Development of Low-Cost In-House Assays for Quantitative Detection of HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBV DNA to Enhance Hepatitis B Virus Diagnostics and Antiviral Screening in Resource-Limited Settings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chronic HBV Patient Clinical Data and Sample Collection
2.2. Quantitative In-House Sandwich ELISA for Detection of HBsAg and HBeAg
2.3. HBV Cell Culture and Viability Assessment
2.4. DNA Isolation from Plasma or Cell Culture Supernatant Using Column-Based, Column-Free, or Boil–Spin Methods
2.5. Quantification of Total HBV DNA
2.6. Z′ Score Calculation
2.7. Cost Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Development of an In-House Sandwich ELISA for the Detection of HBsAg and HBeAg
3.2. Validation of In-House qPCR and Column-Free DNA Isolation Methods for Subsequent HBV DNA Quantification
3.3. Comparison of Silica-Column-Based Nucleic Acid Purification Kit to In-House DNA Isolation Protocols for Determination of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Half-Maximal Effective Concentration (EC50)
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAD | Canadian dollars |
| cccDNA | Covalently closed circular DNA |
| CHB | Chronic hepatitis B |
| CHREB | Conjoint Health Research Ethics Board |
| EC50 | Half-maximal effective concentration |
| ELISA | Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay |
| HBeAg | Hepatitis B e antigen |
| HBsAg | Hepatitis B surface antigen |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| IU/mL | International units per milliliter |
| LLOD | Lower limit of detection |
| OD | Optical density |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PEI U/mL | Paul Ehrlich Institute units per milliliter |
| POC | Point of care |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RLS | Resource-limited setting |
| TDF | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
References
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis B. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Committee on a National Strategy for the Elimination of Hepatitis B and C; Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice; Health and Medicine Division; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Eliminating the Public Health Problem of Hepatitis B and C in the United States: Phase One Report; Buckley, G.J., Strom, B.L., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Revill, P.; Testoni, B.; Locarnini, S.; Zoulim, F. Global strategies are required to cure and eliminate HBV infection. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis B vaccines: WHO position paper, July 2021. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2021, 96, 269–292. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Shen, C.; Jiang, N.; Zou, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Evidence of Residual Ongoing Viral Replication in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Successfully Treated With Nucleos(t)ide Analogues. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 227, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.Q.; Duan, Z.; Dai, E.; Zhang, S.; Han, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, H.; Zhu, B.; Zhao, W.; et al. Tenofovir to Prevent Hepatitis B Transmission in Mothers with High Viral Load. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2324–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.T.Y.; Jackson, K.; Picchio, C.A.; Kramvis, A.; Sonderup, M.; Lemoine, M.; Matthews, G.; Howell, J.; Coffin, C.S.; Hellard, M.; et al. Availability of point-of-care HBV tests in resource-limited settings. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’souza, S.; Lau, K.C.; Coffin, C.S.; Patel, T.R. Molecular mechanisms of viral hepatitis induced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachon, A.; Osiowy, C. Novel biomarkers of hepatitis B virus and their use in chronic hepatitis B patient management. Viruses 2021, 13, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimée, N. DAC List of ODA Recipients; OECD: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Easterbrook, P.; Johnson, C.; Figueroa, C.; Baggaley, R. HIV and hepatitis testing: Global progress, challenges, and future directions. AIDS Rev. 2016, 18, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shenge, J.A.; Osiowy, C. Rapid diagnostics for hepatitis B and C viruses in low-and middle-income countries. Front. Virol. 2021, 1, 742722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quest Diagnostics. Available online: https://newsroom.questdiagnostics.com/index.php?s=30664 (accessed on 2 September 2023).
