Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Brucellosis in European Terrestrial and Marine Wildlife Species and Its Regional Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
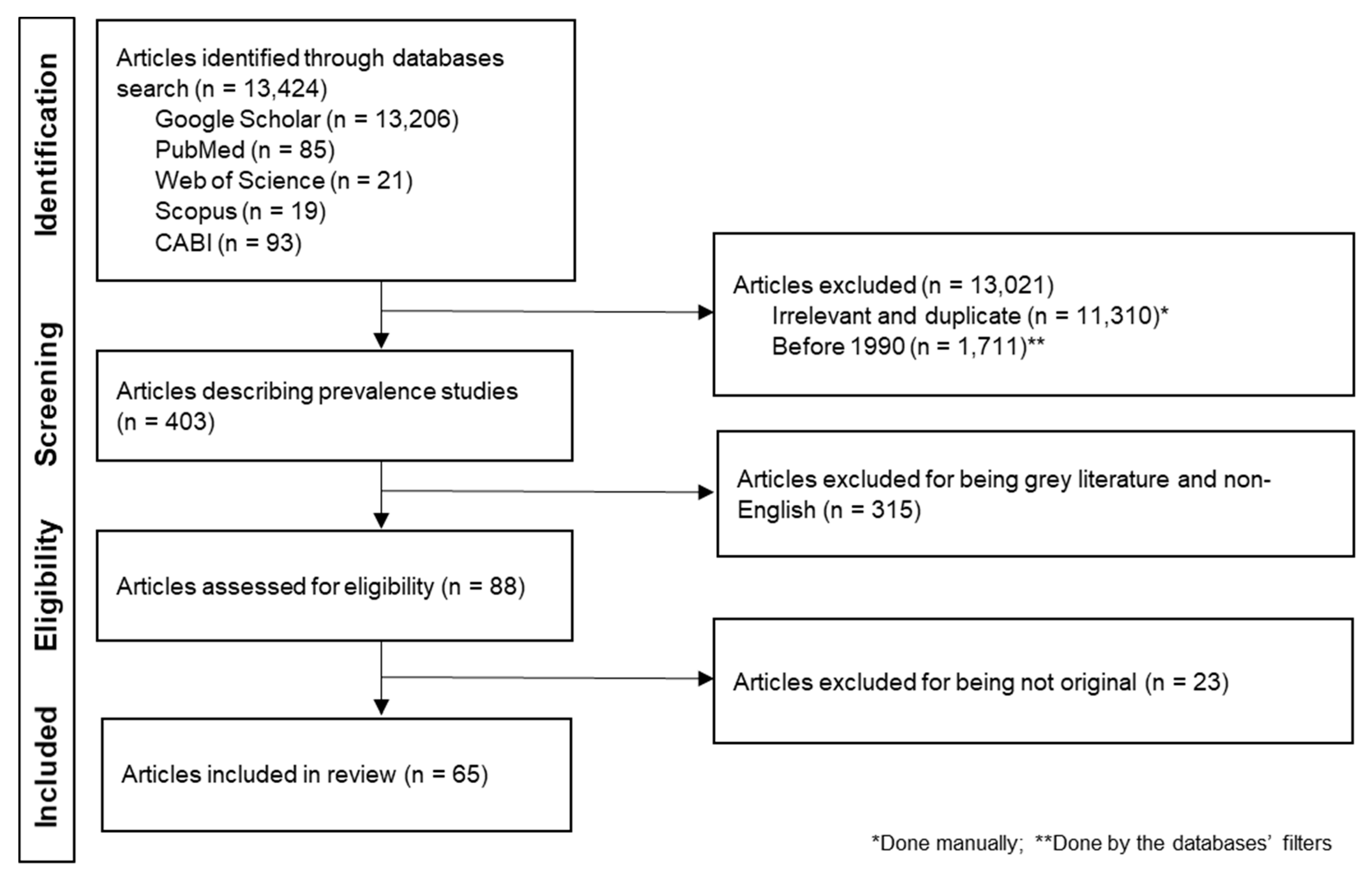
2.1. Literature Source and Search Strategy
2.2. Data Acquisition and Analysis
3. Results
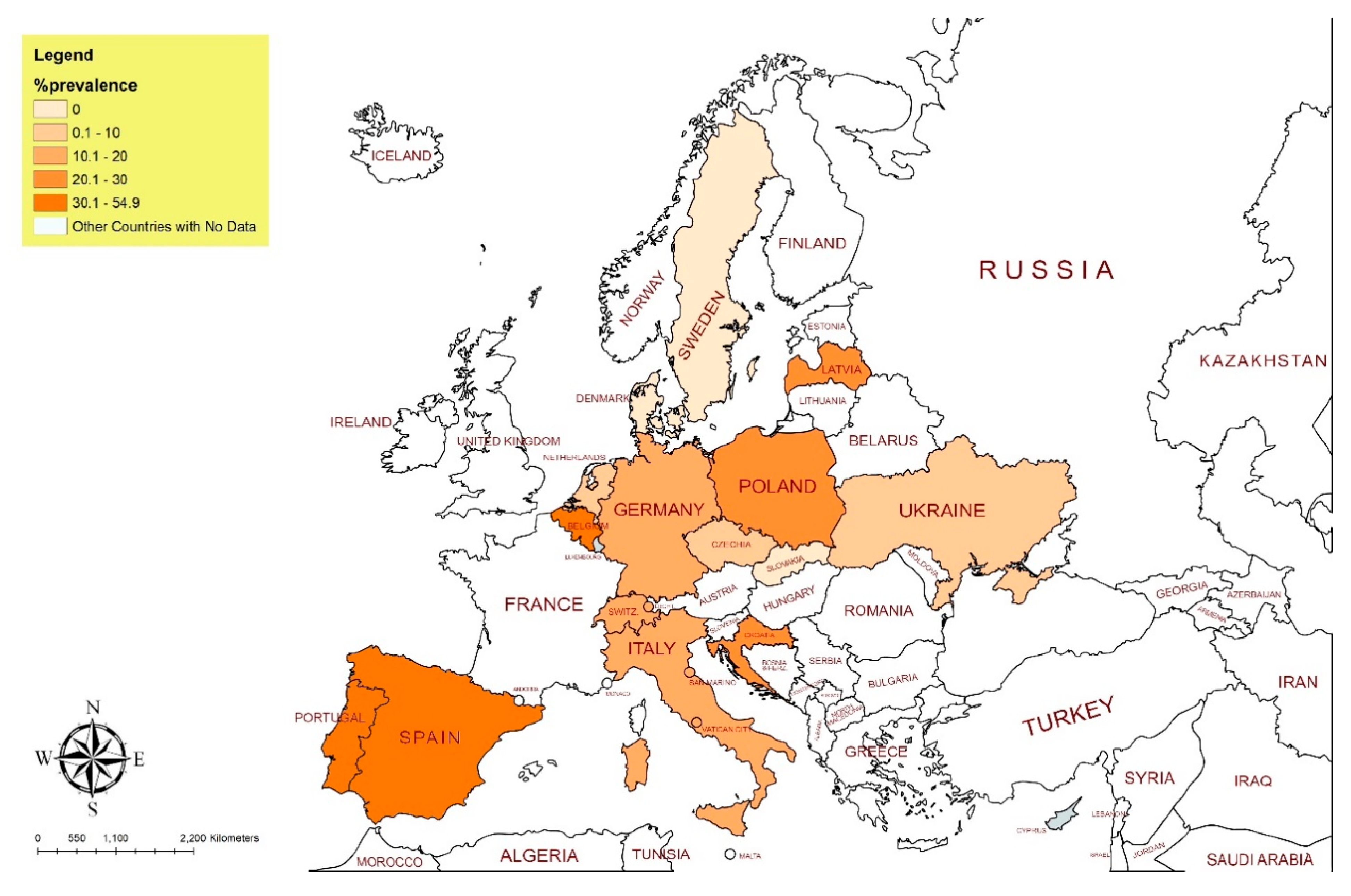
3.1. Data Analysis
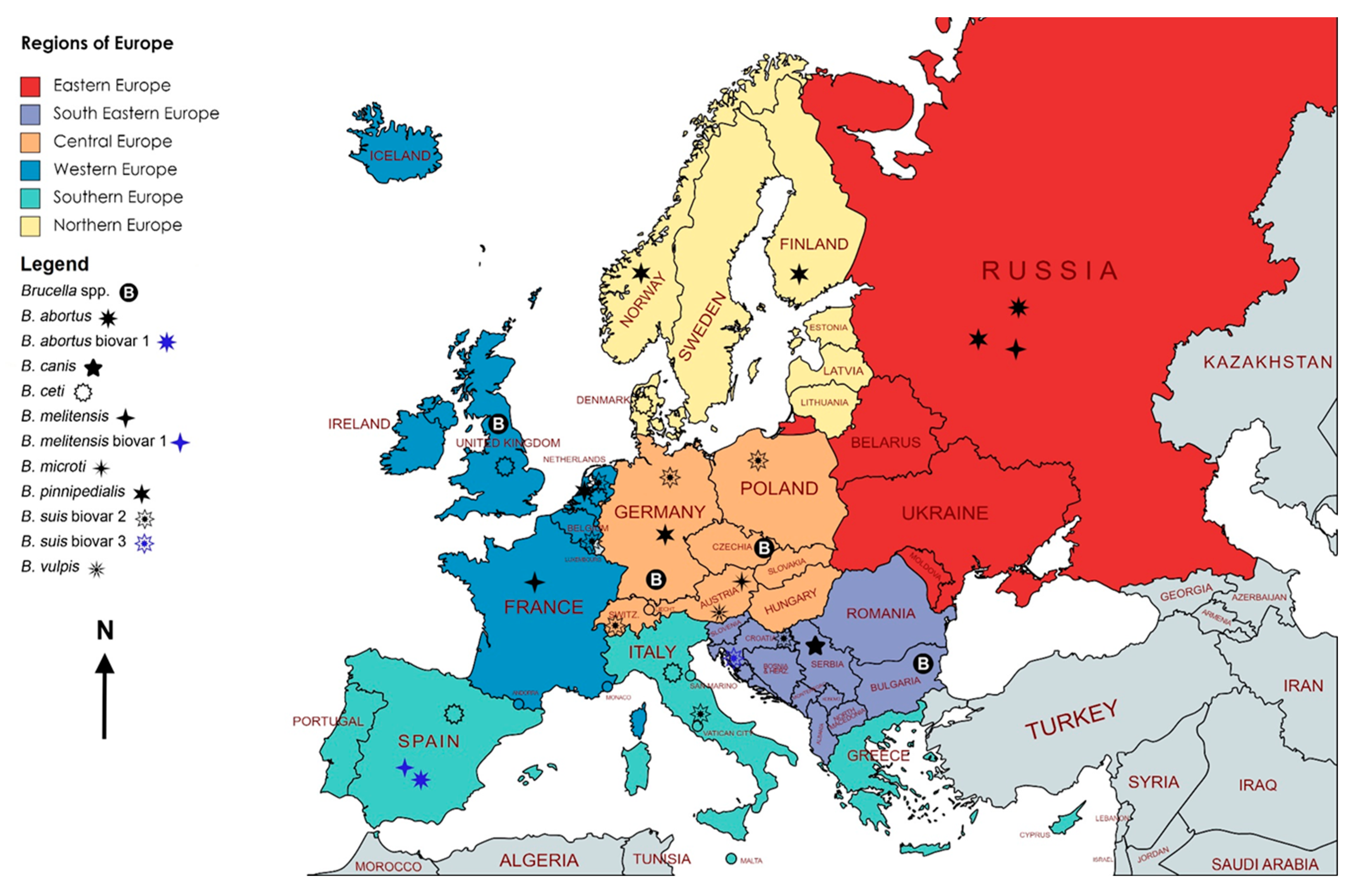
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Brucellosis in European Terrestrial Wildlife
3.2.1. Eastern and South-Eastern Europe
3.2.2. Central Europe
3.2.3. Northern Europe
3.2.4. Southern Europe
3.2.5. Western Europe
3.2.6. Special Territories
| No. | Countries | Region | Host | Serology | Molecular Identification | Citation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Tested | No. Positive | %Prev. | ||||||
| 1 | Ukraine | Eastern Europe | Wild boars | 1344 | 67 | 4.98 | [31] | |
| 2 | Croatia | South-Eastern Europe | Wild boars | 264 | 74 | 28.03 | B. suis bv 2 | [32] |
| 424 | 98 | 23.11 | B. suis bv 2 and bv 3 | [29] | ||||
| 3 | Serbia | Golden Jackals | 216 | -- | -- | B. canis | [30] | |
| 4 | Bulgaria | Wild birds | 706 | -- | -- | Brucella spp. | [33] | |
| 5 | Slovenia | Wild boars | 178 | 0 | 0 | [34] | ||
| 6 | Austria | Central Europe | Red foxes | B. microti | [52] | |||
| B. vulpis | [7] | |||||||
| Brown hare | 311 | 11 | 3.54 | [24] | ||||
| 7 | Czech Republic | Wild boars | 204 | 18 | 8.7 | [42] | ||
| 32 | 2 | 6.25 | [41] | |||||
| Brown hare | 73 | 0 | 0 | [24] | ||||
| 1051 | 17 | 1.62 | [44] | |||||
| 23 | 0 | 0 | [41] | |||||
| Roe deer | 33 | 0 | 0 | [41] | ||||
| Red deer | 24 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Fallow deer | 4 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Mouflon | 2 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Common vole | 4 | -- | -- | Brucella spp. | [47] | |||
| 8 | Germany | Wild boars | 763 | 168 | 22.02 | [39] | ||
| 885 | 107 | 12.09 | [40] | |||||
| Brown hare | 321 | 0 | 0 | [45] | ||||
| Shrews | 113 | 9 | 7.96 | Brucella spp. | [46] | |||
| Voles | 295 | 45 | 15.25 | |||||
| Mouse | 129 | 22 | 17.05 | |||||
| 9 | Poland | European bison | 60 | 0 | 0 | [48] | ||
| 122 | 0 | 0 | [49] | |||||
| 240 | 0 | 0 | [51] | |||||
| Deer | 183 | -- | -- | No isolate was achieved | [50] | |||
| Wild boars | 235 | -- | -- | B. suis bv 2 | ||||
| 4407 | 1077 | 24.44 | [38] | |||||
| 10 | Switzerland | Wild boars | 810 | 90 | 11.05 | No isolate was achieved | [36] | |
| * 611 | 27 | 4.42 | B. suis bv 2 | [37] | ||||
| + 1215 | 153 | 12.59 | ||||||
| ± 462 | 66 | 14.28 | ||||||
| 240 | 86 | 35.83 | [35] | |||||
| 11 | Denmark | Northern Europe | Wild boars | 240 | 0 | 0 | [55] | |
| 12 | Latvia | Wild boars | 1044 | 235 | 22.51 | B. suis bv 2 | [53] | |
| 13 | Norway | Reindeer | 5792 | 0 | 0 | [56] | ||
| 14 | Sweden | Wild boars | 286 | 0 | 0 | [54] | ||
| 15 | Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) | Southern Europe | Barbary sheep | 8 | 0 | 0 | [26] | |
| Mouflon | 75 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Iberian wild goat | 1086 | 1 | 0.09 | B. melitensis bv 1 | ||||
| Chamois | 1410 | 11 | 0.78 | |||||
| Roe deer | 285 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Fallow deer | 342 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Red deer | 5821 | 19 | ≤0.4 | B. abortus bv 1 | ||||
| Wild boars | 4454 | 1470 | 33 | B. suis bv 2 | ||||
| 16 | Italy | Wild boars | 570 | 35 | 6.1 | [58] | ||
| Wild boars | 2267 | 448 | 19.76 | B. suis bv 2 | [57] | |||
| Brown bears | 22 | 2 | 9.09 | [62] | ||||
| Wild boars | 389 | -- | -- | B. suis bv 2 | [59] | |||
| Wild boars | 434 | 58 | 13.5 | [60] | ||||
| Wild Birds | 121 | [63] | ||||||
| Wild boars | 287 | 16 | 5.74 | B. suis bv 2 | [61] | |||
| 17 | Belgium | Western Europe | Wild boars | 1168 | 641 | 54.88 | B. suis bv 2 | [65] |
| 18 | France | Roe deer | 44 | [27] | ||||
| Red deer | 30 | 1 | ||||||
| Chamois | 55 | 1 | B. melitensis | |||||
| Alpine ibex | 24 | 12 | ||||||
| Alpine ibex | 339 | 88 | B. melitensis | [28] | ||||
| 19 | Netherlands | Wild boars | 2057 | 131 | 6.36 | B. suis bv 2 | [66] | |
| 20 | Greenland | Special territory | Polar bears | 96 | 6 | 6.25 | [67] | |
| Greenland muskoxen | 32 | 0 | 0 | |||||
3.3. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Brucellosis in European Marine Wildlife
3.3.1. Eastern and South-Eastern Europe
3.3.2. Central Europe
3.3.3. Northern Europe
3.3.4. Southern Europe
3.3.5. Western Europe
| No. | Countries | Region | Host | Serology | Molecular Identification | Citation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Tested | No. Positive | % Prevalence | ||||||
| 1 | Russia | Eastern Europe | Sea otters | 78 | -- | -- | B. abortus, B. melitensis and B. pinnipedialis | [68] |
| Caspian seals | 71 | 4 | 5.63 | [69] | ||||
| Baikal seals | 7 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Ringed seals | 6 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Beluga whales | 4 | 3 | 75 | |||||
