Pea-Wheat Rotation Affects Soil Microbiota Diversity, Community Structure, and Soilborne Pathogens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site, Experimental Design, and Soil Sampling
2.2. Culturable Microorganisms, Soil Microbiota, and Biodiversity Assessment
2.3. Data Analysis
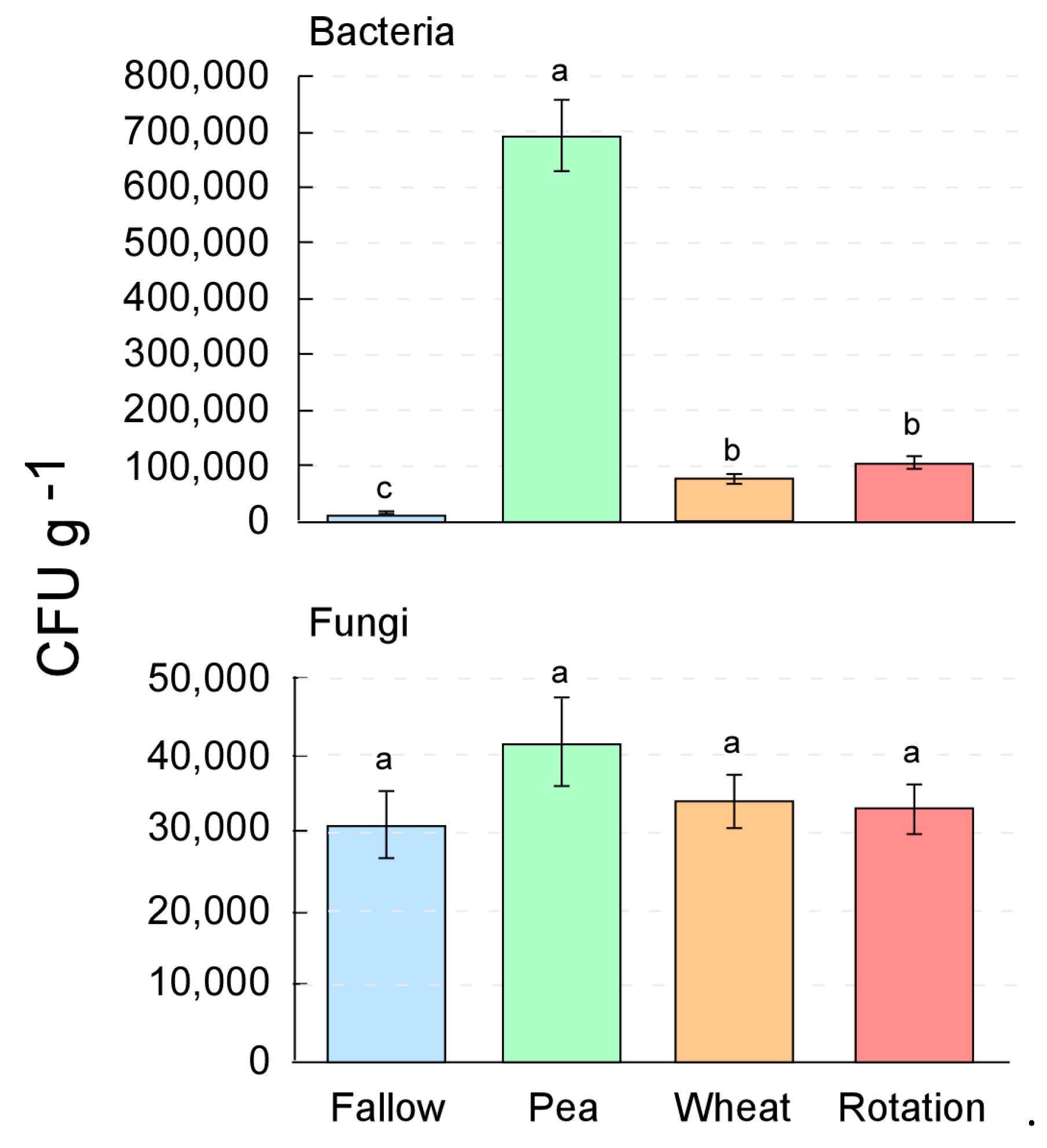
3. Results
3.1. Crop Rotation Effects on the Culturable Microorganisms
3.2. Crop Rotation Effects on Microbial Diversity
3.3. Crop Rotation Effects on Microbiota Structure and Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, M.A. Agroecology: The Science of Sustainable Agriculture; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.-F.; Song, L.-X.; Xia, X.-J.; Mao, W.-H.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Yu, J.-Q. Plant-soil feedbacks and soil sickness: From mechanisms to application in agriculture. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.; Heenan, D. The influence of crop rotation on soil structure and soil physical properties under conventional tillage. Soil Tillage Res. 1996, 37, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäder, P.; Fliessbach, A.; Dubois, D.; Gunst, L.; Fried, P.; Niggli, U. Soil fertility and biodiversity in organic farming. Science 2002, 296, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curl, E.A. Control of plant diseases by crop rotation. Bot. Rev. 1963, 29, 413–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, K.; Gossen, B.; Lafond, G.; Watson, P.; Derksen, D. Effect of tillage and crop rotation on root and foliar diseases of wheat and pea in Saskatchewan from 1991 to 1998: Univariate and multivariate analyses. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2001, 81, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Sturz, A.; Carter, M.; Sanderson, J. Developing disease-suppressive soils through crop rotation and tillage management practices. Soil Tillage Res. 2003, 72, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.R.; Fernandas, J. Survival of wheat pathogens in wheat and soybean residues under conservation tillage systems in southern and central Brazil. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1990, 12, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Subbarao, K.; Schulbach, K.; Koike, S. Effects of crop rotation and irrigation on Verticillium dahliae microsclerotia in soil and wilt in cauliflower. Phytopathology 1998, 88, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osborne, L.E.; Stein, J.M. Epidemiology of Fusarium head blight on small-grain cereals. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarano, G.; Zotti, M.; Antignani, V.; Marra, R.; Scala, F.; Bonanomi, G. Soil sickness and negative plant-soil feedback: A reappraisal of hypotheses. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 99, 545–570. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.; Dick, R.P. Thermal stability and activities of soil enzymes as influenced by crop rotations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, T.O.; Post, W.M. Soil organic carbon sequestration rates by tillage and crop rotation: A global data analysis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1930–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balota, E.L.; Colozzi-Filho, A.; Andrade, D.S.; Dick, R.P. Microbial biomass in soils under different tillage and crop rotation systems. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 38, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupwayi, N.; Rice, W.; Clayton, G. Soil microbial diversity and community structure under wheat as influenced by tillage and crop rotation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrell, A.N.; Shi, Y.; Gan, Y.; Bainard, L.; Germida, J.; Hamel, C. Fungal diversity associated with pulses and its influence on the subsequent wheat crop in the Canadian prairies. Plant Soil 2017, 414, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, S.; Bennett, A.J.; Chandler, D.; Mills, P.; Bending, G.D. Preceding crop and seasonal effects influence fungal, bacterial and nematode diversity in wheat and oilseed rape rhizosphere and soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 126, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacWilliam, S.; Wismer, M.; Kulshreshtha, S. Life cycle and economic assessment of Western Canadian pulse systems: The inclusion of pulses in crop rotations. Agric. Syst. 2014, 123, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Miller, P.; McConkey, B.; Zentner, R.; Stevenson, F.; McDonald, C. Influence of diverse cropping sequences on durum wheat yield and protein in the semiarid northern Great Plains. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Bainard, L.D.; May, W.E.; Hossain, Z.; Hamel, C.; Gan, Y. Intensified pulse rotations buildup pea rhizosphere pathogens in cereal and pulse based cropping systems. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N. Embracing the unknown: Disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, Z.S.; Jacobs, K.; Hawkins, H.-J. The impact of crop rotation on soil microbial diversity: A meta-analysis. Pedobiologia 2016, 59, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, C.; Gan, Y.; Sokolski, S.; Bainard, L.D. High frequency cropping of pulses modifies soil nitrogen level and the rhizosphere bacterial microbiome in 4-year rotation systems of the semiarid prairie. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 126, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Strom, N.; Haarith, D.; Chen, S.; Bushley, K.E. Mycobiome of cysts of the soybean cyst nematode under long term crop rotation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santschi, F.; Gounand, I.; Harvey, E.; Altermatt, F. Leaf litter diversity and structure of microbial decomposer communities modulate litter decomposition in aquatic systems. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cartenì, F.; Deslauriers, A.; Rossi, S.; Morin, H.; De Micco, V.; Mazzoleni, S.; Giannino, F. The physiological mechanisms behind the earlywood-to-latewood transition: A process-based modeling approach. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, G.; De Filippis, F.; Cesarano, G.; La Storia, A.; Zotti, M.; Mazzoleni, S.; Incerti, G. Linking bacterial and eukaryotic microbiota to litter chemistry: Combining next generation sequencing with 13C CPMAS NMR spectroscopy. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 129, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmale, D.; Bergstrom, G. Fusarium Head Blight (FHB) or Scab; APSnet: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dill-Macky, R.; Jones, R. The effect of previous crop residues and tillage on Fusarium head blight of wheat. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, M.R. Fusarium populations in roots of oilseed and pulse crops grown in eastern Saskatchewan. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2007, 87, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, A.; Hamel, C.; Lafond, G.; Gossen, B.D.; Hanson, K.; Germida, J. Soil microbial quality associated with yield reduction in continuous-pea. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 43, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Hamel, C.; Gan, Y.; Vujanovic, V. Pyrosequencing reveals how pulses influence rhizobacterial communities with feedback on wheat growth in the semiarid Prairie. Plant Soil 2013, 367, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijver, A.D.; Mot, R.D. Degradation of pesticides by actinomycetes. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1999, 25, 85–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, S.L.; De Filippis, F.; Zotti, M.; Vandenberg, A.; Hucl, P.; Bonanomi, G. Pea-Wheat Rotation Affects Soil Microbiota Diversity, Community Structure, and Soilborne Pathogens. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020370
Woo SL, De Filippis F, Zotti M, Vandenberg A, Hucl P, Bonanomi G. Pea-Wheat Rotation Affects Soil Microbiota Diversity, Community Structure, and Soilborne Pathogens. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(2):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020370
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Sheridan Lois, Francesca De Filippis, Maurizio Zotti, Albert Vandenberg, Pierre Hucl, and Giuliano Bonanomi. 2022. "Pea-Wheat Rotation Affects Soil Microbiota Diversity, Community Structure, and Soilborne Pathogens" Microorganisms 10, no. 2: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020370
APA StyleWoo, S. L., De Filippis, F., Zotti, M., Vandenberg, A., Hucl, P., & Bonanomi, G. (2022). Pea-Wheat Rotation Affects Soil Microbiota Diversity, Community Structure, and Soilborne Pathogens. Microorganisms, 10(2), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020370








