Influence on Soybean Aphid by the Tripartite Interaction between Soybean, a Rhizobium Bacterium, and an Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material, Bacteria and Fungi Strains, and Insect Samples
2.2. Growth Conditions, Inoculation, and Insect Treatment
2.3. Analysis of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Colonization and Nodule Counting
2.4. Analysis of Fresh and Dry Biomass and Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Carbon Content and Concentration
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Inoculation on Plant Parameters
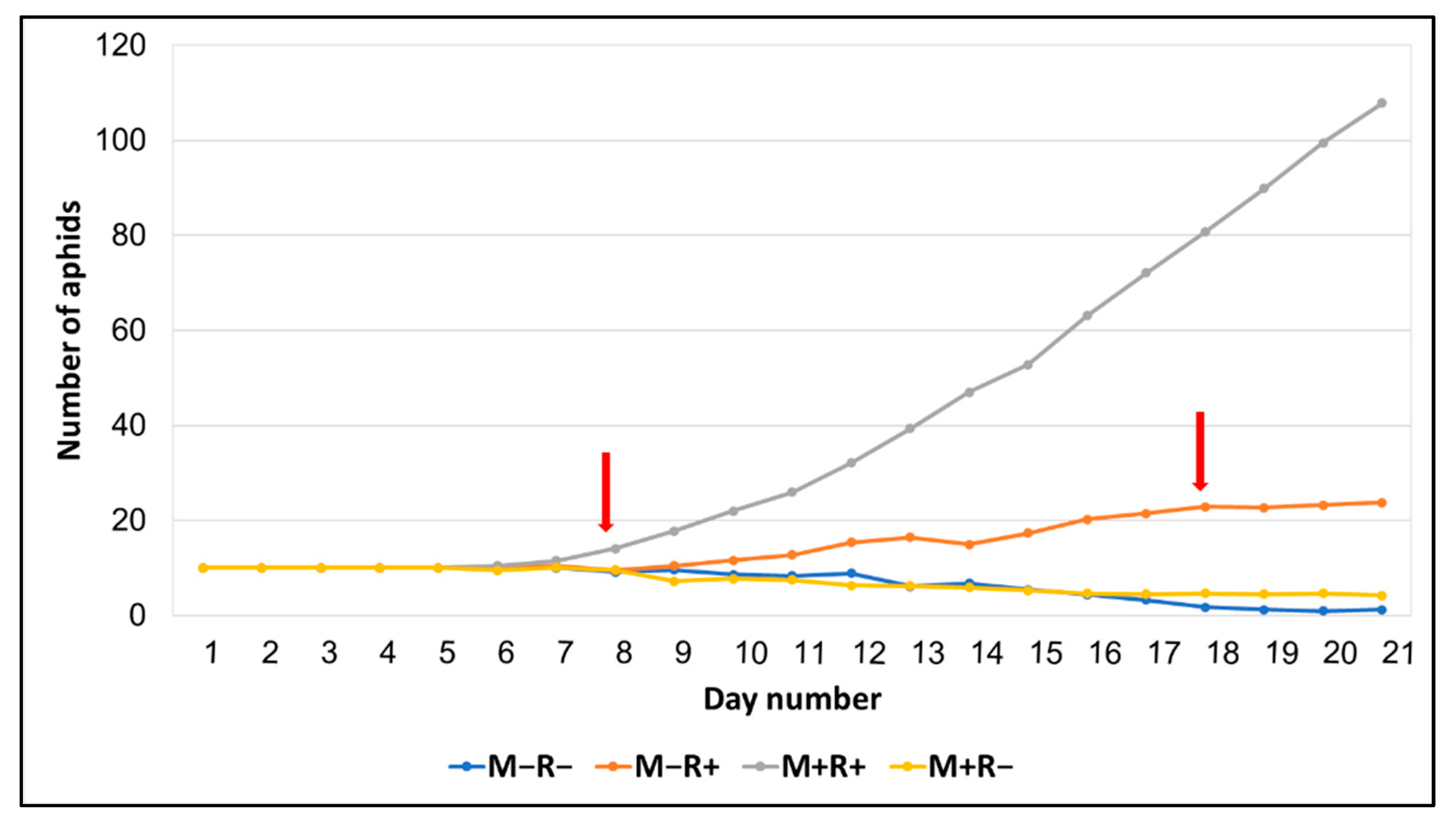
3.2. Effects of Inoculation on Soybean Aphid
3.3. Correlation between Aphid Abundance and Plant Parameters
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ragsdale, D.W.; Voegtlin, D.J.; O’Neil, R.J. Soybean aphid biology in North America. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2004, 97, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Schenk-Hamlin, D.; Zhan, W.; Ragsdale, D.W.; Heimpel, G.E. The soybean aphid in China: A historical review. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2004, 97, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragsdale, D.W.; Landis, D.A.; Brodeur, J.; Heimpel, G.E.; Desneux, N. Ecology and management of the soybean aphid in North America. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccornack, B.P.; Ragsdale, D.W.; Venette, R.C. Demography of soybean aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) at summer temperatures. J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenger, J.A.; Cassone, B.J.; Legeai, F.; Johnston, J.S.; Bansal, R.; Yates, A.D.; Coates, B.S.; Pavinato, V.A.C.; Michel, A. Whole genome sequence of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 123, 102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhainds, M.; Roy, M.; Daigle, G.; Brodeur, J. Toward management guidelines for the soybean aphid in Quebec. I. Feeding damage in relationship to seasonality of infestation and incidence of native predators. Can. Entomol. 2007, 139, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckendorf, E.A.; Catangui, M.A.; Riedell, W.E. Soybean aphid feeding injury and soybean yield, yield components, and seed composition. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragsdale, D.W.; Mccornack, B.P.; Venette, R.C.; Potter, B.D.; Macrae, I.V.; Hodgson, E.W.; O’Neal, M.E.; Johnson, K.D.; O’Neil, R.J.; Difonzo, C.D.; et al. Economic threshold for soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowicz, V.A. A fungal root symbiont modifies plant resistance to an insect herbivore. Oecologia 1997, 112, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, A.T.M.; Islam, M.N.; Liu, F.-H.; Cao, H.-H.; Liu, T.-X. Leaf chemical compositions of different eggplant varieties affect performance of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) nymphs and adults. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqueel, M.A.; Leather, S.R. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer on the growth and survival of Rhopalosiphum padi (L.) and Sitobion avenae (F.) (Homoptera: Aphididae) on different wheat cultivars. Crop Prot. 2011, 30, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noma, T.; Gratton, C.; Colunga-Garcia, M.; Brewer, M.J.; Mueller, E.E.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Heimpel, G.E.; O’Neal, M.E. Relationship of soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to soybean plant nutrients, landscape structure, and natural enemies. Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, T.R.; Boersma, M.; Raubenheimer, D. Stoichiometry: Linking elements to biochemicals. Ecology 2004, 85, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, A.J.; DiFonzo, C.D. Soil potassium deficiency affects soybean phloem nitrogen and soybean aphid populations. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilmon, K.J.; Hodgson, E.W.; O’Neal, M.E.; Ragsdale, D.W. Biology of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in the United States. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2011, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, S.W.; Gratton, C.; Wolkowski, R.P.; Hogg, D.B.; Wedberg, J.L. Effect of soil potassium availability on soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) population dynamics and soybean yield. J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Myers, S.W.; Gratton, C. Influence of potassium fertility on soybean aphid, Aphis glycines Matsumura (Hemiptera: Aphididae), population dynamics at a field and regional scale. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, G.L.; West, E.D.; Herman, T.K. Crops that feed the world 2. Soybean—worldwide production, use, and constraints caused by pathogens and pests. Food Secur. 2011, 3, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossler, J.N.; Zielinski, C.A.; Heath, K.D. Tripartite mutualism: Facilitation or trade-offs between rhizobial and mycorrhizal symbionts of legume hosts. Am. J. Bot. 2015, 102, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qiu, Y.-L. Phylogenetic distribution and evolution of mycorrhizas in land plants. Mycorrhiza 2006, 16, 299–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.E. Mycorrhizal fungi can dominate phosphate supply to plants irrespective of growth responses. PLANT Physiol. 2003, 133, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compant, S.; Clément, C.; Sessitsch, A. Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria in the rhizo- and endosphere of plants: Their role, colonization, mechanisms involved and prospects for utilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, L.J.C.; Germida, J.J. Selective interactions between Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi and Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viceae enhance pea yield and nutrition. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 37, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolduc, A.R. The use of mycorrhizae to enhance phosphorus uptake: A way out the phosphorus crisis. J. Biofertil. Biopestic. 2011, 2, 1000104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.; Williams, A.P.; Griffith, G.W.; Withers, P.J.A. Use of commercial bio-inoculants to increase agricultural production through improved phosphrous acquisition. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 86, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijri, M. Analysis of a large dataset of mycorrhiza inoculation field trials on potato shows highly significant increases in yield. Mycorrhiza 2016, 26, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiru, S.; Mwanza, H.P.; Hijri, M. Analysis of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungal inoculant benchmarks. Microorganisms 2020, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.S.; Nogueira, M.A.; Hungria, M. Microbial inoculants: Reviewing the past, discussing the present and previewing an outstanding future for the use of beneficial bacteria in agriculture. AMB Express 2019, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trdan, S.; Vučajnk, F.; Bohinc, T.; Vidrih, M. The effect of a mixture of two Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria from Argentina on the yield of potato, and occurrence of primary potato diseases and pest—short communication. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2019, 69, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, A.; GéTaz, M.; Rasmann, S.; Sanders, I.R. Identity and combinations of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal isolates influence plant resistance and insect preference: Mycorrhizal-mediated insect preference and performance. Ecol. Entomol. 2013, 38, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gange, A.; Bower, E.; Brown, V. Differential effects of insect herbivory on Arbuscular Mycorrhizal colonization. Oecologia 2002, 131, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, C.; Bennett, A. Mycorrhizal fungal–plant–insect interactions: The importance of a community approach. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadhave, K.R.; Gange, A.C. Interactions involving rhizobacteria and foliar-feeding insects. In Aboveground–Belowground Community Ecology; Ohgushi, T., Wurst, S., Johnson, S.N., Eds.; Ecological Studies; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 234, pp. 117–133. ISBN 978-3-319-91613-2. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijden, M.G.; de Bruin, S.; Luckerhoff, L.; van Logtestijn, R.S.; Schlaeppi, K. A widespread plant-fungal-bacterial symbiosis promotes plant biodiversity, plant nutrition and seedling recruitment. ISME J. 2016, 10, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Tawaraya, K.; Murayama, H.; Sato, S.; Nishizawa, T.; Toyomasu, T.; Murayama, T.; Shiozawa, S.; Yasuda, H. Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi on the abundance of foliar-feeding insects and their natural enemy. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2013, 48, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, Y.M.; Echevarría, A.M.; Carmona, A.M. Respuesta de plantas de tomate (Solanum lycopersicum L.) a la biofertilización líquida con Glomus cubense. Cultiv. Trop. 2014, 35, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, J.; Lozano, E.R.; Poppy, G.M. A simple, light clip-cage for experiments with aphids: A simple clip-cage for experiments with aphids. Agric. For. Entomol. 2018, 20, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; O’Neil, R.J.; Yoo, H.J.S. Suppression of population growth of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines Matsumura, by predators: The identification of a key predator and the effects of prey dispersion, predator abundance, and temperature. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonigle, T.P.; Evans, D.G.; Miller, M.H. Effect of degree of soil disturbance on mycorrhizal colonization and phosphorus absorption by maize in growth chamber and field experiments. New Phytol. 1990, 116, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gange, A.C.; Bower, E.; Stagg, P.G.; Aplin, D.M.; Gillam, A.E.; Bracken, M. A comparison of visualization techniques for recording arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization. New Phytol. 