Development of a Mechatronic System for the Mirror Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
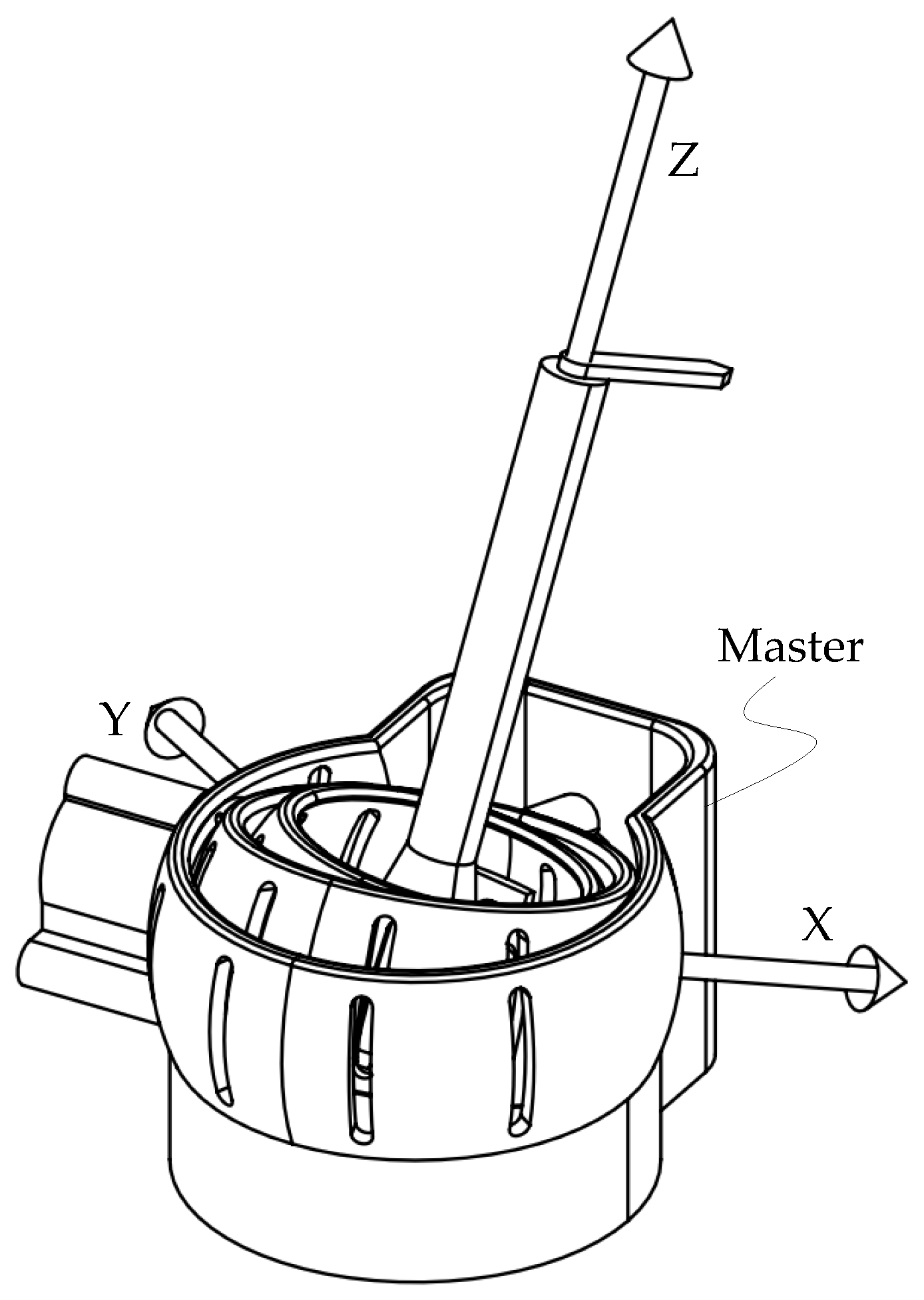
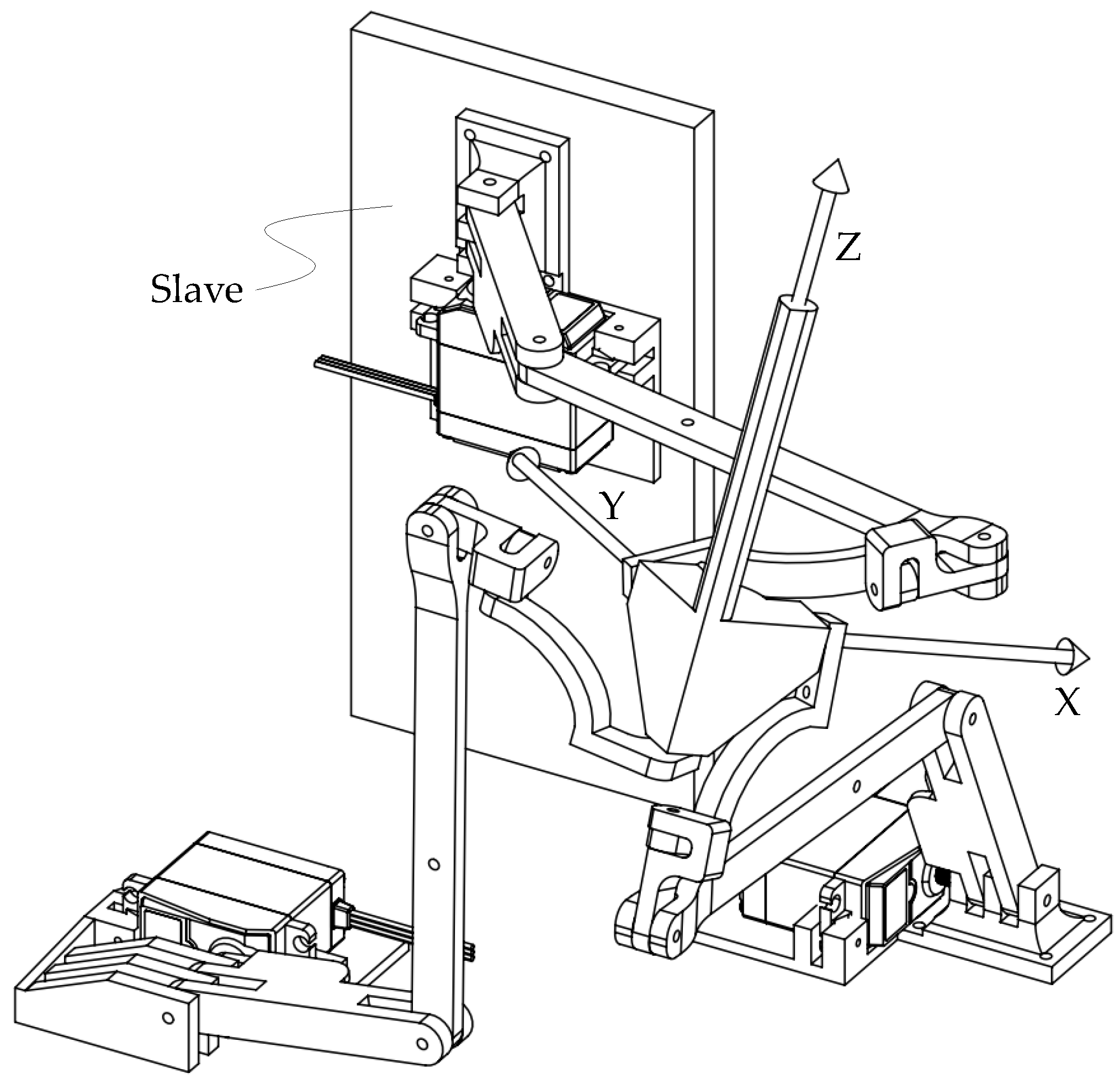
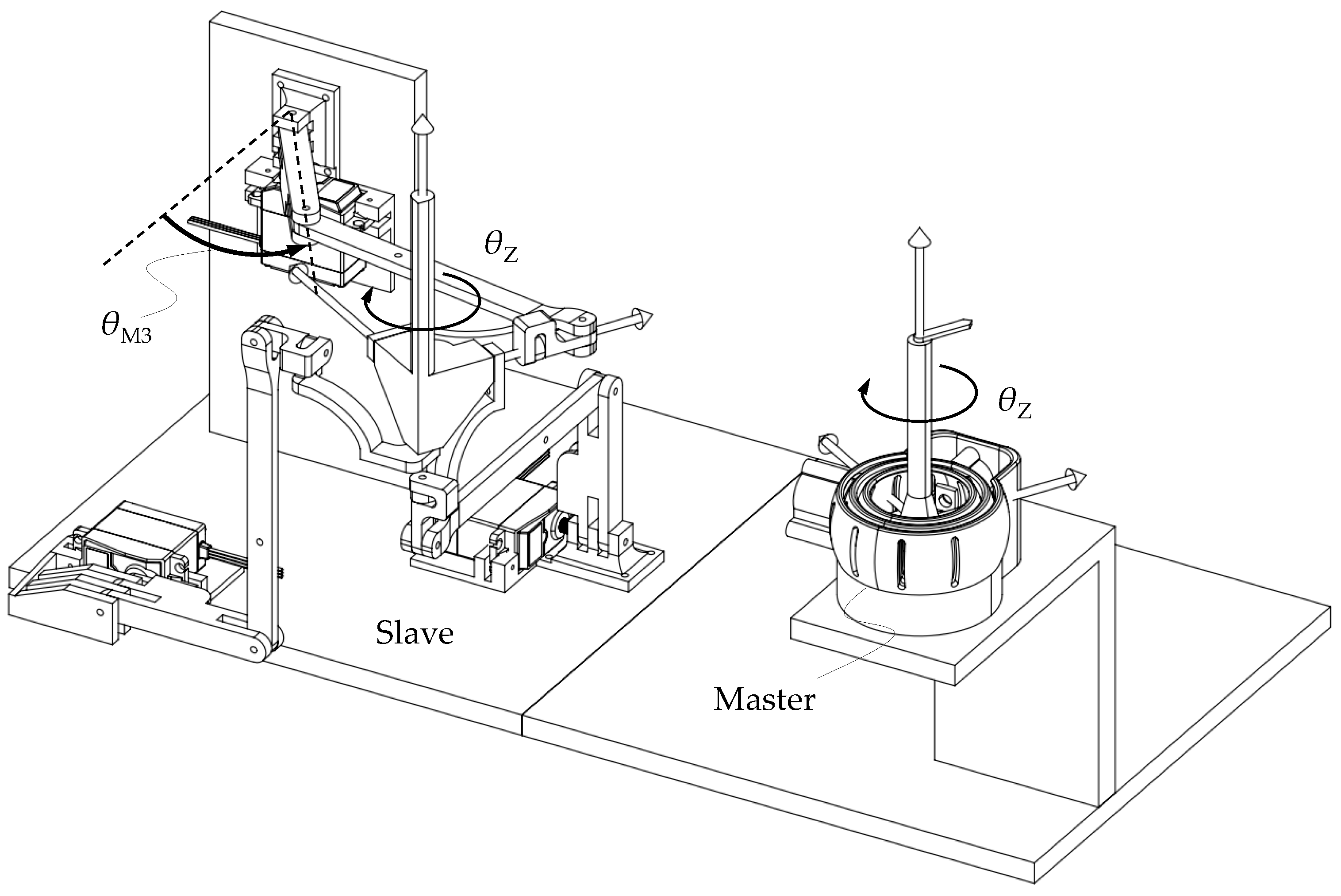
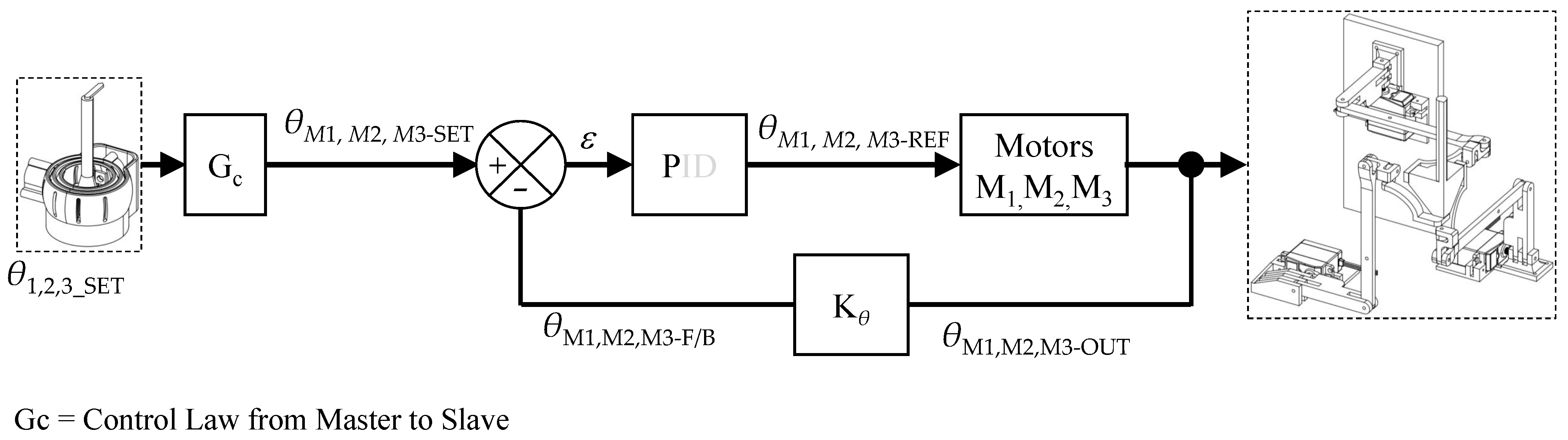
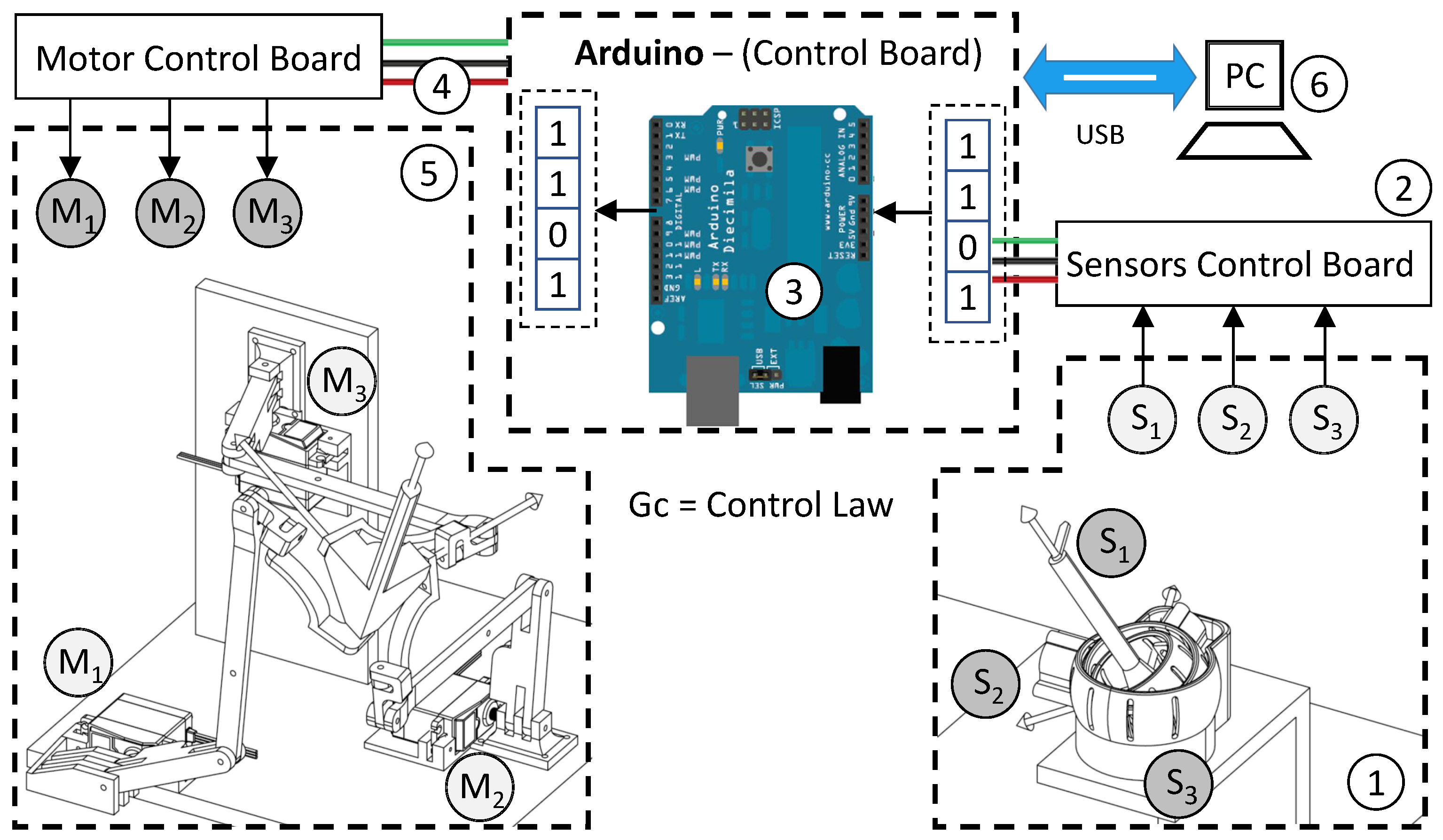
2. Description of the System
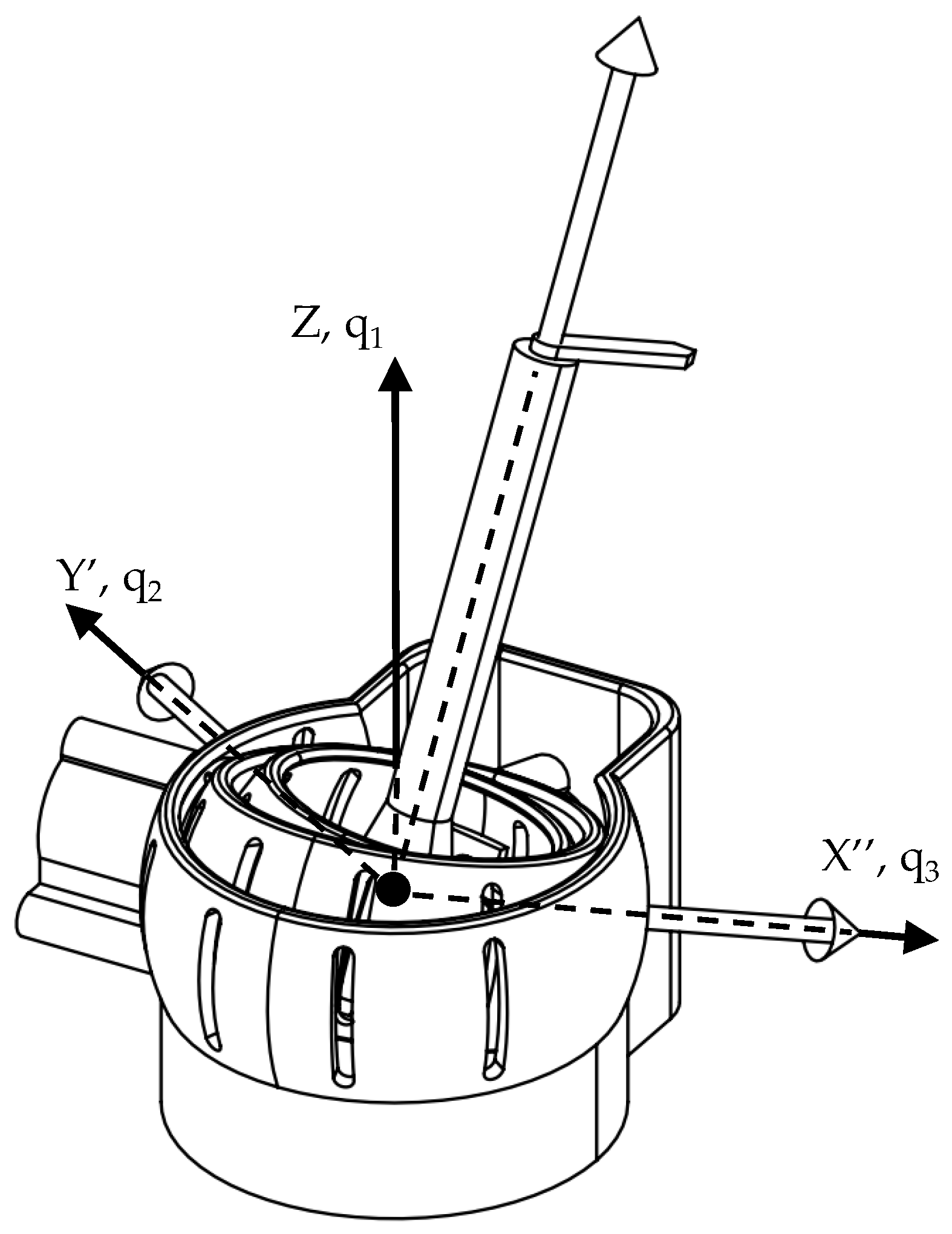
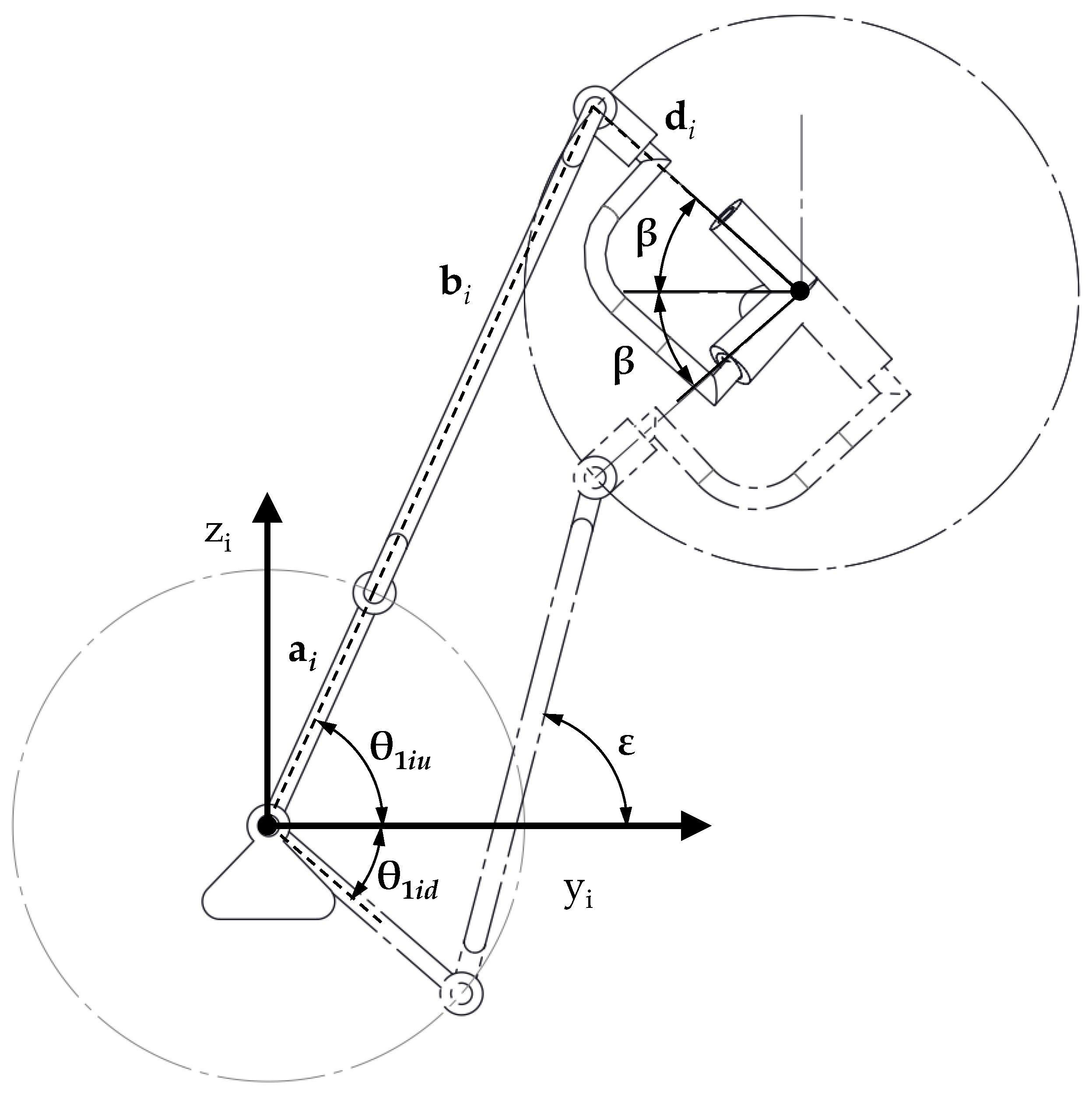
3. Kinematics
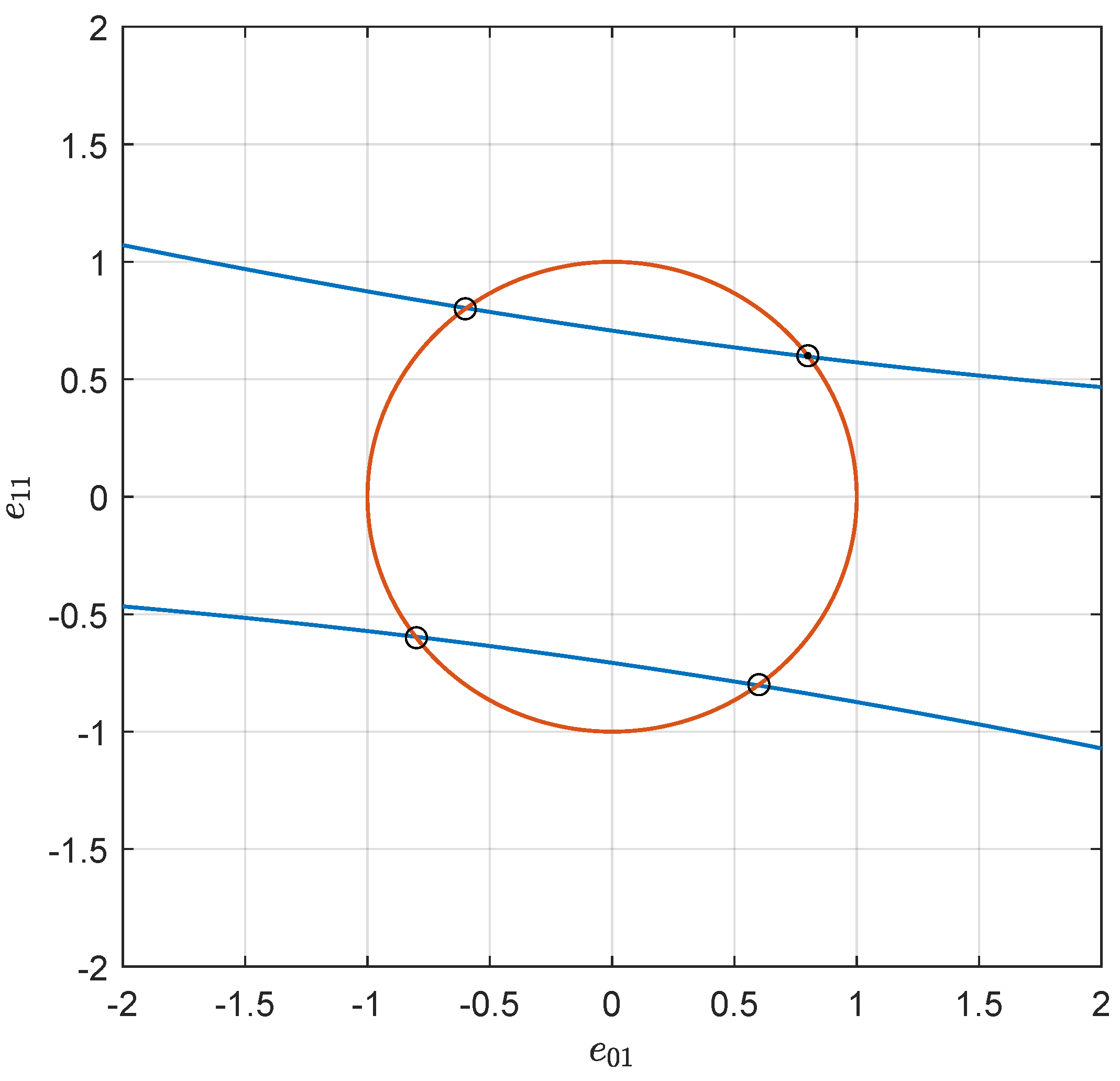
Range of Motion
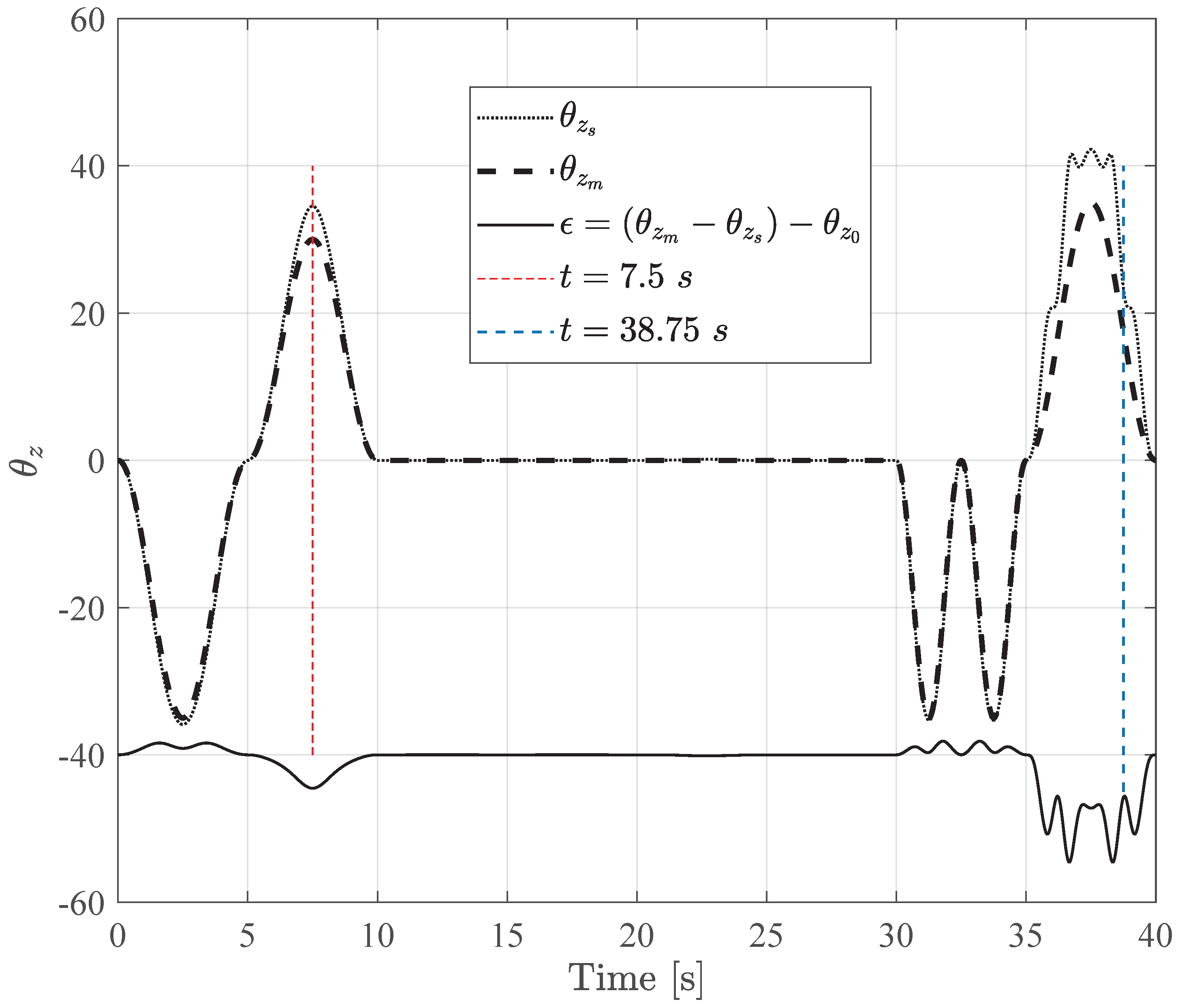
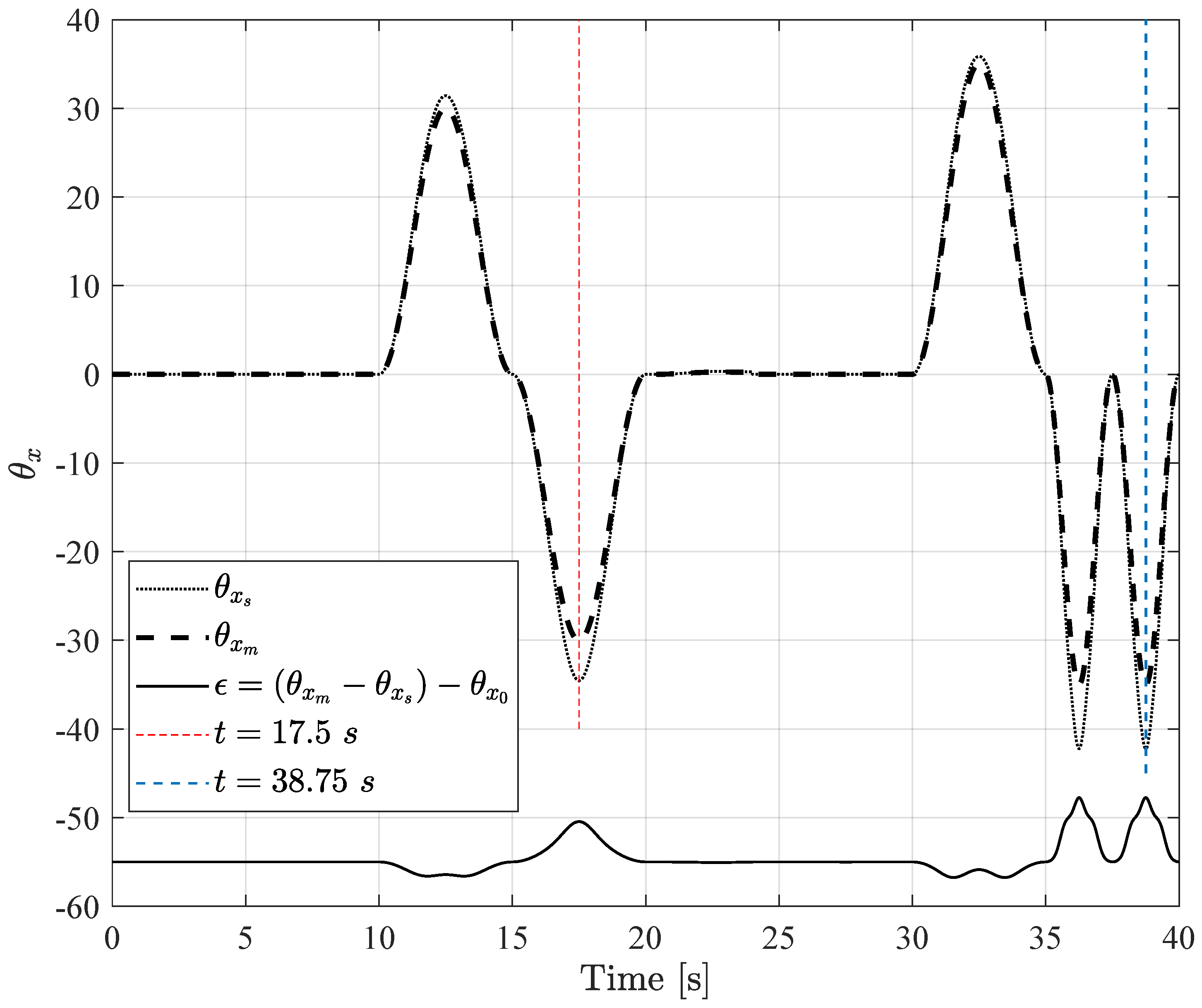
4. Simulation of the System
5. Experimental Set-Up of the System
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kahn, L.E.; Zygman, M.L.; Rymer, W.Z.; Reinkensmeyer, D.J. Robot-assisted reaching exercise promotes arm movement recovery in chronic hemiparetic stroke: A randomized controlled pilot study. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2006, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colombo, R.; Pisano, F.; Micera, S.; Mazzone, A.; Delconte, C.; Carrozza, M.C.; Dario, P.; Minuco, G. Robotic techniques for upper limb evaluation and rehabilitation of stroke patients. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2005, 13, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, P.; Ottaviano, E.; Conte, M.; D’Aguanno, A.; De Carolis, D. The design of a novel tilt seat for inversion therapy. Int. J. Imaging Robot. 