Contamination of Soil, Water, Fresh Produce, and Bivalve Mollusks with Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Selection Process and Data Extraction
2.3. Data Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
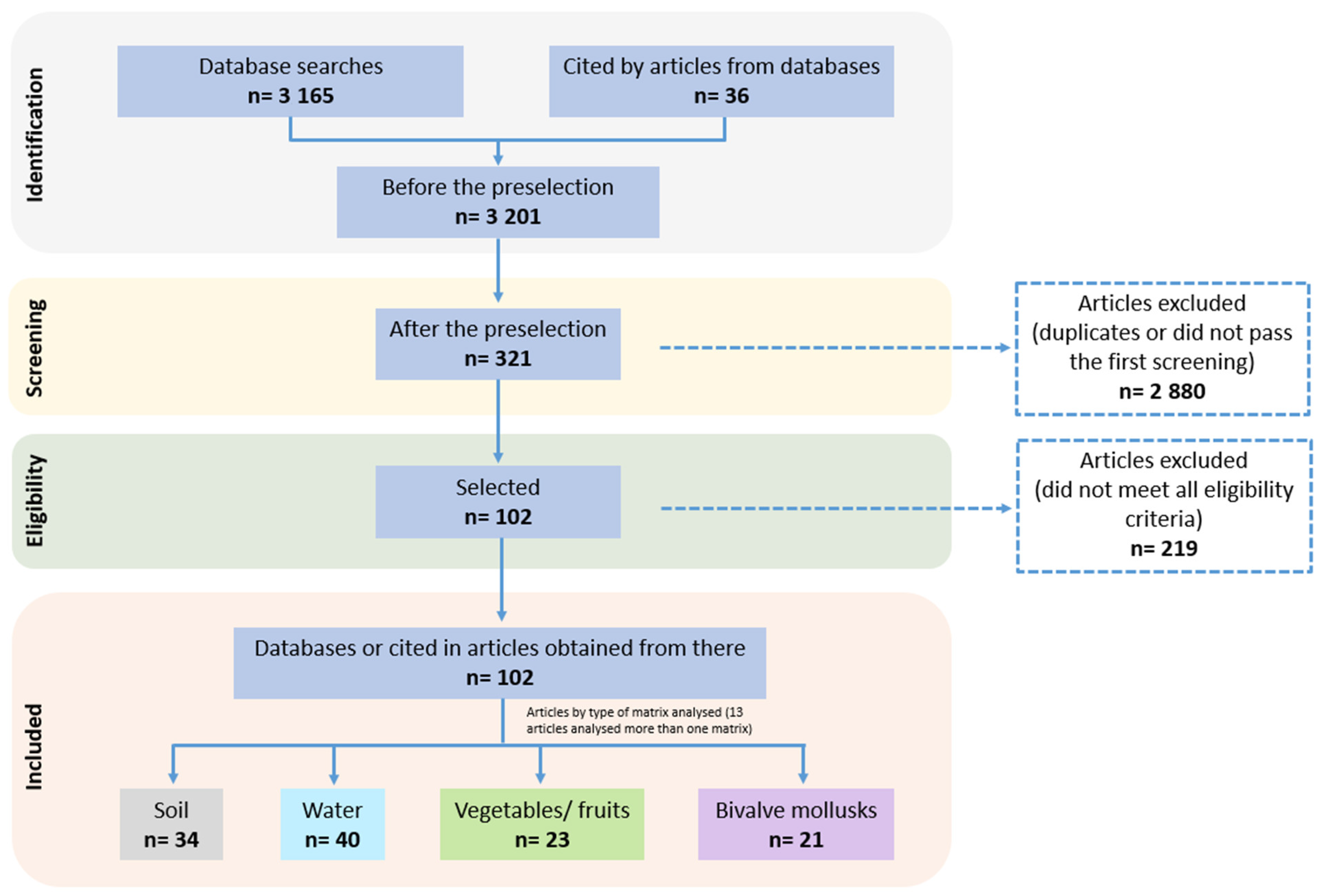
3.1. Literature Search and Article Selection
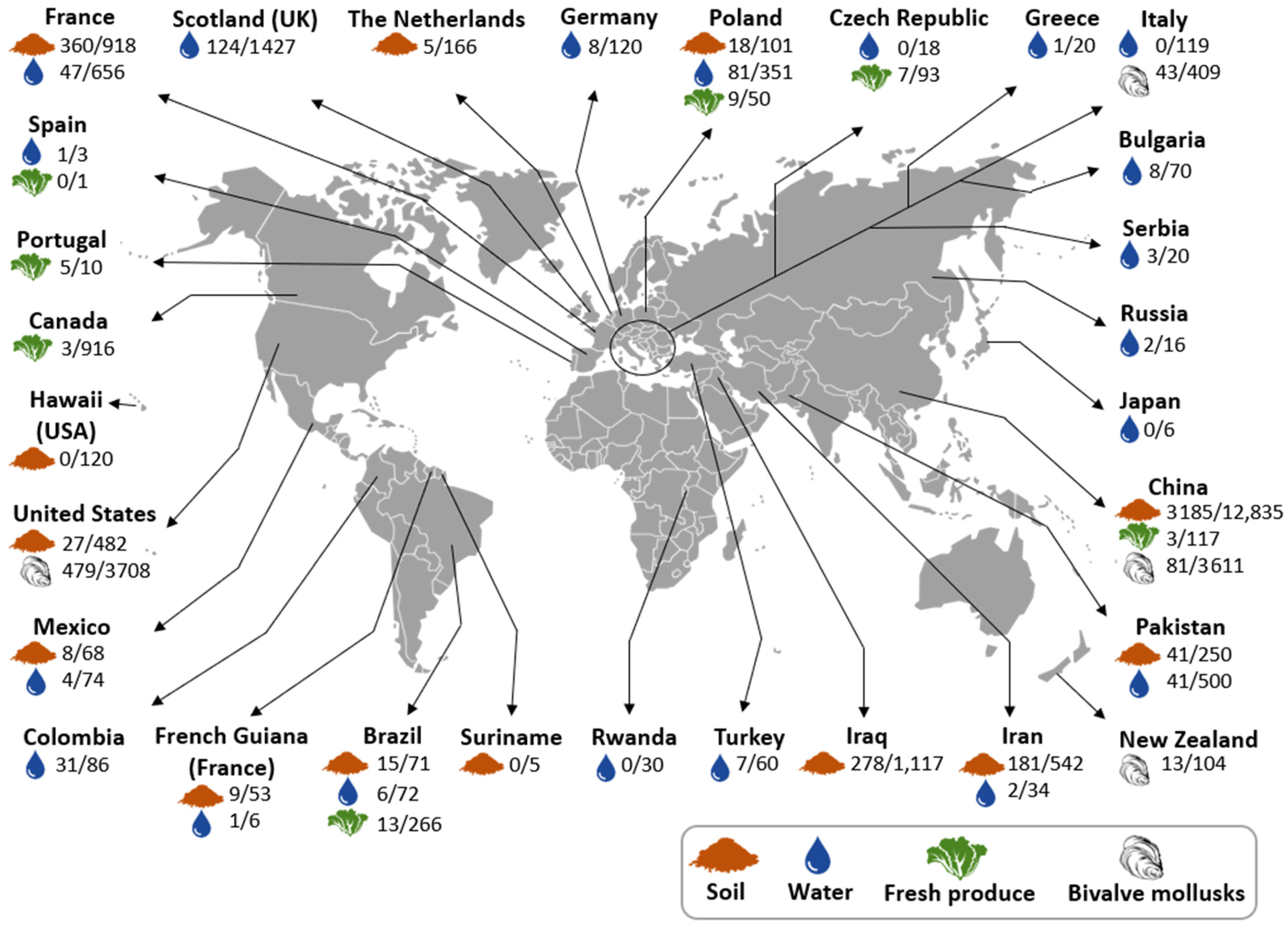
3.2. Toxoplasma gondii Oocyst Detection in Environmental Matrices
| Sampling Strategy | Methods Used | Results | Sources | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling Location (Country) | Sample Origin | No. of Samples Collected | Sample Amount Collected/Sample Size Analyzed (Depth) | Presence of Cats | Link with Human Toxoplasmosis a | Oocyst Recovery Method † | Detection Methods (Molecular Target) | Positive Samples (%) | |
| Brazil | Dairy farm | 5 | 500 g/500 g (no data) | Yes | Yes | Wash, filtration, centrifugation, flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | Mouse bioassay: Sabin Feldman dye test and brain smear confirmed by bioassay in cats | 1 (20.0) b | [56] |
| Brazil | Paddocks from ostrich farms | 40 | 250 g/25 g (5–10 cm) | No data * | No | Wash, filtration, centrifugation, flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | PCR, qPCR (529 RE and 18S rRNA) | 13 (32.5) b | [57] |
| Brazil | Elementary public schools | 31 | 1000 g/no data (5 cm) | No data | No | Flotation and centrifugation | Mouse bioassay: squash Mouse bioassay: histopathology Mouse bioassay: immunohistochemistry Mouse bioassay: indirect fluorescent antibody test (IFAT) | 7 (22.6) 0 10 (32.3) 8 (25.8) | [58] |
| Brazil | Sheep farms | 10, each inoculated in 5 mice | 1 g/1 g (no data) | Yes | No | Wash, flotation, and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) Mouse bioassay IP/PO- PCR (529 RE) Mouse bioassay IP/PO- IFAT | 0 IP: 6 (30.0), PO: 7 (23.3) IP: 14 (70.0), PO: 19 (63.3) | [59] |
| Brazil | Sludge from a cistern, and soil from greenhouses and vegetable gardens | 11 | 500 mL and 100 g/no data (no data) | Yes | Yes | Centrifugation and flotation | PCR (529 RE) | 0 | [60] |
| Brazil | Horticultural properties | 10 | 10 g/10 g (from surface) | Yes | No | Wash and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) | 2 (20) b | [61] |
| China | Schools, parks, farms, and coastal beaches | 2100 | 20 g/no data (5 cm) | No data | No | Wash, flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | PCR, Semi-nPCR, nPCR (529 RE, B1, and ITS-1) | 230 (10.9) d | [62] |
| China | Public parks | 252 | No data/0.5 g (5 cm) | Yes | No | No data | PCR (B1 and 529 RE) LAMP (MIC3, F3, B3, BIP, FIP, LD, BF) | 41 (16.3) d 58 (23.0) | [63] |
| China | Pig farms | 95 | No data/0.5 g (5 cm) | Yes | No | No data | PCR (B1 and 529 RE) LAMP (MIC3, F3, B3, BIP, FIP, LD, BF) | 20 (21.1) 36 (37.9) | [64] |
| China | Urban areas (foci of human habitation, gravel, sand, industrial and commercial land, woodland, grassland) | 9420 | 20 g/4 replicates of 5 g (10 cm) | Yes | No | Wash, flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | qPCR (529 RE) | 2853 (30.3) | [65] |
| China | Swine hoggery | 5 | No data/0.5–5 g (no data) | No data | No | Ultrasonic treatment and sugar flotation | Mouse bioassay: Sabin Feldman dye test and kitten bioassay | 5 (100) b | [49] |
| China | Schools, parks, and grazing area | 268 | No data/5 g (no data) | No data | No | Wash, filtration, centrifugation, flotation, wash, and centrifugation, presumably | Semi-nested PCR (529 RE) | 34 (12.7) d | [66] |
| China | Chicken farms (free-range and scale farms) | 700 | 10–15 g/10–15 g (from surface) | No data | No | No data | PCR (ITS-1) | 7 (1) d | [48] |
| Costa Rica | Yard and coffee plantation | 15 | 10 g/10 g (from surface or 5–7 cm) | Yes | No | Wash, centrifugation, flotation, centrifugation | Mouse bioassay: Dye test and squash | 4 (26.7) b | [67] |
| France | Areas around a hospital where cats defecate | 117 | 200–300 g/10 g (2 cm) | Yes | No | Wash, filtration, centrifugation, flotation, and centrifugation | qPCR (529 RE) | 11 (9.4) b | [68] |
| France | Village areas, crop field, grassland, forest | 243 | 20 g/4 replicates of 5 g (up to 2 cm) | Yes | No | Wash, flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | qPCR (529 RE) | 71 (29.2) | [69] |
| France | Dairy farms | 558 | 20 g/5 g (2 cm) | Yes | No | Wash, centrifugation, flotation, wash, and centrifugation | qPCR (529 RE) | 278 (49.8) | [12] |
| French Guiana (France) | Areas around houses and random sites | 53 | No data/20 g (no data) | Yes | Yes | Wash and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) | 9 (17.0) b,d | [70] |
| Hawaii (USA) | University campus and a natural area reserve | 120 | No data/20 g (10 cm) | Yes | No | Wash, centrifugation, flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | PCR (GRA6) | 0 | [71] |
| Iran | Urban and rural areas | 192 | 300–500 g/7 g (no data) | Yes | No | Wash, centrifugation, flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | nPCR (529 RE) | 150 (78.1) | [72] |
| Iran | Sand pits, playgrounds, public parks, and areas around rubbish dumps | 200 | 400 g/40 g (2–5 cm) | Yes | No | Wash, filtration, centrifugation, flotation, and centrifugation | PCR (GRA6) | 18 (9) d | [73] |
| Iran | Rubbish dumps, children’s playground, parks and public places | 150 | 300 g/no data (3 cm) | No data | No | Wash, centrifugation, flotation, and centrifugation | PCR (B1) | 13 (8.7) d | [74] |
| Iraq | Private gardens, schools, agricultural lands, territory of waste dumps, abandoned lands where children sometimes play, playgrounds, and parks | 1117 | 300 g/40 g (2–5 cm) | Yes | No | No data | nPCR (B1) | 278 (24.9) b | [75] |
| Mexico | Playground boxes | 68 | 10 g/10 g (<2 cm, 2–10 cm or until reaching rock bottom) | Yes | No | Wash, centrifugation, flotation, wash, and centrifugation | nPCR (SAG1) | 8 (11.8) | [76] |
| Panama | Outdoor children’s play areas | 924 | 30 g/30 g (no data) | Yes | Yes | Wash, centrifugation, flotation, and centrifugation | Mouse bioassay: direct agglutination test | 10 (1.1) | [77] |
| Pakistan | Homes, gardens, public enclosures, and backyards from urban and rural areas | 250 c | 300 g/no data (2–5 cm) | Yes | No | No data | PCR (B1, 529 RE) | B1 = 41 (16.4) b 529 RE = 41 (16.4)b | [78] |
| Poland | Sand pits, rubbish dumps and sand heaps | 101 | 300 g/40 g (2–5 cm) | Yes | No | Wash, centrifugation, flotation with centrifugation, attachment to a glass slide and wash of the glass slide | PCR (B1 and 200–300 REP) | 18 (17.8) d | [79] |
| Suriname | Different areas from a village | 5 | 200 g/50 g (no data) | Yes | Yes | Flotation (no more information is given) | qPCR (B1) | 0 | [80] |
| The Netherlands | Residential gardens and a limited number of playgrounds | 166 e | 100 g/25 g (5 cm) | No data | No | Magnetic capture | qPCR (529 RE) | 5 (3.0) | [81] |
| The United States | Cities, state parks, public playgrounds, and community gardens | 482 f | 20–50 g/replicates of 5 g (2–5 cm) | Yes | No | Wash, flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | nPCR (ITS1) | 27 (5.6) d | [82] |
| The United States | Pig farms | 79 | 250 g/250 g (no data) | Yes | No | Wash, filtration, centrifugation, flotation, wash, and centrifugation | Mouse bioassay- squash and serology | 1 (1.3) | [83] |
| Sampling Strategy | Methods Used | Results | Reference | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling Location (Country) | Sample Details | No. of Samples Collected | Sample Volume Collected (Sample Volume Analyzed) (Liters—L) | Water Treatment | Presence of Cats | Link with Human Toxoplasmosis a | Oocyst Recovery Method † | Detection Methods (Molecular Target) | Positive Samples (%) | |
| Brazil | Water from wells | 1750 L filtered through 17 membranes and inoculated into 8 chickens | 50 per well | No data | No data | Yes (endemic toxoplasmosis area) | Filtration | Chicken bioassay: MATMolecular (no data) | 3 (37.5) b 0 | [87] |
| Brazil | Irrigation and municipal water | 3 | 10 | No data | Yes | Yes | Filtration, wash, and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) | 1 (33.3) b | [88] |
| Brazil | Water from cisterns | 3 | 10–20 | No data | Yes | Yes | Filtration, wash, and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) | 0 | [60] |
| Brazil | Irrigation water | 10 | 0.01 | No data | Yes | No | Filtration, wash, and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) | 2 (20.0) | [61] |
