Strongyloidiasis in Southern Alicante (Spain): Comparative Retrospective Study of Autochthonous and Imported Cases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
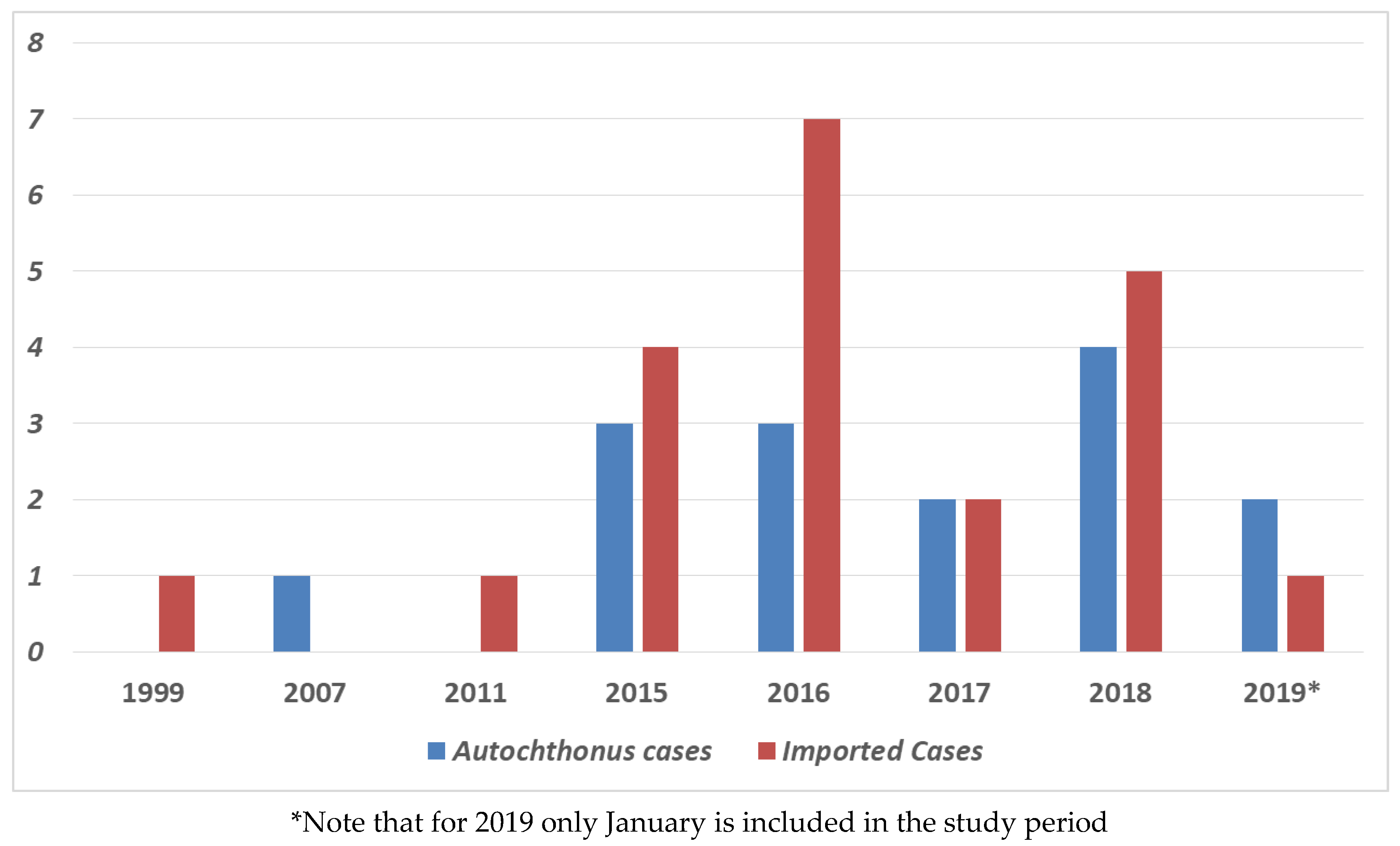
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Requena-Mendez, A.; Buonfrate, D.; Bisoffi, Z.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Advances in the diagnosis of human strongyloidiasis. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2014, 1, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez-Olivencia, G.; Espinosa, M.Á.C.; Martín, A.B.; Núñez, N.I.; de las Parras, E.R.; Núñez, M.L.; Puente, S.P. Imported strongyloidiasis in Spain. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 18, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belhassen-García, M.; Alonso-Sardón, M.; Martinez-Perez, A.; Soler, C.; Carranza-Rodriguez, C.; Pérez-Arellano, J.L.; Muro, A.; Salvador, F. Surveillance of strongyloidiasis in Spanish inpatients (1998–2014). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buonfrate, D.; Requena-Mendez, A.; Angheben, A.; Cinquini, M.; Cruciani, M.; Fittipaldo, A.; Giorli, G.; Gobbi, F.; Piubelli, C.; Bisoffi, Z. Accuracy of molecular biology techniques for the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection—A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schär, F.; Trostdorf, U.; Giardina, F.; Khieu, V.; Muth, S.; Marti, H.; Vounatsou, P.; Odermatt, P. Strongyloides stercoralis: Global distribution and risk factors. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greaves, D.; Coggle, S.; Pollard, C.; Aliyu, S.H.; Moore, E.M. Strongyloides stercoralis infection. BMJ 2013, 347, f4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Requena-Méndez, A.; Chiodini, P.; Bisoffi, Z.; Buonfrate, D.; Gotuzzo, E.; Muñoz, J. The laboratory diagnosis and follow up of strongyloidiasis: A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Fernández, M.T.; Salas-Coronas, J.; Lozano-Serrano, A.B.; Vazquez-Villegas, J.; Cabeza-Barrera, M.I.; Cobo, F. Strongyloidiasis in immigrants in Southern Spain. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2015, 33, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.M.; León, R.; Andreu, M.; De Las Parras, E.R.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.C.; Esteban, Á.; Saugar, J.M.; Torrús, D. Serological study of Trypanosoma cruzi, Strongyloides stercoralis, HIV, human T cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV) and syphilis infections in asymptomatic Latin-American immigrants in Spain. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 109, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge-Maillo, B.; Navarro, M.; Rodríguez, E.; Ramos Rincón, J.M.; Chamorro Tojeiro, S.; Jiménez Sánchez, S.; Casas del Corral, M.J.; López-Vélez, R. Community screening campaign for Strongyloides stercoralis among Latin American immigrants in Spain. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1220–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adell, R.I.; Márquez, V.D. Estrongiloidiasis: Epidemiología, manifestaciones clínicas y diagnóstico. Experiencia en una zona endémica: La comarca de La Safor (Valencia). Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2007, 25, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Sanchez, P.; Pastor-Guzman, A.; Moreno-Guillen, S.; Igual-Adell, R.; Er-Generoso, S.S.; Tornero-Estebanez, C. High prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis among farm workers on the Mediteranan coast of Spain: Analysis of the predictive factors of infections in developed countries. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 69, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaraz, C.O.; Adell, R.I.; Sánchez, P.S.; Blasco, M.J.V.; Sánchez, O.A.; Auñón, A.S.; Calabuig, D.R. Characteristics and geographical profile of strongyloidiasis in healthcare area 11 of the Valencian community (Spain). J. Infect. 2004, 49, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández Rodríguez, C.; Enríquez-Matas, A.; Sanchéz Millán, M.L.; Mielgo Ballesteros, R.; Jukic Beteta, K.D.; Valdez Tejeda, M.; Almonte Durán, P.; Levano Vasquez, J.; Sánchez González, M.J. Strongyloides stercoralis infection: A series of cases diagnosed in an allergy department in Spain. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 22, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Vázquez, C.; González Mediero, G.; Núñez, M.; Pérez, S.; García-Fernaández, J.M.; Gimena, B. Strongyloides stercoralis in the south of Galicia. An. Med. Interna 2003, 20, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayayo, E.; Gomez-Aracil, V.; Azua-Blanco, J.; Azua-Romeo, J.; Capilla, J.; Mayayo, R. Strongyloides stercolaris infection mimicking a malignant tumour in a non-immunocompromised patient. Diagnosis by bronchoalveolar cytology. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valerio, L.; Roure, S.; Fernández-Rivas, G.; Basile, L.; Martínez-Cuevas, O.; Ballesteros, Á.-L.; Ramos, X.; Sabrià, M. North metropolitan working group on imported diseases strongyloides stercoralis, the hidden worm. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 70 cases diagnosed in the north metropolitan area of Barcelona, Spain, 2003–2012. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 107, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Perez, A.; Lopez-Velez, R. Is strongyloidiasis endemic in Spain? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pretel Serrano, L.; Page del Pozo, M.A.; Ramos Guevara, M.R.; Ramos Rincón, J.M.; Martínez Toldos, M.C.; Herrero Huerta, F. Infestación por Strongyloides stercolaris en pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica en la Vega del Segura (Murcia). Presentación de tres casos. Rev. Clínica Española 2001, 201, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Tenza, M.I.; Ruiz-Maciá, J.A.; Navarro-Cots, M.; Gregori-Colomé, J.; Cepeda-Rodrigo, J.M.; Llenas-García, J. Strongyloides stercoralis infection in a Spanish regional hospital: Not just an imported disease. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2018, 36, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, M.; Salvador, F.; Sánchez-Montalvá, A.; Bosch-Nicolau, P.; Molina, I. Strongyloides stercoralis infection: A systematic review of endemic cases in Spain. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, J.C.; Inoue, Y.; Murakami, N.; Horii, Y. Androgen- and Estrogen-dependent sex differences in host resistance to strongyloides venezuelensis infection in wistar rats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2002, 64, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Rincón, M.J.; Navarro-Beltrá, C.; Gil-Anguita, A.M.; Garijo-Saiz, P.E.; Wikman-Jorgensen, P.; Guevara-Hernández, C.; Amador-Prous, V.R.; Sesma, C.; Bernal-Alcaraz, D.; Torrús-Tendero, M.P.; et al. Cribado comunitario de la enfermedad de Chagas y estrongiloidiasis en población latinoamericana en la provincia de Alicante. In Proceedings of the Comunicación oral XXIII Congreso de la Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica, Madrid, Spain, 23–25 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, R.A. Risk factors for strongyloidiasis. Arch. Intern. Med. 1984, 144, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loutfy, M.R.; Wilson, M.; Keystone, J.S.; Kain, K.C. Serology and eosinophil count in the diagnosis and management of strongyloidiasis in a non-endemic area. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 66, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisoffi, Z.; Buonfrate, D.; Sequi, M.; Mejia, R.; Cimino, R.O.; Krolewiecki, A.J.; Albonico, M.; Gobbo, M.; Bonafini, S.; Angheben, A.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of five serologic tests for strongyloides stercoralis infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luvira, V.; Trakulhun, K.; Mungthin, M.; Naaglor, T.; Chantawat, N.; Pakdee, W.; Phiboonbanakit, D.; Dekumyoy, P. Comparative diagnosis of strongyloidiasis in immunocompromised patients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Requena-Méndez, A.; Buonfrate, D.; Gomez-Junyent, J.; Zammarchi, L.; Bisoffi, Z.; Muñoz, J. Evidence-based guidelines for screening and management of strongyloidiasis in non-endemic countries. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saugar, J.M.; Merino, F.J.; Martín-Rabadán, P.; Fernández-Soto, P.; Ortega, S.; Gárate, T.; Rodríguez, E. Application of real-time PCR for the detection of Strongyloides spp. in clinical samples in a reference center in Spain. Acta Trop. 2015, 142, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonfrate, D.; Salas-Coronas, J.; Muñoz, J.; Maruri, B.T.; Rodari, P.; Castelli, F.; Zammarchi, L.; Bianchi, L.; Gobbi, F.; Cabezas-Fernández, T.; et al. Multiple-dose versus single-dose ivermectin for Strongyloides stercoralis infection (Strong Treat 1 to 4): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled superiority trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikman-Jorgensen, P.E.; Llenas-Garcia, J.; Shedrawy, J.; Gascon, J.; Muñoz, J.; Bisoffi, Z.; Requena-Mendez, A. Cost-effectiveness of different strategies for screening and treatment of Strongyloides stercoralis in migrants from endemic countries to the European Union. BMJ Glob. Health 2020, 5, e002321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treviño, A.; Alcantara, L.C.; Benito, R.; Caballero, E.; Aguilera, A.; Ramos, J.M.; de Mendoza, C.; Rodríguez, C.; García, J.; Rodríguez-Iglesias, M.; et al. Molecular epidemiology and clinical features of human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 infection in Spain. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2014, 30, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salvador, F.; Molina, I.; Sulleiro, E.; Burgos, J.; Curran, A.; Van Den Eynde, E.; Villar Del Saz, S.; Navarro, J.; Crespo, M.; Ocaña, I.; et al. Tropical diseases screening in immigrant patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection in Spain. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Llenas-García, J.; Fiorante, S.; Salto, E.; Maseda, D.; Rodríguez, V.; Matarranz, M.; Hernando, A.; Rubio, R.; Pulido, F. Should we look for Strongyloides stercoralis in foreign-born HIV-infected persons? J. Immigr. Minor. Health 2013, 15, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Municipal Database. Statistics, Demography. El Baix Segura. La Vega Baja. Generalitat Valenciana. 2019. Available online: http://www.argos.gva.es/bdmun/pls/argos_mun/DMEDB_COMADATOSINDICADORES.D (accessed on 12 July 2020).


| Variables | Autochthonous (N = 15) | Imported (N = 21) | p | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median age, in years | 71.33 | 53.29 | p = 0.002 | |
| Men | 12 (80%) | 9 (43%) | p = 0.041 | 5.33 (1.15–24.68) |
| Agriculture dedication | 10 (69.2%) | 3 (14.3%) | p = 0.002 | 13.5 (2.4–73.7) |
| Symptomatic patients | 11 (73.3%) | 11 (52.4%) | p = 0.302 | 0.4 (0.75–2.12) |
| Corticosteroid treatment | 4 (26.7%) | 1 (4.8%) | p = 0.138 | 5.77 (0.55–60.60) |
| Eosinophilia | 14 (93.3%) | 16 (75.5%) | p = 0.207 | 4.66 (0.48–45.04) |
| Response to treatment | 13 (85.7%) | 19 (88.9%) | p = 1 | 3.20 (0.22–45.19) |
| Hyperinfection syndrome | 3 (20%) | 0 (0%) | p = 0.064 | 0.80 (0.61–1.03) |
| Death attributed to strongyloidiasis | 2 (13.3%) | 0 (0%) | p = 0.167 | 0.86 (0.71–1.05) |
| Case | Sex, Age in Years | Date of Diagnosis | Occupation | Comorbidities and Risk Factors | Clinical Manifestations | Eosinophilia (Eosinophils/mm3) | Method of Diagnosis (in Serology, Optical Density Index) | Strongyloidiasis Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M, 69 | July 2007 | Farmer | Lung cancer Chemotherapy and radiotherapy | Hemoptysis, Hyperinfection syndrome | Yes (600) | Larvae in sputum Serology not requested | None | Death |
| 2 | M, 72 | March 2015 | Shipper | COPD, Corticosteroids | Hyperinfection syndrome | Yes (2400) | Larvae in large intestine biopsy and fecal samples Serology +(8.88) | Ivermectin + albendazole | Death |
| 3 | F, 73 | May 2015 | Farmer | Diverticulosis | Digestive | Yes (2700) | Serology +(1.93) | Ivermectin + albendazole | Recovery |
| 4 | M, 80 | December 2015 | Farmer | Bladder cancer | Digestive, Skin | Yes (700) | Serology +(4.45) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 5 | M, 85 | May 2016 | Farmer | Biliary disease Low-grade lymphoma | Digestive | Yes (570) | Serology +(6.83) | Ivermectin | Re-treatment (ivermectin) |
| 6 | M, 79 | June 2016 | Unknown | None | Digestive | No | Serology +(3.15) | Ivermectin | Re-treatment (ivermectin +albendazole) |
