Species Detection within the Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato Complex by Novel Probe-Based Real-Time PCRs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
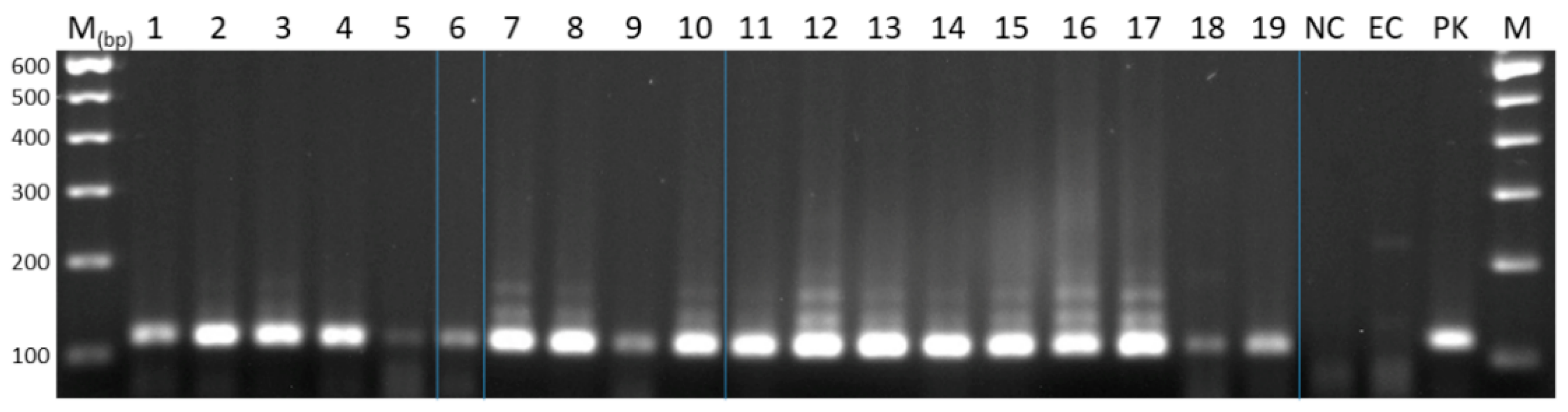
2.1. Primer Selection for the Amplification of E. granulosus s.l. Species Sequences
2.2. Detection of Echinococcus Species by TaqMan® Quantitative PCRs
2.3. Detection of E. granulosus s.l. Species in Faecal Samples
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Primer and DNA Probe Design for qPCRs
4.2. Reference DNA Samples and Faecal Spiking
4.3. Conventional PCR
4.4. Generic Quantitative PCR (SYBR® Green)
4.5. Sequence-Specific DNA Probe Based Quantitative PCR (TaqMan®) and Internal Control
4.6. Sequencing of qPCR Products
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vuitton, D.A.; McManus, D.P.; Rogan, M.T.; Romig, T.; Gottstein, B.; Naidich, A.; Tuxun, T.; Wen, H.; Menezes da Silva, A. World Association of Echinococcosis International consensus on terminology to be used in the field of echinococcoses. Parasite 2020, 27, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, P.; Ammon, A.; Kron, M.; Sinn, G.; Sander, S.; Petersen, L.R.; Gaus, W.; Kern, P. Risk factors for alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2088–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristow, B.N.; Lee, S.; Shafir, S.; Sorvillo, F. Human echinococcosis mortality in the United States, 1990-2007. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romig, T.; Ebi, D.; Wassermann, M. Taxonomy and molecular epidemiology of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato. Vet. Parasitol 2015, 213, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tappe, D.; Stich, A.; Frosch, M. Emergence of polycystic neotropical echinococcosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romig, T.; Deplazes, P.; Jenkins, D.; Giraudoux, P.; Massolo, A.; Craig, P.S.; Wassermann, M.; Takahashi, K.; de la Rue, M. Ecology and Life Cycle Patterns of Echinococcus Species. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 213–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinkar, L.; Laurimae, T.; Sharbatkhori, M.; Mirhendi, H.; Kia, E.B.; Ponce-Gordo, F.; Andresiuk, V.; Simsek, S.; Lavikainen, A.; Irshadullah, M.; et al. New mitogenome and nuclear evidence on the phylogeny and taxonomy of the highly zoonotic tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto. Infect Genet Evol. 2017, 52, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Addy, F.; Wassermann, M.; Kagendo, D.; Ebi, D.; Zeyhle, E.; Elmahdi, I.E.; Umhang, G.; Casulli, A.; Harandi, M.F.; Aschenborn, O.; et al. Genetic differentiation of the G6/7 cluster of Echinococcus canadensis based on mitochondrial marker genes. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassermann, M.; Aschenborn, O.; Aschenborn, J.; Mackenstedt, U.; Romig, T. A sylvatic lifecycle of Echinococcus equinus in the Etosha National Park, Namibia. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2015, 4, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakao, M.; Lavikainen, A.; Yanagida, T.; Ito, A. Phylogenetic systematics of the genus Echinococcus (Cestoda: Taeniidae). Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Yanagida, T.; Konyaev, S.; Lavikainen, A.; Odnokurtsev, V.A.; Zaikov, V.A.; Ito, A. Mitochondrial phylogeny of the genus Echinococcus (Cestoda: Taeniidae) with emphasis on relationships among Echinococcus canadensis genotypes. Parasitology 2013, 140, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, M.; Yanagida, T.; Okamoto, M.; Knapp, J.; Nkouawa, A.; Sako, Y.; Ito, A. State-of-the-art Echinococcus and Taenia: Phylogenetic taxonomy of human-pathogenic tapeworms and its application to molecular diagnosis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, P.; Mastin, A.; van Kesteren, F.; Boufana, B. Echinococcus granulosus: Epidemiology and state-of-the-art of diagnostics in animals. Vet. Parasitol 2015, 213, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siles-Lucas, M.; Casulli, A.; Conraths, F.J.; Muller, N. Laboratory Diagnosis of Echinococcus spp. in Human Patients and Infected Animals. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 96, 159–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackmann, K.; Mattis, R.; Conraths, F.J. Detection of Echinococcus multilocularis in foxes: Evaluation of a protocol of the intestinal scraping technique. J. Vet. Med. B. Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2006, 53, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umhang, G.; Woronoff-Rhen, N.; Combes, B.; Boue, F. Segmental sedimentation and counting technique (SSCT): An adaptable method for qualitative diagnosis of Echinococcus multilocularis in fox intestines. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 128, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, J. Predictive values and quality control of techniques for the diagnosis of Echinococcus multilocularis in definitive hosts. Acta Trop. 2003, 85, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conraths, F.J.; Deplazes, P. Echinococcus multilocularis: Epidemiology, surveillance and state-of-the-art diagnostics from a veterinary public health perspective. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 213, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duscher, G.; Prosl, H.; Joachim, A. Scraping or shaking--a comparison of methods for the quantitative determination of Echinococcus multilocularis in fox intestines. Parasitol. Res. 2005, 95, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachsel, D.; Deplazes, P.; Mathis, A. Identification of taeniid eggs in the faeces from carnivores based on multiplex PCR using targets in mitochondrial DNA. Parasitology 2007, 134, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boubaker, G.; Macchiaroli, N.; Prada, L.; Cucher, M.A.; Rosenzvit, M.C.; Ziadinov, I.; Deplazes, P.; Saarma, U.; Babba, H.; Gottstein, B.; et al. A multiplex PCR for the simultaneous detection and genotyping of the Echinococcus granulosus complex. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knapp, J.; Millon, L.; Mouzon, L.; Umhang, G.; Raoul, F.; Ali, Z.S.; Combes, B.; Comte, S.; Gbaguidi-Haore, H.; Grenouillet, F.; et al. Real time PCR to detect the environmental faecal contamination by Echinococcus multilocularis from red fox stools. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 201, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oines, O.; Isaksson, M.; Hagstrom, A.; Tavornpanich, S.; Davidson, R.K. Laboratory assessment of sensitive molecular tools for detection of low levels of Echinococcus multilocularis-eggs in fox (Vulpes vulpes) faeces. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, B.; Depner, K.; Schirrmeier, H.; Beer, M. A universal heterologous internal control system for duplex real-time RT-PCR assays used in a detection system for pestiviruses. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 136, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casulli, A. Recognising the substantial burden of neglected pandemics cystic and alveolar echinococcosis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e470–e471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budke, C.M.; Deplazes, P.; Torgerson, P.R. Global socioeconomic impact of cystic echinococcosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassermann, M.; Woldeyes, D.; Gerbi, B.M.; Ebi, D.; Zeyhle, E.; Mackenstedt, U.; Petros, B.; Tilahun, G.; Kern, P.; Romig, T. A novel zoonotic genotype related to Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto from southern Ethiopia. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefever, S.; Pattyn, F.; Hellemans, J.; Vandesompele, J. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms and other mismatches reduce performance of quantitative PCR assays. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurimae, T.; Kinkar, L.; Moks, E.; Romig, T.; Omer, R.A.; Casulli, A.; Umhang, G.; Bagrade, G.; Irshadullah, M.; Sharbatkhori, M.; et al. Molecular phylogeny based on six nuclear genes suggests that Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato genotypes G6/G7 and G8/G10 can be regarded as two distinct species. Parasitology 2018, 145, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimov, P.; Schares, G.; Press, S.; Frohlich, A.; Basso, W.; Herzig, M.; Conraths, F.J. Comparison of different commercial DNA extraction kits and PCR protocols for the detection of Echinococcus multilocularis eggs in faecal samples from foxes. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 237, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, S.; Baker, A.; Phillott, A.D.; Skerratt, L.F. BSA reduces inhibition in a TaqMan assay for the detection of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 92, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieger, C.; Hegglin, D.; Schwarzenbach, G.; Mathis, A.; Deplazes, P. Spatial and temporal aspects of urban transmission of Echinococcus multilocularis. Parasitology 2002, 124, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maksimov, P.; Isaksson, M.; Schares, G.; Romig, T.; Conraths, F.J. Validation of PCR-based protocols for the detection of Echinococcus multilocularis DNA in the final host using the Intestinal Scraping Technique as a reference. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svec, D.; Tichopad, A.; Novosadova, V.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Kubista, M. How good is a PCR efficiency estimate: Recommendations for precise and robust qPCR efficiency assessments. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2015, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scientific, T.F. DNA Copy Number and Dilution Calculator. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/de/de/home/brands/thermo-scientific/molecular-biology/molecular-biology-learning-center/molecular-biology-resource-library/thermo-scientific-web-tools/dna-copy-number-calculator.html (accessed on 25 September 2020).




