Screening of Antimicrobial Activities and Lipopeptide Production of Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Vetiver Roots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial and Fungal Strains
2.2. Dual Culture Test of Selected Vetiver Bacterial Endophytes against F. oxysporum and F. culmorum
2.3. Preparation of Supernatant Samples of Bacterial Endophytes
2.4. Antagonism Test of Cell-Free Supernatants of the Selected Vetiver Bacterial Endophytes against Fusarium Species
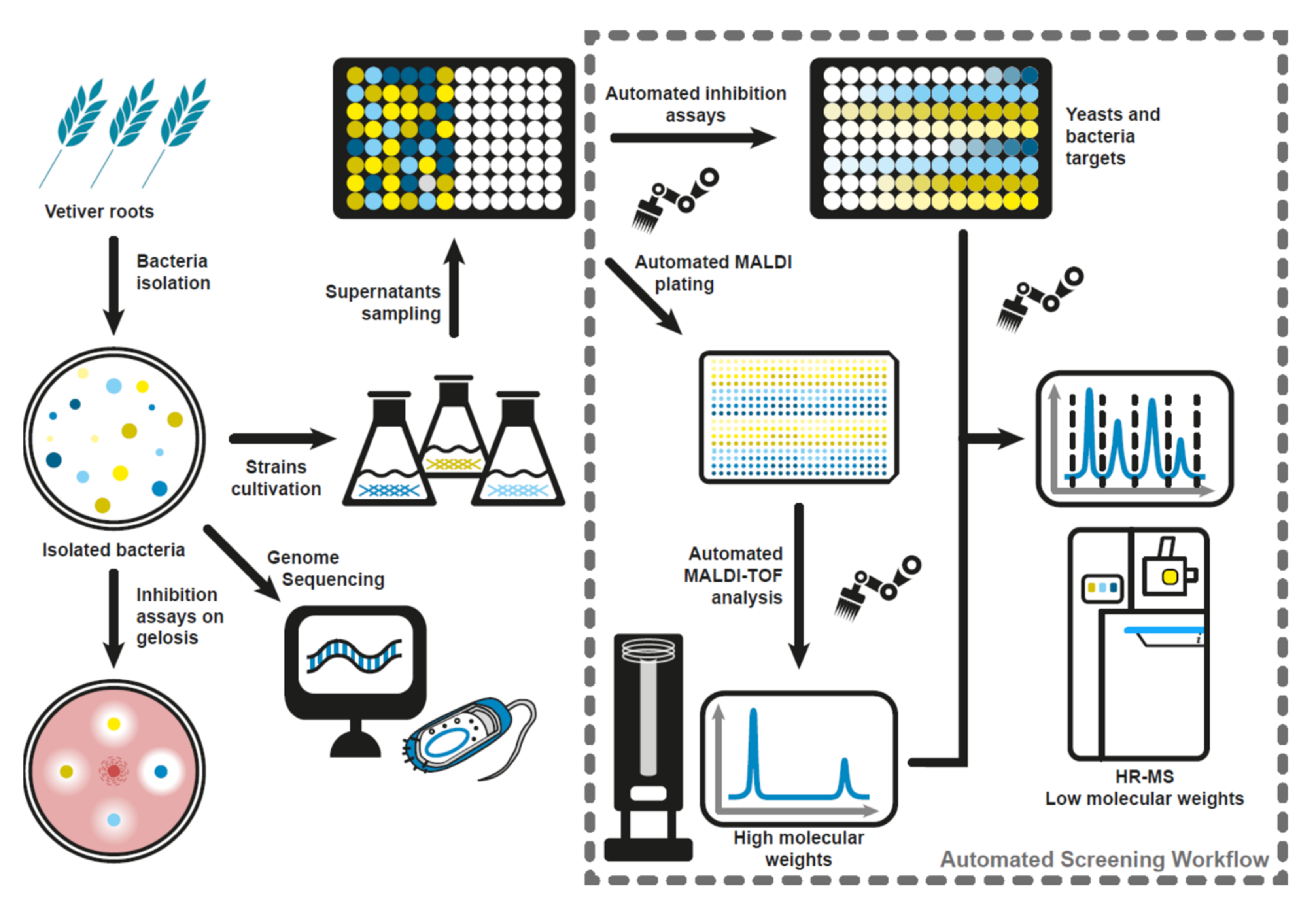
2.5. Fully Automated Workflow for Cell-Free Supernatant Screening for Antimicrobial Metabolites
2.6. Antagonism Test of Cell-Free Supernatant of the Endophytes against E. coli and S. cerevisiae
2.7. Lipopeptide Detection with MALDI-TOF
2.8. Accurate Mass Measurement of Lipopeptides by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS)
2.9. DNA Extraction and Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.10. Effects of Surfactin and Plipastatin on the In Vitro Growth of Fusarium Species
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antifungal Activities of Vetiver Endophytic Bacterial Strains against Plant Pathogens
3.2. Antimicrobial Activities of the Cell-Free Crude Supernatants of the Vetiver Bacterial Endophytes
3.3. Screening for Lipopeptides in Supernatant Samples of Vetiver Endophytes by MALDI-TOF
3.4. Accurate Mass Measurement by LC-HRMS
3.5. Genome Sequencing and NRPS Cluster Characterization
3.6. Antagonistic Activities of Surfactins and Plipastatins against Fusarium Species
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lam, K.S. New aspects of natural products in drug discovery. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bérdy, J. Bioactive microbial metabolites: A personal view. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glare, T.; Caradus, J.; Gelernter, W.; Jackson, T.; Keyhani, N.; Köhl, J.; Marrone, P.; Morin, L.; Stewart, A. Have biopesticides come of age? Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, J.R.; Dachbrodt-Saaydeh, S.; Kudsk, P.; Messéan, A. Toward a reduced reliance on conventional pesticides in European agriculture. Plant Dis. 2015, 100, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brader, G.; Compant, S.; Mitter, B.; Trognitz, F.; Sessitsch, A. Metabolic potential of endophytic bacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castillo, U.; Harper, J.; Strobel, G.; Sears, J.; Alesi, K.; Ford, E.; Lin, J.; Hunter, M.; Maranta, M.; Ge, H.; et al. Kakadumycins, novel antibiotics from Streptomyces Sp. NRRL 30566, an endophyte of Grevillea pteridifolia. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 224, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, A.; Singh, R.; Pandey, K.D. Endophytic bacteria: A new source of bioactive compounds. 3 Biotech. 2017, 7, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, U.F.; Strobel, G.A.; Mullenberg, K.; Condron, M.M.; Teplow, D.B.; Folgiano, V.; Gallo, M.; Ferracane, R.; Mannina, L.; Viel, S.; et al. Munumbicins E-4 and E-5: Novel broad-spectrum antibiotics from Streptomyces NRRL 3052. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 255, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, C.M.; Kenny, G.; Redgrave, B.; Sears, J.; Condron, M.M.; Teplow, D.B.; Strobel, G. Ecomycins, unique antimycotics from Pseudomonas viridiflava. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 84, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, A.-D.; Li, H.-P.; Yuan, Q.-S.; Song, X.-S.; Yao, W.; He, W.-J.; Zhang, J.-B.; Liao, Y.-C. Antagonistic Mechanism of Iturin A and Plipastatin A from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens S76-3 from wheat spikes against Fusarium graminearum. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ongena, M.; Jacques, P. Bacillus lipopeptides: Versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Shi, G.; Wu, L.; Lou, Z.; Huo, R.; Wu, H.; Borriss, R.; Gao, X. Bacillomycin D Produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens is involved in the antagonistic interaction with the plant-pathogenic Fungus Fusarium graminearum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01075–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toral, L.; Rodríguez, M.; Béjar, V.; Sampedro, I. Antifungal activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus XT1 CECT 8661 against Botrytis cinerea. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Yao, J. Characterization of Fusarium graminearum inhibitory lipopeptide from Bacillus subtilis IB. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourmentza, K.; Gromada, X.; Michael, N.; Degraeve, C.; Vanier, G.; Ravallec, R.; Coutte, F.; Karatzas, K.A.; Jauregi, P. Antimicrobial activity of lipopeptide biosurfactants against foodborne pathogen and food spoilage microorganisms and their cytotoxicity. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gond, S.K.; Bergen, M.S.; Torres, M.S.; White, J.F., Jr. Endophytic Bacillus spp. produce antifungal lipopeptides and induce host defence gene expression in maize. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 172, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhl, J.; Kolnaar, R.; Ravensberg, W.J. Mode of action of microbial biological control agents against plant diseases: Relevance beyond efficacy. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldani, I.; Baldani, V.L.D. Characterization of Herbaspirillurn Seropedicae gen. nov. sp. nov. a root-associated nitrogen-fixing bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1986, 36, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Carrión, V.J.; Perez-Jaramillo, J.; Cordovez, V.; Tracanna, V.; de Hollander, M.; Ruiz-Buck, D.; Mendes, L.W.; van Ijcken, W.F.J.; Gomez-Exposito, R.; Elsayed, S.S.; et al. Pathogen-induced activation of disease-suppressive functions in the endophytic root microbiome. Science 2019, 366, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, F.S.; Poehlein, A.; Kröger, C.; Voigt, C.A.; Piepenbring, M.; Bode, H.B.; Daniel, R.; Schäfer, W.; Streit, W.R. Molecular keys to the Janthinobacterium and Duganella spp. interaction with the plant pathogen Fusarium graminearum. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aleti, G.; Sessitsch, A.; Brader, G. Genome mining: Prediction of lipopeptides and polyketides from Bacillus and related firmicutes. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flissi, A.; Ricart, E.; Campart, C.; Chevalier, M.; Dufresne, Y.; Michalik, J.; Jacques, P.; Flahaut, C.; Lisacek, F.; Leclère, V.; et al. Norine: Update of the nonribosomal peptide resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D465–D469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munakata, Y.; Gavira, C.; Genestier, J.; Bourgaud, F.; Hehn, A.; Slezack-Deschaumes, S. Composition and functional comparison of vetiver root endophytic microbiota originating from different geographic locations that show antagonistic activity towards Fusarium graminearum. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 243, 126650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasakthi, S.; Kanchana, D.; Usharani, G.; Saranraj, P. Production of plant growth promoting substance by Pseudomonas fluorescens and Bacillus subtilis isolates from paddy rhizosphere soil of Cuddalore District, Tamil Nadu, India. Int. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 8, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, R.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Liu, P.; Yang, T.; Bao, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X. Identification and evaluation of a potential biocontrol agent, Bacillus subtilis, against Fusarium sp. in apple seedlings. Ann. Microbiol. 2013, 64, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmawan, F.; Fatiah, R.; Jamsari, J. Antifungal abilities of Serratia plymuthica UBCF_13 produced in different types of media and culture time. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 741, 12060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing | Journal of Computational Biology. Available online: https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021 (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Kloosterman, A.M.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; van Wezel, G.P.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. AntiSMASH 6.0: Improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W29–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulier, S.; Nannan, C.; Gillis, A.; Licciardi, F.; Bragard, C.; Mahillon, J. Overview of the antimicrobial compounds produced by members of the Bacillus subtilis group. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kshetri, L.; Naseem, F.; Pandey, P. Role of Serratia sp. as biocontrol agent and plant growth stimulator, with prospects of biotic stress management in plant. In Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria for Sustainable Stress Management; Microorganisms for Sustainability; Sayyed, R.Z., Ed.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2019; Volume 13, pp. 169–200. ISBN 9789811369858. [Google Scholar]
- Kai, M.; Haustein, M.; Molina, F.; Petri, A.; Scholz, B.; Piechulla, B. Bacterial volatiles and their action potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 81, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmann, A.; Aly, A.H.; Lin, W.; Wang, B.; Proksch, P. Co-cultivation—A powerful emerging tool for enhancing the chemical diversity of microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Bergeijk, D.A.; Terlouw, B.R.; Medema, M.H.; van Wezel, G.P. Ecology and genomics of actinobacteria: New concepts for natural product discovery. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, R.C.; Piechulla, B.; Warber, D.; Svatoš, A.; Kai, M. Metabolic profiling of rhizobacteria Serratia plymuthica and Bacillus subtilis revealed intra- and interspecific differences and elicitation of plipastatins and short peptides due to co-cultivation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaijmakers, J.M.; De Bruijn, I.; Nybroe, O.; Ongena, M. Natural functions of lipopeptides from Bacillus and Pseudomonas: More than surfactants and antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 1037–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Teng, K.; Wang, T.; Dong, E.; Zhang, M.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, J. Antimicrobial Bacillus velezensis HC6: Production of three kinds of lipopeptides and biocontrol potential in maize. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loiseau, C.; Schlusselhuber, M.; Bigot, R.; Bertaux, J.; Berjeaud, J.-M.; Verdon, J. Surfactin from Bacillus subtilis displays an unexpected anti-legionella activity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5083–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalache, G.; Balaes, T.; Gostin, I.; Stefan, M.; Coutte, F.; Krier, F. Lipopeptides produced by Bacillus subtilis as new biocontrol products against fusariosis in ornamental plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29784–29793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmyttere, H.; Deweer, C.; Muchembled, J.; Sahmer, K.; Jacquin, J.; Coutte, F.; Jacques, P. Antifungal activities of Bacillus subtilis lipopeptides to two Venturia inaequalis strains possessing different tebuconazole sensitivity. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramarathnam, R.; Bo, S.; Chen, Y.; Fernando, W.G.D.; Xuewen, G.; de Kievit, T. Molecular and biochemical detection of fengycin- and bacillomycin D-producing Bacillus spp., antagonistic to fungal pathogens of canola and wheat. Can. J. Microbiol. 2007, 53, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parveen Rani, R.; Anandharaj, M.; Hema, S.; Deepika, R.; David Ravindran, A. Purification of antilisterial peptide (Subtilosin A) from Novel Bacillus tequilensis FR9 and demonstrate their pathogen invasion protection ability using human carcinoma cell line. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shelburne, C.E.; An, F.Y.; Dholpe, V.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Lopatin, D.E.; Lantz, M.S. The spectrum of antimicrobial activity of the bacteriocin Subtilosin A. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Cell-Free Supernatant *1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | Genbank Accession | Accession (Munakata et al., 2021) | BLAST Top Hit Species | E. coli | S. cerevisiae |
| 1 | OK662633 | M1_08 | Yokenella regensburgei | − | − |
| 2 | OK662634 | P2_02 | Pseudomonas koreensis | − | − |
| 3 | OK662635 | P2_06 | Pseudomonas vancouverensis | − | − |
| 4 | OK662636 | P2_15 | Serratia grimesii | − | − |
| 5 | OK662637 | P2_16 | Pseudomonas vancouverensis | − | − |
| 6 | OK662638 | P2_25 | Pseudomonas vancouverensis | − | − |
| 7 | OK662639 | P2_28 | Microbacterium hominis | − | − |
| 8 | OK662640 | P3_01 | Serratia grimesii | − | − |
| 9 | OK662641 | P3_07 | Serratia grimesii | − | − |
| 10 | OK662959 | P3_08 | Pseudomonas koreensis | − | − |
| 11 | OK662642 | P3_13 | Serratia grimesii | − | − |
| 12 | OK662643 | P3_17 | Serratia grimesii | − | − |
| 13 | OK662644 | P3_18 | Pseudomonas koreensis | − | − |
| 14 | OK662645 | P3_19 | Pseudomonas koreensis | − | − |
| 15 | OK662646 | P3_24 | Pseudomonas koreensis | − | − |
| 16 | OK662647 | P3_25 | Serratia grimesii strain | − | − |
| 17 | OK662648 | P3_26 | Pseudomonas koreensis | − | − |
| 18 | OK662649 | P3_27 | Pseudomonas koreensis | − | − |
| 19 | OK662650 | P3_28 | Serratia grimesii | − | − |
| 20 | OK662651 | P3_29 | Serratia grimesii | − | − |
| 21 | OK662652 | P3_30 | Serratia grimesii | − | − |
| 22 | OK662653 | R22_05 | Bacillus subtilis | +/− | − |
| 23 | OK662654 | R22_06 | Bacillus subtilis | +/− | − |
| 24 | OK662655 | R22_08 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | − | − |
| 25 | OK662656 | R23_08 | Bacillus tequilensis | − | − |
| 26 | OK662657 | R23_12 | Bacillus subtilis | + | − |
| 27 | OK662658 | R23_17 | Bacillus cereus | − | − |
| 28 | OK662659 | R23_28 | Bacillus subtilis | +++ | − |
| 29 | OK662660 | S1_29 | Enterobacter cloacae subsp. dissolvens | +++ | − |
| 30 | OK662661 | S2_11 | Janthinobacterium lividum | − | − |
| 31 | OK662662 | S2_18 | Janthinobacterium lividum | − | − |
| m/z | Strain 22 | Strain 23 | Strain 25 | Strain 26 | Strain 28 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identification | 48 h | 72 h | 48 h | 72 h | 48 h | 72 h | 48 h | 72 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| 724.44 | Plipastatin B C13 [M + H2]2+ Plipastatin A C15 [M + H2]2+ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 746.43 | Plipastatin B C13 [M + Na2]2+ Plipastatin A C15 [M + Na2]2+ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 762.42 | Plipastatin B C13 [M + K2]2+ Plipastatin A C15 [M + K2]2+ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 781.35 | Plipastatin B C18 [M + Na2]2+ | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| 1030.72 | Surfactin C13 [M + Na]+ [Val7] Surfactin C14 [M + Na]+ [Ala4] Surfactin C15 [M + Na]+ | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + |
| 1044.74 | Surfactin C14 [M + Na]+ [Val7] Surfactin C15 [M + Na]+ | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1058.75 | Surfactin C15 [M + Na]+ [Val7] Surfactin C16 [M + Na]+ | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1060.71 | Surfactin C14 [M + K]+ [Val7] Surfactin C15 [M + K]+ | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1074.74 | Surfactin C15 [M + K]+ [Val7] Surfactin C16 [M + K]+ | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1088.73 | Surfactin C16 [M + K]+ [Val7] Surfactin C17 [M + K]+ | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + |
| 1485.86 | Plipastatin B C14 [M + Na]+ Plipastatin A C16 [M + Na]+ | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + |
| 1515.89 | Plipastatin B C15 [M + K]+ Plipastatin A C17 [M + K]+ | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 1571.63 | Plipastatin B C19 [M + K]+ | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | + | + | - |
| B. subtilis Strains | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | Category | 22 | 23 | 26 | 28 | Remarks | |||
| Bacilysin | Other | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | ||||
| Subtilosin A | Thiopeptide | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | ||||
| Bacillibactin | NRP | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | ||||
| Bacillaene | Polyketide + NRP | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | ||||
| Plipastatin | NRP | 100% | 80% 46%, 23% | 100% | 100% | possible peptide chain: Glu-D-Orn-Tyr-D-Thr-Glu-D-Val-Pro-Glu-D-Tyr-Ile | |||
| Surfactin | NRP | 82% | 82% | 82% | 43%, 43%, 8% | possible peptide chain: Glu-Leu-D-Leu-Val-Asp-D-Leu-Leu | |||
| Icosalide A/B | NRP | 100% | |||||||
| Sporulation killing factor | RiPP: Head-to-tail cyclized peptide | 100% | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munakata, Y.; Heuson, E.; Daboudet, T.; Deracinois, B.; Duban, M.; Hehn, A.; Coutte, F.; Slezack-Deschaumes, S. Screening of Antimicrobial Activities and Lipopeptide Production of Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Vetiver Roots. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020209
Munakata Y, Heuson E, Daboudet T, Deracinois B, Duban M, Hehn A, Coutte F, Slezack-Deschaumes S. Screening of Antimicrobial Activities and Lipopeptide Production of Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Vetiver Roots. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(2):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020209
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunakata, Yuka, Egon Heuson, Théo Daboudet, Barbara Deracinois, Matthieu Duban, Alain Hehn, François Coutte, and Sophie Slezack-Deschaumes. 2022. "Screening of Antimicrobial Activities and Lipopeptide Production of Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Vetiver Roots" Microorganisms 10, no. 2: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020209
APA StyleMunakata, Y., Heuson, E., Daboudet, T., Deracinois, B., Duban, M., Hehn, A., Coutte, F., & Slezack-Deschaumes, S. (2022). Screening of Antimicrobial Activities and Lipopeptide Production of Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Vetiver Roots. Microorganisms, 10(2), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020209