2013, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lum, P.S.; Burgar, C.G.; Shor, P.C.; Majmundar, M.; Van der Loos, M. Robot-assisted movement training compared with conventional therapy techniques for the rehabilitation of upper-limb motor function after stroke resonance imaging in healthy subjects. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lo, A.; Guarion, P.; Richards, L.; Haselkorn, J.; Wittenberg, G.; Federman, D.; Ringer, R.; Wagener, T.; Krebs, H.; Volpe, B.; et al. Robot assisted therapy for long-term upper-limb impairment after stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1772–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masiero, S.; Celia, A.; Rosati, G.; Armani, M. Robotic-assisted rehabilitation of the upper limb after acute stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.; Perreault, E. An Assessment of Robot-Assisted Bimanual Movements on Upper Limb Motor Coordination Following Stroke. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 17, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, H.I.; Hogan, N.; Aisen, M.; Volpe, B.T. Robot-aided neurorehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 1998, 6, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harwin, W.S.; Patton, J.L.; Edgerton, V.R. Challenges and opportunities for robot-mediated neurorehabilitation. Proc. IEEE 2006, 94, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, P.S.; Burgar, C.G.; Van der Loos, M.; Shor, P.C.; Majmundar, M.; Yap, R. The mime robotic system for upper-limb neuro-rehabilitation: Results from a clinical trial in subacute stroke. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Koeneman, E.J.; Schultz, R.; Herring, D.; Wanberg, J.; Huang, H.; Sugar, T.; Herman, R.; Koeneman, J.B. Design of a robotic upper extremity repetitive therapy device. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew, D.; Bachrach, B.; Rymer, W.Z.; Beer, R.F. Development of the macarm—A novel cable robot for upper limb neurorehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Homma, K.; Fukuda, O.; Sugawara, J.; Nagata, Y.; Usuba, M. A wire-driven leg rehabilitation system: Development of a 4-dof experimental system. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Kobe, Japan, 20–24 July 2003; pp. 908–913. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zou, Y.; Wang, L.; Pei, X. Hybrid force control based on icmac for an astronaut rehabilitative training robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2012, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rea, P.; Ottaviano, E. Functional Design for Customizing Sit-To-Stand Assisting Devices. J. Bionic Eng. 2018, 15, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rodriguez, A.; Castillo-Garcia, F.J.; Ottaviano, E.; Rea, P.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, A.G. On the effects of the design of cable-Driven robots on kinematics and dynamics models accuracy. Mechatronics 2017, 43, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviano, E.; Castelli, G. A Study on the Effects of Cable Mass and Elasticity in Cable-Based Parallel Manipulators. In ROMANSY 18 Robot Design, Dynamics and Control; CISM International Centre for Mechanical Sciences, Courses and Lectures; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2010; Volume 524, pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Masiero, S.; Armani, M.; Rosati, G. Upper-limb robot-assisted therapy in rehabilitation of acute stroke patients: Focused review and results of new randomized controlled trial. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2011, 48, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, G.; Gallina, P.; Masiero, S.; Rossi, A. Design of a new 5 d.o.f. wire based robot for rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tappeiner, L.; Ottaviano, E.; Husty, M.L. Cable-Driven Robot for Upper Limb Rehabilitation Inspired by the Mirror Therapy. Mech. Mach. Sci. 2018, 50, 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Beom, J.; Koh, S.; Nam, H.S.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.G.; Oh, B.-M.; Chung, S.-G.; Kim, S. Robotic Mirror Therapy System for Functional Recovery of Hemiplegic Arms. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 114, 54521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzei, F.; Läppchen, C.H.; Glauche, V.; Mader, I.; Rijntjes, M.; Weiller, C. Functional plasticity induced by mirror training: The mirror as the element connecting both hands to one hemisphere. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2012, 26, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohle, C.; Püllen, J.; Nakaten, A.; Küst, J.; Rietz, C.; Karbe, H. Mirror therapy promotes recovery from severe hemiparesis: A randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2009, 23, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervane Vural, S.; Nakipoglu Yuzer, G.F.; Sezgin Ozcan, D.; Demir Ozbudak, S.; Ozgirgin, N. Effects of Mirror Therapy in Stroke Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1: A Randomized Controlled Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünert-Plüss, N.; Hufschmid, U.; Santschi, L.; Grünert, J. Mirror therapy in hand rehabilitation: A review of the literature, the st gallen protocol for mirror therapy and evaluation of a case. Br. J. Hand Ther. 2008, 13, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothgangel, A.; Braun, S. Mirror Therapy: Practical Protocol for Stroke Rehabilitation; Pflaum Verlag: Munich, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothgangel, A.S.; Braun, S.M.; Beurskens, A.J.; Seitz, R.J.; Wade, D.T. The clinical aspects of mirror therapy in rehabilitation: A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2011, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, V.S.; Rogers-Ramachandran, D. Synaesthesia in phantom limbs induced with mirrors. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1996, 263, 377–386. [Google Scholar]
- Dere, E.; Ozcan, M.; Canan, S. Three Axis Gimbal Design and Its Application. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Technologies, Computer Engineering and Science (ICATCES’18), Safranbolu, Turkey, 11–13 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, D.; Wu, Y.; Scalzo, A.; Metta, G.; Parmiggiani, A. A Comparison of Robot Wrist Implementations for the iCub Humanoid. Robotics 2019, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callegari, M.; Cammarata, A.; Gabrielli, A.; Ruggiu, M.; Sinatra, R. Analysis and design of a spherical micromechanism with flexure hinges. J. Mech. Des. 2009, 131, 051003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Ruggiu, M. A novel method for the solution of the forward displacement problem of spherical parallel manipulators. ZAMM J. Appl. Math. Mech. 2013, 93, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, R.; Mariani, A.; Ruggiu, M. On the kinematics of the 3-RRUR spherical parallel manipulator. Robotica 2010, 28, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malosio, M.; Negri, S.P.; Pedrocchi, N.; Vicentini, F.; Caimmi, M.; Tosatti, L.M. A spherical parallel three degrees-of-freedom robot for ankle-foot neuro-rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 3356–3359. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, H.; Liu, Y.H.; Liang, Z.C.; Zhao, T. A Novel 2-RRR/UPRR robot mechanism for ankle rehabilitation and its kinematics. Robot 2010, 32, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Li, J.F.; Dong, M.J. Design and workspace analysis of a parallel ankle rehabilitation robot (PARR). J. Healthc. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4164790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Li, R.; Li, D.; Bai, S. An ankle rehabilitation robot based on 3-RRS spherical parallel mechanism. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, T.; Qi, K.; Niu, J.; Guo, S. Module combination based configuration synthesis and kinematic analysis of generalized spherical parallel mechanism for ankle rehabilitation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 166, 104436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Kantu, N.T.; Xu, B.; Swami, C.P.; Saleem, G.T.; Kang, J. A Novel 3-RRR Spherical Parallel Instrument for Daily Living Emulation (SPINDLE) for Functional Rehabilitation of Patients with Stroke. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2021, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatzi, M.; David, C.; Long, D.C.; Celik, O. Comparison of Human-Robot Interaction Torque Estimation Methods in a Wrist Rehabilitation Exoskeleton. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2019, 94, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, J. Introduction to Robotics: Mechanics and Control, 4th ed.; Pearson College Div: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ottaviano, E.; Rea, P.; Castelli, G. THROO: A tracked hybrid rover to overpass obstacles. Adv. Robot. 2014, 28, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, P.; Ottaviano, E. Design and Development of an Inspection Robotic System for Indoor Applications. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2018, 49, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruggiu, M.; Rea, P. Development of a Mechatronic System for the Mirror Therapy. Actuators 2022, 11, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11010014
Ruggiu M, Rea P. Development of a Mechatronic System for the Mirror Therapy. Actuators. 2022; 11(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuggiu, Maurizio, and Pierluigi Rea. 2022. "Development of a Mechatronic System for the Mirror Therapy" Actuators 11, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11010014
APA StyleRuggiu, M., & Rea, P. (2022). Development of a Mechatronic System for the Mirror Therapy. Actuators, 11(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11010014