| Brazil | Drinking water | 4650 L filtered through 56 membranes | No data | Untreated | Yes | Yes | Filtration and centrifugation | PCR (B1) Mouse, chicken, pig and cat bioassays | Positive by at least 1 assay c | [89] |
| Brazil | Surface water used to produce drinking water | 39 | 20 | No data | No data | No | Filtration, wash, and centrifugation | qPCR (B1) | 3 (7.7) | [90] |
| Brazil | Drinking water | 8 | Given ad libitum to the piglets | Treated (process not specified) | No data | Yes | Directly | Piglet bioassay: IFAT Piglet bioassay: tissue PCR (529 RE) Piglet bioassay: tissue mouse bioassay and PCR (529 RE) | 8 (100) 5 (62.5) 5 (62.5) b | [51] |
| Brazil | Farm water | No data (0.003) | No data | No data | Yes | No | Flotation and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) Mouse bioassay | No data | [59] |
| Canada | Untreated water that supplied municipal drinking water treatment plants | 11 | Mean of 1051 | Untreated | No data | Yes | Filtration, wash, centrifugation, flotation, wash, and centrifugation | Mouse bioassay: microscopy from tissue and MAT | 0 | [91] |
| Colombia | Water | 40 | 0.2 or 4 | Boiled and others not specified | No data | Yes | Sedimentation by centrifugation with formalin-ether | nPCR (B1) | 4 (10.0) b,c | [92] |
| Colombia | Surface water before and during treatment, in the treatment plant network and from homes | 46 | 10 | Untreated and treated: coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and chlorination | No data | No | Sedimentation by centrifugation with formalin-ether | nPCR (B1) | 27 (58.6) c | [93] |
| Czech Republic | Irrigation and vegetables washing water | 18 | 10 | No data | Not data | No | Filtration, wash, and centrifugation | qPCR (B1 and 529 RE) | 0 | [94] |
| Egypt | Irrigation water | 54 | No data | No data | No data | No | Filtration and centrifugation | Mouse bioassay- smears and MAT | 9 (16.7) | [95] |
| France | Wastewa-ter | 35 | 20 | Treated and untreated (process not specified) | No data | No | Filtration, wash, centrifugation, immunomagnetic separation of Cryptosporidium spp. and G. duodenalis, centrifugation, and flotation | PCR (529 RE) | 0 | [96] |
| France | Untreated surface, ground, and public drinking water | 139 | 100 (7–100) | No data | No data | No | Filtration, wash, centrifugation, immunomagnetic separation of Cryptosporidium spp. and G. duodenalis, flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | qPCR (B1) Mouse bioassay- agglutination test and smear | 10 (8.0) d 0 | [97] |
| France | Untreated surface, ground, and public drinking water | 482 | 5–100 | No data | No data | No | Filtration, wash, centrifugation, immunomagnetic separation of Cryptosporidium spp. and G. duodenalis, centrifugation, flotation, and centrifugation | PCR (B1 and 529 RE) | 37 (7.7) e | [98] |
| French Guiana (France) | Water from cisterns, little streams, and brooks | 6 | 10 | No data | Yes | Yes | Filtration and presumably wash, centrifugation, flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) | 1 (16.7) b,c | [70] |
| Germany | Wastewa-ter | 25 | 1 | Untreated and treated: mechanical and biological treatments | No data | No | Filtration (sieve and cellulose filters), wash, and centrifugation | PCR (B1) | 0 | [99] |
| Germany | Variable: drinking water and others not specified | 95 | 5–2500 | Treated and untreated (process not specified) | No data | No | Flocculation for WWTPs, filtration for drinking, groundwater and surface water, then centrifugation and flotation for samples | LAMP (B1) | 8 (8.4) | [100] |
| Greece Bulgaria Japan | River, reservoir, well, spring, tap, sewage, and recreational water | 20 34 6 | 10 | No data | No data | No | Flocculation, centrifugation, discontinuous sucrose gradients, wash, and centrifugation | nPCR (18S rRNA) | 1 (5) b 3 (8.8) b 0 | [50] |
| Iran | Natural water | 34 | 5 | No data | No data | No | Filtration, wash, centrifugation, and flotation | LAMP (B1) | 2 (5.8) | [101] |
| Italy | Wastewa-ter | 119 | 10–20 | Sand, membrane-bioreactor, plug-flow reactor, and membrane ultrafiltration | No data | No | Filtration, wash, centrifugation, and flotation | qPCR (B1-multiplex) | 0 | [102] |
| Mexico | Public drinking water | 74 | 5 | Chlorination | No data | No | Filtration, wash, centrifugation, flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | nPCR (SAG1) | 4 (5.4) | [103] |
| Pakistan | Drinking, recreational, and irrigation water | 500 | No data | No data | No data | No | Flocculation or filtration | PCR (B1 and 529 RE) | 41 (8.2) b | [78] |
| Poland | Drinking water | 114 | 5 | No data | Yes | Yes | Filtration, wash, centrifugation, flotation with centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | PCR (no data) | 31 (27.2) | [104] |
| Poland | Drinking and natural water | 201 | 5 | No data | Yes | Yes | Filtration, wash, centrifugation, flotation with centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | PCR (B1) Mouse bioassay of 14 PCR positive samples-tissue PCR or agglutination test | 43 (21.4) b,c Tissue PCR: 9 (64.3), agglutination test: 3 (21.4) b | [105] |
| Poland | Bathing and drinking water | 36 | 50 | No data | No data | No | Filtration, wash, and centrifugation | nPCR (B1) | 7 (19.4) c | [106] |
| Russia Bulgaria | Natural water | 16 36 | No data | No data | No data | No | Flocculation, wash, and discontinuous sucrose gradient | nPCR (18S rRNA) LAMP (B1) | 2 (12.5) f 5 (13.9) f 9 (56.3) f 16 (44.4) f | [107] |
| Rwanda | Irrigation and post-harvest washing water | 30 | 1 | Untreated those from rivers, lagoons, marshlands, and lakes | No data | No | No data | PCR (529 RE) | 0 | [108] |
| Scotland | Public water supply | 1427 | Up to 1000 | No data | No data | No | Filtration, centrifugation, immunomagnetic separation of Cryptosporidium spp. and centrifugation | qPCR (529 RE) | 124 (8.8) c,g | [109] |
| Serbia | Surface water from rivers | 20 | 10 | No data | No data | No | Filtration, wash, and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) | 3 (15.0) c | [110] |
| Spain presumably | Irrigation water | 3 | 1.5 | No data | No data | No | Centrifugation | qPCR (18S rRNA) | 1 (33.3) b,c | [111] |
| Turkey | Natural water | 60 | 10 | No data | No data | No | Flocculation, centrifugation, wash, and discontinuous sucrose gradient | nPCR (18S rRNA) LAMP (B1) | 7 (11.7) c,h 15 (25.0) | [112] |
| The United States | Presumably drinking water for animals | No data | 0.05 | No data | Yes | No | Centrifugation | Mouse bioassay-agglutination test and examination | No data | [83] |
| Sampling Strategy | Methods Used | Results | Reference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling Location (Country) | Matrix | Production Type (Organic and/or Conventional) | Product Presentation (Bulk, Packaged or Ready to Eat—RTE) | No. of Samples Collected | Sample Mass Collected (Sample Mass Analyzed) | Presence of Cats | Linked with Human Toxoplasmosis a | Oocyst Recovery Method † | Detection Methods (Molecular Target) | Positive Samples (%) | |
| Brazil | Lettuce | No data | No data | 4 | No data | Yes | Yes | Wash, scraping, and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) | 0 | [88] |
| Brazil | Crisp lettuce, regular lettuce, chicory, rocket, and parsley | Organic and conventional | No data | 220 c | 50 g | No data | No | Wash, filtration, and centrifugation | PCR (B1 and 529 RE) | 9 (3.8) | [118] |
| Brazil | Vegetable clumps (no more details given) | No data | No data | 11 | 50 g | Yes | Yes | Wash, filtration, and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) | 0 | [60] |
| Brazil | Crisp lettuce, arugula, chicory, chives, purple lettuce, spinach, and chard | Organic | No data | 42 | 50 g | Yes | No | Wash, filtration, and centrifugation | PCR (529 RE) | 4 (9.5) e | [61] |
| Canada | Variable ‡ | Organic and conventional | Bulk and packaged | 1171 | 35 ± 0.5 g | No data | No | Wash, centrifugation, and flotation | qPCR (18S rDNA) | 3 (0.3) b | [52] |
| China | Lettuce, pak choi, Chinese cabbage, rape, asparagus, Chrysanthemum coronarium, endive, Chinese chives, cabbage, red cabbage, and spinach | No data | No data | 279 | No data | No data | No | Wash, flocculation, and centrifugation | qPCR (B1) | 10 (3.6) b | [19] |
| Colombia | Lettuce, cabbage, cucumber, carrot, and tomato | No data | No data | 30 | 200 g | No data | Yes | Wash, sedimentation/centrifugation with formalin ether | nPCR (B1) | 1 (3.3) b,e | [92] |
| Colombia | Strawberries | No data | Bulk and packaged | 120 | 250 g (3 replicates of 30 g) | No data | No | Wash and centrifugation | qPCR (529 RE-multiplex) | 6 (5.0) b | [119] |