| 2 | Croatia | South-Eastern Europe | Bottlenose dolphins | 4 | -- | -- | B. ceti ST27 | [70] |
| 3 | Germany | Central Europe | Harbor seals | 2105 | -- | -- | B. pinnipedialis | [72] |
| Common seals | 426 | B. pinnipedialis | [71] | |||||
| Harbor porpoises | 298 | |||||||
| Grey seals | 34 | |||||||
| Hooded seals | 3 | |||||||
| Common dolphins | 3 | |||||||
| White-beaked dolphin | 1 | |||||||
| Ringed seal | 1 | |||||||
| Pilot whale | 1 | |||||||
| Minke whale | 1 | |||||||
| 6 | Finland | Northern Europe | Grey seals | 122 | -- | -- | B. pinnipedialis | [75] |
| 5 | Norway | Harp and hooded seals | 9 | 0 | 0 | [25] | ||
| Hooded seals | 379 | 59 | 15.57 | B. pinnipedialis | [74] | |||
| Hooded seals | 29 | 9 | 31.03 | B. pinnipedialis | [73] | |||
| Ringed seals | 20 | 0 | 0 | No isolate was achieved | ||||
| 6 | Sweden | Ringed seals | 12 | 2 | 16.67 | [25] | ||
| Harp seals | 6 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Hooded seals | 3 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| 7 | Spain | Southern Europe | Striped dolphins | 2 | 2 | B. ceti | [77] | |
| Bottlenose dolphin | 1 | 1 | B. ceti | |||||
| Striped dolphins | 16 | 2 | 12.5 | [76] | ||||
| Risso’s dolphins | 4 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Bottlenose dolphins | 2 | 1 | 50 | |||||
| Short-beaked common dolphin | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Fin whale | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| 8 | Italy | Striped dolphins | 8 | 1 | 12.5 | B. ceti | [78] | |
| 9 | Netherlands | Western Europe | Wild grey seals | 11 | 1 | 9.09 | [80] | |
| Harbor seals | 40 | 16 | 40 | B. pinnipedialis | ||||
| Porpoises | 112 | -- | -- | B. ceti ST23 | [79] | |||
| 10 | UK | Common seals | 140 | 69 | Brucella spp. | [81] | ||
| Harbor porpoise | 18 | 5 | ||||||
| Baikal seals | 45 | 0 | ||||||
| Grey seals | 31 | 10 | ||||||
| Common dolphin | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Atlantic white-sided dolphin | 1 | Brucella spp. | [82] | |||||
| Striped dolphin | 2 | |||||||
| Hooded seal | 1 | |||||||
| Grey seal | 1 | |||||||
| European otter | 1 | |||||||
| Bottlenose dolphin | 1 | Brucella spp. | [89] | |||||
| Grey seal | 62 | 6 | 9.68 | [83] | ||||
| Common seal | 12 | 1 | 8.33 | |||||
| Harbor porpoise | 35 | 11 | 31.42 | |||||
| Common dolphin | 29 | 9 | 31.03 | |||||
| Striped dolphin | 4 | 1 | 25 | |||||
| White-beaked dolphin | 4 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Atlantic white-sided dolphin | 2 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Bottlenose dolphin | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Pilot whale | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Risso’s dolphin | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Killer whale | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Blainville’s beaked whale | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Long-finned pilot whale | 1 | B. ceti | [84] | |||||
| Sowerby’s beaked whale | 10 | B. ceti | ||||||
| Harbor seals | 343 | 87 | 25.36 | Brucella spp. | [85] | |||
| Risso’s dolphin | 1 | -- | -- | B. ceti | [86] | |||
| Killer whale | 1 | -- | -- | |||||
| Common minke whale | 1 | B. ceti | [87] | |||||
| 11 | North Atlantic Ocean | Harp seals | 811 | 15 | 1.85 | [88] | ||
| Hooded seals | 137 | 48 | 35.04 | |||||
| Ringed seal | 49 | 5 | 10.20 | |||||
| Bearded seal | 16 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Fin whale | 108 | 12 | 11.11 | |||||
| Sei whale | 49 | 7 | 14.28 | |||||
| Minke whale | 216 | 17 | 7.87 | Brucella spp. | ||||
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dadar, M.; Shahali, Y.; Fakhri, Y.; Godfroid, J. The global epidemiology of Brucella infections in terrestrial wildlife: A meta-analysis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.-F.; Gong, Q.-L.; Zhao, B.; Ma, B.-Y.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.-H.; Wang, Q.; Leng, X.; Zong, Y.; et al. Seroprevalence of brucellosis in buffalo worldwide and associated risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, G.; Osterman, B.; Godfroid, J.; Jacques, I.; Cloeckaert, A. Brucella ceti sp. nov. and Brucella pinnipedialis sp. nov. for Brucella strains with cetaceans and seals as their preferred hosts. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2688–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, H.; Nockler, K.; Gollner, C. Brucella inopinata sp. nov., isolated from a breast implant infection. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, H.; Hubalek, Z.; Sedlácek, I.; Vergnaud, G.; Tomaso, H.; Al Dahouk, S.; Melzer, F.; Kämpfer, P.; Neubauer, H.; Cloeckaert, A.; et al. Brucella microti sp. nov. isolated from the common vole Microtus arvalis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whatmore, A.; Davison, N.; Cloeckaert, A.; Al Dahouk, S.; Zygmunt, M.; Brew, S.; Perrett, L.; Koylass, M.; Vergnaud, G.; Quance, C.; et al. Brucella papionis sp. nov. isolated from baboons (Papio spp.). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 4120–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, H.C.; Revilla-Fernandez, S.; Al Dahouk, S.; Hammerl, J.A.; Zygmunt, M.S.; Cloeckaert, A.; Koylass, M.; Whatmore, A.M.; Blom, J.; Vergnaud, G.; et al. Brucella vulpis sp. nov., isolated from mandibular lymph nodes of red foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 2090–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Huang, Y.E.; Chen, J.Y.; Lai, C.H.; Mao, Y.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Liu, P.Y. Genomics of Ochrobactrum pseudogrignonense (newly named Brucella pseudogrignonensis) reveals a new blaOXA subgroup. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.P.; Pembroke, J.T. The Genus Ochrobactrum as major opportunistic pathogens. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, K.; Tatar, F.; Schmoock, G.; Wareth, G.; Neubauer, H.; Erganįs, O. Tracking the diversity and Mediterranean lineage of Brucella melitensis isolates from different animal species in Turkey using MLVA-16 genotyping. Ger. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 2, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.K.; Sehrawat, A.; Tiwari, R.; Prasad, M.; Gulati, B.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Chhabra, R.; Karthik, K.; Patel, S.K.; Pathak, M. Bovine brucellosis–a comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 2021, 41, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Ghani, S.R.; Azit, N.A.; Mohd Fadzil, S.; Pang, N.T.P.; Rahim, S.S.S.A.; Hassan, M.R.; Jeffree, M.S. Risk factors and outbreak management of brucellosis in Asia: A meta-analysis. Infektološki Glas. 2021, 41, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareth, G.; Dadar, M.; Ali, H.; Hamdy, M.E.R.; Al-Talhy, A.M.; Elkharsawi, A.R.; Tawab, A.; Neubauer, H. The perspective of antibiotic therapeutic challenges of brucellosis in the Middle East and North African (MENA) countries: Current situation and therapeutic management. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e1253–e1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elrashedy, A.; Gaafer, M.; Mousa, W.; Nayel, M.; Salama, A.; Zaghawa, A.; Elsify, A.; Dawood, A.S. Immune response and recent advances in diagnosis and control of brucellosis. Ger. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 2, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolzaya, B.; Selenge, T.; Narangarav, T.; Gantsetseg, D.; Erdenechimeg, D.; Zinsstag, J.; Schelling, E. Representative seroprevalences of human and livestock brucellosis in two Mongolian provinces. EcoHealth 2014, 11, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Granados, L.M.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D.G.; Zambrano-Varon, J.L.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Brucellosis in Colombia: Current status and challenges in the control of an endemic disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri Nejad, R.; Krecek, R.C.; Khalaf, O.H.; Hailat, N.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Brucellosis in the Middle East: Current situation and a pathway forward. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfroid, J.; Käsbohrer, A. Brucellosis in the European Union and Norway at the turn of the twenty-first century. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 90, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union One Health 2020 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06971. [Google Scholar]
- Wareth, G.; Abdeen, A.; Ali, H.; Bardenstein, S.; Blasco, J.M.; Cardoso, R.; Corrêa De Sá, M.I.; Cvetnić, Ž.; de Massis, F.; El-Diasty, M.; et al. Brucellosis in the Mediterranean Countries: History, Prevalence, Distribution, Current Situation and Attempts at Surveillance and Control; World Organization for Animal Health (OIE): Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Buhmann, G.; Paul, F.; Herbst, W.; Melzer, F.; Wolf, G.; Hartmann, K.; Fischer, A. Canine brucellosis: Insights into the epidemiologic situation in Europe. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahir, Y.; Al-Farsi, A.; Al-Marzooqi, W.; Al-Toobi, A.; Gaafar, O.M.; Jay, M.; Corde, Y.; Bose, S.; Al-Hamrashdi, A.; Al-Kharousi, K.; et al. Investigation on Brucella infection in farm animals in Saham, Sultanate of Oman with reference to human brucellosis outbreak. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mick, V.; Le Carrou, G.; Corde, Y.; Game, Y.; Jay, M.; Garin-Bastuji, B. Brucella melitensis in France: Persistence in wildlife and probable spillover from Alpine Ibex to domestic animals. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelmayer, R.; Vodnansky, M.; Paulsen, P.; Gansterer, A.; Treml, F. Explorative study on the seroprevalence of Brucella-, Francisella-and Leptospira antibodies in the European hare (Lepus europaeus Pallas) of the Austrian-Czech border region. Wien. Tierarztl. Mon. 2005, 92, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Sonne, C.; Andersen-Ranberg, E.; Rajala, E.L.; Agerholm, J.S.