- Gani, A.W.; Wei, W.; Shi, R.Z.; Ng, E.; Nguyen, M.; Chua, M.S.; So, S.; Wang, S.X. An Automated, Quantitative, and Multiplexed Assay Suitable for Point-of-Care Hepatitis B Virus Diagnostics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission of Hepatitis B Virus Guidelines on Antiviral Prophylaxis in Pregnancy Policy Brief; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Gogal Jr, R.M.; Walsh, J.E. A new rapid and simple non-radioactive assay to monitor and determine the proliferation of lymphocytes: An alternative to [3H] thymidine incorporation assay. J. Immunol. Methods 1994, 170, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhomwegen, J.; Kwasiborski, A.; Diop, A.; Boizeau, L.; Hoinard, D.; Vray, M.; Bercion, R.; Ndiaye, B.; Dublineau, A.; Michiyuki, S.; et al. Development and clinical validation of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay to diagnose high HBV DNA levels in resource-limited settings. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1858.e9–1858.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kim, S.; Ryu, W.S. DDX3 DEAD-Box RNA helicase inhibits hepatitis B virus reverse transcription by incorporation into nucleocapsids. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5815–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. elife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Chung, T.D.; Oldenburg, K.R. A Simple Statistical Parameter for Use in Evaluation and Validation of High Throughput Screening Assays. J. Biomol. Screen 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Industries, F. HBsAg Antibody (10-H05H). Available online: https://www.biosynth.com/p/10-H05H/hbsag-antibody (accessed on 31 August 2023).
