Disalicylic Acid Provides Effective Control of Pectobacterium brasiliense
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Bacteria and Growth Conditions
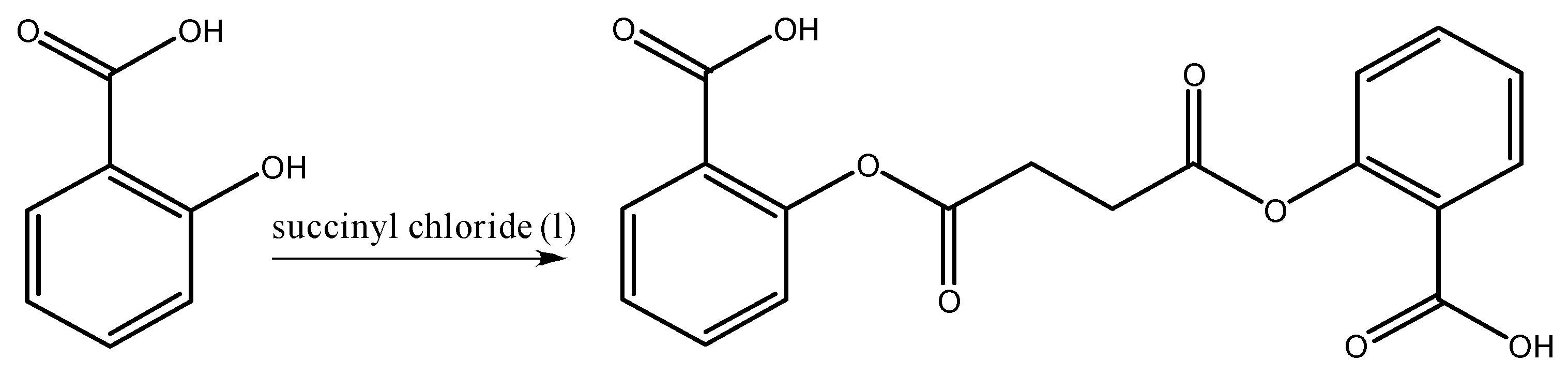
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Homology Modeling and Docking
2.4. MIC Assay
2.5. Biofilm-Inhibition Assay
2.6. Qualitative Assays for the Detection of AHL Molecules
2.7. Quantitative Assay for AHL Molecules Using CV026
2.8. Bioluminescence-Based, Quantitative Assay of AHL Molecules
2.9. Activities of Hydrolytic Enzymes
2.10. Virulence Assays
2.11. Effects of Bis(2-carboxyphenyl) on AHL Synthesis by E. coli DH5α QS-Negative Strain Complemented with Expi from Pb1692
3. Results
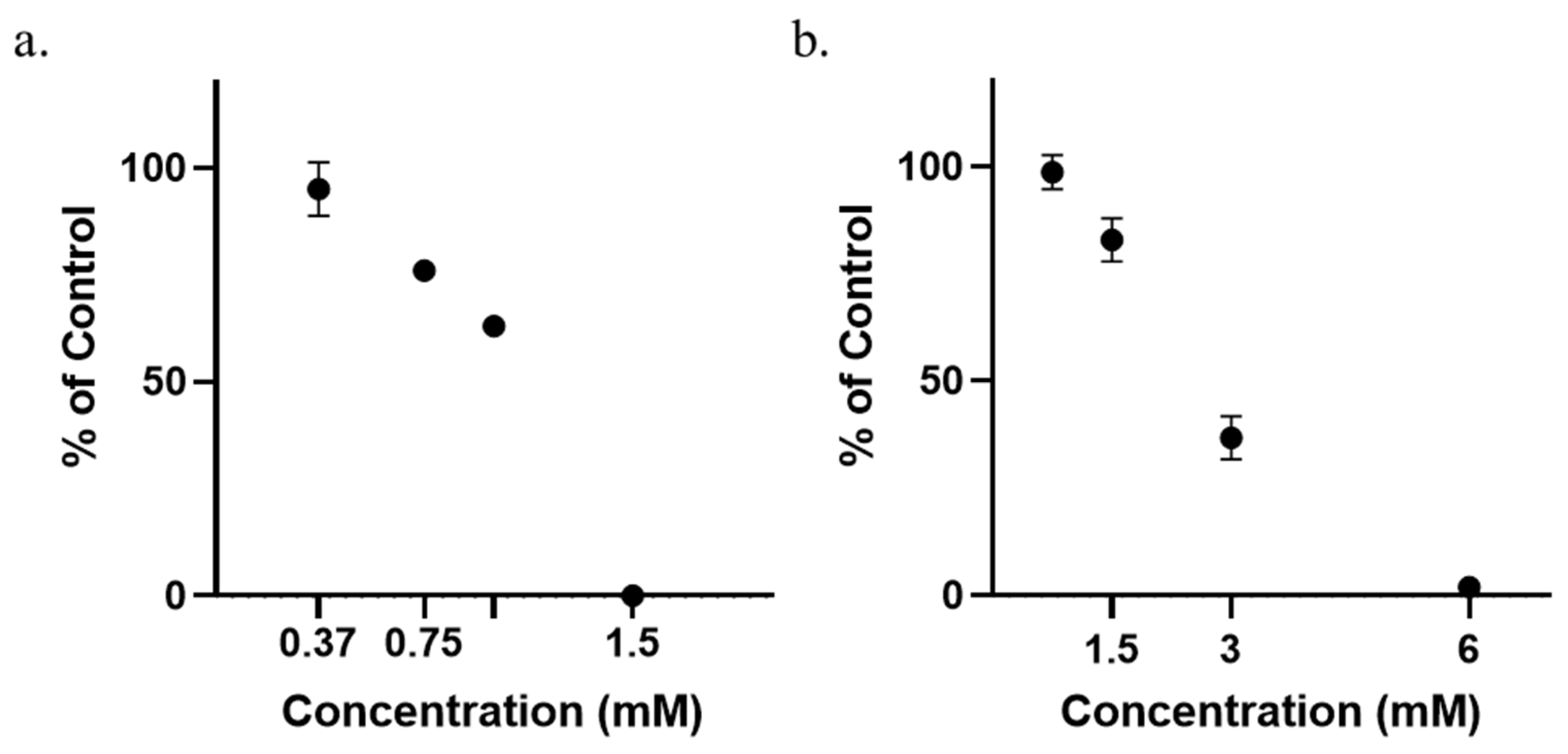
3.1. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
3.2. Molecular Docking of SAM, SA and DSA to ExpI
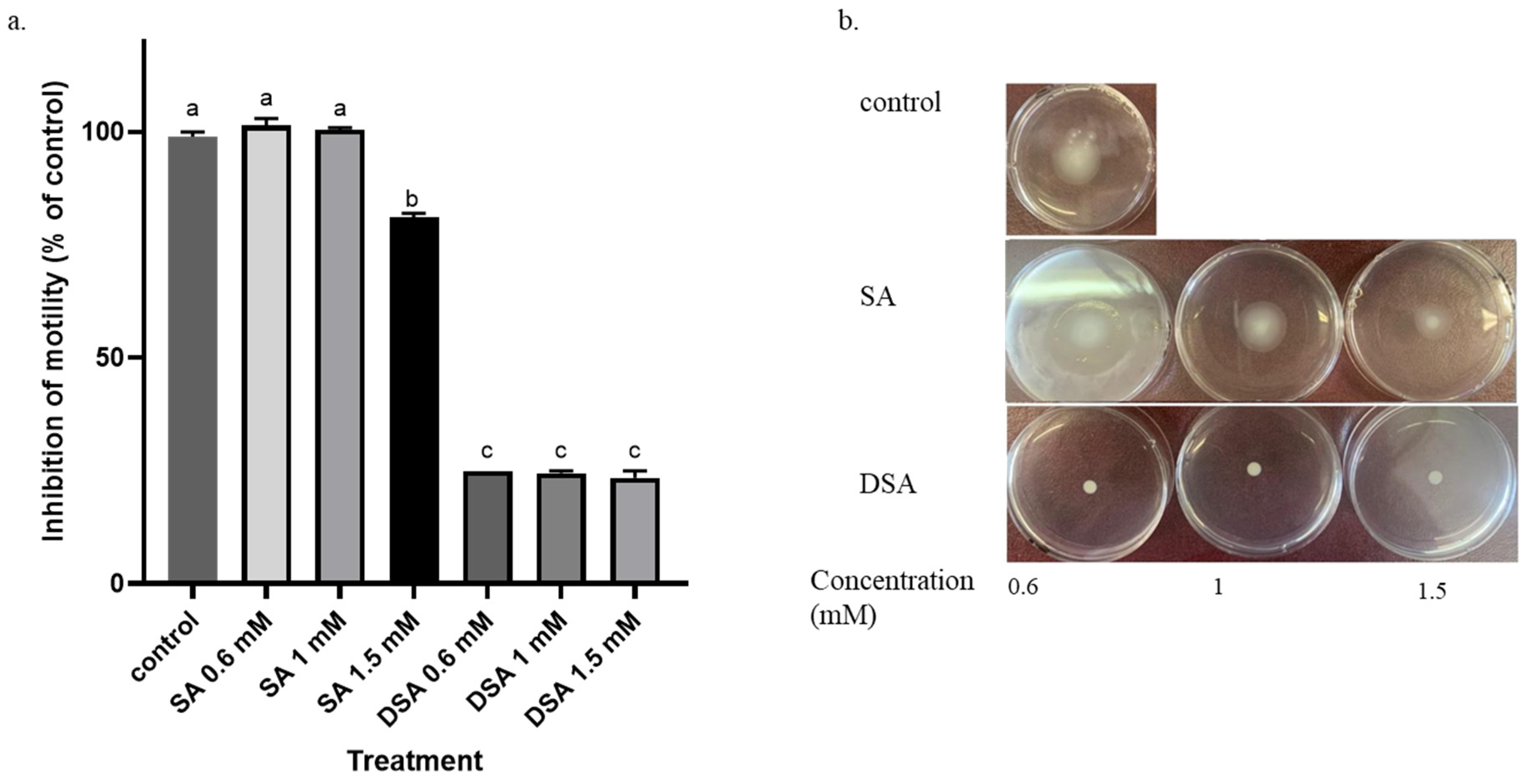
3.3. Effects of DSA and SA on Motility
3.4. Biofilm Formation
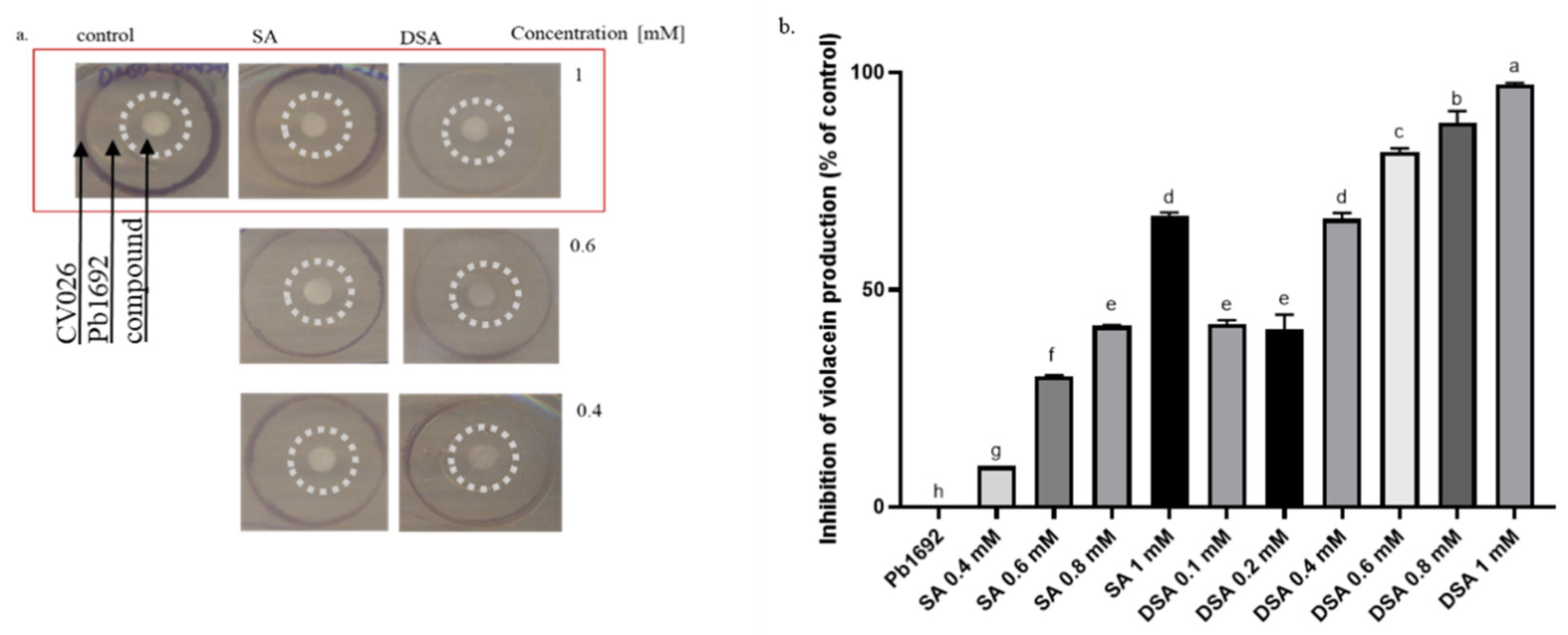
3.5. Effects of DSA on the Production of QS-Signaling Molecules
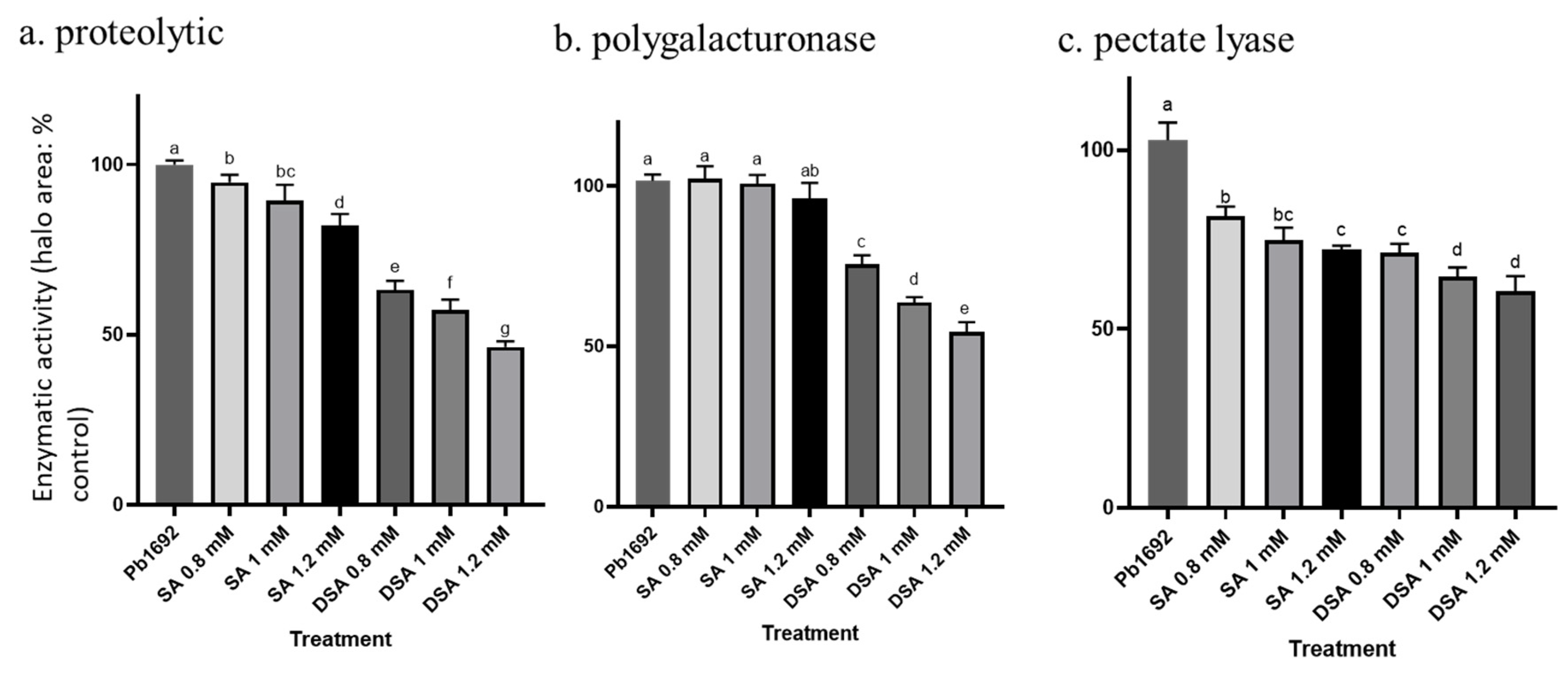
3.6. Effects of DSA on Exoenzyme Activity
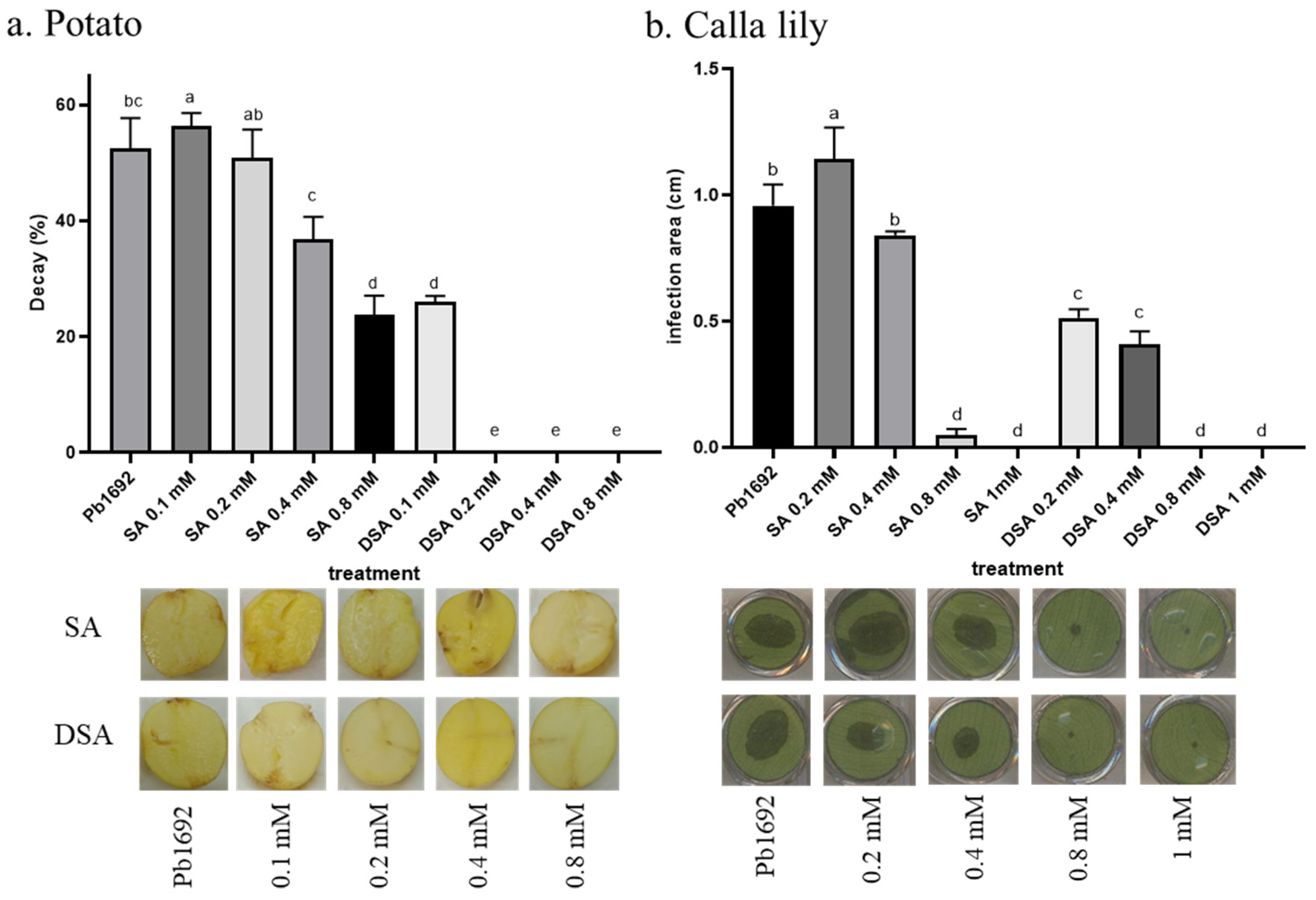
3.7. Infection following Applications of SA or DSA
3.8. Effect of DSA on AHL Biosynthesis in DH5α
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gullino, M.L.; Albajes, R.; Al-Jboory, I.; Angelotti, F.; Chakraborty, S.; Garrett, K.A.; Hurley, B.P.; Juroszek, P.; Makkouk, K.; Pan, X.; et al. Scientific Review of the Impact of Climate Change on Plant Pests; FAO on behalf of the IPPC Secretariat: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, J.R.; Khazanov, N.; Khadka, N.; Charkowski, A.O.; Burdman, S.; Carmi, N.; Yedidia, I.; Senderowitz, H. Direct binding of salicylic acid to Pectobacterium N-acyl-homoserine lactone synthase. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, J.R.; Khazanov, N.; Charkowski, A.; Faigenboim, A.; Senderowitz, H.; Yedidia, I. Interkingdom signaling interference: The effect of plant-derived small molecules on quorum sensing in plant-pathogenic bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2021, 59, 153–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corina Vlot, A.; Dempsey, D.A.; Klessig, D.F. Salicylic acid, a multifaceted hormone to combat disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klessig, D.F.; Choi, H.W.; Dempsey, D.A. Systemic acquired resistance and salicylic acid: Past, present, and future. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2018, 31, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šamec, D.; Karalija, E.; Šola, I.; Vujčić Bok, V.; Salopek-Sondi, B. The role of polyphenols in abiotic stress response: The influence of molecular structure. Plants 2021, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, D.A.; Klessig, D.F. How does the multifaceted plant hormone salicylic acid combat disease in plants and are similar mechanisms utilized in humans? BMC Biol 2017, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klessig, D.F.; Tian, M.; Choi, H.W. Multiple targets of salicylic acid and its derivatives in plants and animals. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bandara, M.B.K.; Zhu, H.; Sankaridurg, P.R.; Willcox, M.D.P. Salicylic acid reduces the production of several potential virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with microbial keratitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 4453–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asfour, H. Anti-quorum sensing natural compounds. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, J.R.; Burdman, S.; Lipsky, A.; Yariv, S.; Yedidia, I. Plant phenolic acids affect the virulence of Pectobacterium aroidearum and P. carotovorum ssp. brasiliense via quorum-sensing regulation. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 487–500. [Google Scholar]
