From Rest to Growth: Life Collisions of Gordonia polyisoprenivorans 135
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Culture and Cultivation Conditions
2.2. Obtaining the Resting Forms
2.3. Viability of the Vegetative Cells and CLC
2.4. Microscopically Techniques
2.4.1. Phase Contrast Microscopy
2.4.2. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.4.3. Electron Microscopy
2.5. X-ray Microanalysis
2.6. Assessment of Cells Metabolic Activity
2.7. G. polyisoprenivorans 135 Cells Immobilization and Bioreceptor Development
2.8. Polarographic Measurement of Cell Respiration and BDO Activity in Nonimmobilized G. polyisoprenivorans Cells
2.9. Measurement of BDO Activity in Immobilized G. polyisoprenivorans Cells
2.10. Obtaining a Cell-Free Extract
2.11. Determination of Enzyme Activity in Cell-Free Extract
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Obtaining Resting G. polyisoprenivorans Cells 135
3.1.1. Viability of the Vegetative Cells and CLC
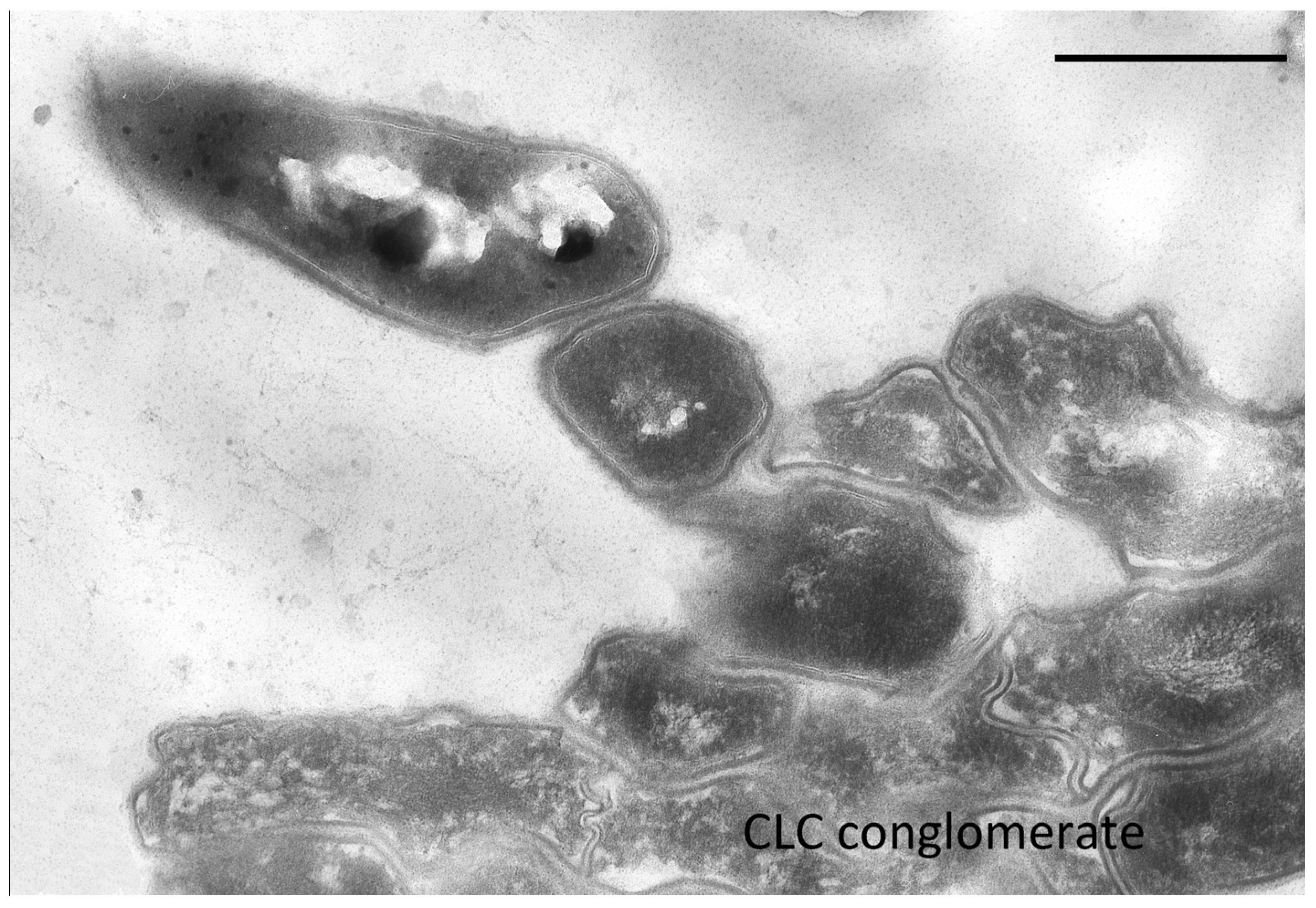
3.1.2. Morphology and Ultrastructural Organization of G. polyisoprenivorans 135 Resting Cells
3.1.3. Protein Content in Cells and Enzymatic Activity Assay
3.2. Peculiarities of Exit from Dormancy of Gordonia polyisoprenivorans 135 Cells
3.3. Activation of Benzoate Utilization Enzymes in G. polyisoprenivorans 135 Cells
3.4. Dynamics of BDO Activity in G. polyisoprenivorans 135 Cells during Vegetative Growth-Rest-Vegetative Growth Transition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arenskötter, M.; Bröker, D.; Steinbüchel, A. Biology of the Metabolically Diverse Genus Gordonia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3195–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arenskötter, M.; Baumeister, D.; Berekaa, M.M.; Pötter, G.; Kroppenstedt, R.M.; Linos, A.; Steinbüchel, A. Taxonomic characterization of two rubber degrading bacteria belonging to the species Gordonia polyisoprenivorans and analysis of hyper variable regions of 16S rDNA sequences. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 205, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Kong, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Jia, M.; Yu, X. Characterization and Genomic Analysis of a Highly Efficient Dibutyl Phthalate-Degrading Bacterium Gordonia sp. Strain QH-12. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heine, T.; Zimmerling, J.; Ballmann, A.; Kleeberg, S.B.; Rückert, C.; Busche, T.; Winkler, A.; Kalinowski, J.; Poetsch, A.; Scholtissek, A.; et al. On the Enigma of Glutathione-Dependent Styrene Degradation in Gordonia rubripertincta CWB2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00154-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kummer, C.; Schumann, P.; Stackebrandt, E. Gordonia alkanivorans sp. nov., isolated from tar-contaminated soil. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49 Pt 4, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.B.; Brown, R.; Oldfield, C.; Gilbert, S.C.; Iliarionov, S.; Goodfellow, M. Gordonia amicalis sp. nov., a novel dibenzothiophene-desulphurizing actinomycete. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50 Pt 6, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delegan, Y.; Kocharovskaya, Y.; Frantsuzova, E.; Streletskii, R.; Vetrova, A. Characterization and genomic analysis of Gordonia alkanivorans 135, a promising dibenzothiophene-degrading strain. Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 29, e00591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.; Crombie, A.T.; El Khawand, M.; Sims, L.; Whited, G.M.; McGenity, T.J.; Colin Murrell, J. Identification and characterisation of isoprene-degrading bacteria in an estuarine environment. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 3526–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagilla, K.R.; Sood, A.; Kim, H. Gordonia (nocardia) amarae foaming due to biosurfactant production. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowani, H.; Kulkarni, M.; Zinjarde, S.; Javdekar, V. Gordonia and Related Genera as Opportunistic Human Pathogens Causing Infections of Skin, Soft Tissues, and Bones. In The Microbiology of Skin, Soft Tissue, Bone and Joint Infections; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowani, H.; Kulkarni, M.; Zinjarde, S. An insight into the ecology, diversity and adaptations of Gordonia species. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowani, H.; Kulkarni, M.; Zinjarde, S. Harnessing the catabolic versatility of Gordonia species for detoxifying pollutants. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 382–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzyzga, O. The strengths and weaknesses of Gordonia: A review of an emerging genus with increasing biotechnological potential. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 38, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yu, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, C.; Kang, Y.; Li, H.; Lou, J. Bacteremia due to Gordonia polyisoprenivorans: Case report and review of literature. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andryukov, B.G.; Karpenko, A.A.; Lyapun, I.N.; Matosova, E.V.; Bynina, M.P. Bacterial Spores: Mechanisms of Stability and Targets for Modern Biotechnologies. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2019, 20, 15329–15344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, J.; Shah, I.M. Exit from dormancy in microbial organisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, A.O.; Moran, C.P., Jr. Structure, Assembly, and Function of the Spore Surface Layers. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 555–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, E.A.; Miller, D.A.; Angert, E.R. Sporulation in Bacteria: Beyond the Standard Model. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minsky, A.; Shimoni, E.; Frenkiel-Krispin, D. Stress, order and survival. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Vela, G.R. Survival of Azotobacter spp. in Dry Soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1986, 51, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadoff, H.L. Encystment and germination in Azotobacter vinelandii. Bacteriol. Rev. 1975, 39, 516–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willey, J.; Sandman, K.M.; Wood, D.H. Encystment and Excystment. In Prescott’s Microbiolgy Eleventh Edition; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2019; p. 560. [Google Scholar]
- Mulyukin, A.L.; Suzina, N.E.; Duda, V.I.; El’-Registan, G.I. Structural and physiological diversity among cystlike resting cells of bacteria of the genus Pseudomonas. Microbiology 2008, 77, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuchin, A.M.; Mulyukin, A.L.; Suzina, N.E.; Duda, V.I.; El-Registan, G.I.; Kaprelyants, A.S. Dormant forms of Mycobacterium smegmatis with distinct morphology. Microbiology 2009, 155, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solyanikova, I.P.; Suzina, N.E.; Egozarian, N.S.; Polivtseva, V.N.; Prisyazhnaya, N.V.; El-Registan, G.I.; Mulyukin, A.L.; Golovleva, L.A. The response of soil Arthrobacter agilis lush13 to changing conditions: Transition between vegetative and dormant state. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. Part B 2017, 52, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzina, N.E.; Ross, D.V.; Shorokhova, A.P.; Abashina, T.N.; Polivtseva, V.N.; Esikova, T.Z.; Machulin, A.V.; Mulyukin, A.L.; Duda, V.I. Cytophysiological characteristics of the vegetative and dormant cells of Stenotrophomonas sp. strain FM3, a bacterium isolated from the skin of a Xenopus laevis frog. Microbiology 2018, 87, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solyanikova, I.P.; Golovlev, E.L.; Lisnyak, O.V.; Golovleva, L.A. Isolation and characterization of catechol 1,2-dioxygenases from Rhodococcus rhodnii strain 135 and Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain 89: Comparison with analogous enzymes of the ordinary and modified ortho-cleavage pathways. Biochemistry-Moscow 1999, 64, 824–831. [Google Scholar]