| Assay Name | Primer Name | Product Size | Specificity | Sequence | Final Concentration | Gene | Accession No | Position in Mitochondrial Genome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1_3_qPCR | Eg_G1-3_cox1_7122_F | 109 | E. granulosus sensu stricto (G1, G3) | AGGGGCTGGTGTTGGTTGGA | 200 nM | Cox1 | KJ559023, NC_008075.1, KJ162553 | 7122–7141 |
| Eg_G1-3_cox1_7230_R | TGAAACACCAGCCAAATGCAGAGA | 200 nM | 7230–7207 | |||||
| Eg_G1-3_cox1_7149_P | 6-Fam or Cy5-TCC GCC GTT GTC CTC GTC GT-BHQ-1 | 200 nM | 7149–7168 | |||||
| G4_qPCR | g4_cox1_F | 109 | E. equinus (G4) | AGG TGC TGG TGT TGG TTG AA | 200 nM | Cox1 | NC_020374 | 9408–9427 |
| g4_cox1_R | AGA AAC ACC TGC CAA ATG CAA AGA | 200 nM | 9516–9493 | |||||
| g4_cox1_P | Cy3.5-TCC GCC GTT GTC TTC TTC AT-BMN-Q590 | 200 nM | 9435–9454 | |||||
| G5_qPCR | ND5_1433_G5_F | 127 | E. ortleppi (G5) | TGATGGCTGGTAGCGGTGGT | 200 nM | Nad5 | AB235846 | 1433–1452 |
| ND5_1475_G5_P | Cy5.5-ACAGGCCTGTTGTGTATGGGTCA-BMN-Q650 | 200 nM | 1475–1497 | |||||
| ND5_1559_G5_R | ACCCCAATAAACGGAACCCCAGA | 200 nM | 1559–1537 | |||||
| G6_10_qPCR | COX3_2458_Ec_F | 123 | E. canadensis (G6–8, G10) | GTTGTTTTGGTTTGTGTTGGGTTGT | 200 nM | Cox3 | NC_011121.1 MH301022 | 2458–2482 |
| COX3_2505_Ec_P | FAM or Cy5-TGGGTTGTGTGCTAGGGTTCATCA-MGB | 200 nM | 2505–2528 | |||||
| COX3_2580_Ec_R | ACCAAAAATCGCCACCTCACT | 200 nM | 2580–2560 | |||||
| Internal control PCR, IC2 PCR | EGFP1-F | Hoffmann et al., 2006 | Hoffmann et al., 2006 | GAC CAC TAC CAG CAG AAC AC | 500 nM | EGFP | Hoffmann et al., 2006 | |
| EGFP1 | 5′-HEX- AGC ACC CAG TCC GCC CTG AGC A -BHQ1 | 160 nM | ||||||
| EGFP2-R | GAA CTC CAG CAG GAC CAT G | 500 nM |
| Reference DNA | qPCR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Genotype | G1_3_qPCR | G4_qPCR | G5_10_qPCR | G5_10_qPCR |
| E. granulosus s.s. | G1 | 31.65 | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq |
| E. granulosus s.s. | G3 | 28.53 | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq |
| E. granulosus s.s. | G3 | 27.68 | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq |
| E. granulosus s.s. | Gx | 36.90 | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq |
| E. granulosus s.s. | Gx | 37.46 | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq |
| E. equinus | G4 | No Cq | 39.06 | No Cq | No Cq |
| E. equinus | G4 | No Cq | 24.02 | No Cq | No Cq |
| E. ortleppi | G5 | No Cq | No Cq | 27.53 | 28.02 |
| E. ortleppi | G5 | No Cq | No Cq | 35.96 | 35.54 |
| E. ortleppi | G5 | No Cq | No Cq | 26.02 | 26.54 |
| E. canadensis | G6 | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | 37.56 |
| E. canadensis | G6 | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | 28.37 |
| E. canadensis | G7 | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | 25.57 |
| E. canadensis | G8 | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | 29.6 |
| E. canadensis | G10 | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | 27.11 |
| E. canadensis | G10 | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | 21.0 |
| E. vogeli | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | |
| E. felidis | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | |
| E. cf. granulosus | G-Omo | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq |
| T. saginata | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | |
| T. saginata | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | |
| T. hydatigena | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | |
| E. multilocularis | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | |
| T. hydatigena | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | No Cq | |
