Prophylaxis and Remediation for Future Pandemic Pathogens—(Lessons from a Post-COVID World)
Abstract
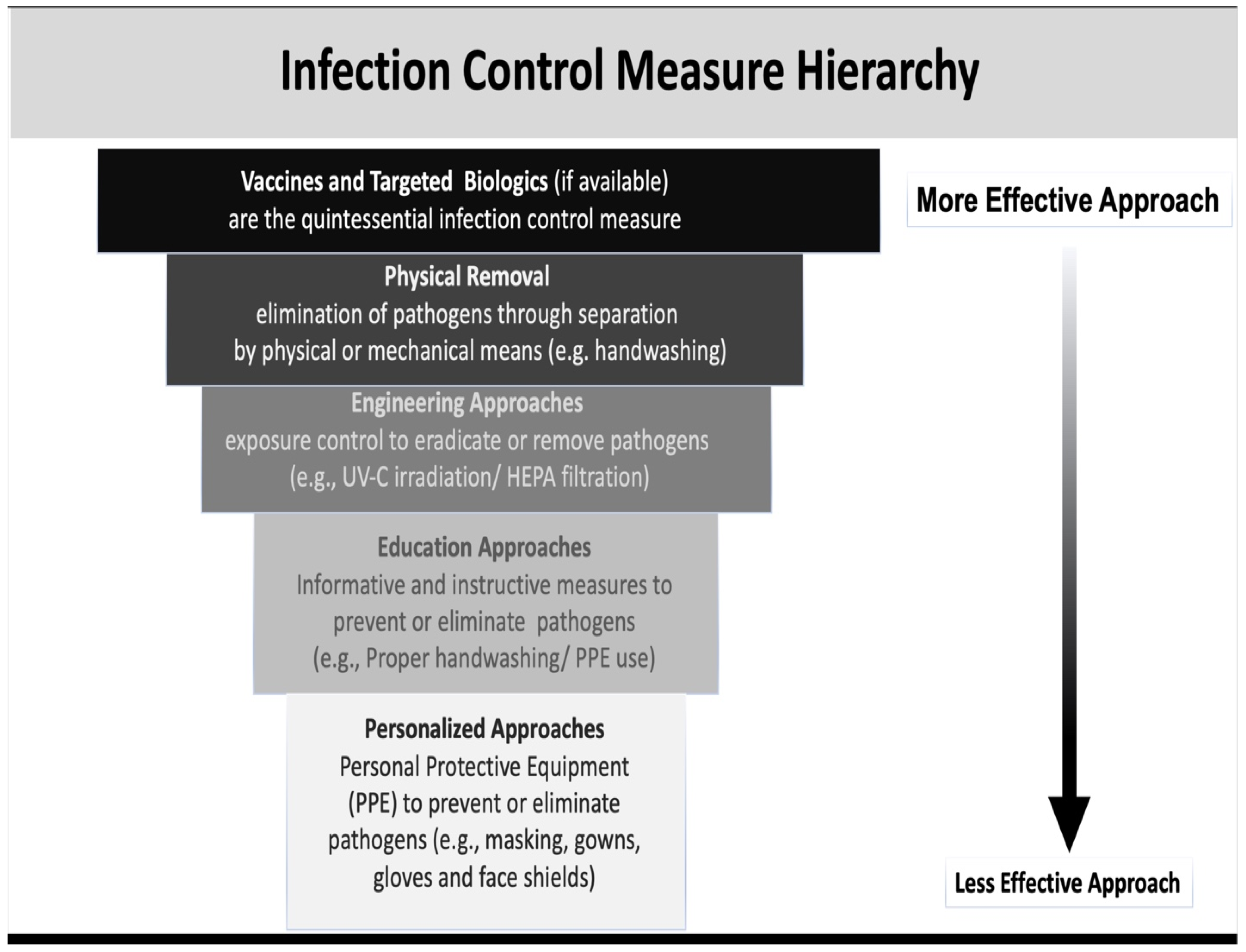
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Applied IEP Findings to Mask Design
2.2. Testing Chamber
2.3. Electronic Wearable Device Design
2.4. Virus and Surrogate Viral Modeling
3. Background and Significance
3.1. Physical Transmission Engineering Controls
3.2. Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation Engineering Controls
4. Results
Virus Structure and Isoelectric Point (IEP) Characterization
5. Applied IEP and Structural Characteristics to Improve PPE
6. Electrical Engineering Approaches
7. Virucidal Substrate Coatings for Prophylaxis
8. Conclusions and Future Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Zhu, J.; Song, J.; Sun, H.; et al. Eurasian avian-like H1N1 swine influenza virus with 2009 pandemic viral genes facilitating human infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17204–17210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radonovich, L.J., Jr.; Simberkoff, M.S.; Bessesen, M.T.; Brown, A.C.; Cummings, D.A.T.; Gaydos, C.A.; Los, J.G.; Krosche, A.E.; Gibert, C.L.; Gorse, G.J.; et al. Perl TMN95 Respirators vs Medical Masks for Preventing Influenza Among Health Care Personnel. Randomized Clin. Trial. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2019, 322, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boone, S.A.; Gerba, C.P. Significance of Fomites in the Spread of Respiratory and Enteric Viral Disease. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wood, J.P.; Richter, W.; Sunderman, M.M.; Calfee, M.W.; Serre, S.; Mickelsen, L. Evaluating the environmental persistence and inactivation of MS2 bacteriophage and the presumed Ebola virus surrogate phi6 using low concentration hydrogen peroxide vapor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3581–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, D. Is the coronavirus airborne? Experts can’t agree. Nature 2020, 580, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO. Scientific Brief: Modes of Transmission of Virus Causing COVID-19: Implications for IPC Precaution Recommendations; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, N.; Wei, J.; Yen, H.-L. Short-range airborne route dominates exposure of respiratory infection during close contact. Build. Environ. 2020, 176, 106859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, P.Y.; Coleman, K.K.; Tan, Y.K.; Ong, S.W.X.; Gum, M.; Lau, S.K.; Lim, X.F.; Lim, A.S.; Sutjipto, S.; Lee, P.H.; et al. Detection of Air and Surface Contamination by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Hospital Rooms of Infected Patients. medRxiv 2020, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tellier, R.; Li, Y.; Cowling, B.J.; Tang, J.W. Recognition of aerosol transmission of infectious agents: A commentary. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Booth, C.M.; Clayton, M.; Crook, B.; Gawn, J. Effectiveness of surgical masks against influenza bioaerosols. J. Hosp. Infect. 2013, 84, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsley, W.G.; Derk, R.C.; Coyle, J.P.; Martin, S.B., Jr.; Mead, K.R.; Blachere, F.M.; Beezhold, D.H.; Brooks, J.T.; Boots, T.; Noti, J.D. Efficacy of portable air cleaners and masking for reducing indoor exposure to simulated exhaled SARS-CoV-2 aerosols—United States. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.T.; Phillips, K.M.; Speth, M.M.; Besser, G.; Mueller, C.A.; Sedaghat, A.R. Portable HEPA purifiers to eliminate airborne SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 166, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, A.M.; Gracia-Pinilla, M.Á.; Pillai, S.C.; O’Shea, K. UV and visible light-driven production of hydroxyl radicals by reduced forms of N, F, and P codoped titanium dioxide. Molecules 2019, 24, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tseng, C.-C.; Li, C.