Innate Immune Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
2.4. Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. The Assessment of Methodological Quality and Risk of Bias
3. SARS-CoV-2 Innate Immune System Response
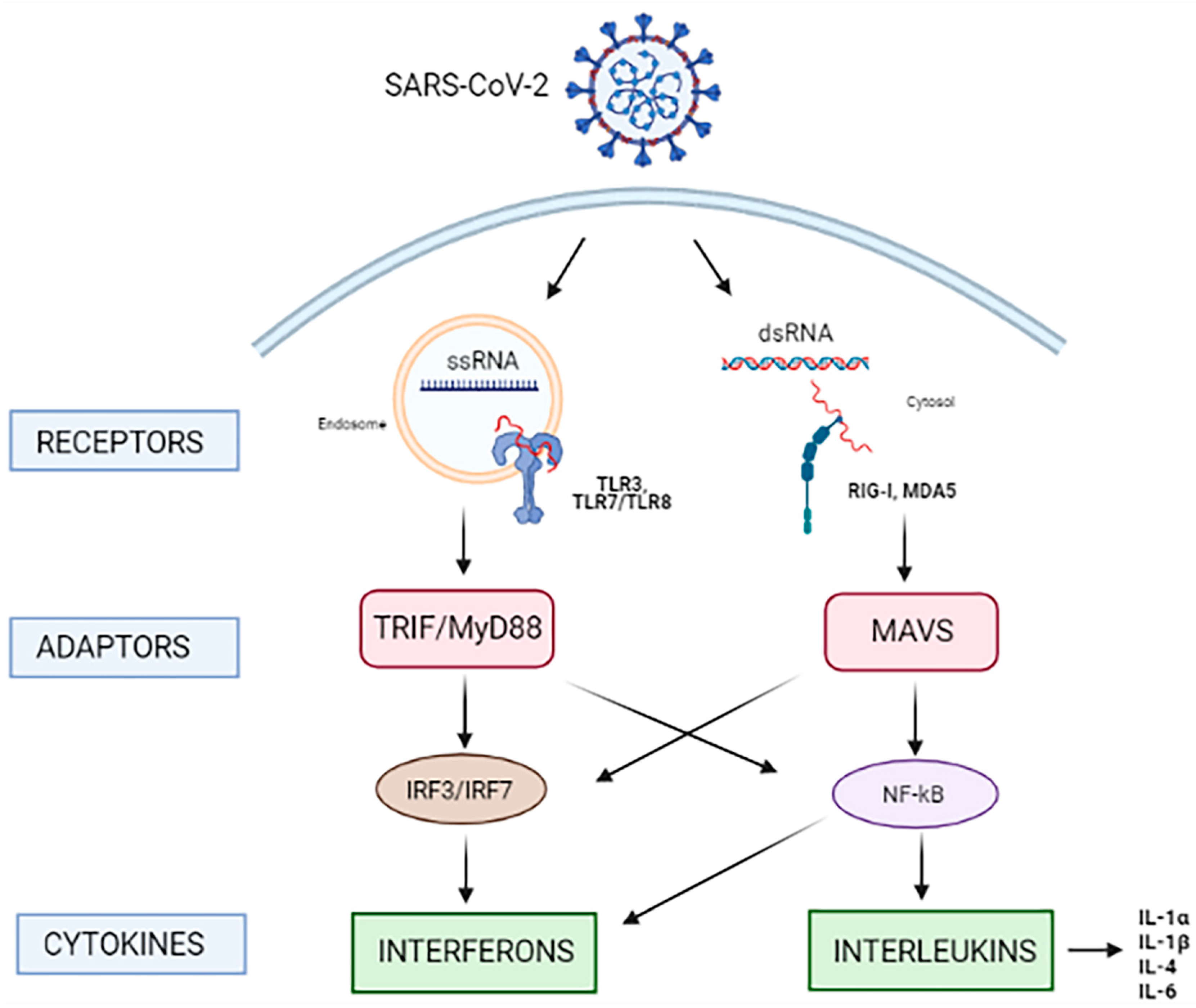
3.1. RNA-Sensing of SARS-CoV-2
3.2. SARS-CoV-2 Inflammasome and Interferon Response
3.3. SARS-CoV-2 Effect on Monocytes and Macrophages
3.4. Role of Neutrophils in COVID-19
3.5. SARS-CoV-2 Effect on Natural Killer Cells Activity
4. SARS-CoV-2 Innate Response and Acquired Immunity Cross-Talk
5. SARS-CoV-2 Immuno-Escaping Mechanisms
6. Conclusions/Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, M.; Ahmad, B.; Choi, S.; Woo, H.G. Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD are responsible for stronger ACE2 binding and poor anti-SARS-CoV mAbs cross-neutralization. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 3402–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.-S.; Lian, J.-Q.; Zhang, Z.; Du, P.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, H.-Y.; Geng, J.-J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 invades host cells via a novel route: CD147-spike protein. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Ojha, R.; Pedro, L.D.; Djannatian, M.; Franz, J.; Kuivanen, S.; van der Meer, F.; Kallio, K.; Kaya, T.; Anastasina, M.; et al. Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity. Science 2020, 370, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekol Abebe, E.; Mengie Ayele, T.; Tilahun Muche, Z.; Asmamaw Dejenie, T. Neuropilin 1: A Novel Entry Factor for SARS-CoV-2 Infection and a Potential Therapeutic Target. Biologics 2021, 15, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, D.; Simioni, C.; Neri, L.M.; Rizzo, R.; Semprini, C.M.; Occhionorelli, S.; Laface, I.; Sanz, J.M.; Schiuma, G.; Rizzo, S.; et al. Relevance of VEGF and CD147 in different SARS-CoV-2 positive digestive tracts characterized by thrombotic damage. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayi, B.S.; Leibowitz, J.A.; Woods, A.T.; Ammon, K.A.; Liu, A.E.; Raja, A. The role of Neuropilin-1 in COVID-19. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Qin, C.; Wu, G.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, D.; et al. CD147 antibody specifically and effectively inhibits infection and cytokine storm of SARS-CoV-2 and its variants delta, alpha, beta, and gamma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisblum, Y.; Schmidt, F.; Zhang, F.; DaSilva, J.; Poston, D.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Muecksch, F.; Rutkowska, M.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Michailidis, E.; et al. Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants. eLife 2020, 9, e61312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.F. Immune Response, Inflammation, and the Clinical Spectrum of COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Li, W.; Xie, J.; Hou, Y.; You, C. Cytokine storm induced by SARS-CoV-2. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 509, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultze, J.L.; Aschenbrenner, A.C. COVID-19 and the human innate immune system. Cell 2021, 184, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Group, P.-P. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mantel, N.; Haenszel, W. Statistical Aspects of the Analysis of Data from Retrospective Studies of Disease. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1959, 22, 719–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fung, T.S.; Liu, D.X. Human Coronavirus: Host-Pathogen Interaction. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 529–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.L.; Barton, G.M. Trafficking of endosomal Toll-like receptors. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.E.; Lee, H.K. Current Understanding of the Innate Control of Toll-like Receptors in Response to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Barragan, L.; Zust, R.; Weber, F.; Spiegel, M.; Lang, K.S.; Akira, S.; Thiel, V.; Ludewig, B. Control of coronavirus infection through plasmacytoid dendritic-cell-derived type I interferon. Blood 2007, 109, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanmohammadi, S.; Rezaei, N. Role of Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2735–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S. Double-Stranded RNA Sensors and Modulators in Innate Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 349–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, S.A.; Sariol, A.; Perlman, S. Innate immune and inflammatory responses to SARS-CoV-2: Implications for COVID-19. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, G.; Mugione, A.; Sanchez, A.M.; Vigano, P.; Candiani, M.; Somigliana, E.; Roncarolo, M.G.; Panina-Bordignon, P.; Gregori, S. HLA-G expressing DC-10 and CD4(+) T cells accumulate in human decidua during pregnancy. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perlman, S.; Dandekar, A.A. Immunopathogenesis of coronavirus infections: Implications for SARS. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Subbarao, K. The Immunobiology of SARS*. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 443–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, D.; Gentili, V.; Rizzo, S.; Schiuma, G.; Beltrami, S.; Strazzabosco, G.; Fernandez, M.; Caccuri, F.; Caruso, A.; Rizzo, R. TLR3 and TLR7 RNA Sensor Activation during SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulas, K.; Farsalinos, K.; Zanidis, C. Activation of TLR7 and Innate Immunity as an Efficient Method against COVID-19 Pandemic: Imiquimod as a Potential Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Renner, D.M.; Comar, C.E.; Whelan, J.N.; Reyes, H.M.; Cardenas-Diaz, F.L.; Truitt, R.; Tan, L.H.; Dong, B.; Alysandratos, K.D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 induces double-stranded RNA-mediated innate immune responses in respiratory epithelial-derived cells and cardiomyocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Sato, S.; Sotoyama, Y.; Orba, Y.; Sawa, H.; Yamauchi, H.; Sasaki, M.; Takaoka, A. RIG-I triggers a signaling-abortive anti-SARS-CoV-2 defense in human lung cells. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.M.; Geng, T.T.; Harrison, A.G.; Wang, P.H. Differential roles of RIG-I like receptors in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beacon, T.H.; Su, R.C.; Lakowski, T.M.; Delcuve, G.P.; Davie, J.R. SARS-CoV-2 multifaceted interaction with the human host. Part II: Innate immunity response, immunopathology, and epigenetics. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 2331–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorch, S.K.; Kubes, P. An emerging role for neutrophil extracellular traps in noninfectious disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Biermann, M.H.; Brauner, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Herrmann, M. New Insights into Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: Mechanisms of Formation and Role in Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabrizi, Z.A.; Khosrojerdi, A.; Aslani, S.; Hemmatzadeh, M.; Babaie, F.; Bairami, A.; Shomali, N.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; Safari, R.; Mohammadi, H. Multi-facets of neutrophil extracellular trap in infectious diseases: Moving beyond immunity. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 105066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Stadler, S.; Correll, S.; Li, P.; Wang, D.; Hayama, R.; Leonelli, L.; Han, H.; Grigoryev, S.A.; et al. Histone hypercitrullination mediates chromatin decondensation and neutrophil extracellular trap formation. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 184, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortolotti, D.; Gentili, V.; Rizzo, S.; Schiuma, G.; Beltrami, S.; Spadaro, S.; Strazzabosco, G.; Campo, G.; Carosella, E.D.; Papi, A.; et al. Increased sHLA-G Is Associated with Improved COVID-19 Outcome and Reduced Neutrophil Adhesion. Viruses 2021, 13, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Herrmann, M.; Zhao, Y.; Munoz, L.E. Receptor-Mediated NETosis on Neutrophils. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 775267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veras, F.P.; Pontelli, M.C.; Silva, C.M.; Toller-Kawahisa, J.E.; de Lima, M.; Nascimento, D.C.; Schneider, A.H.; Caetite, D.; Tavares, L.A.; Paiva, I.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-triggered neutrophil extracellular traps mediate COVID-19 pathology. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrancais, E.; Mallavia, B.; Zhuo, H.; Calfee, C.S.; Looney, M.R. Maladaptive role of neutrophil extracellular traps in pathogen-induced lung injury. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, M.; Yang, L.; Gu, J.; Wu, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, T. Inhibition of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase-4 Prevents Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Remote Lung Injury. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 1724206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasaraju, T.; Tang, B.M.; Herrmann, M.; Muller, S.; Chow, V.T.K.; Radic, M. Neutrophilia and NETopathy as Key Pathologic Drivers of Progressive Lung Impairment in Patients with COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.J.; Adrover, J.M.; Baxter-Stoltzfus, A.; Borczuk, A.; Cools-Lartigue, J.; Crawford, J.M.; Dassler-Plenker, J.; Guerci, P.; Huynh, C.; Knight, J.S.; et al. Targeting potential drivers of COVID-19: Neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strich, J.R.; Ramos-Benitez, M.J.; Randazzo, D.; Stein, S.R.; Babyak, A.; Davey, R.T.; Suffredini, A.F.; Childs, R.W.; Chertow, D.S. Fostamatinib Inhibits Neutrophils Extracellular Traps Induced by COVID-19 Patient Plasma: A Potential Therapeutic. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, C.F.; Nett, J.E. Neutrophil extracellular traps in fungal infection. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 89, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Shen, M.; Yu, Z.; Ge, W.; Chen, K.; Tian, M.; Xiao, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Jia, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 N protein promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation to induce hyperinflammation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paludan, S.R.; Mogensen, T.H. Innate immunological pathways in COVID-19 pathogenesis. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabm5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, T.L.; Swartz, T.H. Targeting the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Severe COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, W. NLRP3 Inflammasome-A Key Player in Antiviral Responses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Zhong, L.; Deng, J.; Peng, J.; Dan, H.; Zeng, X.; Li, T.; Chen, Q. High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gassart, A.; Martinon, F. Pyroptosis: Caspase-11 Unlocks the Gates of Death. Immunity 2015, 43, 835–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Cai, T.; Wang, F.; Shao, F. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 2015, 526, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.T.; Wan, H.; Hu, L.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhong, C.Q.; Han, J. Gasdermin D is an executor of pyroptosis and required for interleukin-1beta secretion. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, M.; Shao, F.; Yu, D.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid suppresses host pyroptosis by blocking Gasdermin D cleavage. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e108249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Dong, X.; Ma, R.; Wang, W.; Xiao, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Ren, L.; et al. Activation and evasion of type I interferon responses by SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Smith, N.; Pere, H.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; et al. Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Science 2020, 369, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastard, P.; Rosen, L.B.; Zhang, Q.; Michailidis, E.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Zhang, Y.; Dorgham, K.; Philippot, Q.; Rosain, J.; Beziat, V.; et al. Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science 2020, 370, eabd4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastard, P.; Gervais, A.; Le Voyer, T.; Rosain, J.; Philippot, Q.; Manry, J.; Michailidis, E.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Eto, S.; Garcia-Prat, M.; et al. Autoantibodies neutralizing type I IFNs are present in ~4% of uninfected individuals over 70 years old and account for ~20% of COVID-19 deaths. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabl4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalinger, Z.B.; Elliott, R.; Rose, K.M.; Weiss, S.R. MDA5 Is Critical to Host Defense during Infection with Murine Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12330–12340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, S.; Hou, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, T.; Tang, H.; Du, W.; Wang, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 ORF9b inhibits RIG-I-MAVS antiviral signaling by interrupting K63-linked ubiquitination of NEMO. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Lee, J.H.; Parker, Z.M.; Acharya, D.; Chiang, J.J.; van Gent, M.; Riedl, W.; Davis-Gardner, M.E.; Wies, E.; Chiang, C.; et al. ISG15-dependent activation of the sensor MDA5 is antagonized by the SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease to evade host innate immunity. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.W.; Zhang, H.N.; Meng, Q.F.; Xie, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.X.; Wang, X.N.; Qi, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Orf9b suppresses type I interferon responses by targeting TOM70. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 998–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhuang, M.W.; Deng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nan, M.L.; Zhang, X.J.; Gao, C.; Wang, P.H. SARS-CoV-2 ORF9b antagonizes type I and III interferons by targeting multiple components of the RIG-I/MDA-5-MAVS, TLR3-TRIF, and cGAS-STING signaling pathways. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 5376–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Deng, J.; Han, L.; Zhuang, M.W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nan, M.L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 NSP5 and N protein counteract the RIG-I signaling pathway by suppressing the formation of stress granules. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeldt, C.J.; Cerikan, B.; Cortese, M.; Frankish, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Plociennikowska, A.; Heigwer, F.; Prasad, V.; Joecks, S.; Burkart, S.S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces a pro-inflammatory cytokine response through cGAS-STING and NF-kappaB. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domizio, J.; Gulen, M.F.; Saidoune, F.; Thacker, V.V.; Yatim, A.; Sharma, K.; Nass, T.; Guenova, E.; Schaller, M.; Conrad, C.; et al. The cGAS-STING pathway drives type I IFN immunopathology in COVID-19. Nature 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Furth, R.; Cohn, Z.A. The origin and kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1968, 128, 415–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, P.B.; Marcovecchio, P.; Hamers, A.A.J.; Hedrick, C.C. Nonclassical Monocytes in Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamanickam, A.; Kumar, N.P.; Pandiarajan, A.N.; Selvaraj, N.; Munisankar, S.; Renji, R.M.; Venkatramani, V.; Murhekar, M.; Thangaraj, J.W.V.; Kumar, M.S.; et al. Dynamic alterations in monocyte numbers, subset frequencies and activation markers in acute and convalescent COVID-19 individuals. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassler, K.; Schulte-Schrepping, J.; Warnat-Herresthal, S.; Aschenbrenner, A.C.; Schultze, J.L. The Myeloid Cell Compartment-Cell by Cell. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 269–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Christman, J.W. Editorial: Alveolar Macrophages in Lung Inflammation and Resolution. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhury, A.; Das, N.C.; Patra, R.; Mukherjee, S. In silico analyses on the comparative sensing of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA by the intracellular TLRs of humans. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2476–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.K.; Sharma, U.; Wasson, M.K.; Jain, A.; Hassan, M.I.; Prakash, H. Macrophage Activation Syndrome and COVID 19: Impact of MAPK Driven Immune-Epigenetic Programming by SARS-Cov-2. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 763313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, C.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Xing, L.; Peng, L.; et al. Exuberant elevation of IP-10, MCP-3 and IL-1ra during SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with disease severity and fatal outcome. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaninov, N. In the eye of the COVID-19 cytokine storm. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Rial, J.; Rivero-Calle, I.; Salas, A.; Martinon-Torres, F. Role of Monocytes/Macrophages in Covid-19 Pathogenesis: Implications for Therapy. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 2485–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, J.; Dong, X.P.; Jiang, G.; Peiris, M. SARS: Clinical virology and pathogenesis. Respirology 2003, 8, S6–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ren, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, J.; Xiao, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Jiang, S.; et al. Heightened Innate Immune Responses in the Respiratory Tract of COVID-19 Patients. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 883–890.e882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Deng, W.; Huang, B.; Gao, H.; Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Wei, Q.; Yu, P.; Xu, Y.; Qi, F.; et al. The pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 in hACE2 transgenic mice. Nature 2020, 583, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwaciak, I.; Salkowska, A.; Karas, K.; Dastych, J.; Ratajewski, M. Nucleocapsid and Spike Proteins of the Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 Induce IL6 in Monocytes and Macrophages-Potential Implications for Cytokine Storm Syndrome. Vaccines 2021, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Hou, J.; Li, H.; Cao, D.; Guo, M.; Ling, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, Y.; et al. An inter-correlated cytokine network identified at the center of cytokine storm predicted COVID-19 prognosis. Cytokine 2021, 138, 155365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajnzylber, J.; Regan, J.; Coxen, K.; Corry, H.; Wong, C.; Rosenthal, A.; Worrall, D.; Giguel, F.; Piechocka-Trocha, A.; Atyeo, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, S.; Anguita, J.; Hoffmeyer, A.; Zapton, T.; Ihle, J.N.; Fikrig, E.; Rincón, M. Inhibition of Th1 Differentiation by IL-6 Is Mediated by SOCS1. Immunity 2000, 13, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, L.; Cheng, M.L.