Trichogenic Silver-Based Nanoparticles for Suppression of Fungi Involved in Damping-Off of Cotton Seedlings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trichoderma Isolates
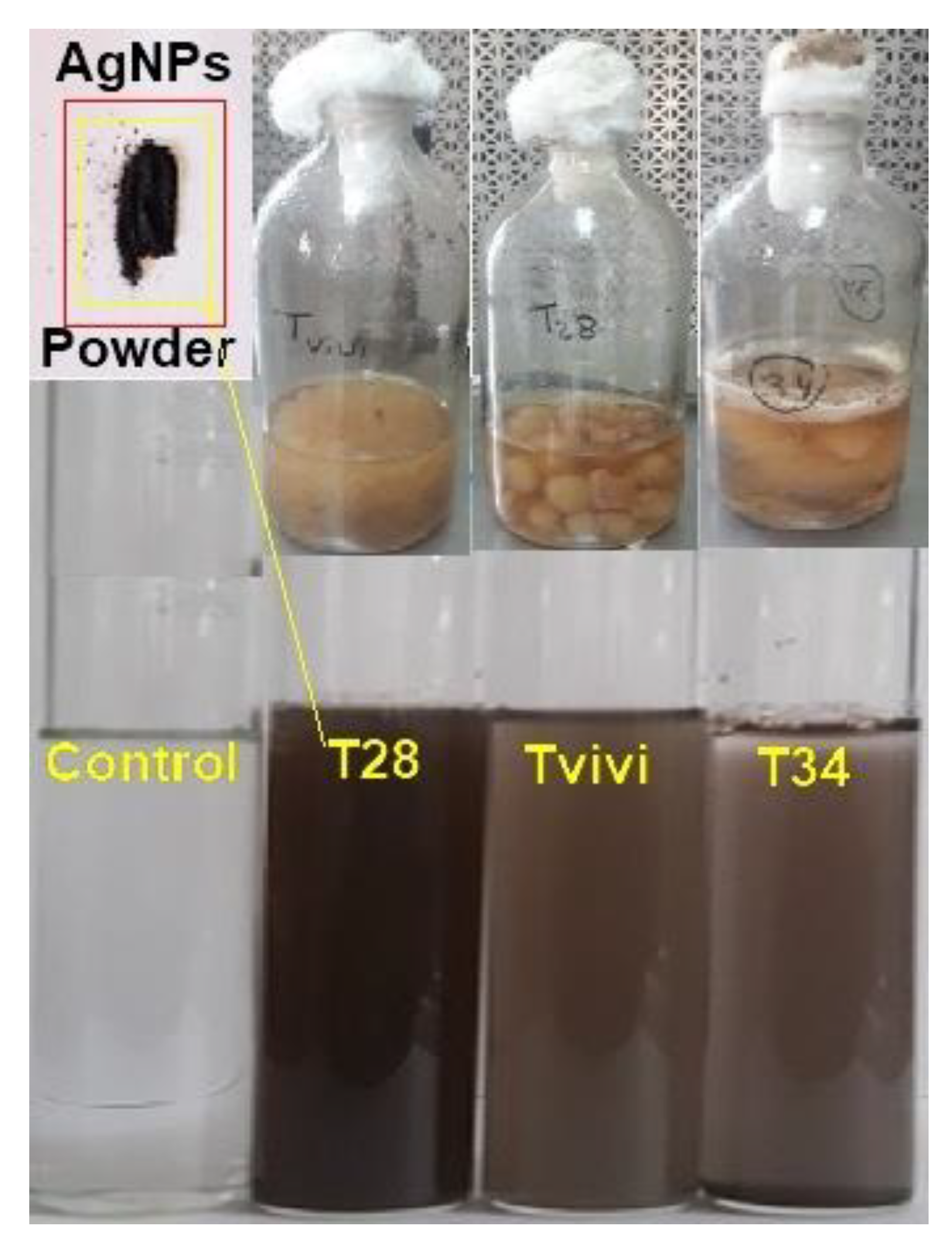
2.2. Preparation of Fungal Filtrate and Tricoh-Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
2.3. AgNPs Characterization
2.3.1. UV-Vis Spectrophotometer Analysis
2.3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3.3. Dynamic Light Scattering and Zeta Potential assays
2.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.3.5. Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX)
2.4. In Vitro Antifungal Activity of AgNPs
2.5. Antifungal Activity under Greenhouse Conditions
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles
3.1.1. UV-Visible Spectral Analysis
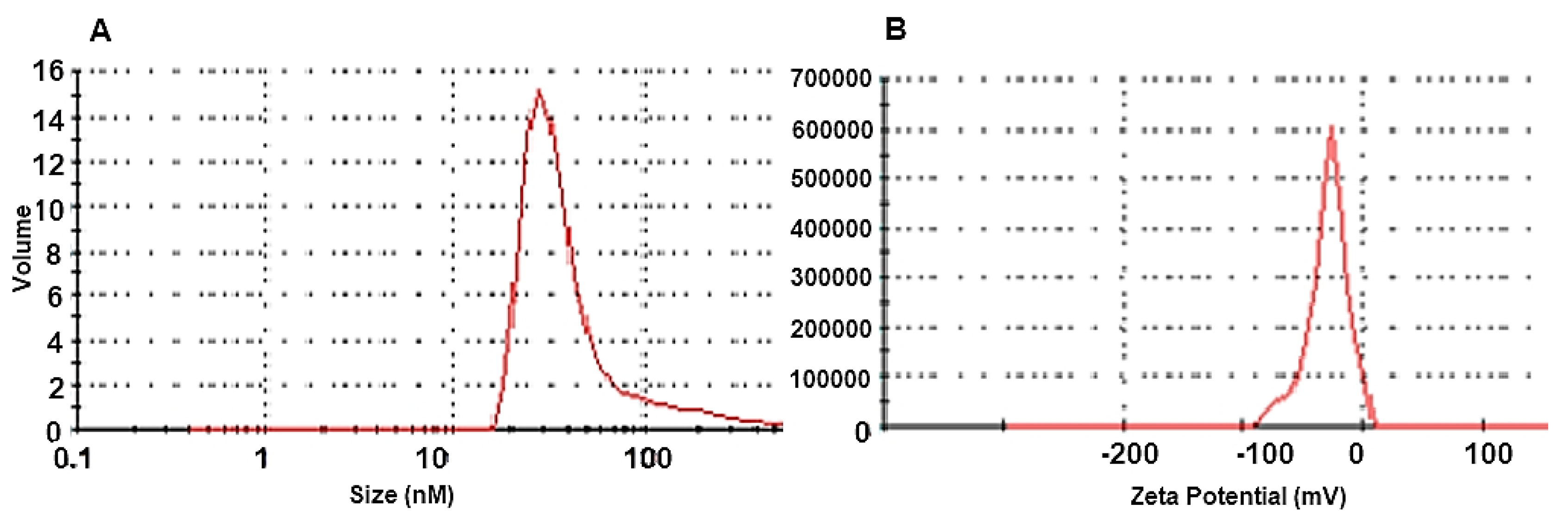
3.1.2. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Zeta Potential Analysis
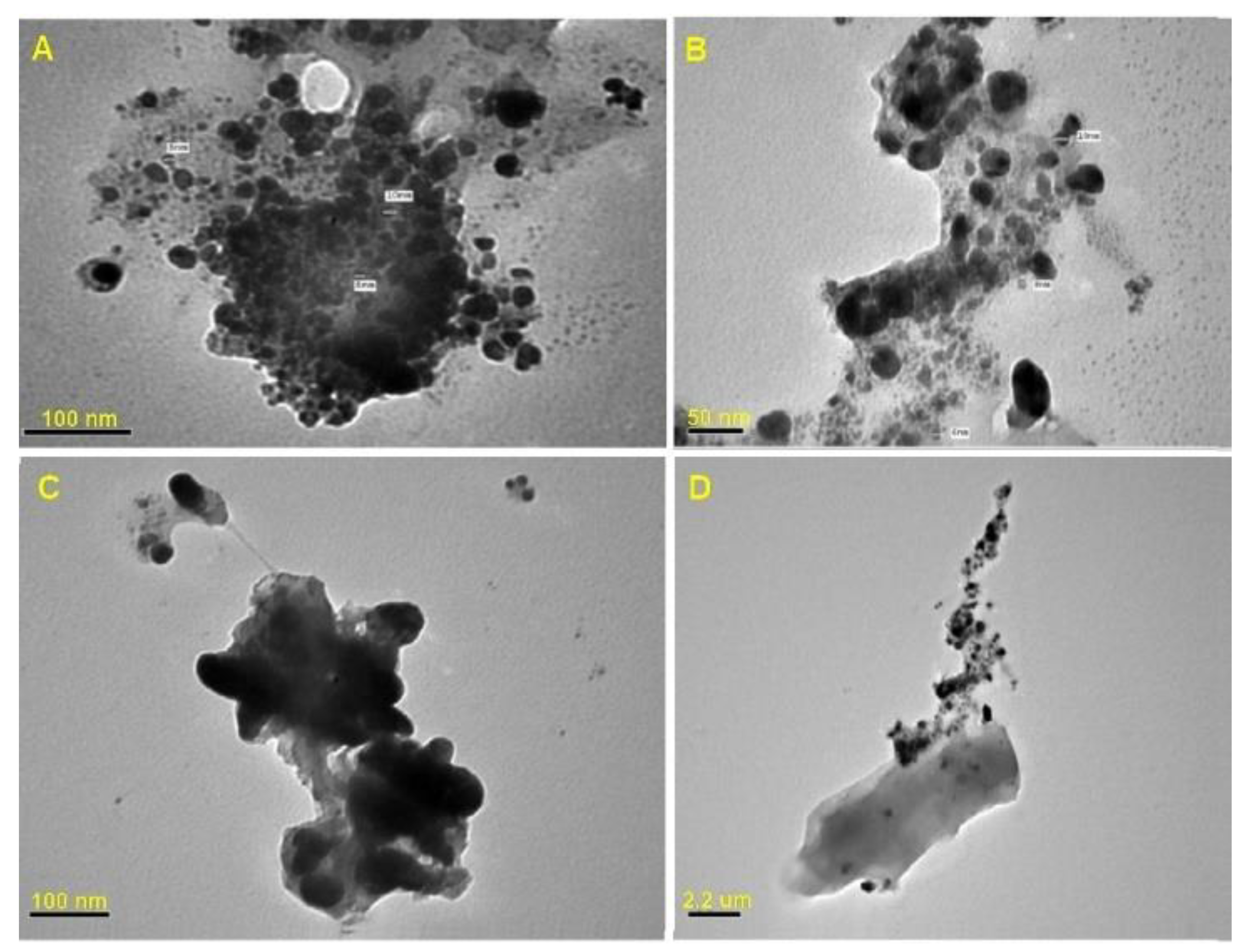
3.1.3. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Analysis
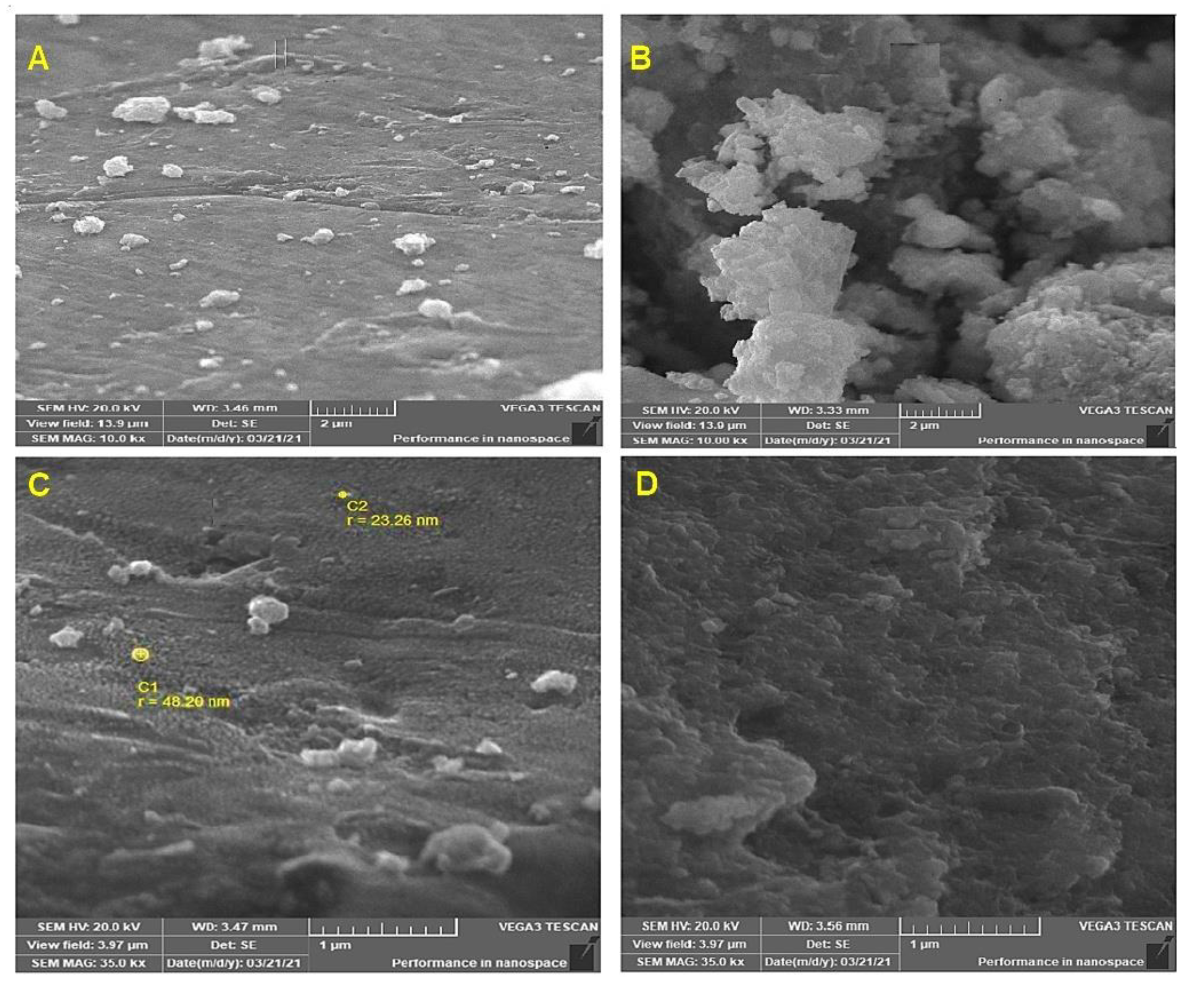
3.1.4. Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis (SEM)
3.1.5. Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX) Analysis
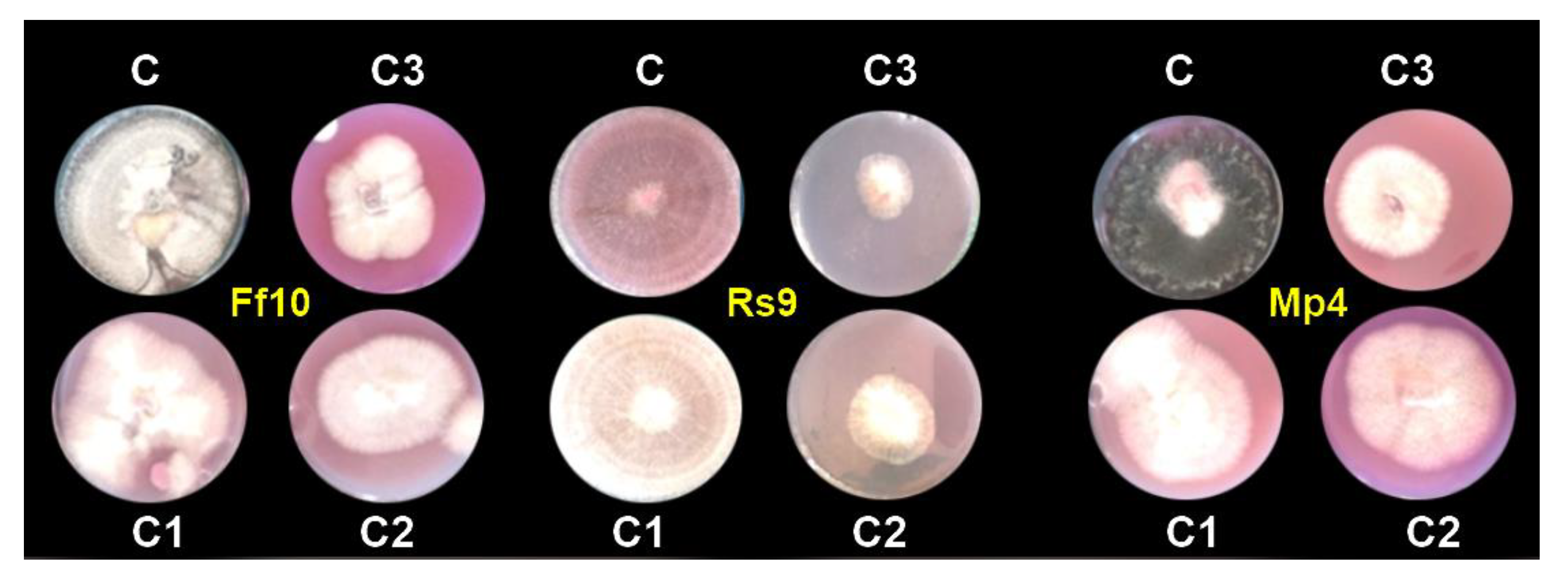
3.1.6. Antifungal Activity of AgNPs under In Vitro Conditions
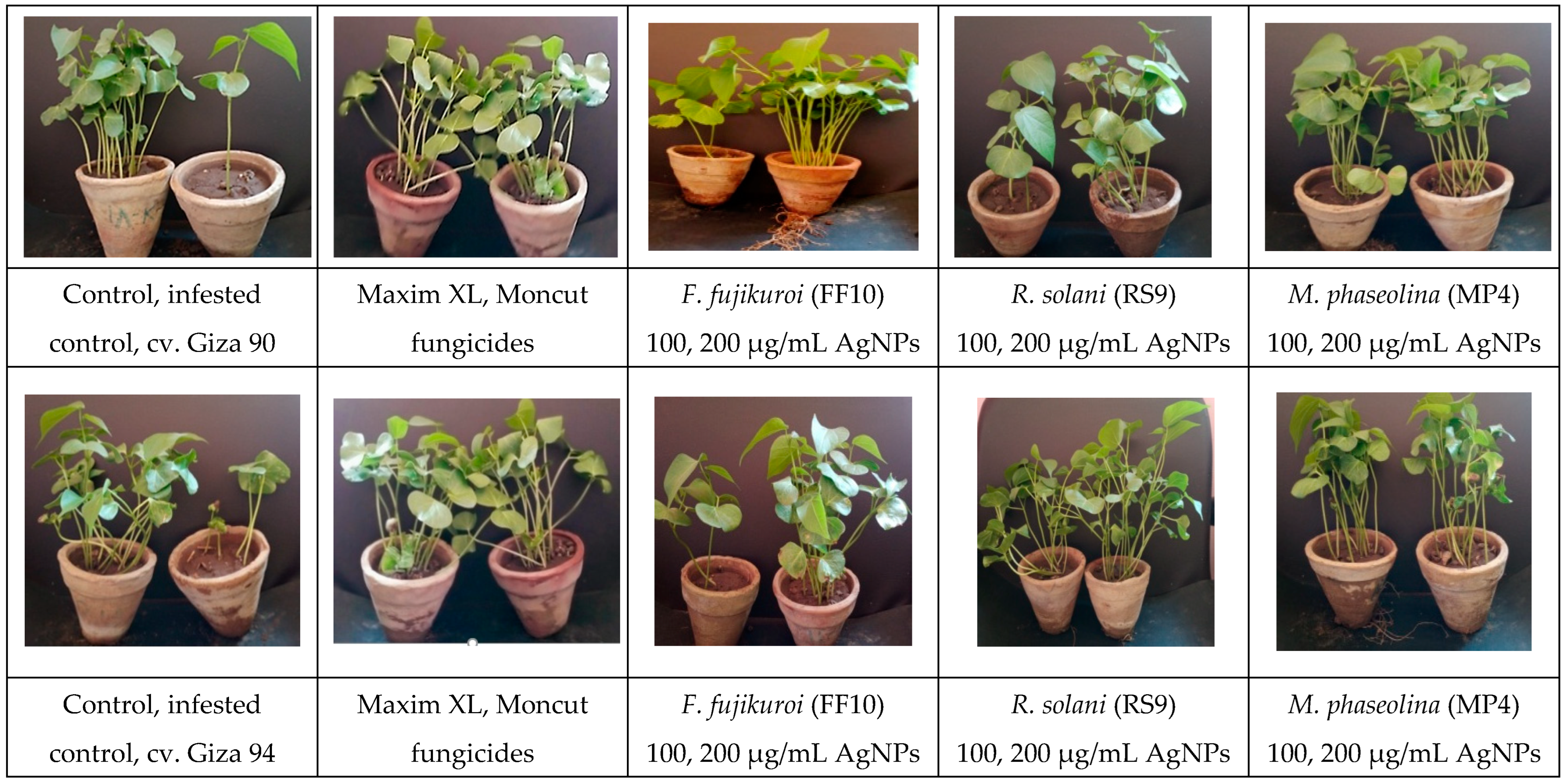
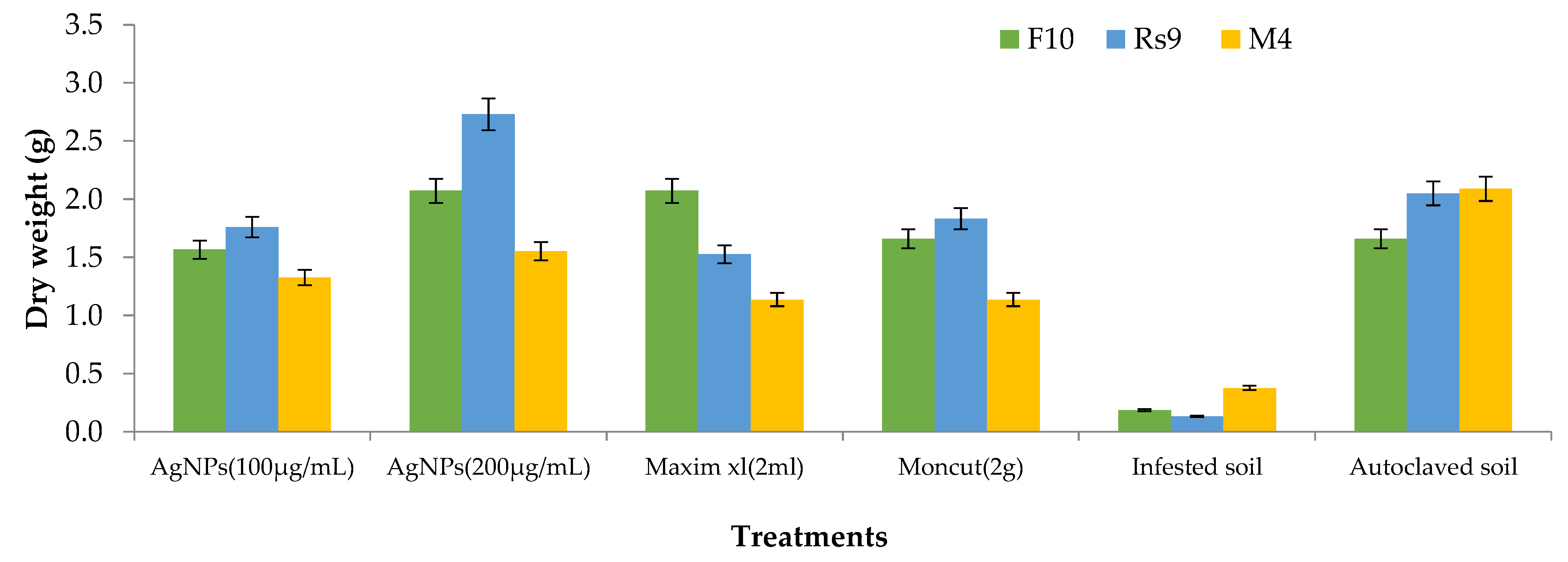
3.1.7. Antifungal Activity of AgNPs under Greenhouse Pot Conditions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watkins, G.M. Compendium of Cotton Diseases; The American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1981; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Moustafa-Mahmoud, S.M.; Ragab, M.M.; Sumner, D.R.; Ragab, M.M. Biological Control of Rhizoctonia solani (AG-4) in Cotton Seedlings. Egypt. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 73, 561–573. [Google Scholar]
- El-Akkad-Salwa, A.F. Studies on Anastomosis Groups of Rhizoctonia solani. Ph.D. Thesis, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Asran-Amal, A.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Omar, M.R.; Aly, A.A. Antagonistic Potential of Trichoderma spp. against Rhizoctonia solani and Use of M13 Microsatellite-Primed PCR to Evaluate the Antagonist Genetic Variation. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2005, 112, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Omar, M.R.; Aly, A.A. First Report of Rhizoctonia solani AG-7 on Cotton in Egypt. J. Phytopathol. 