- van der Merwe, J.J.; Coutinho, T.A.; Korsten, L.; van der Waals, J.E. Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis causing blackleg on potatoes in South Africa. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 126, 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, L.C.M.; Ferreira, R.B.R.; Buckner, M.M.C.; Finlay, B.B. Quorum sensing in bacterial virulence. Microbiology 2010, 156, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleleki, L.N.; Pretorius, R.G.; Tanui, C.K.; Mosina, G.; Theron, J. A quorum sensing-defective mutant of Pectobacterium carotovorum ssp. brasiliense 1692 is attenuated in virulence and unable to occlude xylem tissue of susceptible potato plant stems. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 18, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhuang, X.; Chu, W. Tea polyphenols as an antivirulence compound disrupt quorum-sensing regulated pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valente, R.S.; Nadal-Jimenez, P.; Carvalho, A.F.P.; Vieira, F.J.D.; Xavier, K.B. Signal integration in quorum sensing enables cross-species induction of virulence in Pectobacterium wasabiae. mBio 2017, 8, e00398-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faure, D.; Dessaux, Y. Quorum sensing as a target for developing control strategies for the plant pathogen Pectobacterium. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 119, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha Neto, A.C.; Maraschin, M.; Di Piero, R.M. Antifungal activity of salicylic acid against Penicillium expansum and its possible mechanisms of action. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 215, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, R.d.S.; Balbino, B.L.; Andrade, G.; Dias, M.C.P.S.; Alvarenga, T.A.; Pedroso, R.C.N.; Pimenta, L.P.; Lucarini, R.; Pauletti, P.M.; Januário, A.H.; et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-Candida spp. activity of plant-derived products. Plants 2019, 8, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braga, A.L.; Rafique, J. Synthesis of biologically relevant small molecules containing selenium. Part B. Anti-infective and anticancer compounds. In PATAI’S Chemistry of Functional Groups; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2014; pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Claudius, A.K.; Kankipati, C.S.; Kilari, R.S.; Hassan, S.; Guest, K.; Russell, S.T.; Perry, C.J.; Stark, L.A.; Nicholl, I.D. Identification of aspirin analogues that repress NF-κB signalling and demonstrate anti-proliferative activity towards colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- CLSI M07; Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically. 11th ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018.
- O’Toole, G.A. Microtiter dish biofilm formation assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 2011, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClean, K.H.; Winson, M.K.; Fish, L.; Taylor, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Camara, M.; Daykin, M.; Lamb, J.H.; Swift, S.; Bycroft, B.W.; et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: Exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chenia, H. Anti-quorum sensing potential of crude Kigelia africana fruit extracts. Sensors 2013, 13, 2802–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yan, C.