Adaptive Fuzzy Fault-Tolerant Attitude Control for a Hypersonic Gliding Vehicle: A Policy-Iteration Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Description
2.1. Nonlinear Model of an HGV’s Attitude System
2.2. T–S Fuzzy Modeling of an HGV
2.3. Actuator Fault Model
2.4. Control Objective
3. Main Results
3.1. PI-Based Normal Controller
| Algorithm 1: Model-based PI algorithm |
1. Initialization: Select , choose any reasonable policy ; 2. Policy evaluation: Solve the following equations for 3. Policy improvement: 4. If the convergence condition is satisfied, stop; else, go to step 2. |
3.2. PI-Based Fuzzy FTC Control
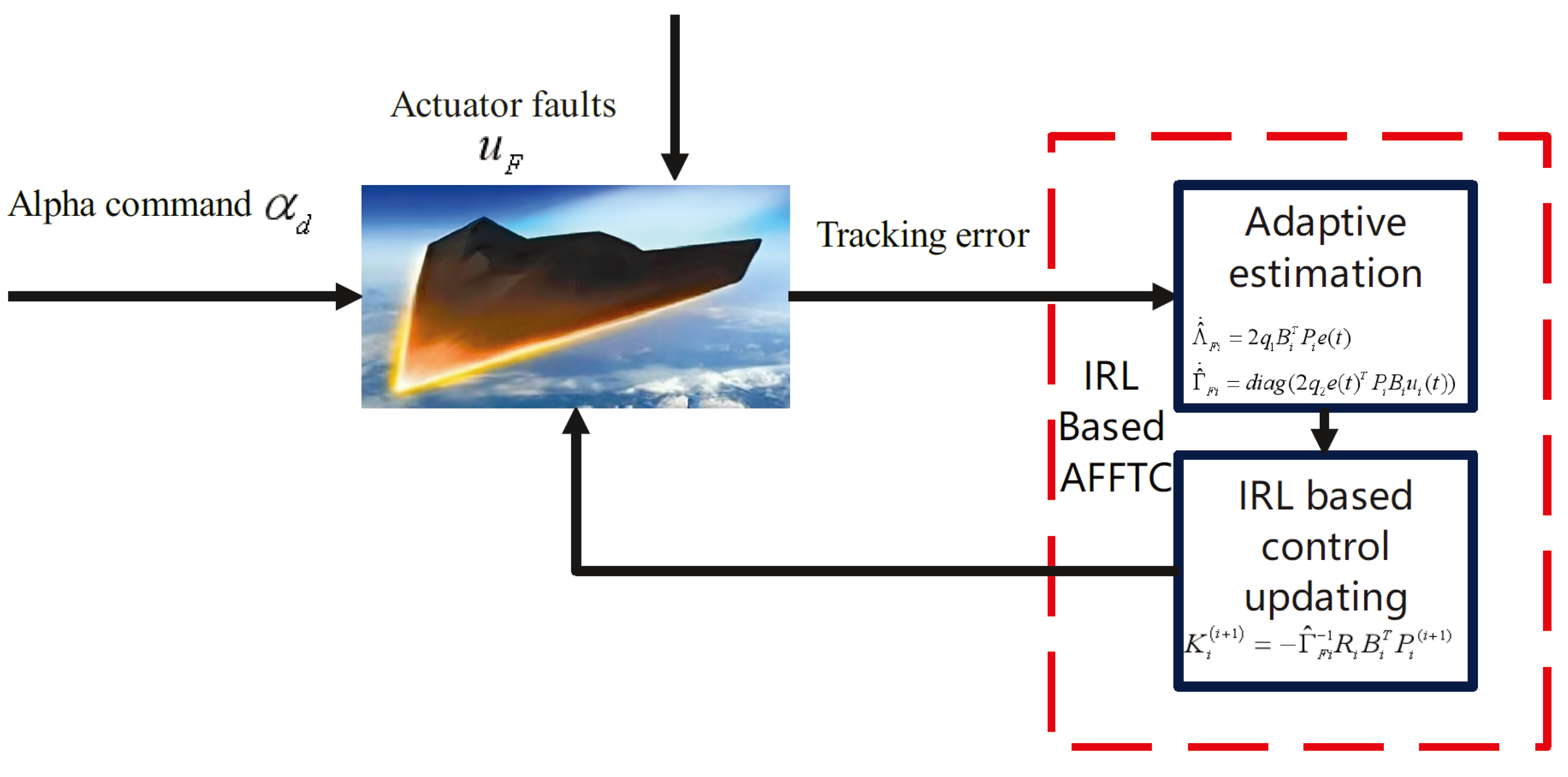
3.3. IRL-Based Fuzzy FTC Control
| Algorithm 2: IRL-based fuzzy FTC control algorithm |
1. Initialization: Select , choose any reasonable policy , ; 2. Policy evaluation: Solve the following equations for 3. Policy improvement: and
4. If the convergence condition is satisfied, stop; else, go to step 2. |
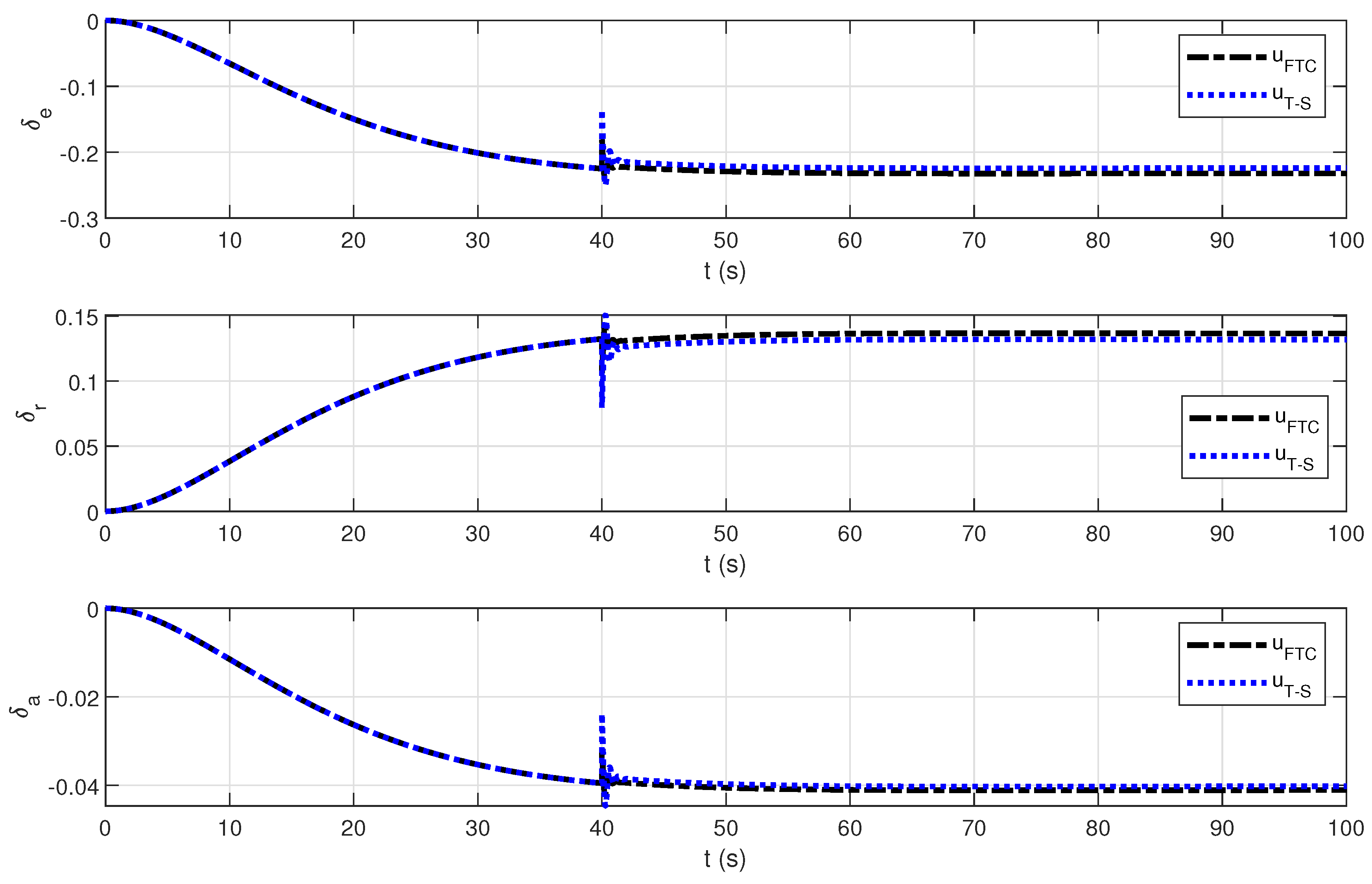
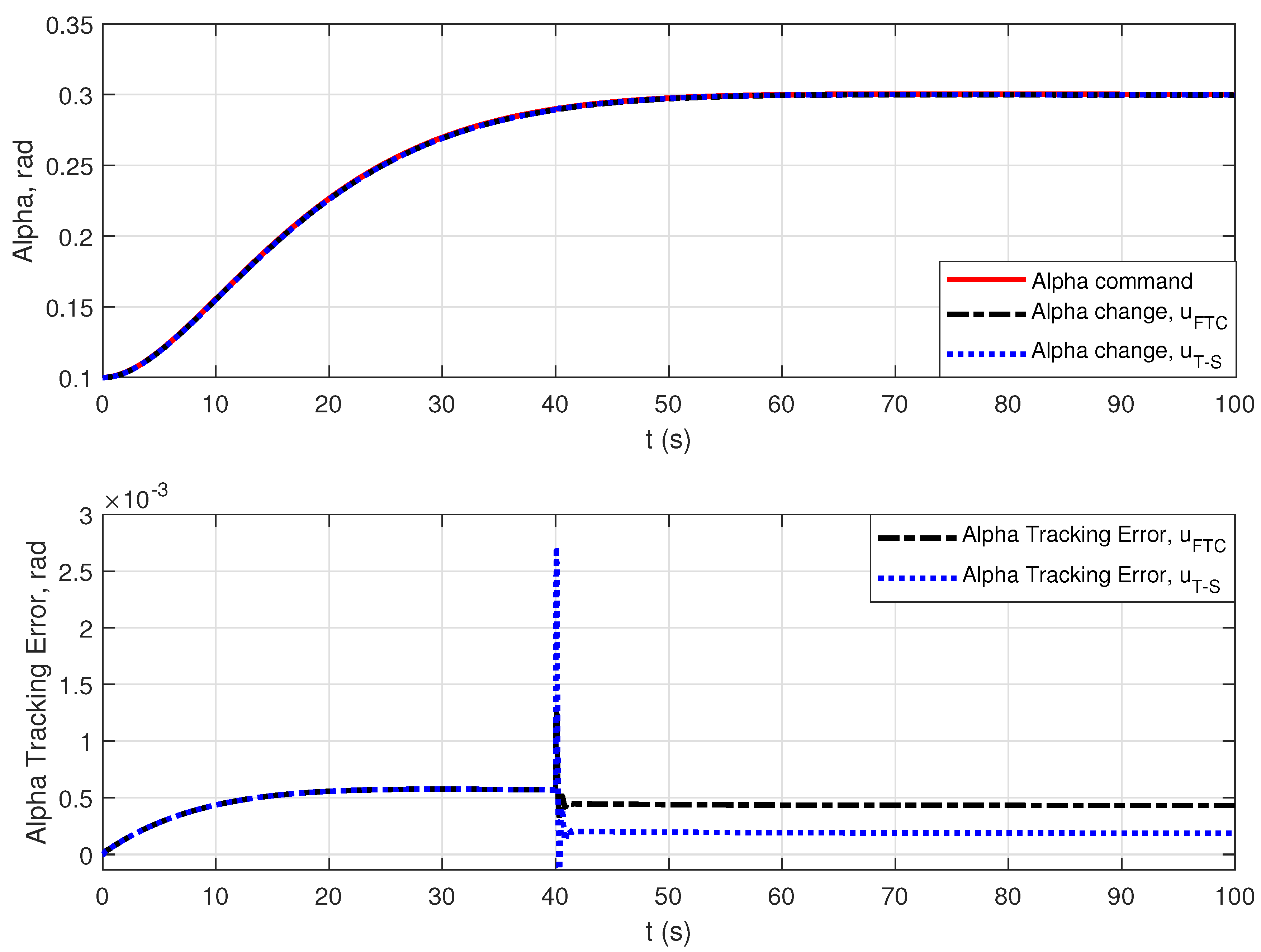
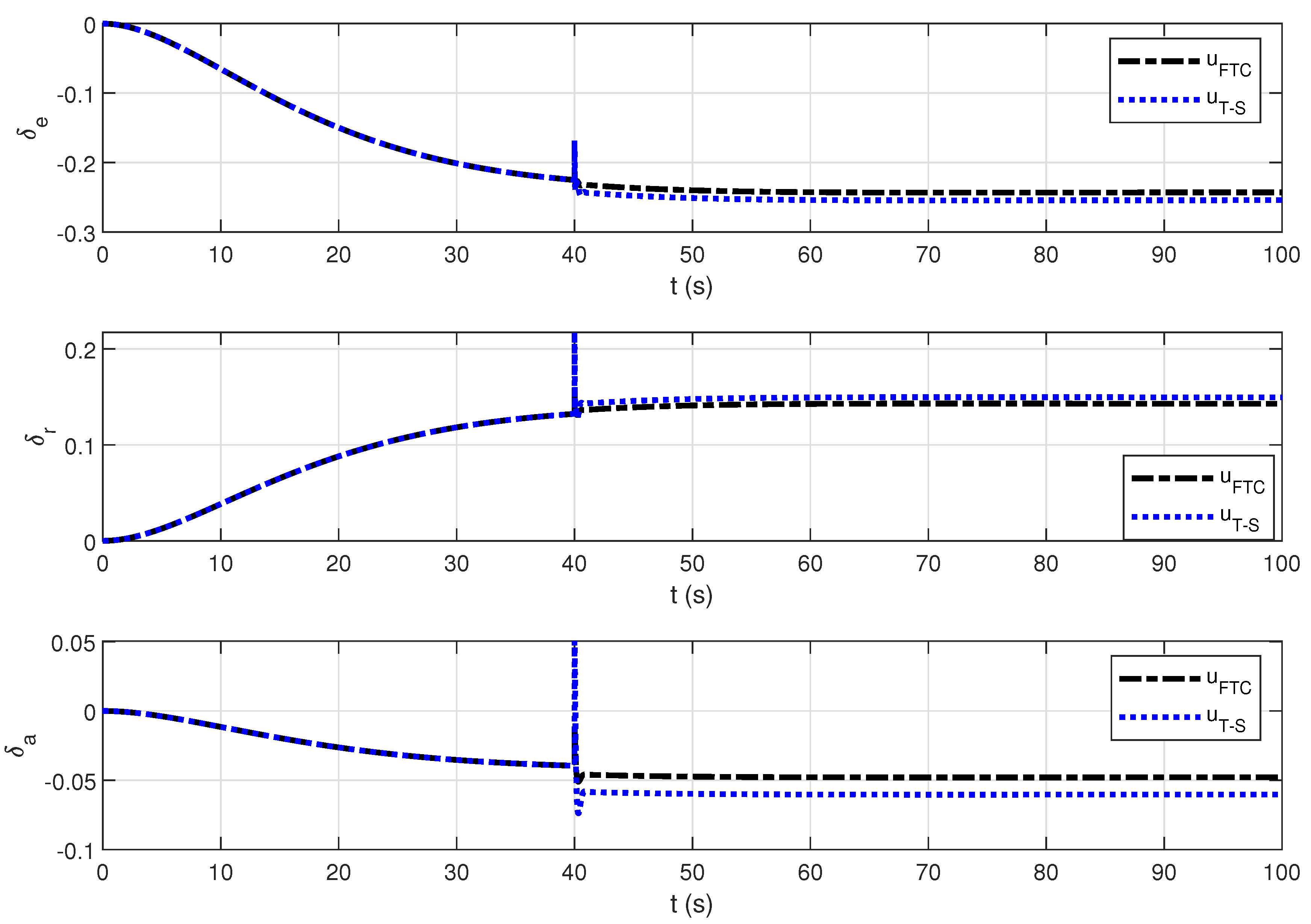
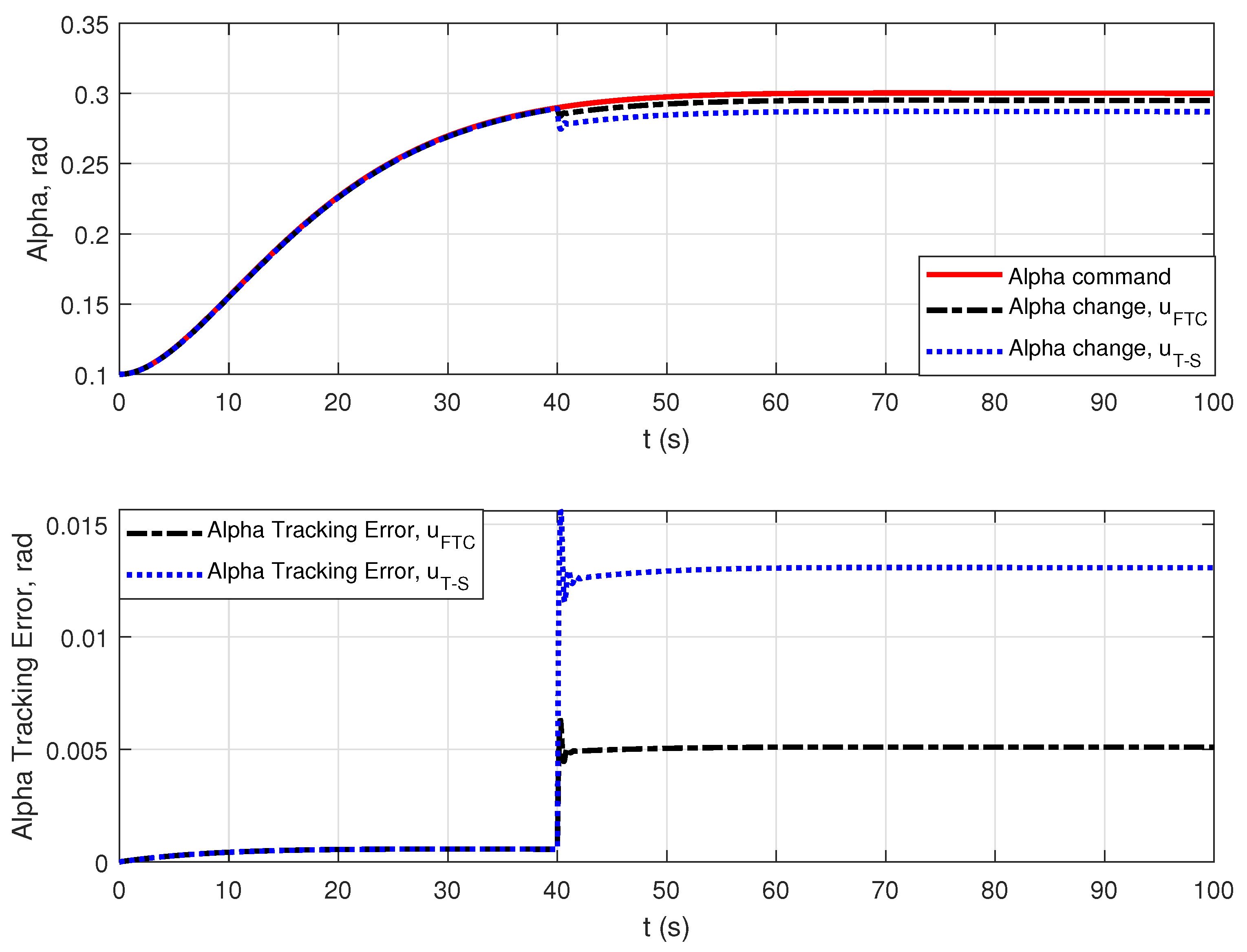
4. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, X.; Wang, H. Active disturbance rejection based trajectory linearization control for hypersonic reentry vehicle with bounded uncertainties. ISA Trans. 2015, 54, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, B. Composite observer-based optimal attitude-tracking control with reinforcement learning for hypersonic vehicles. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J. Fuzzy adaptive non-affine attitude tracking control for a generic hypersonic flight vehicle. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, C.; Qian, C.; Wang, L. Linear parameter varying switching attitude control for a near space hypersonic vehicle with parametric uncertainties. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2015, 46, 3019–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y. Fixed-time actuator fault accommodation applied to hypersonic gliding vehicles. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, D.; Qi, R.; Jiang, B. Adaptive fault-tolerant attitude control for hypersonic reentry vehicle subject to complex uncertainties. J. Frankl. Inst. 2022, 359, 5458–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wang, C.; Kao, Y. Adaptive fixed-time quantized fault-tolerant attitude control for hypersonic reentry vehicle. Neurocomputing 2023, 520, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Meng, Y.; Hu, S.; Peng, Z.; Shi, W. Adaptive fault-tolerant attitude tracking control for hypersonic vehicle with unknown inertial matrix and states constraints. IET Control Theory Appl. 2023, 17, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, J. Adaptive control for hypersonic vehicles with time-varying faults. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 1442–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, X. Adaptive multivariable integral TSMC of a hypersonic gliding vehicle with actuator faults and model uncertainties. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2007, 22, 2723–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Liu, S.; Hu, X. Fault-tolerant Attitude Control for Hypersonic Flight Vehicle Subject to Actuators Constrain: A Model Predictive Static Programming Approach. IEEE J. Miniaturization Air Space Syst. 2023, 4, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Yu, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, R.; Gao, F. Iterative learning fault-tolerant control for injection molding processes against actuator faults. J. Process Control 2017, 59, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poongodi, T.; Saravanakumar, T.; Mishra, P.P.; Zhu, Q. Extended Dissipative Control for Markovian Jump Time-Delayed Systems with Bounded Disturbances. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5685324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Gao, F. Constrained model predictive fault-tolerant control for nonlinear batch processes with time delay by integrating a LRF method and a switching strategy. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 287, 119762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Ji, W.; Chadli, M. A novel fuzzy output feedback dynamic sliding mode controller design for two-dimensional nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 29, 2869–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Lam, H.K.; Xiao, B.; Wu, L. Tracking Control for Nonlinear Systems with Actuator Saturation via Interval Type-2 TS Fuzzy Framework. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 7085–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Karimi, H.R.; Yin, T.; Fu, S. Asynchronous H filtering for semi-Markov jump TS fuzzy systems within partial state delay and deception attack: Applied to aircraft-pilot state estimation. J. Frankl. Inst. 2022, 360, 9265–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, L.; Chen, F.; Wen, C. Multiple-step fault estimation for interval type-II TS fuzzy system of hypersonic vehicle with time-varying elevator faults. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1729881417699149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, W.; Huang, S.; Wang, R.; Yan, W.; Gevorgian, V.; Gao, D.W. Data-driven optimal control strategy for virtual synchronous generator via deep reinforcement learning approach. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 9, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; He, H. Continuous-Time Distributed Policy Iteration for Multicontroller Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 2372–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Liu, D.; Huang, T.; Liu, J. Output Tracking Control Based on Adaptive Dynamic Programming with Multistep Policy Evaluation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 49, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M. Adaptive Fault-Tolerant Tracking Control for Discrete-Time Multiagent Systems via Reinforcement Learning Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Wu, T.; Weng, R.; Han, M.; Zhao, Y. Safe Reinforcement Learning With Stability Guarantee for Motion Planning of Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 5435–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Wang, M.; Wei, Q.; Lu, J. A new neuro-optimal nonlinear tracking control method via integral reinforcement learning with applications to nuclear systems. Neurocomputing 2022, 483, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Luo, B.; Xue, S. Integral reinforcement learning-based optimal output feedback control for linear continuous-time systems with input delay. Neurocomputing 2021, 460, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Jin, Y.; Song, Y. Fault-tolerant adaptive tracking control of Euler-Lagrange systems—An echo state network approach driven by reinforcement learning. Neurocomputing 2022, 484, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Gao, F. Reinforcement Learning-Based Optimal Fault-Tolerant Tracking Control of Industrial Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 16014–16024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, L.; Zhang, R.; Gao, F. H∞ output feedback fault-tolerant control of industrial processes based on zero-sum games and off-policy Q-learning. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2023, 179, 108421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wu, L.; Hu, C.; Gao, H. Fuzzy guaranteed cost tracking control for a flexible air-breathing hypersonic vehicle. IET Control Theory Appl. 2012, 6, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Rule NO. | Premise Variables |
|---|---|
| 1 | S |
| 2 | M |
| 3 | B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Hu, C.; Pei, H.; Li, H.; Hu, X. Adaptive Fuzzy Fault-Tolerant Attitude Control for a Hypersonic Gliding Vehicle: A Policy-Iteration Approach. Actuators 2024, 13, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070259
Liu M, Hu C, Pei H, Li H, Hu X. Adaptive Fuzzy Fault-Tolerant Attitude Control for a Hypersonic Gliding Vehicle: A Policy-Iteration Approach. Actuators. 2024; 13(7):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070259
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Meijie, Changhua Hu, Hong Pei, Hongzeng Li, and Xiaoxiang Hu. 2024. "Adaptive Fuzzy Fault-Tolerant Attitude Control for a Hypersonic Gliding Vehicle: A Policy-Iteration Approach" Actuators 13, no. 7: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070259
APA StyleLiu, M., Hu, C., Pei, H., Li, H., & Hu, X. (2024). Adaptive Fuzzy Fault-Tolerant Attitude Control for a Hypersonic Gliding Vehicle: A Policy-Iteration Approach. Actuators, 13(7), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13070259






