Screening for Virulence-Related Genes via a Transposon Mutant Library of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Using a Galleria mellonella Larvae Infection Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Plasmids
2.2. Construction of Tn Library
2.3. Identification of Insertion Sites in Tn Library
2.4. Screening the Virulence Attenuated S. suis Mutants Using G. mellonella Larvae
2.5. Construction of hxtR Deletion Mutant and Complemented Strain
2.6. Mouse Infection Experiment
2.7. Whole Blood Bactericidal Assay
2.8. Phagocytosis Assay
2.9. Morphology Observation
2.10. Growth Measurements
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
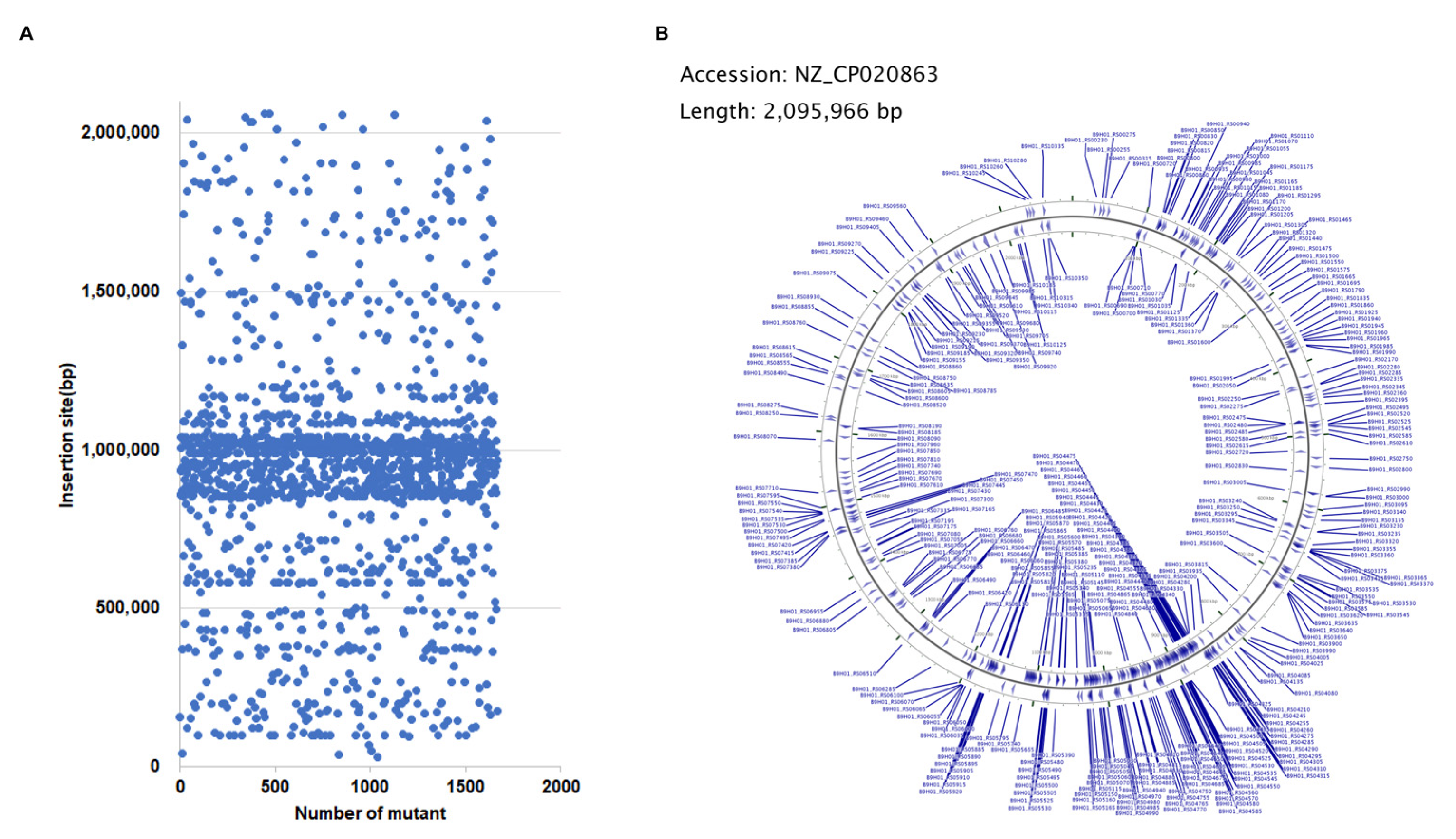
3.1. Mutants Construction and Insertion Sites Mapping
3.2. Virulence Assessment in G. mellonella Larvae
3.3. Decreased Virulence of ΔhxtR in Larvae and Mice
3.4. Reduced Resistant Abilities of ΔhxtR to Whole Blood Killing and Phagocytosis
3.5. hxtR Is Involved in Cell Morphology and Growth of S. suis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lun, Z.-R.; Wang, Q.-P.; Chen, X.-G.; Li, A.-X.; Zhu, X.-Q. Streptococcus suis: An emerging zoonotic pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J.P.; Zanen, H.C. Meningitis Caused by Streptococcus suis in Humans. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangkaew, S.; Chaiwarith, R.; Tharavichitkul, P.; Supparatpinyo, K. Streptococcus suis infection: A series of 41 cases from Chiang Mai University Hospital. J. Infect. 2006, 52, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent-an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Cao, M.; Hu, D.; Wang, C. Streptococcus suis infection: An emerging/reemerging challenge of bacterial infectious diseases? Virulence 2014, 5, 477–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, A.G.; Bolitho, S.; Lindsay, H.; Khan, S.; Bryant, C.; Norton, P.; Ward, P.; Leigh, J.; Morgan, J.; Riches, H.; et al. Generation and Characterization of a Defined Mutant of Streptococcus suis Lacking Suilysin. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 2732–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lun, S.; Perez-Casal, J.; Connor, W.; Willson, P. Role of suilysin in pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis capsular serotype 2. Microb. Pathog. 2003, 34, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.E.; Damman, M.; van der Velde, J.; Wagenaar, F.; Wisselink, H.J.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Smits, M.A. Identification and characterization of the cps locus of Streptococcus suis serotype 2: The capsule protects against phagocytosis and is an important virulence factor. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruening, P.; Fulde, M.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Goethe, R. Structure, Regulation, and Putative Function of the Arginine Deiminase System of Streptococcus suis. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, X.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; Fan, H. Screening for phagocytosis resistance-related genes via a transposon mutant library of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Virulence 2020, 11, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josi, C.; Burki, S.; Vidal, S.; Dordet-Frisoni, E.; Citti, C.; Falquet, L.; Pilo, P. Large-Scale Analysis of the Mycoplasma bovis Genome Identified Non-essential, Adhesion- and Virulence-Related Genes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinbaum, R.L.; Urbach, J.M.; Liberati, N.T.; Djonovic, S.; Adonizio, A.; Carvunis, A.-R.; Ausubel, F.M. Genome-Wide Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence-Related Genes Using a Caenorhabditis elegans Infection Model. