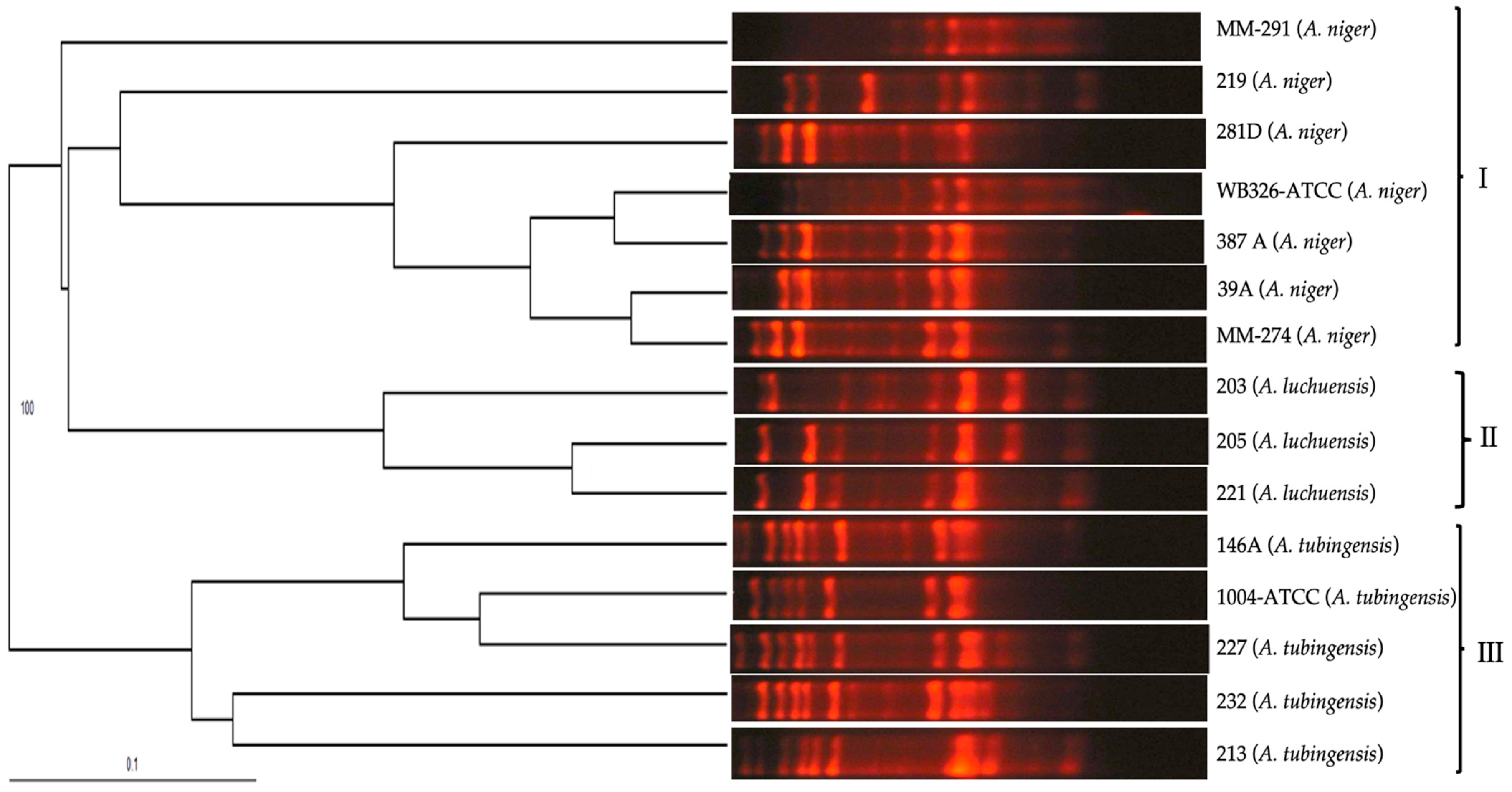
3.2. RAPD-PCR with Primers OPF-01, P54, and 1253 to Generate Polymorphic Patterns Specific to A. fumigatus, A. flavus, and A. niger, Respectively
3.3. Evaluation of the Specificity of Primers OPF-01, P54, and 1253
3.4. Sensitivity and Specificity of Primers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peláez, T.; Muñoz, P.; Guinea, J.; Valerio, M.; Giannella, M.; Klaassen, C.H.; Bouza, E. Outbreak of invasive aspergillosis after major heart surgery caused by spores in the air of the intensive care unit. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, e24–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latgé, J.P.; Chamilos, G. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis in 2019. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 33, e00140-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaz, R.; Denning, D. Aspergillosis: Causes, types and treatment. Pharm. J. 2019, 303, 7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoth, F. Aspergillus fumigatus-related species in clinical practice. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badiee, P.; Boekhout, T.; Mahmoudabadi, A.Z.; Mohammadi, R.; Mousavi, S.A.A.; Najafzadeh, M.J.; Soltani, J.; Hashemi, J.; Diba, K.; Ghadimi-Moghadam, A.; et al. Multicenter study of susceptibility of Aspergillus species isolated from Iranian university hospitals to seven antifungal agents. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02539-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Das, A.; Shivaprakash, M.R. Invasive aspergillosis in developing countries. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49, S35–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, W.W.; Walsh, T.J. Denning DW. The invasive and saprophytic syndromes due to Aspergillus spp. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43, S207–S238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, O.; Lamoth, F.; Mikulska, M.; Viscoli, C.; Verweij, P.; Bretagne, S. European Conference on Infections in Leukemia (ECIL) Laboratory Working Groups. ECIL recommendations for the use of biological markers for the diagnosis of invasive fungal diseases in leukemic patients and hematopoietic SCT recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012, 47, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanio, A.; Bretagne, S. Difficulties with molecular diagnostic tests for mould and yeast infections: Where do we stand? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoran, T.; Sartori, B.; Sappl, L.; Aigner, M.; Sánchez-Reus, F.; Rezusta, A.; Chowdhary, A.; Taj-Aldeen, S.J.; Arendrup, M.C.; Oliveri, S.; et al. Azole-resistance in Aspergillus terreus and related species: An emerging problem or a rare phenomenon? Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, A.J.; Aguado, J.M.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Denning, D.W.; Groll, A.H.; Lagrou, K.; Lass-Florl, C.; Lewis, R.E.; Munoz, P.; Verweij, P.E.; et al. Diagnosis and management of Aspergillus diseases: Executive summary of the 2017 ESCMID-ECMM-ERS guideline. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, e1–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tissot, F.; Agrawal, S.; Pagano, L.; Petrikkos, G.; Groll, A.H.; Skiada, A.; Lass-Florl, C.; Calandra, T.; Viscoli, C.; Herbrecht, R. ECIL-6 guidelines for the treatment of invasive candidiasis, aspergillosis and mucormycosis in leukemia and hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. Haematologica 2017, 102, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, R.A.; Visagie, C.M.; Houbraken, J.; Hong, S.B.; Hubka, V.; Klaassen, C.H.W.; Perrone, G.; Seifert, K.A.; Susca, A.; Tanney, J.B.; et al. Phylogeny, identification and nomenclature of the genus Aspergillus. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 78, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, M.M.; Sampaio, P.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Pais, C.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C.; Zancope-Oliveira, R.M. Rapid identification of Sporothrix species by T3B fingerprinting. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2159–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, A.; Sampaio, P.; Almeida, J.; Pais, C. Study of Molecular Epidemiology of Candidiasis in Portugal by PCR Fingerprinting of Candida Clinical Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5899–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, W.; Maszewska, K.; Sorrell, T.C. PCR fingerprinting: A convenient molecular tool to distinguish between Candida dubliniensis and Candida albicans. Med. Mycol. 2001, 39, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanos, M.; Schonian, G.; Meyer, W.; Schweynoch, C.; Graser, Y.; Mitchell, T.G.; Presber, W.; Tietz, H.J. Rapid identification of Candida species by DNA fingerprinting with PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermani, F.; Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M.; Gholami-Shabani, M.; Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M. Diversity, molecular phylogeny and fingerprint profiles of airborne Aspergillus species using random amplified polymorphic DNA. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia-Ledezma, O.E.; Castro-Fuentes, C.A.; Duarte-Escalante, E.; Frías-De-León, M.G.; Reyes-Montes, M.D.R. Selection of Polymorphic Patterns Obtained by RAPD-PCR through Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses to Differentiate Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, R.W. Permanent stained mycological preparations obtained by slide culture. Mycologia 1950, 42, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersulyte, D.; Woods, J.P.; Keath, E.J.; Goldman, W.E.; Berg, D.E. Diversity among clinical isolates of Histoplama capsulatum detected by polymerase chain reaction with arbitrary primers. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 7075–7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, J.P.; Kersulyte, D.; Goldman, W.E.; Berg, D.E. Fast DNA isolation from Histoplasma capsulatum: Methodology for arbitrary primer polymerase chain reaction-based epidemiological and clinical studies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohlf, F.J. NTSYS-pc: Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System, version 2.1; Exeter Software: Setauket, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, S.J. Multi-resistant aspergillosis due to cryptic species. Mycopathologia 2014, 178, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.B.; Shin, H.D.; Hong, J.; Frisvad, J.C.; Nielsen, P.V.; Varga, J.; Samson, R.A. New taxa of Neosartorya and Aspergillus in Aspergillus section Fumigati. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2008, 93, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.W. Phylogenetic analysis of Aspergillus species using DNA sequences from four loci. Mycologia 2008, 100, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.B.; Park, C.; Cho, S.Y.; Chun, H.S.; Lee, D.G. Development of multiplex real-time PCR for rapid identification and quantitative analysis of Aspergillus species. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, G.A.; Coelho, I.; Reynoso, M.M.; Soleiro, C.; Cavaglieri, L.R. Characterization and genetic variability of feed-borne and clinical animal/human Aspergillus fumigatus strains using molecular markers. Med. Mycol. 2015, 53, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.B.; Kim, D.H.; Park, I.C.; Choi, Y.J.; Shin, H.D.; Samson, R. Re-identification of Aspergillus fumigatus sensu lato based on a new concept of species delimitation. J. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraj, M.; Vishruth, P.; Ramesh, T.; Lipton, A.P. RAPD fingerprinting and demonstration of genetic variation in three pathogens isolated from mangrove environment. Asian J. Biotechnol. 2011, 3, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ): Area under the curve of A. fumigatus isolates tested in this study. (
): Area under the curve of A. fumigatus isolates tested in this study. ( ): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].
): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].
 ): Area under the curve of A. fumigatus isolates tested in this study. (
): Area under the curve of A. fumigatus isolates tested in this study. ( ): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].
): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].
 ): Area under the curve of A. flavus isolates tested in this study (
): Area under the curve of A. flavus isolates tested in this study ( ): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].
): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].
 ): Area under the curve of A. flavus isolates tested in this study (
): Area under the curve of A. flavus isolates tested in this study ( ): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].
): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].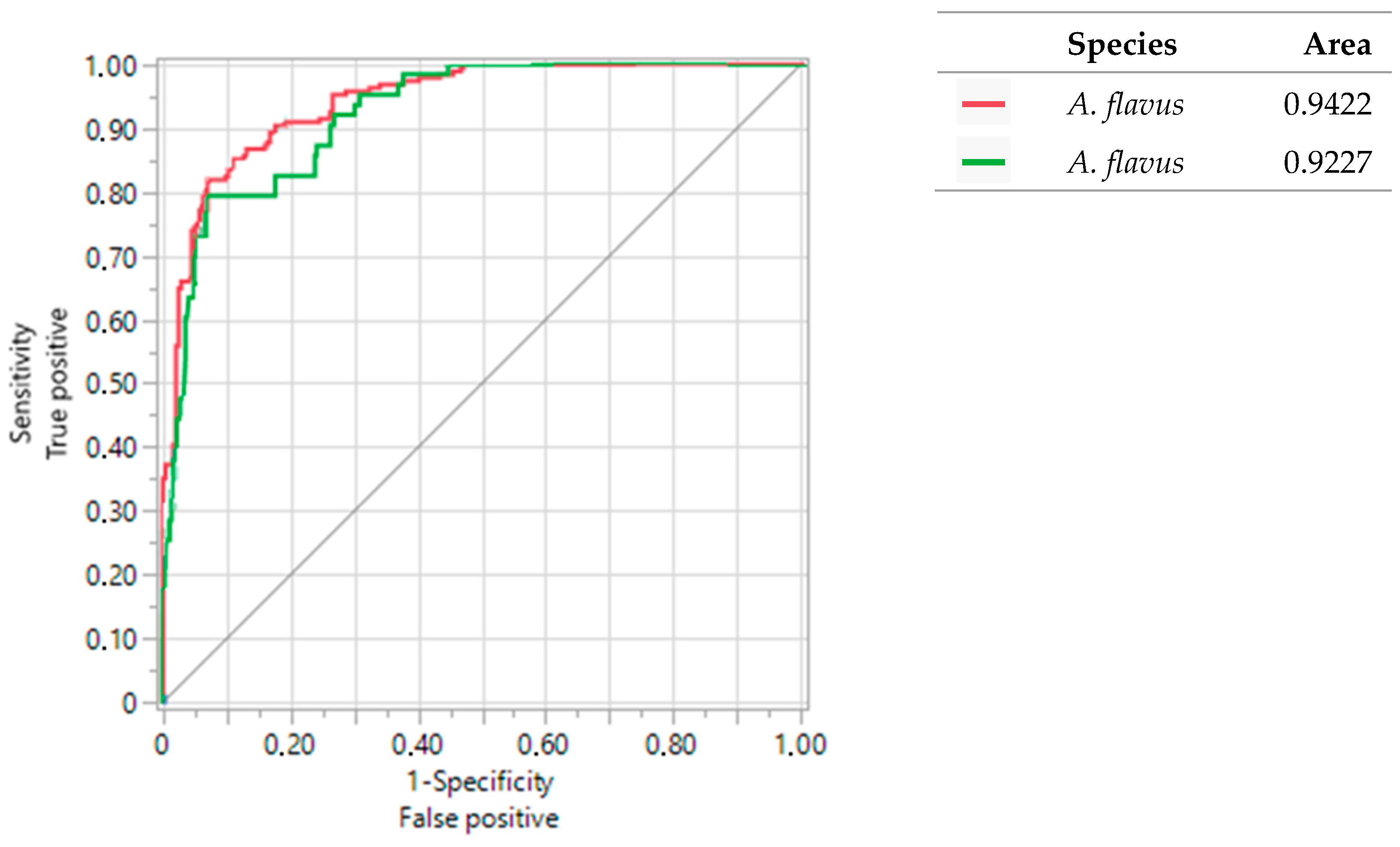
 ): Area under the curve of A. niger isolates tested in this study (
): Area under the curve of A. niger isolates tested in this study ( ): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].
): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].
 ): Area under the curve of A. niger isolates tested in this study (
): Area under the curve of A. niger isolates tested in this study ( ): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].
): Area under the curve obtained by Valencia-Ledezma et al. [19].
| Specie | Isolate/GenBank Accession No. | Geographical Origin |
|---|---|---|
| A. fumigatus | MM-34/MN637747 | Mexico |
| A. fumigatus | MM-92/MN637737 | Mexico |
| A. fumigatus | MM-09/MN637704 | Mexico |
| A. fumigatus | MM-36/MN637733 | Mexico |
| A. fumigatus | MM-46/MN637727 | Mexico |
| A. fumigatus | MM-10 /MN637732 | Mexico |
| A. fumigatus | MM-38/MN637734 | Mexico |
| A. fumigatus | MM-33/MN637724 | Mexico |
| A. fumigatus | MM-46 /MN637727 | Mexico |
| A. fumigatus | MM-35/MN637736 | Mexico |
| A. fumigatus | MM-98/MN637741 | Mexico |
| A. fumigatus | MM-17 /MT196113 | Argentina |
| A. fumigatus | MM-05/MN637755 | Argentina |
| A. fumigatus | MM-86 /MN637757 | Argentina |
| A. fumigatus | MM-03 /MN637749 | Argentina |
| A. fumigatus | MM-78 /MN637765 | Argentina |
| A. fumigatus | MM-24 /MN637767 | Argentina |
| A. fumigatus | MM-75/MN637773 | Argentina |
| A. fumigatus | MM-21/ OM892865 | Argentina |
| A. fumigatus | MM-16/ OM89286 | Argentina |
| A. fumigatus | MM-51//MN637777 | Francia |
| A. fumigatus | MM-56 /MN637779 | Francia |
| A. fumigatus | MM63/MT196114 | Peru |
| A. fumigatus | MM-263/MT347701.1 | Cuba |
| A. fumigatus | MM-265/MT347702.1 | Cuba |
| A. fumigatus | MM-308/MT347703.1 | Cuba |
| A. fumigatus | 21 INCMNSZ (32-16076) | Mexico |
| A. lentulus | 18 INCMNSZ (459) | Mexico |
| A. hiratsukae | 19 INCMNSZ (73-1904) | Mexico |
| A. hiratsukae | 17 INCMNSZ (3IC) | Mexico |
| A. flavus | 323C/OM89286 | ND |
| A. flavus | 87A/OM892858 | ND |
| A. flavus | A40/OM892868 | ND |
| A. flavus | 370B/OM892869 | ND |
| A. flavus | MM-234/MT347712.1 | ND |
| A. flavus | MM-224/MT347711.1 | ND |
| A. flavus | MM-392/OQ560605 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-211/OQ560592 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-202/OQ560583 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-397/OQ560608 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-398/OQ560609 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-203/OQ560584 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-212/OQ560593 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-214/OQ560595 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-217/OQ560597 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-206/OQ560587 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-390/OQ560603 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-205/OQ560586 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-394/OQ560606 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-220/OQ560600 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-207/OQ560588 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-396/OQ560607 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-400/OQ560611 | Mexico |