| PCR Name | Specificity | Efficiency with Cloned PCR Products | Efficiency Clinical DNA | Detection Limit (Copy Number/µL at Cq) with Cloned PCR Products | Detection Limit in Cq with Clinical DNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1_3_qPCR (single-plex) | E. granulosus s.s. (G1, G3) | 100.7% (R2 = 0.99, slope = −3.34) | 96.3% (R2 = 0.99, slope = −3.41) | 0.8/µL at Cq 36 (± 0.9) | 38.24 (± 0.1) |
| G4_qPCR (single-plex) | E. equinus (G4) | 106.7% (R2 = 0.99, slope = −3.32) | 93.7% (R2 = 0.99, slope = −3.48) | 0.6/µL at Cq 39 (± 0.6) | 38 (± 1) |
| G5_G10_qPCR (duplex) | E. ortleppi (G5) | 100.7% (R2 = 0.99, slope = −3.34) | 97.3% (R2 = 0.99, slope = −3.39) | 1.4/µL at Cq 36 (± 0.7) | 37 (± 0.4) |
| G5_G10_qPCR (duplex) | E. canadensis (G6–8, G10) | 101.6% (R2 = 0.99, slope = −3.28) | 99.9% (R2 = 0.99, slope = −3.33) | 1.4/µL at Cq 36 (± 0.8) | 38.6 (± 0.17) |
| PCR Name | Specificity | 1:100 § | 1:100 * | 1:1000 * | 1:10,000 * | 1:100,000 * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1_3_qPCR+IC_qPCR (duplex) | G1, G3 | 24.5 | 30.1 (± 0.6) | 35.2 (± 1) | neg. | neg. |
| G4_qPCR+IC_qPCR (duplex) | G4 | 20.2 | 27.4 (± 0.5) | 30.7 (± 1) | 35.8 (± 0.06) | neg. |
| G5_10_qPCR+IC_qPCR (triplex) | G5 | 21,37 | 30.3 (± 0.17) | 32.4 (± 0.22) | neg. | neg. |
| G5_10_qPCR+IC_qPCR (triplex) | G6–8, G10 | 24.2 | 31.2 (± 0.02) | 32.6 (± 0.22) | neg. | neg. |
| Species | Genotype | Animal Origin | Geographical Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. granulosus s.s. | G1 | Cattle | Armenia |
| E. granulosus s.s. | G3 | Sheep | Armenia |
| E. granulosus s.s. | G3 | Sheep | France |
| E. granulosus s.s. | Gx | Cattle | Armenia |
| E. granulosus s.s. | Gx | Schaf | Ethiopia |
| E. equinus | G4 | Zebra | Namibia |
| E. equinus | G4 | NA | NA |
| E. ortleppi | G5 | NA | NA |
| E. ortleppi | G5 | Cattle | Kenya |
| E. ortleppi | G5 | Cattle | Zambia |
| E. canadensis | G6 | Camel | Kenya |
| E. canadensis | G6 | Camel | Kenya |
| E. canadensis | G7 | NA | NA |
| E. canadensis | G8 | NA | Russia |
| E. canadensis | G10 | NA | NA |
| E. canadensis | G10 | Deer (Cervus sp.) | Russia |
| E. vogeli | NA | NA | |
| E. felidis | Warthog | Namibia | |
| E. cf. granulosus | G-Omo | Human | Ethiopia |
| T. saginata | Cattle | Ethiopia | |
| T. hydatigena | Dog | Ethiopia | |
| E. multilocularis | Red fox | Germany |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maksimov, P.; Bergmann, H.; Wassermann, M.; Romig, T.; Gottstein, B.; Casulli, A.; Conraths, F.J. Species Detection within the Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato Complex by Novel Probe-Based Real-Time PCRs. Pathogens 2020, 9, 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100791
Maksimov P, Bergmann H, Wassermann M, Romig T, Gottstein B, Casulli A, Conraths FJ. Species Detection within the Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato Complex by Novel Probe-Based Real-Time PCRs. Pathogens. 2020; 9(10):791. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100791
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaksimov, Pavlo, Hannes Bergmann, Marion Wassermann, Thomas Romig, Bruno Gottstein, Adriano Casulli, and Franz J. Conraths. 2020. "Species Detection within the Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato Complex by Novel Probe-Based Real-Time PCRs" Pathogens 9, no. 10: 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100791
APA StyleMaksimov, P., Bergmann, H., Wassermann, M., Romig, T., Gottstein, B., Casulli, A., & Conraths, F. J. (2020). Species Detection within the Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato Complex by Novel Probe-Based Real-Time PCRs. Pathogens, 9(10), 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100791







