Investigating the Therapeutic Effects of Albendazole, Mebendazole, and Praziquantel Nanocapsules in Hydatid Cyst-Infected Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Sources
2.2. Nanocapsules Preparation
2.3. Zeta, Scanning Electron Microscope, and Particle Size Analysis
2.4. Protoscolex Collection
2.5. Mouse Treatments with Nanocapsule Drugs
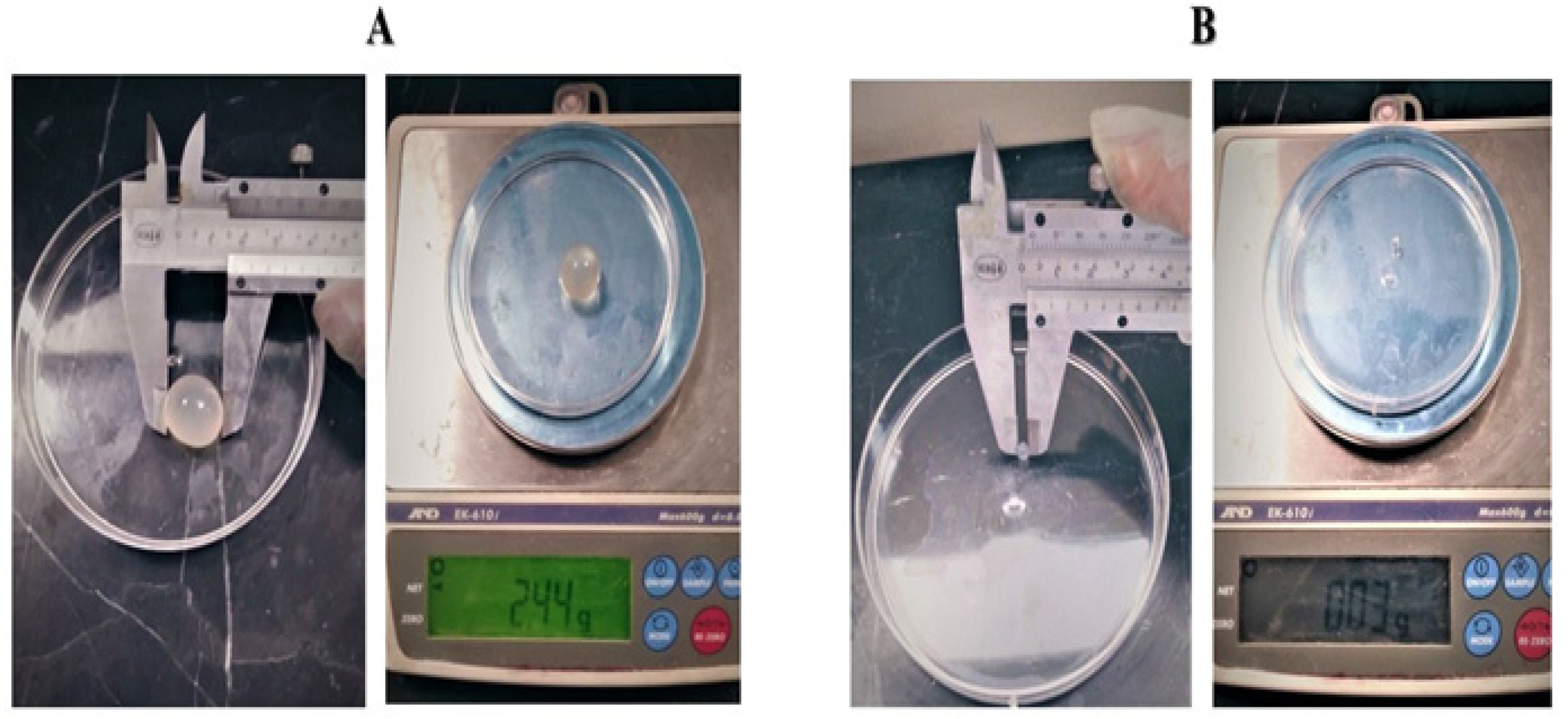
2.6. Parasitological Studies
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
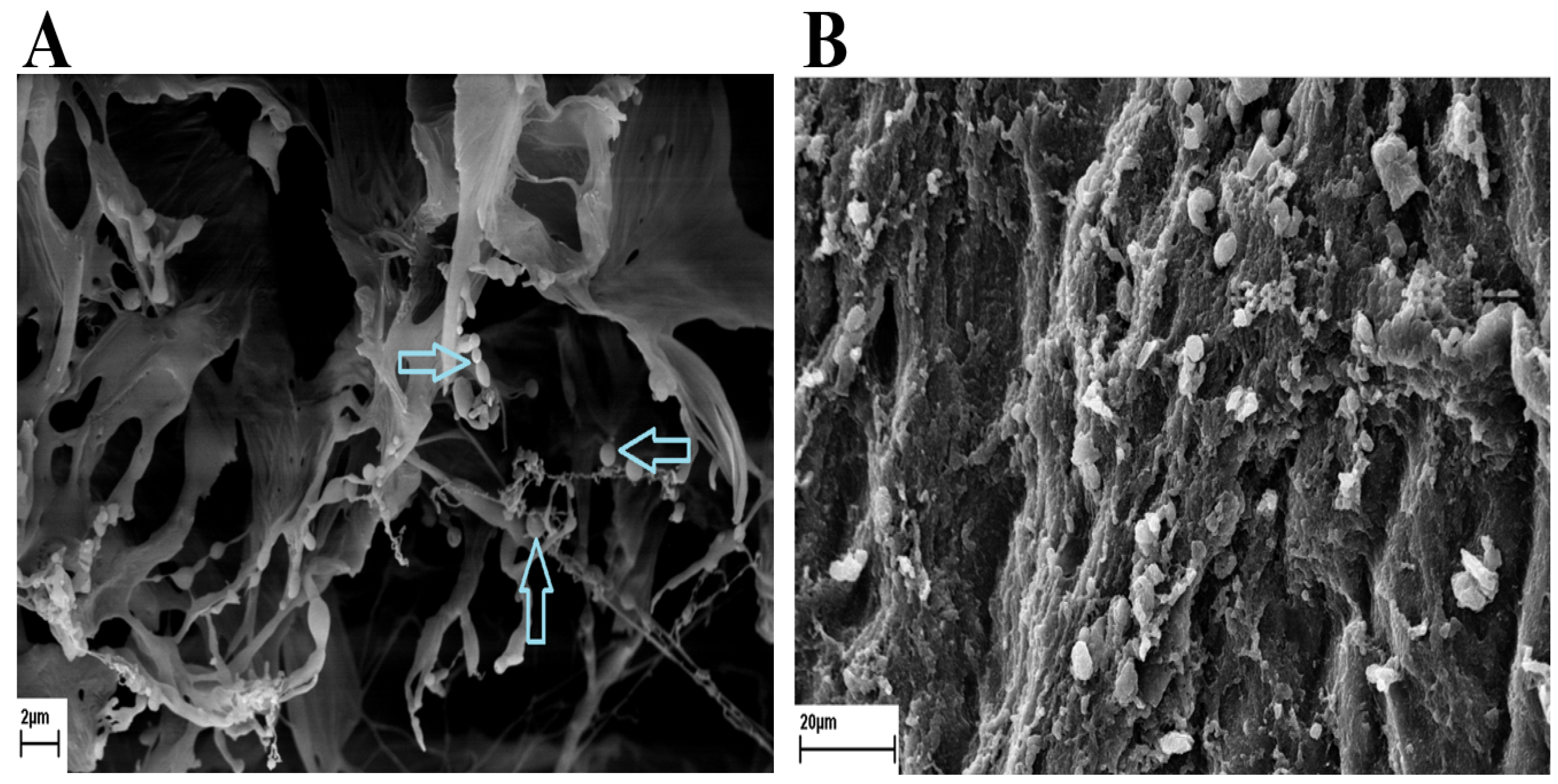
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscope
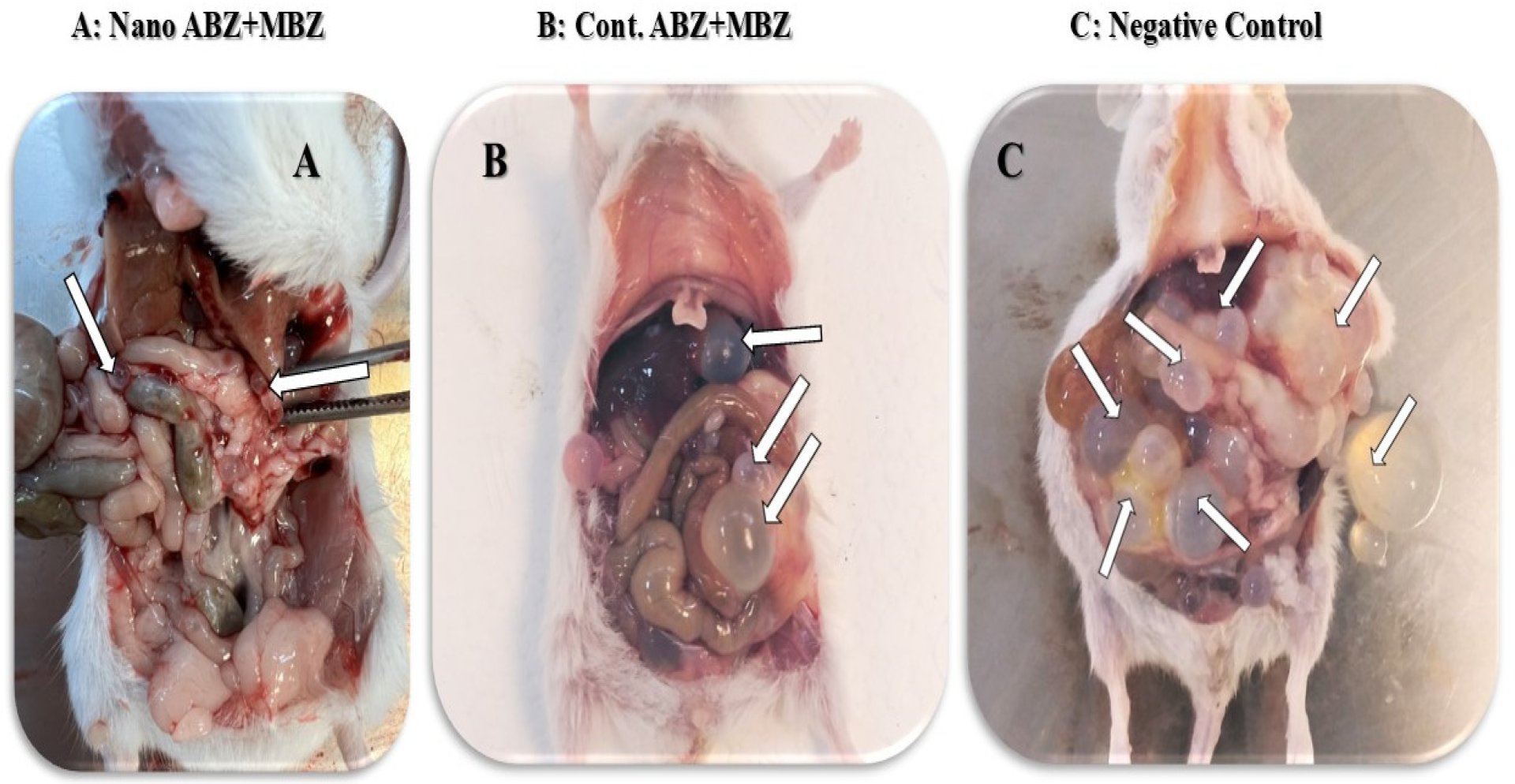
3.2. Mouse Treatment with Nanocapsule Drugs
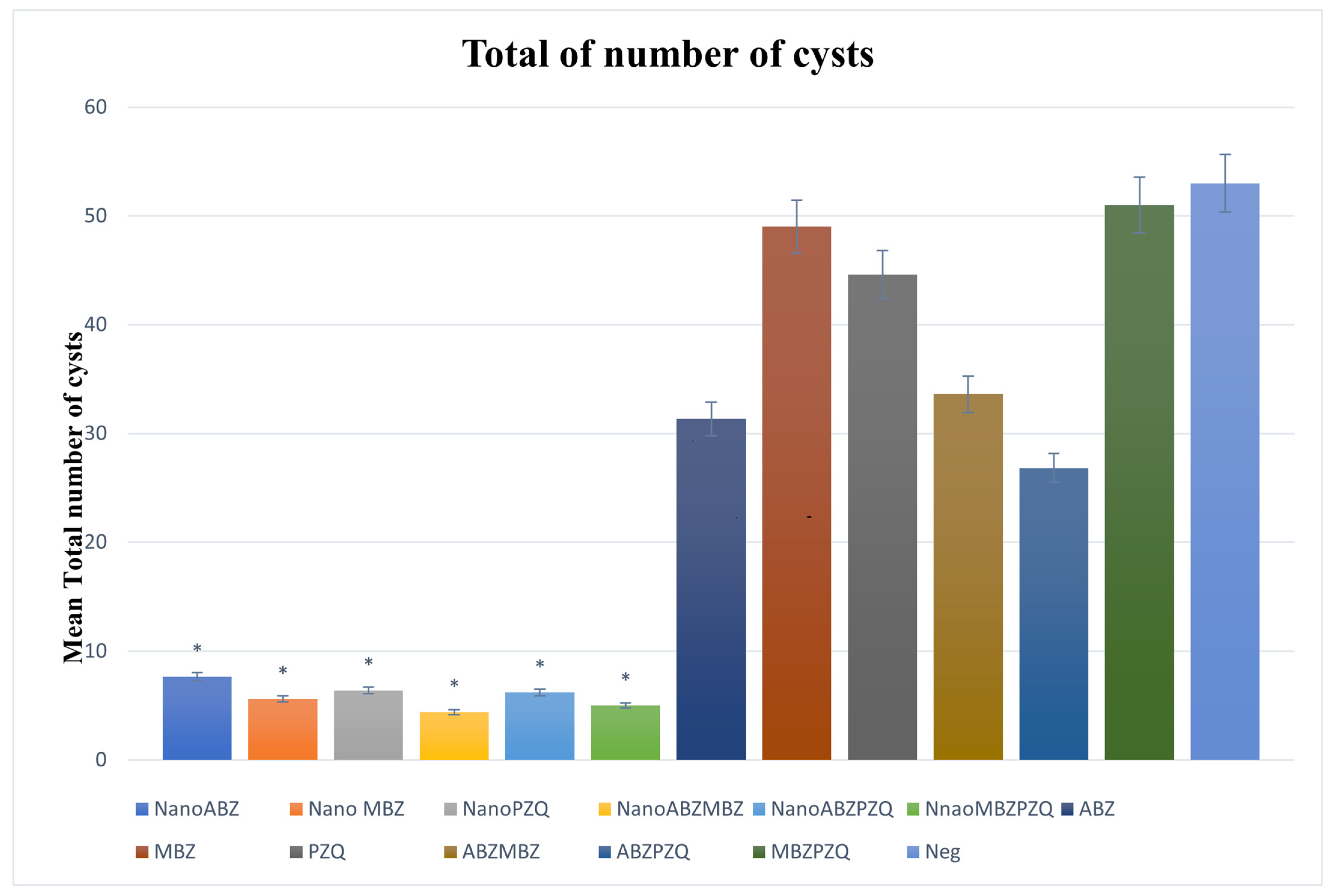
3.2.1. Number of Cysts
3.2.2. Total Cysts Weight
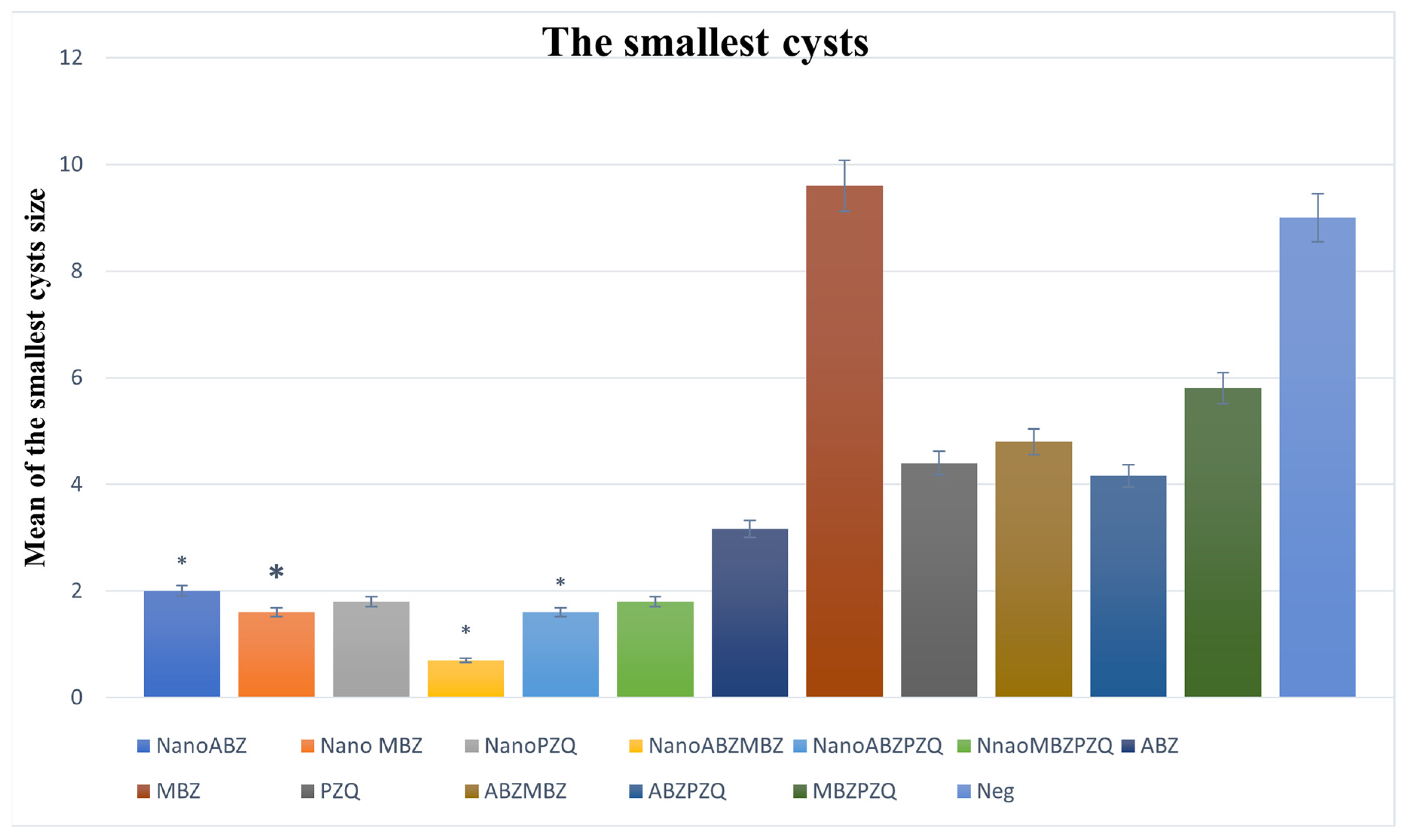
3.2.3. Minimum Cyst Size
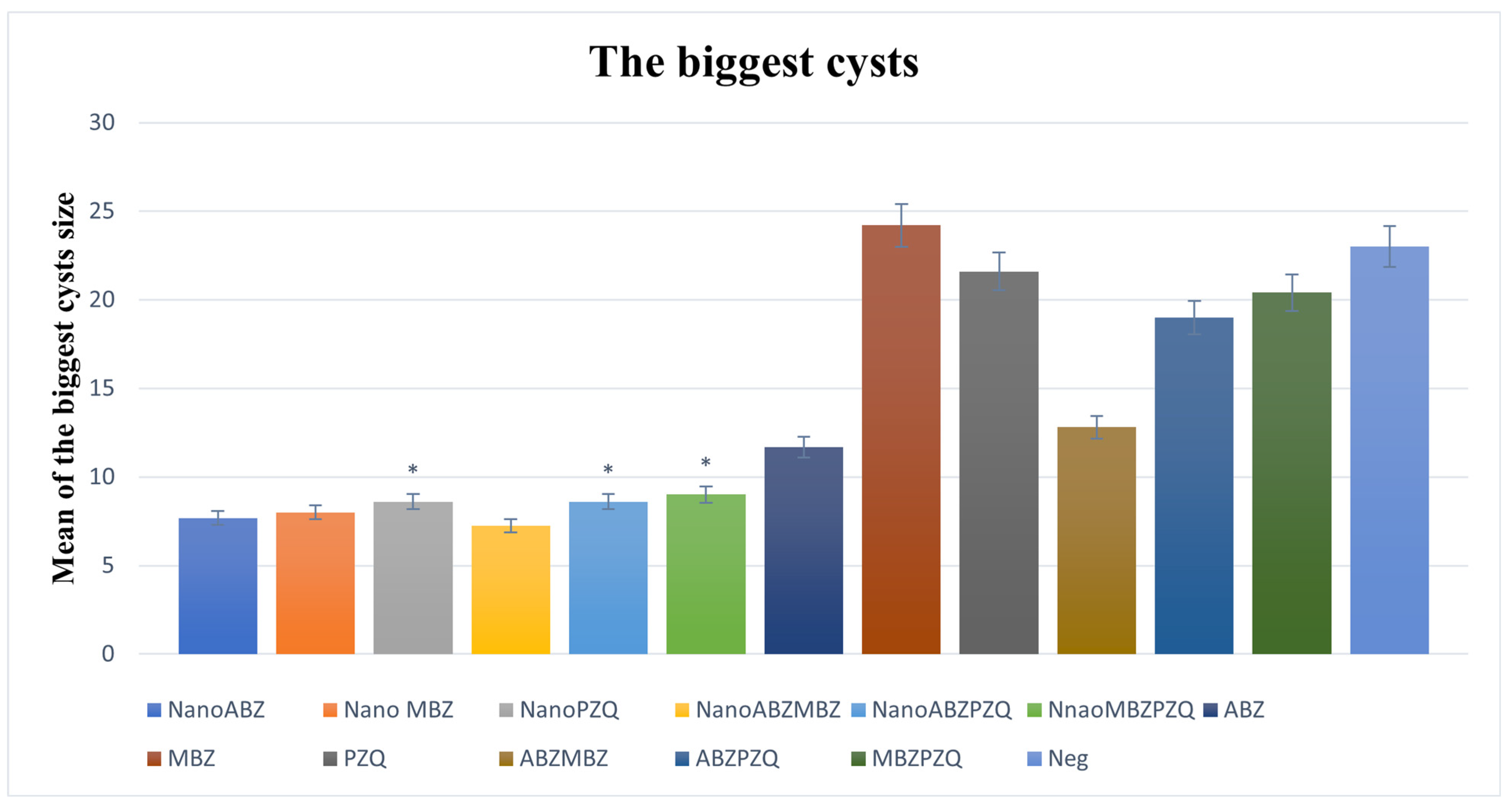
3.2.4. Maximum Cyst Size
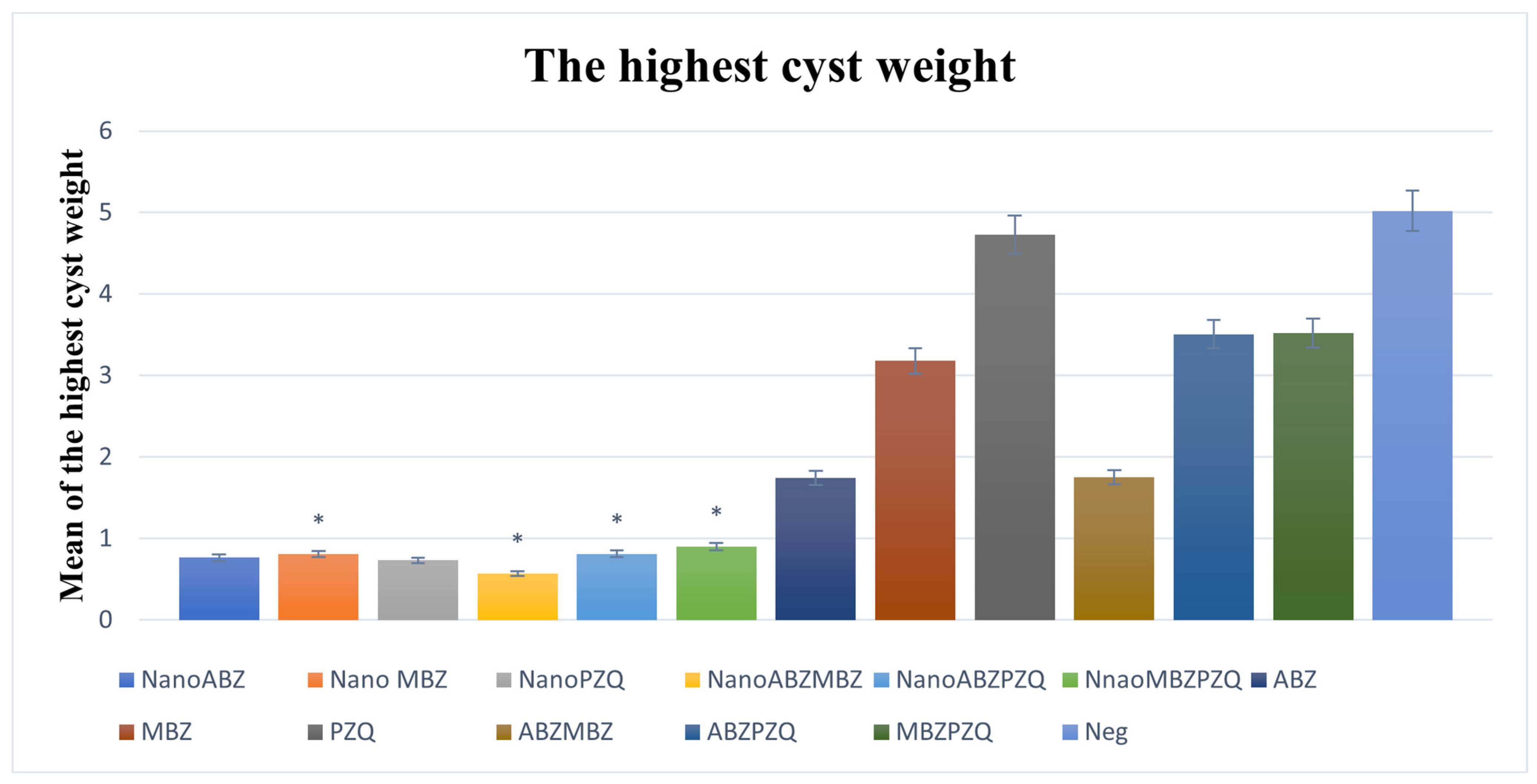
3.2.5. Maximum Cyst Weight
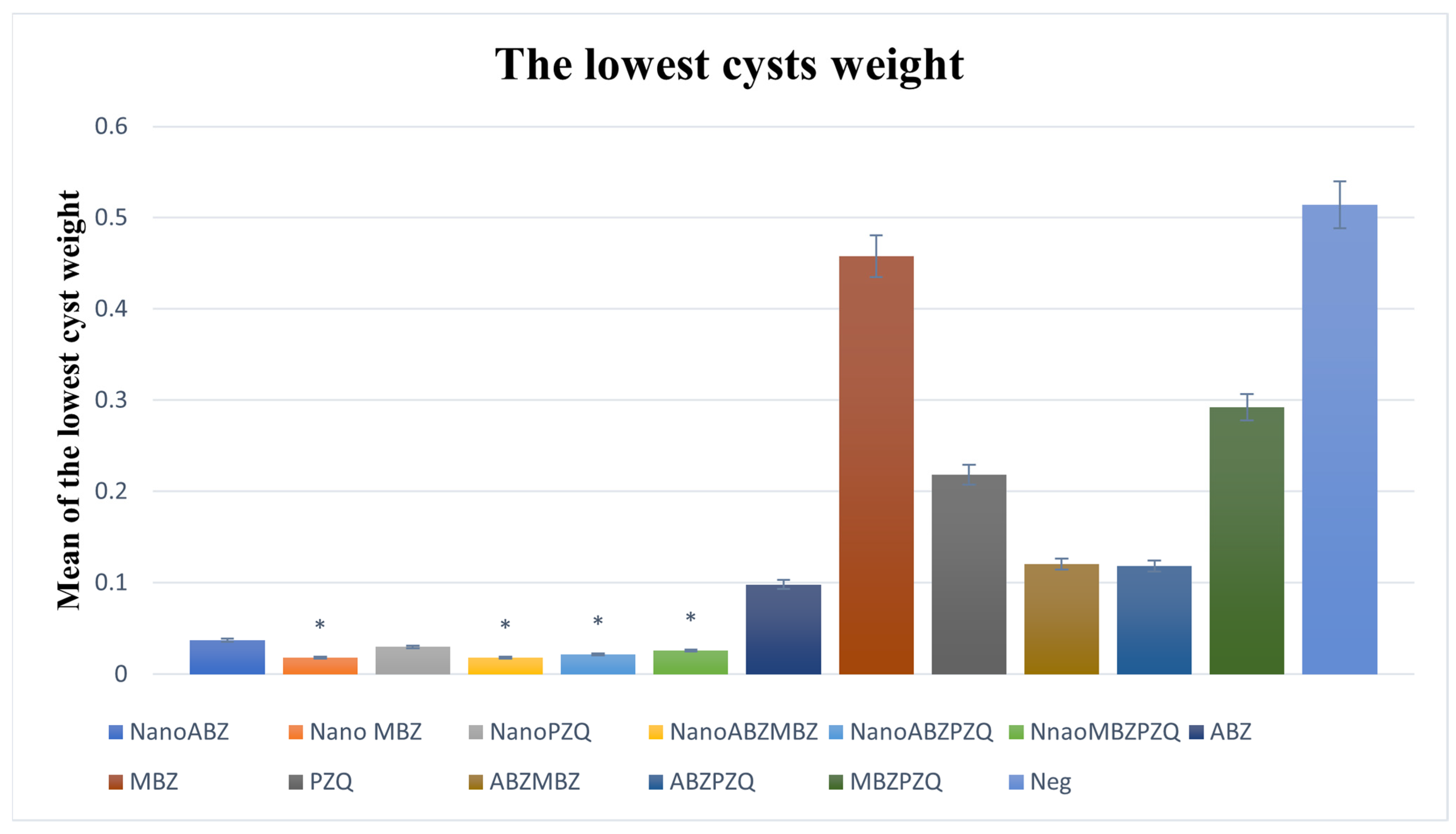
3.2.6. Minimum Cyst Weight
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woolsey, I.D.; Miller, A.L. Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato and Echinococcus multilocularis: A review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R. Biology and systematics of Echinococcus. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 65–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuitton, D.A.; McManus, D.P.; Rogan, M.T.; Romig, T.; Gottstein, B.; Naidich, A.; Tuxun, T.; Wen, H.; da Silva, A.M. International consensus on terminology to be used in the field of echinococcoses. Parasite 2020, 27, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Vuitton, L.; Tuxun, T.; Li, J.; Vuitton, D.A.; Zhang, W.; McManus, D.P. Echinococcosis: Advances in the 21st century. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casulli, A.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Tamarozzi, F. Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato. Trend. Parasitol. 2019, 35, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadr, S.; Charbgoo, A.; Borji, H. Interactions between innate immunity system and Echinococcus granulosus: Permission for vaccine development. Ser. Med. Sci. 2022, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Santucciu, C.; Ferrari, P.A.; Grimaldi, G.; Murenu, A.; Nemolato, S.; Bonelli, P.; Masala, G.; Porcu, G.S.; Cherchi, R. Environmental influence on the occurrence of multi-organ cystic echinococcosis infection in a patient from Sardinia, Italy. Diseases 2023, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umhang, G.; Bastien, F.; Cartet, A.; Ahmad, H.; van der Ark, K.; Berg, R.; Bonelli, P.; Davidson, R.K.; Deplazes, P.; Deksne, G. Detection of Echinococcus spp. and other taeniid species in lettuces and berries: Two international multicenter studies from the MEmE project. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Shi, Y.; Kang, X.; Rousu, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, M.; Ainiwaer, A.; Zheng, X.; Wang, M.; Jiensihan, B. Echinococcus granulosus: The establishment of the metacestode in the liver is associated with control of the CD4+ T-cell-mediated immune response in patients with cystic echinococcosis and a mouse model. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 983119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrieu, E.; Uchiumi, L.; Salvitti, J.C.; Sobrino, M.; Panomarenko, O.; Tissot, H.; Mercapide, C.H.; Sustercic, J.; Arezo, M.; Mujica, G. Epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of cystic echinococcosis in asymptomatic carriers. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 113, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, P.L.; Schantz, P.M. 281—Echinococcus species (agents of cystic, alveolar, and polycystic echinococcosis). In Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 4th ed.; Long, S.S., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2012; pp. 1356–1362.e1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohiolei, J.A.; Yan, H.-B.; Li, L.; Magaji, A.A.; Luka, J.; Zhu, G.-Q.; Isaac, C.; Odoya, M.E.; Wu, Y.-T.; Alvi, M.A. Cystic echinococcosis in Nigeria: First insight into the genotypes of Echinococcus granulosus in animals. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widdicombe, J.; Basáñez, M.-G.; Entezami, M.; Jackson, D.; Larrieu, E.; Prada, J.M. The economic evaluation of cystic echinococcosis control strategies focused on zoonotic hosts: A scoping review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, M.; Alemu, H.H.; Marami, L.M.; Garedo, D.R.; Bodena, E.B. Cystic Echincoccoosis: A comprehensive review on life cycle, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical Spectrum, diagnosis, public health and economic implications, treatment, and control. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. Res 2022, 6, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, K.; Wen, B.; Fu, T.; Qin, X.; Li, R.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shao, Z. Changes in the global epidemiological characteristics of cystic echinococcosis over the past 30 years and projections for the next decade: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. J. Glob. Health 2024, 14, 04056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogea, M.-O.; Ciomaga, B.-F.; Muntean, M.-M.; Muntean, A.-A.; Popa, M.I.; Popa, G.L. Cystic echinococcosis in the early 2020s: A review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucher, M.A.; Macchiaroli, N.; Baldi, G.; Camicia, F.; Prada, L.; Maldonado, L.; Avila, H.G.; Fox, A.; Gutiérrez, A.; Negro, P. Cystic echinococcosis in South America: Systematic review of species and genotypes of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato in humans and natural domestic hosts. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2016, 21, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, M.A.; Alsayeqh, A.F. Food-borne zoonotic echinococcosis: A review with special focus on epidemiology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1072730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Miao, L.; Wang, W.; Zhou, X. Global, regional and national burden of human cystic echinococcosis from 1990 to 2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, Q.; Younus, M.; Sadiq, S.; Iqbal, S.; Idrees, A.; Khan, S.; Zia, R. Prevalence and associated risk factors of cystic echinococcosis in food animals--A neglected and prevailing zoonosis. Pak. Vet. J. 2022, 42, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Borhani, M.; Fathi, S.; Lahmar, S.; Ahmed, H.; Abdulhameed, M.F.; Fasihi Harandi, M. Cystic echinococcosis in the Eastern Mediterranean region: Neglected and prevailing! PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, A.; Amarir, F.; Filali, H.; Thys, S.; Rhalem, A.; Kirschvink, N.; Raes, M.; Marcotty, T.; Oukessou, M.; Duchateau, L. The socio-economic burden of cystic echinococcosis in Morocco: A combination of estimation method. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelbaset, A.E.; Yagi, K.; Nonaka, N.; Nakao, R. Cystic echinococcosis in humans and animals in Egypt: An epidemiological overview. Cur. Res. Parasitol. Vector-Borne Dis. 2021, 1, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casulli, A.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Petrone, D.; Fabiani, M.; Bobić, B.; Carmena, D.; Šoba, B.; Zerem, E.; Gargaté, M.J.; Kuzmanovska, G. Unveiling the incidences and trends of the neglected zoonosis cystic echinococcosis in Europe: A systematic review from the MEmE project. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, e95–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuestenberg, J.; Gruener, B.; Oeztuerk, S.; Mason, R.A.; Haenle, M.M.; Graeter, T.; Akinli, A.S.; Kern, P.; Kratzer, W. Diagnostics in cystic echinococcosis: Serology versus ultrasonography. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 25, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojkovic, M.; Rosenberger, K.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Junghanss, T.; Hosch, W. Diagnosing and staging of cystic echinococcosis: How do CT and MRI perform in comparison to ultrasound? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano-Román, R.; Sánchez-Ovejero, C.; Hernández-González, A.; Casulli, A.; Siles-Lucas, M. Serological diagnosis and follow-up of human cystic echinococcosis: A new hope for the future? BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 428205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, D.P.; Gray, D.J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y. Diagnosis, treatment, and management of echinococcosis. BMJ 2012, 344, e3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Mandal, M.D. Human cystic echinococcosis: Epidemiologic, zoonotic, clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2012, 5, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keong, B.; Wilkie, B.; Sutherland, T.; Fox, A. Hepatic cystic echinococcosis in Australia: An update on diagnosis and management. ANZ J. Surg. 2018, 88, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, A.; Stadelmann, B.; Rufener, R.; Spiliotis, M.; Boubaker, G.; Müller, J.; Müller, N.; Gorgas, D.; Gottstein, B. Treatment of echinococcosis: Albendazole and mebendazole–what else? Parasite 2014, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Tirado, V.; Alonso-Sardón, M.; Lopez-Bernus, A.; Romero-Alegría, Á.; Burguillo, F.J.; Muro, A.; Carpio-Pérez, A.; Munoz Bellido, J.L.; Pardo-Lledias, J.; Cordero, M. Medical treatment of cystic echinococcosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Bliziotis, I.A. Albendazole for the treatment of human echinococcosis: A review of comparative clinical trials. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 334, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavidia, C.M.; Gonzalez, A.E.; Barron, E.A.; Ninaquispe, B.; Llamosas, M.; Verastegui, M.R.; Robinson, C.; Gilman, R.H. Evaluation of oxfendazole, praziquantel and albendazole against cystic echinococcosis: A randomized clinical trial in naturally infected sheep. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.; Hu, W. In vivo and in vitro efficacies of mebendazole, mefloquine and nitazoxanide against cyst echinococcosis. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, R.A.; Lira, M.G.S.; Licá, I.C.L.; Frazão, G.C.C.G.; Dos Santos, V.A.F.; Mendes Filho, A.C.C.; Rodrigues, J.G.M.; Miranda, G.S.; Carvalho, R.C.; Nascimento, F.R.F. Praziquantel: An update on the mechanism of its action against schistosomiasis and new therapeutic perspectives. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2022, 252, 111531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xie, W.; Li, P. Severe adverse reaction induced by albendazole and praziquantel for cystic echinococcosis. IDCases 2023, 34, e01895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadr, S.; Poorjafari Jafroodi, P.; Haratizadeh, M.J.; Ghasemi, Z.; Borji, H.; Hajjafari, A. Current status of nano-vaccinology in veterinary medicine science. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 9, 2294–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjafari, A.; Sadr, S.; Santucciu, C.; Masala, G.; Bayat, M.; Lotfalizadeh, N.; Borji, H.; Partovi Moghaddam, S.; Hajjafari, K. Advances in detecting cystic echinococcosis in intermediate hosts and new diagnostic tools: A literature review. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadr, S.; Lotfalizadeh, N.; Abbasi, A.M.; Soleymani, N.; Hajjafari, A.; Roohbaksh Amooli Moghadam, E.; Borji, H. Challenges and prospective of enhancing hydatid cyst chemotherapy by nanotechnology and the future of nanobiosensors for diagnosis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, N.; Dobakhti, F.; Faghihzadeh, S.; Haniloo, A. In-vitro and in-vivo effects of chitosan-praziquantel and chitosan-albendazole nanoparticles on Echinococcus granulosus Metacestodes. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Ali, A.A. Effect of selenium nanoparticles against protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus in vitro and hydatid cysts in mice. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 36, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, S.M.; Shnawa, B.H.; Jalil, P.J.; Ahmed, M.H. Assessment of the therapeutic efficacy of silver nanoparticles against secondary cystic echinococcosis in BALB/c mice. Surfaces 2022, 5, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, M.M.; Moazeni, M.; Alizadeh, M.; Abedi, M.; Tamaddon, A.-M. Evaluation of the efficacy of albendazole sulfoxide (ABZ-SO)–loaded chitosan-PLGA nanoparticles in the treatment of cystic echinococcosis in laboratory mice. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 4233–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navvabi, A.; Homaei, A.; Khademvatan, S.; Ansari, M.H.K.; Keshavarz, M. Combination of TiO2 nanoparticles and Echinometra mathaeis gonad extracts: In-vitro and in-vivo scolicidal activity against hydatid cysts. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 22, 101432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryamand, S.; Khademvatan, S.; Tappeh, K.H.; Heshmatian, B.; Jelodar, A. In vitro and in-vivo scolicidal activities of Holothuria leucospilota extract and CeO2 nanoparticles against hydatid cyst. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2019, 14, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassef, N.E.; Saad, A.