1999, 142, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babikova, Z.; Gilbert, L.; Randall, K.C.; Bruce, T.J.A.; Pickett, J.A.; Johnson, D. Increasing phosphorus supply is not the mechanism by which arbuscular mycorrhiza increase attractiveness of bean (Vicia faba) to aphids. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 5231–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolboac, S.-D.; Jäntschi, L. Pearson versus Spearman, Kendall’s Tau correlation analysis on structure-activity relationships of biologic active compounds. Leonardo J. Sci. 2006, 23, 179–200. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J.M.; Mescher, M.C.; De Moraes, C.M. Plant—Rhizobia mutualism influences aphid abundance on soybean. Plant Soil 2009, 323, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, N.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Ohgushi, T. Community-wide effects of below-ground rhizobia on above-ground arthropods. Ecol. Entomol. 2011, 36, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, Q.; Chen, F.; Yan, X.; Liao, H. Effects of co-inoculation with Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi and Rhizobia on soybean growth as related to root architecture and availability of N and P. Mycorrhiza 2011, 21, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, S.M.; Goos, R.J.; Swenson, S.J.; Foster, S.P.; Schatz, B.G.; Lawley, Y.E.; Prischmann-Voldseth, D.A. Impact of nitrogen fixing and Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria on a phloem-feeding soybean herbivore. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 86, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazani, O.; Friedman, J. Is IAA the major root growth factor secreted from plant-growth-mediating bacteria? J. Chem. Ecol. 1999, 25, 2397–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dénarié, J.; Debellé, F.; Promé, J.-C. Rhizobium lipo-chitooligosaccharide nodulation factors: Signaling molecules mediating recognition and morphogenesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996, 65, 503–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.; Mescher, M.; De Moraes, C. Plant dependence on rhizobia for nitrogen influences induced plant defenses and herbivore performance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 1466–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, E.; Coll, M. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae): Variation in size, color, and reproduction. J. Econ. Entomol. 2001, 94, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.E. Phloem-sap feeding by animals: Problems and solutions. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, C.A.; Whitham, T.G. Mycorrhizae-herbivore interactions: Population and community consequences. In Mycorrhizal Ecology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2002; pp. 295–320. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, S.; Borie, F.; Bolan, N.; Cornejo, P. Phytoremediation of metal-polluted soils by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 741–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, N.A.; Kiers, E.T.; Hazzard, R.V.; Adler, L.S. Context-dependency of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi on plant-insect interactions in an agroecosystem. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balog, A.; Loxdale, H.D.; Bálint, J.; Benedek, K.; Szabó, K.-A.; Jánosi-Rancz, K.-T.; Domokos, E. The Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus irregularis affects arthropod colonization on sweet pepper in both the field and greenhouse. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzo, E.; Rizzo, E.; Fereres, A.; Gomez, S.K. High Levels of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungus colonization on Medicago truncatula reduces plant suitability as a host for pea aphids (Acyrthosiphon pisum). Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koricheva, J.; Gange, A.C.; Jones, T. Effects of mycorrhizal fungi on insect herbivores: A meta-analysis. Ecology 2009, 90, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gange, A.C.; Bower, E.; Brown, V.K. Positive effects of an Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungus on aphid life history traits. Oecologia 1999, 120, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babikova, Z.; Gilbert, L.; Bruce, T.; Dewhirst, S.Y.; Pickett, J.A.; Johnson, D. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi and aphids interact by changing host plant quality and volatile emission. Funct. Ecol. 2014, 28, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, J.; Ekbom, B. The effect of different plant nutrient regimes on the aphid Macrosiphum euphorbiae growing on Petunia. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2002, 104, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takács, T.; Cseresnyés, I.; Kovács, R.; Parádi, I.; Kelemen, B.; Szili-Kovács, T.; Füzy, A. Symbiotic Effectivity of Dual and Tripartite associations on soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) cultivars inoculated with Bradyrhizobium japonicum and AM Fungi. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.P.; Staehelin, C.; Vierheilig, H.; Wiemken, A.; Jabbouri, S.; Broughton, W.J.; Vogeli-Lange, R.; Boller, T. Rhizobial nodulation factors stimulate mycorrhizal colonization of nodulating and nonnodulating soybeans. Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.C.; Martinez-Medina, A.; Lopez-Raez, J.A.; Pozo, M.J. Mycorrhiza-induced resistance and priming of plant defenses. J. Chem. Ecol. 2012, 38, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Plant Parameters | Inoculant Treatments | F | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M−R− | M+R− | M−R+ | M+R+ | |||
| AM fungus root colonization (%) | 0 | 21.7 ± 3.05 | 0 | 37.4 ± 6.31 | 32.32 | <0.0001 |
| Number of nodules | 5.12 ± 2.20 a | 3.50 ± 1.32 a | 44.38 ± 7.21 b | 56.50 ± 3.25 b | 44.54 | <0.0001 |
| Shoot fresh biomass (g/plant) | 4.15 ± 0.60 a | 6.81 ± 0.72 ab | 10.03 ± 0.92 b | 17.93 ± 0.30 c | 41.73 | <0.0001 |
| Shoot dry biomass (g/plant) | 1.05 ± 0.10 a | 1.49 ± 0.16 ab | 2.40 ± 0.23 b | 4.64 ± 0.40 c | 40.94 | <0.0001 |
| Root fresh biomass (g/plant) | 4.66 ± 0.80 a | 5.78 ± 0.47 ab | 5.70 ± 0.49 ab | 7.85 ± 0.71 b | 4.38 | 0.012 |
| Root dry biomass (g/plant) | 0.31 ± 0.05 a | 0.41 ± 0.04 ab | 0.43 ± 0.03 ab | 0.60 ± 0.06 b | 5.91 | 0.003 |
| Total nitrogen (mg/plant) | 22.3 ± 4.41 a | 43.9 ± 9.13 a | 97.4 ± 11.13 b | 176.9 ± 11.69 c | 59.40 | <0.0001 |
| Total phosphorus (mg/plant) | 5.95 ± 0.80 a | 9.58 ± 0.87 b | 7.99 ± 0.40 ab | 9.97 ± 0.77 b | 7.18 | 0.0016 |
| Total carbon (mg/plant) | 464 ± 45.90 a | 649 ± 74.03 ab | 1070 ± 105.40 b | 2053 ± 170.34 c | 43.06 | <0.0001 |
| Nitrogen concentration (mg/g) | 20.1 ± 2.9 a | 27.0 ± 2.8 a | 39.4 ± 1.0 b | 38.2 ± 1.4 b | 27.27 | <0.0001 |
| Phosphorus concentration (mg/g) | 5.25 ± 0.52 c | 6.45 ± 0.31 d | 3.46 ± 0.30 b | 2.22 ± 0.22 a | 34.78 | <0.0001 |