| Czech Republic | Carrot, cucumber, lettuce (butterhead lettuce, iceberg lettuce, little gem, and lollo lettuce) | No data | Bulk and packaged (just for lettuce) | 292 | 100 g | No data | No | Wash and centrifugation | qPCR (B1 and 529 RE) | 28 (9.6) b | [94] |
| Egypt | Lettuce, carrot, and cucumber | No data | No data | 54 | 150 g | No data | No | Wash, filtration, and centrifugation | Mouse bioassay: smears + MAT | 7 (13.0) | [95] |
| Italy | Mix salad: curly and escarole lettuce, red radish, rocket salad, and carrots | No data | RTE | 648 (72 pools) | 100 g | No data | No | Wash and centrifugation | qPCR (B1) | 5 (0.8) b | [120] |
| Pakistan | Apple, banana, guava, cabbage, brinjal, and tomato | No data | No data | 250 | No data | No data | No | No data | PCR (B1 and 529 RE) | 12 (4.8) e | [78] |
| Poland | Strawberries, radish, carrot, and lettuce | No data | No data | 216 | 1–20 units, 500–1000 g | Yes (in farms-home gardens) | No | Wash, flocculation, and centrifugation | qPCR (B1) | 21 (9.7) b | [38] |
| Spain Portugal | Lettuce, carrot, parsley, watercress, coriander, mix salad, arugula, strawberries, raspberries, and blueberries | Organic and conventional | Bulk, packaged, and RTE | 9 26 | 64–3600 g | No data | No | Wash, centrifugation, immunomagnetic separation of Cryptosporidium spp. and G. duodenalis | PCR (529 RE) | 2 (22.2) b,d 13 (50.0) b,d | [37] |
| Switzerland | Lettuce (different types, but not specified) | No data | No data | 100 | 900–1800 g (pools of 9 lettuce) | No data | No | Wash, filtration, and centrifugation | PCR (B1) | 6 (6.0) b,e | [121] |
| Sampling Strategy | Methods Used | Results | Reference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling Location (Country) | Sample Type (Scientific Names) | Samples Collected | Sample Units per Pool or Sample Mass (Length) | Type of Tissue or Material Analyzed | Oocyst Recovery Method † | Detection Methods (Molecular Target if Apply) | Positive Samples (%) | |
| Brazil | Oysters (Crassostrea rhizophorae), mussels (Mytella guyanensis) | 80 pools | 5–15 units/pool | Whole oyster or mussel | Wash, filtration, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | nPCR (B1) Mouse bioassay- smear + IFAT | 2 (2.5) a,b 0 | [130] |
| Brazil | Oysters (Crassostrea rhizophorae) | 208 pools of each tissue | 3 units/pool (no data) | Gills and digestive glands | Not performed * | PCR (529 RE) nPCR (SAG1) | 0 17 (8.1) b | [131] |
| Brazil | Oysters (Crassostrea spp.) | 120 pools | 10 units/pool (no data) | Gills, gastrointestinal tract, and intervalvular liquid | Not performed * | nPCR (B1) | 7 (5.8) b | [132] |
| Brazil | Oysters (Crassostrea spp.) | 80 pools of each tissue | 5 units/pool (no data) | Gills and digestive glands (visceral mass) | Not performed* | nPCR (SAG1) | 2 (2.5) b | [54] |
| China | Oysters (not specified) | 998 | 1 unit (no data) | Hemolymph, digestive glands and gills | Centrifugation | Semi nPCR (B1) | 26 (2.6) b | [133] |
| China | Mussels (Mytilus edulis) | 2215 | 1 unit (no data) | Gills, digestive glands and hemolymph | Not performed * | Semi nPCR (B1) | 55 (2.5) b | [134] |
| China | Oysters (Concha ostreae) | 398 | 1 g/sample (no data) | Digestive tract tissues | Not performed * | PCR (ITS1) | 0 | [135] |
| France | Mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) | 96 pools | 9 units/pool (18–25 mm) | Whole mussel | Enzyme digestion, centrifugation | qPCR (529 RE) | 3 (3.1) | [136] |
| Italy | Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) | 409 | 25 mg (>5 cm) | Digestive gland | Not performed * | qPCR (B1) | 43 (10.5) b | [137] |
| Italy | Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis, Mytilus edulis) | 135 pools | 10 g (no data | Intestinal tissues | Wash, filtration, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | End-point PCRs (B1 and 529 RE) | 10 (7.4) b | [138] |
| Italy | Oysters (Crassostrea gigas), mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis), clams (Tapes philippinarum, Tapes decussatus) | 62 pools of each tissue | 11–30 units/pool (no data) | Digestive glands, gills and hemolymph | For hemolymph: flotation, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation. Not specified for digestive glands and gills | nPCR and FLAG- qPCR (B1) | 2 (3.2) | [139] |
| New Zealand | Mussels (Perna canaliculus) | 104 | 1 unit (no data) | Hemolymph | Centrifugation | nPCR (dhps) | 13 (12.5) b | [23] |
| Tunisia | Clams (Ruditapes decussatus), oysters (Pinctada radiata), mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis, Perna perna) | 87 pools | 9–18 units/pool (no data) | No data | Wash, filtration, centrifugation, wash, and centrifugation | qPCR (B1) | 4 (4.6) a,b | [140] |
| Turkey | Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) | 53 pools | 15 units/pool (5–8 cm) | Gills and digestive system | Filtration and centrifugation | qPCR (B1) + HRM | 5 (9.4) b | [141] |
| Turkey Italy | Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) | 53 pools 60 pools | 15 units/pool (no data) 500 g (no data) | Gills and digestive system Hemolymph, gills and digestive glands | Flotation or filtration and centrifugation | qPCR + HRM (B1) | 7 (13.2) 0 | [102] |
| The United States | Oysters (Crassostrea virginica) | 1440 | 50–100 mg wet weight of total tissue (no data) | Mantle, gills and rectum | Not performed * | qPCR (ITS1) | 446 a (31.0) | [55] |
| The United States ‡ | Mussels (M. californianus), gaper clams (Tresus nuttallii), pismo clams (Tivela stultorum) | 1109 | 50 mg of digestive tissue or 50–100 μL of pelleted hemolymph (no data) | Hemocytes and digestive gland | Not performed * | qPCR (18S rRNA) | 1 (0.1) a,b | [21] |
| The United States ‡ | Mussels (Mytilus californianus) | 959 | 1 unit (no data) | Hemolymph | Centrifugation | nPCR (ITS1 and B1) | 13 (1.4) b | [22] |
| The United States | Mussels (Mytilus spp.) | 41 | 1 unit (no data) | Hemolymph, gills and digestive glands | Filtration and centrifugation | qPCR and end- point PCR (529 RE) | 19 (46.3) a,b | [53] |
| The United States | Clams (Mya arenaria), mussels (Geukensia demissa, Mytilus edulis), oysters (Crassostrea virginica) | 159 | 1 unit (no data) | Digestive gland, mantle, gills, foot, and siphon | Not performed * | PCR (GRA6) | 0 | [142] |
| The United States | Mussel (Mytilus californianus) | Analyzed pools, but the exact number was not Specified (total of units = 959) | 30 units/pool (≥3 cm) | Hemolymph | Not performed * | PCR (ITS1, 529 bp and B1) | 13 (1.5) b,c | [117] |
3.3. Sampling Strategies
3.3.1. Soil
3.3.2. Water
3.3.3. Fresh Produce
3.3.4. Bivalve Mollusks
3.4. Toxoplasma gondii Oocyst Detection Methodology
4. Conclusions and Considerations for Future Research
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiss, L.M.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis: A History of Clinical Observations. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marstrand, J.; Kurtzhals, J.A.L.; Fuchs, H.J.; Nielsen, H.V.; Jokelainen, P. The Disease Burden of Ocular Toxoplasmosis in Denmark in 2019: Estimates Based on Laboratory Testing of Ocular Samples and on Publicly Available Register Data. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2021, 15, e00229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eza, D.E.; Lucas, S.B. Fulminant Toxoplasmosis Causing Fatal Pneumonitis and Myocarditis. HIV Med. 2006, 7, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokelainen, P.; Simola, O.; Rantanen, E.; Näreaho, A.; Lohi, H.; Sukura, A. Feline Toxoplasmosis in Finland: Cross-Sectional Epidemiological Study and Case Series Study. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bowen, L.N.; Smith, B.; Reich, D.; Quezado, M.; Nath, A. HIV-Associated Opportunistic CNS Infections: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.J.; Lalle, M.; Paulsen, P. Why We Need a European Focus on Foodborne Parasites. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 214, 107900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, K.; Bahia-Oliveira, L.; Dixon, B.; Dumètre, A.; de Wit, L.A.; VanWormer, E.; Villena, I. Environmental Transmission of Toxoplasma gondii: Oocysts in Water, Soil and Food. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeria, S.; Dubey, J.P. Foodborne Transmission of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in the Last Decade. An Overview. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slana, I.; Bier, N.; Bartosova, B.; Marucci, G.; Possenti, A.; Mayer-Scholl, A.; Jokelainen, P.; Lalle, M. Molecular Methods for the Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Fresh Produce: An Extensive Review. Microorgonisms 2021, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attias, M.; Teixeira, D.E.; Benchimol, M.; Vommaro, R.C.; Crepaldi, P.H.; De Souza, W. The Life-Cycle of Toxoplasma gondii Reviewed Using Animations. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumètre, A.; Dardé, M.-L.L. How to Detect Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Environmental Samples? FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, J.A.; Kurdzielewicz, S.; Jeanniot, E.; Dupuis, E.; Marnef, F.; Aubert, D.; Villena, I.; Poulle, M.L. Spatial Distribution of Soil Contaminated with Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Relation to the Distribution and Use of Domestic Cat Defecation Sites on Dairy Farms. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowie, W.R.; King, A.S.; Werker, D.H.; Isaac-Renton, J.L.; Bell, A.; Eng, S.B.; Marion, S.A. Outbreak of Toxoplasmosis Associated with Municipal Drinking Water. The BC Toxoplasma Investigation Team. Lancet 1997, 350, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Ferreira, F.; Caldart, E.T.; Pasquali, A.K.S.; Mitsuka-Breganó, R.; Freire, R.L.; Navarro, I.T. Patterns of Transmission and Sources of Infection in Outbreaks of Human Toxoplasmosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wainwright, K.E.; Miller, M.A.; Barr, B.C.; Gardner, I.A.; Melli, A.C.; Essert, T.; Packham, A.E.; Truong, T.; Lagunas-Solar, M.; Conrad, P.A. Chemical Inactivation of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Water. J. Parasitol. 2007, 93, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza Alizadeh, A.; Jazaeri, S.; Shemshadi, B.; Hashempour-Baltork, F.; Sarlak, Z.; Pilevar, Z.; Hosseini, H. A Review on Inactivation Methods of Toxoplasma gondii in Foods. Pathog. Glob. Health 2018, 112, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis—A Waterborne Zoonosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohweyer, J.; Dumètre, A.; Aubert, D.; Azas, N.; Villena, I. Tools and Methods for Detecting and Characterizing Giardia, Cryptosporidium, and Toxoplasma Parasites in Marine Mollusks. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lass, A.; Ma, L.; Kontogeorgos, I.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Karanis, P. First Molecular Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Vegetable Samples in China Using Qualitative, Quantitative Real-Time PCR and Multilocus Genotyping. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, B.; Lemenach, K.; Devier, M.H.; Ameur, W.B.; Etcheber, H.; Budzinski, H.; Cachot, J.; Driss, M.R. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Surface Sediments from the Bizerte Lagoon, Tunisia: Levels, Sources, and Toxicological Significance. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2653–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Miller, W.A.; Conrad, P.A.; James, E.R.; Melli, A.C.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Dabritz, H.A.; Packham, A.E.; Paradies, D.; Harris, M.; et al. Type X Toxoplasma gondii in a Wild Mussel and Terrestrial Carnivores from Coastal California: New Linkages between Terrestrial Mammals, Runoff and Toxoplasmosis of Sea Otters. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, K.; Vanwormer, E.; Aguilar, B.; Conrad, P.A. Surveillance for Toxoplasma gondii in California Mussels (Mytilus californianus) Reveals Transmission of Atypical Genotypes from Land to Sea. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4177–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupe, A.; Howe, L.; Burrows, E.; Sine, A.; Pita, A.; Velathanthiri, N.; Vallée, E.; Hayman, D.; Shapiro, K.; Roe, W.D. First Report of Toxoplasma gondii Sporulated Oocysts and Giardia duodenalis in Commercial Green-Lipped Mussels (Perna canaliculus) in New Zealand. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, D.S.; Collins, M.V.; Mitchell, S.M.; Wetch, C.N.; Rosypal, A.C.; Flick, G.J.; Zajac, A.M.; Lindquist, A.; Dubey, J.P. Survival of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Eastern Oysters (Crassostrea virginica). J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 1054–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palos-Ladeiro, M.; Bigot, A.; Aubert, D.; Hohweyer, J.; Favennec, L.; Villena, I.; Geffard, A. Protozoa Interaction with Aquatic Invertebrate: Interest for Watercourses Biomonitoring. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabritz, H.A.; Conrad, P.A. Cats and Toxoplasma: Implications for Public Health. Zoonoses Public Health 2010, 57, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remes, N.; Kärssin, A.; Must, K.; Tagel, M.; Lassen, B.; Jokelainen, P. Toxoplasma gondii Seroprevalence in Free-Ranging Moose (Alces alces) Hunted for Human Consumption in Estonia: Indicator Host Species for Environmental Toxoplasma gondii Oocyst Contamination. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2018, 11, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-García, G.; Davidson, R.; Jokelainen, P.; Klevar, S.; Spano, F.; Seeber, F. Identification of Oocyst-Driven Toxoplasma gondii Infections in Humans and Animals through Stage-Specific Serology—Current Status and Future Perspectives. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, A.; Villena, I.; Dumètre, A.; Escotte-Binet, S.; Favennec, L.; Dubey, J.P.; Aubert, D.; La Carbona, S. Evaluation of Propidium Monoazide–Based QPCR to Detect Viable Oocysts of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marciano, M.A.M.; Silva, R.A.; Barbosa, M.L.; Ferreira, A.R.S.; Pereira-Chioccola, V.L. Determination of the Viability of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts by PCR Real-Time after Treatment with Propidium Monoazide. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. 2020, 62, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Shapiro, K.; Rajal, V.B.; Packham, A.; Aguilar, B.; Rueda, L.; Wuertz, S. Quantification of Viable Protozoan Parasites on Leafy Greens Using Molecular Methods. Food Microbiol. 2021, 99, 103816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakakhel, M.A.; Wu, F.; Anwar, Z.; Saif, I.; Akbar, N.u.; Gul, N.; Ali, I.; Feng, H.; Wang, W. The Presence of Toxoplasma gondii in Soil, Their Transmission, and Their Influence on the Small Ruminants and Human Population: A Review. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 104850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrouch, S.; Escotte-Binet, S.; Harrak, R.; Huguenin, A.; Flori, P.; Favennec, L.; Villena, I.; Hafid, J. Detection Methods and Prevalence of Transmission Stages of Toxoplasma gondii, Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. in Fresh Vegetables: A Review. Parasitology 2020, 147, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, B.; Ahmadi, N.; Olfatifar, M.; Gorgipour, M.; Taghipour, A.; Abdoli, A.; Khorshidi, A.; Foroutan, M.; Mirzapour, A. Toxoplasma Oocysts in the Soil of Public Places Worldwide: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 115, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayeri, T.; Sarvi, S.; Daryani, A. Toxoplasma gondii in Mollusks and Cold-Blooded Animals: A Systematic Review. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. BMJ 2009, 339, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marques, C.S.; Sousa, S.; Castro, A.; Da Costa, J.M.C. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Fresh Vegetables and Berry Fruits. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lass, A.; Pietkiewicz, H.; Szostakowska, B.; Myjak, P. The First Detection of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in Environmental Fruits and Vegetables Samples. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying Heterogeneity in a Meta-Analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhin, E.Z.; Tadesse, G. A Meta-Analysis of the Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Animals and Humans in Ethiopia. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatam-Nahavandi, K.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Rahimi, M.T.; Pagheh, A.S.; Zarean, M.; Dezhkam, A.; Ahmadpour, E. Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Domestic and Wild Felids as Public Health Concerns: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toxosources Deliverable—Work Package 3. 2021. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/5812067#.YgjKZd_MI2w (accessed on 31 December 2021).
