Microbiological Risks to Health Associated with the Release of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and β-Lactam Antibiotics Through Hospital Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. HWW Discharge Points of the HJM
2.2. HWW Collection and In Situ Temperature Determination
2.3. Determination of HWW Quality Standard Parameters
2.4. Quantification of β-Lactam-Resistant Bacterial Populations in HWW
2.5. Bacterial Identification by Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF)
2.6. Detection of β-Lactam Resistance Genes in Resistant Bacteria
2.7. Detection and Quantification of β-Lactam Antibiotics in HWW
2.8. Identification of Risks Associated with HWW by Means of a Vester Matrix
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Standard HWW Parameters
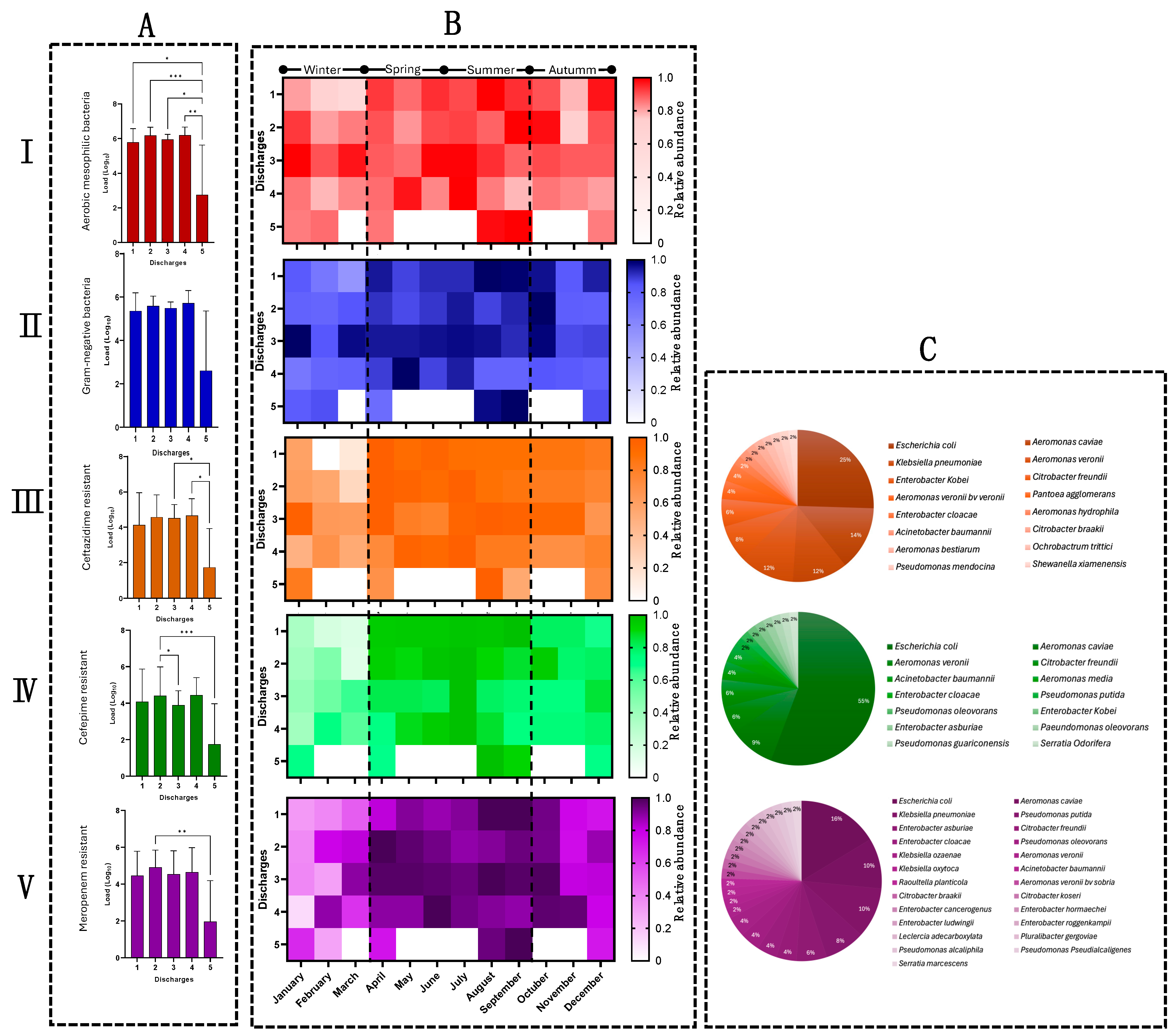
3.2. Quantification of Bacterial Populations in HWW
3.3. The Release of β-Lactam-Resistant Bacteria Shows Seasonal Behavior
3.4. Microbiological Identification Revealed ESKAPE Bacteria and Emerging Pathogens in HWW
3.5. Detection of Carbapenems and Cephalosporin Resistance Genes
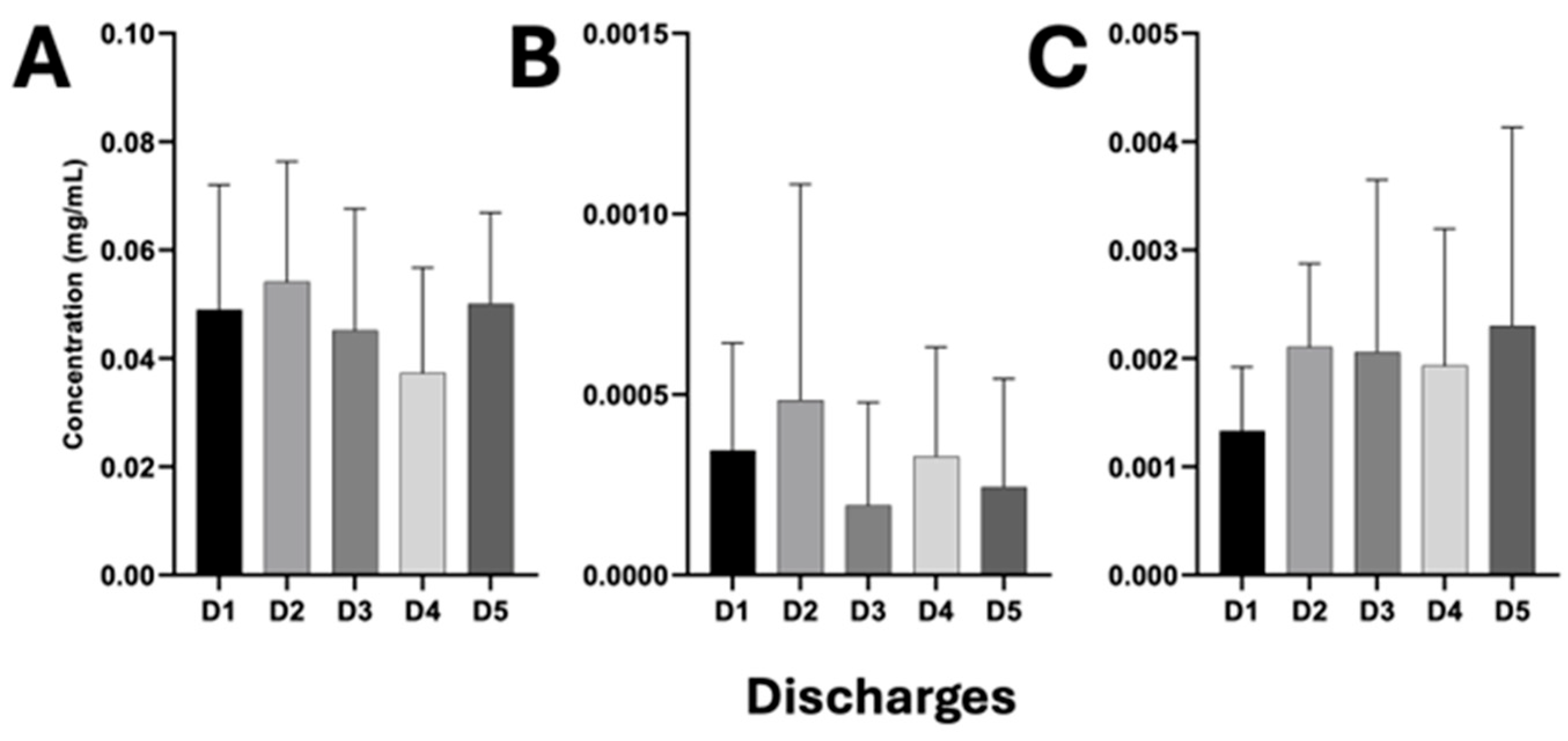
3.6. Release of β-Lactam Antibiotics Through HWW Discharges from the HJM
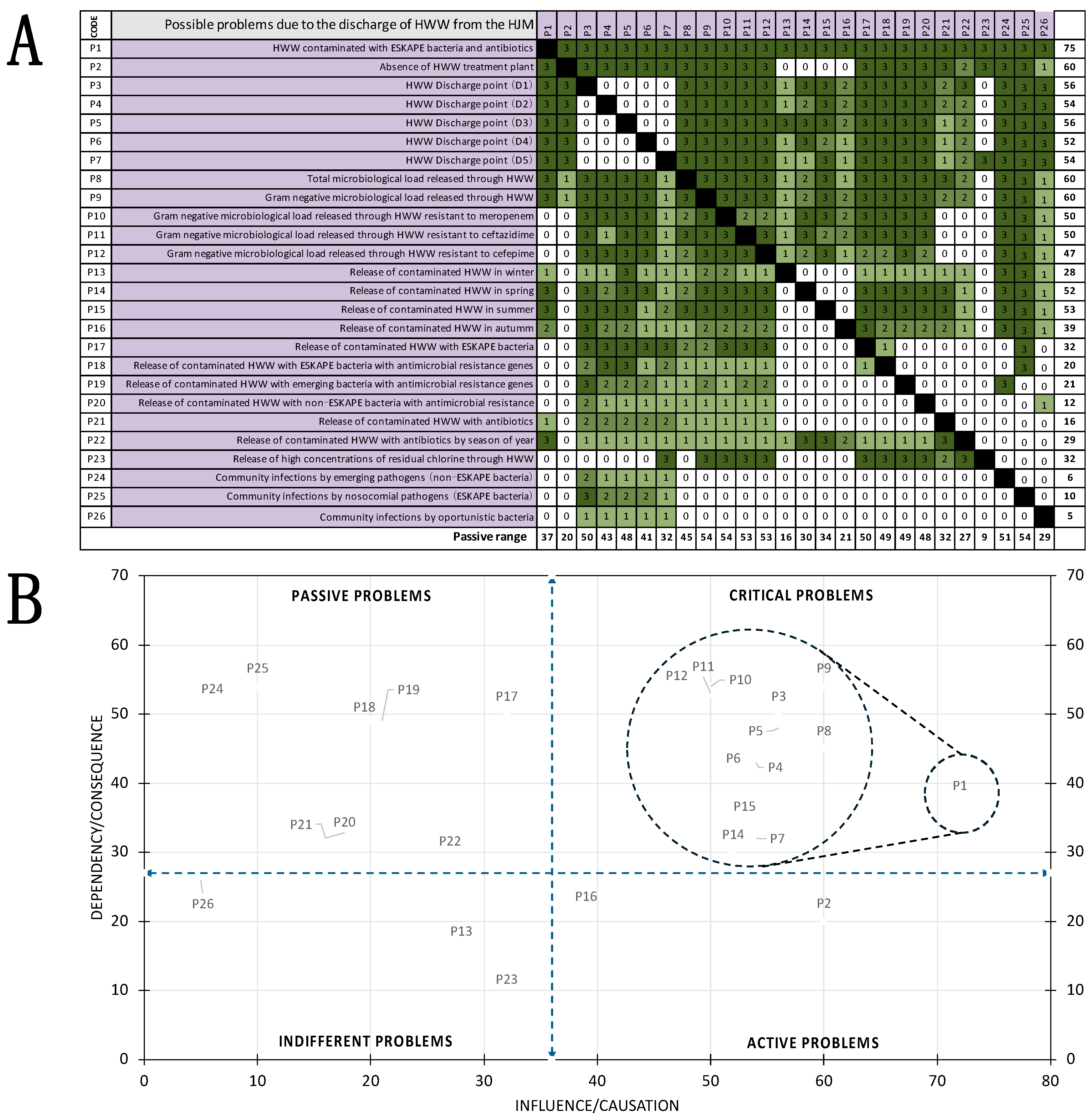
3.7. Vester Matrix to Identify Problems Associated with HWW
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhandari, G.; Chaudhary, P.; Gangola, S.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, A.; Rafatullah, M.; Chen, S. A Review on Hospital Wastewater Treatment Technologies: Current Management Practices and Future Prospects. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.A.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Majdi, H.S.; Zabibah, R.S.; Taherian, M.; Prasetio, D.B.; Gabr, G.A.; Asban, P.; Kiani, A.; Sarkohaki, S. Hospital wastewater treatment methods and its impact on human health and environments. Rev. Environ. Health 2024, 39, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.T.; Shah, I.A.; Ihsanullah, I.; Naushad, M.; Ali, S.; Shah, S.H.A.; Mohammad, A.W. Hospital wastewater as a source of environmental contamination: An overview of management practices, environmental risks, and treatment processes. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 101990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, B.S. Contaminant Properties of Hospital Clinical Laboratory Wastewater: A Physiochemical and Microbiological Assessment. J. Environ. Protect. 