Biological and Genetic Heterogeneity in Trypanosoma dionisii Isolates from Hematophagous and Insectivorous Bats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Parasite Morphology and Induction of Metacyclogenesis
2.2. Multilocus Enzyme Electrophoresis
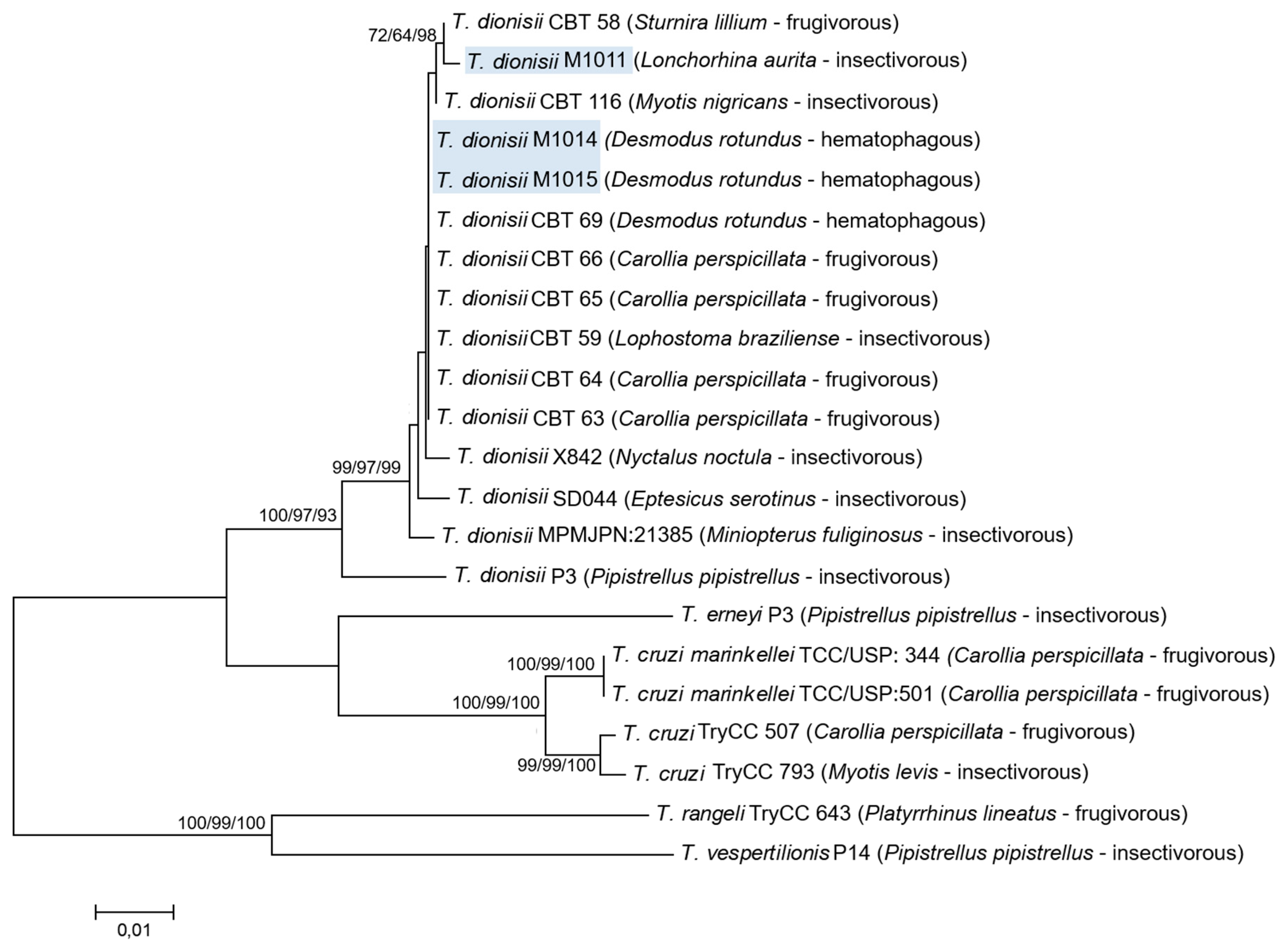
2.3. Molecular Characterization and Sequencing Analysis
2.4. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Light Microscopy of Samples
4.2. Parasite Morphology and Induction of Metacyclogenesis
4.3. Multilocus Enzyme Electrophoresis (MLEE)
4.4. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Assays
4.5. Sequencing Analysis
4.6. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lukes, J.; Butenko, A.; Hashimi, H.; Maslov, D.A.; Votypka, J.; Yurchenko, V. Trypanosomatids are much more than just trypanosomes: Clues from the expanded family tree. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslov, D.A.; Opperdoes, F.R.; Kostygov, A.Y.; Hashimi, H.; Lukeš, J.; Yurchenko, V. Recent advances in trypanosomatid research: Genome organization, expression, metabolism, taxonomy and evolution. Parasitology 2019, 146, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.R.; Greens, S.M.; Chalonel, L.A.; Gabora, K.M. Trypanosoma (Schizotrypanum) dionisii of Pipistrellus pipistrellus (Chiroptera): Intra- and extracellular development in vitro. Parasitology 1972, 65, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavazzana, M.; Marcili, A.; Lima, L.; Maia da Silva, F.; Junqueira, A.C.; Veludo, H.H.; Viola, L.B.; Campaner, M.; Nunes, V.L.; Paiva, F.; et al. Phylogeographical, ecological and biological patterns shown by nuclear (SSU rRNA and gGAPDH) and mitochondrial (Cytb) genes of trypanosomes of the subgenus Schizotrypanum parasitic in Brazilian bats. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L.; Ortíz, S.; Osorio, G.; Torrico, M.C.; Torrico, F.; Solari, A. Phylogenetic analysis of Bolivian bat trypanosomes of the subgenus Schizotrypanum based on cytochrome b sequence and minicircle analyses. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodo, C.L.; Goodwinb, C.C.; Mayes, B.C.; Mariscal, J.A.; Waldrupd, K.A.; Hamer, A.S. Trypanosome species including Trypanosoma cruzi in sylvatic and peridomestic bats of Texas. Acta Trop. 2016, 164, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafie, E.; Rupa, F.H.; Takano, A.; Suzuki, K.; Maeda, K.; Sato, H. First record of Trypanosoma dionisii of the T. cruzi clade from the Eastern bent-winged bat (Miniopterus fuliginosus) in the Far East. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Han, H.J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, J.W.; Luo, L.M.; Wen, H.L.; Qin, X.R.; Zhou, C.M.; Qi, R.; Yu, H.; et al. Trypanosoma dionisii in insectivorous bats from northern China. Acta Trop. 2019, 193, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linhart, P.; Banďouchová, H.; Zukal, J.; Votypka, J.; Kokurewicz, T.; Dundarova, H.; Apoznanski, G.; Heger, T.; Kubickova, A.; Nemcova, M.; et al. Trypanosomes in Eastern and Central European bats. Acta Vet. Brno 2020, 89, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dario, M.A.; Lisboa, C.V.; Costa, L.M.; Morateli, R.; Nascimento, M.P.; Costa, L.P.; Leite, Y.L.R.; Llewellyn, M.S.; Xavier, S.C.C.; Roque, A.L.R.; et al. High Trypanosoma spp. diversity is maintained by bats and triatomines in Espírito Santo state, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.C.B.; Lisboa, C.V.; Xavier, S.C.C.; Dario, M.A.; Verde, R.S.; Calouro, A.M.; Roque, A.L.R.; Jansen, A.M. Trypanosoma sp. diversity in Amazonian bats (Chiroptera; Mammalia) from Acre State, Brazil. Parasitology 2018, 145, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bento, E.C.; Gómez-Hernández, C.; Batista, L.R.; Anversa, L.; Pedrosa, A.L.; Lages-Silva, E.; Ramírez, J.D.; Ramirez, L.E. Identification of bat trypanosomes from Minas Gerais state, Brazil, based on 18S rDNA and Cathepsin-L-like targets. