Photo-Responsive Liquid Crystal Elastomer Coils Inspired by Tropism Movements of Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
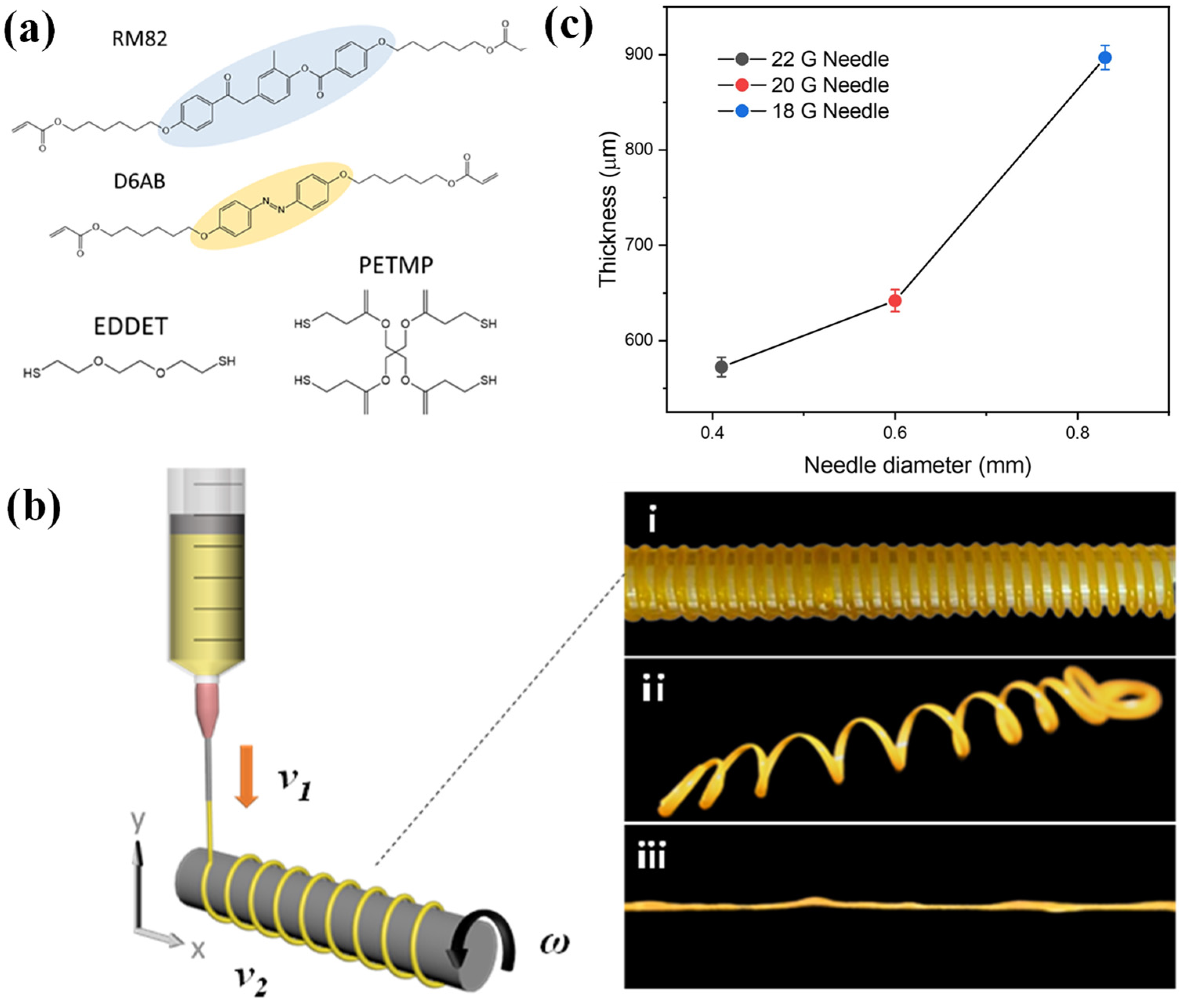
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the LCE Ink
2.3. Fabrication of the Coil-Shaped LC Oligomer
2.4. Fabrication of the LCE Coil
2.5. Sample Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection and Optimization of the LCE Ink
3.2. Effect of Extrusion Parameters on the Morphology of LCE Coil
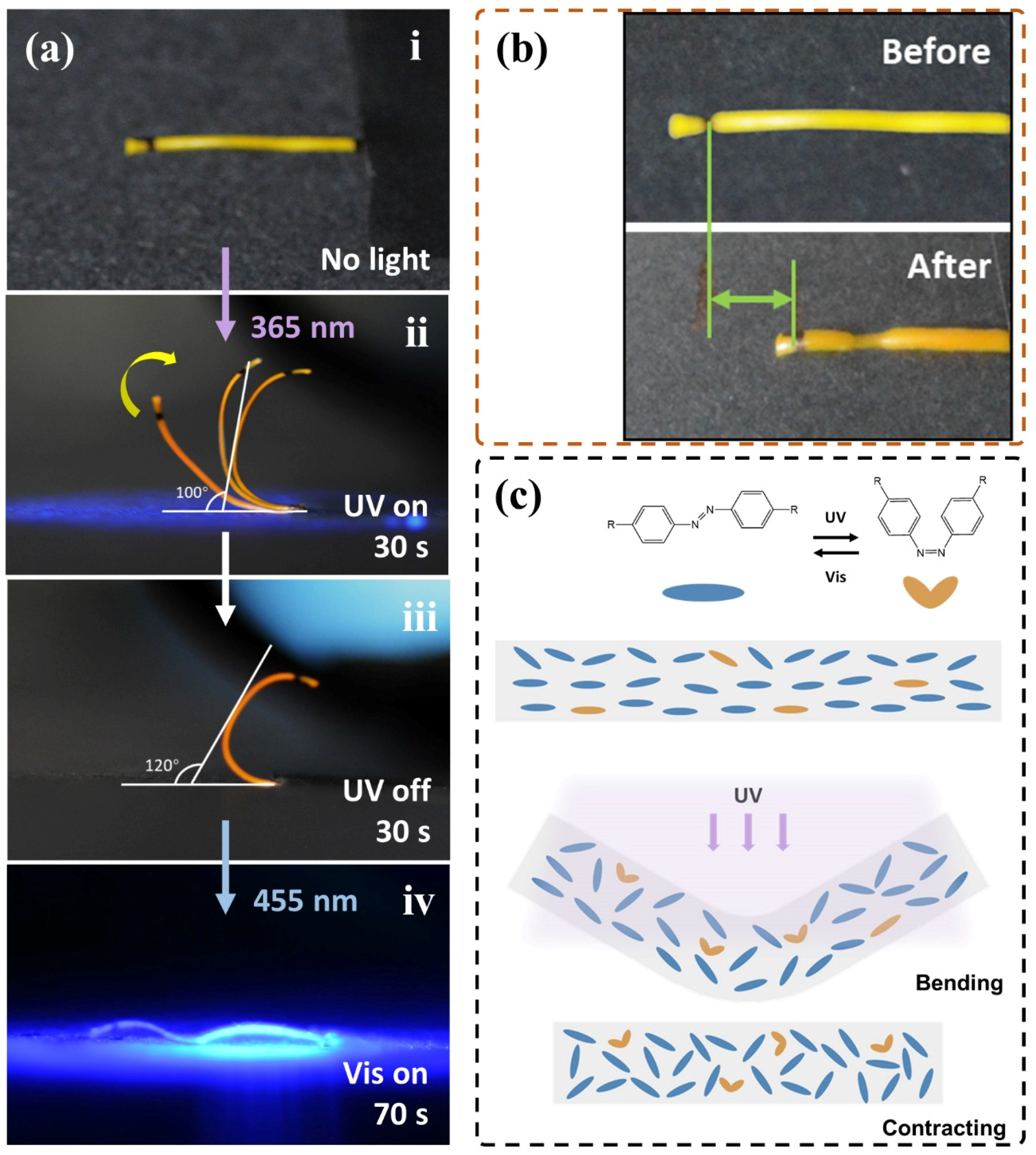
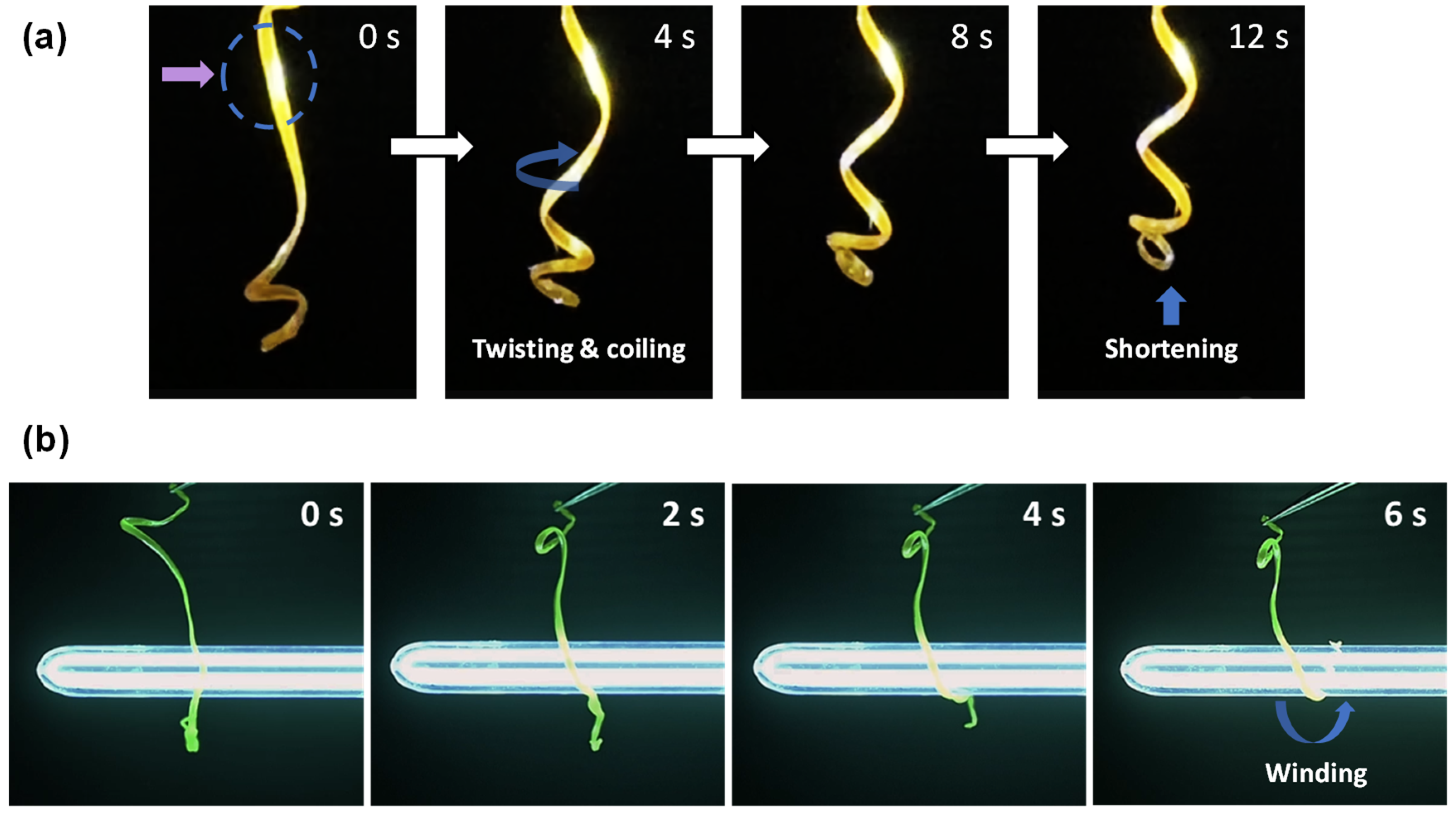
3.3. Photomechanical Response of the LCE Coil to UV Light
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Gilroy, S. Plant tropisms. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, R275–R277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gerbode, S.J.; Puzey, J.R.; McCormick, A.G.; Mahadevan, L. How the Cucumber Tendril Coils and Overwinds. Science 2012, 337, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, C.; Cho, M.; Ahn, S.-H. Soft Tendril-Inspired Grippers: Shape Morphing of Programmable Polymer–Paper Bilayer Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 10419–10427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, R.; Chan, K.H.; Lu, X.; Sun, J.; Ho, G.W. A Biomimetic Conductive Tendril for Ultrastretchable and Integratable Electronics, Muscles, and Sensors. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3898–3907. [Google Scholar]
- Must, I.; Sinibaldi, E.; Mazzolai, B. A variable-stiffness tendril-like soft robot based on reversible osmotic actuation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 344. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, J.; Zidek, T.; Harbel, C.; Yoon, S.; Strickland, F.S.; Kumar, S.; Shin, M. Soft Robotics: A Review of Recent Developments of Pneumatic Soft Actuators. Actuators 2020, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, S.; Golecki, H.M. Gelatin Soft Actuators: Benefits and Opportunities. Actuators 2023, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, G.; Yu, H. Ultraviolet-visible-near-infrared light-responsive soft materials: Fabrication, photomechanical deformation and applications. Responsive Mater. 2024, 2, e20240016. [Google Scholar]