-C. Inactivation of Viruses on Surfaces by Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2007, 4, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulauf, K.E.; Green, A.B.; Ba, A.N.N.; Jagdish, T.; Reif, D.; Seeley, R.; Dale, A.; Kirby, J.E. Microwave-Generated Steam Decontamination of N95 Respirators Utilizing Universally Accessible Materials. ASM J. mBio 2020, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.M.; Ko, G. Effect of ultraviolet germicidal irradiation on viral aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5460–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDevitt, J.J.; Lai, K.M.; Rudnick, S.N.; Houseman, E.A.; First, M.W.; Milton, D.K. Characterization of UVC light sensitivity of vaccinia virus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5760–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.; Peccia, J.; Fabian, P.; Martyny, J.W.; Fennelly, K.P.; Hernandez, M.; Miller, S.L. Efficacy of ultraviolet germicidal irradiation of upper-room air in inactivating air- borne bacterial spores and mycobacteria in full-scale studies. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDevitt, J.J.; Rudnick, S.N.; Radonovich, L.J. Aerosol susceptibility of influenza virus to UV-C light. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1961, 78, 1666–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Doremalen, N.; Bushmake, T.; Morris, D.H.; Holbrook, M.G.; Gamble, A.; Williamson, B.N.; Tamin, A.; Harcourt, J.L.; Thornburg, N.J.; Gerber, S.I.; et al. Aerosol and surface stability of HCoV-19 (SARS-CoV-2) compared to SARS-CoV-1. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1564–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorci, M.; Fink, T.D.; Sharma, V.; Singh, S.; Chen, R.; Arduini, B.L.; Dovidenko, K.; Heldt, C.L.; Palermo, E.F.; Zha, R.H. Virucidal N95 Respirator Face Masks via Ultrathin Surface-Grafted Quaternary Ammonium Polymer Coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 25135–25146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, R.; Lo, C.W.; Wada, S.; Somei, J.; Ochiai, H.; Murakami, T.; Saito, N.; Ogawa, T.; Shinjo, A.; Benno, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 disinfection of air and surface contamination by TiO(2) photocatalyst-mediated damage to viral morphology, RNA, and protein. Viruses 2021, 13, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboubakr, A.H.; Sharafeldin, T.A.; Goyal, S.M. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses in the environment and on common touch surfaces and the influence of climatic conditions: A review. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, E.; Garland, J.; Pillai, S.D. Electrostatic Forces Control Nonspecific Virus Attachment to Lettuce. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oss, C. Acid—Base interfacial interactions in aqueous media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1993, 78, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysikopoulos, C.V.; Syngouna, V.I. Attachment of bacteriophages MS2 and ΦX174 onto kaolinite and montmorillonite: Extended-DLVO interactions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 92, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Areo, O.; Joshi, P.U.; Obrenovich, M.; Tayahi, M.; Heldt, C.L. Single-Particle Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Isoelectric Point and Comparison to Variants of Interest. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Po, H.N.; Senozan, N. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: Its history and limitations. J. Chem. Educ. 2001, 78, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.A.; Herbert, B.; Sullivan, G.M.; Parrish, C.R.; Zadori, Z.; Tijssen, P.; Rossmann, M.G. The Structure of Porcine Parvovirus: Comparison with Related Viruses. J. Mol. Bio. 2002, 315, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shajahan, A.; Supekar, N.T.; Gleinich, A.S.; Azadi, P. Deducing the N- and O-glycosylation profile of the spike protein of novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Glycobiology 2020, 30, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.R.; Burnham, M.S.; Lute, S.C.; Johnson, S.A.; Walsh, A.A.; Brorson, K.A.; Roush, D.J. Defining the mechanistic binding of viral particles to a multi-modal anion exchange resin. Biotechnol. Prog. 2018, 34, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.K.; Evans, S.T.; Freed, A.S.; Keba, J.J.; Baer, Z.C.; Rege, K.; Cramer, S.M. Utilization of lysozyme charge ladders to examine the effects of protein surface charge distribution on binding affinity in ion exchange systems. Langmuir 2010, 26, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, I.M.; Abdelmalek, D.H.; Elshahat, M.E.; Elfiky, A.A. COVID-19 spike-host cell receptor GRP78 binding site prediction. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.D.; Wang, C.; Acevedo-Vélez, C.; Gellman, S.H.; Abbott, N.L. Modulation of hydrophobic interactions by proximally immobilized ions. Nature 2015, 517, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Vijayaragavan, K.S.; Heldt, C.L. Virus adsorption of water-stable quaternized chitosan nanofibers. Carbohydr. Res. 2014, 387, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Heldt, C.L. Adsorption of a non-enveloped mammalian virus to functionalized nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 121, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Bromley, E.K.; Joshi, P.U.; Long, F.; Caryn, L. Heldt Virus Isoelectric Point Determination Using Single-Particle Chemical Force Microscopy. Langmuir 2020, 36, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. China Novel Coronavirus, and T. Research, A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HMDB Website. Available online: https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0000230 (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM). Airborne Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Virtual Workshop, 26 to 27 August 2020; NASEM: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, H.H.; Ayala-Núñez, N.V.; Ixtepan Turrent, L.d.C.; Rodríguez Padilla, C. Bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Satoh, H.; Mitani, M. Theoretical study on electronic structures of FeOO, FeOOH, FeO(H2O), and FeO in hemes: As intermediate models of dioxygen reduction in cytochrome c oxidace. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2007, 101, 1410–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestry-Rodriguez, N.; Sicairos-Ruelas, E.E.; Gerba, C.P.; Bright, K.R. Silver as a Disinfectant. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.; Greenfield, R.; Frick, L. The persistence of antimicrobial effects in fabrics and garments embedded with silver after home and industrial launderings. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2015, 43, S43–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galdiero, S.; Falanga, A.; Vitiello, M.; Cantisani, M.; Marra, V.; Galdiero, M. Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antiviral Agent. Molecules 2011, 16, 8894–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, M.; Fu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Suo, H.; Kong, X.; Li, H. A review of different ventilation modes on thermal comfort, air quality and virus spread control. Build Environ. 2022, 212, 108831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.H.; Joe, Y.H.; Piri, A.; An, S.; Hwang, J. Determination of Air Filter Anti-Viral Efficiency against an Airborne Infectious Virus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, J.P.; Derk, R.C.; Lindsley, W.G.; Boots, T.; Blachere, F.M.; Reynolds, J.S.; McKinney, W.G.; Sinsel, E.W.; Lemons, A.R.; Beezhold, D.H.; et al. Reduction of exposure to simulated respiratory aerosols using ventilation, physical distancing, and universal masking. Indoor Air 2022, 32, e12987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, K.; Fu, S. Positively charged and flexible SiO2@ZrO2 nanofibrous membranes and their application in adsorption and separation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 13018–13025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Gao, A.; Cheng, J. A negative voltage generator for the sample-and-hold circuit in charge-domain pipelined ADCs. In Proceedings of the 2014 12th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), Guilin, China, 28–31 October 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakutani, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Nonomura, T.; Takikawa, Y.; Takami, T.; Toyoda, H. A Simple Electrostatic Precipitator for Trapping Virus Particles Spread via Droplet Transmission. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsuzuka, K.; Hatakeyama, F.; Asano, K.; Aonuma, S. Fundamental characteristics of electrostatic wafer chuck with insulating sealant. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2000, 36, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, L. Trapping virus in a shell. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.; Huang, A.; Li, Z.; Tufekci, Z.; Zdimal, V.; van der Westhuizen, H.M.; von Delft, A.; Price, A.; Fridman, L.; Tang, L.H.; et al. An evidence review of face masks against COVID-19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2014564118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, M.H.; Cheng, W.; Goh, S.S.; Kong, J.; Li, B.; Lim, J.Y.C.; Mao, L.; Wang, S.; Xue, K.; Yang, L.; et al. Face Masks in the New COVID-19 Normal: Materials, Testing, and Perspectives. Research 2020, 2020, 7286735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, J.R.; Schuksz, M.; Esko, J.D. Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature 2007, 446, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiie, T.; Maeda, M.; Kimura, M.; Hama, Y.; Uchida, M.; Kimura, Y. Structural Features of N-Glycans of Seaweed Glycoproteins: Predominant Occurrence of High-Mannose Type N-Glycans in Marine Plants. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 1996–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McHugh, D.J. A Guide to the Seaweed Industry, FAO Fisheries Technical Paper 441; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Millet, J.K.; Seron, K.; Labitt, R.N.; Danneels, A.; Palmer, K.E.; Whittaker, G.R.; Dubuisson, J.; Belouzard, S. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection is inhibited by griffithsin. Antiviral Res. 2016, 133, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihranyan, A.; Edsman, K.; Strømme, M. Rheological properties of cellulose hydrogels prepared from Cladophora cellulose powder. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie, J.-J.; Fang, J.-M. Development of effective anti-influenza drugs: Congeners and conjugates—A review. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maru, I.; Ohnishi, J.; Ohta, Y.; Tsukada, Y. Why is sialic acid attracting interest now? Complete enzymatic synthesis of sialic acid with N-acylglucosamine 2-epimerase. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2002, 93, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, E.J.; Binkley, S.B. The structure and chemistry of colominic acid. Biochemistry 1964, 3, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kragl, U.; Gygax, D.; Ghisalba, O.; Wandrey, C. Enzymatic 2-step synthesis of N-acetylneuraminic acid in the enzyme membrane reactor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1991, 30, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudian, M.; Noble, D.; Drake, C.; Middleton, R.; Montgomery, D.; Piercey, J.; Ramlakhan, D.; Todd, M.; Dawson, M. An efficient process for production of N-acetylneuraminic acid using N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1997, 20, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.O.; Yi, J.K.; Lee, S.G.; Takahashi, S.; Kim, B.G. Production of N-acetylneuraminic acid from N-acetylglucosamine and pyruvate using recombinant human renin binding protein and sialic acid aldolase in one pot. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2004, 35, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Xu, P. One-pot bio-synthesis: N-acetyl-D-neuraminic acid production by a powerful engineered whole-cell catalyst. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Björk, L.; Cresson, O. Correlation Between Concentration of Hypothiocyanate and Antibacterial Effect of the Lactoperoxidase System Against Escherichia coli. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 919–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Oettingen, W.F.; Neal, P.A.; Donahue, D.D. The Toxicity and Potential Dangers of Toluene: Preliminary Report. JAMA 1942, 118, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, C.; Mastromarino, P.; Riccioli, A.; Orsi, N. Electrostatic interactions in the early events of VSV infection. Res. Virol. 1991, 142, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obrenovich, M.E.; Tayahi, M.B.; Heidt, C.L.; Emancipator, S.N. Prophylaxis and Remediation for Future Pandemic Pathogens—(Lessons from a Post-COVID World). Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122407
Obrenovich ME, Tayahi MB, Heidt CL, Emancipator SN. Prophylaxis and Remediation for Future Pandemic Pathogens—(Lessons from a Post-COVID World). Microorganisms. 2022; 10(12):2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122407
Chicago/Turabian StyleObrenovich, Mark E., Moncef B. Tayahi, Caryn L. Heidt, and Steven N. Emancipator. 2022. "Prophylaxis and Remediation for Future Pandemic Pathogens—(Lessons from a Post-COVID World)" Microorganisms 10, no. 12: 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122407
APA StyleObrenovich, M. E., Tayahi, M. B., Heidt, C. L., & Emancipator, S. N. (2022). Prophylaxis and Remediation for Future Pandemic Pathogens—(Lessons from a Post-COVID World). Microorganisms, 10(12), 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122407




