Abstract
Spent mushroom substrates (SMSs) can be developed as a biofertilizer through composting. Here, we investigated the dynamics of bacterial and fungal communities during commercial composting and the effect of swine and poultry manure on their communities through MiSeq pyrosequencing. Weissella paramesenteroides and Lactobacillus helveticus were dominant bacterial species in the composts with soy waste (SMS-SW), whereas Thermotogaceae sp. and Ureibacillus sp. were dominant in the composts with swine and poultry manure (SMS-PM). For the fungal community, Flammulina velutipes was dominant in SMS-SW, whereas Trichosporon asahii, Candida catenulate, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Candida tropicalis were dominant in SMS-PM. The addition of manure affected the bacterial community significantly. Redundancy analysis indicated that bacterial communities were affected by temperature, potassium, and potassium oxide and fungal communities by temperature, Kjeldahl nitrogen, organic matter, and ammonium nitrogen. Our findings can guide future research on composting microbiology.
1. Introduction
Mushrooms are crucial crops in Taiwan and other countries, and their total production in 2016 generated a revenue of approximately $430 million. Most cultivated mushrooms are grown on substrates comprising rice straw, rice bran, wheat bran, chicken manure, and sawdust or wood chip. Rice straw and sawdust derived from different types of trees are used as basic raw materials for cultivating edible mushrooms. After mushrooms are harvested, a considerable amount of the spent mushroom substrate (SMS) is left. According to Finney et al. [1], 1 kg of fresh mushrooms results in 5 kg of SMS (i.e., 2 kg dry weight). In the past, SMSs were considered as wastes and exerting adverse effects on the environments. These SMSs are rich in nutrients and can be applied as high-quality composts [2,3]) or soil conditioners in agriculture. Because of circular economy trends, SMSs are considered valuable resources for sustainable utilization.
Composting is a critical tool for the future of biological waste management [4]. Various microbes and their metabolites contribute to the composting process. The succession and dynamics of these microbes change with alterations in environmental parameters such as temperature, pH, and CO2 evolution rate [5]. Both culture-dependent and culture-independent methods have been used to describe changed in microbial composition during composting [5,6]. However, most studies have focused on the bacterial community in bench-scale composting reactors [7,8]. Few studies have focused on the dynamics of the fungal community and an industrial-scale composting system.
Commercial compost is prepared using a large-scale composting system involving various techniques such as in-vessel composting, open air-turned windrows, or in-vessel tunnel composting. In most cases, various starting materials of composting on an industrial scale were used, and few reports have focused on the dynamics of the microbial community on an industrial scale. In Taiwan, a rectangular agitated bed composting system in a building is used to process SMSs. The system was adopted in many areas because it encourages shorter composting periods.
Monitoring the composting process and changes in bacterial and fungal communities is essential to understand underlying mechanisms and obtain high-quality products. Here, we characterized the co-composting process of swine and poultry manure with SMSs in an industrial-scale composting system. Our specific objectives were (1) to study changes in bacterial and fungal communities during composting, (2) to investigate the physiochemical characteristics of composts during composting, and (3) to determine the relationship between the microbial community and compost characteristics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Composting Materials and Processing
The experiments including one treatment and one control, and each group was conducted in two windrow tests. The treatment group (SMS-PM) was composed of SMS and swine and poultry manure, while the control contained the same composition, without swine poultry manure (SMS-SW). The SMS was obtained from several commercial Flammulina velutipes operations located in Taiwan. SMS-PM comprised a mixture of SMS with swine and poultry manure at a 6:4 ratio (v/v), whereas SMS-SW included SMS and soy waste at a 6:4 ratio (v/v). The weights of both starting materials were 200 tons. Before the start of the co-composting process, the starting materials were mixed and homogenized via a large stirring machine and the initial moisture content was adjusted to approximately 50–55% by water spraying.
A rectangular agitated bed composting system was used for processing the SMS. This system combines controlled aeration with periodic turning. The composting occurred between walls that form long, narrow channels, referred to as beds. A rail or channel on the top of each wall supports and guides a compost-turning machine. A loader places raw materials at the front end of the bed. As the turning machine moves forward on the rails, it mixes the compost and discharges the compost behind itself. With each turn, the machine moves the compost at a set distance toward the end of the bed. The turning machines work in a manner similar to windrow turners, using rotating paddles or flails to agitate materials, break up clumps of particles, and maintain porosity. The machine includes a conveyor to move the compost and work automatically. In this study, the bed dimensions were 67 m × 3 m × 1.5 m. The turning frequency was turned every 2 to 3 days. The composting period was 30 days in summer with daily turning and 60 days in winter with turning every 2 days.
2.2. Sampling
Compost samples were collected at three sampling sites in each treatment. The sampling sites were located at the front (sample 1), middle (sample 2), and back end (sample 3) of the bed. At each sampling site, we cut the compost into piles and obtained six samples randomly from exposed edges. DNA was extracted from each sample. Six DNA samples were obtained from each sampling site. All the six DNA samples from one sampling site were mixed, leading to three combined compost DNA samples per treatment.
2.3. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
DNA was extracted from 0.25 g of each compost sample by using a ZymoBIOMICS DNA Miniprep Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA). The six DNA samples obtained from one sampling site were mixed for next-generation sequencing. Tri-Biotech (Taipei, Taiwan) was entrusted to conduct subsequent-generation sequencing, and the 16S rRNA V3-V4 sequence of bacteria and the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region of fungi were analyzed. The V3-V4 regions of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene were amplified using primer 341F (5′-CCT ACG GGN GGC WGC AG-3′) and 805R (5′-GAC TAC HVG GGT ATC TAA TCC-3′) [9] with different barcodes for the V3-V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene [10]. The ITS regions of the fungal rRNA gene were analyzed using primer ITS1F (5′-CTT GGT CAT TTA GAG GAA GTA A-3′) and ITS2 (5′-GCT GCG TTC TTC ATC GAT GC-3′) [11,12]. The 5′ end of 341F and ITS1F was barcoded with 8-bp error correcting barcodes [10] to enable sample multiplexing.
Each PCR was performed in a 25-μL reaction volume containing 1× HiFi Fidelity reaction buffer (Kapa Biosystems, Wilmington, MA, USA), 0.3 μM forward primer, 0.3 μM reverse primer, 1 μM dNTP mix (Kapa Biosystems), 0.5 U HiFi DNA polymerase (Kapa Biosystems), 2 ng DNA, and nuclease-free water. The amplification protocol comprised one denaturation step at 95 °C for 3 min, 25 cycles of denaturation at 98 °C for 20 s, annealing at 57.5 °C for 20 s, extension at 72 °C for 20 s, and a final extension at 72 °C for 3 min. A template-free reaction was used as the control. PCR products were separated in a 2.0% agarose gel (w/v) and purified using a QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen, New Delhi, India), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The purified DNA was quantified using a Qubit dsDNA BR Assay Kit (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) in Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer (Invitrogen), and the individual samples were pooled in equimolar proportions. The final DNA pool was sent to the NGS facility at Tri-I Biotech (Taipei, Taiwan) for paired-end Illumina MiSeq sequencing.