2016, 7, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, J.M.; Fernández, E.; Curiel, E. In vivo transfer of plasmid pRAS1 between Aeromonas salmonicida and Aeromonas hydrophila in artificially infected Cyprinus carpio L. J. Fish. Dis. 2010, 33, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, J.M.; Vázquez, N.J.; Fernández, E.; Curiel, E. Inability of some Aeromonas hydrophila strains to act as recipients of plasmid pRAS1 in conjugal transfer experiments. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 64, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, Z.; López, M.P.; Delgado, L.; Dendooven, L.; Bello, J.M. Mesophilic strains of Aeromonas spp. can acquire the multidrug resistance plasmid pRAS1 in horizontal transfer experiments at low temperatures. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, J.; Cazares, A.; Schulenburg, H. The ESKAPE mobilome contributes to the spread of antimicrobial resistance and CRISPR-mediated conflict between mobile genetic elements. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2023, 51, 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marutescu, L.G.; Popa, M.; Gheorghe, I.; Barbu, I.C.; Rodríguez, D.; Berglund, F.; Blaak, H.; Flach, C.F.; Kemper, M.A.; Spießberger, B.; et al. Wastewater treatment plants, an “escape gate” for ESCAPE pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1193907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolbiecki, D.; Paukszto, Ł.; Krawczyk, K.; Korzeniewska, E.; Sawicki, J.; Harnisz, M. Genomic and metagenomic analysis reveals shared resistance genes and mobile genetic elements in E. coli and Klebsiella spp. isolated from hospital patients and hospital wastewater at intra- and inter-genus level. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2024, 261, 114423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denissen, J.; Reyneke, B.; Waso, M.; Havenga, B.; Barnard, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, W. Prevalence of ESKAPE pathogens in the environment: Antibiotic resistance status, community-acquired infection and risk to human health. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 244, 114006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcudi, D.; Sosa, E.J.; Lamberghini, R.; Garnero, A.; Tosoroni, D.; Decca, L.; Gonzalez, L.; Kuyuk, M.A.; Lopez, T.; Herrero, I.; et al. MRSA dynamic circulation between the community and the hospital setting: New insights from a cohort study. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, A.; Seki, M.; Higashiguchi, M.; Tachibana, I.; Kumanogoh, A.; Tomono, K. Community-acquired, hospital-acquired, and healthcare-associated pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2014, 12, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, A.; Palacios, Z.R.; López, L.E.; Rodríguez, J. Rates, predictors and mortality of community-onset bloodstream infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.; Gbaguidi, H.; Cholley, P.; Hocquet, D.; Sauget, M.; Bertrand, X. Hospital-diagnosed infections with Escherichia coli clonal group ST131 are mostly acquired in the community. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.; Wang, Y.C.; Kuo, S.C.; Shih, F.H.; Chen, T.L.; How, C.K.; Yang, Y.S.; Lee, Y.T. Community-acquired bloodstream infections caused by Acinetobacter baumannii: A matched case-control study. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2018, 51, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urzua, M.M.; Aquino, A.; Castelan, J.A.; Merida, J.; Ribas, R.M.; Belmont, L.; Jimenez, A.; Aparicio, G. Detection of carbapenemases in Enterobacterales and other Gram-negative bacilli recovered from hospital and municipal wastewater in Mexico City. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26576. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaria De Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales. NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-003-ECOL-1997, Que Establece los Límites Máximos Permisibles de Contaminantes para las Aguas Residuales Tratadas Que se Reusen en Servicios al Público; DOF: Cuauhtémoc, Mexico, 1997; Available online: https://diariooficial.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=4893449&fecha=21/09/1998#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Secretaría De Comercio Y Fomento Industrial. NORMA Mexicana. Nmx-AA-007-SCFI-2013. Análisis De Agua MEDICIÓN de la Temperatura en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas. Mexico. 2013. Available online: http://legismex.mty.itesm.mx/normas/aa/aa007-2014_01.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Secretaría De Comercio Y Fomento Industrial. NORMA MEXICANA. NMX-AA-108-SCFI-2001, Calidad del Agua Determinación de Cloro Libre y Cloro Total. México. 2001. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166806/NMX-AA-108-SCFI-2001.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Secretaría De Comercio Y Fomento Industrial. NORMA MEXICANA. NMX-AA-008-SCFI-2016, Análisis de Agua. Medición del pH en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas. México. 2001. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166767/NMX-AA-008-SCFI-2016.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Blaize, J.F.; Suter, E.; Corbo, C.P. Serial dilutions and plating: Microbial enumeration. MyJoVE Corp. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakon, S.K.; Mohamad, Z.A.; Jamilan, M.A.; Hashim, H.; Kuman, M.Y.; Shaharudin, R.; Ahmad, N.; Muhamad, N.A. Prevalence of Antibiotic-Resistant Pathogenic Bacteria and Level of Antibiotic Residues in Hospital Effluents in Selangor, Malaysia: Protocol for a Cross-sectional Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2023, 12, e39022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 34th ed.; CLSI Suppl. M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mauri, M.; Elli, T.; Caviglia, G.; Uboldi, G.; Azzi, M. RAWGraphs: A Visualisation Platform to Create Open Outputs. Assoc. Comput. Mach. 2017, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cureño, M.A.; Plascencia, E.S.; Loyola, M.Á.; Cruz, C.; Nolasco, A.E.; Durán, E.M.; Ibáñez, G.; Gómez, E.; Tamayo, M.C.; Tamayo, Y.J.; et al. Gram-Negative ESKAPE Bacteria Surveillance in COVID-19 Pandemic Exposes High-Risk Sequence Types of Acinetobacter baumannii MDR in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Pathogens 2024, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés, I.A.; Juárez, J.C.; Cu, C.; Flores, R.; Durán, E.M.; Cruz, C.; Gutiérrez, V.H.; Sosa, O.; Escobar, N.; Bravata, J.C.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae blaNDM-1 carrying a class 1 integron causing a hospital outbreak in a Mexican attention center. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyola, M.A.; Durán, E.M.; Cruz, C.; Márquez, L.M.; Bravata, J.C.; Cortés, I.A.; Cureño, M.A.; Ibáñez, G.; Fernández, V.; Castro, G.; et al. ESKAPE bacteria characterization reveals the presence of Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa outbreaks in COVID-19/VAP patients. Am. J. Infect. Control 2023, 51, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnegan, A.; Sao, S.S.; Huchko, M.J. Using a chord diagram to visualize dynamics in contraceptive use: Bringing data into practice. Glob. Health Sci. Pract. 2019, 7, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A. The Influence Matrix Methodology: A Technical Report. Landcare Research Contract Report. New Zealand, 2006. Available online: https://icm.landcareresearch.co.nz/knowledgebase/publications/public/imatrix_tech_report.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Durán, E.M.; Cruz, C.; Ibáñez, G.; Bravata, J.C.; Sosa, O.; Delgado, L.; León, G.; Cortés, I.A.; Cureño, M.A.; Castro, G.; et al. Clonal dispersion of Acinetobacter baumannii in an intensive care unit designed to patients COVID-19. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cureño, M.A.; Durán, E.M.; Cruz, C.; Ibáñez, G.; Rojo, M.I.; Moncayo, C.V.; Loyola, M.Á.; Castro, G.; Hernández, D.M.R.; Bello, J.M. Impact of the modification of a cleaning and disinfection method of mechanical ventilators of COVID-19 patients and ventilator-associated pneumonia: One year of experience. Am J. Infect. Control. 