- Martinot-Peignoux, M.; Lapalus, M.; Asselah, T.; Marcellin, P. HB sAg quantification: Useful for monitoring natural history and treatment outcome. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, F.; Dewint, P.; Leroux-Roels, G. Evaluation of a new rapid test for the combined detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen and hepatitis B virus e antigen. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4603–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiagen. DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit. Available online: https://www.qiagen.com/us/products/discovery-and-translational-research/dna-rna-purification/dna-purification/genomic-dna/dneasy-blood-and-tissue-kit (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Laird, P.W.; Zijderveld, A.; Linders, K.; Rudnicki, M.A.; Jaenisch, R.; Berns, A. Simplified mammalian DNA isolation procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhin, E.M.; El Yamani, N.; Rundén-Pran, E.; Dusinska, M. The alamar blue assay in the context of safety testing of nanomaterials. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 981701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, W.E.; Ray, A.S.; Yang, H.; Qi, X.; Xiong, S.; Zhu, Y.; Miller, M.D. Intracellular Metabolism and In Vitro Activity of Tenofovir against Hepatitis B Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinazi, R.F.; Bassit, L.; Clayton, M.M.; Sun, B.; Kohler, J.J.; Obikhod, A.; Arzumanyan, A.; Feitelson, M.A. Evaluation of single and combination therapies with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine in vitro and in a robust mouse model supporting high levels of hepatitis B virus replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 6186–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.; Gish, R.G. Point of care diagnostic testing for hepatitis B virus. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2020, 19, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seck, A.; Ndiaye, F.; Maylin, S.; Ndiaye, B.; Simon, F.; Funk, A.L.; Fontanet, A.; Takahashi, K.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Mishiro, S.; et al. Poor Sensitivity of Commercial Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Hepatitis B e Antigen in Senegal, West Africa. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segeral, O.; Dim, B.; Durier, C.; Prak, S.; Chhim, K.; Vong, C.; Pech, S.; Tiv, S.; Nem, B.; Hout, K.; et al. Hepatitis B e Antigen (HBeAg) Rapid Test and Alanine Aminotransferase Level–Based Algorithm to Identify Pregnant Women at Risk of HBV Mother-to-Child Transmission: The ANRS 12345 TA PROHM Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, e587–e593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembele, B.; Affi-Aboli, R.; Kabran, M.; Sevede, D.; Goha, V.; Adiko, A.C.; Kouamé, R.; Allah-Kouadio, E.; Inwoley, A. Evaluation of four rapid tests for detection of hepatitis B surface antigen in ivory coast. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 6315718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijtink, R.; Snobl, J.; Kruining, J.; Kerkhof-Los, C.; De Man, R.; Janssen, H.; Schalm, S. Quantitative measurement of HBeAg in chronic hepatitis B: A comparison between a radioimmunoassay a fluorescence ELISA and a chemiluminescence ELISA. J. Med. Virol. 1995, 47, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.-L.; Huang, C.-F.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Huang, J.-F.; Dai, C.-Y.; Yu, M.-L.; Chuang, W.-L. Comparison of the Abbott RealTime HBV assay with the Roche Cobas AmpliPrep/Cobas TaqMan HBV assay for HBV DNA detection and quantification. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 60, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karra, V.K.; Chowdhury, S.J.; Ruttala, R.; Polipalli, S.K.; Kar, P. Clinical Significance of Quantitative HBsAg Titres and its Correlation With HBV DNA Levels in the Natural History of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2016, 6, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Shen, L.; Phyo, W.W.; Cloherty, G.; Butler, E.K.; Kuhns, M.C.; McNamara, A.L.; Holzmayer, V.; Gersch, J.; Anderson, M. Quantitative