- Emelyanova, E.V.; Suzina, N.E.; Polivtseva, V.N.; Reshetilov, A.N.; Solyanikova, I.P. Survival and biodegradation activity of Gordonia polyisoprenivorans 135: Basics of a biosensor receptor. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2017, 53, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlatov, S.N.; Maltseva, O.V.; Shevchenko, V.I.; Golovleva, L.A. Degradation of Chlorophenols by a Culture of Rhodococcus-erythropolis. Microbiology 1989, 58, 647–651. [Google Scholar]
- Solyanikova, I.P.; Suzina, N.E.; Emelyanova, E.V.; Polivtseva, V.N.; Pshenichnikova, A.B.; Lobanok, A.G.; Golovleva, L.A. Morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics of a benzoate-degrading strain Rhodococcus opacus 1CP under stress conditions. Microbiology 2017, 86, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayaishi, O.; Katagiri, M.; Rothberg, S. Studies on oxygenases; pyrocatechase. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 229, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, M. [65] Metapyrocatechase (Pseudomonas). Methods Enzymol. 1970, 17, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hugenholtz, J.; Abee, T.; Molenaar, D. Glutathione Protects Lactococcus lactis against Oxidative Stress. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlömann, M.; Schmidt, E.; Knackmuss, H.J. Different types of dienelactone hydrolase in 4-fluorobenzoate-utilizing bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 5112–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solyanikova, I.P.; Suzina, N.E.; Egozarjan, N.S.; Polivtseva, V.N.; Mulyukin, A.L.; Egorova, D.O.; El-Registan, G.I.; Golovleva, L.A. Structural and functional rearrangements in the cells of actinobacteria Microbacterium foliorum BN52 during transition from vegetative growth to a dormant state and during germination of dormant forms. Microbiology 2017, 86, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.R.; Dabrowski, L.; Stringer, S.; Moezelaar, R.; Brocklehurst, T.F. High pressure in combination with elevated temperature as a method for the sterilisation of food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Impe, J.; Smet, C.; Tiwari, B.; Greiner, R.; Ojha, S.; Stulić, V.; Vukušić, T.; Režek Jambrak, A. State of the art of nonthermal and thermal processing for inactivation of micro-organisms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casabianca, A.; Orlandi, C.; Barbieri, F.; Sabatini, L.; Di Cesare, A.; Sisti, D.; Pasquaroli, S.; Magnani, M.; Citterio, B. Effect of starvation on survival and virulence expression of Aeromonas hydrophila from different sources. Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.A.; Arabolaza, A.; Rodríguez, E.; Gramajo, H.; Alvarez, H.M. Metabolism of triacylglycerols in Rhodococcus species: Insights from physiology and molecular genetics. J. Mol. Biochem. 2013, 2, 2119–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seufferheld, M.J.; Kim, K.M.; Whitfield, J.; Valerio, A.; Caetano-Anollés, G. Evolution of vacuolar proton pyrophosphatase domains and volutin granules: Clues into the early evolutionary origin of the acidocalcisome. Biol. Direct 2011, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez, S.; Jerez, C.A. Copper ions stimulate polyphosphate degradation and phosphate efflux in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5177–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remonsellez, F.; Orell, A.; Jerez, C.A. Copper tolerance of the thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus metallicus: Possible role of polyphosphate metabolism. Microbiology 2006, 152, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scherer, P.A.; Bochem, H.P. Energy-dispersive X-ray microanalysis of the methanogen Methanosarcina barkeri “Fusaro” grown on methanol and in the presence of heavy metals. Curr. Microbiol. 