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geng, S.; Jiao, X.; Barrow, P.; Pan, Z.; Chen, X. Virulence determinants of Salmonella Gallinarum biovar Pullorum identified by PCR signature-tagged mutagenesis and the spiC mutant as a candidate live attenuated vaccine. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, M.; Xie, X.; Dong, Y.; Du, H.; Wang, N.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Identification of novel virulence-related genes in Aeromonas hydrophila by screening transposon mutants in a Tetrahymena infection model. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, F.; Dong, Y.; Pan, X.; Cheng, G.; Dong, R.; Hu, D.; Feng, X.; et al. The involvement of sortase A in high virulence of STSS-causing Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Arch. Microbiol. 2009, 191, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Punaro, M.C.; Segura, M.; Plante, M.-M.; Lacouture, S.; Rivest, S.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suisSerotype 2, an Important Swine and Human Pathogen, Induces Strong Systemic and Cerebral Inflammatory Responses in a Mouse Model of Infection. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1842–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Lu, C. Transcriptome profiling of zebrafish infected with Streptococcus suis. Microb. Pathog. 2010, 48, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccaria, E.; Cao, R.; Wells, J.M.; Van Baarlen, P. A Zebrafish Larval Model to Assess Virulence of Porcine Streptococcus suis Strains. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, B.A.; Rozen, D. A Streptococcus pneumoniae infection model in larvae of the wax moth Galleria mellonella. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 31, 2653–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.M.; Adenwalla, N.; Wiles, S.; Proft, T. Galleria mellonella larvae as an infection model for group A streptococcus. Virulence 2013, 4, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velikova, N.; Kavanagh, K.; Wells, J.M. Evaluation of Galleria mellonella larvae for studying the virulence of Streptococcus suis. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, R. Identification of Streptococcus suis genes preferentially expressed under iron starvation by selective capture of transcribed sequences. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 292, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takamatsu, D.; Osaki, M.; Sekizaki, T. Thermosensitive Suicide Vectors for Gene Replacement in Streptococcus suis. Plasmid 2001, 46, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamatsu, D.; Osaki, M.; Sekizaki, T. Construction and Characterization of Streptococcus suis–Escherichia coli Shuttle Cloning Vectors. Plasmid 2001, 45, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ding, Y.; Li, T.; Wan, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Zhou, R. A Fur-like protein PerR regulates two oxidative stress response related operons dpr and metQIN in Streptococcus suis. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slater, J.; Allen, A.; May, J.; Bolitho, S.; Lindsay, H.; Maskell, D. Mutagenesis of Streptococcus equi and Streptococcus suis by transposon Tn917. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 93, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P.; Wishart, D.S. Circular genome visualization and exploration using CGView. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y. KEGG Mapper for inferring cellular functions from protein sequences. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monk, I.R.; Shah, I.M.; Xu, M.; Tan, M.