2021, 49, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarde, M.; Velazquez, M.E.; Bobadilla del Valle, M.; Cornejo, P.; Carrillo, B.A.; Ponce de León, A.; Sassoé, A.; Saturno, P.; Alpuche, C.M. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns and Clonal Distribution of E. coli, Enterobacter spp. and Acinetobacter spp. Strains Isolated from Two Hospital Wastewater Plants. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarde, M.; Velazquez, M.E.; Bobadilla, M.; Carrillo, B.A.; Cornejo, P.; Ponce de León, A.; Sassoé, A.; Alpuche, C.M. Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Hospital Wastewater: Identification of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella spp. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarde, M.; Velazquez, M.E.; Godoy, E.E.; Carrillo, B.A.; Cornejo, P.; Sassoé, A.; Ponce, A.; Saturno, P.; Alpuche, C.M. Presence and Persistence of ESKAPEE Bacteria before and after Hospital Wastewater Treatment. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolbiecki, D.; Korzeniewska, E.; Czatzkowska, M.; Harnisz, M. The Impact of Chlorine Disinfection of Hospital Wastewater on Clonal Similarity and ESBL-Production in Selected Bacteria of the Family Enterobacteriaceae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagar, V.; Ansari, F.; Vaiyapuri, M.; Joseph, T.C. Virulent and multidrug-resistant Aeromonas in aquatic environments of Kerala, India: Potential risks to fish and humans. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2025, 56, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalvo, E.; Veiga, F.; Rodríguez, H.; Traglia, G.; Vay, C.; Almuzara, M. Identification and antibiotic susceptibility of Aeromonas spp. in a University Hospital in the city of Buenos Aires. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2024. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, K.; Borowiak, M.; Strauch, E.; Deneke, C.; Richter, M.H.; The German Aeromonas Study Group. Emerging Aeromonas spp. infections in Europe: Characterization of human clinical isolates from German patients. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1498180. [Google Scholar]
- Bello, J.M.; Cabrero, O.A.; Ibáñez, G.; Hernández, C.; Pelcastre, L.I.; Gonzalez, L.U.; Castro, G. Horizontal Gene Transfer and Its Association with Antibiotic Resistance in the Genus Aeromonas spp. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.T.; Cazacu, A.C.; Allen, C.H. Pantoea agglomerans, a plant pathogen causing human disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, H.; Pervin, N.; Israr, M.; Kamal, K.R.; Marwat, A.; Khan, M. A Rare Case of Raoultella planticola Urinary Tract Infection in a Patient With Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2018, 6, 2324709618780422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, A.; Di Palo, D.M.; Galano, A.; Becciani, S.; Montagnani, C.; Pecile, P.; Galli, L.; Rossolini, G.M. Intestinal carriage of Shewanella xiamenensis simulating carriage of OXA-48-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 82, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayet, S.; Lang, S.; Garnier, P.; Pierron, A.; Plantin, J.; Toko, L.; Royer, P.Y.; Villemain, M.; Klopfenstein, T.; Gendrin, V. Leclercia adecarboxylata as Emerging Pathogen in Human Infections: Clinical Features and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.J.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.O.; Hong, J.S.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, K. First Case Report of Human Infection With Ochrobactrum tritici Causing Bacteremia and Cholecystitis. Ann. Lab. Med. 2016, 36, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Weiss, Z.F.; Hoffmann, M.; Seetharaman, S.; Taffner, S.; Allerd, M.; Luo, Y.; Pearson, Z.; Baker, M.A.; Klompas, M.; Bry, L.; et al. Nosocomial Pluralibacter gergoviae Isolates Expressing NDM and KPC Carbapenemases Characterized Using Whole-Genome Sequencing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0109322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-L.; Ko, W.-C.; Wu, C.-J. Complexity of β-lactamases among clinical Aeromonas isolates and its clinical implications. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2012, 45, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buelow, E.; Dauga, C.; Carrion, C.; Mathé, H.; Achaibou, S.; Gaschet, M.; Jové, T.; Chesneau, O.; Kennedy, S.P.; Ploy, M.C.; et al. Hospital and urban wastewaters shape the matrix and active resistome of environmental biofilms. Water Res. 2023, 1, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Larsson, D.G. Concentrations of antibiotics predicted to select for resistant bacteria: Proposed limits for environmental regulation. Environ Int. 2016, 86, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, D.; Axtmann, K.; Holstein, N.; Felder, C.; Voigt, A.; Färber, H.; Ciorba, P.; Szekat, C.; Schallenberg, A.; Böckmann, M.; et al. Antibiotic concentrations in raw hospital wastewater surpass minimal selective and minimum inhibitory concentrations of resistant Acinetobacter baylyi strains. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 5721–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Salud, Reglamento de la ley General de Salud en Materia de Investigación para la Salud; DOF: Cuauhtémoc, Mexico, 1987; Available online: https://www.diputados.gob.mx/LeyesBiblio/regley/Reg_LGS_MIS.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2024).