HBeAg is a strong predictor of HBeAg loss among patients receiving pegylated interferon. Antivir. Res. 2024, 227, 105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissinger, A.; Volkers, P.; Scheiblauer, H.; Nick, S.; WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization; World Health Organization. Collaborative Study to Establish a World Health Organization International Standard for Hepatitis B e Antigen (HBeAg); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Prevention, Care and Treatment of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Coffin, C.S.; Tang, A.; Osiowy, C.; Jimenez, C.; Graham, C.; Cohen, C. What will it take to eliminate hepatitis B as a public health threat in the United States and Canada? Clin. Liver. Dis. 2024, 23, e0182. [Google Scholar]
- Pley, C.M.; McNaughton, A.L.; Matthews, P.C.; Lourenço, J. The global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e004275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokaya, J.; McNaughton, A.L.; Burbridge, L.; Maponga, T.; O’Hara, G.; Andersson, M.; Seeley, J.; Matthews, P.C. A blind spot? Confronting the stigma of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection—A systematic review. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
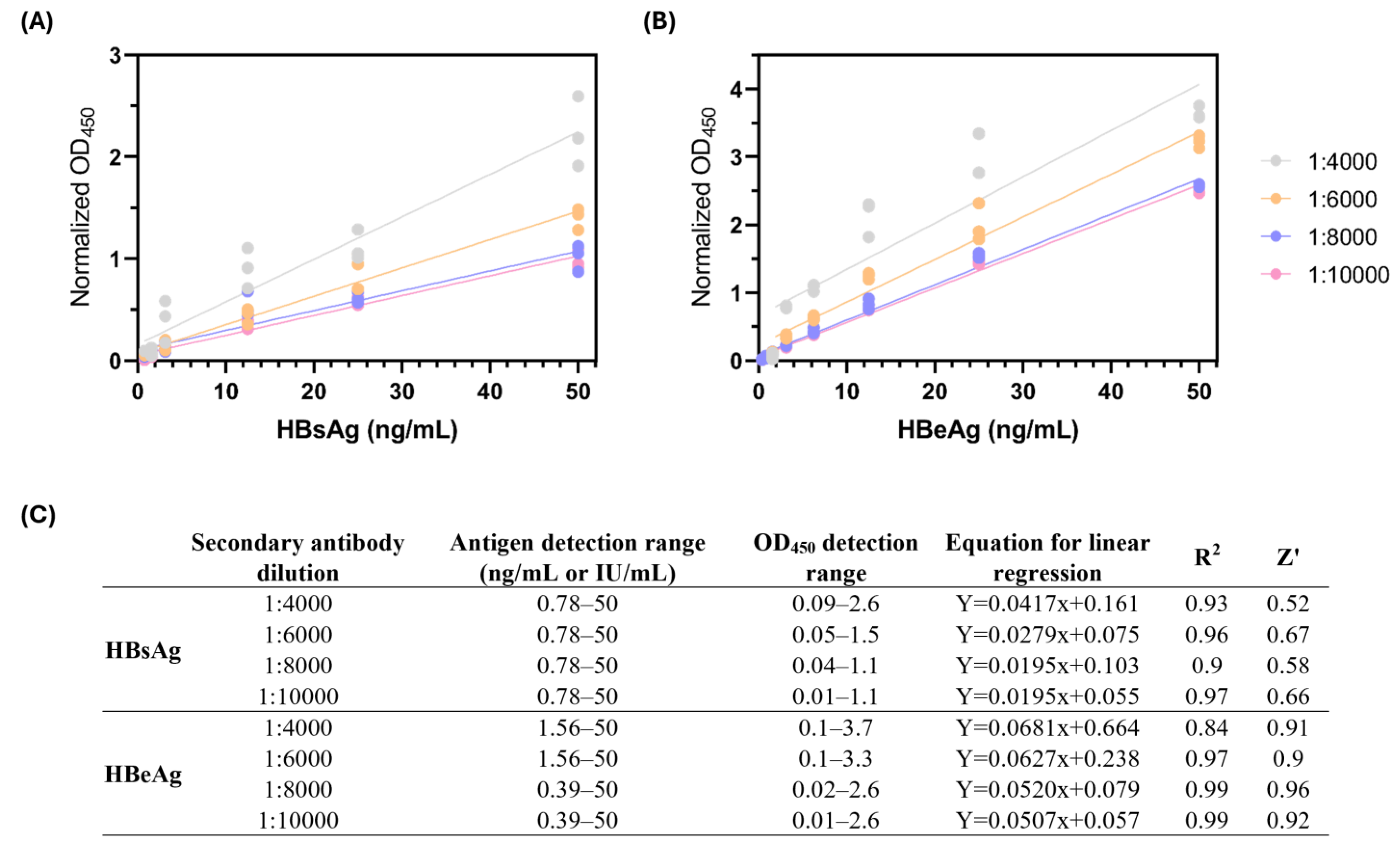
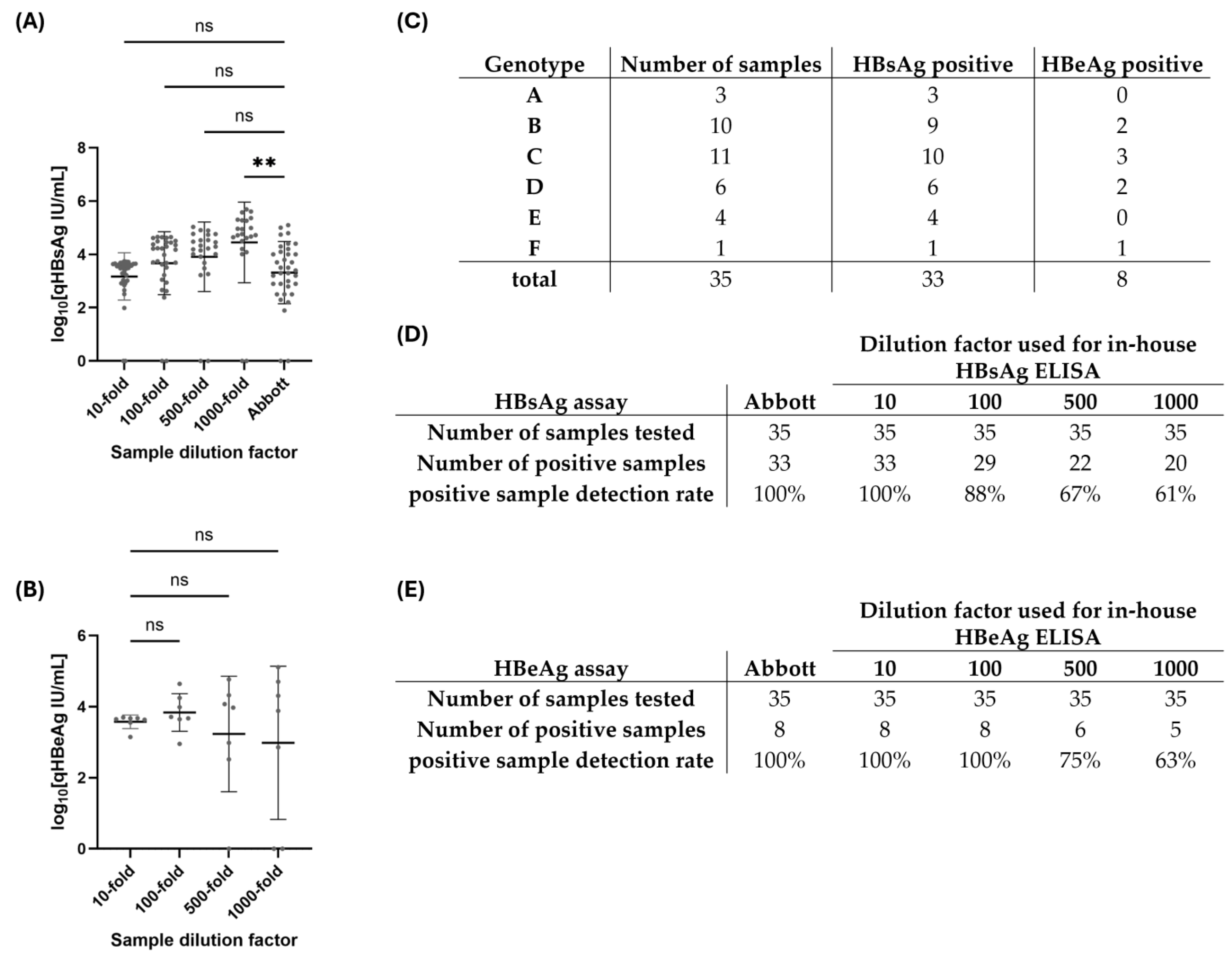
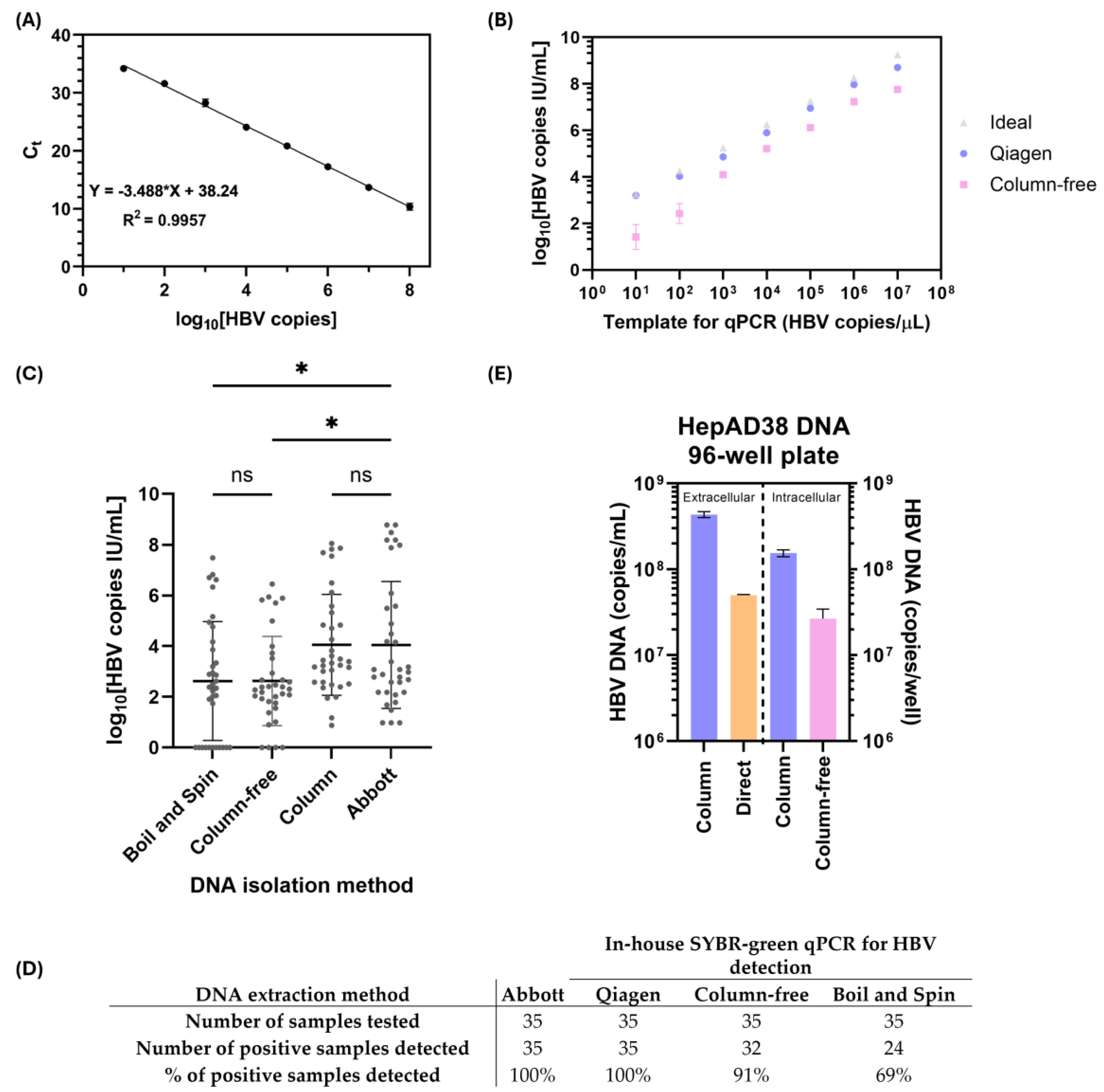
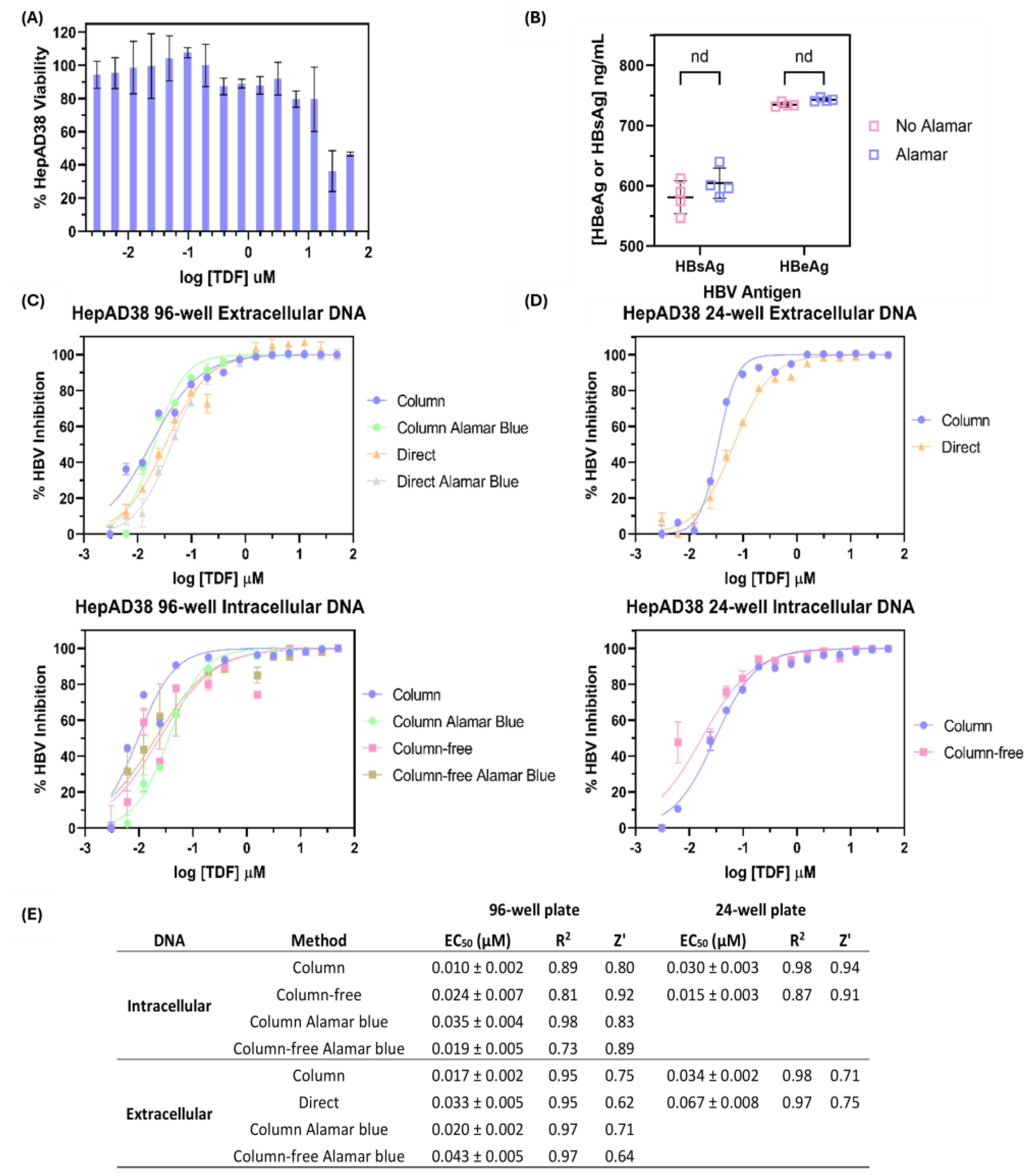
| HBV DNA Copies (log10IU/mL) | Quantitative HBsAg ELISA (log10IU/mL) | HBeAg ELISA Qualitative (-/+) or Quantitative (log10IU/mL) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient ID | HBV Genotype | Abbott Architect DNA Isolation and qPCR | Silica Column DNA Isolation and In-House qPCR | Column-Free DNA Isolation and In-House qPCR | Boil–Spin DNA Isolation and In-House qPCR | Abbott Architect qHBsAg | In-House qHBsAg (1:10 Dilution) | Abbott Architect HBeAg | In-House qHBeAg (1:10 Dilution) |