The quality control of the raw sequencing data was performed using the quality control tool of the CLC Genomics Workbench. We adopted stringent conditions to process data and finally generated effective reads by modifying the MiSeq SOP [13,14]. All the effective reads obtained from all samples were clustered into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) at 97% sequence similarity by using USEARCH. Next, we classified OTUs based on reads taxonomy. If ≥51% reads in an OTU belonged to the same taxon (e.g., species), it was chosen as the taxonomic classification of the OTU. If <51% reads in an OTU belonged to the same taxon, the calculation was replicated at a higher taxonomic level (e.g., genus). The representative sequences of OTUs were taxonomically annotated using the SILVA database.
2.4. Physiochemical Analysis
Six compost samples from each sampling site were combined into one mixed compost sample. For each mixed compost sample, the physiochemical parameters were analyzed. Temperature was measured using a compost thermometer. The pH of the compost (1:10 w/v waste: water extract) was analyzed following the method reported by Kalamdhad et al. [15]. The moisture content was determined by drying the samples at 60 °C for 24 h. The electrical conductivity of the samples was analyzed using an electrical conductivity meter following Agriculture Fertilizer Standards (AFS) 2905-1. The total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN) content was analyzed using the Kjeldahl method [16]. The contents of ammonium nitrogen and total potassium were detected per AFS1111-1 and AFS2130-2, respectively. Volatile solids were determined using the loss ignition method (on a dry mass basis) at 550 °C for 2 h. The total organic carbon (TOC) content was calculated from volatile solids. The total phosphorus (TP; acid digest) content was examined using the stannous chloride method [17]. The potassium content was determined through atomic absorption, and the phosphorus content was determined colorimetrically following [18].
2.5. Statistical Analyses
The relative abundance of microbes in each sample was recorded as a binary matrix, which was used to calculate the Bray–Curtis similarity index [19] and construct nonparametric multidimensional scaling (MDS) plots using Primer 6 software (version 6.1.15; Primer-E, Plymouth, UK). The significance of differences found in the OTU-based structures of bacterial and fungal communities between SMS-PM and SMS-SW was assessed by performing the permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) and analysis of similarity (ANOSIM) with Bray-Curtis similarities using Primer 6. Similarity percentage (SIMPER) analysis was performed to determine microbial OTUs that were primarily responsible for the observed differences by using Primer 6. Redundancy analysis [20], as implemented in the ‘‘Vegan’’ package for R software [21], was used to analyze relationships between physiochemical parameters and microbial profiles.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physiochemical Characteristics of Composts
The physiochemical characteristics of the six samples are listed in Table 1. The temperature increased from 38.33 °C in the front to 43.50 °C in the middle and decreased from 43.50 °C to 39.33 °C in the back end in SMS-SW treatment. Similar trend also found in SMS-PW treatment. The moisture content decreased from the front to the back end in both the treatments. Microorganisms strongly decomposed the organic matters in the composts, which released heat and improved temperature. The high temperature not only promoted decomposition of the organic matters, but also accelerated water volatilization [22]. The temperature in the SMS-PM was higher than that in the SMS-SM. The total organic carbon content ranged from 93.40% to 96.83% in the SMS-SW samples and from 85.95% to 92.35% in the SMS-PM samples. The total organic carbon content in the SMS-SW samples was higher than that in the SMS-PW samples. This may because the addition of animal manure provides additional microorganisms whose respiration and activity can cause heat accumulation [23].

Table 1.
Characteristics of physical-chemical during composting.
The total nitrogen content ranged from 28.70 to 82.85 mg/L in the SMS-SW samples and from 54.82 to 87.26 mg/L in the SMS-PM samples, whereas the total potassium content was approximately 2.42–2.49 mg/L and 2.93–3.99 mg/L, respectively. Nitrogen and potassium are essential nutrients for plant growth. Higher the total nitrogen and total potassium contents were observed in SMS-PW samples (Table 1). This indicated that the addition of manure to the SMS-PM compost demonstrated an increasing trend in the contents of total nitrogen and total potassium. Co-composting of swine and poultry manure with spent mushroom substrates could improve compost quality by increasing the nutritional content [24].
3.2. Bacterial and Fungal Diversity
The composition of bacterial 16S rRNA and fungal ITS sequences was determined using the illumina platform. In total, six DNA samples were amplified and sequenced. For bacteria, the effective reads generated by high-throughput sequencing were 43,920 (SMS-SW1), 42,365 (SMS-SW2), 43,295 (SMS-SW3), 41,682 (SMS-PM1), 42,226 (SMS-PM2), 41,616(SMS-PM3). In total, effective tags generated by high-throughput sequencing were aggregated at 97% sequence similarity, yielding 45,021 bacterial OTUs. These OTUs comprised 953 species, 772 genera belonging to 244 families.
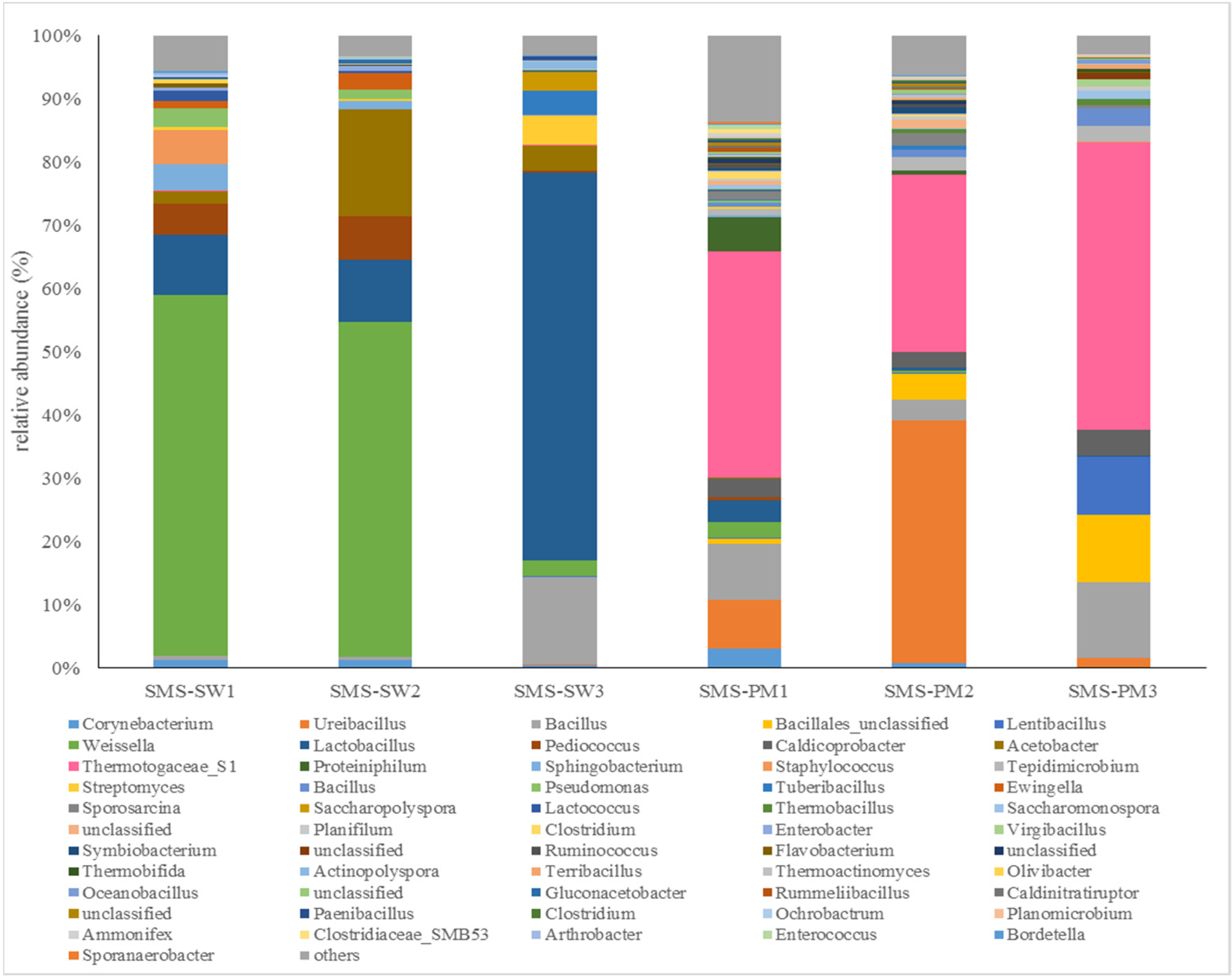
Firmicutes, Thermotogae, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Bacteroidetes were the main bacterial phyla in all the samples. Firmicutes (66.37%) was the most dominant bacteria in all the samples, followed by Thermotogae (18.29%), Proteobacteria (7.29%), Actinobacteria (4.54%), and Bacteroidetes (3.25%). The communities at the genus level were considerably different between the two treatments. The bacterial compositions at the genus level are illustrated in Figure 1. Weissella and Lactobacillus were the dominant genera in SMS-SW. The relative abundance of Weissella was 57.06%, 52.95%, and 2.59% in SMS-SW1 (front), SMS-SW2 (middle), and SMS-SW3 (back), which decreased from the front site to the back site (Figure 1). The relative abundance of Lactobacillus increased from the front site (9.48%) to the back site (61.30%).