- Dubey, J.P. History of the Discovery of the Life Cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mac Kenzie, W.R.; Schell, W.L.; Blair, K.A.; Addiss, D.G.; Peterson, D.E.; Hoxie, N.J.; Kazmierczak, J.J.; Davis, J.P. Massive Outbreak of Waterborne Cryptosporidium Infection in Milwaukee, Wisconsin: Recurrence of Illness and Risk of Secondary Transmission. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 21, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, E.B.; Matte, T.D.; O’Brien, T.R.; McKinley, T.W.; Logsdon, G.S.; Rose, J.B.; Ungar, B.L.P.; Word, D.M.; Wilson, M.A.; Long, E.G.; et al. Large Community Outbreak of Cryptosporidiosis Due to Contamination of a Filtered Public Water Supply. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mac Kenzie, W.R.; Hoxie, N.J.; Proctor, M.E.; Gradus, M.S.; Blair, K.A.; Peterson, D.E.; Kazmierczak, J.J.; Addiss, D.G.; Fox, K.R.; Rose, J.B.; et al. A Massive Outbreak in Milwaukee of Cryptosporidium Infection Transmitted through the Public Water Supply. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayer, R.; Graczyk, T.K.; Lewis, E.J.; Trout, J.M.; Parley, C.A. Survival of Infectious Cryptosporidium parvum Oocysts in Seawater and Eastern Oysters (Crassostrea virginica) in the Chesapeake Bay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.C.; He, Y.; Han, D.G.; Zhang, Z.C.; Li, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.X.; Yan, R.F.; Li, X.R. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Chicken and Soil of Chicken Farms in Nanjing Region, China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, S.; Tsunoda, K.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Matsui, T.; Nishikawa, H. Detection and Confirmation of Toxoplasma Oocysts in the Soil. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1975, 37, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourenti, C.; Karanis, P. Evaluation and Applicability of a Purification Method Coupled with Nested PCR for the Detection of Toxoplasma Oocysts in Water. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minuzzi, C.E.; Fernandes, F.D.; Portella, L.P.; Bräunig, P.; Sturza, D.A.F.; Giacomini, L.; Salvagni, E.; Ribeiro, J.d.S.; Silva, C.R.; Difante, C.M.; et al. Contaminated Water Confirmed as Source of Infection by Bioassay in an Outbreak of Toxoplasmosis in South Brazil. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, L.F.; Gajadhar, A.A. Detection of Cyclospora cayetanensis, Cryptosporidium spp., and Toxoplasma gondii on Imported Leafy Green Vegetables in Canadian Survey. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2016, 2, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staggs, S.E.; Keely, S.P.; Ware, M.W.; Schable, N.; See, M.J.; Gregorio, D.; Zou, X.; Su, C.; Dubey, J.P.; Villegas, E.N. The Development and Implementation of a Method Using Blue Mussels (Mytilus spp.) as Biosentinels of Cryptosporidium spp. and Toxoplasma gondii Contamination in Marine Aquatic Environments. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 4655–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.M.; Silva, A.L.P.; Watanabe, K.F.C.; Bezerra, N.P.C.; Bezerra, D.C.; Gomes, H.M.; Freire, T.B.; Dos Santos, L.S.; de C. Neta, A.V.; Silva, E.M.C.; et al. First Report of Detection of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in Oysters (Crassostrea sp.) in the State of Maranhão. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2020, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquis, N.D.; Bishop, T.J.; Record, N.R.; Countway, P.D.; Fernández Robledo, J.A. Molecular Epizootiology of Toxoplasma gondii and Cryptosporidium parvum in the Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) from Maine (USA). Pathogens 2019, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coutinho, S.G.; Lobo, R.; Dutra, G. Isolation of Toxoplasma from the Soil during an Outbreak of Toxoplasmosis in a Rural Area in Brazil. J. Parasitol. 1982, 68, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.C.; Langoni, H. Risk Factors and Molecular Typing of Toxoplasma gondii Isolated from Ostriches (Struthio camelus) from a Brazilian Slaughterhouse. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 225, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dos Santos, T.R.; Nunes, C.M.; Luvizotto, M.C.R.; de Moura, A.B.; Lopes, W.D.Z.; da Costa, A.J.; Bresciani, K.D.S. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Environmental Samples from Public Schools. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 171, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felicio, P.; Villalobos, E.; Lara, M.; Cunha, E.; Carvalho, P.; Chiebao, D.; Gabriel, F.; Nassar, A.; Nogueira, A.; Okuda, L.; et al. Eco-Epidemiology of Toxoplasmosis in Ruminant and the Experimental Model of Evidence from Mice Bioassay for Transmission of Infection Starting of Contaminated Soil Samples Confirmed by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Indirect Immunofluorescence Reacti. Glob. Vet. 2011, 6, 78–90. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto-Ferreira, F.; Mitsuka-Breganó, R.; Monica, T.C.; Martins, F.D.C.; De Matos, L.R.N.; Mareze, M.; Nino, B.D.S.L.; Narciso, S.G.; Freire, R.L.; Navarro, I.T. Investigation and Environmental Analysis of Samples from Outbreak of Toxoplasmosis at Research Institution in Londrina. Electron. Braz. J. Vet. Parasitol 2019, 28, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinto-Ferreira, F.; Caldart, E.T.; Freire, R.L.; Mitsuka-Breganó, R.; de Freitas, F.M.; Miura, A.C.; Mareze, M.; Martins, F.D.C.; Urbano, M.R.; Seifert, A.L.; et al. The Effect of Water Source and Soil Supplementation on Parasite Contamination in Organic Vegetable Gardens. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2018, 27, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cong, W.; Zhang, N.Z.; Hu, R.S.; Zou, F.C.; Zou, Y.; Zhong, W.Y.; Wu, J.J.; Fallaize, C.J.; Zhu, X.Q.; Elsheikha, H.M. Prevalence, Risk Factors and Genotype Distribution of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in Soil in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.; Feng, H.L.; Nie, H.; Tu, P.; Zhang, Q.L.; Hu, M.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhao, J.L. Survey on the Contamination of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in the Soil of Public Parks of Wuhan, China. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 184, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Hu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J. Soil Contamination of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Pig Farms in Central China. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 187, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Qin, H.; Xiao, J. Land Use and Soil Contamination with Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Urban Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Meng, P.; Ye, Q.; Pu, Y.-H.; Yang, X.-Y.; Luo, J.-X.; Zhang, N.-Z.; Zhang, D.-L. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Soils in Northwestern China Using a New Semi-Nested PCR Assay. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, A.; Frenkel, J.K.; Cerdas, L. Isolation of Toxoplasma from Soil. J. Parasitol. 1973, 59, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, E.; Lemoine, M.; Poulle, M.L.; Ravat, M.C.; Romand, S.; Thulliez, P.; Villena, I.; Aubert, D.; Rabilloud, M.; Riche, B.; et al. Spatial Distribution of Soil Contamination by Toxoplasma gondii in Relation to Cat Defecation Behaviour in an Urban Area. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotteland, C.; Gilot-Fromont, E.; Aubert, D.; Poulle, M.L.; Dupuis, E.; Dardé, M.L.; Forin-Wiart, M.A.; Rabilloud, M.; Riche, B.; Villena, I. Spatial Distribution of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Soil in a Rural Area: Influence of Cats and Land Use. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaizot, R.; Nabet, C.; Laghoe, L.; Faivre, B.; Escotte-Binet, S.; Djossou, F.; Mosnier, E.; Henaff, F.; Blanchet, D.; Mercier, A.; et al. Outbreak of Amazonian Toxoplasmosis: A One Health Investigation in a Remote Amerindian Community. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.A.; Lepczyk, C.A.; Haman, K.H.; Morden, C.W.; Crow, S.E.; Jensen, N.; Lohr, M.T. Toxoplasma gondii Detection in Fecal Samples from Domestic Cats (Felis catus) in Hawaii. Pac. Sci. 2018, 72, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghparast-Kenari, B.; Sarvi, S.; Sharif, M.; Ahmadpour, E.; Hosseini, S.A.; Daryani, A. Isolation and Genotypic Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii Based on GRA6 Gene from Environmental Soil Samples in Mazandaran Province, North of Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2020, 15, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saki, J.; Khademvatan, S.; Yousefi, E.; Tavalla, M.; Abdizadeh, R. Detection and Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii Isolated from Soil in Ahvaz, Southwest of Iran. J. Parasit. Dis. 2017, 41, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tavalla, M.; Oormazdi, H.; Akhlaghi, L.; Shojaee, S.; Razmjou, E.; Hadighi, R.; Meamar, A. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii Isolates from Soil Samples in Tehran, Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2013, 8, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, D.N.; Muhsin, S.S.; Chyiad, A.L. Comparative Study in Detection of Toxoplasma gondii on Soil Sample from Baghdad and Kut Cities by Using PCR. Indian J. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2019, 13, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Ortega, G.A.; Chan-Pérez, J.I.; Ortega-Pacheco, A.; Guzmán-Marín, E.; Edwards, M.; Brown, M.A.; Jiménez-Coello, M.; Hernández-Cortazar, I.B. Screening of Zoonotic Parasites in Playground Sandboxes of Public Parks from Subtropical Mexico. J. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7409076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, J.K.; Hassanein, K.M.; Hassanein, R.S.; Brown, E.; Thulliez, P.; Quintero- Nunez, R. Transmission of Toxoplasma gondii in Panama City, Panama: A Five-Year Prospective Cohort Study of Children, Cats, Rodents, Birds, and Soil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 53, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, A.; Maqbool, A.; Qamar, F.; Ashraf, K.; Anjum, A. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Environmental Matrices (Water, Soil, Fruits and Vegetables). Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lass, A.; Pietkiewicz, H.; Modzelewska, E.; Dumètre, A.; Szostakowska, B.; Myjak, P. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Environmental Soil Samples Using Molecular Methods. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demar, M.; Ajzenberg, D.; Maubon, D.; Djossou, F.; Panchoe, D.; Punwasi, W.; Valery, N.; Peneau, C.; Daigre, J.-L.; Aznar, C.; et al. Fatal Outbreak of Human Toxoplasmosis along the Maroni River: Epidemiological, Clinical, and Parasitological Aspects. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, e88–e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, H.; Exel, K.E.; Swart, A.; Bonačić Marinović, A.A.; Dam-Deisz, C.; van der Giessen, J.W.B.; Opsteegh, M. Digging into Toxoplasma gondii Infections via Soil: A Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, L.A.; Kilpatrick, A.M.; VanWormer, E.; Croll, D.A.; Tershy, B.R.; Kim, M.; Shapiro, K. Seasonal and Spatial Variation in Toxoplasma gondii Contamination in Soil in Urban Public Spaces in California, United States. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Weigel, R.M.; Siegel, A.M.; Thulliez, P.; Kitron, U.D.; Mitchell, M.A.; Mannelli, A.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.E.; Shen, S.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; et al. Sources and Reservoirs of Toxoplasma gondii Infection on 47 Swine Farms in Illinois. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awobode, H.O.; Ohiolei, J.A.; Adekeye, T.A.; Adeyi, A.O.; Anumudu, C.I. Shedding Proportion of Toxoplasma gondii-like Oocysts in Feral Cats and Soil Contamination in Oyo State, Nigeria. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2020, 11, e00181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrouch, S.; Ajgoune, H.; Hoummadi, L.; Amraouza, Y.; Maarouf, A.; Boularbah, A.; Admou, B.; Hafid, J. First Investigation of The Occurrence of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Urban Soil in Marrakesh, Morocco. Comp. Parasitol. 2020, 87, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Rego E Silva, G.N.; dos Remédios Freitas Carvalho Branco, M.; Rodrigues, Z.M.R.; dos Santos, A.M.; Pereira, P.R.M.; do Socorro da Silva, M.; de Sousa Nunes, A.T.; Júnior, A.R.J.; Medeiros, M.N.L.; Pedrozo E Silva de Azevedo, C.; et al. Toxoplasmosis Outbreak in Brazil, 2006—Revisited. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2019, 7, e00117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, F.P.; Alves, M.d.G.; Martins, L.M.; Rangel, A.L.P.; Dubey, J.P.; Hill, D.; Bahia-Oliveira, L.M.G. Waterborne Toxoplasmosis Investigated and Analysed under Hydrogeological Assessment: New Data and Perspectives for Further Research. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, M.A.; Pinto-Ferreira, F.; de Almeida, R.P.A.; Martins, F.D.C.; Pires, A.L.; Mareze, M.; Mitsuka-Breganó, R.; Freire, R.L.; da Rocha Moreira, R.V.; Borges, J.M.; et al. Artisan Fresh Cheese from Raw Cow’s Milk as a Possible Route of Transmission in a Toxoplasmosis Outbreak, in Brazil. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, L.; Garcia Bahia-Oliveira, L.M.; Wada, M.Y.; Jones, J.L.; Tuboi, S.H.; Carmo, E.H.; Ramalho, W.M.; Camargo, N.J.; Trevisan, R.; Graça, R.M.T.; et al. Waterborne Toxoplasmosis, Brazil, from Field to Gene. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvani, A.T.; Christ, A.P.G.; Padula, J.A.; Barbosa, M.R.F.; de Araújo, R.S.; Sato, M.I.Z.; Razzolini, M.T.P. Real-Time PCR Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Surface Water Samples in São Paulo, Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac-Renton, J.; Bowie, W.R.; King, A.; Irwin, G.S.; Ong, C.S.; Fung, C.P.; Shokeir, M.O.; Dubey, J.P. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Drinking Water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2278–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luna, J.C.; Zamora, A.; Hernández-Arango, N.; Muñoz-Sánchez, D.; Pinzón, M.I.; Cortés-Vecino, J.A.; Lora-Suarez, F.; Gómez-Marín, J.E. Food Safety Assessment and Risk for Toxoplasmosis in School Restaurants in Armenia, Colombia. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 3449–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triviño-Valencia, J.; Lora, F.; Zuluaga, J.D.; Gomez-Marin, J.E. Detection by PCR of Pathogenic Protozoa in Raw and Drinkable Water Samples in Colombia. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slany, M.; Dziedzinska, R.; Babak, V.; Kralik, P.; Moravkova, M.; Slana, I. Toxoplasma gondii in Vegetables from Fields and Farm Storage Facilities in the Czech Republic. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Tras, W.F.; Tayel, A.A.; El-Kady, N.N. Source Diversity of Toxoplasma gondii Infection during Meal Preparation. J. Food Saf. 2012, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, L.; Richard, F.; Stefania, S.; Goulet, M.; Gosselin, S.; Gonçalves, A.; Rocher, V.; Paffoni, C.; Dumètre, A. Contribution of Treated Wastewater to the Microbiological Quality of Seine River in Paris. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5222–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villena, I.; Aubert, D.; Gomis, P.; Ferté, H.; Inglard, J.C.; Denis-Bisiaux, H.; Dondon, J.M.; Pisano, E.; Ortis, N.; Pinon, J.M. Evaluation of a Strategy for Toxoplasma gondii Oocyst Detection in Water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4035–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aubert, D.; Villena, I. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Water: Proposition of a Strategy and Evaluation in Champagne-Ardenne Region, France. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2009, 104, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajonina, C.; Buzie, C.; Möller, J.; Otterpohl, R. The Detection of Entamoeba histolytica and Toxoplasma gondii in Wastewater. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2018, 81, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallas-Lindemann, C.; Sotiriadou, I.; Mahmoodi, M.R.; Karanis, P. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Different Water Resources by Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP). Acta Trop. 2013, 125, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.R.; Kazemi, B.; Haghighi, A.; Karanis, P. Detection of Acanthamoeba and Toxoplasma in River Water Samples by Molecular Methods in Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2015, 10, 250–257. [Google Scholar]
- Marangi, M.; Giangaspero, A.; Lacasella, V.; Lonigro, A.; Gasser, R.B. Multiplex PCR for the Detection and Quantification of Zoonotic Taxa of Giardia, Cryptosporidium and Toxoplasma in Wastewater and Mussels. Mol. Cell. Probes 2015, 29, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Cortazar, I.B.; Acosta-Viana, K.Y.; Guzman-Marin, E.; Ortega-Pacheco, A.; Segura-Correa, J.C.; Jimenez-Coello, M. Presence of Toxoplasma gondii in Drinking Water from an Endemic Region in Southern Mexico. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka, J.; Wójcik-Fatla, A.; Dutkiewicz, J. Occurrence of Toxoplasma gondii in Water from Wells Located on Farms. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2006, 13, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sroka, J.; Wojcik-Fatla, A.; Szymanska, J.; Dutkiewicz, J.; Zajac, V.; Zwolinski, J. The Occurrence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in People and Animals from Rural Environment of Lublin Region—Estimate of Potential Role of Water as a Source of Infection. Ann. Agric. Env. Med. 2010, 17, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Adamska, M. Molecular Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Natural Surface Water Bodies in Poland. J. Water Health 2018, 16, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriadou, I.; Karanis, P. Evaluation of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Water Samples and Comparative Findings by Polymerase Chain Reaction and Immunofluorescence Test (IFT). Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 62, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ssemanda, J.N.; Reij, M.W.; van Middendorp, G.; Bouw, E.; van der Plaats, R.; Franz, E.; Muvunyi, C.M.; Bagabe, M.C.; Zwietering, M.H.; Joosten, H. Foodborne Pathogens and Their Risk Exposure Factors Associated with Farm Vegetables in Rwanda. Food Control 2018, 89, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, B.; Shaw, H.; Innocent, G.; Guido, S.; Hotchkiss, E.; Parigi, M.; Opsteegh, M.; Green, J.; Gillespie, S.; Innes, E.A.; et al. Molecular Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Water Samples from Scotland and a Comparison between the 529bp Real-Time PCR and ITS1 Nested PCR. Water Res. 2015, 87, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ćirković, V.; Uzelac, A.; Milicić, D.; Klun, I.; Đurković-Đaković, O. First Detection of Toxoplasma gondii (Nicolle & Manceaux, 1908) (Eucoccidiorida: Sarcocystidae) in River Waters in Serbia. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2020, 7, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, Y.; Moreno-Mesonero, L.; Amorós, I.; Pérez, R.; Morillo, J.A.; Alonso, J.L. Multiple Identification of Most Important Waterborne Protozoa in Surface Water Used for Irrigation Purposes by 18S RRNA Amplicon-Based Metagenomics. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koloren, Z. Sensitive and Cost-Effective Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Water Supplies of the Black Sea in Turkey by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP). Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2013, 27, 3543–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verant, M.L.; D’Ozouville, N.; Parker, P.G.; Shapiro, K.; Vanwormer, E.; Deem, S.L. Attempted Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Environmental Waters Using a Simple Approach to Evaluate the Potential for Waterborne Transmission in the Galápagos Islands, Ecuador. Ecohealth 2014, 11, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimir, A.R.; Linn, T.C. Detection of Toxoplasmosis in Environmental Samples at a Wet Market of a Capital City Centre. Acta Med. 2011, 54, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortiz-Pineda, C.; Guiguet-Leal, D.A.; da Silva-Fiuza, V.R.; Jose, J.; Borelli, G.; Durigan, M.; Pena, H.F.J.; Bueno Franco, R.M. Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts, Giardia Cysts and Cryptosporidium Oocysts in Outdoor Swimming Pools in Brazil. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfadaly, H.A.; Hassanain, N.A.; Hassanain, M.A.; Barakat, A.M.; Shaapan, R.M. Evaluation of Primitive Ground Water Supplies as a Risk Factor for the Development of Major Waterborne Zoonosis in Egyptian Children Living in Rural Areas. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, K.; Silver, M.; Byrne, B.A.; Berardi, T.; Aguilar, B.; Melli, A.; Smith, W.A. Fecal Indicator Bacteria and Zoonotic Pathogens in Marine Snow and California Mussels (Mytilus californianus). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioro, A.A.; Tiyo, B.T.; Colli, C.M.; De Souza, C.Z.; Garcia, J.L.; Gomes, M.L.; Falavigna-Guilherme, A.L. First Detection of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in the Fresh Leafs of Vegetables in South America. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Pineda, C.; Temesgen, T.T.; Robertson, L.J. Multiplex Quantitative PCR Analysis of Strawberries from Bogotá, Colombia, for Contamination with Three Parasites. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradonna, T.; Marangi, M.; Del Chierico, F.; Ferrari, N.; Reddel, S.; Bracaglia, G.; Normanno, G.; Putignani, L.; Giangaspero, A. Detection and Prevalence of Protozoan Parasites in Ready-to-Eat Packaged Salads on Sale in Italy. Food Microbiol. 2017, 67, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggisberg, A.R.; Alvarez Rojas, C.A.; Kronenberg, P.A.; Miranda, N.; Deplazes, P. A Sensitive, One-Way Sequential Sieving Method to Isolate Helminths’ Eggs and Protozoal Oocysts from Lettuce for Genetic Identification. Pathogens 2020, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Megrin, W.A.I. Prevalence Intestinal Parasites in Leafy Vegetables in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Trop. Med. 2010, 5, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haq, S.; Maqbool, A.; Javed Khan, U.; Yasmin, G.; Sultana, R. Parasitic Contamination of Vegetables Eaten Raw in Lahore. Pak. J. Zool. 2014, 46, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros, F.A.; de Oliveira, T.R.; Málaga, S.M.R. Segurança Dos Alimentos: Influência Sazonal Na Contaminação Parasitária Em Alface (Lactuca sativa L.) Comercializada Em Feiras Livres de Belém, Pará. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2019, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, R.G.; Kadhim, H.A.H.; Ali, J.F. Diagnostic Study on Intestinal Parasites Isolated from Raw Consumed Vegetables in Misan City/Iraq. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Rad, S.; Chaabane-Banaoues, R.; Lahmar, I.; Oumaima, H.; Mezhoud, H.; Babba, H.; Oudni-M’Rad, M. Parasitological Contamination of Vegetables Sold in Tunisian Retail Markets with Helminth Eggs and Protozoan Cysts. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardona, Z.; Al Hindi, A.; Hafidi, M.; Boumezzough, A.; Boussaa, S. Occurrence of Toxoplasma gondii on Raw Leafy Vegetables in Gaza, Palestine. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.I. Prevalence of Enteric Parasites in Raw Leafy Vegetables in Baghdad City, Iraq. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.O.; El Fadaly, A.H.; Zaki, M.S.; Barakat, A.M. Incidence of Zoonotic Parasites In Egyptian Raw Vegetable Salads. Life Sci. J. 2016, 13, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmerini, P.O.; Gennari, S.M.; Pena, H.F.J. Analysis of Marine Bivalve Shellfish from the Fish Market in Santos City, São Paulo State, Brazil, for Toxoplasma gondii. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 170, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, L.A.; Santos, L.K.N.S.S.; Brito, P.A.; Maciel, B.M.; Da Silva, A.V.; Albuquerque, G.R. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in Brazilian Oysters (Crassostrea rhizophorae). Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 4658–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, T.R.M.; Rocha, K.S.; Silva, J.; Mesquita, G.S.S.; Rosário, M.K.S.; Ferreira, M.F.S.; Honorio, B.E.T.; Melo, H.F.R.; Barros, F.N.L.; Scofield, A.; et al. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Crassostrea spp. Oysters Cultured in an Estuarine Region in Eastern Amazon. Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.; Zhang, N.Z.; Hou, J.L.; Wang, X.C.; Ma, J.G.; Zhu, X.Q.; Chen, G.J. First Detection and Genetic Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in Market-Sold Oysters in China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 54, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.; Zhang, N.Z.; Yuan, D.Q.; Zou, Y.; Li, S.; Liang, Z.L. Detection and Genetic Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in Market-Sold Mussels (Mytilus edulis) in Certain Provinces of China. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 136, 103687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Tao, L.F.; Xu, L.X.; Yan, R.F.; Song, X.K.; Li, X.R. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Shellfish and Fish in Parts of China. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 200, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerambrun, E.; Palos Ladeiro, M.; Bigot-Clivot, A.; Dedourge-Geffard, O.; Dupuis, E.; Villena, I.; Aubert, D.; Geffard, A. Zebra Mussel as a New Tool to Show Evidence of Freshwater Contamination by Waterborne Toxoplasma gondii. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santoro, M.; Viscardi, M.; Boccia, F.; Borriello, G.; Lucibelli, M.G.; Auriemma, C.; Anastasio, A.; Veneziano, V.; Galiero, G.; Baldi, L.; et al. Parasite Load and STRs Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii Isolates From Mediterranean Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) in Southern Italy. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedde, T.; Marangi, M.; Papini, R.; Salza, S.; Normanno, G.; Virgilio, S.; Giangaspero, A. Toxoplasma gondii and Other Zoonotic Protozoans in Mediterranean Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) and Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis): A Food Safety Concern? J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putignani, L.; Mancinelli, L.; Del Chierico, F.; Menichella, D.; Adlerstein, D.; Angelici, M.C.; Marangi, M.; Berrilli, F.; Caffara, M.; di Regalbono, D.A.F.; et al. Investigation of Toxoplasma gondii Presence in Farmed Shellfish by Nested-PCR and Real-Time PCR Fluorescent Amplicon Generation Assay (FLAG). Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghozzi, K.; Marangi, M.; Papini, R.; Lahmar, I.; Challouf, R.; Houas, N.; Ben Dhiab, R.; Normanno, G.; Babba, H.; Giangaspero, A. First Report of Tunisian Coastal Water Contamination by Protozoan Parasites Using Mollusk Bivalves as Biological Indicators. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, U.; Marangi, M.; Papini, R.; Ozkoc, S.; Bayram Delibas, S.; Giangaspero, A. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii and Cyclospora cayetanensis in Mytilus galloprovincialis from Izmir Province Coast (Turkey) by Real Time PCR/High-Resolution Melting Analysis (HRM). Food Microbiol. 2014, 44, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tei, F.; Kowalyk, S.; Reid, J.; Presta, M.; Yesudas, R.; Mayer, D.C. Assessment and Molecular Characterization of Human Intestinal Parasites in Bivalves from Orchard Beach, NY, USA. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubey, J.P. Outbreaks of Clinical Toxoplasmosis in Humans: Five Decades of Personal Experience, Perspectives and Lessons Learned. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstratiou, A.; Ongerth, J.; Karanis, P. Evolution of Monitoring for Giardia and Cryptosporidium in Water. Water Res. 2017, 123, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javanmard, E.; Mirsamadi, E.S.; Olfatifar, M.; Ghasemi, E.; Saki, F.; Mirjalali, H.; Zali, M.R.; Karanis, P. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Vegetables in Iran: A Nineteen-Years Meta-Analysis Review. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1629–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lélu, M.; Villena, I.; Dardé, M.L.; Aubert, D.; Geers, R.; Dupuis, E.; Marnef, F.; Poulle, M.L.; Gotteland, C.; Dumètre, A.; et al. Quantitative Estimation of the Viability of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5127–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lélu, M.; Gilot-Fromont, E.; Aubert, D.; Richaume, A.; Afonso, E.; Dupuis, E.; Gotteland, C.; Marnef, F.; Poulle, M.L.; Dumètre, A.; et al. Development of a Sensitive Method for Toxoplasma gondii Oocyst Extraction in Soil. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 183, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilberman, A.; Zimmels, Y.; Starosvetsky, J.; Zuckerman, U.; Armon, R. A Two-Phase Separation Method for Recovery of Cryptosporidium Oocysts from Soil Samples. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 203, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, S.A.; Bettahar, M. Straining, Attachment, and Detachment of Cryptosporidium Oocysts in Saturated Porous Media. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii Oocyst Survival under Defined Temperatures. J. Parasitol. 1998, 84, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.L.; Dubey, J.P. Waterborne Toxoplasmosis—Recent Developments. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 124, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.; Smith, B.A.; Fazil, A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Extreme Weather Events and Other Weather-Related Variables on Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Fresh Surface Waters. J. Water Health 2015, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barlaam, A.; Temesgen, T.T.; Tysnes, K.R.; Rinaldi, L.; Ferrari, N.; Sannella, A.R.; Normanno, G.; Cacciò, S.M.; Robertson, L.J.; Giangaspero, A. Contamination of Fresh Produce Sold on the Italian Market with Cyclospora cayetanensis and Echinococcus multilocularis. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, E.L.; Webster, N.J. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts on Organic and Conventionally Grown Produce. Food Microbiol. 2021, 99, 103798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on the Risk Posed by Pathogens in Food of Non-animal Origin. Part 2 (Salmonella and Norovirus in Leafy Greens Eaten Raw as Salads). EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaidez, C.; Soto, M.; Gortares, P.; Mena, K. Occurrence of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Irrigation Water and Its Impact on the Fresh Produce Industry. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2005, 15, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkush, K.D.; Miller, M.A.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Gardner, I.A.; Packham, A.E.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Tenter, A.M.; Barr, B.C.; Conrad, P.A. Molecular and Bioassay-Based Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Oocyst Uptake by Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palos-Ladeiro, M.; Bigot-Clivot, A.; Aubert, D.; Villena, I.; Geffard, A. Assessment of Toxoplasma gondii Levels in Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) by Real-Time PCR: An Organotropism Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 13693–13701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.L.; Dargelas, V.; Roberts, J.; Press, C.; Remington, J.S.; Montoya, J.G. Risk Factors for Toxoplasma gondii Infection in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fritz, H.; Conrad, P. Antibodies to the Surface of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts and Methods of Use Thereof. U.S. Patent 10429386B2, 18 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, S.; Almeida, A.; Delgado, L.; Conceição, A.; Marques, C.; da Costa, J.M.C.; Castro, A. RTgOWP1-f, a Specific Biomarker for Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumètre, A.; Dardé, M.L. Immunomagnetic Separation of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts Using a Monoclonal Antibody Directed against the Oocyst Wall. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 61, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumètre, A.; Dardé, M.-L. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Water by an Immunomagnetic Separation Method Targeting the Sporocysts. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harito, J.B.; Campbell, A.T.; Tysnes, K.R.; Robertson, L.J. Use of Lectin-Magnetic Separation (LMS) for Detecting Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Environmental Water Samples. Water Res. 2017, 127, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chalmers, R.M.; Katzer, F.; La Carbona, S.; Lalle, M.; Razakandrainibe, R.; Robertson, L.J.; Robinson, G.; Šoba, B.; Temesgen, T.; Mayer-Scholl, A. A Guide to Standardise Artificial Contamination Procedures with Protozoan Parasite Oocysts or Cysts during Method Evaluation, Using Cryptosporidium and Leafy Greens as Models. Food Control 2022, 134, 108678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schares, G.; Globokar Vrhovec, M.; Tuschy, M.; Joeres, M.; Bärwald, A.; Koudela, B.; Dubey, J.P.; Maksimov, P.; Conraths, F.J. A Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction for the Specific Detection of Hammondia hammondi and Its Differentiation from Toxoplasma gondii. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupe, A.; Howe, L.; Shapiro, K.; Roe, W.D. Comparison of PCR Assays to Detect Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Green-Lipped Mussels (Perna canaliculus). Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, M.E.; Boothroyd, J.C. Rapid Identification of Virulent Type I Strains of the Protozoan Pathogen Toxoplasma gondii by PCR-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Analysis at the B1 Gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, C.; Shwab, E.K.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Dubey, J.P. Moving towards an Integrated Approach to Molecular Detection and Identification of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 2010, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajzenberg, D.; Collinet, F.; Mercier, A.; Vignoles, P.; Dardé, M.-L. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii Isolates with 15 Microsatellite Markers in a Single Multiplex PCR Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4641–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jokelainen, P.; Murat, J.-B.; Nielsen, H.V. Direct Genetic Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from Clinical Samples from Denmark: Not Only Genotypes II and III. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Escobar, M.; Maksimov, P.; Joeres, M.; Álvarez-García, G.; Jokelainen, P.; Schares, G.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Calero-Bernal, R. Lights and Shades in Genotyping: European Toxoplasma gondii Needs a Closer Look Using Harmonised Approaches. In Proceedings of the Annual Scientific 2021, Copenhagen, Denmark, 9–11 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ware, M.W.; Augustine, S.A.J.; Erisman, D.O.; See, M.J.; Wymer, L.; Hayes, S.L.; Dubey, J.P.; Villegas, E.N. Determining UV Inactivation of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts by Using Cell Culture and a Mouse Bioassay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5140–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rousseau, A.; La Carbona, S.; Dumètre, A.; Robertson, L.J.; Gargala, G.; Escotte-Binet, S.; Favennec, L.; Villena, I.; Gérard, C.; Aubert, D. Assessing Viability and Infectivity of Foodborne and Waterborne Stages (Cysts/Oocysts) of Giardia Duodenalis, Cryptosporidium spp., and Toxoplasma gondii: A Review of Methods. Parasite 2018, 25, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis in Pigs-The Last 20 Years. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 164, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Su, R.; Lu, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Jian, F.; Yang, Y. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii in Food Animals and Humans (2000–2017) from China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.; Berg, R.; Tagel, M.; Must, K.; Deksne, G.; Enemark, H.L.; Alban, L.; Johansen, M.V.; Nielsen, H.V.; Sandberg, M.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Domestic Pigs, Sheep, Cattle, Wild Boars, and Moose in the Nordic-Baltic Region: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2019, 5, e00100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonade, I.R.; Ginani, V.C.; Riquette, R.F.R.; Gurgel-Gonçalves, R.; Mendes, V.S.; Machado, E.R. Good Manufacturing Practices of Minimally Processed Vegetables Reduce Contamination with Pathogenic Microorganisms. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. 2019, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meireles, L.R.; Ekman, C.C.J.; de Andrade, H.F.; Luna, E.J.d.A. Human toxoplasmosis outbreaks and the agent infecting form. Findings from a systematic review. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. 2015, 57, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thebault, A.; Kooh, P.; Cadavez, V.; Gonzales-Barron, U.; Villena, I. Risk Factors for Sporadic Toxoplasmosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microb. Risk Anal. 2021, 17, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Riahi, S.M.; Esfandyari, S.; Habibpour, H.; Mollalo, A.; Mirzapour, A.; Behniafar, H.; Mohammadi Moghadam, S.; Azizi Kyvanani, N.; Aghaei, S.; et al. Geo-Climatic Factors and Prevalence of Chronic Toxoplasmosis in Pregnant Women: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Matrix | No. of Studies Included | Pooled Detection Rates (95% CI) | Heterogeneity Test | Egger’s Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2 (%) | Q (X2) | Q/df | Q-p (P) | t | p | |||
| Soil | 25 | 17.3 (11.0–23.7) | 99.3 | 3388.03 | 24 | <0.001 | 1.08 | 0.292 |
| Water | 28 a | 9.2 (6.3–12.0) | 85.4 | 205.09 | 23 | <0.001 | 2.33 | 0.030 |
| Fresh produce | 8 b | 5.2 (1.7–8.8) | 78.2 | 36.76 | 8 | <0.001 | 9.09 | <0.001 |
| Bivalve mollusks | 10 c | 6.8 (4.4–9.2) | 98.8 | 757.99 | 9 | <0.001 | 2.82 | 0.030 |
| Total | 71 * | 12.0 (10.0–14.0) | 98.9 | 6679.21 | 74 | <0.001 | 4.41 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López Ureña, N.M.; Chaudhry, U.; Calero Bernal, R.; Cano Alsua, S.; Messina, D.; Evangelista, F.; Betson, M.; Lalle, M.; Jokelainen, P.; Ortega Mora, L.M.; et al. Contamination of Soil, Water, Fresh Produce, and Bivalve Mollusks with Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030517
López Ureña NM, Chaudhry U, Calero Bernal R, Cano Alsua S, Messina D, Evangelista F, Betson M, Lalle M, Jokelainen P, Ortega Mora LM, et al. Contamination of Soil, Water, Fresh Produce, and Bivalve Mollusks with Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(3):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030517
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez Ureña, Nadia María, Umer Chaudhry, Rafael Calero Bernal, Santiago Cano Alsua, Davide Messina, Francisco Evangelista, Martha Betson, Marco Lalle, Pikka Jokelainen, Luis Miguel Ortega Mora, and et al. 2022. "Contamination of Soil, Water, Fresh Produce, and Bivalve Mollusks with Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts: A Systematic Review" Microorganisms 10, no. 3: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030517
APA StyleLópez Ureña, N. M., Chaudhry, U., Calero Bernal, R., Cano Alsua, S., Messina, D., Evangelista, F., Betson, M., Lalle, M., Jokelainen, P., Ortega Mora, L. M., & Álvarez García, G. (2022). Contamination of Soil, Water, Fresh Produce, and Bivalve Mollusks with Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms, 10(3), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030517