-G.E.; Harba, N.M.; Beshay, E.V.; Gouda, M.A.; Shendi, S.S.; Mohamed, A.S.E.-D. Evaluation of the therapeutic efficacy of albendazole-loaded silver nanoparticles against Echinococcus granulosus infection in experimental mice. J. Parasit. Dis. 2019, 43, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa, G.V.U.; Pensel, P.E.; Elissondo, M.C.; Bruni, S.F.S.; Benoit, J.-P.; Palma, S.D.; Allemandi, D.A. Albendazole-lipid nanocapsules: Optimization, characterization and chemoprophylactic efficacy in mice infected with Echinococcus granulosus. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 198, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, M.; Haniloo, A.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Faghihzadeh, S. Efficiency of flubendazole-loaded mPEG-PCL nanoparticles: A promising formulation against the protoscoleces and cysts of Echinococcus granulosus. Acta Trop. 2018, 187, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelowdar, A.; Rafiei, A.; Abbaspour, M.R.; Rashidi, I.; Rahdar, M. Efficacy of combined albendazol and praziquntel and their loaded solid lipid nanoparticles components in chemoprophylaxis of experimental hydatidosis. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensel, P.E.; Gamboa, G.U.; Fabbri, J.; Ceballos, L.; Bruni, S.S.; Alvarez, L.I.; Allemandi, D.; Benoit, J.P.; Palma, S.D.; Elissondo, M.C. Cystic echinococcosis therapy: Albendazole-loaded lipid nanocapsules enhance the oral bioavailability and efficacy in experimentally infected mice. Acta Trop. 2015, 152, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadnia, S.; Moazeni, M.; Mohammadi-Samani, S.; Oryan, A. In vivo evaluation of the efficacy of albendazole sulfoxide and albendazole sulfoxide loaded solid lipid nanoparticles against hydatid cyst. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 135, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorouri, N.; Soleymani, N.; Sadr, S.; Rahdar, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, E.; Borji, H. Investigating the therapeutic effects of curcumin nanocapsules in hydatid cyst-infected mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2024, 267, 108860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleymani, N.; Sadr, S.; Santucciu, C.; Rahdar, A.; Masala, G.; Borji, H. Evaluation of the in-vitro effects of albendazole, mebendazole, and praziquantel nanocapsules against protoscolices of hydatid cyst. Pathogens 2024, 13, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Lei, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Xing, G.; Lv, H.; Jiang, Y. Protoscolicidal effects of chenodeoxycholic acid on protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 167, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihian, P.; Hajipour, N.; Hassanzadeh, P. Effect of temperature and salinity on survival of protoscoleces of hydatid cyst in liver in-vitro. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2024, 21, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttenschoen, K.; Carli Buttenschoen, D. Echinococcus granulosus infection: The challenge of surgical treatment. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2003, 388, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saeedi, M.; Ramouz, A.; Khajeh, E.; El Rafidi, A.; Ghamarnejad, O.; Shafiei, S.; Ali-Hasan-Al-Saegh, S.; Probst, P.; Stojkovic, M.; Weber, T.F. Endocystectomy as a conservative surgical treatment for hepatic cystic echinococcosis: A systematic review with single-arm meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawi, A.E.; Alanazi, A.D.; Baharvand, P.; Sepahvand, M.; Mahmoudvand, H. High potency of organic and inorganic nanoparticles to treat cystic echinococcosis: An evidence-based review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnawa, B.H. Advances in the use of nanoparticles as anti-cystic echinococcosis agents: A review article. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2018, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamarozzi, F.; Vuitton, L.; Brunetti, E.; Vuitton, D.A.; Koch, S. Non-surgical and non-chemical attempts to treat echinococcosis: Do they work? Parasite 2014, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Tirado, V.; Romero-Alegria, A.; Pardo-Lledías, J.; Alonso-Sardón, M.; Lopez-Bernus, A.; Sampedro, J.Q.; Bellvis, L.M.; Iglesias Gomez, A.; Muro, A.; Muñoz Bellido, J.L. Management of cystic echinococcosis in the last two decades: What have we learned? Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 112, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadr, S.; Ahmadi Simab, P.; Niazi, M.; Yousefsani, Z.; Lotfalizadeh, N.; Hajjafari, A.; Borji, H. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy on parasitic drug resistance. Exp. Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2024, 22, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, W.; Dai, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Li, F. Status and prospect of novel treatment options toward alveolar and cystic echinococcosis. Acta Trop. 2022, 226, 106252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Huayu, M.; Mu, Y.; Tang, F.; Ge, R.-L. Ubenimex combined with albendazole for the treatment of Echinococcus multilocularis-induced alveolar echinococcosis in mice. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1320308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.-D.; Ji-De, A.; Liu, L.-X.; Fan, H.-N. Current status of drug therapy for alveolar echinococcosis. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permana, A.D.; Paredes, A.J.; Zanutto, F.V.; Amir, M.N.; Ismail, I.; Bahar, M.A.; Sumarheni; Palma, S.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Albendazole nanocrystal-based dissolving microneedles with improved pharmacokinetic performance for enhanced treatment of cystic echinococcosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 38745–38760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.S.; Ferreira, C.S.; Branquinha, M.H.; Santos, A.L.; Chaud, M.V.; Jain, S.; Cardoso, J.C.; Kovačević, A.B.; Souto, E.B.; Severino, P. Overcoming multi-resistant leishmania treatment by nanoencapsulation of potent antimicrobials. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 2123–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaouina, S.; Aouf, A.; Touati, A.; Ali, H.; Elkhadragy, M.; Yehia, H.; Farouk, A. Effect of nanoencapsulation on the antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of algerian Origanum glandulosum Desf. against multidrug-resistant clinical isolates. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri Darvish, H.; Bahrami, A.; Jafari, S.M.; Williams, L. Micro/nanoencapsulation strategy to improve the efficiency of natural antimicrobials against Listeria monocytogenes in food products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1241–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opatha, S.A.T.; Titapiwatanakun, V.; Chutoprapat, R. Transfersomes: A promising nanoencapsulation technique for transdermal drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, S.; Kalam, N.; Shaikh, M.F.; Hasnain, M.S.; Hafiz, A.K.; Ansari, M.T. Nanoencapsulation of polyphenols as drugs and supplements for enhancing therapeutic profile-a review. Cur. Mol. Pharmacol. 2022, 15, 77–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SShnawa, B.H.; Al-Ali, S.J.; Swar, S.O. Nanoparticles as a new approach for treating hydatid cyst disease. Vet. Pathobiol. Public Health 2021, 1, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, M.; Haniloo, A.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Ahmadi, N. In-vitro evaluation of albendazole-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers on Echinococcus granulosus microcysts and their prophylactic efficacy on experimental secondary hydatidosis. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 4049–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, D.; Pan, Y.; Qu, W.; Hao, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Xie, S. Nanoparticles for antiparasitic drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 1206–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharedeh, R.H.; Rezigue, M.; Bashatwah, R.M.; Amawi, H.; Aljabali, A.A.; Obeid, M.A.; Tambuwala, M.M. Nanomaterials as a potential target for infectious parasitic agents. Cur. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 828–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Nanoparticles | Animal | Gender | Drug Dosage | Treatment Period | Result | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selenium nanoparticles(SeNPs) | Mus musculus BALB/c | male | protoscoleces processed with 50, 100, 150, 200 µg/mL Se NPs | 3, 4, 5 months post infestation | The reduction rate was 90% in mice injected with exposed protoscoleces at 150 µg/mL in the next 4–5 months of infection. | S.A. Mohammed and A.A. Ali. (2022) [42] |
| Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) accomplished using Zizyphus spina-christi leaves. | BALB/c | male and female | 50, 100, 200, 300 mg/kg | 30 days | Ag NPs did not induce any adverse effects or signs and no death. Change in the appearance of the liver hydatid cysts from hyaline to milky cloudy. | S.M. Hamad et al. (2022) [43] |
| Albendazole sulfoxide (ABZ-SO)-loaded Chitosan–PLGA | Laboratory mice | - | 10 mg/kg | 45 days at a daily dose | The weight and volume of cysts were statistically significant | M.M. Darvishi. et al. (2020) [44] |
| Sea urchin gonad extraction combined with Tio2 NPs | BALB/c mice | - | 15 µg/mL | 3 months | Reduction in number, size, and volume of the cysts. | A. Navvabi. et al. (2019) [45] |
| Holothuria leucospilota extract and CeO2 nanoparticles | BALB/c mice | male | 50 mg/kg | 1 month | Decrease in number of cysts, size, and volume of cyst. | S. Aryamand. et al. (2019) [46] |
| Albendazole-loaded silver nanoparticles | Laboratory-bred albino mice | female | 200 mg/kg/d for 5 consecutive days per week | 8 weeks | All the treated groups showed significant reductions in size and weight. | N.E. Nassef. et al. (2019) [47] |