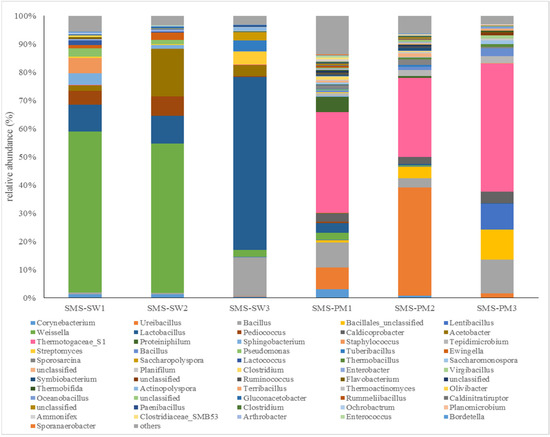
Figure 1.
Dynamic changes in the bacterial community at the genus level from spent mushroom substrate with soy wastes (SMS-SW) and with swine and poultry manure (SMS-PW). The relative abundance of genus was >0.1% in at least one sample. Genera with relative abundance <0.1% were grouped as “others”.
In this study, the relative abundance of Weissella spp. decreased from SMS-SW1 to SMS-SW3. Weissella was dominant in the early stages of SMS-SW composting but decreased in the late stage. Weissella is a Gram-positive lactic acid bacterium [25]. Weissella spp. have been found on the skin and in the milk and feces of animals; in the saliva, breast milk, feces, and vagina of humans; and in plants and vegetables [25,26]. Weissella were also dominant in the silage fermentation with soybean [27] and soy sauce fermentation [28]. The additional of soy waste might provide the bacterial inoculum. Tran et al. [29] found that Weissella inhibited vigorous organic matter degradation by accumulating acetic acid during composting process [2]. The decrease of Weissella in this study suggested the composting process was accelerated in the late stage. In this study, the relative abundance of Lactobacillus spp. increased from SMS-SW1 to SMS-SW3. Lactobacillus spp. could produce lactic acid and bacteriocins against pathogens [30]. The increase of their population in the late stage could increase the safety and quality of final products [31].
Themotogaceae S1 (26.98%) and Ureibacillus (11.88%) were the dominant genera in SMS-PW (Figure 1). Members of the Thermotogaceae family are moderately thermophilic to hyperthermophilic [32]. They degraded and utilized a wide range of simple and complex carbohydrates [33]. Ureibacillus comprises thermophilic, aerobic, endospore-forming bacteria. Ureibacillus spp. have been isolated from air [34], soil [35], and composts [36]. Most Ureibacillus species can grow at 35–65 °C, with the optimal growth temperature being 50–60 °C [36]. During composting, the temperature rises to 50–60 °C in SMS-PW treatment. Thus, hot compost represents a favorable habitat for these thermophilic isolates. Wan et al. [37] found that inoculation with a group of microorganisms consisting of Bacillus, Ureibacillus, Geobacillus and Paracoccus prolonged the thermophilic stage in composting, increasing the temperature with maximum temperature 68 °C. They suggest that inoculation with microorganisms were helpful in facilitating the process of composting.