2010, 158, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.W. Epidemiological and Mycofloral Relationships in Cotton Seedling Disease in Mississippi. Phytopathology 1982, 72, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colyer, P.D. Frequency and Pathogenicity of Fusarium spp. Associated with Seedling Diseases of Cotton in Louisiana. Plant Dis. 1988, 72, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Asran-Amal, A.M.; Omar, M.R.; Aly, A.A.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Asran-Amal, A.M.; Omar, M.R.; Aly, A.A. Frequency and Diversity of Fusarium spp. Colonizing Roots of Egyptian Cottons: Häufigkeit Und Viefalt von Fusarium-Pilfen an Wurzeln Der Ägyptischen Baumwolle. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2006, 39, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, O.D.; Sinclair, J.B. Biology and Pathology of Macrophomina phaseolina; Imprensia Universidade Federal de Vicosa: Viçosa, MG, Brazil, 1978; 166p. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Periakaruppan, R.; Rajeshkumar, S. Agri-Waste and Microbes for Production of Sustainable Nanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; 772p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kim, Y.-J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.-C. Biological Synthesis of Nanoparticles from Plants and Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakumaran, M.D.; Ramachandran, R.; Balashanmugam, P.; Mukeshkumar, D.J.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Mycosynthesis of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: Optimization, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity against Human Pathogens. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 182, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, Z.K.; Hawar, S.N.; Sulaiman, G.M. Extracellular Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Penicillium italicum and Its Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Cytotoxicity Activities. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubicek, C.P.; Mach, R.L.; Peterbauer, C.K.; Lorito, M. Trichoderma: From Genes to Biocontrol. J. Plant Pathol. 2011, 83, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, F.B.d.R.; Cerqueira, F.M.; Silva, R.d.N.; Ulhoa, C.J.; Lima, A.L. Mycoparasitism Studies of Trichoderma harzianum Strains against Rhizoctonia solani: Evaluation of Coiling and Hydrolytic Enzyme Production. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qualhato, T.F.; Lopes, F.A.C.; Steindorff, A.S.; Brandão, R.S.; Jesuino, R.S.A.; Ulhoa, C.J. Mycoparasitism Studies of Trichoderma species against Three Phytopathogenic Fungi: Evaluation of Antagonism and Hydrolytic Enzyme Production. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraceto, L.F.; Maruyama, C.R.; Guilger, M.; Mishra, S.; Keswani, C.; Singh, H.B.; de Lima, R. Trichoderma harzianum-Based Novel Formulations: Potential Applications for Management of Next-Gen Agricultural Challenges: Applications of Trichoderma harzianum-Based Novel Formulations. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, S.A.; Ouf, S.A.; Albarakaty, F.M.; Habeb, M.M.; Aly, A.A.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A. Trichoderma harzianum-Mediated ZnO Nanoparticles: A Green Tool for Controlling Soil-Borne Pathogens in Cotton. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilger-Casagrande, M.; Germano-Costa, T.; Pasquoto-Stigliani, T.; Fraceto, L.F.; de Lima, R. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Employing Trichoderma harzianum with Enzymatic Stimulation for the Control of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konappa, N.; Udayashankar, A.C.; Dhamodaran, N.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Jagannath, S.; Uzma, F.; Pradeep, C.K.; De Britto, S.; Chowdappa, S.; Jogaiah, S. Ameliorated Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties by Trichoderma harzianum Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, V.; Kumar, J.; Sisodia, R.; Shakil, N.A.; Walia, S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Trichoderma harzianum and Their Bio-Efficacy Evaluation against Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumonia. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 55, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaravadivelan, C.; Padmanabhan, M.N. Effect of Mycosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Filtrate of Trichoderma Harzianum against Larvae and Pupa of Dengue Vector Aedes egypti L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 4624–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, J.; Rajput, R.S.; Bajpai, R.; Teli, B.; Sarma, B.K. Trichoderma: A Globally Dominant Commercial Biofungicide. In Soil Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirpara, D.G.; Gajera, H.P. Green Synthesis and Antifungal Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles Derived from Chitin-induced Exometabolites of Trichoderma interfusant. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamawi, R.; El-Shafey, R.A. Inhibition Effects of Silver Nanoparticles against Rice Blast Disease Caused by Magnaporthe grisea. Egypt. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 91, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Guo, R.; Ji, S.; Fan, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. Isolation of Trichoderma from Forestry Model Base and the Antifungal Properties of Isolate TpsT17 toward Fusarium oxysporum. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 231, 126371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, K.; Gao, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, H.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Xian, H.; Li, S.; et al. Trichoderma biodiversity in major ecological systems of China. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elamawi, R.M.; Al-Harbi, R.E.; Hendi, A.A. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Trichoderma longibrachiatum and Their Effect on Phytopathogenic Fungi. Egypt J. Biol. Pest Control 2018, 28, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Fazilati, M.; Mousavi, S.M.; Nazem, H. Anti-Bacterial/Fungal and Anti-Cancer Performance of Green Synthesized Ag Nanoparticles Using Summer Savory Extract. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2020, 15, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göl, F.; Aygün, A.; Seyrankaya, A.; Gür, T.; Yenikaya, C.; Şen, F. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Camellia sinensis Mediated Silver Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Ceramic Applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 250, 123037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgorban, A.M.; Al-Rahmah, A.N.; Sayed, S.R.; Hirad, A.; Mostafa, A.A.F.; Bahkali, A.H. Antimicrobial Activity and Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Trichoderma viride. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2016, 30, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Roy, M.; Mandal, B.P.; Dey, G.K.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Ghatak, J.; Tyagi, A.K.; Kale, S.P. Green Synthesis of Highly Stabilized Nanocrystalline Silver Particles by a Non-Pathogenic and Agriculturally Important Fungus T. Asperellum Nanotechnol. 2008, 19, 075103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimzadeh, M.A.; Naghizadeh, A.; Amiri, O.; Shirzadi-Ahodashti, M.; Mortazavi-Derazkola, S. Green and Facile Synthesis of Ag Nanoparticles Using Crataegus pentagyna Fruit Extract (CP-AgNPs) for Organic Pollution Dyes Degradation and Antibacterial Application. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 94, 103425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, U.B.; Bapat, V.A. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Artocar-Pus Heterophyllus Lam. Seed Extract and Its Antibacterial Activity. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 46, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Bhat, M.P.; Udayashankar, A.C.; Lakshmeesha, T.R.; Geetha, N.; Jogaiah, S. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Dillenia indica-mediated Silver Nanoparticles and Their Biological Activity. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, 5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomah, A.A.; Alamer, I.S.A.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.-Z. Mycosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Screened Trichoderma Isolates and Their Antifungal Activity against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikandaselvi, S.; Sathya, V.; Vadivel, V.; Sampath, N.; Brindha, P. Evaluation of Bio Control Potential of AgNPs Synthesized from Trichoderma viride. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, A.; Manchanda, P.; Bhardwaj, S.; Singh, G. Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles from aqueous extracts of sweet lime fruit and callus tissues possess variable antioxidant and antimicrobial potentials. Inorganic Nanometal Chem. 2020, 50, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ouay, B.; Stellacci, F. Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles: A Surface Science Insight. Nano Today 2015, 10, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrucka, R.; Długaszewska, J. Biosynthesis and Antibacterial Activity of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Trifolium pretense Flower Extract. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomoni, R.; Léo, P.; Montemor, A.F.; Rinaldi, B.G.; Rodrigues, M. Antibacterial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2017, 10, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.S.; Elamawi, R.M. Evaluation of Phytotoxicity, Cytotoxicity, and Genotoxicity of ZnO Nanoparticles in Vicia faba. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 18972–18984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffan, M.; Rose, J.; Bottero, J.-Y.; Lowry, G.V.; Jolivet, J.-P.; Wiesner, M.R. Towards a Definition of Inorganic Nanoparticles from an Environmental, Health and Safety Perspective. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Saifullah, A.M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Azadirachta indica aqueous Leaf Extract. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2016, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Udomluck, N.; Chang, J.; Park, H.; Kim, K. Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Encapsulated in Poly-N-Isopropylacrylamide-Based Polymeric Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, S. Bacterial Silver Resistance: Molecular Biology and Uses and Misuses of Silver Compounds. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayabharathi, R.; Sathya, A.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Extracellular Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Streptomyces griseoplanus SAI-25 and Its Antifungal Activity against Macrophomina phaseolina, the Charcoal Rot Pathogen of Sorghum. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-J.; Sung, W.S.; Suh, B.K.; Moon, S.-K.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, D.G. Antifungal Activity and Mode of Action of Silver Nano-Particles on Candida albicans. Biometals 2009, 22, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawoud, T.M.; Yassin, M.A.; El-Samawaty, A.R.M.; Elgorban, A.M. Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Nigrospora oryzae Showed Antifungal Activity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasen, H.J. A Historical Review of the Use of Silver in the Treatment of Burns. II. Renewed Interest for Silver. Burns 2000, 26, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.A.; Abyaneh, M.K.; Gosavi, S.W.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Pasricha, R.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, M.I. Nitrate Reductase-Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from AgNO3. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, K.; Mansoori, G.A.; Karimi, S. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Fungus Trichoderma reesei. Insci. J. 2011, 1, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, T.; Rincón, A.M.; Limón, M.C.; Codón, A.C. Biocontrol Mechanisms of Trichoderma Strains. Int. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Chaloupka, K.; Malam, Y.; Seifalian, A.M. Nanosilver as a New Generation of Nanoproduct in Biomedical Applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, M.; Dille, J.; Godet, S. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, D.; Qian, Y.; Guan, B.; Gao, S.; Cui, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Wang, L. Fungus-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aspergillus terreus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Ryu, D.S.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, D.S. Antibacterial Activity of Silver-Nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 39, 77–85. [Google Scholar]