| 1 | B | 2.18 | 1.17 | 1.93 | n.d. | 2.9 | 3.3 | - | n.d. |
| 2 | D | 8.18 | 6.49 | 4.99 | 5.16 | 5.1 | 3.7 | + | 3.68 |
| 3 | A | 2.78 | 3.44 | 1.55 | n.d. | 3.5 | 3.5 | - | n.d. |
| 4 | B | 5.58 | 4.70 | 3.52 | 2.94 | 2.9 | 3.4 | - | n.d. |
| 5 | C | 2.78 | 3.33 | 1.38 | 2.49 | 3.2 | 3.6 | - | n.d. |
| 6 | C | 2.68 | 3.05 | 2.59 | n.d. | 3.4 | 3.7 | - | n.d. |
| 7 | E | 3.08 | 3.39 | 2.47 | 2.86 | 2.8 | 3.0 | - | n.d. |
| 8 | E | 2.98 | 3.61 | 2.08 | 1.91 | 2.2 | 2.9 | - | n.d. |
| 9 | E | 3.18 | 3.25 | 2.41 | 2.02 | 3.7 | 3.6 | - | n.d. |
| 10 | D | 2.08 | 2.51 | 2.01 | 2.05 | 4.1 | 3.6 | - | n.d. |
| 11 | C | 0.98 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 2.62 | n.d. | n.d. | - | n.d. |
| 12 | B | 7.98 | 7.68 | 5.82 | 6.82 | 4.8 | 3.7 | + | 3.53 |
| 13 | C | 2.58 | 2.58 | n.d. | n.d. | 4 | 3.7 | - | n.d. |
| 14 | A | 2.58 | 2.58 | 2.66 | 2.23 | 3.2 | 3.5 | - | n.d. |
| 15 | E | 3.38 | 3.82 | 2.27 | 2.89 | 3 | 2.8 | - | n.d. |
| 16 | D | 8.78 | 7.55 | 5.89 | 6.33 | 5 | 3.6 | - | 3.70 |
| 17 | D | 2.18 | 3.01 | 2.18 | n.d. | 2.5 | 3.0 | - | n.d. |
| 18 | B | 4.88 | 4.83 | 1.82 | 4.17 | 3.3 | 3.6 | - | n.d. |
| 19 | B | 1.68 | 2.39 | 1.76 | n.d. | 2.3 | 3.5 | - | n.d. |
| 20 | C | 8.78 | 8.05 | 6.45 | 7.48 | 4.3 | 3.7 | + | 3.15 |
| 21 | B | 1.78 | 1.99 | 2.12 | 2.34 | 1.9 | 2.5 | - | n.d. |
| 22 | B | 4.18 | 3.49 | 2.66 | n.d. | 3.7 | 3.7 | - | n.d. |
| 23 | D | 1.48 | 1.95 | 1.01 | n.d. | 4 | 3.6 | - | n.d. |
| 24 | C | 8.48 | 7.82 | 5.94 | 6.70 | 4.4 | 3.2 | + | 3.67 |
| 25 | C | 2.88 | 3.23 | 2.38 | 2.38 | 2.5 | 2.0 | - | n.d. |
| 26 | C | 2.18 | 2.48 | n.d. | n.d. | 3.3 | 2.7 | - | n.d. |
| 27 | B | 0.98 | 3.18 | n.d. | n.d. | 2.5 | 2.9 | - | n.d. |
| 28 | A | 4.48 | 5.32 | 2.04 | 3.86 | 4 | 3.6 | - | n.d. |
| 29 | D | 3.08 | 3.16 | 2.31 | 1.74 | 3.8 | 3.5 | - | n.d. |
| 30 | B | 7.88 | 7.86 | 5.70 | 6.62 | 4.2 | 3.7 | + | 3.65 |
| 31 | B | 0.98 | 2.36 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | - | n.d. |