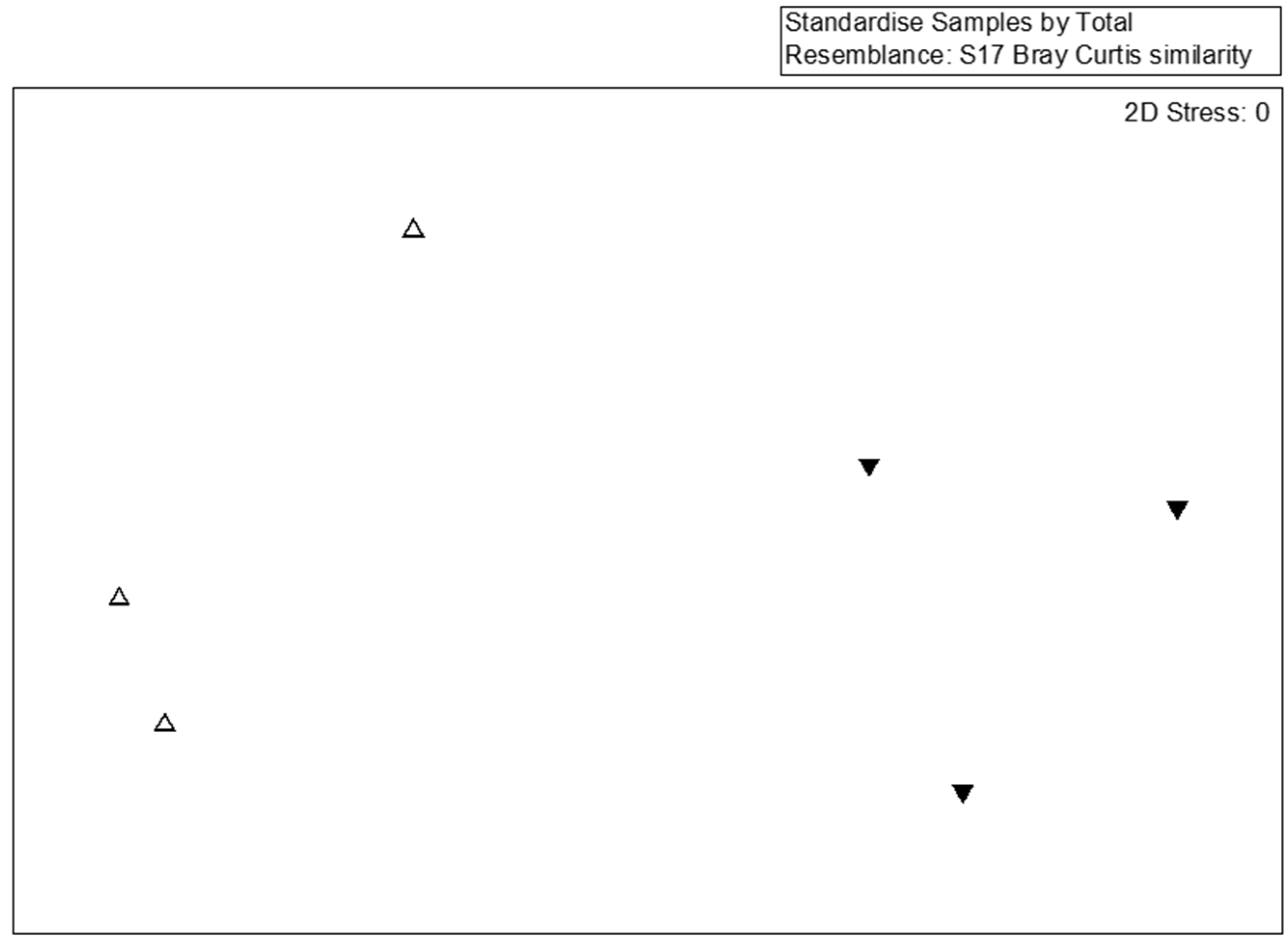
For a detailed analysis of the bacterial community, 77 dominant species (the abundance >1% at any sample) were selected for MDS, PERMANOVA, and SIMPER analyses. The species-level MDS plot illustrates that bacterial communities in SMS-PW and SMS-SW were distinct (Figure 2). Our findings indicated that the addition of swine and poultry manure affected the bacterial community. However, the PERMANOVA test show the difference was not significant (p = 0.1). This might be caused by the limited sample sizes.
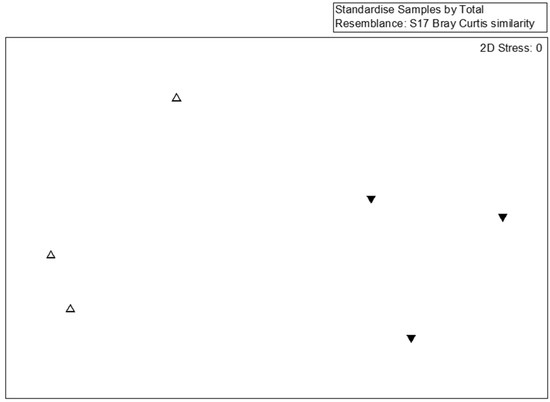
Figure 2.
Multidimensional scaling of the bacterial community at the species lever from six compost samples. Bacterial taxa with relative abundances >0.1% in at least one sample were considered. Symbols indicate different treatments: triangle, spent mushroom substrate with soy wastes; inverted triangle, spent mushroom substrate with swine and poultry manure.
The SIMPER test indicated that Thermotogaceae sp., W. paramesenteroides, Ureibacillus sp., Lactobacillus helveticus, and W. cibaria were the main contributors to variations between bacterial communities in both the treatments, contributing 21.38%, 13.61%, 9.14%, 5.97%, and 5.06% dissimilarity, respectively (Table 2). Weissella paramesenteroides, L. helveticus, and W. cibaria were dominant in the SMS-SW samples, whereas Thermotogaceae sp. and Ureibacillus sp. were dominant in the SMS-PM samples (Table 2). Most strains of W. paramesenteroides can grow at 10–37 °C, with the optimal temperature being 20–30 °C [25]. However, the thermophilic W. paramesenteroides can survive at temperatures as high as 55 °C in thermophilic composts [38]. W. paramesenteroides dominated in the SMS-SW samples where the temperature was 38–43 °C.

Table 2.
Similarity percentage (SIMPER) analysis showing the five most influential species that contribute to the difference in the bacterial or fungal community structure between the spent mushroom substrate with addition of soy wastes (SMS-SW) and swine and poultry manure (SMS-PM).
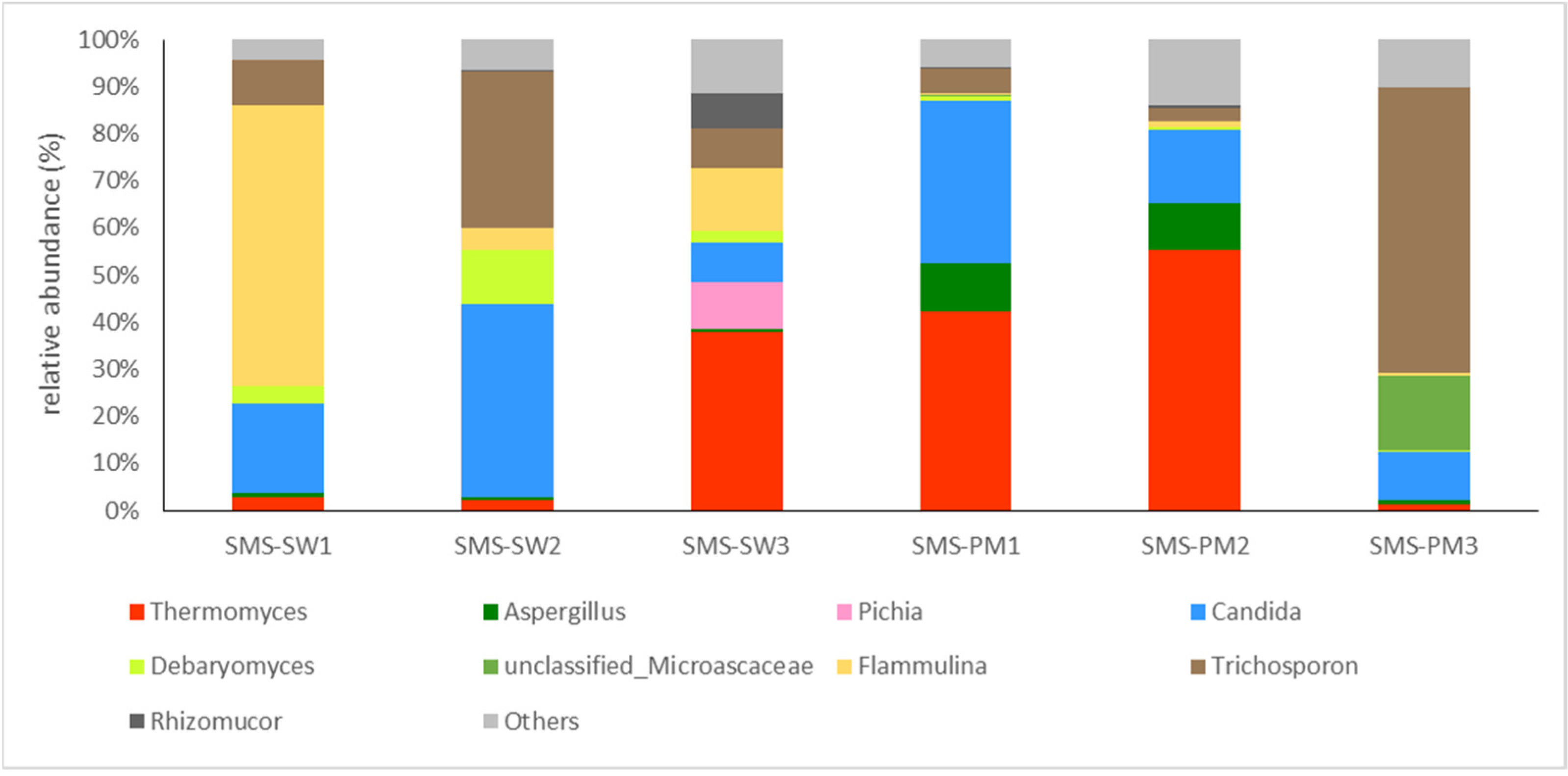
Basidiomycota (62.48%) and Ascomycota (35.11%) were the main fungi in all the samples. The fungal compositions at the genus level are illustrated in Figure 3. Flammulina (16.45%), Candida (14.44%), Trichosporon (10.82%), and Thermomyces (9.05%) were the dominant genera in SMS-SW, whereas Thermomyces (20.95%), Trichosporon (14.48%), and Candida (12.73%) were the dominant genera in SMS-PW (Figure 3).