- Tateyama, A.; Nakanishi, T. Responsive molecular liquid materials. Responsive Mater. 2023, 1, e20230001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.-G.; Li, Q. Multiple degrees-of-freedom programmable soft-matter-photonics: Configuration, manipulation, and advanced applications. Responsive Mater. 2024, 2, e20230029. [Google Scholar]
- McCracken, J.M.; Donovan, B.R.; White, T.J. Materials as Machines. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906564. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Ferrer, A. Liquid Crystal Elastomers: Materials and Applications; de Jeu, W.H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 23, pp. 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J. Mechanochromic Response of Spiropyran-Incorporated Liquid Crystalline Elastomer Network and the Mechanochromic Enhancement by Nano Zinc Oxide. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2300175. [Google Scholar]
- Ryabchun, A.; Li, Q.; Lancia, F.; Aprahamian, I.; Katsonis, N. Shape-Persistent Actuators from Hydrazone Photoswitches. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.K.; Ware, T.H.; Lee, K.M.; Tondiglia, V.P.; White, T.J. Photoinduced Topographical Feature Development in Blueprinted Azobenzene-Functionalized Liquid Crystalline Elastomers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 5819–5826. [Google Scholar]
- Pilz da Cunha, M.; Debije, M.G.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Bioinspired light-driven soft robots based on liquid crystal polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6568–6578. [Google Scholar]
- Ube, T.; Kawasaki, K.; Ikeda, T. Photomobile Liquid-Crystalline Elastomers with Rearrangeable Networks. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8212–8217. [Google Scholar]
- Wie, J.J.; Shankar, M.R.; White, T.J. Photomotility of polymers. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13260. [Google Scholar]
- Iamsaard, S.; Aßhoff, S.J.; Matt, B.; Kudernac, T.; Cornelissen, J.J.L.M.; Fletcher, S.P.; Katsonis, N. Conversion of light into macroscopic helical motion. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Lin, B.-P.; Yang, H. A plant tendril mimic soft actuator with phototunable bending and chiral twisting motion modes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13981. [Google Scholar]