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Ye, F.; Ye, Q.; Zhu, G.; Li, X.; Wang, P.; et al. Impaired Cellular Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in Severe COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 603563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, H.; Senju, S.; Matsumura, K.; Swain, S.L.; Nishimura, Y. IL-6-mediated environmental conditioning of defective Th1 differentiation dampens antitumour immune responses in old age. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, W.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, B.S. Th17 cells enhance viral persistence and inhibit T cell cytotoxicity in a model of chronic virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boumaza, A.; Gay, L.; Mezouar, S.; Diallo, A.B.; Michel, M.; Desnues, B.; Raoult, D.; Scola, B.L.; Halfon, P.; Vitte, J.; et al. Monocytes and macrophages, targets of SARS-CoV-2: The clue for Covid-19 immunoparalysis. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Guo, R.; Lei, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qian, H.; Dai, T.; Zhang, T.; Lai, Y.; et al. Frontline Science: COVID-19 infection induces readily detectable morphologic and inflammation-related phenotypic changes in peripheral blood monocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; VanBlargan, L.A.; Bloyet, L.M.; Rothlauf, P.W.; Chen, R.E.; Stumpf, S.; Zhao, H.; Errico, J.M.; Theel, E.S.; Liebeskind, M.J.; et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations that attenuate monoclonal and serum antibody neutralization. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 477–488.e474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlyamani, I.; Venet, F.; Coudereau, R.; Gossez, M.; Monneret, G. Monocyte HLA-DR Measurement by Flow Cytometry in COVID-19 Patients: An Interim Review. Cytom. A 2020, 97, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, A.; Radrizzani, D.; Vigano, P.; Mazzone, A.; Brando, B. Decrease of Non-Classical and Intermediate Monocyte Subsets in Severe Acute SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cytom. A 2020, 97, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinetti, T.; Hirzel, C.; Fux, M.; Walti, L.N.; Schober, P.; Stueber, F.; Luedi, M.M.; Schefold, J.C. Reduced Monocytic Human Leukocyte Antigen-DR Expression Indicates Immunosuppression in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 131, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilk, A.J.; Rustagi, A.; Zhao, N.Q.; Roque, J.; Martinez-Colon, G.J.; McKechnie, J.L.; Ivison, G.T.; Ranganath, T.; Vergara, R.; Hollis, T.; et al. A single-cell atlas of the peripheral immune response to severe COVID-19. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Netea, M.G.; Rovina, N.; Akinosoglou, K.; Antoniadou, A.; Antonakos, N.; Damoraki, G.; Gkavogianni, T.; Adami, M.E.; Katsaounou, P.; et al. Complex Immune Dysregulation in COVID-19 Patients with Severe Respiratory Failure. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 992–1000.e1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parackova, Z.; Zentsova, I.; Bloomfield, M.; Vrabcova, P.; Smetanova, J.; Klocperk, A.; Meseznikov, G.; Casas Mendez, L.F.; Vymazal, T.; Sediva, A. Disharmonic Inflammatory Signatures in COVID-19: Augmented Neutrophils’ but Impaired Monocytes’ and Dendritic Cells’ Responsiveness. Cells 2020, 9, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Tinello, C.; Vatrella, A.; De Sarro, G.; Pelaia, G. Lung under attack by COVID-19-induced cytokine storm: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14, 1753466620933508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meizlish, M.L.; Pine, A.B.; Bishai, J.D.; Goshua, G.; Nadelmann, E.R.; Simonov, M.; Chang, C.H.; Zhang, H.; Shallow, M.; Bahel, P.; et al. A neutrophil activation signature predicts critical illness and mortality in COVID-19. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Du, C.; et al. Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, D.; Guo, M.; Jiang, A.; Guo, D.; Hu, W.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.; et al. Transcriptomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 patients. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Yang, J.; Xu, F.; Zhou, J.; Wan, L.; Xu, X.; Le, A.; et al. Immune characteristics distinguish patients with severe disease associated with SARS-CoV-2. Immunol. Res. 2020, 68, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Allamargot, C.; Perlman, S. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2-Induced Immune Activation and Death of Monocyte-Derived Human Macrophages and Dendritic Cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eda, H.; Burnette, B.L.; Shimada, H.; Hope, H.R.; Monahan, J.B. Interleukin-1beta-induced interleukin-6 production in A549 cells is mediated by both phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4. Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante-Silva, L.H.A.; Carvalho, D.C.M.; Lima, E.A.; Galvao, J.; da Silva, J.S.F.; Sales-Neto, J.M.; Rodrigues-Mascarenhas, S. Neutrophils and COVID-19: The road so far. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, E.A.; He, X.-Y.; Denorme, F.; Campbell, R.A.; Ng, D.; Salvatore, S.P.; Mostyka, M.; Baxter-Stoltzfus, A.; Borczuk, A.C.; Loda, M.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to immunothrombosis in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. Blood 2020, 136, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Yalavarthi, S.; Shi, H.; Gockman, K.; Zuo, M.; Madison, J.A.; Blair, C.; Weber, A.; Barnes, B.J.; Egeblad, M.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, R.; Bortolotti, D.; Bolzani, S.; Fainardi, E. HLA-G Molecules in Autoimmune Diseases and Infections. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moretta, A.; Bottino, C.; Vitale, M.; Pende, D.; Cantoni, C.; Mingari, M.C.; Biassoni, R.; Moretta, L. Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.; Schiuma, G.; Beltrami, S.; Gentili, V.; Rizzo, R.; Bortolotti, D. Role of KIR Receptor in NK Regulation during Viral Infections. Immuno 2021, 1, 305–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zhou, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Tao, Y.; Xie, C.; Ma, K.; Shang, K.; Wang, W.; et al. Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients with Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ding, J.; Huang, Q.; Tang, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.; Miao, H. Lymphopenia predicts disease severity of COVID-19: A descriptive and predictive study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, G.; Song, G.; Liu, S.; Sun, D.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Z. Functional exhaustion of antiviral lymphocytes in COVID-19 patients. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 533–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Wu, D.; Guo, W.; Cao, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Yu, H.; et al. Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, W.; Su, W.; Tang, H.; Le, W.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Xie, L.; Li, J.; Ye, J.; et al. Immune cell profiling of COVID-19 patients in the recovery stage by single-cell sequencing. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazeldine, J.; Lord, J.M. The impact of ageing on natural killer cell function and potential consequences for health in older adults. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gounder, S.S.; Abdullah, B.J.J.; Radzuanb, N.; Zain, F.; Sait, N.B.M.; Chua, C.; Subramani, B. Effect of Aging on NK Cell Population and Their Proliferation at Ex Vivo Culture Condition. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2018, 2018, 7871814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wen, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Single-cell landscape of bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.S.; van Eeden, C.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W. Fatal COVID-19 infections: Is NK cell dysfunction a link with autoimmune HLH? Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Fang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Shu, T.; Wang, A.; Huang, M.; Jin, L.; Deng, F.; Qiu, Y.; Zhou, X. SARS-CoV-2 N protein antagonizes type I interferon signaling by suppressing phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of STAT1 and STAT2. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, A.; Salvati, L.; Maggi, L.; Capone, M.; Vanni, A.; Spinicci, M.; Mencarini, J.; Caporale, R.; Peruzzi, B.; Antonelli, A.; et al. Impaired immune cell cytotoxicity in severe COVID-19 is IL-6 dependent. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4694–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, D.; Gentili, V.; Rizzo, S.; Rotola, A.; Rizzo, R. SARS-CoV-2 Spike 1 Protein Controls Natural Killer Cell Activation via the HLA-E/NKG2A Pathway. Cells 2020, 9, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anfossi, N.; Andre, P.; Guia, S.; Falk, C.S.; Roetynck, S.; Stewart, C.A.; Breso, V.; Frassati, C.; Reviron, D.; Middleton, D.; et al. Human NK cell education by inhibitory receptors for MHC class I. Immunity 2006, 25, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Llano, M.; Carretero, M.; Ishitani, A.; Navarro, F.; Lopez-Botet, M.; Geraghty, D.E. HLA-E is a major ligand for the natural killer inhibitory receptor CD94/NKG2A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5199–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Littera, R.; Chessa, L.; Deidda, S.; Angioni, G.; Campagna, M.; Lai, S.; Melis, M.; Cipri, S.; Firinu, D.; Santus, S.; et al. Natural killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors trigger differences in immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.C.; Liu, X.R.; Selvakumar, A.; Mickelson, E.; O’Reilly, R.J.; Dupont, B. Killer Ig-like receptor haplotype analysis by gene content: Evidence for genomic diversity with a minimum of six basic framework haplotypes, each with multiple subsets. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 5118–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, D.; Gonzalez, A.; Gilmore, P.M. Studies on the expression of the deleted KIR2DS4*003 gene product and distribution of KIR2DS4 deleted and nondeleted versions in different populations. Hum. Immunol. 2007, 68, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saresella, M.; Trabattoni, D.; Marventano, I.; Piancone, F.; La Rosa, F.; Caronni, A.; Lax, A.; Bianchi, L.; Banfi, P.; Navarro, J.; et al. NK Cell Subpopulations and Receptor Expression in Recovering SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 6111–6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewett, A. The Potential Effect of Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 on NK Cells; A Perspective on Potential Therapeutic Interventions. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Market, M.; Angka, L.; Martel, A.B.; Bastin, D.; Olanubi, O.; Tennakoon, G.; Boucher, D.M.; Ng, J.; Ardolino, M.; Auer, R.C. Flattening the COVID-19 Curve With Natural Killer Cell Based Immunotherapies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nyodu, R.; Maurya, V.K.; Saxena, S.K. Host Immune Response and Immunobiology of Human SARS-CoV-2 Infection. In Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19); Medical Virology: From Pathogenesis to Disease Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, J.M.; Gerlach, T.; Elbahesh, H.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Saletti, G. Influenza virus-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell-mediated immunity induced by infection and vaccination. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 119, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman Nurdianto, A.; Rohmah, M.K. Perspective of molecular immune response of SARS-COV-2 infection. J. Teknol. Lab. 2020, 9, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.X.; Liu, B.Z.; Deng, H.J.; Wu, G.C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.K.; Liao, P.; Qiu, J.F.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.F.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azkur, A.K.; Akdis, M.; Azkur, D.; Sokolowska, M.; van de Veen, W.; Bruggen, M.C.; O’Mahony, L.; Gao, Y.; Nadeau, K.; Akdis, C.A. Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 and mechanisms of immunopathological changes in COVID-19. Allergy 2020, 75, 1564–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, P.; Sunita, P.; Pattanayak, S.P. Molecular Insights into the Crosstalk between Immune Inflammation Nexus and SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 3813–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.; David, J.K.; Maden, S.K.; Wood, M.A.; Weeder, B.R.; Nellore, A.; Thompson, R.F. Human Leukocyte Antigen Susceptibility Map for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00510-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poulton, K.; Wright, P.; Hughes, P.; Savic, S.; Welberry Smith, M.; Guiver, M.; Morton, M.; van Dellen, D.; Tholouli, E.; Wynn, R.; et al. A role for human leucocyte antigens in the susceptibility to SARS-Cov-2 infection observed in transplant patients. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2020, 47, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, A.; Magistroni, P.; Vespasiano, F.; Bella, A.; Bellino, S.; Puoti, F.; Alizzi, S.; Vaisitti, T.; Boros, S.; Grossi, P.A.; et al. HLA and AB0 Polymorphisms May Influence SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Severity. Transplantation 2021, 105, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.C. Innate and adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 in humans: Relevance to acquired immunity and vaccine responses. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 204, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creech, C.B.; Walker, S.C.; Samuels, R.J. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. JAMA 2021, 325, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Evolution of antibody immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbiani, D.F.; Gaebler, C.; Muecksch, F.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Wang, Z.; Cho, A.; Agudelo, M.; Barnes, C.O.; Gazumyan, A.; Finkin, S.; et al. Convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent individuals. Nature 2020, 584, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.O.; Jette, C.A.; Abernathy, M.E.; Dam, K.A.; Esswein, S.R.; Gristick, H.B.; Malyutin, A.G.; Sharaf, N.G.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; Lee, Y.E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody structures inform therapeutic strategies. Nature 2020, 588, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.O.; West, A.P., Jr.