| Treatment | Rate of Treatments |
|---|---|
| 1—autoclaved soil | R. solani (1 g), both of F. fujikuroi and M. phaseolina (50 g) for sterilized sorghum/kg soil |
| 2—infested soil | R. solani (1 g), both of F. fujikuroi and M. phaseolina (50 g) for sterilized sorghum/kg soil |
| 3—Moncut | 2 g/kg seeds |
| 4—Maxim XL | 2 mL/L |
| 5—AgNPs | 100 µg mL−1 |
| 6—AgNPs | 200 µg mL−1 |
| Growth Variables and Sources of Variation | D.F | Mean Square | F. Value | p ≥ F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration of AgNPs(C) | 3 | 4.606 | 79.302 | 0.000 |
| Fungus(F) | 2 | 48.113 | 828.388 | 0.000 |
| F × C | 6 | 5.622 | 96.798 | 0.000 |
| Error | 22 | 0.058 |
| Radial Growth (cm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | FF10 | RS9 | MP4 | Mean |
| AgNPs 20 μg/mL | 6.000 | 9.000 | 6.750 | 7.250 |
| AgNPs 40 μg/mL | 5.333 | 9.000 | 6.333 | 6.889 |
| AgNPs 100 μg/mL | 4.000 | 2.250 | 4.167 | 3.472 |
| Control | 9.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 | 9.000 |
| Mean | 6.083 | 7.313 | 6.563 | 6.653 |
| Growth Variables and Sources of Variation | D.F | Mean Square | F. Value | p ≥ F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survival | ||||
| Fungi (F) | 2 | 62.93 | 0.28 | 0.76 |
| Treatments (T) | 5 | 3805.20 | 16.89 | 0.00 |
| F × T | 10 | 71.46 | 0.32 | 0.97 |
| Error | 34 | 225.32 | ||
| Plant height | ||||
| Fungi (F) | 2 | 21.65 | 1.72 | 0.19 |
| Treatments (T) | 5 | 212.09 | 16.84 | 0.00 |
| F × T | 10 | 52.94 | 4.20 | 0.00 |
| Error | 34 | 12.60 | ||
| Dry weight | ||||
| Fungi (F) | 2 | 0.75 | 3.51 | 0.04 |
| Treatments (T) | 5 | 3.94 | 18.32 | 0.00 |
| F × T | 10 | 0.34 | 1.59 | 0.15 |
| Error | 34 | 0.22 |
| Treatments | Silver/Survival/Giza90 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FF10 (%) | RS9 (%) | MP4 (%) | Mean (%) | |
| AgNPs (100 μg/mL) | 60.000 | 70.000 | 76.667 | 68.889 |
| AgNPs (200 μg/mL) | 90.000 | 86.667 | 93.333 | 90.000 |
| Maxim ×L (2 mL) | 86.667 | 86.667 | 90.000 | 87.778 |
| Moncut (2 g) | 86.667 | 83.333 | 83.333 | 84.444 |
| Infested soil | 30.000 | 16.667 | 26.667 | 24.445 |
| Autoclaved soil | 90.000 | 96.667 | 93.333 | 93.333 |
| Mean | 73.889 | 73.333 | 77.222 | 74.815 |
| Growth Variables and Sources of Variation | D.F | Mean Square | F. Value | p ≥ F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survival | ||||
| Fungi (F) | 2 | 93.24 | 0.37 | 0.69 |
| Treatments (T) | 5 | 4579.66 | 18.25 | 0.00 |