- Aßhoff, S.J.; Lancia, F.; Iamsaard, S.; Matt, B.; Kudernac, T.; Fletcher, S.P.; Katsonis, N. High-Power Actuation from Molecular Photoswitches in Enantiomerically Paired Soft Springs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 3261–3265. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Nakano, M.; Ikeda, T. Directed bending of a polymer film by light. Nature 2003, 425, 145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sawa, Y.; Ye, F.; Urayama, K.; Takigawa, T.; Gimenez-Pinto, V.; Selinger, R.L.B.; Selinger, J.V. Shape selection of twist-nematic-elastomer ribbons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6364–6368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.M.; Bunning, T.J.; White, T.J. Autonomous, Hands-Free Shape Memory in Glassy, Liquid Crystalline Polymer Networks. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2839–2843. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liao, W.; Yang, Z. Liquid Crystal Elastomer Twist Fibers toward Rotating Microengines. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107840. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Yang, Z. Smart liquid crystal elastomer fibers. Matter 2025, 8, 101950. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, E.-H.; Luu, K.; Park, S.-Y. Mechano-Actuated Light-Responsive Main-Chain Liquid Crystal Elastomers. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 5397–5409. [Google Scholar]
- Luu, K.; Park, S.-Y. Shape-Persistent Liquid Crystal Elastomers with Cis-Stable Crosslinkers Containing Ortho-Methyl-Substituted Azobenzene. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, Z. Liquid Crystal Elastomer Hollow Fibers as Artificial Muscles with Large and Rapid Actuation Enabled by Thermal-Pneumatic Enhanced Effect. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2402403. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Urban, M.W. Recent advances and challenges in designing stimuli-responsive polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ambulo, C.P.; Burroughs, J.J.; Boothby, J.M.; Kim, H.; Shankar, M.R.; Ware, T.H. Four-dimensional Printing of Liquid Crystal Elastomers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 37332–37339. [Google Scholar]
- Kotikian, A.; Truby, R.L.; Boley, J.W.; White, T.J.; Lewis, J.A. 3D Printing of Liquid Crystal Elastomeric Actuators with Spatially Programed Nematic Order. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 30, 1706164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, D.J.; Yuan, C.; Kuang, X.; Li, V.C.; Blake, P.; Romero, M.L.; Hammel, I.; Yu, K.; Qi, H.J. Long Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fibers with Large Reversible Actuation Strains for Smart Textiles and Artificial Muscles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 19514–19521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Yang, Z. 3D printing programmable liquid crystal elastomer soft pneumatic actuators. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Annapooranan, R.; Zeng, J.; Chen, R.; Cai, S. Electrospun liquid crystal elastomer microfiber actuator. Sci. Rob. 2021, 6, eabi9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Wang, J.; Lv, J.A. Bioinspired Liquid Crystalline Spinning Enables Scalable Fabrication of High-Performing Fibrous Artificial Muscles. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2211800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelebart, A.H.; Mc Bride, M.; Schenning, A.P.H.J.; Bowman, C.N.; Broer, D.J. Photoresponsive Fiber Array: Toward Mimicking the Collective Motion of Cilia for Transport Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 5322–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Pozo, M.; Liu, L.; Pilz da Cunha, M.; Broer, D.J.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Direct Ink Writing of a Light-Responsive Underwater Liquid Crystal Actuator with Atypical Temperature-Dependent Shape Changes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Choi, S.; Lee, J.; Jung, J.; Yeo, J.; Kim, J.T.; Ryu, S.; Ahn, S.-K.; Kang, J.; Poulin, P.; et al. Human-muscle-inspired single fibre actuator with reversible percolation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wei, A.; Zhang, Y.; Mensah, A.; Yin, R.; Lv, P.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Q. Scalable functionalized liquid crystal elastomer fiber soft actuators with multi-stimulus responses and photoelectric conversion. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 2587–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; del Pozo, M.; Mohseninejad, F.; Debije, M.G.; Broer, D.J.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Light Tracking and Light Guiding Fiber Arrays by Adjusting the Location of Photoresponsive Azobenzene in Liquid Crystal Networks. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 2000732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, L.; Cao, X.; Xu, J.; Dai, S.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yuan, N.; Ding, J. Monodomain liquid crystal elastomer bionic muscle fibers with excellent mechanical and actuation properties. iScience 2023, 26, 106357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.