Epstein–Barr Virus and Helicobacter Pylori Co-Infection in Non-Malignant Gastroduodenal Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biology and Disease Associations of H. pylori and EBV
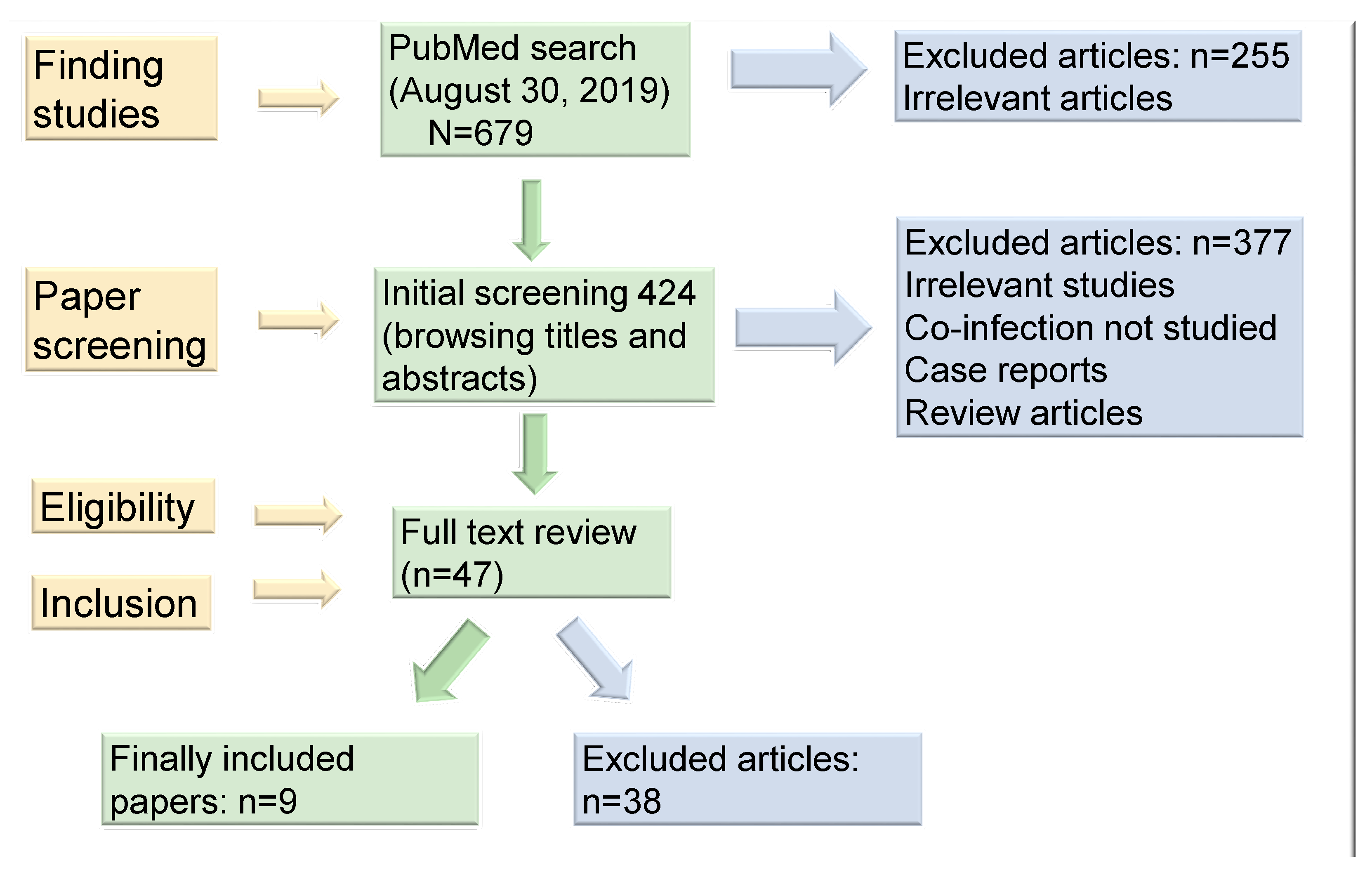
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Study Selection and Data Extraction
