Wave Energy Linear Generator System Including a Newly Designed Wave Roller Mechanical Interface
Abstract
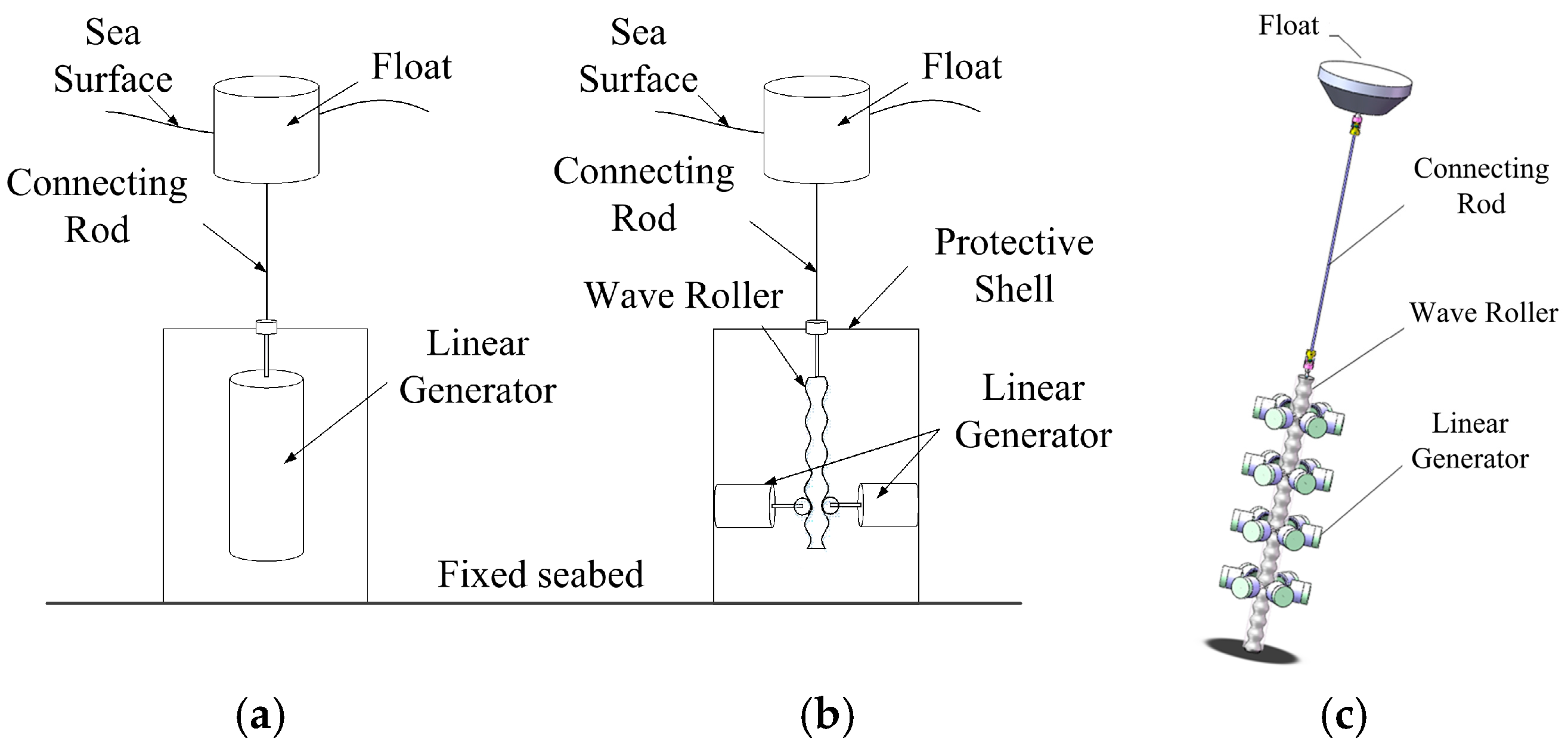
1. Introduction
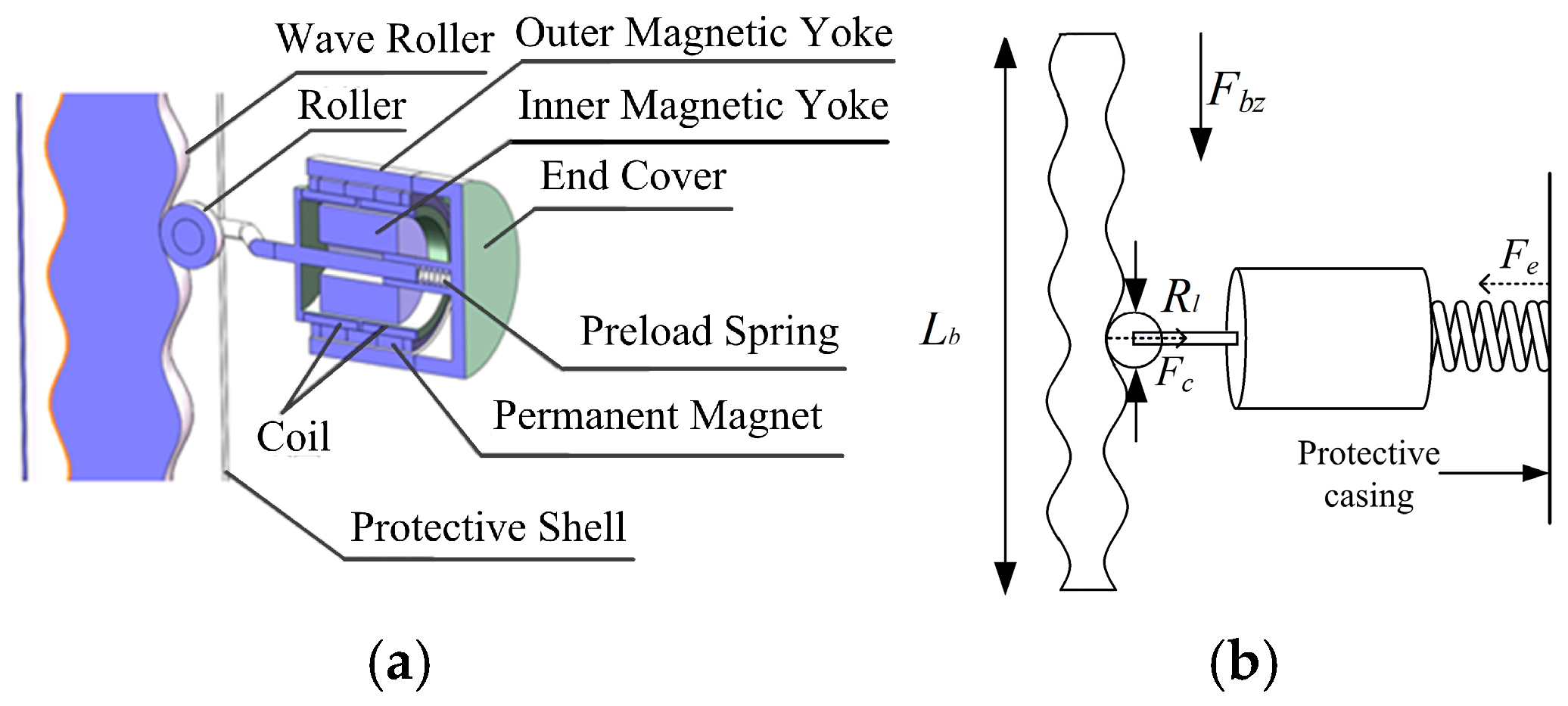
2. Design of a Novel Wave-Roller-Based Driving Mechanical Interface
3. Tuning of Key Parameters in the Novel Moving-Coil Wave Power Generation Device
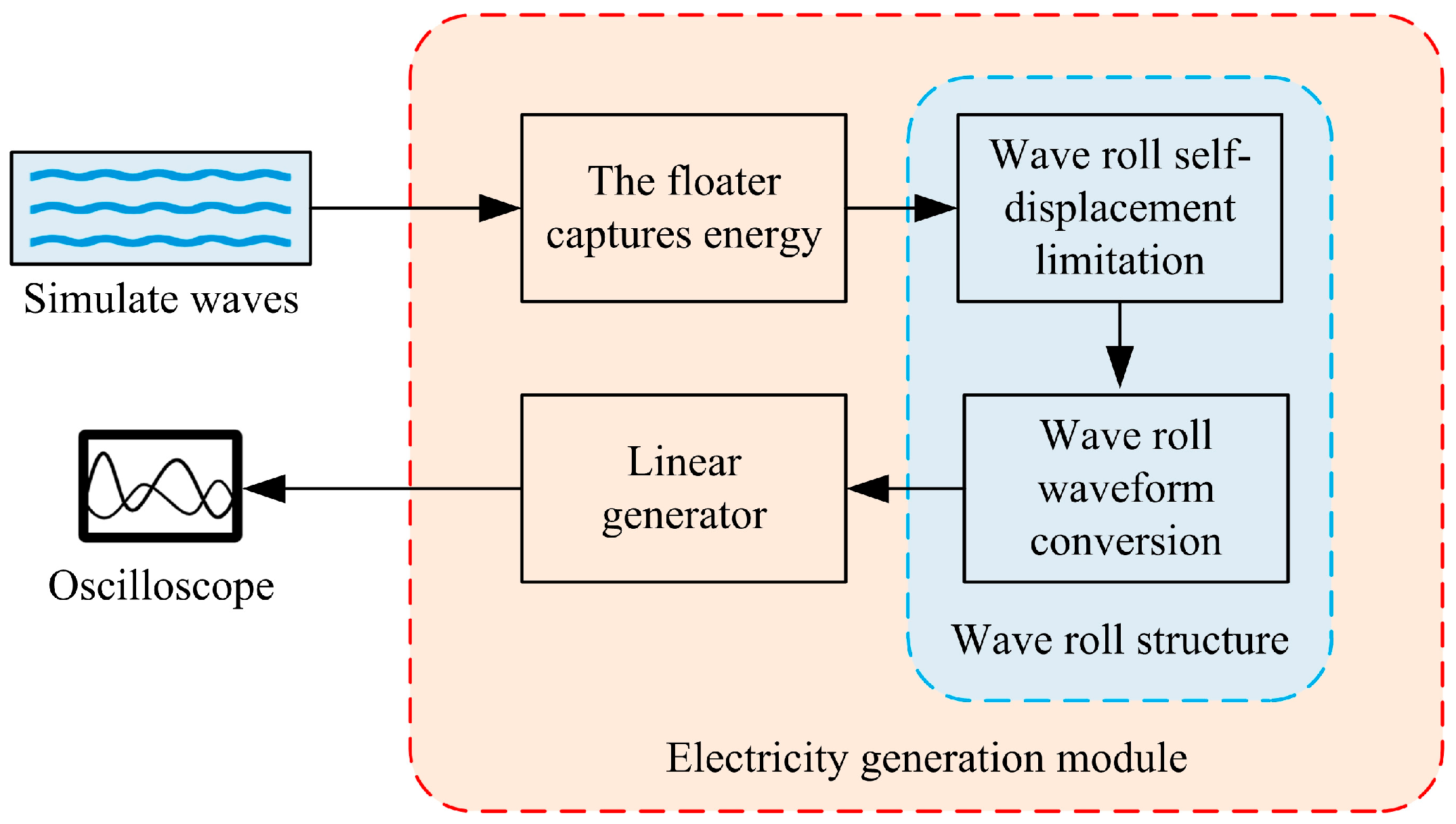
4. Simulation Analysis
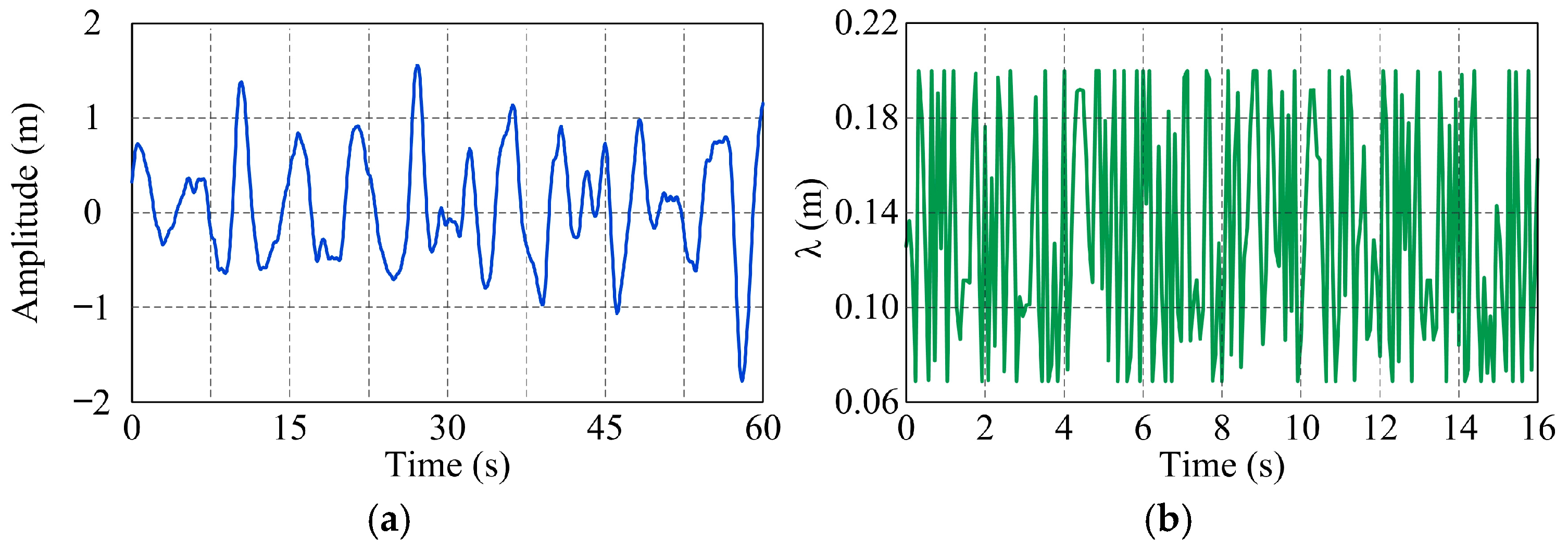
4.1. Determination of Optimal Wavelength for the Wave Roller
4.2. Simulation of the Entire New Power Generation Device
4.2.1. Simulation of the Wave Roller Structure
4.2.2. Power Absorption Rate of the New Power Generation Device
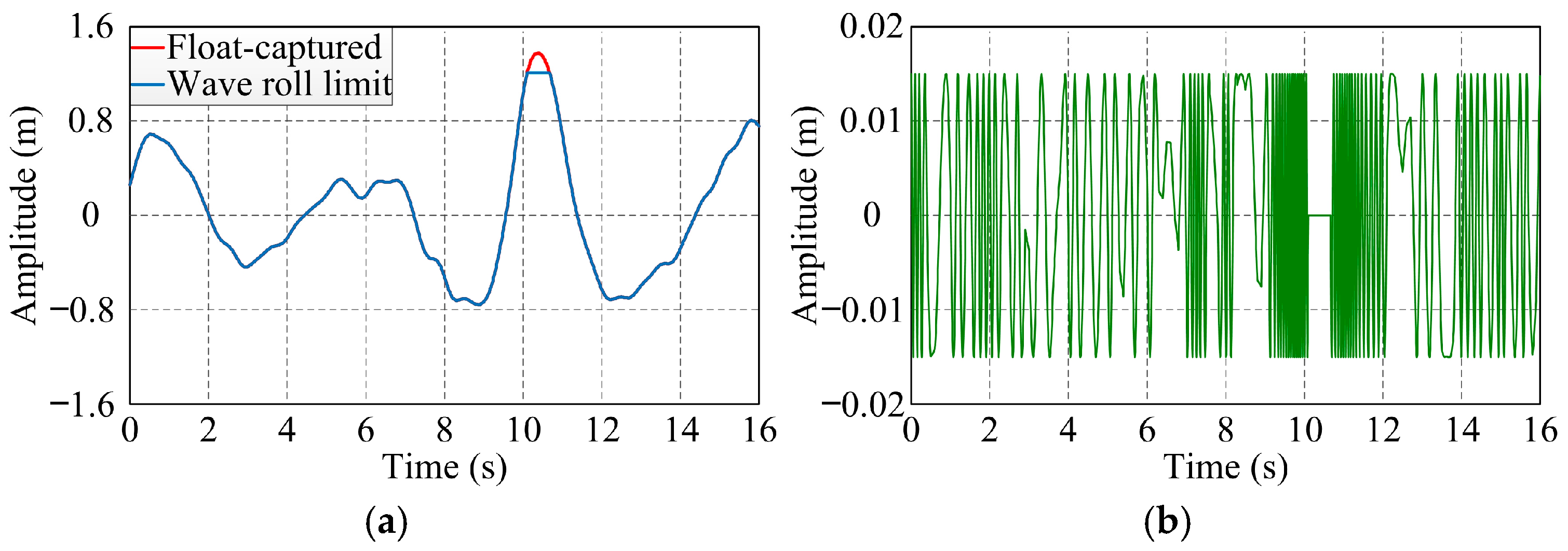
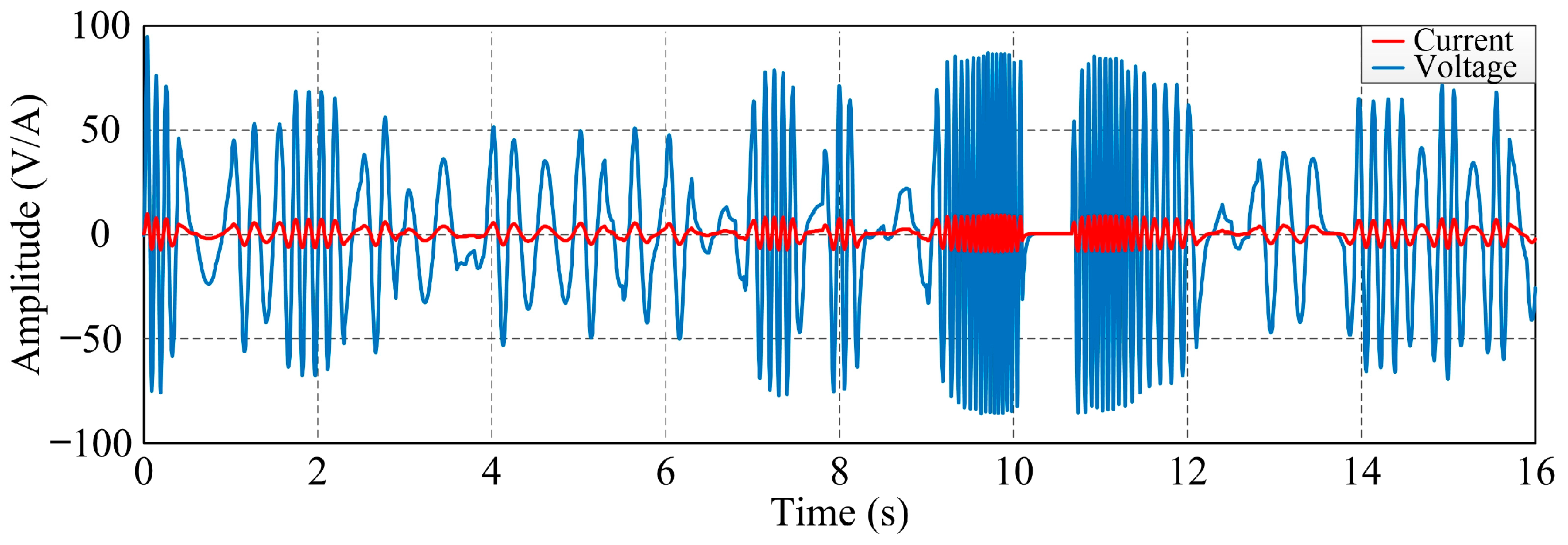
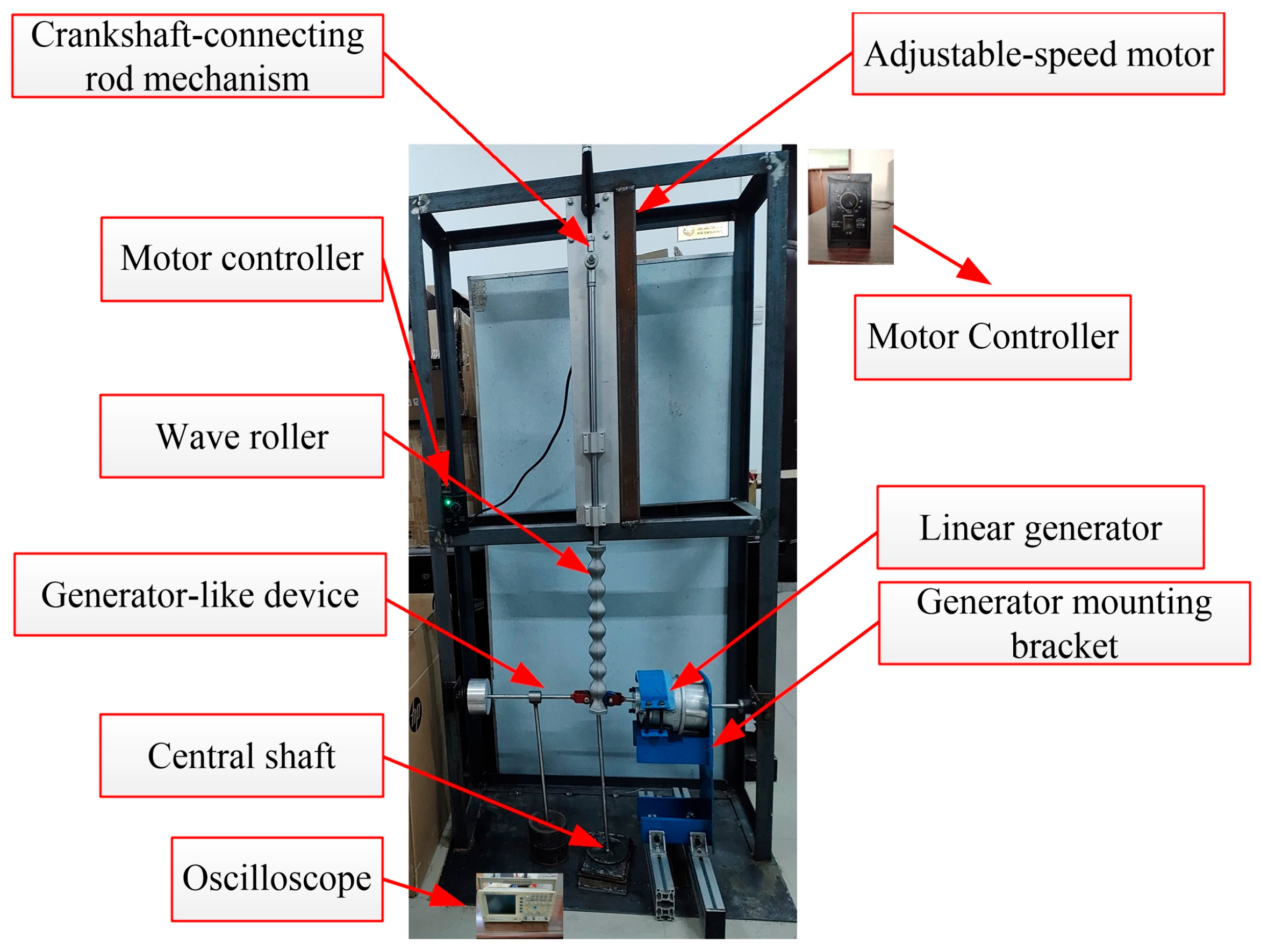
5. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, C.; Mao, H.Y.; You, Z.J.; Shi, H.Y.; Gao, S. Study on the distribution of wave energy resources in China and the applicability of wave energy generation device. Mar. Sci. 2018, 42, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.M.; Ma, C.L.; Chen, F.Y.; Liu, L.; Ge, Y.Z.; Peng, J.P.; Wu, H.Y.; Wang, Q.B. Exploitation and Technical Progress of Marine Renewable Energy. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2018, 36, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.X.; Wang, H.F.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.B. Reflections on the exploitation and utilization of marine renewable energy under the background of ocean power. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2018, 36, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Shen, M.H.; Ma, R.F.; Yang, H.S.; Chen, Y.N. Marine resource economy and strategy under the background of marine ecological civilization construction. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 829–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.B. Principle and Device of the Ocean Wave Energy Conversion; Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi, D.; Fernandes, J.; Falcão, A.; Bergmann, C. Analysis of the degradation in the Wells turbine blades of the Pico oscillating-water-column wave energy plant. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 115, 109368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, S.; Aggidis, G.A. Development of multi-oscillating water columns as wave energy converters. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 107, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.H. Overall design and optimization of dish overtopping wave energy generation system. Ship Sci. Technol. 2017, 39, 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Renzi, E.; Doherty, K.; Henry, A.; Dias, F. How does Oyster work? The simple interpretation of Oyster mathematics. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 2014, 47, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Sheng, S.W.; You, Y.G.; Wang, S.L.; Wang, Z.; Peng. Development Status and Application Direction of Wave Energy Generation Technology. Adv. New Renew. Energy 2019, 7, 374–378. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, B.; Vogel, C.; Willden, R.; Zang, J.; Zhang, L. Hydrodynamic performance of a floating breakwater as an oscillating-buoy type wave energy converter. Appl. Energy 2020, 257, 113996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.B.; Monteiro-Neto, C.; da Costa, M.R.; Martins, R.R.M.; dos Santos Vieira, F.C.; de Andrade-Tubino, M.F.; Bastos, A.L.; de Almeida Tubino, R. Size structure, reproduction, and growth of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) caught by the pole-and-line fleet in the southwest Atlantic. Fish. Res. 2019, 212, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Göteman, M. Real-time latching control strategies for the solo Duck wave energy converter in irregular waves. Appl. Energy 2018, 222, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R. Design, simulation, and testing of a novel hydraulic power take-off system for the Pelamis wave energy converter. Renew. Energy 2006, 31, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palha, A.; Mendes, L.; Fortes, C.J.; Brito-Melo, A.; Sarmento, A. The impact of wave energy farms in the shoreline wave climate: Portuguese pilot zone case study using Pelamis energy wave devices. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, S.L.; Wang, Z.P.; Lin, H.J.; Ye, Y. Research on Wave Energy Converter Sharp Eagle 1. Nav. Archit. Mar. Eng. Eng. 2015, 37, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, S.W.; Wang, S.L.; Lin, H.J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; You, Y.G.; Wang, Z.P. Open sea tests of 100 kw wave energy convertorsharp eagle wanshan. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2019, 40, 709–714. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Dong, S.L.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, B.C. Multi-physics coupling modeling method for the rolling-spherical triboelectric nanogenerator. Tribology 2020, 40, 680–686. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Wang, A.C.; Ding, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator: A foundation of the energy for the new era. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1802906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, Z.; Tang, G. Experimental study of the hydrodynamic performance of a U-oscillating water column wave energy converter. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 265, 112598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Bai, N.Z.; Kang, Q.; Nie, Z.X.; Huang, X.R. A Review of the Development of Wave Power System and the Research on Direct-Drive Wave Power System. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2014, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Research on Single-Phase Oscillating Permanent Magnet Linear Generator; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.Z.; Song, W.; Wang, Q.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, H.; Chen, B.Q. The wave height and period distribution characteristics around Bei Shuang Island in summer. Mar. Forecast. 