| F × T | 10 | 408.13 | 1.63 | 0.14 |
| Error | 34 | 250.94 | ||
| Plant height | ||||
| Fungi (F) | 2 | 7.89 | 0.24 | 0.79 |
| Treatments (T) | 5 | 272.93 | 8.17 | 0.00 |
| F × T | 10 | 40.05 | 1.20 | 0.33 |
| Error | 34 | 33.39 | ||
| Dry weight | ||||
| Fungi (F) | 2 | 0.19 | 0.56 | 0.58 |
| Treatments (T) | 5 | 5.38 | 15.71 | 0.00 |
| F × T | 10 | 0.35 | 1.00 | 0.46 |
| Error | 34 | 0.34 |
| Silver/Survival/Giza94 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | FF10 %Transformed a | RS9 %Transformed a | MP4 %Transformed a | Mean %Transformed a | ||||
| AgNPs (100 μg/mL) | 40.000 | 38.853 | 16.667 | 15.000 | 80.000 | 63.930 | 45.556 | 39.261 |
| AgNPs (200 μg/mL) | 90.000 | 75.000 | 83.333 | 70.763 | 93.333 | 77.707 | 88.889 | 74.490 |
| Maxim XL (2 mL) | 80.000 | 67.860 | 76.667 | 65.840 | 76.667 | 61.910 | 77.778 | 65.203 |
| Moncut (2 g) | 83.333 | 70.077 | 93.333 | 77.707 | 90.000 | 75.000 | 88.889 | 74.261 |
| Infested soil | 16.667 | 19.223 | 30.000 | 28.077 | 6.667 | 12.293 | 17.778 | 19.864 |
| Autoclaved soil | 86.667 | 72.783 | 86.667 | 72.293 | 83.333 | 66.147 | 85.556 | 70.408 |
| Mean | 66.111 | 57.299 | 64.444 | 54.947 | 71.667 | 59.498 | 67.407 | 57.248 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaki, S.A.; Ouf, S.A.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Asran, A.A.; Hassan, M.M.; Kalia, A.; Albarakaty, F.M. Trichogenic Silver-Based Nanoparticles for Suppression of Fungi Involved in Damping-Off of Cotton Seedlings. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020344
Zaki SA, Ouf SA, Abd-Elsalam KA, Asran AA, Hassan MM, Kalia A, Albarakaty FM. Trichogenic Silver-Based Nanoparticles for Suppression of Fungi Involved in Damping-Off of Cotton Seedlings. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(2):344. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020344
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaki, Shimaa A., Salama A. Ouf, Kamel A. Abd-Elsalam, Amal A. Asran, Mohamed M. Hassan, Anu Kalia, and Fawziah M. Albarakaty. 2022. "Trichogenic Silver-Based Nanoparticles for Suppression of Fungi Involved in Damping-Off of Cotton Seedlings" Microorganisms 10, no. 2: 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020344
APA StyleZaki, S. A., Ouf, S. A., Abd-Elsalam, K. A., Asran, A. A., Hassan, M. M., Kalia, A., & Albarakaty, F. M. (2022). Trichogenic Silver-Based Nanoparticles for Suppression of Fungi Involved in Damping-Off of Cotton Seedlings. Microorganisms, 10(2), 344. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020344