3.2. Studies Included
4. Results
4.1. Studies Assessing EBV by Serological Methods.
4.2. Studies EBV Infection Directly Assessing in Gastric Tissues
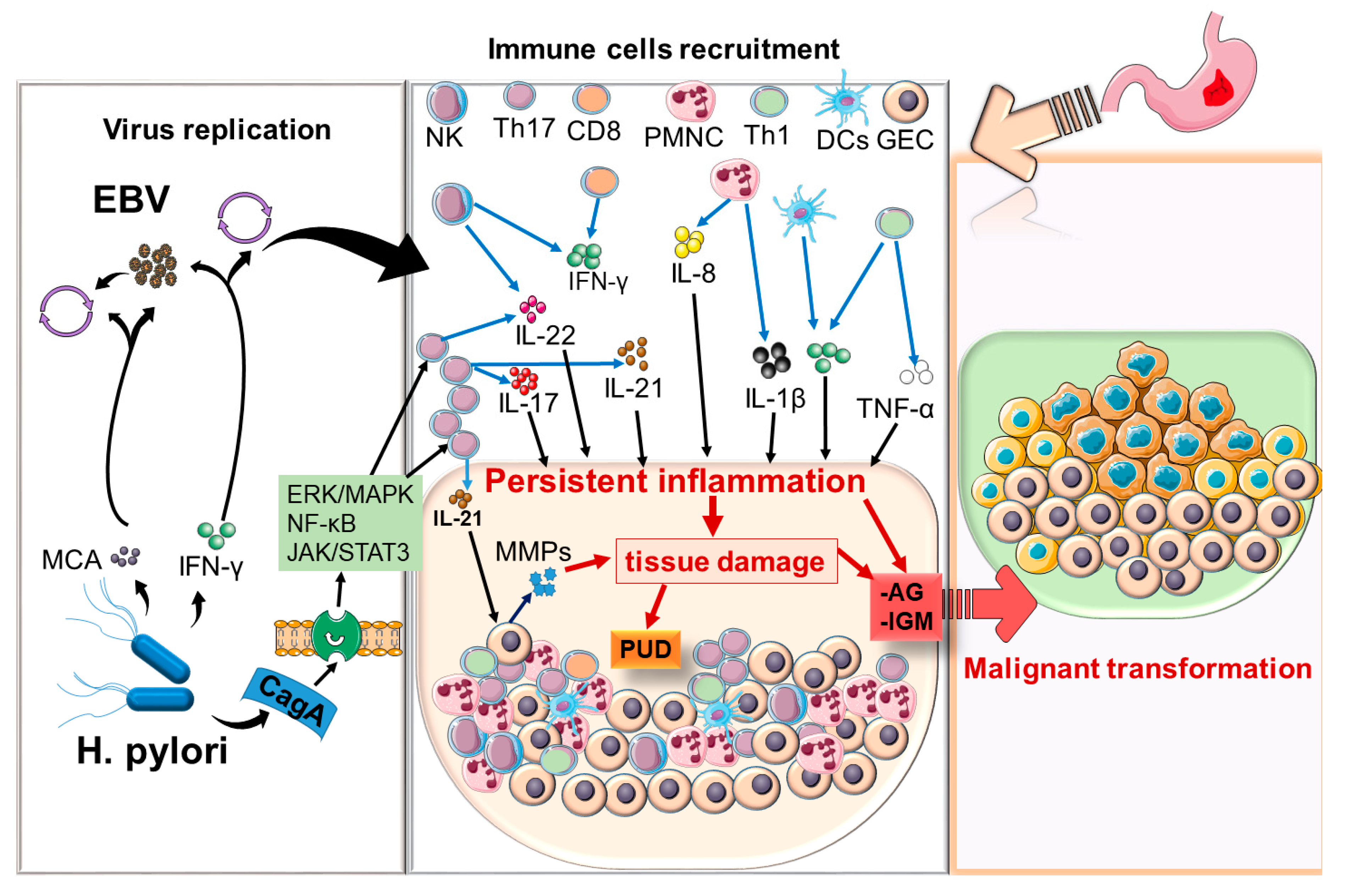
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EBV | Epstein-Barr virus |
| NMGDs | non-malignant gastroduodenal disorders |
| PUD | Peptic ulcer disease |
| GERD | gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| NSAIDS | nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| FD | functional dyspepsia |
| BabA | blood group antigen binding adhesion |
| OipA | outer inflammatory protein A |
| SabA | sialic acid-binding adhesion |
| VacA | vacuolating cytotoxin A |
| CagA | cytotoxin associated gene A |
| CTL | cytotoxic T lymphocytes |
| NK | natural killer cells |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| IFN-γ | interferon-γ |
| TLR9 | toll-like receptor 9 |
| MMP-1 | matrix metalloprotease-1 |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| EBER | EBV-encoded RNA |
| EBNA | Epstein–Barr nuclear antigens |
| VCA | viral capsid antigen |
| EA | early antigen |
| PMNC | Polymorphonuclear cells |
| MNC | mononuclear cells |
| NAG | Non-atrophic gastritis |
| BZLF1 | BamHI Z Leftward reading Frame 1 |
| BARF1 | means BamHI A rightward open-reading frame-1 |
| HCMV | human cytomegalovirus |
References
- Stanghellini, V.; Chan, F.K.; Hasler, W.L.; Malagelada, J.R.; Suzuki, H.; Tack, J.; Talley, N.J. Gastroduodenal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1380–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talley, N.J.; Ford, A.C. Functional Dyspepsia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1853–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masuy, I.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Tack, J. Review article: Treatment options for functional dyspepsia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1134–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanghellini, V. Functional Dyspepsia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Beyond Rome IV. Dig. Dis. 2017, 35, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adriani, A.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Astegiano, M.; Durazzo, M.; Saracco, G.M.; Pellicano, R. Irritable bowel syndrome: The clinical approach. Panminerva Med. 2018, 60, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolka, A.J.; Schubert, M.L. Helicobacter pylori-Induced Changes in Gastric Acid Secretion and Upper Gastrointestinal Disease. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 400, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkeis-Veits, C.; Vieth, M. Non-malignant Helicobacter pylori-Associated Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzás, G.M. Benign and malignant gastroduodenal diseases associated with Helicobacter pylori: A narrative review and personal remarks in 2018. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2018, 64, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, A.; Chan, F.K.L. Peptic ulcer disease. Lancet 2017, 390, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Mondragón, M.G.; Carreón-Talavera, R.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Gomez-Delgado, A.; Torres, J.; Fuentes-Pananá, E.M. Epstein Barr virus and Helicobacter pylori co-infection are positively associated with severe gastritis in pediatric patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-López, J.L.; Torres, J.