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, J.L.M.; Minuzzi-Souza, T.T.C.; Silva, L.R.; Oliveira, A.C.; Mendonça, V.J.; Nitz, N.; Aguiar, L.M.S.; Gurgel-Gonçalves, R. High frequency of trypanosomatids in gallery forest bats of a Neotropical savanna. Acta Trop. 2018, 177, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoare, C.A. The Trypanosomes of mammals. In A Zoological Monograph; Blackweel Scientific Publications: Oxford/Edinburg, UK, 1972; pp. 327–400. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, R.A.; Molyneux, D.H. Schizotrypanum in British bats. Parasitology 1988, 97, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneux, D.H. Trypanosomes of bats. In Parasitprotoz; Kreier, J.P., Baker, J.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991; pp. 195–224. [Google Scholar]
- Dario, M.A.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Barros, J.H.S.; Xavier, S.C.C.; D’Andrea, O.S.; Roque, A.L.R.; Jansen, A.M. Ecological scenario and Trypanosoma cruzi DTU characterization of a fatal acute Chagas disease case transmitted orally (Espírito Santo state, Brazil). Parasite Vector 2016, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.S.; Lima, L.; Xavier, S.C.C.; Herrera, H.M.; Rocha, F.L.; Roque, A.L.R.; Teixeira, M.M.G.; Jansen, A.M. Uncovering Trypanosoma spp. diversity of wild mammals by the use of DNA from blood clots. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 8, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, F.Y.; Cortez, C.; Alves, R.M.; Yoshida, N. Mammalian cell invasion by closely related Trypanosoma species T. dionisii and T. cruzi. Acta Trop. 2012, 121, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.R.; Thompson, G.B. Two species of Trypanosoma from British bats. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1971, 65, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, S.R.; Baker, J.R. Proceedings: Limited survival of Trypanosoma (Schizotrypanum) dionisii in Rhodnius prolixus. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1975, 69, 433. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, K.J.; Glauert, A.M.; Svvennsen, R.J.; Thomas, H.; Morris, J.; Franks, D. Evasion of the oxidative microbicidal activity of human monocytes by trypomastigotes of Trypanosoma dionisii. Parasitology 1981, 83, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauert, A.M.; Baker, J.R.; Selden, L.F. Mechanism of entry and development of Trypanosoma dionisii in non-phagocytic cells. J. Cell Sci. 1982, 56, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petry, K.; Schottelius, J.; Baltz, T. Purification of metacyclic trypomastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma dionisii from culture using an epimastigote-specific monoclonal antibody. Parasitol. Res. 1987, 73, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel, D.A.; Lisboa, C.V.; Novaes, R.L.M.; Silva, B.A.; Souza, R.F.; Jansen, A.M.; Moratelli, R.; Roque, A.L. Isolation and characterization of trypanosomatids, including Crithidia mellificae, in bats from the Atlantic Forest of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, L.; Maia da Silva, F.; Neves, L.; Attias, M.; Takata, C.S.A.; Campaner, M.; Souza, W.; Hamilton, P.B.; Teixeira, M.M. Evolutionary insights from bat trypanosomes: Morphological developmental and phylogenetic