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.; Desforges, J.-P.; Eulaers, I.; Jenssen, B.M.; Koch, A.; Rosing-Asvid, A. Seroprevalence for Brucella spp. in Baltic ringed seals (Phoca hispida) and East Greenland harp (Pagophilus groenlandicus) and hooded (Cystophora cristata) seals. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2018, 198, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, P.M.; Boadella, M.; Arnal, M.; de Miguel, M.J.; Revilla, M.; Martínez, D.; Vicente, J.; Acevedo, P.; Oleaga, Á.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; et al. Spatial distribution and risk factors of brucellosis in Iberian wild ungulates. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garin-Bastuji, B.; Hars, J.; Drapeau, A.; Cherfa, M.-A.; Game, Y.; Le Horgne, J.-M.; Rautureau, S.; Maucci, E.; Pasquier, J.-J.; Jay, M. Reemergence of Brucella melitensis infection in wildlife, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, S.; Gilot-Fromont, E.; Freycon, P.; Thébault, A.; Game, Y.; Toïgo, C.; Petit, E.; Barthe, M.-N.; Reynaud, G.; Jaÿ, M. High shedding potential and significant individual heterogeneity in naturally-infected Alpine ibex (Capra ibex) with Brucella melitensis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvetnic, Z.; Spicic, S.; Toncic, J.; Majnaric, D.; Benic, M.; Albert, D.; Thiebaud, M.; Garin-Bastuji, B. Brucella suis infection in domestic pigs and wild boar in Croatia. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2009, 28, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirović, D.; Chochlakis, D.; Tomanović, S.; Sukara, R.; Penezić, A.; Tselentis, Y.; Psaroulaki, A. Presence of Leishmania and Brucella species in the golden jackal Canis aureus in Serbia. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 728516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyskun, A.; Polishchuk, O.; Piankivska, I.; Pyskun, O.; Moroz, O.; Pishchanskyi, O.; Aliekseieva, H. Presence of antibodies against Brucella spp. in serum samples from wild boars in Ukraine. Porc. Res. 2019, 9, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetnic, Z.; Mitak, M.; Ocepek, M.; Lojkic, M.; Terzic, S.; Jemersic, L.; Humski, A.; Habrun, B.; Sostaric, B.; Brstilo, M.; et al. Wild boars (Sus scrofa) as reservoirs of Brucella suis biovar 2 in Croatia. Acta Vet. Hung. 2003, 51, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najdenski, H.; Dimova, T.; Zaharieva, M.M.; Nikolov, B.; Petrova-Dinkova, G.; Dalakchieva, S.; Popov, K.; Hristova-Nikolova, I.; Zehtindjiev, P.; Peev, S.; et al. Migratory birds along the Mediterranean—Black Sea Flyway as carriers of zoonotic pathogens. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018, 64, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengust, G.; Valencak, Z.; Bidovec, A. A serological survey of selected pathogens in wild boar in Slovenia. J. Vet. Med. B 2006, 53, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Abril, C.; Hinicacute, V.; Brodard, I.; Thür, B.; Fattebert, J.; Hüssy, D.; Ryser-Degiorgis, M.-P. Free-ranging wild boar: A disease threat to domestic pigs in Switzerland? J. Wildl. Dis. 2011, 47, 868–879, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köppel, C.; Knopf, L.; Ryser, M.P.; Miserez, R.; Thür, B.; Stärk, K.D.C. Serosurveillance for selected infectious disease agents in wild boars (Sus scrofa) and outdoor pigs in Switzerland. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2007, 53, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuenberger, R.; Boujon, P.; Thür, B.; Miserez, R.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Rüfenacht, J.; Stärk, K.D.C. Prevalence of classical swine fever, Aujeszky’s disease and brucellosis in a population of wild boar in Switzerland. Vet. Rec. 2007, 160, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulowski, K.; Iwaniak, W.; Zlotnicka, J.; Da, M.S.; Weiner, M.; Lipowski, A.; Jablonski, A. Survey of the anti-Brucella antibody status determined by ELISA testing in wild boars in Poland. Med. Weter 2015, 71, 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Al Dahouk, S.; Nöckler, K.; Tomaso, H.; Splettstoesser, W.D.; Jungersen, G.; Riber, U.; Petry, T.; Hoffmann, D.; Scholz, H.C.; Hensel, A.; et al. Seroprevalence of brucellosis, tularemia, and yersiniosis in wild boars (Sus scrofa) from north-eastern Germany. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2005, 52, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzer, F.; Lohse, R.; Nieper, H.; Liebert, M.; Sachse, K. A serological study on brucellosis in wild boars in Germany. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2006, 53, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubálek, Z.; Juticová, Z.; Svobodová, Š.; Halouzka, J. A Serologic survey for some bacterial and viral zoonoses in game animals in the Czech Republic. J. Wildl. Dis. 1993, 29, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubálek, Z.; Treml, F.; Juricova, Z.; Hunady, M.; Halouzka, J.; Janik, V.; Bill, D. Serological survey of the wild boar (Sus scrofa) for tularaemia and brucellosis in South Moravia, Czech Republic. Vet. Med. Praha 2002, 47, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulowski, K.; Iwaniak, W.; Weiner, M.; Zlotnicka, J. Characteristics of Brucella strains isolated from animals in Poland. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 16, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treml, F.; Pikula, J.; Bandouchova, H.; Horakova, J. European brown hare as a potential source of zoonotic agents. Vet. Med. Praha 2007, 52, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandölich, K.; Wisser, J.; Schmüser, H.; Fehlberg, U.; Neubauer, H.; Grunow, R.; Nikolaou, K.; Priemer, J.; Thiede, S.; Streich, W.J.; et al. Epizootiologic and ecologic investigations of European Brown Hares (Lepus europaeus) in selected populations from Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. J. Wildl. Dis. 2003, 39, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Ulrich, R.G.; Imholt, C.; Scholz, H.C.; Jacob, J.; Kratzmann, N.; Nöckler, K.; Al Dahouk, S. Molecular survey on brucellosis in rodents and shrews—natural reservoirs of novel Brucella species in Germany? Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubálek, Z.; Scholz, H.; Sedláček, I.; Melzer, F.; Sanogo, Y.; Nesvadbová, J. Brucellosis of the common vole (Microtus arvalis). Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007, 7, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, J.; Anusz, K. Serologic survey for bovine pathogens in free-ranging European bison from Poland. J. Wildl. Dis. 1991, 27, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salwa, A.; Anusz, K.; Arent, Z.; Paprocka, G.; Kita, J. Seroprevalence of selected viral and bacterial pathogens in free-ranging European bison. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2007, 10, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, M.; Iwaniak, W.; Szulowski, K. Identification of Brucella DNA in lymph tissue from deer (Cervus elaphus) and wild boars (Sus scrofa) by the use of BCSP31 PCR and AMOS-PCR. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2009, 53, 609–612. [Google Scholar]
- Krzysiak, M.K.; Jabłoński, A.; Iwaniak, W.; Krajewska, M.; Kęsik-Maliszewska, J.; Larska, M. Seroprevalence and risk factors for selected respiratory and reproductive tract pathogen exposure in European bison (Bison bonasus) in Poland. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 215, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, H.C.; Hofer, E.; Vergnaud, G.; Le Fleche, P.; Whatmore, A.M.; Al Dahouk, S.; Pfeffer, M.; Krüger, M.; Cloeckaert, A.; Tomaso, H. Isolation of Brucella microti from mandibular lymph nodes of red foxes, Vulpes vulpes, in lower Austria. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009, 9, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantina-Ievina, L.; Avsejenko, J.; Cvetkova, S.; Krastina, D.; Streikisa, M.; Steingolde, Z.; Vevere, I.; Rodze, I. Seroprevalence of Brucella suis in eastern Latvian wild boars (Sus scrofa). Acta Vet. Scand. 2018, 60, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmsten, A.; Magnusson, U.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; González-Barrio, D.; Dalin, A.-M. A Serologic survey of pathogens in wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Sweden. J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 54, 229–237, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, H.H.; Takeuchi-Storm, N.; Enemark, H.L.; Nielsen, S.T.; Larsen, G.; Chriél, M. Surveillance of important bacterial and parasitic infections in Danish wild boars (Sus scrofa). Acta Vet. Scand. 2020, 62, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åsbakk, K.; Stuen, S.; Hansen, H.; Forbes, L. A serological survey for brucellosis in reindeer in Finnmark county, northern Norway. Rangifer 1999, 19, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bergagna, S.; Zoppi, S.; Ferroglio, E.; Gobetto, M.; Dondo, A.; Giannatale, E.D.; Gennero, M.S.; Grattarola, C. Epidemiologic survey for Brucella suis biovar 2 in a wild boar (Sus scrofa) population in northwest Italy. J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilo, C.; Addis, G.; Deidda, M.; Tedde, M.T.; Liciardi, M. A serosurvey for brucellosis in wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Sardinia, Italy. J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sabatino, D.; Garofolo, G.; Di Provvido, A.; Zilli, K.; Foschi, G.; Di Giannatale, E.; Ciuffetelli, M.; De Massis, F. Brucella suis biovar 2 Multi Locus Sequence Type ST16 in wild boars (Sus scrofa) from Abruzzi region, Italy. Introduction from Central-Eastern Europe? Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnaro, S.; D’Ambrosi, F.; Petruccelli, A.; Ferrara, G.; D’Alessio, N.; Iovane, V.; Veneziano, V.; Fioretti, A.; Pagnini, U. A serological survey of brucellosis in Eurasian wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Campania Region, Italy. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilia, G.; Fratini, F.; Turchi, B.; Angelini, M.; Cerri, D.; Bertelloni, F. Genital Brucella suis biovar 2 infection of wild boar (Sus scrofa) hunted in Tuscany (Italy). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Francesco, C.E.; Gentile, L.; Di Pirro, V.; Ladiana, L.; Tagliabue, S.; Marsilio, F. Serologic evidence for selected infectious diseases in Marsican brown bears (Ursus arctos marsicanus) in Italy (2004–09). J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebani, V.V.; Guardone, L.; Bertelloni, F.; Perrucci, S.; Poli, A.; Mancianti, F. Survey on the Presence of bacterial and parasitic zoonotic agents in the feces of wild birds. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffuri, A.; Giacometti, M.; Tranquillo, V.M.; Magnino, S.; Cordioli, P.; Lanfranchi, P. Serosurvey of roe deer, chamois and domestic sheep in the central Italian Alps. J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grégoire, F.; Mousset, B.; Hanrez, D.; Michaux, C.; Walravens, K.; Linden, A. A serological and bacteriological survey of brucellosis in wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Belgium. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tulden, P.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kroese, M.; Engelsma, M.; de Zwart, F.; Szot, D.; Bisselink, Y.; van Setten, M.; Koene, M.; Willemsen, P. Monitoring results of wild boar (Sus scrofa) in The Netherlands: Analyses of serological results and the first identification of Brucella suis biovar 2. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2020, 10, 1794668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonne, C.; Andersen-Ranberg, E.; Rajala, E.L.; Agerholm, J.S.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.; Desforges, J.-P.; Eulaers, I.; Gustavson, K.; Jenssen, B.M.; Koch, A. Prevalence of antibodies against Brucella spp. in West Greenland polar bears (Ursus maritimus) and East Greenland muskoxen (Ovibos moschatus). Polar Biol. 2018, 41, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, T.L.; Johnson, C.K.; Burdin, A.; Gill, V.A.; Doroff, A.M.; Tuomi, P.; Smith, W.A.; Goldstein, T. Brucella infection in Asian Sea Otters (Enhydra lutris lutris) on Bering Island, Russia. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, K.; Abe, E.; Amano, M.; Miyazaki, N.; Boltunov, A.; Katsumata, E.; Maruyama, T. Detection of serum antibodies to Brucella in Russian aquatic mammals. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetnić, Ž.; Duvnjak, S.; Đuras, M.; Gomerčić, T.; Reil, I.; Zdelar-Tuk, M.; Špičić, S. Evidence of Brucella strain ST27 in bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) in Europe. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 196, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Siebert, U.; Stede, M.; König, A.; Weiss, R.; Baljer, G. Incidence of Brucella species in marine mammals of the German North Sea. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 81, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, U.; Rademaker, M.; Ulrich, S.A.; Wohlsein, P.; Ronnenberg, K.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E. Bacterial microbiota in Harbor Seals (Phoca vitulina) from the North Sea of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, around the time of Morbillivirus and Influenza epidemics. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tryland, M.; Sørensen, K.K.; Godfroid, J. Prevalence of Brucella pinnipediae in healthy hooded seals (Cystophora cristata) from the North Atlantic Ocean and ringed seals (Phoca hispida) from Svalbard. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 105, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nymo, I.H.; Tryland, M.; Frie, A.K.; Haug, T.; Foster, G.; Rødven, R.; Godfroid, J. Age-dependent prevalence of anti-Brucella antibodies in hooded seals Cystophora cristata. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2013, 106, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirvelä-Koski, V.; Nylund, M.; Skrzypczak, T.; Heikkinen, P.; Kauhala, K.; Jay, M.; Isomursu, M. Isolation of Brucella pinnipedialis from grey seals (Halichoerus grypus) in the Baltic Sea. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bressem, M.-F.; Van Waerebeek, K.; Raga, J.A.; Godfroid, J.; Brew, S.D.; MacMillan, A.P. Serological evidence of Brucella species infection in odontocetes from the south Pacific and the Mediterranean. Vet. Rec. 2001, 148, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidoro-Ayza, M.; Ruiz-Villalobos, N.; Pérez, L.; Guzmán-Verri, C.; Muñoz, P.M.; Alegre, F.; Barberán, M.; Chacón-Díaz, C.; Chaves-Olarte, E.; González-Barrientos, R.; et al. Brucella ceti infection in dolphins from the Western Mediterranean Sea. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofolo, G.; Petrella, A.; Lucifora, G.; Di Francesco, G.; Di Guardo, G.; Pautasso, A.; Iulini, B.; Varello, K.; Giorda, F.; Goria, M.; et al. Occurrence of Brucella ceti in striped dolphins from Italian Seas. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maio, E.; Begeman, L.; Bisselink, Y.; van Tulden, P.; Wiersma, L.; Hiemstra, S.; Ruuls, R.; Gröne, A.; Roest, H.-I.-J.; Willemsen, P.; et al. Identification and typing of Brucella spp. in stranded harbour porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) on the Dutch coast. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroese, M.V.; Beckers, L.; Bisselink, Y.J.W.M.; Brasseur, S.; van Tulden, P.W.; Koene, M.G.J.; Roest, H.I.J.; Ruuls, R.C.; Backer, J.A.; IJzer, J.; et al. Brucella pinnipedialis in Grey Seals (Halichoerus grypus) and Harbor Seals (Phoca vitulina) in The Netherlands. J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 54, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, H.; Jahans, K.; MacMillan, A.; Reid, R.; Thompson, P.; Foster, G. Brucella species infection in North Sea seal and cetacean populations. Vet. Rec. 1996, 138, 647–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.; Jahans, K.; Reid, R.; Ross, H. Isolation of Brucella species from cetaceans, seals and an otter. Vet. Rec. 1996, 138, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepson, P.D.; Brew, S.; MacMillan, A.P.; Baker, J.R.; Barnett, J.; Kirkwood, J.K.; Kuiken, T.; Robinson, I.R.; Simpson, V.R. Antibodies to Brucella in marine mammals around the coast of England and Wales. Vet. Rec. 1997, 141, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, G.; Whatmore, A.M.; Dagleish, M.P.; Baily, J.L.; Deaville, R.; Davison, N.J.; Koylass, M.S.; Perrett, L.L.; Stubberfield, E.J.; Reid, R.J.; et al. Isolation of Brucella ceti from a long-finned Pilot Whale (Globicephala melas) and a Sowerby’s Beaked Whale (Mesoploden bidens). J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, J.L.; Stubberfield, E.J.; Foster, G.; Brownlow, A.; Hall, A.J.; Perrett, L.L. Exposure of harbour seals Phoca vitulina to Brucella in declining populations across Scotland. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 126, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, N.J.; Dagleish, M.P.; Dale, E.-J.; Ten Doeschate, M.; Muchowski, J.; Perrett, L.L.; Rocchi, M.; Whatmore, A.M.; Brownlow, A.C. First confirmed reports of the isolation of Brucella ceti from a Risso’s dolphin Grampus griseus and a killer whale Orcinus orca. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2021, 145, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, N.J.; Perrett, L.L.; Dawson, C.; Dagleish, M.P.; Haskins, G.; Muchowski, J.; Whatmore, A.M. Brucella ceti infection in a common minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata) with associated pathology. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tryland, M.; Kleivane, L.; Alfredsson, A.; Kjeld, M.; Arnason, A.; Stuen, S.; Godfroid, J. Evidence of Brucella infection in marine mammals in the North Atlantic Ocean. Vet. Rec. 1999, 144, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, C.; Perrett, L.; Young, E.; Davison, N.; Monies, R. Isolation of Brucella species from a bottlenosed dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). Vet. Rec. 2006, 158, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, H.; Kirkemo, A.M.; Handeland, K. Wildlife as source of zoonotic infections. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Barrio, D. Zoonoses and Wildlife: One Health Approach. Animals 2022, 12, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, S.; Thébault, A.; Rossi, S.; Marchand, P.; Petit, E.; Toïgo, C.; Gilot-Fromont, E. Targeted strategies for the management of wildlife diseases: The case of brucellosis in Alpine ibex. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, G.; Thompson, P.N.; Saegerman, C.; Marcotty, T.; Letesson, J.J.; de Bolle, X.; Godfroid, J. Brucellosis in wildlife in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneipp, C.C.; Sawford, K.; Wingett, K.; Malik, R.; Stevenson, M.A.; Mor, S.M.; Wiethoelter, A.K. Brucella suis Seroprevalence and associated risk factors in dogs in Eastern Australia, 2016 to 2019. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 727641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurgiutiu, D.; Banis, C.; Hunt, E.; Mincer, J.; Nicolardi, C.; Weltman, A.; Stanek, D.; Matthews, S.; Siegenthaler, C.; Blackmore, C.; et al. Brucella suis infection associated with feral swine hunting—Three states, 2007–2008. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2009, 58, 618–621. [Google Scholar]