| 32 | C | 6.08 | 6.12 | 3.99 | 4.94 | 4.4 | 3.7 | + | 3.63 |
| 33 | C | 4.15 | 4.26 | 2.39 | 3.20 | 2.9 | 3.3 | - | n.d. |
| 34 | C | 5.49 | 5.58 | 3.72 | 4.76 | 3.5 | 3.6 | - | n.d. |
| 35 | F | 6.43 | 4.83 | 2.93 | 3.34 | 4.74 | 3.6 | + | 3.55 |
| Marker Detection | Technology | Detection Method | Turnaround Time | Limit of Detection | Sample Volume | Result Type | Cost/Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBsAg | Abbott Architect HBsAg qualitative | chemiluminescence ELISA | 1 h | 0.041 IU/mL | 10–150 µL | qualitative | USD $25 * | [14,15] |
| Abbott Architect HBsAg quantitative | chemiluminescence ELISA | 1 h | 0.041 IU/mL | 10–150 µL | quantitative | USD $400 * | [14,15] | |
| Lateral flow | colorimetric | 30 min | 0.1–2 IU/mL | 50 µL | qualitative | USD $0.4–2.8 | [33] | |
| In-house ELISA | chemiluminescence ELISA | 4–24 h | 0.78 IU/mL | 2–20 µL | quantitative | CAD $0.18–0.20 | Table S1 | |
| HBeAg | Abbott Architect | chemiluminescence ELISA | 1 h | 0.5 PEI U/mL | 10–150 µL | qualitative | USD $65 * | [14,15,34] |
| Lateral flow assay | colorimetric | 30 min | 316 PEI U/mL | 50 µL | qualitative | USD $0.4–2.8 | [13] | |
| In-house ELISA | chemiluminescence ELISA | 4–24 h | 0.39 PEI U/mL | 1 µL | quantitative | CAD $0.20 | Table S1 | |
| HBV DNA | Abbott Architect | qPCR | 1 h | 10 HBV copies IU/mL | 0.5–1 mL | quantitative | USD $325 * | [14,35] |
| Silica column + in-house qPCR | qPCR | 3.5 h | 1.8 × 103 HBV copies IU/mL | 50 µL | quantitative | CAD $4.9 | Tables S2 and S4 | |
| Column-free DNA extraction (patient plasma) + qPCR | qPCR | 3 h | 1.8 × 104 HBV copies IU/mL | 50 µL | quantitative | CAD $0.49 | Tables S3 and S4 | |
| Boil–spin + qPCR | qPCR | 2 h 15 min | >2.0 × 104 HBV copies IU/mL | 50 µL | quantitative | CAD $0.43 | [18] | |
| Column-free DNA extraction (cultured cells) + qPCR | qPCR | 3 h | 1.8 × 104 HBV copies IU/mL | cells in 96-well plate | quantitative | CAD $0.48 | Tables S3 and S4 | |