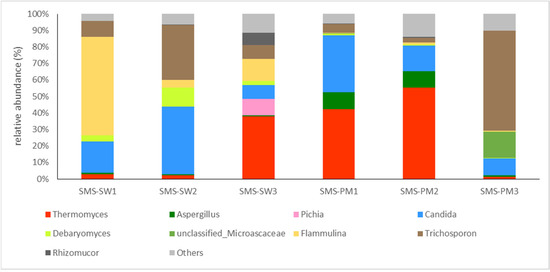
Figure 3.
Dynamic changes of the fungal community at the genus level from spent mushroom substrate with soy wastes (SMS-SW) and with swine and poultry manure (SMS-PW). The relative abundance of genus was >0.1% in at least one sample. Genera with relative abundance <0.1% were grouped as “others”.
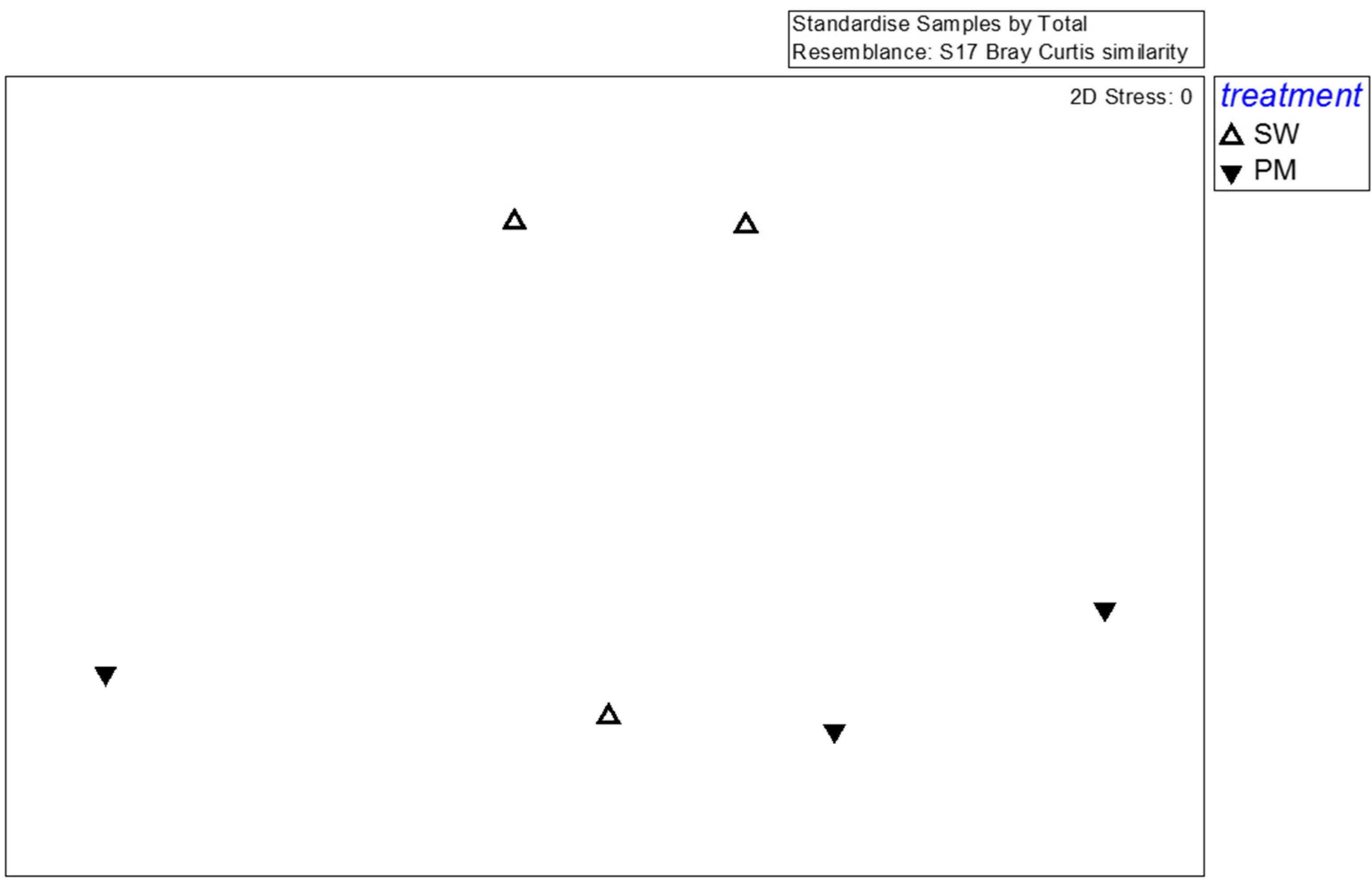
For fungi, the effective reads generated by high-throughput sequencing were 41,353 (SMS-SW1), 42,726 (SMS-SW2), 39,068 (SMS-SW3), 39,959 (SMS-PM1), 38,566 (SMS-PM2), 40,821 (SMS-PM3). In total, effective tags generated by high-throughput sequencing were aggregated at 97% sequence similarity, yielding 741 fungal OTUs. These OTUs comprised 290 species, 176 genera belonging to 107 families. For a detailed analysis of the fungal community, 35 dominant species (the abundance >1% at any sample) were selected for MDS, PERMANOVA, and SIMPER analyses. The species-level MDS plot illustrates that fungal communities in SMS-PW and SMS-SW were non-significantly distinct (p = 0.4; Figure 4). The SIMPER test indicated that Flammulina velutipes, Trichosporon asahii, Candida catenulate, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Candida tropicalis were the main contributors to variations between fungal communities in both the treatments, contributing to 21.52%, 16.75%, 12.9%, 8.95%, and 7.47% dissimilarity, respectively (Table 2). Flammulina velutipes was dominant in the SMS-SW samples, whereas Trichosporon asahii, Candida catenulate, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Candida tropicalis were dominant in the SMS-PM samples (Table 2).