| 7 | M, 71 | November 2016 | Gardener | Colon adenocarcinoma | Asymptomatic | Yes (2400) | Larvae in large intestine biopsy and fecal samples Serology +(8.88) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 8 | M, 80 | March 2017 | Farmer | COPD, Atrial fibrillation Diabetes | Disseminated Strongyloidiasis Meningitis | Yes (640) | Larvae in fecal cultures and fresh fecal samples. Serology +(1.16) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 9 | M, 83 | May 2017 | Farmer | Prolactinoma, Diabetes | Asymptomatic | Yes (1450) | Serology +(6.85) | Ivermectin | Dead (surgery) |
| 10 | F, 49 | January 2018 | Unknown | Rheumatoid arthritis | Asymptomatic | Yes (780) | Serology +(1.35) | None | Lost to follow-up |
| 11 | M, 74 | May 2018 | Farmer | Renal insufficiency | Skin | Yes (900) | Serology +(3.41) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 12 | F, 25 | June 2018 | Unknown | None | Asymptomatic | Yes (810) | Serology +(1.32) | None | Lost to follow-up |
| 13 | M, 89 | June 2018 | Farmer | Hypereosinophilic syndrome | Skin | Yes (1700) | Serology +(14.35) | None | Dead |
| 14 | M, 80 | January 2019 | Unknown | None | Asymptomatic | Yes (1660) | Serology +(10.10) | Albendazole | Seroreversion |
| 15 | M, 61 | January 2019 | Printer | Gastroesophageal reflux | Digestive | Yes (510) | Serology +(2.90) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| Case | Sex, Age in Years | Date of Diagnosis | Country of Case Origin | Occupation | Comorbidities and Risk Factors | Clinical Manifestations | Eosinophilia (Eosinophils/mm3) | Method of Diagnosis (in Serology, Optical Density Index) | Strongyloidiasis Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M, 70 | May 1999 | Algeria | Unknown | Bladder cancer, asthma Corticosteroids | Digestive | Yes (670) | Larvae in duodenal biopsy; serology not requested | Thiabendazole | Lost to follow-up |
| 2 | F, 80 | August 2011 | Dominican Republic | Housekeeper | None | Digestive | Yes (3000) | Larvae in fresh stool samples and duodenal fluid; serology result unknown | Ivermectin | Clinical recovery |
| 3 | F, 78 | July 2015 | UK | Salesperson | COPD | Digestive | No | Serology +(1.73) | Ivermectin | Lost to follow-up |
| 4 | M, 57 | September 2015 | Ecuador | Metallurgy | Biliary disease | Digestive | Yes (1000) | Serology +(3.33) | None | Lost to follow-up |
| 5 | M, 38 | November 2015 | Bolivia | Farmer | Chagas | Asymptomatic | No (140) | Serology +(1.67) | Ivermectin | Lost to follow-up |
| 6 | M, 51 | December 2015 | Bolivia | Construction worker | Chagas | Asymptomatic | Yes (1300) | Serology +(13.33) | Ivermectin | Serological response |
| 7 | M, 52 | January 2016 | Bolivia | Unknown | Chagas | Asymptomatic | Yes (1390) | Serology +(13.73) | Ivermectin | Serological response |
| 8 | M, 52 | March 2016 | Bolivia | Farmer | Chagas | Asymptomatic | Yes (880) | Larvae in duodenal biopsy; Serology +(15.86) | Ivermectin | Serological response |
| 9 | M, 48 | May 2016 | Bolivia | Construction worker | Chagas | Digestive | Yes (830) | Serology +(7.54) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 10 | F, 50 | December 2016 | Bolivia | Caregiver | Chagas | Digestive | No (320) | Serology +(7.92) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 11 | F, 35 | June 2016 | Bolivia | Unknown | None | Asymptomatic | Unknown | Serology +(14.16) | Ivermectin | Serological response |