| Direct HBV quantification from supernatant of cultured cells | qPCR | 2 h | 1.8 × 104 HBV copies IU/mL | cells in 96-well plate | quantitative | CAD $0.43 | Tables S3 and S4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’souza, S.; Al-Yasiri, L.; Chen, A.; Boghici, D.T.; van Marle, G.; Corcoran, J.A.; Patel, T.R.; Coffin, C.S. Development of Low-Cost In-House Assays for Quantitative Detection of HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBV DNA to Enhance Hepatitis B Virus Diagnostics and Antiviral Screening in Resource-Limited Settings. Pathogens 2025, 14, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030258
D’souza S, Al-Yasiri L, Chen A, Boghici DT, van Marle G, Corcoran JA, Patel TR, Coffin CS. Development of Low-Cost In-House Assays for Quantitative Detection of HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBV DNA to Enhance Hepatitis B Virus Diagnostics and Antiviral Screening in Resource-Limited Settings. Pathogens. 2025; 14(3):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030258
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’souza, Simmone, Layla Al-Yasiri, Annie Chen, Dan T. Boghici, Guido van Marle, Jennifer A. Corcoran, Trushar R. Patel, and Carla S. Coffin. 2025. "Development of Low-Cost In-House Assays for Quantitative Detection of HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBV DNA to Enhance Hepatitis B Virus Diagnostics and Antiviral Screening in Resource-Limited Settings" Pathogens 14, no. 3: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030258
APA StyleD’souza, S., Al-Yasiri, L., Chen, A., Boghici, D. T., van Marle, G., Corcoran, J. A., Patel, T. R., & Coffin, C. S. (2025). Development of Low-Cost In-House Assays for Quantitative Detection of HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBV DNA to Enhance Hepatitis B Virus Diagnostics and Antiviral Screening in Resource-Limited Settings. Pathogens, 14(3), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030258