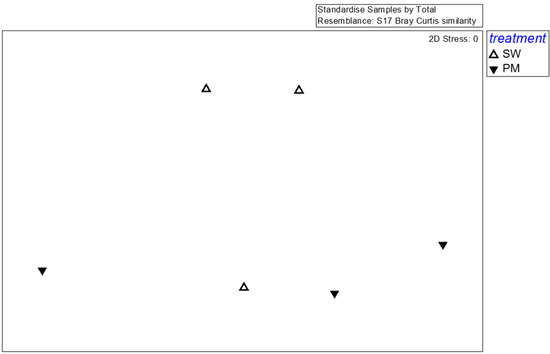
Figure 4.
Multidimensional scaling of the fungal community at the species level from six compost samples. Fungal taxa with relative abundance >0.1% in at least one sample were considered. Symbols indicate different treatments: triangle, spent mushroom substrate with soy wastes; inverted triangle, spent mushroom substrate with swine and poultry manure.
A shift in fungal taxa during composting was observed. Thermomyces lanuginosus was present in both the treated samples. The relative abundance was 2.69%, 2.25%, and 37.78% in three sampling sites in SMS-SW and 42.27%, 55.43%, and 1.26% in SMS-PM, respectively. Thermomyces lanuginosus was reported to be dominant in mushroom compost [23,39] and can degrade hemicellulose during composting [40]. The relative abundance of Thermomyces lanuginosus suggested that the degradation of hemicellulose appeared in the late period of SMS-SW compost and the early period of SMS-PM. Additionally, T. lanuginosus was abundant in the compost at a higher temperature (>55 °C). In summary, T. lanuginosus was widely distributed in mushroom composts, with higher abundance under higher temperatures.
The SMS was obtained from several commercial F. velutipes operations. F. velutipes was dominant in the SMS-SW samples. The relative abundance of F. velutipes decreased, indicating that their biomass was degraded during composting. Candida tropicalis and Trichosporon asahii were present in both the treated samples and were more abundant in SMS-PM. Two fungal species were opportunistic pathogens. Therefore, compost operators should limit the exposure and spread of airborne fungal spores and colonies during composting.
3.3. Correlations between Microbiota and Physiochemical Parameters during Composting
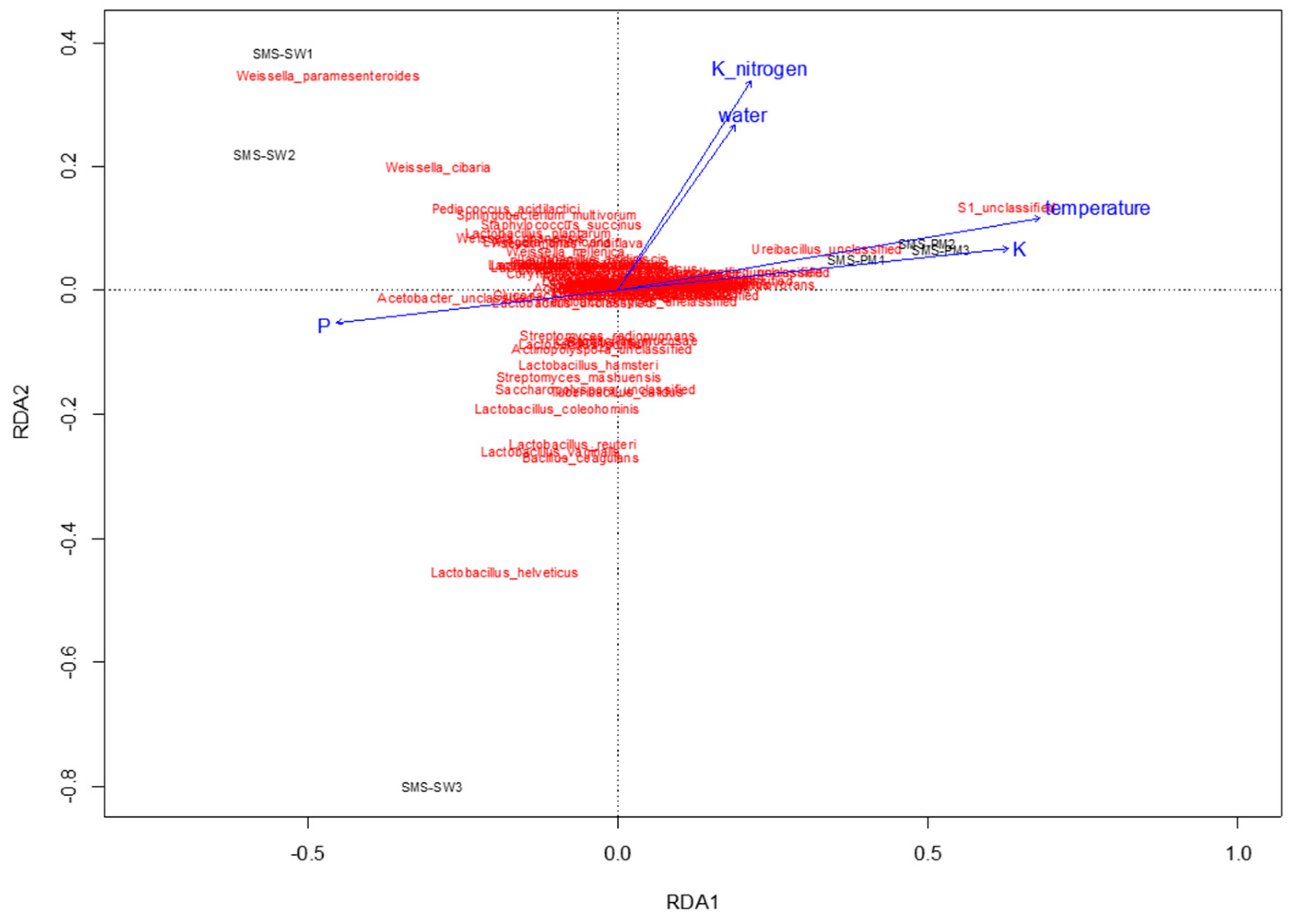
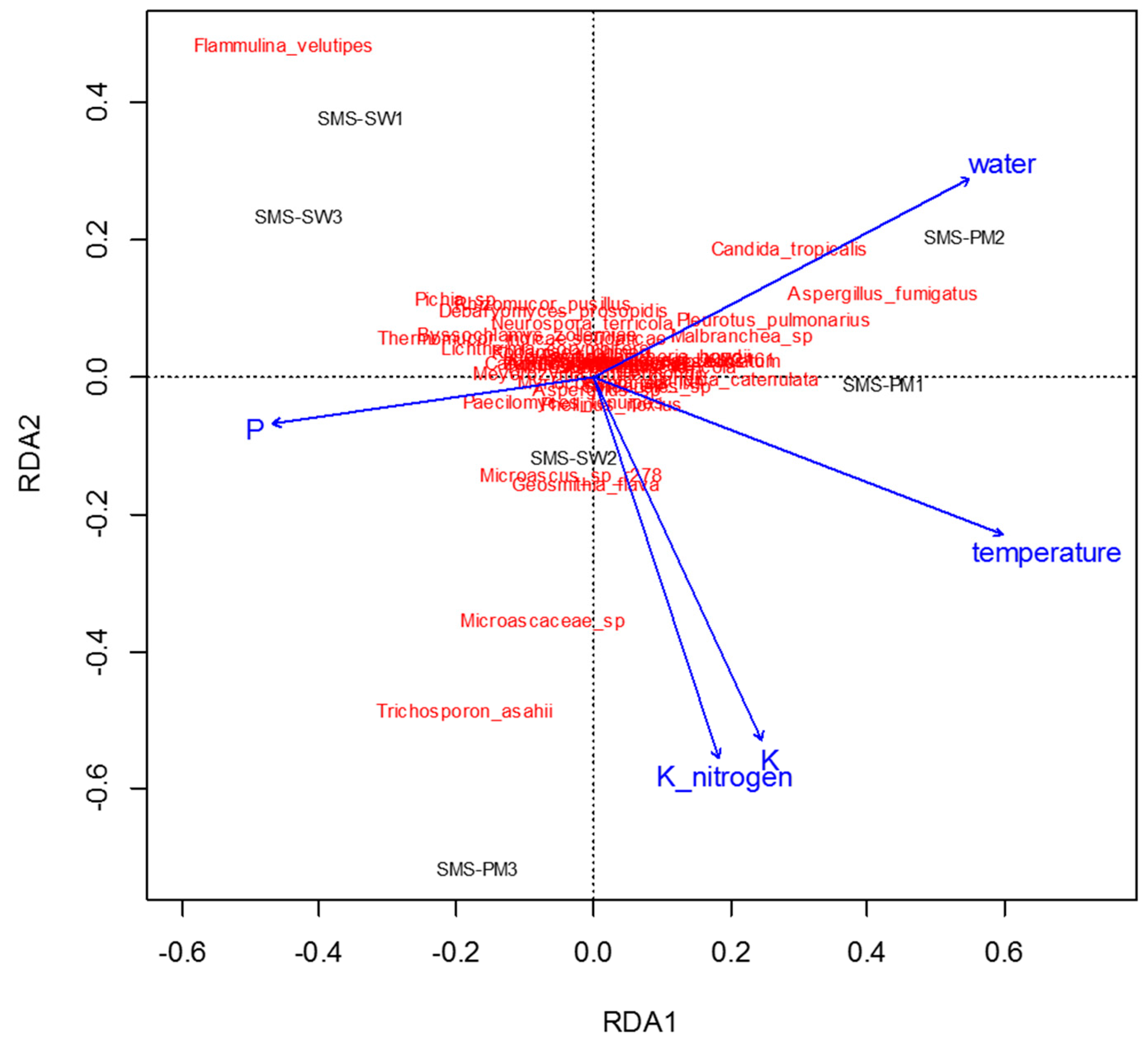
To determine physiochemical parameters that best explained the variation in microbial communities, redundancy analysis was performed to predict principal coordinates (Figure 5 and Figure 6) by using a linear combination of several physiochemical parameters (Table 1). These physiochemical factors, namely temperature; pH; moisture content; electrical conductivity