evidence of a new species Trypanosoma (Schizotrypanum) erneyi sp nov in african bats closely related to Trypanosoma (Schizotrypanum) cruzi and Allied Species. Protist 2012, 163, 856–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, I.C.L.; Da Costa, A.P.; Gennari, S.M.; Marcili, A. Survey of Trypanosoma and Leishmania in wild and domestic animals in an Atlantic rainforest fragment and surroundings in the state of Espírito Santo, Brazil. J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, P.B.; Cruickshank, C.; Stevens, J.R.; Teixeira, M.M.; Mathews, F. Parasites reveal movement of bats between the New and Old Worlds. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 63, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, C. Nova tripanozomiaze humana. Estudos sobre a morfolojia e o ciclo evolutivo do Schizotrypanum cruzi n. gen, n. sp.; ajente etiolojico de nova entidade morbida do homem. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 1999, 1, 11–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, S.; Zulantay, I.; Apt, W.; Saavedra, M.; Solari, A. Transferability of Trypanosoma cruzi from mixed human host infection to Triatoma infestans and from insects to axenic culture. Parasitol. Int. 2015, 64, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, P.L.; Mcclure, A.G.; Gallaspy, M.D.; Waleckx, E.; Woods, A.S.; Monroy, M.C.; Stevens, L. The diversity of the Chagas parasite Trypanosoma cruzi infecting the main Central American vector Triatoma dimidiata from Mexico to Colombia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.H.S.; Romijn, P.C.; Baptista, C.; Pinto, A.G.S.; Madeira, M.F. Relato da infecção natural de morcegos por flagelados tripanosomatídeos em diferentes municípios do Estado do Rio de Janeiro. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2008, 41, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.H.S.; Lima, L.; Schubach, A.O.; Teixeira, M.M.G. Trypanosoma madeirae sp. n.; A species of the clade T. cruzi associated with the neotropical common vampire bat Desmodus rotundus. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 8, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcili, A.; Costa, A.P.; Soares, H.S.; Acosta, C.; De Lima, J.T.; Minervino, A.H.; Melo, A.T.; Aguiar, D.M.; Pacheco, R.C.; Gennari, S.M. Isolation and phylogenetic relationships of bat trypanosomes from different biomes in Mato Grosso, Brazil. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, P.B.; Stevens, J.R.; Gaunt, M.W.; Gidley, J.; Gibson, W.C. Trypanosomes are monophyletic, evidence from genes for glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase and small subunit ribosomal RNA. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcili, A.; Lima, L.; Valente, V.C.; Valente, S.A.; Batista, J.S.; Junqueira, A.C.; Souza, A.I.; da Rosa, J.A.; Campaner, M.; Lewis, M.D.; et al. Comparative phylogeography of Trypanosoma cruzi TCIIc, new hosts association with terrestrial ecotopes and spatial clustering. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, P.B.; Teixeira, M.M.G.; Stevens, J.R. The evolution of Trypanosoma cruzi: The “bat seeding” hypothesis. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, J.D.; Tapia-Calle, G.; Muñoz-Cruz, G.; Poveda, C.; Rendón, L.M.; Hincapié, E.; Guhl, F. Trypanosome species in neo-tropical bats: Biological evolutionary and epidemiological implications. Infec. Genet. Evol. 2014, 22, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Telfer, S.; Burthe, S.; Bennett, M.; Begon, M. Trypanosomes, fleas and field voles, ecological dynamics of a host-vector-parasite interaction. Parasitology 2005, 3, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, A.; Ravel, S.; Mateille, T.; Janelle, J.; Patrel, D.; Cuny, G.; Frutos, R. Vector competence of Glossina palpalis gambiensis for Trypanosoma bruceis. l. and genetic diversity of the symbiont Sodalis glossinidius. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, P.A. Leishmania sand fly interaction, progress and challenges. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shofield, C.J. Trypanosoma cruzi—The vectos-parasite paradox. Memb. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2000, 95, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lampo, M.; Feliciangeli, M.D.; Márques, L.M.; Bastidas, C.; Lau, P. A possible role of bats as a blood source for the Leishmania vector Lutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera, Psychodidae). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 62, 718–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assis, G.F.M.; Azeredo, B.V.M.; Fuente, A.L.C.; Diotaiuti, L.; Lana, M. Domiciliation of Triatoma pseudomaculata (Corrêa e Espínola 1964) in the Jequitinhonha valley, State of Minas Gerais. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2007, 40, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinkelle, C.J. Developmental stages of Trypanosoma cruzi-like flagellates in Cavernicola pilosa. Rev. Biol. Trop. 1982, 30, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leal, E.S.B.; Gomes-Silva, F.F.; Filho, D.Q.G.; Júnior, S.M.A.; Neves, R.M.L.; Telino-Júnior, W.R. Update of the distribution of Lonchorhina aurita (Chiroptera), a vulnerable cave-dwelling bat in Brazil. Neotrop. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 13, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.E.; Rasweiler, J.J.; D´Alessandro, A. Experimental transmission of the parasitic flagellates Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma rangeli between triatomine bugs or mice and captive neotropical bats. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2007, 102, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerich, L.B.; Emmanuelle-Machado, P.; Santos, K.; Grisard, E.C.; Steindel, M. Differentiation of Trypanosoma rangeli: High production of infective trypomastigote forms in vitro. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupolillo, E.; Grimaldi, G.; Mimen, H. A general classification of new world Leishmania using numeral zymotaxonomy. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1994, 50, 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisard, E.C.; Sturm, N.R.; Campbell, D.A. A new species of trypanosome Trypanosoma desterrensis sp. n isolated from South American bats. Parasitology 2003, 127, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D. jModelTest, phylogenetic model averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlee, D.; Sneath, P.H.A.; Sokal, R.R.; Freeman, W.H. Numerical Taxonomy. The Principles and Practice of Numerical Classification. Syst. Zool. 1975, 24, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Trypanosoma spp. Isolates | Host Species | Geographic Origin | GenBank Accession Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18S rDNA | gGAPDH | Cytb | |||
| T. dionisii | |||||
| M1011 * | Lonchorhina aurita | Rio de Janeiro/BR | MH047820 | MN233645 | MH047823 |
| M1014 * | Desmodus rotundus | Rio de Janeiro/BR | MH047821 | MN233646 | MH047824 |
| M1015 * | Desmodus rotundus | Rio de Janeiro/BR | MH047822 | MN233647 | MH047825 |
| CBT 116 | Myotis nigricans | Espírito Santo/BR | KF557751 | KF557742 | - |
| CBT 69 | Desmodus rotundus | Espírito Santo/BR | KF557750 | KF557741 | - |