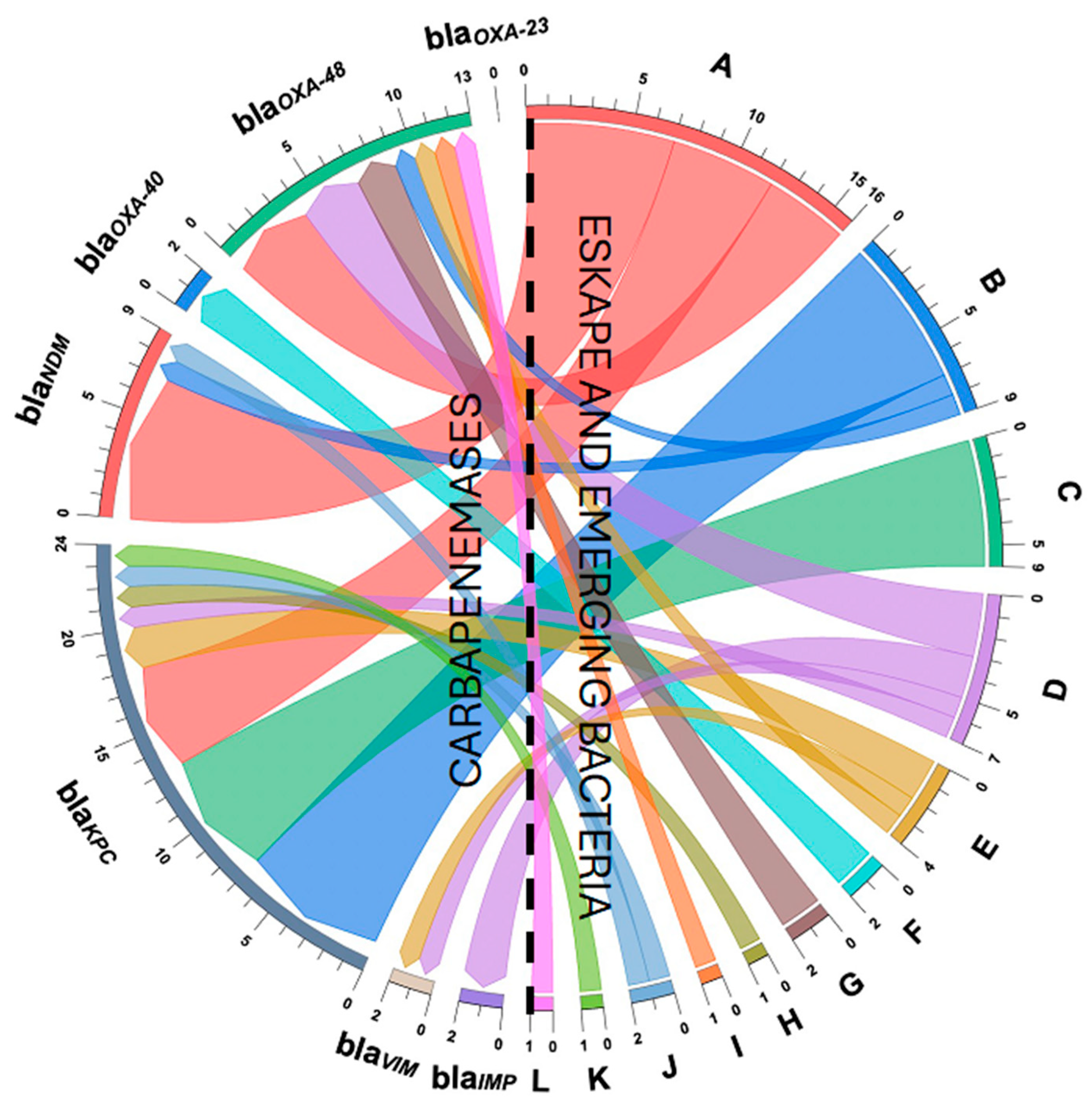
| Microorganisms | Genes Encoding Carbapenemases n (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallo-β-Lactamases | Serine β-Lactamases | Coexistence(n/%) | ||||||
| blaIMP | blaVIM | blaNDM | blaOXA-40 | blaOXA-48 | blaOXA-23 | blaKPC | ||
| Escherichia coli (n = 12) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 7 (77.3) | 0 (0) | 4 (30.7) | 0 (0) | 5 (20.8) | blaKPC + blaNDM (4/33.3) |
| Citrobacter freundii (n = 7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 6 (25) | (0/0) |
| Enterobacter spp. (n = 3) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (7.7) | 0 (0) | 2 (8.3) | blaVIM + blaOXA-48 (1/33.3) |
| Acinetobacter baumannii (n = 2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | (0/0) |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae (n = 2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (15.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | (0/0) |
| Serratia marcescens (n = 1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (4.1) | (0/0) |
| Aeromonas caviae (n = 7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (11.1) | 0 (0) | 1 (7.7) | 0 (0) | 7 (29.2) | blaKPC + blaNDM (1/14.3) |
| Aeromonas media (n = 1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (4.1) | (0/0) |
| Aeromonas hydrophila (n = 1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (7.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | (0/0) |
| Klebsiella oxytoca (n = 1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (11.1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (4.1) | blaKPC + blaNDM (1/100) |
| Pantoea agglomerans (n = 1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (7.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | (0/0) |
| Pseudomonas non-aeruginosa (n = 6) | 2 (100) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (23.1) | 0 (0) | 1 (4.1) | blaVIM + blaOXA-48 (1/16.6) |