value; TKN; and ammonium nitrogen, total potassium, TOC, and TP contents, accounted for 61.8% (Figure 5) and 36.55% (Figure 6) of the variation in bacterial and fungal communities, respectively. Relative abundance of Thermotogaceae_S1_unclassified and Ureibacillus sp. was increased with the increase of temperature, whiles some taxa dominant in SMS-SW, such as Weissella cibaria and W. paramesenteroides show the reverse trend. Total potassium (P) also raised with increased relative abundance of Thermotogaceae_S1_unclassified.
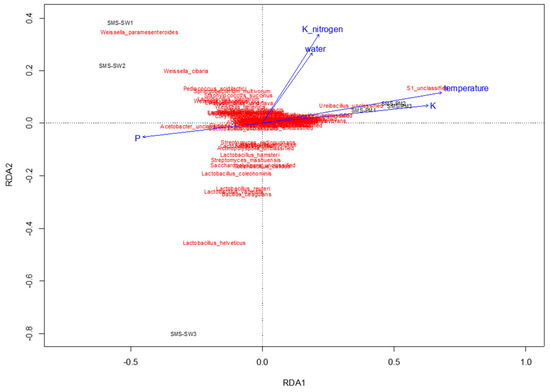
Figure 5.
Redundancy analysis assessing the relationship between environmental factors (blue arrows) and bacterial communities (red). The arrows indicate the size and direction of the coefficients of physiochemical variables in the linear model.
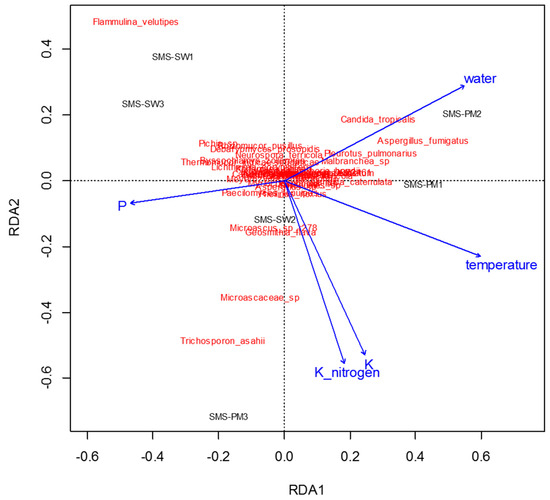
Figure 6.
Redundancy analysis assessing the relationship between environmental factors (blue arrows) and fungal communities (red). The arrows indicate the size and direction of the coefficients of physiochemical variables in the linear model.
4. Conclusions
In the present study, shifts in microbial community and physiochemical characteristics were observed during composting through an industrial composting system. Weissella paramesenteroides and Lactobacillus helveticus were dominant bacterial species in the composts with soy waste (SMS-SW), whereas Thermotogaceae sp. and Ureibacillus sp. were dominant in the composts with swine and poultry manure (SMS-PM). For the fungal community, Flammulina velutipes was dominant in SMS-SW, whereas Trichosporon asahii, Candida catenulate, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Candida tropicalis were dominant in SMS-PM. Bacterial and fungal communities were changed by the addition of swine and poultry manure. Changes in physiochemical parameters could explain the variation in microbial communities. Bacterial communities were affected by temperature, potassium, and potassium oxide, whereas fungal communities were affected by temperature, Kjeldahl nitrogen, organic matter, and ammonium nitrogen. The data and analyses provided a rich source for additional investigations of composting microbiology.