| 12 | F, 50 | July 2016 | Bolivia | Unknown | Chagas | Asymptomatic | Yes (750) | Serology +(6.71) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 13 | F, 80 | October 2016 | Jamaica | Nurse | Unknown | Digestive | Yes (1100) | Serology +(2.37) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 14 | F, 37 | March 2017 | Bolivia | Farmer | None | Digestive | Yes (1000) | Serology +(5.19) | Ivermectin | Re-treatment (ivermectin) |
| 15 | M, 68 | July 2017 | Colombia | Unknown | None | Asymptomatic | Yes (1300) | Serology +(1.85) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 16 | F, 44 | February 2018 | Morocco | Unknown | Meningioma | Asymptomatic | Unknown | Serology +(1.30) | Ivermectin | Lost to follow-up |
| 17 | F, 58 | June 2018 | Bolivia | Housekeeper | Chagas | Digestive | Yes (700) | Serology +(4.82) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 18 | F, 40 | September 2018 | Bolivia | Unknown | Chagas | Asymptomatic | Unknown | Serology +(1.15) | Ivermectin | Lost to follow-up |
| 19 | F, 57 | October 2018 | Bolivia | Housekeeper | Chagas | Asymptomatic | Yes (990) | Serology +(6.83) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 20 | F, 37 | December 2018 | Morocco | Unknown | Hydatidosis | Respiratory | Yes (3960) | Serology +(2.66) | Ivermectin | Seroreversion |
| 21 | M, 37 | January 2019 | Morocco | Shopkeeper | None | Asymptomatic | Yes (510) | Serology +(2.36) | Ivermectin | Lost to follow-up |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucas Dato, A.; Pacheco-Tenza, M.I.; Borrajo Brunete, E.; Martínez López, B.; García López, M.; González Cuello, I.; Gregori Colomé, J.; Navarro Cots, M.; Saugar, J.M.; García-Vazquez, E.; et al. Strongyloidiasis in Southern Alicante (Spain): Comparative Retrospective Study of Autochthonous and Imported Cases. Pathogens 2020, 9, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080601
Lucas Dato A, Pacheco-Tenza MI, Borrajo Brunete E, Martínez López B, García López M, González Cuello I, Gregori Colomé J, Navarro Cots M, Saugar JM, García-Vazquez E, et al. Strongyloidiasis in Southern Alicante (Spain): Comparative Retrospective Study of Autochthonous and Imported Cases. Pathogens. 2020; 9(8):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080601
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucas Dato, Ana, María Isabel Pacheco-Tenza, Emilio Borrajo Brunete, Belén Martínez López, María García López, Inmaculada González Cuello, Joan Gregori Colomé, María Navarro Cots, José María Saugar, Elisa García-Vazquez, and et al. 2020. "Strongyloidiasis in Southern Alicante (Spain): Comparative Retrospective Study of Autochthonous and Imported Cases" Pathogens 9, no. 8: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080601
APA StyleLucas Dato, A., Pacheco-Tenza, M. I., Borrajo Brunete, E., Martínez López, B., García López, M., González Cuello, I., Gregori Colomé, J., Navarro Cots, M., Saugar, J. M., García-Vazquez, E., Ruiz-Maciá, J. A., & Llenas-García, J. (2020). Strongyloidiasis in Southern Alicante (Spain): Comparative Retrospective Study of Autochthonous and Imported Cases. Pathogens, 9(8), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080601