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Mantilla, A.; Leal, Y.A.; Fuentes-Pananá, E.M. Evidence of Epstein-Barr virus association with gastric cancer and non-atrophic gastritis. Viruses 2014, 6, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zong, L.; Seto, Y. CpG island methylator phenotype, Helicobacter pylori, Epstein-Barr virus, and microsatellite instability and prognosis in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Bae, B.N.; Kang, G.; Kim, H.J.; Park, K. Cytokine expression associated with Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus infection in gastric carcinogenesis. APMIS 2017, 125, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugge, M.; Genta, R.M.; Di Mario, F.; El-Omar, E.M.; El-Serag, H.B.; Fassan, M.; Hunt, R.H.; Kuipers, E.J.; Malfertheiner, P.; Sugano, K.; et al. Gastric Cancer as Preventable Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Moral-Hernández, O.; Castañón-Sánchez, C.A.; Reyes-Navarrete, S.; Martínez-Carrillo, D.N.; Betancourt-Linares, R.; Jiménez-Wences, H.; de la Peña, S.; Román-Román, A.; Hernández-Sotelo, D.; Fernández-Tilapa, G. Multiple infections by EBV, HCMV and Helicobacter pylori are highly frequent in patients with chronic gastritis and gastric cancer from Southwest Mexico: An observational study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98, e14124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooi, J.K.Y.; Lai, W.Y.; Ng, W.K.; Suen, M.M.Y.; Underwood, F.E.; Tanyingoh, D.; Malfertheiner, P.; Graham, D.Y.; Wong, V.W.S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoder, G.; Muhammad, J.S.; Mahmoud, I.; Soliman, S.S.M.; Burucoa, C. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori and Its Associated Factors among Healthy Asymptomatic Residents in the United Arab Emirates. Pathogens 2019, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crowe, S.E. Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmiela, M.; Gonciarz, W. Molecular mimicry in Helicobacter pylori infections. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3964–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejías-Luque, R.; Gerhard, M. Immune Evasion Strategies and Persistence of Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 400, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, N.R.; Hartung, M.L.; Müller, A. Life in the human stomach: Persistence strategies of the bacterial pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagoonee, S.; Pellicano, R. Helicobacter pylori: Molecular basis for colonization and survival in gastric environment and resistance to antibiotics. A short review. Infect. Dis. 2019, 51, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rickinson, A. The Global Landscape of EBV-Associated Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Napoli, A.; Al-Jadiri, M.F.; Talerico, C.; Duranti, E.; Pilozzi, E.; Trivedi, P.; Anastasiadou, E.; Alsaadawi, A.R.; Al-Darraji, A.F.; Al-Hadad, S.A.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) positive classical Hodgkin lymphoma of Iraqi children: An immunophenotypic and molecular characterization of Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells. Pediatric Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 2068–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.L.; Takami, A.; Trung, L.Q.; Kato, S.; Nakao, S. Resveratrol Prevents EBV Transformation and Inhibits the Outgrowth of EBV-Immortalized Human B Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, G.S.; Long, H.M.; Brooks, J.M.; Rickinson, A.B.; Hislop, A.D. The immunology of Epstein-Barr virus-induced disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 787–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Z.; Chen, H.; Castro, F.A.; Hu, J.K.; Brenner, H. Epstein-Barr virus infection and gastric cancer: A systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015, 94, e792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoura-Etoh, J.; Gotoh, K.; Sato, R.; Ogata, M.; Kaku, N.; Fujioka, T.; Nishizono, A. Helicobacter pylori-associated oxidant monochloramine induces reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in gastric epithelial cells latently infected with EBV. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allison, C.C.; Ferrand, J.; McLeod, L.; Hassan, M.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M.; Grubman, A.; Bhathal, P.S.; Dev, A.; Sievert, W.; Jenkins, B.J.; et al. Nucleotide oligomerization domain 1 enhances IFN-γ signaling in gastric epithelial cells during Helicobacter pylori infection and exacerbates disease severity. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3706–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cárdenas-Mondragón, M.G.; Torres, J.; Sánchez-Zauco, N.; Gómez-Delgado, A.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Maldonado-Bernal, C.; Fuentes-Pananá, E.M. Elevated levels of Interferon-γ are associated with Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in patients with the intestinal type of gastric cancer. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 7069242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dixon, B.R.E.A.; Hossain, R.; Patel, R.V.; Algood, H.M.S. Th17 Cells in Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Dichotomy of Help and Harm. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahal, E.A.; Hajjar, H.; Rajeh, M.; Yamout, B.; Abdelnoor, A.M. Epstein-Barr Virus and Human herpes virus 6 Type A DNA Enhance IL-17 Production in Mice. Viral Immunol. 2015, 28, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiomi, S.; Toriie, A.; Imamura, S.; Konishi, H.; Mitsufuji, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Yamaoka, Y.; Ota, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Imanishi, J.; et al. IL-17 is involved in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric inflammatory responses in a mouse model. Helicobacter 2008, 13, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salloum, N.; Hussein, H.M.; Jammaz, R.; Jiche, S.; Uthman, I.W.; Abdelnoor, A.M.; Rahal, E.A. Epstein-Barr virus DNA modulates regulatory T-cell programming in addition to enhancing interleukin-17A production via Toll-like receptor 9. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbo, A.; Olivares-Villagómez, D.; Hontecillas, R.; Bassaganya-Riera, J.; Chaturvedi, R.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Delgado, A.; Washington, M.K.; Wilson, K.T.; Algood, H.M. Systems modeling of the role of interleukin-21 in the maintenance of effector CD4+ T cell responses during chronic Helicobacter pylori infection. MBio 2014, 5, e01243-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caruso, R.; Fina, D.; Peluso, I.; Fantini, M.C.; Tosti, C.; Del Vecchio Blanco, G.; Paoluzi, O.A.; Caprioli, F.; Andrei, F.; Stolfi, C.; et al. IL-21 is highly produced in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa and promotes gelatinases synthesis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5957–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagheri, N.; Azadegan-Dehkordi, F.; Shirzad, M.; Zamanzad, B.; Rahimian, G.; Taghikhani, A.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Shirzad, H. Mucosal interleukin-21 mRNA expression level is high in patients with Helicobacter pylori and is associated with the severity of gastritis. Cent.-Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 40, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebre, M.C.; Vieira, P.L.; Tang, M.W.; Aarrass, S.; Helder, B.; Newsom-Davis, T.; Tak, P.P.; Screaton, G.R. Synovial IL-21/TNF-producing CD4. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, C.; Estévez, O.A.; Fernández, S.; Aguado, R.; Rumbao, J.M.; Gonzalez, T.; Pérez-Navero, J.L.; Santamaría, M. Interleukin-21 overexpression dominates T cell response to Epstein-Barr virus in a fatal case of X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome type 1. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Paschale, M.; Clerici, P. Serological diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus infection: Problems and solutions. World J. Virol. 2012, 1, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smatti, M.K.; Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Ali, N.H.; Pintus, G.; Abou-Saleh, H.; Nasrallah, G.K. Epstein-Barr Virus Epidemiology, Serology, and Genetic Variability of LMP-1 Oncogene Among Healthy Population: An Update. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzás, G.M.; Konderák, J. Co-infection with Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus in benign upper digestive diseases: An endoscopic and serologic pilot study. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2016, 4, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buzás, G.M.; Lotz, G.; Schneider, F.; Józan, J. Changing prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the 9th district of Budapest. A retrospective endoscopic study, 1997–2012. Orv. Hetil. 2013, 154, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Mondragón, M.G.; Torres, J.; Flores-Luna, L.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Carreón-Talavera, R.; Gomez-Delgado, A.; Kasamatsu, E.; Fuentes-Pananá, E.M. Case–control study of Epstein–Barr virus and Helicobacter pylori serology in Latin American patients with gastric disease. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxena, A.; Nath Prasad, K.; Chand Ghoshal, U.; Krishnani, N.; Roshan Bhagat, M.; Husain, N. Association of Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus with gastric cancer and peptic ulcer disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattoor, J.; Koriyama, C.; Akiba, S.; Itoh, T.; Ding, S.; Eizuru, Y.; Abraham, E.K.; Chandralekha, B.; Amma, N.S.; Nair, M.K. Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma in southern India: A comparison with a large-scale Japanese series. J. Med. Virol. 2002, 68, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Goepfert, R.; Akiba, S.; Koriyama, C.; Ding, S.; Reyes, E.; Itoh, T.; Minakami, Y.; Eizuru, Y. Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma: Evidence of age-dependence among a Mexican population. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 6096–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, C.A.; Castillo, M.; Chavez, I.; Barreda, F.; Suarez, N.; Nieves, J.; Bernabe, L.A.; Valdivia, D.; Ruiz, E.; Dias-Neto, E.; et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection, ist virulent genotypes, and Epstein-Barr virus in Peruvian patients with chronic gastritis and gastric cancer. J. Glob. Oncol. 2019, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, C.R.; de Oliveira, K.S.; Ferraz, J.J.; Leal, M.F.; Calcagno, D.Q.; Seabra, A.D.; Khayat, A.S.; Montenegro, R.C.; Alves, A.P.; Assumpção, P.P.; et al. Occurrence of Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus infection in endoscopic and gastric cancer patients from Northern Brazil. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shukla, S.K.; Prasad, K.N.; Tripathi, A.