Author Contributions
W.-R.L. conceived and designed the experiments. W.-R.L. and H.-Y.L. conducted the field and lab research, analyzed and process data. L.-C.L. analyzed the physio-chemical characterization of the composts. W.-R.L. and S.-Y.H. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (MOST), grant number MOST 108-2321-B-080-001 and Ministry of Economic Affairs, Taiwan (MOEA) grant number MOEA 110-EC-17-A-22-0525.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to acknowledge Po-Hung Wu, Wan-Ping Chiang and Mei-Huei Chen for collecting samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Finney, K.N.; Ryu, C.; Sharifi, V.N.; Swithenbank, J. The reuse of spent mushroom compost and coal tailings for energy recovery: Comparison of thermal treatment technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polat, E.; Uzun, H.; Topçuo, B.; Önal, K.; Onus, A.N. Effects of spent mushroom compost on quality and productivity of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) grown in greenhouses. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- Uzun, I. Use of spent mushroom compost in sustainable fruit production. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2004, 12, 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Ayilara, M.S.; Olanrewaju, O.S.; Babalola, O.O.; Odeyemi, O. Waste Management through Composting: Challenges and Potentials. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasaki, K.; Hirai, H.; Mimoto, H.; Quyen, T.N.M.; Koyama, M.; Takeda, K. Succession of microbial community during vigorous organic matter degradation in the primary fermentation stage of food waste composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.P.; Martins, L.F.; Pereira, R.V.; Thomas, A.M.; Barbosa, D.; Lemos, L.N.; Silva, G.M.M.; Moura, L.M.S.; Epamino, G.W.C.; Digiampietri, L.; et al. Microbial community structure and dynamics in thermophilic composting viewed through metagenomics and metatranscriptomics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, V.S.; Dhamodharan, K.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Characterization of bacterial community structure during in-vessel composting of agricultural waste by 16S rRNA sequencing. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Guo, X.; Zhou, L.; Yao, Q.; Zhu, H. Study of Biochemical and Microbiological Properties During Co-composting of Spent Mushroom Substrates and Chicken Feather. Waste Biomass-Valorization 2017, 10, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlemann, D.P.R.; Labrenz, M.; Jürgens, K.; Bertilsson, S.; Waniek, J.J.; Andersson, A.F. Transitions in bacterial communities along the 2000 km salinity gradient of the Baltic Sea. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motooka, D.; Fujimoto, K.; Tanaka, R.; Yaguchi, T.; Gotoh, K.; Maeda, Y.; Furuta, Y.; Kurakawa, T.; Goto, N.; Yasunaga, T.; et al. Fungal ITS1 Deep-Sequencing Strategies to Reconstruct the Composition of a 26-Species Community and Evaluation of the Gut Mycobiota of Healthy Japanese Individuals. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamdhad, A.S.; Singh, Y.K.; Ali, M.; Khwairakpam, M.; Kazmi, A. Rotary drum composting of vegetable waste and tree leaves. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6442–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.C. Methods of Soil and Tissue Analysis Used in the Analytical Laboratory; Canadian Forestry Service Information Report 1977, MM-X-78; Maritimes Forest Research Centre, Canadian Forestry Service, Department of the Environment: Fredericton, NB, Canada, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 17th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Anderson, M.J. Distance-based redundancy analysis: Testing multispecies responses in multifactorial ecological experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 1999, 69, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Peter Solymos, M.; Stevens, H.H.; Wagner, H. Package ‘Vegan’. Community Ecol. Package 2013, 2, 1–295. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.-J.; Zeng, G.-M.; Huang, D.-L.; Yu, H.-Y.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Dai, F.; Huang, G.-H. Use of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and sawdust as adsorbents of ammoniacal nitrogen in aerobic composting process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, B.; Xi, C.; Luo, X.; Yuan, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, H.; Cui, Z. Effect of pig manure on the chemical composition and microbial diversity during co-composting with spent mushroom substrate and rice husks. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 251, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X. Changes in physical, chemical, and microbiological properties during the two-stage co-composting of green waste with spent mushroom compost and biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvie, E.I. Genus Leuconostoc. In Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 8th ed.; Buchanan, R.E., Gibbons, N.E., Eds.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1974; pp. 529–550. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, V.; Quero, G.M.; Cho, G.S.; Kabisch, J.; Meske, D.; Neve, H.; Bockelmann, W.; Franz, C.M. The genus Weissella: Taxonomy, ecology and biotechnological potential. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Su, R.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J. Assessing the fermentation quality and microbial community of the mixed silage of forage soybean with crop corn or sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Qian, M.; Shen, Y.; Qin, X.; Huang, H.; Yang, H.; He, Y.; Bai, W. An high-throughput sequencing approach to the preliminary analysis of bacterial communities associated with changes in amino acid nitrogen, organic acid and reducing sugar contents during soy sauce fermentation. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, Q.N.M.; Mimoto, H.; Koyama, M.; Nakasaki, K. Lactic acid bacteria modulate organic acid production during early stages of food waste composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, C.; Donders, G.G.; Palmeira-De-Oliveira, R.; Queiroz, J.A.; Tomaz, C.; Martinez-De-Oliveira, J. Bacteriocin production of the probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus KS400. AMB Express 2018, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Q.; Huang, W.; Zheng, H.; Gao, X.; Yu, J.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z. Lactobacillus plantarum improves the efficiency of sheep manure composting and the quality of the final product. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 297, 122456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahle, H.; Hannisdal, B.; Steinsbu, B.O.; Ommedal, H.; Einen, J.; Jensen, S.; Larsen, O.; Øvreås, L.; Norland, S. Evolution of temperature optimum in Thermotogaceae and the prediction of trait values of uncultured organisms. Extremophiles 2011, 15, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, R.; Langworthy, T.A.; König, H.; Thomm, M.; Woese, C.R.; Sleytr, U.B.; Stetter, K.O. Thermotoga maritima sp. nov. represents a new genus of unique extremely thermophilic eubacteria growing up to 90 ℃. Arch. Microbiol. 1986, 144, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Laukkanen, M.; Nurmiaho-Lassila, E.L.; Rainey, F.A.; Niemela, S.I.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M. Bacillus thermosphaericus sp. nov.: A new thermophilic ureolytic bacillus isolated from air. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1995, 18, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortina, M.G.; Pukall, R.; Schumann, P.; Mora, D.; Parini, C.; Manachini, P.L.; Stackebrandt, E. Ureibacillus gen. nov., a new genus to accommodate Bacillus thermosphaericus (Anderson et al. 1995), emendation of Ureibacillus thermosphaericus and description of Ureibacillus terrenus sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 5, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Weon, H.-Y.; Kwon, S.-W.; Go, S.-J.; Park, Y.-K.; Schumann, P.; Fritze, D. Ureibacillus suwonensis sp. nov., isolated from cotton waste composts. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Wang, X.; Cong, C.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Hou, F.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L. Effect of inoculating microorganisms in chicken manure composting with maize straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, R.; Otawa, K.; Ozutsumi, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Abdel-Mohsein, H.S.; Nakai, Y. Development and analysis of microbial characteristics of an acidulocomposting system for the treatment of garbage and cattle manure. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Ma, A.; Zhuang, G.; Chen, G.; Liu, W. Diversity and dynamics of the microbial community on decomposing wheat straw during mushroom compost production. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 170, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Madlala, A.M.; Prior, B.A. Thermomyces lanuginosus: Properties of strains and their hemicellulases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).