| Total = 44 | 2 (100) | 2 (100) | 9 (100) | 2 (100) | 13 (100) | 0 (0) | 24 (100) | 8 (18.2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nolasco-Rojas, A.E.; Cruz-Del-Agua, E.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Loyola-Cruz, M.Á.; Ayil-Gutiérrez, B.A.; Tamayo-Ordóñez, M.C.; Tamayo-Ordoñez, Y.d.J.; Rojas-Bernabé, A.; Tamayo-Ordoñez, F.A.; Durán-Manuel, E.M.; et al. Microbiological Risks to Health Associated with the Release of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and β-Lactam Antibiotics Through Hospital Wastewater. Pathogens 2025, 14, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050402
Nolasco-Rojas AE, Cruz-Del-Agua E, Cruz-Cruz C, Loyola-Cruz MÁ, Ayil-Gutiérrez BA, Tamayo-Ordóñez MC, Tamayo-Ordoñez YdJ, Rojas-Bernabé A, Tamayo-Ordoñez FA, Durán-Manuel EM, et al. Microbiological Risks to Health Associated with the Release of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and β-Lactam Antibiotics Through Hospital Wastewater. Pathogens. 2025; 14(5):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050402
Chicago/Turabian StyleNolasco-Rojas, Andres E., Eder Cruz-Del-Agua, Clemente Cruz-Cruz, Miguel Ángel Loyola-Cruz, Benjamín A. Ayil-Gutiérrez, María C. Tamayo-Ordóñez, Yahaira de J. Tamayo-Ordoñez, Araceli Rojas-Bernabé, Francisco A. Tamayo-Ordoñez, Emilio M. Durán-Manuel, and et al. 2025. "Microbiological Risks to Health Associated with the Release of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and β-Lactam Antibiotics Through Hospital Wastewater" Pathogens 14, no. 5: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050402
APA StyleNolasco-Rojas, A. E., Cruz-Del-Agua, E., Cruz-Cruz, C., Loyola-Cruz, M. Á., Ayil-Gutiérrez, B. A., Tamayo-Ordóñez, M. C., Tamayo-Ordoñez, Y. d. J., Rojas-Bernabé, A., Tamayo-Ordoñez, F. A., Durán-Manuel, E. M., Paredes-Mendoza, M., Márquez-Valdelamar, L. M., Jiménez-Zamarripa, C. A., Ocharan-Hernández, E., Zárate-Segura, P. B., García-Hernández, O., Sosa-Hernández, O., Vásquez-Jiménez, E., Calzada-Mendoza, C. C., & Bello-López, J. M. (2025). Microbiological Risks to Health Associated with the Release of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and β-Lactam Antibiotics Through Hospital Wastewater. Pathogens, 14(5), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050402