| CBT 66 | Carollia perspicillata | Espírito Santo/BR | KF557749 | KF557740 | - |
| CBT 65 | Carollia perspicillata | Espírito Santo/BR | KF557748 | KF557739 | - |
| CBT 64 | Carollia perspicillata | Espírito Santo/BR | KF557747 | KF557738 | - |
| CBT 63 | Carollia perspicillata | Espírito Santo/BR | KF557746 | KF557737 | - |
| CBT 59 | Lophostoma braziliense | Espírito Santo/BR | KF557745 | KF557736 | - |
| CBT 58 | Sturnira lillium | Espírito Santo/BR | KF557744 | KF557735 | - |
| P3 | Pipistrellus pipistrellus | England | AJ009151 | AJ620271 | - |
| X842 | Nyctalus noctula | England | FN599058 | FN599055 | - |
| MPM < JPN > :21385 | Miniopterus fuliginosus | Japan | LC326397 | LC326399 | - |
| SD044 | Eptesicus serotinus | China | MH393943 | MH393931 | - |
| TryCC 1087 | Sturnira lillium | Goiás/BR | - | - | FJ900253 |
| TryCC 1314 | Sturnira lillium | Paraná/BR | - | - | FJ900254 |
| TryCC 1059 | Eptesicus brasiliensis | Tocantins/BR | - | - | FJ900252 |
| TryCC 211 | Eptesicus brasiliensis | São Paulo/BR | - | - | FJ900249 |
| TryCC 454 | Desmodus rotundus | Mato Grosso do Sul/BR | - | - | FJ900250 |
| TryCC 495 | Carollia perspicillata | Roraima/BR | - | - | FJ900251 |
| TryCC 1110 | Carollia perspicillata | São Paulo/BR | - | - | FJ002263 |
| 272 | Carollia perspicillata | Guacharos/BO | - | - | JN651290 |
| 274 | Carollia perspicillata | Guacharos/BO | - | - | JN651291 |
| T. erneyi | |||||
| TCC 1293 | Tadarida sp. | Chupanga/MZ | JN040987 | JN040964 | JN040956 |
| TCC 1936 | Mops condylurus | Chupanga/MZ | - | - | JN040960 |
| T. c. marinkellei | |||||
| TCC 344 | Carollia perspicillata | Rondonia/BR | FJ001664 | GQ140360 | KT327330 |
| TCC 501 | Carollia perspicillata | Rondonia/BR | FJ001665 | GQ140361 | JN543702 |
| T. c. cruzi | |||||
| TryCC 793 | Myotis levis | São Paulo/BR | FJ900241 | GQ140358 | - |
| TryCC 507 | Carollia perspicillata | Amazonas/BR | FJ900240 | GQ140352 | FJ002256 |
| TCC1994 | Myotis levis | São Paulo/BR | - | - | KT327329 |
| T. rangeli | |||||
| TCC 643 | Platyrrhinus lineatus | Mato Grosso do Sul/BR | FJ900242 | GQ140364 | - |
| TryCC 643 | Platyrrhinus lineatus | Mato Grosso do Sul/BR | - | - | JN040963 |
| T. vespertilionis | |||||
| P14 | Pipistrellus pipistrellus | England | AJ009166 | AJ620283 | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barros, J.H.d.S.; Roque, A.L.R.; Xavier, S.C.d.C.; Nascimento, K.C.S.; Toma, H.K.; Madeira, M.d.F. Biological and Genetic Heterogeneity in Trypanosoma dionisii Isolates from Hematophagous and Insectivorous Bats. Pathogens 2020, 9, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090736
Barros JHdS, Roque ALR, Xavier SCdC, Nascimento KCS, Toma HK, Madeira MdF. Biological and Genetic Heterogeneity in Trypanosoma dionisii Isolates from Hematophagous and Insectivorous Bats. Pathogens. 2020; 9(9):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090736
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarros, Juliana Helena da Silva, André Luiz Rodrigues Roque, Samanta Cristina das Chagas Xavier, Kátia Cristina Silva Nascimento, Helena Keiko Toma, and Maria de Fatima Madeira. 2020. "Biological and Genetic Heterogeneity in Trypanosoma dionisii Isolates from Hematophagous and Insectivorous Bats" Pathogens 9, no. 9: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090736
APA StyleBarros, J. H. d. S., Roque, A. L. R., Xavier, S. C. d. C., Nascimento, K. C. S., Toma, H. K., & Madeira, M. d. F. (2020). Biological and Genetic Heterogeneity in Trypanosoma dionisii Isolates from Hematophagous and Insectivorous Bats. Pathogens, 9(9), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090736