-W.; Foster, T.J. Transforming the Untransformable: Application of Direct Transformation To Manipulate Genetically Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. MBio 2012, 3, e00277-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, S.; Xu, T.; Fang, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhu, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, R. The Surface-Exposed Protein SntA Contributes to Complement Evasion in Zoonotic Streptococcus suis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Wan, Y.; Tao, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, R. A novel fibronectin-binding protein of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 contributes to epithelial cell invasion and in vivo dissemination. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalia, A.B.; Weiser, J.N. Minimization of Bacterial Size Allows for Complement Evasion and Is Overcome by the Agglutinating Effect of Antibody. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haas, B.; Vaillancourt, K.; Bonifait, L.; Gottschalk, M.; Grenier, D. Hyaluronate lyase activity of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 and modulatory effects of hyaluronic acid on the bacterium’s virulence properties. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, P.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Teng, L.; Zhou, M.; Bei, W.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. Identification of a cell wall-associated subtilisin-like serine protease involved in the pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microb. Pathog. 2010, 48, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifait, L.; Dominguez-Punaro, M.D.L.C.; Vaillancourt, K.; Bart, C.; Slater, J.; Frenette, M.; Gottschalk, M.; Grenier, D. The cell envelope subtilisin-like proteinase is a virulence determinant for Streptococcus suis. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, H.-B.; Yuan, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, X.-K.; Zheng, Y.-L.; Wei, K.-H.; Zhang, X.-M.; Geng, H.-R.; et al. Proteome analysis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Proteomics 2007, 8, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Fittipaldi, N.; Calzas, C.; Gottschalk, M. Critical Streptococcus suis Virulence Factors: Are They All Really Critical? Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.R.; Churchward, G.G. Conjugative transposition. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 49, 455–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifait, L.; Vaillancourt, K.; Gottschalk, M.; Frenette, M.; Grenier, D. Purification and characterization of the subtilisin-like protease of Streptococcus suis that contributes to its virulence. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibberson, C.B.; Jones, C.L.; Singh, S.; Wise, M.C.; Hart, M.E.; Zurawski, D.V.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus hyaluronidase is a CodY-regulated virulence factor. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 4253–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yesilkaya, H.; Spissu, F.; Carvalho, S.M.; Terra, V.S.; Homer, K.A.; Benisty, R.; Porat, N.; Neves, A.R.; Andrew, P.W. Pyruvate Formate Lyase Is Required for Pneumococcal Fermentative Metabolism and Virulence. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 5418–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCallum, N.; Hinds, J.; Ender, M.; Berger-Bachi, B.; Stutzmann Meier, P. Transcriptional Profiling of XdrA, a New Regulator of spa Transcription in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5151–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Si, M.; Chen, C.; Zhong, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Su, T.; Yang, G. MsrR is a thiol-based oxidation-sensing regulator of the XRE family that modulates C. glutamicum oxidative stress resistance. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wei, R.; Li, R.; Zhao, D.; Ge, M.; Yao, Q.; Yu, X. The XRE Family Transcriptional Regulator SrtR in Streptococcus suis Is Involved in Oxidant Tolerance and Virulence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 8, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, S.; Pan, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yao, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G. XRE family transcriptional regulator XtrSs modulates Streptococcus suis fitness under hydrogen peroxide stress. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gao, T.; Zhong, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Pan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, H.; et al. The Novel Streptococcal Transcriptional Regulator XtgS Negatively Regulates Bacterial Virulence and Directly Represses PseP Transcription. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Strains, Plasmids, or Primers | Relevant Characteristics and/or Sequences | Source or Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| S. suis SC19 | Virulent serotype 2 strain | [22] |
| ΔhxtR | A hxtR gene deletion mutant of S. suis SC19 | This work |
| CΔhxtR | A complementary strain of SC19 ΔhxtR | This work |
| E. coli DH5α | F-endA1 glnV44 thi-1 recA1 relA1 gyrA96 deoRnupGΦ80dlacZΔM15 Δ(lacZYA-argF) U169, hsdR17(r K-m K+), λ- | Vazyme |
| Plasmids | ||
| pTV408 | For construction of S. suis transposon library (KanR, ErmR, AmpR) | Dr. Tracy Wang |
| pSET4s | E. coli-S. suis shuttle vector (SpcR) | [23] |
| pSET4s-H | Derived from pSET4s used to knock out hxtR in SC19; SpcR | This work |
| pSET2 | E. coli-S. suis shuttle vector (SpcR) | [24] |
| pSET2-CH | Derived from pSET2 for functional complementation of hxtR (SpcR) | This work |
| Primers for identification of pTV408 transformant | ||
| JPM48 | AATGCGGCCGCATGTCAGACATTTTAAA | This work |
| JPM49 | TTTATCTGGAACATCTGTGG | This work |
| JPM50 | AAGGGACCACCTATGATGTG | This work |
| JPM51 | CAGAAGGCAATGTCATACCA | This work |
| Primers for identification of S. suis SC19 | ||
| 16SrRNA-F | GTAGTCCACGCCGTAAACG | This work |
| 16SrRNA-R | TAAACCACATGCTCCACCGC | This work |
| GDH-F | GCAGCGTATTCTGTCAAACG | This work |
| GDH-R | CCATGGACAGATAAAGATGG | This work |
| Primers for Linker PCR | ||
| 254 | CGACTGGACCTGGA | This work |
| 256 | GATAAGCAGGGATCGGAACCTCCAGGTCCAGTCG | This work |
| Tn917-seq | AGAGAGATGTCACCGTCAAGT | This work |
| 258 | GATAAGCAGGGATCGGAACC | This work |
| Primers for ΔhxtR and CΔhxtR | ||
| ΔhxtR-A | AATTCGAGCTCGGTACCCGGCATCTCCAGCATTTTCCTTC | This work |
| ΔhxtR-B | TAGGCTTAAAAATCATAAAATATCACCTAAAATCATGATTGTC | This work |
| ΔhxtR-C | TTAGGTGATATTTTATGATTTTTAAGCCTAGTTAATCACTAGT | This work |
| ΔhxtR-D | GCCTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGGGTTTCTGTAGAAGATTTTCCTA | This work |
| ΔhxtR-outF | CATGCTGACAGGATAGACATAGGA | This work |
| ΔhxtR-outR | AAGAGCAAGAATTTGGCATCG | This work |
| CΔhxtR-F | AATTCGAGCTCGGTACCCGGTCGTAATCGGCTAATAAGTC | This work |
| CΔhxtR-R | GCCTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGATCAATCTGGACTATAAATATCTACAA | This work |
| M13F | GTAAAACGACGGCCAGT | This work |
| M13R | CAGGAAACAGCTATGAC | This work |
| 5150-F | ATGAAAAGGATTACAGAGATTTCTTG | This work |
| 5150-R | TCATGTGAGAGGTTTTGACC | This work |
| hxtR-F | ATGATTTTAGGTGATATTTTAAAAGAATACCG | This work |
| hxtR-R | TCAATCTGGACTATAAATATCTACAACTT | This work |
| 5160-F | ATGTGGCCGGAGGAAAAGA | This work |
| 5160-R | TCAACTTTTTTGCTTTTCTTTTTCCTTGA | This work |
| Strain | Locus Tag | Product | Cumulative Mortality within 12, 18, and 24 hpi | Animal Modelref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. suis SC19 | 4/6; 6/6; 6/6 | |||
| Transcription regulator | ||||
| Tn1864 | B9H01_RS05155 | XRE family transcriptional regulator | 1/6; 2/6; 2/6 | |
| Tn491 | B9H01_RS04445 | DNA-binding response regulator | 1/6; 1/6; 6/6 | |
| Transporter | ||||
| Tn722 | B9H01_RS07420 | Voltage-gated chloride channel protein | 2/6; 2/6; 3/6 | |
| Tn1673 | B9H01_RS04375 | MULTISPECIES: ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 1/6; 3/6; 3/6 | |