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lv, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.; Xia, X. Punicalagin inhibits Salmonella virulence factors and has anti-quorum-sensing potential. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6204–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winson, M.K.; Swift, S.; Fish, L.; Throup, J.P.; Jørgensen, F.; Chhabra, S.R.; Bycroft, B.W.; Williams, P.; Stewart, G.S.A.B. Construction and analysis of luxCDABE-based plasmid sensors for investigating N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 163, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, B.; Rodgers, H.C.; Camara, M.; Knox, A.J.; Williams, P.; Hardman, A. Direct detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones in cystic fibrosis sputum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 207, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dumenyo, C.K.; Chatterjee, A.K. Inactivation of rsmA leads to overproduction of extracellular pectinases, cellulases, and proteases in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora in the absence of the starvation/cell density-sensing signal, N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto, T.; Golan, A.; Yishay, M.; Bilkis, I.; Ben-Ari, J.; Yedidia, I. Priming of antimicrobial phenolics during induced resistance response towards Pectobacterium carotovorum in the ornamental monocot calla lily. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10315–10322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.A.; Lee, S.J.; Park, N.H.; Mechesso, A.F.; Birhanu, B.T.; Kang, J.; Reza, M.A.; Suh, J.-W.; Park, S.C. Impact of phenolic compounds in the acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing regulatory pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deb, J.; Dibra, H.; Shan, S.; Rajan, S.; Manneh, J.; Kankipati, C.S.; Perry, C.J.; Nicholl, I.D. Activity of aspirin analogues and vanillin in a human colorectal cancer cell line. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pun, M.; Khazanov, N.; Galsurker, O.; Weitman, M.; Kerem, Z.; Senderowitz, H.; Yedidia, I. Phloretin, an apple phytoalexin, affects the virulence and fitness of Pectobacterium brasiliense by interfering with quorum-sensing. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, J.R.; Burdman, S.; Lipsky, A.; Yedidia, I. Effects of plant antimicrobial phenolic compounds on virulence of the genus Pectobacterium. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing signal–response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidsson, P.R.; Kariola, T.; Niemi, O.; Tapio Palva, E. Pathogenicity of and plant immunity to soft rot pectobacteria. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, G. Flagella and bacterial pathogenicity. J. Basic Microbiol. 2013, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Põllumaa, L.; Alamäe, T.; Mäe, A. Quorum sensing and expression of virulence in pectobacteria. Sensors 2012, 12, 3327–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murata, H.; Chatterjee, A.; Liu, Y.; Chatterjee, A.K. Regulation of the production of extracellular pectinase, cellulase, and protease in the soft rot bacterium Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora: Evidence that aepH of E. carotovora subsp. carotovora 71 activates gene expression in E. carotovora subsp. carotovora, E. carotovora subsp. atroseptica, and Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3150–3159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beceiro, A.; Tomás, M.; Bou, G. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence: A successful or deleterious association in the bacterial world? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 185–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caramona, A.; Coimbra, I.; Pinto, T.; Aparício, S.; Madeira, P.J.A.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Marto, J.; Almeida, A.J. Repurposing of marine raw materials in the formulation of innovative plant protection products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 4221–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A.K.S.; Rudden, M.; Smyth, T.J.; Dooley, J.S.G.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Natural quorum sensing inhibitors effectively downregulate gene expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3521–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, C.; Mou, Z. Salicylic acid and its function in plant immunity. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, L.E.; Carbone, A.L.; Römling, U.; Uhrich, K.E.; Chikindas, M.L. Salicylic acid-based poly(anhydride esters) for control of biofilm formation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, A.M.L.; Bowden, S.D.; Burr, T.; Coulthurst, S.J.; Monson, R.E.; Salmond, G.P.C. Quorum sensing, virulence and secondary metabolite production in plant soft-rotting bacteria. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 1165–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Coulthurst, S.J.; Pritchard, L.; Hedley, P.E.; Ravensdale, M.; Humphris, S.; Burr, T.; Takle, G.; Brurberg, M.-B.; Birch, P.R.J.; et al. Quorum sensing coordinates brute force and stealth modes of infection in the plant pathogen Pectobacterium atrosepticum. PLoS Pathol. 2008, 4, e1000093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Van Wees, S.C.M.; Ton, J.; Van Pelt, J.A.; Van Loon, L.C. Signalling in Rhizobacteria-Induced Systemic Resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biol. 2002, 4, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prithiviraj, B.; Bais, H.P.; Weir, T.; Suresh, B.; Najarro, E.H.; Dayakar, B.V.; Schweizer, H.P.; Vivanco, J.M. Down-regulation of virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by salicylic acid attenuates its virulence on Arabidopsis thaliana and Caenorhabditis elegans. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kupferwasser, L.I.; Yeaman, M.R.; Nast, C.C.; Kupferwasser, D.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Palma, M.; Cheung, A.L.; Bayer, A.S. Salicylic acid attenuates virulence in endovascular infections by targeting global regulatory pathways in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Glide Emodel (kcal mol−1) | Docking SP Score (kcal mol−1) | Protein/Ligand |
|---|---|---|
| −65.9 | −6.8 | ExpI/SAM |
| −61.7 | −5.6 | ExpI/DSA |
| −30.9 | −5.0 | ExpI/SA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuizer, S.; Pun, M.; Yedidia, I.; Kerem, Z. Disalicylic Acid Provides Effective Control of Pectobacterium brasiliense. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122516
Tuizer S, Pun M, Yedidia I, Kerem Z. Disalicylic Acid Provides Effective Control of Pectobacterium brasiliense. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(12):2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122516
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuizer, Sapir, Manoj Pun, Iris Yedidia, and Zohar Kerem. 2022. "Disalicylic Acid Provides Effective Control of Pectobacterium brasiliense" Microorganisms 10, no. 12: 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122516
APA StyleTuizer, S., Pun, M., Yedidia, I., & Kerem, Z. (2022). Disalicylic Acid Provides Effective Control of Pectobacterium brasiliense. Microorganisms, 10(12), 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122516