| Carbon concentration (mg/g) | 431 ± 3.0 ab | 426 ± 3.0 a | 438 ± 2.6 b | 438 ± 3.9 b | 5.75 | 0.005 |
| Ratio N:P | 4.30 ± 0.91 a | 4.35 ± 0.54 a | 12.13 ± 1.30 b | 18.28 ± 1.61 c | 38.80 | <0.0001 |
| Ratio P:N | 3.00 ± 0.53 b | 2.62 ± 0.36 b | 0.89 ± 0.09 a | 0.58 ± 0.05 a | 36.93 | <0.0001 |
| Aphid Parameters | Inoculant Treatments | F | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M−R− | M+R− | M−R+ | M+R+ | |||
| Aphid number (8 days) | 9.12 ± 0.40 a | 9.50 ± 0.46 a | 9.62 ± 0.46 a | 14.12 ± 1.77 b | 6.31 | 0.003 |
| Aphid number (18 days) | 1.75 ± 1.06 a | 4.62 ± 2.96 a | 22.88 ± 5.8 b | 80.75 ± 15.6 c | 41.71 | 0.0001 |
| Aphid number (21 days) (sqrt) | 0.60 ± 0.35 a | 1.30 ± 0.60 a | 4.57 ± 0.64 b | 9.94 ± 1.13 c | 16.47 | 0.001 |
| Aphid body length (µm) | 1304 ± 32 a | 1421 ± 30 a | 1323 ± 41 a | 1320 ± 40 a | 2.68 | 0.105 |
| Left hind tibia length (µm) | 661 ± 18.9 a | 692 ± 18.1 a | 667 ± 25.4 a | 662 ± 22.4 a | 0.70 | 0.403 |
| Variables A | Variables B | Kendall tau Coefficient | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aphid size | Tibia length | 0.45 | <0.0001 |
| Final aphid colony size | Nitrogen concentration | 0.57 | <0.0001 |
| Phosphorus concentration | −0.58 | <0.0001 | |
| Carbon concentration | 0.32 | 0.01 | |
| Nodulation | 0.63 | <0.0001 | |
| AM fungus colonization | 0.35 | 0.009 | |
| Shoot dry mass | 0.74 | <0.0001 | |
| Root dry mass | 0.48 | 0.0001 | |
| Nodulation | Nitrogen concentration | 0.49 | <0.0001 |
| Phosphorus concentration | −0.53 | <0.0001 | |
| Carbon concentration | 0.27 | 0.03 | |
| AM fungus colonization | 0.18 | 0.18 | |
| Shoot dry mass | 0.64 | 0.0001 | |
| Root dry mass | 0.47 | 0.0002 | |
| AM fungus colonization | Nitrogen concentration | 0.18 | 0.180 |
| Phosphorus concentration | −0.15 | 0.273 | |
| Carbon concentration | 0.03 | 0.821 | |
| Shoot dry mass | 0.39 | 0.003 | |
| Root dry mass | 0.36 | 0.007 | |
| Shoot dry mass | Nitrogen concentration | 0.59 | <0.0001 |
| Phosphorus concentration | −0.58 | <0.0001 | |
| Carbon concentration | 0.33 | 0.008 | |
| Root dry mass | Nitrogen concentration | 0.31 | 0.012 |
| Phosphorus concentration | −0.36 | 0.003 | |
| Carbon concentration | 0.22 | 0.077 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dabré, É.E.; Hijri, M.; Favret, C. Influence on Soybean Aphid by the Tripartite Interaction between Soybean, a Rhizobium Bacterium, and an Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungus. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061196
Dabré ÉE, Hijri M, Favret C. Influence on Soybean Aphid by the Tripartite Interaction between Soybean, a Rhizobium Bacterium, and an Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungus. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(6):1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061196
Chicago/Turabian StyleDabré, Élisée Emmanuel, Mohamed Hijri, and Colin Favret. 2022. "Influence on Soybean Aphid by the Tripartite Interaction between Soybean, a Rhizobium Bacterium, and an Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungus" Microorganisms 10, no. 6: 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061196
APA StyleDabré, É. E., Hijri, M., & Favret, C. (2022). Influence on Soybean Aphid by the Tripartite Interaction between Soybean, a Rhizobium Bacterium, and an Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungus. Microorganisms, 10(6), 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061196