1983, 9, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docampo, R.; de Souza, W.; Miranda, K.; Rohloff, P.; Moreno, S.N.J. Acidocalcisomes—Conserved from bacteria to man. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, C.; Jendrossek, D. Acidocalcisomes and Polyphosphate Granules Are Different Subcellular Structures in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02759-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seufferheld, M.; Vieira, M.C.F.; Ruiz, F.A.; Rodrigues, C.O.; Moreno, S.N.J.; Docampo, R. Identification of organelles in bacteria similar to acidocalcisomes of unicellular eukaryotes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 29971–29978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seufferheld, M.; Lea, C.R.; Vieira, M.; Oldfield, E.; Docampo, R. The H+-pyrophosphatase of Rhodospirillum rubrum is predominantly located in polyphosphate-rich acidocalcisomes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51193–51202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solyanikova, I.P.; Emelyanova, E.V.; Shumkova, E.S.; Egorova, D.O.; Korsakova, E.S.; Plotnikova, E.G.; Golovleva, L.A. Peculiarities of the degradation of benzoate and its chloro- and hydroxy-substituted analogs by actinobacteria. Intern. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2015, 100, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzina, N.E.; Polivtseva, V.N.; Shorokhova, A.P.; Ross, D.V.; Abashina, T.N.; Machulin, A.V.; El’-Registan, G.I.; Solyanikova, I.P. Ultrastructural Organization and Enzymes of the Antioxidant Defense System in the Dormant Cells of Gram-Negative Bacteria Stenotrophomonas sp. Strain FM3 and Morganella morganii subsp. sibonii Strain FF1. Microbiology 2019, 88, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, F.B.; Kallel, H.; Bakhrouf, A. Enzymatic, outer membrane proteins and plasmid alterations of starved Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus cells in seawater. Arch. Microbiol. 2009, 191, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirog, T.P.; Grinberg, T.A.; Malashenko, Y.R. Protective functions of exopolysaccharides produced by an Acinetobacter sp. Microbiology 1997, 66, 279–283. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki, R.; Song, S.; Benedik, M.J.; Wood, T.K. Persister Cells Resuscitate Using Membrane Sensors that Activate Chemotaxis, Lower cAMP Levels, and Revive Ribosomes. iScience 2020, 23, 100792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solyanikova, I.P.; Mulyukin, A.L.; Suzina, N.E.; El-Registan, G.I.; Golovleva, L.A. Improved xenobiotic-degrading activity of Rhodococcus opacus strain 1cp after dormancy. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. Part B 2011, 46, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagita, T.; Ichikawa, T.; Tsuji, T.; Kamata, Y.; Ito, K.; Sasaki, M. Two trophic groups of bacteria, oligotrophs and eutrophs: Their distributions in fresh and sea water areas in the central Northern Japan. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 1978, 24, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminov, R.I. Kinetika Rosta Mikroorganizmov s Raznymi Ekologicheskimi Kharakteristikami [Growth Kinetics of Microorganisms with Different Ecological Characteristics]. Ph.D. Thesis, Pushchino, Russia, 1987. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Koronelli, T.V.; Nesterova, E.D. Ecological Strategies of bacteria utilizing hydrophobic substrates. Microbiology 1990, 59, 691694. [Google Scholar]