| Tn1 | B9H01_RS00985 | Sugar ABC transporter permease | 0/6; 2/6; 4/6 | |
| Others | ||||
| Tn1862 | B9H01_RS01125 | Formate C-acetyltransferase (PFL) | 0/6; 0/6; 0/6 | |
| Tn509 | B9H01_RS05230 | Peptidase | 1/6; 2/6; 2/6 | |
| Tn513 | B9H01_RS05380 | SAM-dependent methyltransferase | 0/6; 1/6; 2/6 | |
| Tn1712 | B9H01_RS07385 | Site-specific integrase | 1/6; 2/6; 2/6 | |
| Tn28 | B9H01_RS04890 | DUF1836 domain-containing protein | 1/6; 1/6; 3/6 | |
| Tn140 | B9H01_RS05665 | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase | 2/6; 2/6; 3/6 | |
| Tn271 | B9H01_RS05640 | Beta-glucuronidase | 0/6; 1/6; 3/6 | |
| Tn660 | B9H01_RS05870 | Hyaluronidase | 0/6; 0/6; 0/6 | Not tested [34] |
| Tn1803 | B9H01_RS05855 | Hyaluronidase | 1/6; 3/6; 4/6 | Not tested [34] |
| Tn4 | B9H01_RS04330 | Phosphomannomutase/phosphoglucomutase | 0/6; 2/6; 4/6 | |
| Tn98 | B9H01_RS03990 | Subtilisin-like serine protease (SspA) | 1/6; 2/6; 4/6 | Mouse and pig [35,36] |
| Tn220 | B9H01_RS03140 | Carbamate kinase (ArcC belongs to ADS) | 0/6; 2/6; 2/6 | Not tested [9,37] |
| Tn376 | B9H01_RS10315 | Glycosyl hydrolase | 0/6; 1/6; 4/6 | |
| Tn454 | B9H01_RS05605 | Beta-hexosamidase | 0/6; 4/6; 4/6 | |
| Tn496 | B9H01_RS03375 | DUF975 domain-containing protein | 1/6; 3/6; 4/6 | |
| Tn866 | B9H01_RS04990 | 1,4-alpha-glucan branching protein (GlgB) | 1/6; 3/6; 4/6 | |
| Tn1823 | B9H01_RS05160 | A/G-specific adenine glycosylase | 1/6; 3/6; 4/6 | |
| Tn15 | B9H01_RS04765 | Glucan-binding protein | 0/6; 5/6; 5/6 | |
| Tn316 | B9H01_RS05135 | Integrase | 1/6; 2/6; 5/6 | |
| Tn656 | B9H01_RS06130 | Histidine triad protein | 1/6; 3/6; 5/6 | |
| Tn1761 | B9H01_RS00820 | Type II secretion pathway, pseudopilin (PulG) | 1/6; 3/6; 5/6 | |
| Hypothetical protein | ||||
| Tn1624 | B9H01_RS03005 | Hypothetical protein | 0/6; 3/6; 4/6 | |
| Tn122 | B9H01_RS04405 | Hypothetical protein | 1/6; 2/6; 3/6 | |
| Tn12 | B9H01_RS00275 | Hypothetical protein | 1/6; 3/6; 4/6 | |
| Tn29 | B9H01_RS05145 | Hypothetical protein | 1/6; 3/6; 4/6 | |
| Tn524 | B9H01_RS04840 | Hypothetical protein | 1/6; 3/6; 4/6 | |
| Tn983 | B9H01_RS03005 | Hypothetical protein | 0/6; 4/6; 5/6 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, J.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Q.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Huang, Q.; et al. Screening for Virulence-Related Genes via a Transposon Mutant Library of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Using a Galleria mellonella Larvae Infection Model. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050868
Fan J, Zhao L, Hu Q, Li S, Li H, Zhang Q, Zou G, Zhang L, Li L, Huang Q, et al. Screening for Virulence-Related Genes via a Transposon Mutant Library of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Using a Galleria mellonella Larvae Infection Model. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(5):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050868
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Jingyan, Lelin Zhao, Qiao Hu, Siqi Li, Haotian Li, Qianqian Zhang, Geng Zou, Liangsheng Zhang, Lu Li, Qi Huang, and et al. 2022. "Screening for Virulence-Related Genes via a Transposon Mutant Library of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Using a Galleria mellonella Larvae Infection Model" Microorganisms 10, no. 5: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050868
APA StyleFan, J., Zhao, L., Hu, Q., Li, S., Li, H., Zhang, Q., Zou, G., Zhang, L., Li, L., Huang, Q., & Zhou, R. (2022). Screening for Virulence-Related Genes via a Transposon Mutant Library of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Using a Galleria mellonella Larvae Infection Model. Microorganisms, 10(5), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050868