| A. flavus | MM-218/OQ560598 | Mexico |
| A. tamarii | 2 INCMNSZ (172) | Mexico |
| A. tamarii | 3 INCMNSZ (181) | Mexico |
| A. niger | MT410061 | ND |
| A. niger | 387A/OM892858 | Mexico |
| A. niger | 39A/OM892859 | Mexico |
| A. niger | MM-353/MT410079 | Cuba |
| A. niger | MM-333/MT410073 | Cuba |
| A. niger | MM-309/MT410068 | Cuba |
| A. niger | MM-338/MT410075 | Cuba |
| A. niger | MM-339/MT410076 | Cuba |
| A. niger | MM-273/MT410061 | Cuba |
| A. niger | MM-294/MT410066 | Cuba |
| A. niger | MM-274/MT410062 | Cuba |
| A. niger | MM-291/MT410063 | Cuba |
| A. niger | MM-341/ | ND |
| A. niger | MM-314/ | ND |
| A. niger | 6 INCMNSZ (219) | Mexico |
| A. niger | MM-295/MT410067 | Cuba |
| A. niger | 281D/OM892871 | Mexico |
| A. tubingensis | 146A/OM892872 | Mexico |
| A. tubingensis | 10 INCMNSZ (232) | Mexico |
| A. tubingensis | 13 INCMNSZ (227) | Mexico |
| A. tubingensis | 7 INCMNSZ (213) | Mexico |
| A. luchuensis | 1 INCMNSZ (203) | Mexico |
| A. luchuensis | 8 INCMNSZ (205) | Mexico |
| A. luchuensis | 9 INCMNSZ (221) | Mexico |
| Species | Strain ATCC |
|---|---|
| A. fumigatus | MYA3626 |
| A. flavus | 9343D-2 |
| A. lentulus | 3566 |
| A. niger | WB326 |
| A. tubingensis | 1004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castro-Fuentes, C.A.; Frías-De-León, M.G.; González-Villaseñor, M.d.C.; Duarte-Escalante, E.; Valencia-Ledezma, O.E.; Martínez-Gamboa, A.; Meraz-Ríos, B.; Reyes-Montes, M.d.R. Evaluation of Primers OPF-01, P54, and 1253 to Identify A. fumigatus, A. flavus, and A. niger from Polymorphic Patterns Obtained by RAPD-PCR. Pathogens 2024, 13, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13070574
Castro-Fuentes CA, Frías-De-León MG, González-Villaseñor MdC, Duarte-Escalante E, Valencia-Ledezma OE, Martínez-Gamboa A, Meraz-Ríos B, Reyes-Montes MdR. Evaluation of Primers OPF-01, P54, and 1253 to Identify A. fumigatus, A. flavus, and A. niger from Polymorphic Patterns Obtained by RAPD-PCR. Pathogens. 2024; 13(7):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13070574
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastro-Fuentes, Carlos Alberto, María Guadalupe Frías-De-León, María del Carmen González-Villaseñor, Esperanza Duarte-Escalante, Omar Esteban Valencia-Ledezma, Areli Martínez-Gamboa, Beatriz Meraz-Ríos, and María del Rocío Reyes-Montes. 2024. "Evaluation of Primers OPF-01, P54, and 1253 to Identify A. fumigatus, A. flavus, and A. niger from Polymorphic Patterns Obtained by RAPD-PCR" Pathogens 13, no. 7: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13070574
APA StyleCastro-Fuentes, C. A., Frías-De-León, M. G., González-Villaseñor, M. d. C., Duarte-Escalante, E., Valencia-Ledezma, O. E., Martínez-Gamboa, A., Meraz-Ríos, B., & Reyes-Montes, M. d. R. (2024). Evaluation of Primers OPF-01, P54, and 1253 to Identify A. fumigatus, A. flavus, and A. niger from Polymorphic Patterns Obtained by RAPD-PCR. Pathogens, 13(7), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13070574