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; Hoffmann, M.A.G.; Sharaf, N.G.; Hoffman, P.R.; Koranda, N.; Gristick, H.B.; Gaebler, C.; Muecksch, F.; et al. Structures of Human Antibodies Bound to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Reveal Common Epitopes and Recurrent Features of Antibodies. Cell 2020, 182, 828–842 e816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Schmidt, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Muecksch, F.; Barnes, C.O.; Finkin, S.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Cipolla, M.; Gaebler, C.; Lieberman, J.A.; et al. mRNA vaccine-elicited antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and circulating variants. Nature 2021, 592, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.Q.; Huang, M.; Sun, X.; Deng, F.; Wang, H.; Ning, Y.J. Immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2 from interferon antiviral system. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuga, Y.; Zhu, B.; Jang, K.J.; Yoo, J.S. Innate immune sensing of coronavirus and viral evasion strategies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhuang, M.W.; Han, L.; Zhang, J.; Nan, M.L.; Zhan, P.; Kang, D.; Liu, X.; Gao, C.; Wang, P.H. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) membrane (M) protein inhibits type I and III interferon production by targeting RIG-I/MDA-5 signaling. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S. Why are RNA virus mutation rates so damn high? PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e3000003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duchene, S.; Featherstone, L.; Haritopoulou-Sinanidou, M.; Rambaut, A.; Lemey, P.; Baele, G. Temporal signal and the phylodynamic threshold of SARS-CoV-2. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parczewski, M.; Ciechanowicz, A. Molecular epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2: A review of current data on genetic variability of the virus. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2020, 131, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengist, H.M.; Kombe Kombe, A.J.; Mekonnen, D.; Abebaw, A.; Getachew, M.; Jin, T. Mutations of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Implications on immune evasion and vaccine-induced immunity. Semin. Immunol. 2021, 55, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.J.; Guo, H.; Luo, G. Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) of SARS-CoV-2, a global urgent public health alert! J. Med. Virol. 2021, 94, 1255–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Su, B.; Guo, X.; Sun, W.; Deng, Y.; Bao, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, C.; et al. Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Identified by High-Throughput Single-Cell Sequencing of Convalescent Patients’ B Cells. Cell 2020, 182, 73–84.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Deng, Y.Q.; Ye, Q.; Cao, L.; Sun, C.Y.; Fan, C.; Huang, W.; Sun, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, L.; et al. Structural basis for neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV by a potent therapeutic antibody. Science 2020, 369, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agerer, B.; Koblischke, M.; Gudipati, V.; Montano-Gutierrez, L.F.; Smyth, M.; Popa, A.; Genger, J.W.; Endler, L.; Florian, D.M.; Muhlgrabner, V.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mutations in MHC-I-restricted epitopes evade CD8(+) T cell responses. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabg6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, F.; Luo, B.; Yuan, Y.; Xia, B.; Ma, X.; Yang, T.; Yu, F.; et al. The ORF8 protein of SARS-CoV-2 mediates immune evasion through down-regulating MHC-Iota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overacre-Delgoffe, A.E.; Chikina, M.; Dadey, R.E.; Yano, H.; Brunazzi, E.A.; Shayan, G.; Horne, W.; Moskovitz, J.M.; Kolls, J.K.; Sander, C.; et al. Interferon-gamma Drives Treg Fragility to Promote Anti-tumor Immunity. Cell 2017, 169, 1130–1141.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiuma, G.; Beltrami, S.; Bortolotti, D.; Rizzo, S.; Rizzo, R. Innate Immune Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030501
Schiuma G, Beltrami S, Bortolotti D, Rizzo S, Rizzo R. Innate Immune Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(3):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030501
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiuma, Giovanna, Silvia Beltrami, Daria Bortolotti, Sabrina Rizzo, and Roberta Rizzo. 2022. "Innate Immune Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection" Microorganisms 10, no. 3: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030501
APA StyleSchiuma, G., Beltrami, S., Bortolotti, D., Rizzo, S., & Rizzo, R. (2022). Innate Immune Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Microorganisms, 10(3), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030501