-J.; Park, S.-Y. Effects of network structure of main-chain liquid crystal elastomer on its thermal actuation performance. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 110, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Kizhakidathazhath, R.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Robust cholesteric liquid crystal elastomer fibres for mechanochromic textiles. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Valenzuela, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Feng, W. Smart chiral liquid crystal elastomers: Design, properties and application. Smart Mol. 2024, 2, e20230025. [Google Scholar]
- del Pozo, M.; Sol, J.A.H.P.; Schenning, A.P.H.J.; Debije, M.G. 4D Printing of Liquid Crystals: What’s Right for Me? Adv. Mater. 2021, 34, 2104390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakacki, C.M.; Nair, D.P.; Torbati, A.H.; Saed, M.O. Synthesis of Programmable Main-chain Liquid-crystalline Elastomers Using a Two-stage Thiol-acrylate Reaction. J Vis Exp. 2016, 107, e53546. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cai, S. Three-dimensional printing of functionally graded liquid crystal elastomer. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc0034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ikeda, T. Soft Actuators Based on Liquid-Crystalline Elastomers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5416–5418. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino, T.; Kondo, M.; Mamiya, J.I.; Kinoshita, M.; Yu, Y.; Ikeda, T. Three-Dimensional Photomobility of Crosslinked Azobenzene Liquid-Crystalline Polymer Fibers. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1361–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, H.; Fei, G.; Yu, B.; Tong, X.; Xia, H.; Zhao, Y. Liquid-Crystalline Dynamic Networks Doped with Gold Nanorods Showing Enhanced Photocontrol of Actuation. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Norikane, Y.; Azumi, R.; Koyama, E. Light-induced mechanical response in crosslinked liquid-crystalline polymers with photoswitchable glass transition temperatures. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lugger, S.J.D.; Ceamanos, L.; Mulder, D.J.; Sánchez-Somolinos, C.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. 