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Krishnani, N.; Husain, N. Expression profile of latent and lytic transcripts of epstein-barr virus in patients with gastroduodenal diseases: A study from northern India. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.K.; Prasad, K.N.; Tripathi, A.; Singh, A.; Saxena, A.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Krishnani, N.; Husain, N. Epstein-Barr virus DNA load and its association with Helicobacter pylori infection in gastroduodenal diseases. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, Y.; Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.M.; Choe, Y.H. Co-Infection with Cytomegalovirus and Helicobacter pylori in a Child with Ménétrier’s Disease. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2013, 16, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crespo, P.; Dias, N.; Marques, N.; Saraiva da Cunha, J. Gastritis as a manifestation of primary CMV infection in an immunocompetent host. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokama, A.; Taira, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kinjo, N.; Kinjo, F.; Takahashi, K.; Fujita, J. Cytomegalovirus gastritis. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 2, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiwara, E.; Koriyama, C.; Akiba, S.; Itoh, T.; Minakami, Y.; Chirinos, J.L.; Watanabe, J.; Takano, J.; Miyagui, J.; Hidalgo, H.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma in Lima, Peru. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 24, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza, D.; Herrera, P.; Gilman, R.H.; Lanfranco, J.; Tapia, M.; Bussalleu, A.; Tenorio, J.H.; Guillén-Rodríguez, C.E.; Arróspide, M.T.; Piscoya, A.; et al. Variation in the prevalence of gastric cancer in Perú. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, M.Q.; Silva, C.I.; Braga-Neto, M.B.; Fialho, A.B.; Nunes Fialho, A.; Barbosa, A.M.; Cruz, F.W.; Rocha, G.A.; Queiroz, D.M.; Braga, L.L. Helicobacter pylori vacA and cagA genotypes in patients from northeastern Brazil with upper gastrointestinal diseases. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo. Cruz. 2012, 107, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.M.; Kim, E.H. Epstein-Barr Virus and Gastric Cancer Risk: A Meta-analysis With Meta-regression of Case-control Studies. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2016, 49, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohnishi, N.; Yuasa, H.; Tanaka, S.; Sawa, H.; Miura, M.; Matsui, A.; Higashi, H.; Musashi, M.; Iwabuchi, K.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Transgenic expression of Helicobacter pylori CagA induces gastrointestinal and hematopoietic neoplasms in mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yong, X.; Tang, B.; Li, B.S.; Xie, R.; Hu, C.J.; Luo, G.; Qin, Y.; Dong, H.; Yang, S.M. Helicobacter pylori virulence factor CagA promotes tumorigenesis of gastric cancer via multiple signaling pathways. Cell Commun. Signal. 2015, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatakeyama, M. Helicobacter pylori CagA and gastric cancer: A paradigm for hit-and-run carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsusaka, K.; Funata, S.; Fukayama, M.; Kaneda, A. DNA methylation in gastric cancer, related to Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 3916–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.K.; Yu, J.; Chan, M.T.; To, K.F.; Cheng, A.S. Combinatorial epigenetic deregulation by Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus infections in gastric tumourigenesis. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukayama, M.; Kunita, A.; Kaneda, A. Gastritis-Infection-Cancer Sequence of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1045, 437–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saju, P.; Murata-Kamiya, N.; Hayashi, T.; Senda, Y.; Nagase, L.; Noda, S.; Matsusaka, K.; Funata, S.; Kunita, A.; Urabe, M.; et al. Host SHP1 phosphatase antagonizes Helicobacter pylori CagA and can be downregulated by Epstein-Barr virus. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Jin, Y.; Chen, F.; Ni, H.; Hu, C.; Xu, Y.; Xuan, H.; Hu, D.; Deng, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Clinicopathological evidence of Hepatitis B Virus infection in the development of gastric adenocarcinoma. J. Med. Virol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.L.; Matsumoto, A.; Tanaka, H.; Matsumura, I. Gastric microbiota: An emerging player in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric malignancies. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, O.O.; Dai, Z.; Nie, Y.; Zhao, G.; Cao, L.; Nakatsu, G.; Wu, W.K.; Wong, S.H.; Chen, Z.; Sung, J.J.Y.; et al. Mucosal microbiome dysbiosis in gastric carcinogenesis. Gut 2018, 67, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, T.; Llorca, L.; Perez-Perez, G. Impact of the Microbiota and Gastric Disease Development by Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 400, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, R.; Nakahama, Y.; Nguyen, V.; Espinoza, J.L. The Host-Microbe Interplay in Human Papillomavirus-Induced Carcinogenesis. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Antibody | Active Infection | Past Infection | Reactivation |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCA IgM | positive | negative | negative |
| VCA IgG | positive | positive | positive |
| EBNA IgM | positive | negative | positive |
| EBNA IgG | negative | positive | positive |
| EA-D IgG | negative | negative | positive |
| Study/Country | Method | Disease | No. Tested | EBV Positivity | H. pylori Positivity | Co-Infection Positivity | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buza´s et al. 2015 [43] Hungary | EBV: ELISA test (IgG and IgM) against EBV viral capsid protein (VCA) H. pylori: -Giemsa stain -IgG-chemiluminescence | PUD | 40 | 75% | 72.5% | 60% | Higher prevalence of H. pylori + EBV co-infection along with higher anti-IgG levels found in duodenal ulcer. Could be attributed to an increased viral load or a stronger immune response |
| FD | 33 | 51.2% | 33.3% | 18.1% | |||
| GERD | 31 | 51.6% | 25.8% | 12.9% | |||
| Overall | 104 | 70.1% | 56.7% | 30% | |||
| Cárdenas-Mondragón et al. 2012 [10]. Mexico | EBV: ELISA test (IgG and IgM) against EBV VCA H. pylori: ELISA test (IgG) against H. pylori whole-cell extracts and against CagA protein | Non-atrophic gastritis (NAG) | 333 pediatric patients (median age 10.1 ± 3.7) | 64.3% | 53.4% | 1.8 (1–11.8) | EBV + H. pylori co-infection: significantly associated with severe gastritis. 2.4% (1%–9.7%) |
| Cárdenas-Mondragón et al. 2015 [45] Mexico and Paraguay | EBV: ELISA test (IgG and IgM) against EBV VCA H. pylori: ELISA test (IgG) against H. pylori whole-cell extracts and against CagA protein | Non-atrophic gastritis (NAG) | 225 patients (median age 30) | 32 (14.3%) | 18 (8%) | 175 (77.7%) | EBV collaborates with H. pylori to induce severe inflammation, increasing the risk of malignant transformation |