2021, 38, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Xu, Z. Simulation of deep-water waves based on JONSWAP spectrum and realization by MATLAB. In Proceedings of the 2011 19th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Shanghai, China, 24–26 June 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Engström, J.; Kurupath, V.; Isberg, J.; Leijon, M. A resonant two body system for a point absorbing wave energy converter with direct-driven linear generator. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 124904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.T. Study on Hydrodynamics of Oscillating Float-Type Wave Energy Extractor; Zhejiang Ocean University: Zhoushan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter Name | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Spring constant/(N/mm) | k | 5.4 |
| Coil resistance/Ω | Rc | 20.9 |
| Number of coil turns/Turns | - | 640 |
| Enameled wire diameter/mm | dc | 0.5 |
| Mover stroke/mm | Xm | ±15.0 |
| Wave roller length/m | Lb | 1.2 |
| Wave roller stroke/m | Xw | ±1.2 |
| Roller radius/mm | Rw | 8 |
| Roller mass/kg | mr | 0.05 |
| Month | Significant Wave Height Range/m | Average Period/s | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.5 | 0.5~1.2 | 1.2~2.5 | >2.5 | 0~3 | 3~4 | 4~5 | 5~6 | >6 | |
| 6 | 8.08 | 23.38 | 1.16 | 0 | 0 | 13.35 | 16.95 | 2.30 | 0.02 |
| 7 | 14.95 | 15.86 | 2.71 | 0.25 | 0 | 16.54 | 13.08 | 3.66 | 0.48 |
| 8 | 7.46 | 23.36 | 2.80 | 0 | 0 | 2.43 | 14.99 | 10.96 | 5.23 |
| Overall | 30.48 | 62.60 | 6.67 | 0.25 | 0 | 32.32 | 45.02 | 16.92 | 5.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Liu, N.; Liu, X. Wave Energy Linear Generator System Including a Newly Designed Wave Roller Mechanical Interface. Actuators 2025, 14, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14030147
Chen H, Liu N, Liu X. Wave Energy Linear Generator System Including a Newly Designed Wave Roller Mechanical Interface. Actuators. 2025; 14(3):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14030147
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hongyue, Naisheng Liu, and Xianyang Liu. 2025. "Wave Energy Linear Generator System Including a Newly Designed Wave Roller Mechanical Interface" Actuators 14, no. 3: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14030147
APA StyleChen, H., Liu, N., & Liu, X. (2025). Wave Energy Linear Generator System Including a Newly Designed Wave Roller Mechanical Interface. Actuators, 14(3), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14030147