- Elmonir, W.; Abdel-Hamid, N.H.; Hamdy, M.E.R.; Beleta, E.I.M.; El-Diasty, M.; Melzer, F.; Wareth, G.; Neubauer, H. Isolation and molecular confirmation of Brucella suis biovar 2 from slaughtered pigs: An unanticipated biovar from domestic pigs in Egypt. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailles, A.; Ogielska, M.; Kemiche, F.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Brieu, N.; Burnusus, Z.; Creuwels, A.; Danjean, M.P.; Guiet, P.; Nasser, V.; et al. Brucella suis biovar 2 infection in humans in France: Emerging infection or better recognition? Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumaker, B.A. Detection and Transmission Dynamics of Brucella Abortus in the Greater Yellowstone Area; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Godfroid, J.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Saegerman, C.; Blasco, J. Brucellosis in terrestrial wildlife. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2013, 32, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wareth, G.; Melzer, F.; El-Diasty, M.; Schmoock, G.; Elbauomy, E.; Abdel-Hamid, N.; Sayour, A.; Neubauer, H. Isolation of Brucella abortus from a dog and a cat confirms their biological role in re-emergence and dissemination of bovine brucellosis on dairy farms. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, e27–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, T.; Melzer, F.; Khan, I.; Iqbal, M.; Saqib, M.; Hammad Hussain, M.; Schwarz, S.; Neubauer, H. Serological and molecular investigation of Brucella species in dogs in Pakistan. Pathogens 2019, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.G.; Adams, L.G.; Ficht, T.A.; Cheville, N.F.; Payeur, J.P.; Harley, D.R.; House, C.; Ridgway, S.H. Brucella-induced abortions and infection in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1999, 30, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nymo, I.H.; Tryland, M.; Godfroid, J. A review of Brucella infection in marine mammals, with special emphasis on Brucella pinnipedialis in the hooded seal (Cystophora cristata). Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfroid, J.; Nielsen, K.; Saegerman, C. Diagnosis of brucellosis in livestock and wildlife. Croat. Med. J. 2010, 51, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.-B.; Xiao, D.; Liu, J.-Y.; Bi, H.-M.; Zheng, Z.-R.; Wang, L.-D.; Yang, X.-W.; Tian, G.-Z.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Piao, D.-R.; et al. Fluorescence polarization assay improves the rapid detection of human brucellosis in China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2021, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGiven, J.A.; Tucker, J.D.; Perrett, L.L.; Stack, J.A.; Brew, S.D.; MacMillan, A.P. Validation of FPA and cELISA for the detection of antibodies to Brucella abortus in cattle sera and comparison to SAT, CFT, and iELISA. J. Immunol. Methods 2003, 278, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfroid, J. Brucellosis in livestock and wildlife: Zoonotic diseases without pandemic potential in need of innovative one health approaches. Arch. Public Health 2017, 75, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wareth, G.; Pletz, M.W.; Neubauer, H.; Murugaiyan, J. Proteomics of Brucella: Technologies and their applications for basic research and medical microbiology. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bonaventura, G.; Angeletti, S.; Ianni, A.; Petitti, T.; Gherardi, G. Microbiological laboratory diagnosis of human brucellosis: An overview. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henaux, V.; JaŸ, M.; Siebeke, C.; Calavas, D.; Ponsart, C. Review of bovine brucellosis surveillance in Europe in 2015. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2018, 37, 805–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamil, T.; Akar, K.; Erdenlig, S.; Murugaiyan, J.; Sandalakis, V.; Boukouvala, E.; Psaroulaki, A.; Melzer, F.; Neubauer, H.; Wareth, G. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Brucellosis in European Terrestrial and Marine Wildlife Species and Its Regional Implications. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101970
Jamil T, Akar K, Erdenlig S, Murugaiyan J, Sandalakis V, Boukouvala E, Psaroulaki A, Melzer F, Neubauer H, Wareth G. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Brucellosis in European Terrestrial and Marine Wildlife Species and Its Regional Implications. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(10):1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101970
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamil, Tariq, Kadir Akar, Sevil Erdenlig, Jayaseelan Murugaiyan, Vassilios Sandalakis, Evridiki Boukouvala, Anna Psaroulaki, Falk Melzer, Heinrich Neubauer, and Gamal Wareth. 2022. "Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Brucellosis in European Terrestrial and Marine Wildlife Species and Its Regional Implications" Microorganisms 10, no. 10: 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101970
APA StyleJamil, T., Akar, K., Erdenlig, S., Murugaiyan, J., Sandalakis, V., Boukouvala, E., Psaroulaki, A., Melzer, F., Neubauer, H., & Wareth, G. (2022). Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Brucellosis in European Terrestrial and Marine Wildlife Species and Its Regional Implications. Microorganisms, 10(10), 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101970