| Reference/Country | Tissue/Method | Disease | No. Tested | EBV (%) Positivity | H. pylori Positivity | Co-Infection Positivity | Caga Positivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [49] Castaneda et.al. Peru | Gastric biopsy specimens H. pylori: qPCR detection of hspA and UreA genes EBV: PCR detection of BNRF1 gene | Chronic gastritis | 165 | 4 (2.4) | 112 (67.9) | 2 (1.2) | |
| Comparative samples: GC | 375 | 72 (19.2) | 228 (60.8) | 40 (10.7) | |||
| Overall | 540 | 76 (14.1) | 340 (63.0) | 42 (7.8) | |||
| [15] Moral-Hernández et al. 2019. Mexico. | Gastric biopsy specimens H. pylori: 16S rRNA gene detection by PCR EBV: PCR detection of EBNA1 gene | Chronic gastritis | 106 | 74 (69.8) | 51 (48.1) | 27 (25.4) | |
| Comparative samples: gastric cancer | 32 | 30 (87.5) | 13 (40.6) | 12 (37.5) | |||
| Overall | 138 | 104 (75.4) | 64 (46.4) | 39 (28.2) | |||
| [50] de Souza et al. 2014. Brazil | Gastric biopsy specimens H. pylori: Rapid urease test and PCR EBV: Eber1 detection by ISH | Juvenile patients with upper gastrointestinal symptoms | 62 | 2 (3.2) | 31 (50) | 1 (1.6) | 20 (32.3) |
| Comparative samples: adults with similar symptoms | 39 | 2 (5.1) | 27 (69.2) | 2 (5.1) | 20 (51.3) | ||
| Comparative samples 2: adults with gastric cancer | 125 | 12 (9.6) | 110 (88) | 12 (9.6) | 84 (67.2) | ||
| [51] Shukla et al. 2012. India | Gastric biopsy specimens H. pylori: Rapid urease test and PCR for urea gene EBV: PCR for detection of EBNA-1 gene and also BZLF1, BARF1 and BcLF1 genes | Non-ulcer dyspepsia | 120 | 36 (30) | Unreported | Unreported | Unreported |
| PUD | 30 | 19 (63.3) | Unreported | Unreported | Unreported | ||
| Comparative samples: gastric cancer | 50 | 40 (80) | Unreported | Unreported | Unreported | ||
| Overall | 200 | 95 (47.5) | 105 (52.5) | 56 (28) | Unreported | ||
| [52] Shukla et al. 2011. India | Gastric biopsy specimens H. pylori: Rapid urease test and PCR for urea gene EBV: PCR for detection of EBNA-1 gene | Non-ulcer dyspepsia | 100 | 37 (37) | 46 (46) | 23 (23) | |
| PUD | 50 | 35 (70) | 41 (82) | 31 (62) | |||
| Comparative samples: gastric cancer | 50 | 45 (90) | 31 | 27 | |||
| Overall | 200 | 117 (58.5) | 118 (59) | 81 (40/5) | |||
| [46] Saxena et al. 2008. India | Gastric biopsy specimens H. pylori: Rapid urease test and PCR for urea gene EBV: PCR for detection of EBNA-1 gene H. pylori Ureasa test PCR | Non ulcer dyspepsia | 241 | 90 (37.3) | 133 (55.2) | 71 (29.5) | |
| PUD | 45 | 34 (75.6) | 36 (80) | 28 (62.2) | |||
| Comparative samples: gastric cancer | 62 | 51 (82.3) | 35 (56.5) | 29 (46.8) | |||
| Overall | 348 | 175 (50.3) | 204 (58.6) | 128 (36.8) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dávila-Collado, R.; Jarquín-Durán, O.; Dong, L.T.; Espinoza, J.L. Epstein–Barr Virus and Helicobacter Pylori Co-Infection in Non-Malignant Gastroduodenal Disorders. Pathogens 2020, 9, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020104
Dávila-Collado R, Jarquín-Durán O, Dong LT, Espinoza JL. Epstein–Barr Virus and Helicobacter Pylori Co-Infection in Non-Malignant Gastroduodenal Disorders. Pathogens. 2020; 9(2):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020104
Chicago/Turabian StyleDávila-Collado, Ramsés, Oscar Jarquín-Durán, Le Thanh Dong, and J. Luis Espinoza. 2020. "Epstein–Barr Virus and Helicobacter Pylori Co-Infection in Non-Malignant Gastroduodenal Disorders" Pathogens 9, no. 2: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020104
APA StyleDávila-Collado, R., Jarquín-Durán, O., Dong, L. T., & Espinoza, J. L. (2020). Epstein–Barr Virus and Helicobacter Pylori Co-Infection in Non-Malignant Gastroduodenal Disorders. Pathogens, 9(2), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020104