4D Printing of Supramolecular Liquid Crystal Elastomer Actuators Fueled by Light. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 8, 2201472. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, M.; Yu, Y.L.; Ikeda, T. How does the initial alignment of mesogens affect the photoinduced bending behavior of liquid-crystalline elastomers? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1378–1382. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J.; Broer, D.J. Programmable and adaptive mechanics with liquid crystal polymer networks and elastomers. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, T.; Mamiya, J.I.; Yu, Y. Photomechanics of Liquid-Crystalline Elastomers and Other Polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 506–528. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J. Photomechanical Effects in Liquid-Crystalline Polymer Networks and Elastomers. In Photomechanical Materials, Composites, and Systems; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 153–177. [Google Scholar]
- Dattler, D.; Fuks, G.; Heiser, J.; Moulin, E.; Perrot, A.; Yao, X.; Giuseppone, N. Design of Collective Motions from Synthetic Molecular Switches, Rotors, and Motors. Chem. Rev. 2019, 120, 310–433. [Google Scholar]
- Beharry, A.A.; Woolley, G.A. Azobenzene photoswitches for biomolecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4422. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, X.; Ran, Z.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, K.-L. Photo-Responsive Liquid Crystal Elastomer Coils Inspired by Tropism Movements of Plants. Actuators 2025, 14, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14040171
Zhan X, Ran Z, Li J, Zhu J, Zhang Z, Yang K-L. Photo-Responsive Liquid Crystal Elastomer Coils Inspired by Tropism Movements of Plants. Actuators. 2025; 14(4):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14040171
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Xiyun, Zhiyu Ran, Jiajun Li, Jiaqi Zhu, Zhibo Zhang, and Kun-Lin Yang. 2025. "Photo-Responsive Liquid Crystal Elastomer Coils Inspired by Tropism Movements of Plants" Actuators 14, no. 4: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14040171
APA StyleZhan, X., Ran, Z., Li, J., Zhu, J., Zhang, Z., & Yang, K.-L. (2025). Photo-Responsive Liquid Crystal Elastomer Coils Inspired by Tropism Movements of Plants. Actuators, 14(4), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14040171