| Albendazole LNCs | CF-1 mice | female | 5 mg/kg/d | 1 month | 4 out of the 10 ABZ-LNC-treated mice did not develop any cysts. -Changes in the germinal layer. | G.V.U. Gamboa. et al. (2019) [48] |
| Chitosan–praziquantel and chitosan–albendazole nanoparticles | DBA/2 mice | male | 25 mg/kg | 21 days | Reduced the cyst numbers. | N. Torabi. et al. (2018) [41] |
| Flubendazole-loaded mPEG-PCL NPs | BALB/c mice | - | 1, 5, 10 μg/mL/d | 1 month | Reduced the weight and number of the cysts. (94.64% and 70.21%) | M. Farhadi. et al. (2018) [49] |
| Albendazole and praziquantel with loaded solid lipid nanoparticles components | BALB/c | female | 50 mg/kg. 5 consecutive days and 2-day break every week | 3-month treatment and 2-month rest | Reduced the wet weight and size of developed cysts (85%) | A. Jelowdar. et al. (2017) [50] |
| Albendazole -LNCs | CF-1 mice | female | 5 mg/kg | 1 month | Cysts from ABZ-LNC-treated mice were 1.7-fold higher than those detected in plasma (control). | P.E. Pensel. et al. (2015) [51] |
| Albendazole sulfoxide and albendazole sulfoxide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles | Balb/c mice | - | 0.5, 2 mg/kg/48 h | 15 days | size and weight in the treated animals were reduced. | S. Ahmadnia. (2013) [52] |
| Groups | Treatments | Dose |
|---|---|---|
| n° | Nanocapsule Groups | |
| 1 | Nano-ABZ | 1 mg/kg |
| 2 | Nano-MBZ | 1 mg/kg |
| 3 | Nano-PZQ | 1 mg/kg |
| 4 | Nano-ABZ + MBZ | 1 mg/kg, (Both at 1 mg/mL final concentration), (Both ABZ + MBZ in the one nanocapsule) |
| 5 | Nano-ABZ + PZQ | 1 mg/kg, (Both at 1 mg/mL final concentration), (Both ABZ + PZQ in the one nanocapsule) |
| 6 | Nano-MBZ + PZQ | 1 mg/kg, (Both at 1 mg/mL final concentration), (Both MBZ + PZQ in the one nanocapsule) |
| Positive control groups with only drugs | ||
| 7 | ABZ | 150 mg/kg |
| 8 | MBZ | 150 mg/kg |
| 9 | PZQ | 600 mg/kg |
| 10 | ABZ + MBZ | 150 mg/kg + 150 mg/kg |
| 11 | ABZ + PZQ | 150 mg/kg + 600 mg/kg |
| 12 | MBZ + PZQ | 150 mg/kg + 600 mg/kg |
| Negative Control group | ||
| 13 | PBS | 1 mg/mL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soleymani, N.; Sadr, S.; Santucciu, C.; Rahdar, A.; Masala, G.; Borji, H. Investigating the Therapeutic Effects of Albendazole, Mebendazole, and Praziquantel Nanocapsules in Hydatid Cyst-Infected Mice. Pathogens 2025, 14, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030240
Soleymani N, Sadr S, Santucciu C, Rahdar A, Masala G, Borji H. Investigating the Therapeutic Effects of Albendazole, Mebendazole, and Praziquantel Nanocapsules in Hydatid Cyst-Infected Mice. Pathogens. 2025; 14(3):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030240
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoleymani, Nooshinmehr, Soheil Sadr, Cinzia Santucciu, Abbas Rahdar, Giovanna Masala, and Hassan Borji. 2025. "Investigating the Therapeutic Effects of Albendazole, Mebendazole, and Praziquantel Nanocapsules in Hydatid Cyst-Infected Mice" Pathogens 14, no. 3: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030240
APA StyleSoleymani, N., Sadr, S., Santucciu, C., Rahdar, A., Masala, G., & Borji, H. (2025). Investigating the Therapeutic Effects of Albendazole, Mebendazole, and Praziquantel Nanocapsules in Hydatid Cyst-Infected Mice. Pathogens, 14(3), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030240