- Ivshina, I.B.; Pshenichnov, R.A.; Oborin, A.A. Propanokislyayushchiye Rodokokki [Propane-Oxidizing Rhodococci]; USC AS USSR: Sverdlovsk, Russia, 1987. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Klimova, N.E.; Zlatkin, I.V.; Nikitin, D.I. Analysis of the taxonomic characteristics of oligotrophic bacteria using membrane-protein components. Microbiology 1993, 62, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- de Carvalho, C.C.C.R. Whole cell biocatalysts: Essential workers from Nature to the industry. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelkafi, S.; Labat, M.; Gam, Z.B.A.; Lorquin, J.; Casalot, L.; Sayadi, S. Optimized conditions for the synthesis of vanillic acid under hypersaline conditions by Halomonas elongata DSM 2581T resting cells. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Cultivation Period | V, mL | Protein Content in Cell-Free Extracts, mg/mL | Cat 1,2-DO Activity, U/mg of Protein | Cat 2,3-DO Activity, U/mg of Protein | Catalase Activity, U/mg of Protein | Glutathione Reductase Activity, U/mg of Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 days | 4.1 | 5.0 ± 0.2 | 0.0023 ± 0.0006 | 0.0008 ± 0.0004 | 0.0043 ± 0.0006 | 0.0038 ± 0.0008 |
| 2 weeks | 8.8 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 0.0031 ± 0.0008 | 0.0006 ± 0.0002 | 0.0564 ± 0.0012 | 0.0044 ± 0.0012 |
| 1 month | 7.1 | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 0.0034 ± 0.0007 | 0.00008 ± 0.00004 | 0.1445 ± 0.0007 | 0.0131 ± 0.0039 |
| 2 months | 5.1 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 0.0022 ± 0.0004 | 0.00011 ± 0.00003 | 0.1636 ± 0.0012 | 0.0029 ± 0.0004 |
| 3 months | 4.4 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0.1435 ± 0.0009 | 0.0021 ± 0.0008 |
| 6 months | 3.6 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0.0038 ± 0.0004 | 0.0024 ± 0.0002 |
| Cell Storage Time in LB Medium | Cultivation Time in Medium with Benzoate | Protein Content in Cell-Free Extracts, mg/mL | Cat 1,2-DO Activity, U/mg of Protein | Cat 2,3-DO Activity, U/mg of Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 days | 5 h | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 0.0360 ± 0.008 | 0.0018 ± 0.0004 |
| 2 months | 0.48 ± 0.02 | 0.0022 ± 0.0005 | 0.0010 ± 0.0003 | |
| 3 days | 1 day | 1.24 ± 0.06 | 0.178 ± 0.006 | 0.0023 ± 0.0007 |
| 2 months | 0.82 ± 0.01 | 0.098 ± 0.003 | 0.0021 ± 0.0002 | |
| 3 days | 5 days | 2.17 ± 0.01 | 0.155 ± 0.002 | 0.0340 ± 0.0105 |
| 2 months | 1.64 ± 0.05 | 0.147 ± 0.005 | 0.0280 ± 0.009 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suzina, N.E.; Sorokin, V.V.; Polivtseva, V.N.; Klyueva, V.V.; Emelyanova, E.V.; Solyanikova, I.P. From Rest to Growth: Life Collisions of Gordonia polyisoprenivorans 135. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020465
Suzina NE, Sorokin VV, Polivtseva VN, Klyueva VV, Emelyanova EV, Solyanikova IP. From Rest to Growth: Life Collisions of Gordonia polyisoprenivorans 135. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(2):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020465
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuzina, Nataliya E., Vladimir V. Sorokin, Valentina N. Polivtseva, Violetta V. Klyueva, Elena V. Emelyanova, and Inna P. Solyanikova. 2022. "From Rest to Growth: Life Collisions of Gordonia polyisoprenivorans 135" Microorganisms 10, no. 2: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020465
APA StyleSuzina, N. E., Sorokin, V. V., Polivtseva, V. N., Klyueva, V. V., Emelyanova, E. V., & Solyanikova, I. P. (2022). From Rest to Growth: Life Collisions of Gordonia polyisoprenivorans 135. Microorganisms, 10(2), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020465







